Flexible Pavement Distress
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
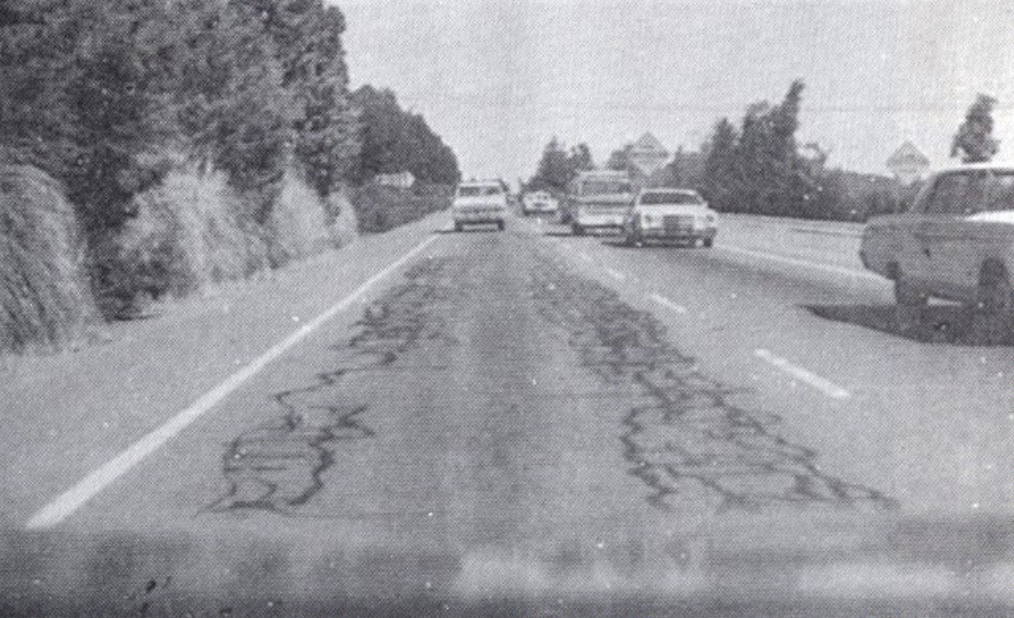
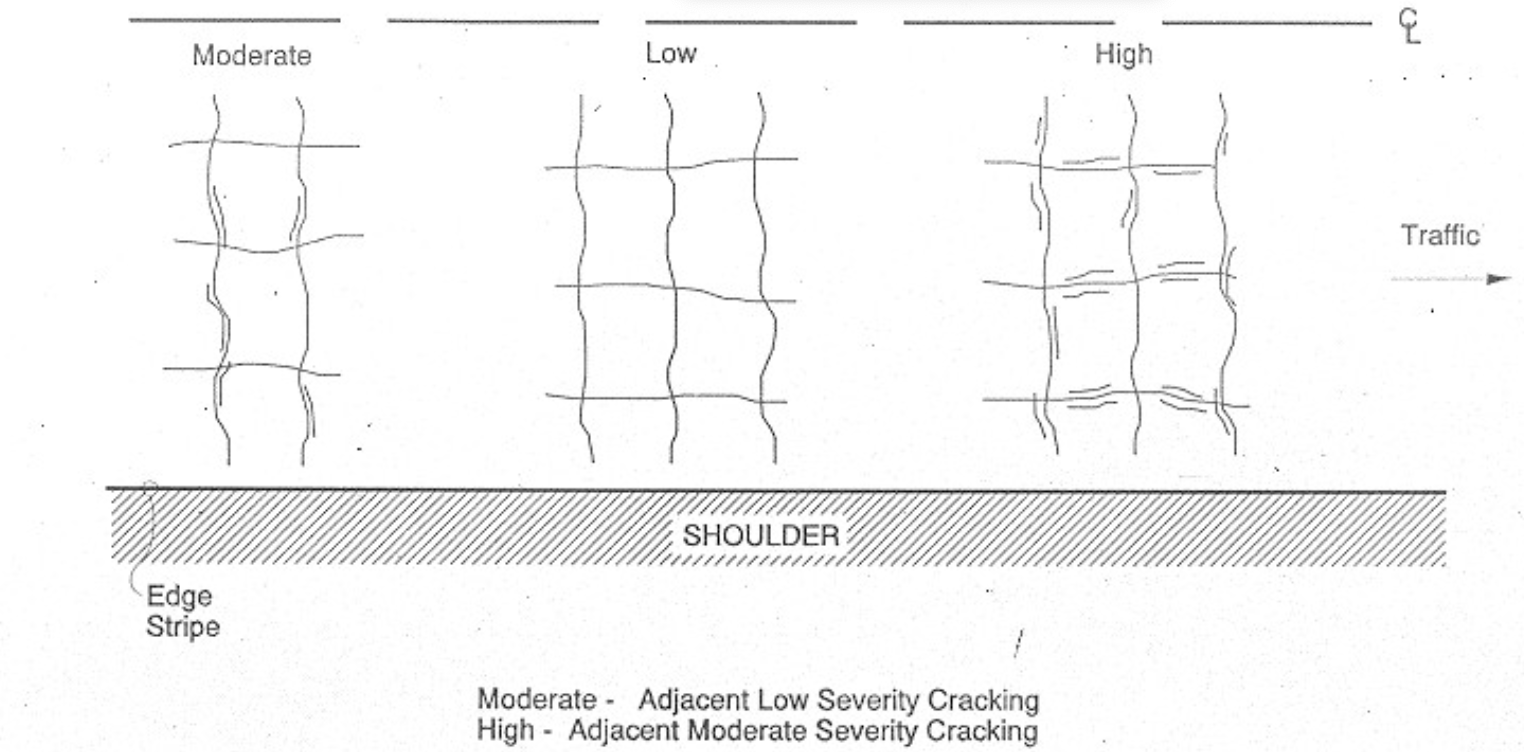
Alligator or Fatigue Cracking
series of interconnecting cracks caused by fatigue failure in BASE under REPEATED traffic LOADING, cracks propagate to surface

Block Cracking (Thermal Cracking)
BLOCK cracks divide asphalt surface, NOT load induced, mostly COLD shrinkage in hot mix asphalt
