4. Integumentary System
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
6 Functions of the skin :
1.Barrier functions
2.Resistance to trauma and infection - keratin/acid mantle
3. Vitamin D synthesis
4. Sensation
5. Thermoregulation: Vasoconstriction/vasodilation
6. Transdermal absorption
Barrier function of the skin includes:
Waterproofing / UV radiation/Harmful chemicals
Resistance to trauma and infection includes:
Keratin/Acid mantle
kertin's job in the skin
-creates a strong barrier that protects against physical trauma, prevents water loss, and blocks pathogens from entering.
( a tough, fibrous protein on outer layer of hair,skin and nails )
Acid Mantle's job in the skin
(mantle=cover)
- stops the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi, helping to prevent infections through sweat.
( a thin, slightly acidic film on the skin's surface, made of sweat, sebum, and other secretions )
Thermoregulation: Vasoconstriction/vasodilation (skin function)
job/definition
Vasoconstriction: Blood vessels narrow to keep heat in and warm the body. (diameter decreases)
Vasodilation: Blood vessels widen to release heat and cool the body. (diameter increase)
Thermoregulation meaning
the process by which the body maintains its internal temperature within a certain range, regardless of external conditions.
Vasoconstriction
job/definition
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessels.
Job: It helps retain heat by reducing blood flow to the skin.
Vasodilation
job/definition
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels.
Job: It helps release heat by increasing blood flow to the skin, cooling the body.
When will vasoconstriction occur?
When your body is cold, to keep heat in.
It helps retain heat by reducing blood flow to the skin.
When will vasodilation occur?
When your body is hot, to cool .
It helps release heat by increasing blood flow to the skin, cooling the body.
Vitamin D synthesis skin function
job/definition
helps the body absorb calcium, which is important for strong bones, immune function, and overall health.
Transdermal absorption skin function
job/definition
Administration of certain drugs via injections or adhesive patches
Structure of the skin (3 big layers)
(top to bottom)
-epidermis
-dermis
-hypodermis
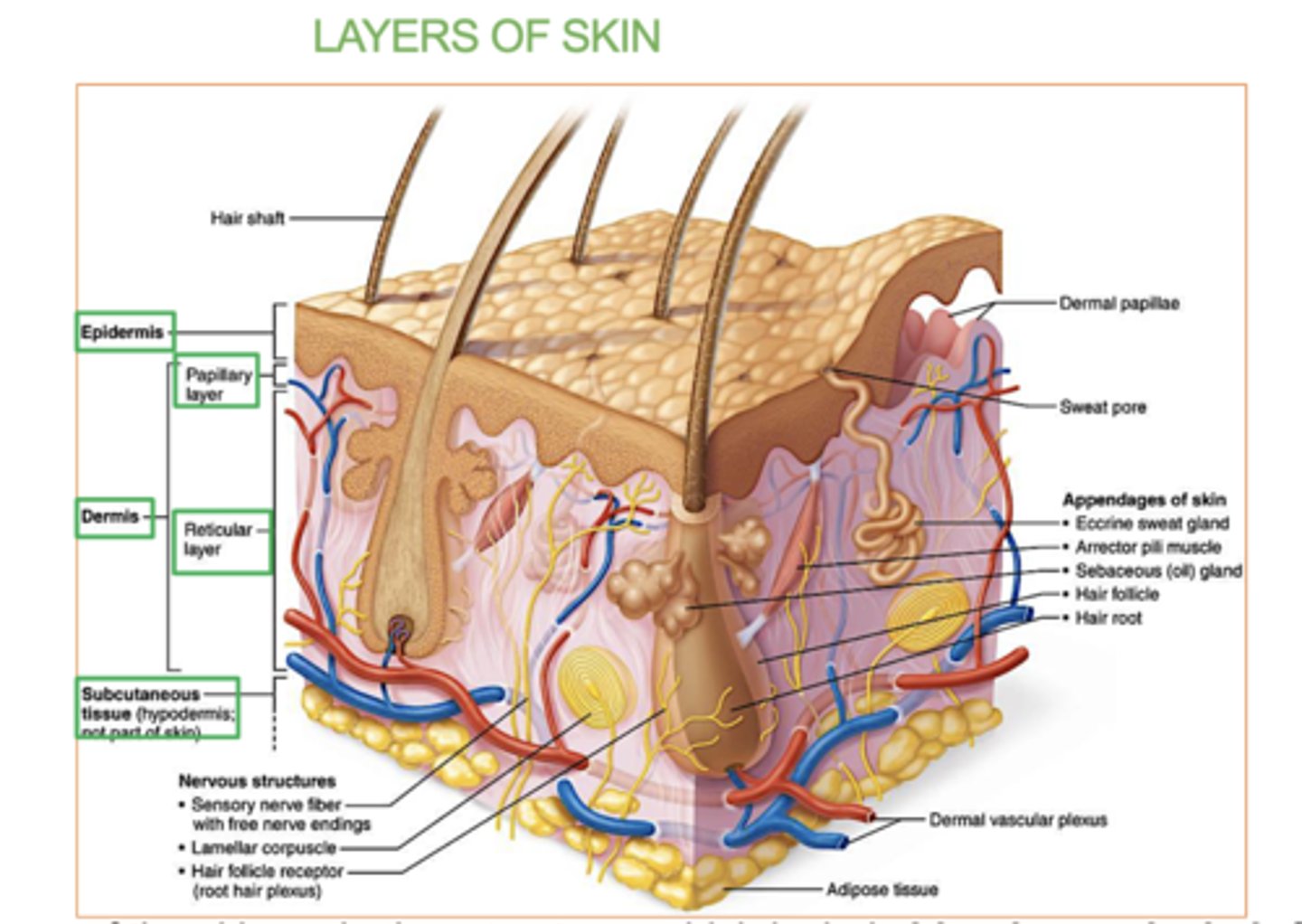
Epidermis job/definition
the outermost layer of the skin, made of tightly packed cells.
