E155 Thermoregulation Strategies & Hypothermia
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
first aid in the field for severe hypothermia
move the pt gently
cover with blankets
warm (not hot) beverages (if pt is conscious)
warm, dry compress on neck and chest only
ER treatments for severe hypothermia
warm infusion - infuse warm salien through IV
airway rewarming - warm humidified air thru a nasal cannula or O2 mask
irrigation - use a catheter to irrigate body cavities (abs and/or pleural) with warm saline
do not allow the pt to make suddent movements, especially sitting up
tense muscles = pass out
cardiac issues (cardiac arrest) from the rush of blood and dispersal to extremities
do not apply a warm compress to the arms or legs
induce heat shock locally; redistribution of blood to periphery
do not give an alcoholic beverage
vasodilation = lose more heat at periphery
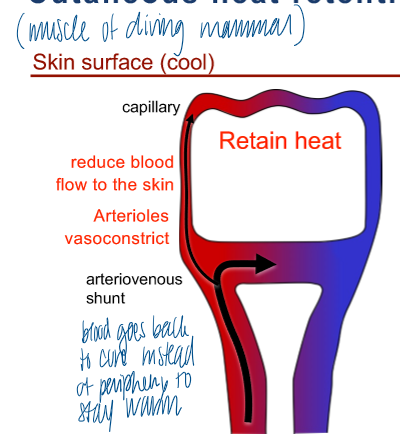
cutaneous heat retention
arteriovenous shunt = causes blood to go back to core instead of periphery to stay warm
reduce blood flow to the skin
arterioles vasoconstrict
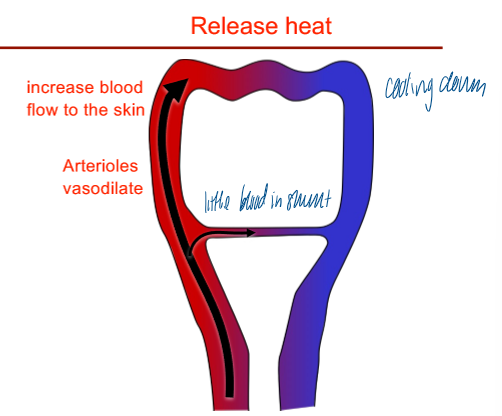
cutaneous heat loss
arterioles vasodilate = increase blood flow to the skin
little blood in the shunt to release blood at the skin surface
when heat is released, how is it being carried away from the body?
radiation = cannot see wavelengths but this is still the main mech
not convection b/c requires fluids, like air
mechanism of metabolism
like a water turbine where water flowing down gradient generates energy
uncoupling protein produces heat by bringing H+ out of the cell and down conc gradient
NADH serves as the e shuttle that moves e- from glycolysis and citric acid cycle (H2O as byproduct)
plants generating heat
when the lotus is warm, it releases organic for insect to smell
counter current exchange
always moving down conc gradient until it is fully warmed
changes in blood temp as it travels from the foot of a penguin back to the body
increases in temp as it moves toward the core