Binder in Flexible Pavement Distresses
binder selection base on local day/night temperatures
cracks can potentially heal b/c of binder
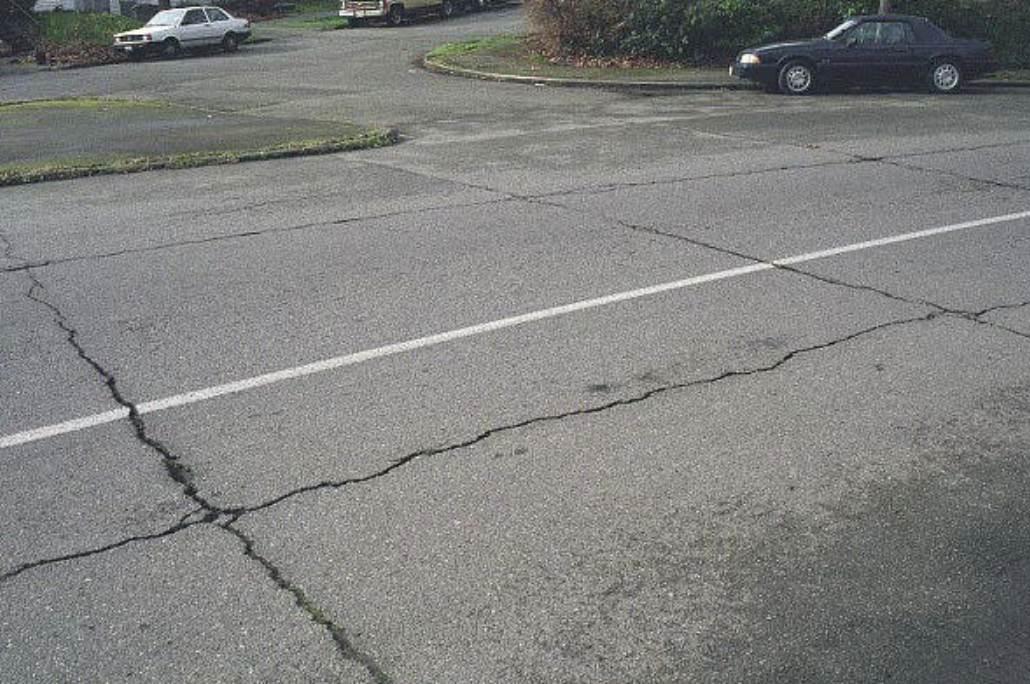
Joint Reflection Cracking from Concrete Slab
occurs on asphalt surface over a JOINTED concrete slab along transverse and longitudinal joints, where pavements are WIDENED, caused by moisture and movement in concrete slab

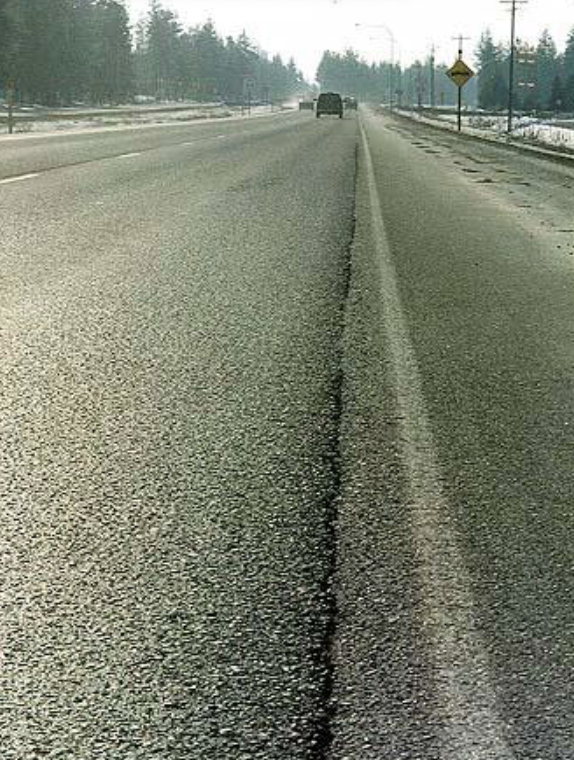
Lane/Shoulder Drop-off or Heave
difference in ELEVATION between traffic lane and shoulder, due to consolidation or settlement
Longitudinal Cracking
Longitudinal or traverse cracks to CENTERLINE, caused by poor construction, shrinkage, and reflective cracks, TOP down, most common distress in GA

Tire Contact Stresses
vertical stress distributions = quite low
traverse stress distributions = quite high
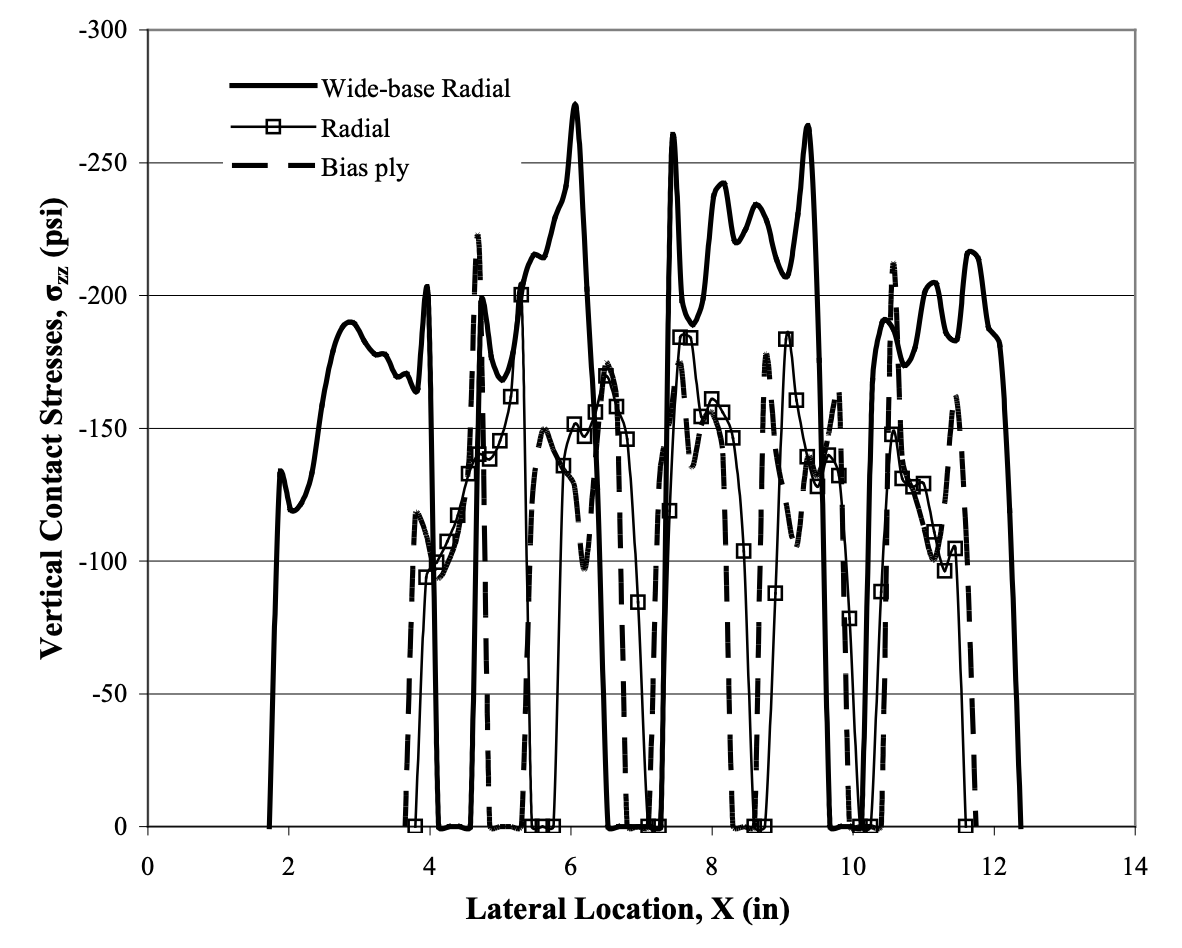
Radial vs Bias Ply Tires
Radial (more common) = rigid tread, flexible wall
Bias Ply = flexible tread, rigid wall
Water Bleeding
water seeps out of joints/cracks/porous HMA layer
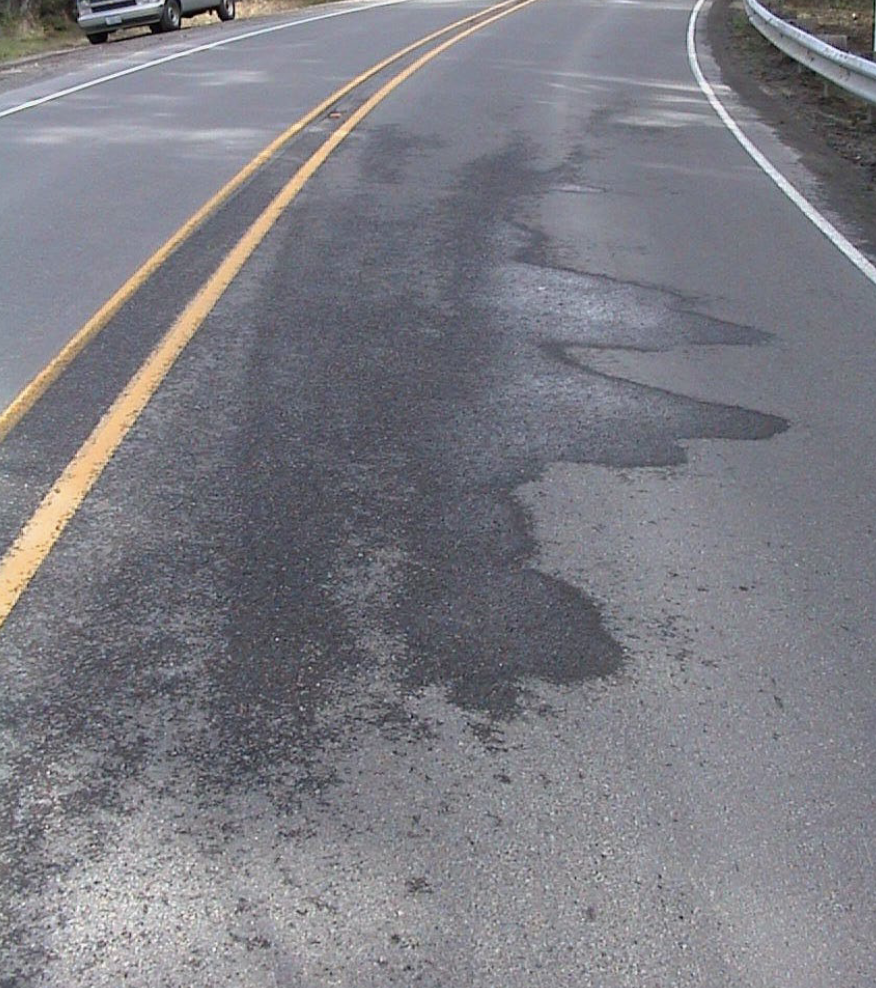

Water Pumping
water and fine material is ejected from underlying layers by moving loads
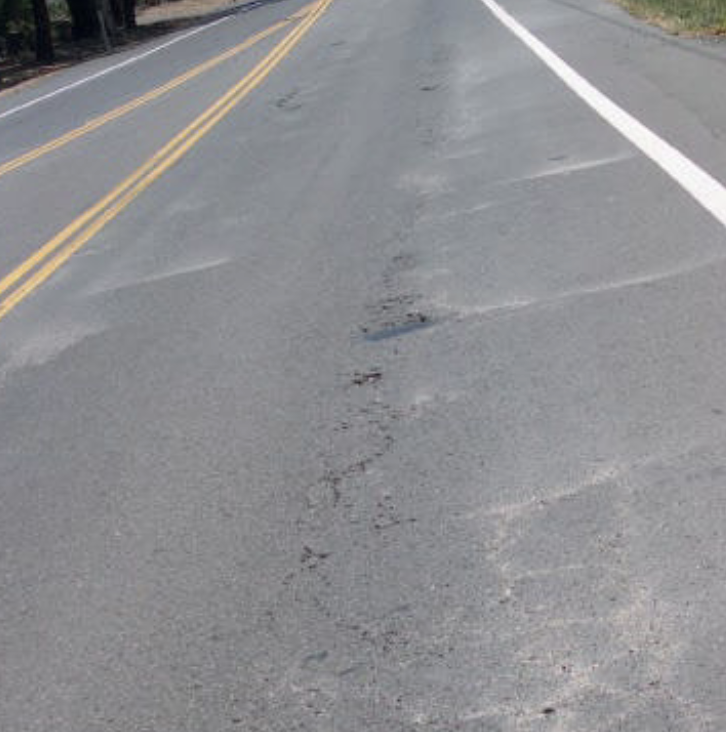

Water Bleeding/Pumping Cause
porous pavement as a result of inadequate compaction during construction (paver & compactor must be closer together), high water table, poor drainage
Rutting (Consolidation/Instability)
depressions that form in the wheel paths
Causes
rounded aggregate (Mississippi)
low air voids
insufficient thickness
soft binder
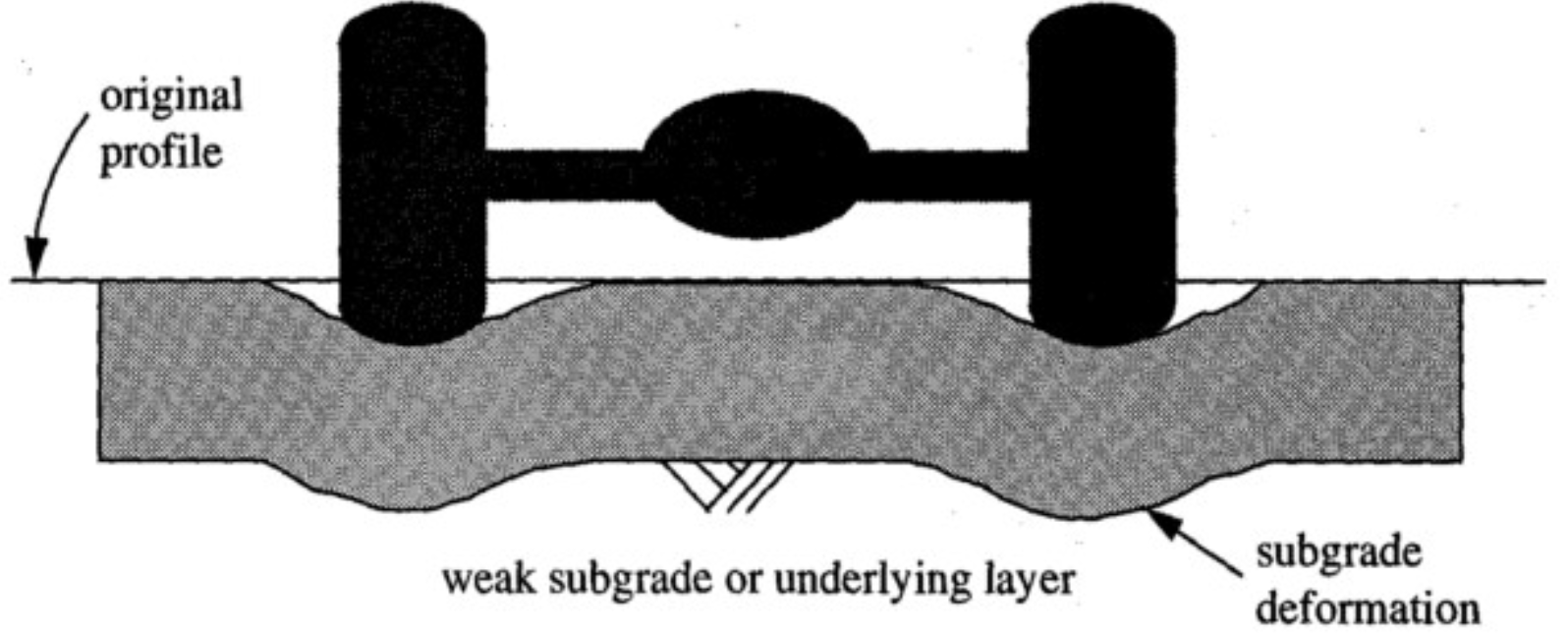
Consolidation Rutting
repetitive application of wheels loads due to reduction in AIR voids or permanent DEFORMATION of subgrade/base
Asphalt/Traffic Speed Relationship
stiff at high speeds
relaxes at slow/stopping speeds
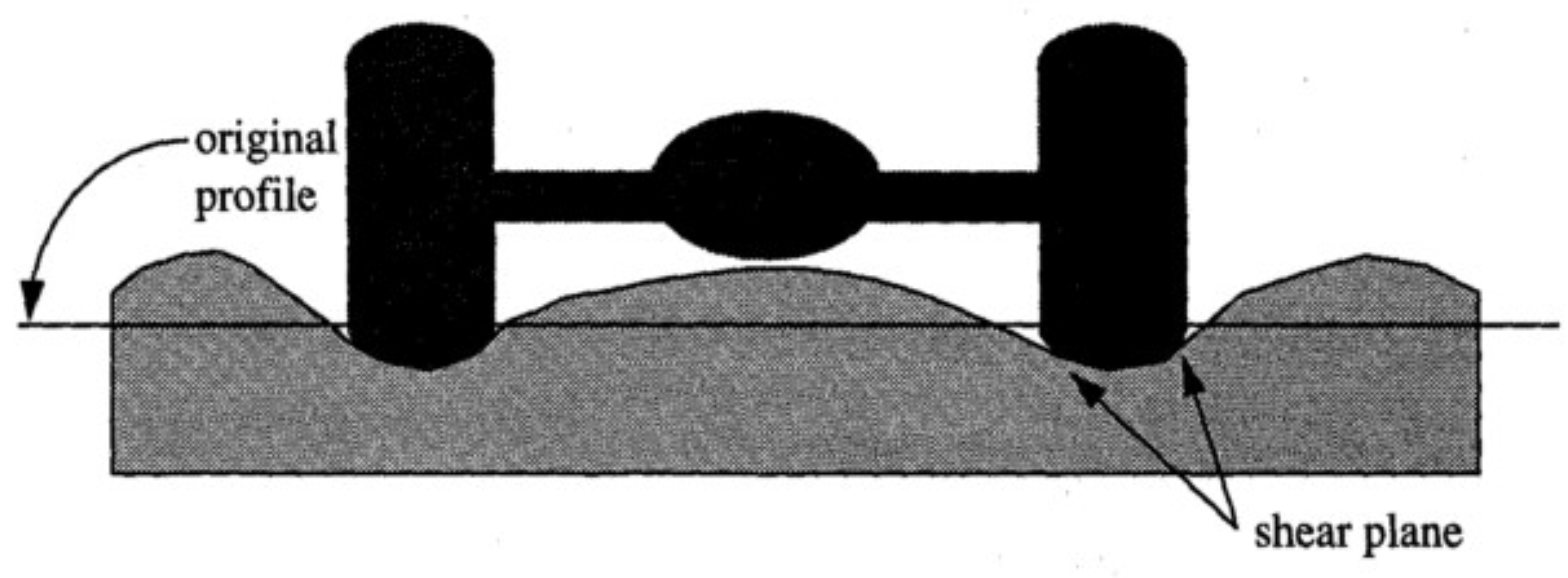
Instability Rutting
material issue within first 2 inches, asphalt gets “SHOVED” over
Binder Bleeding
excess asphalt BINDER on surface of pavement, not enough air voids
Binder Bleeding Causes
excess prime or tack coats
excess asphalt mixture
drain-down
contamination with diesel
Slippage
crescent or half-moon shaped cracks, 2 ends points into the direction of traffic, cause by thin layers & issues with tack coat
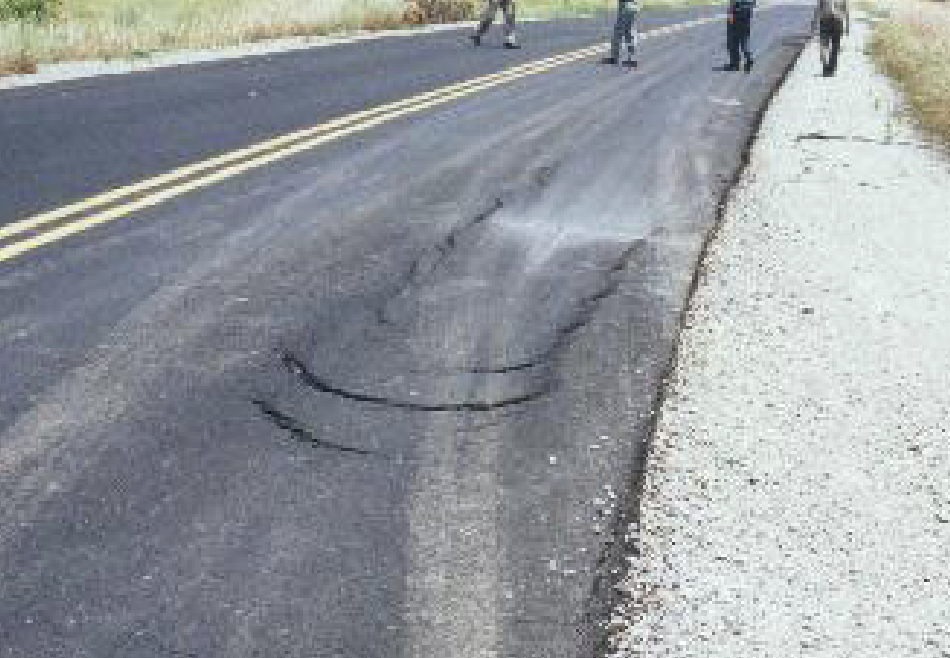

Swell
upward bulge caused by swelling soils or PCC blowup
Corrugation
ripples at traffic acceleration zones
Depression
localized elevation difference due to soil or built up
Potholes
broken pavement due to fatigue cracking or freeze/thaw
Ravelling and weathering
stripping of aggregates