-
Job: It protects against germs, UV rays, and water loss while helping with skin renewal.
What determines whether a skin is "thick" or "thin"?
the Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what is the epidermis made up of?
(not the layers)
-Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
a type of tissue made of multiple layers of flat cells with a tough, protective outer layer of keratin.
( protects against physical damage, dehydration, and infection. Found mainly in the skin's epidermis )
what is the Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What makes up the epidermis.
its a type of tissue made of multiple layers of flat cells with a tough, protective outer layer of keratin.
Dermis definition
the thick, middle layer of skin that provides strength, flexibility.
houses blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and glands.
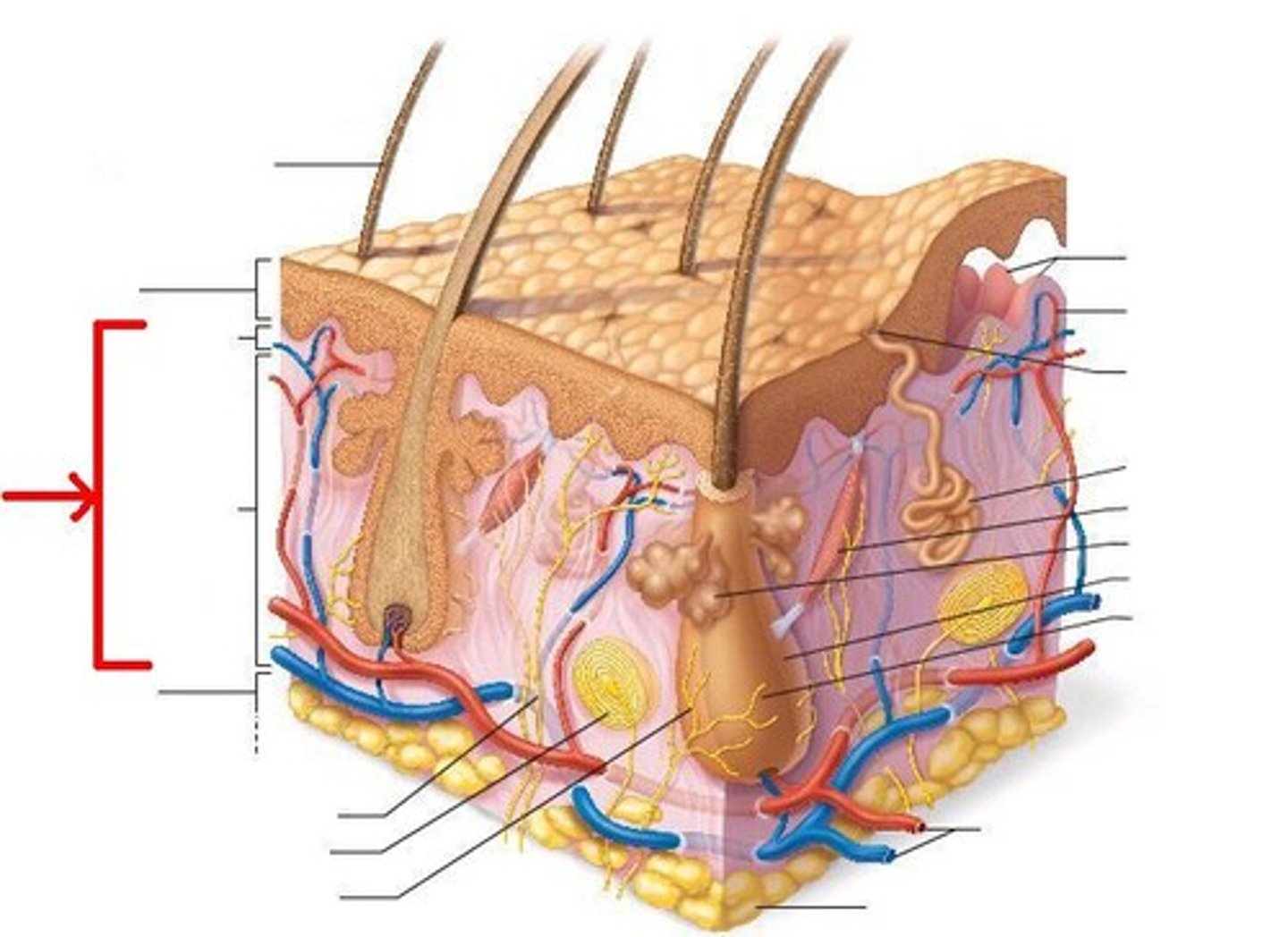
Dermis 2 layers
papillary and reticular
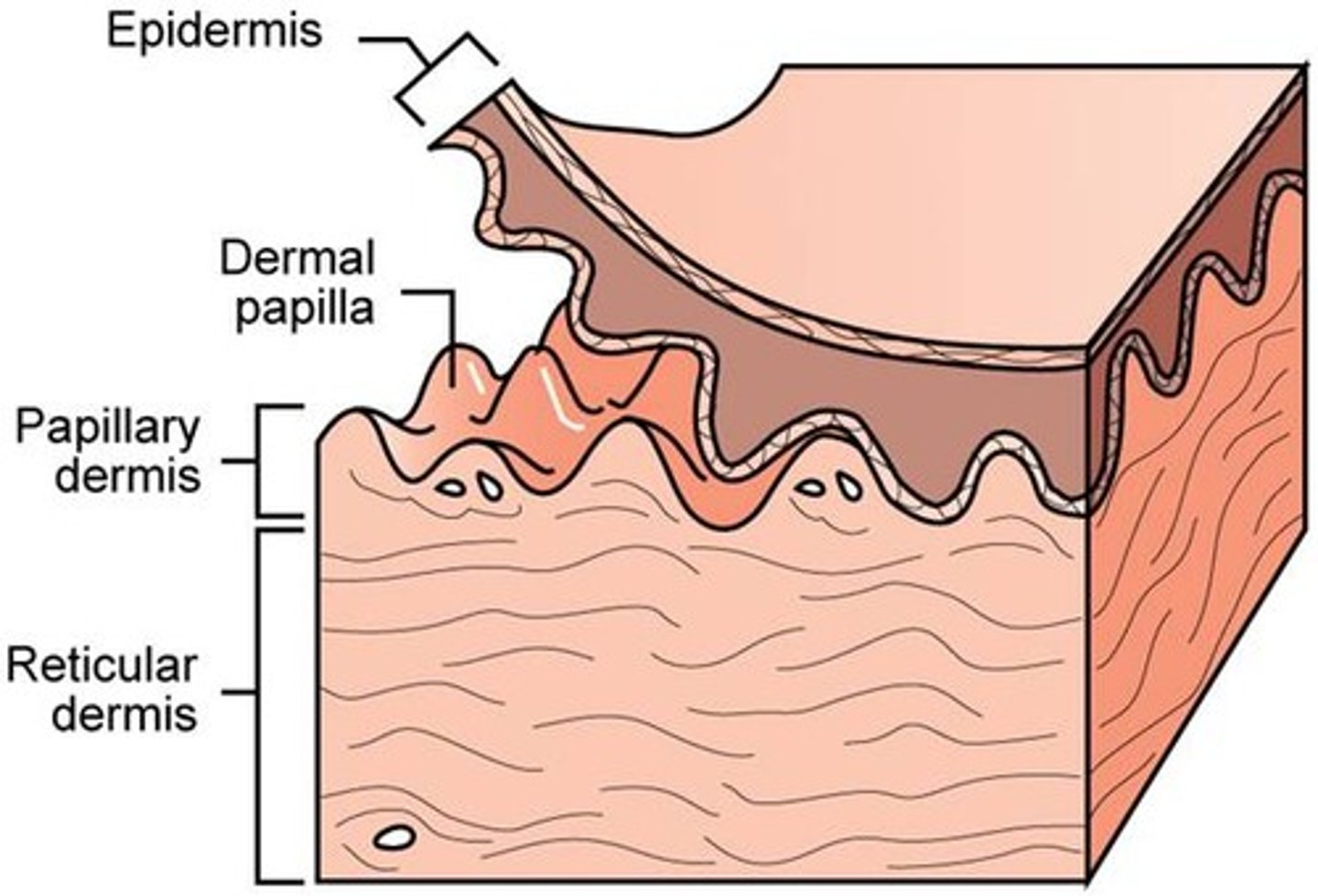
Dermis 2 layers definitions
Papillary layer - Thin, upper layer with collagen and capillaries that nourish the skin and support touch receptors.
(Areolar connective tissue)
Reticular layer - Thicker, deeper layer with dense connective tissue, providing strength and elasticity.
(Dense irregular connective tissue)
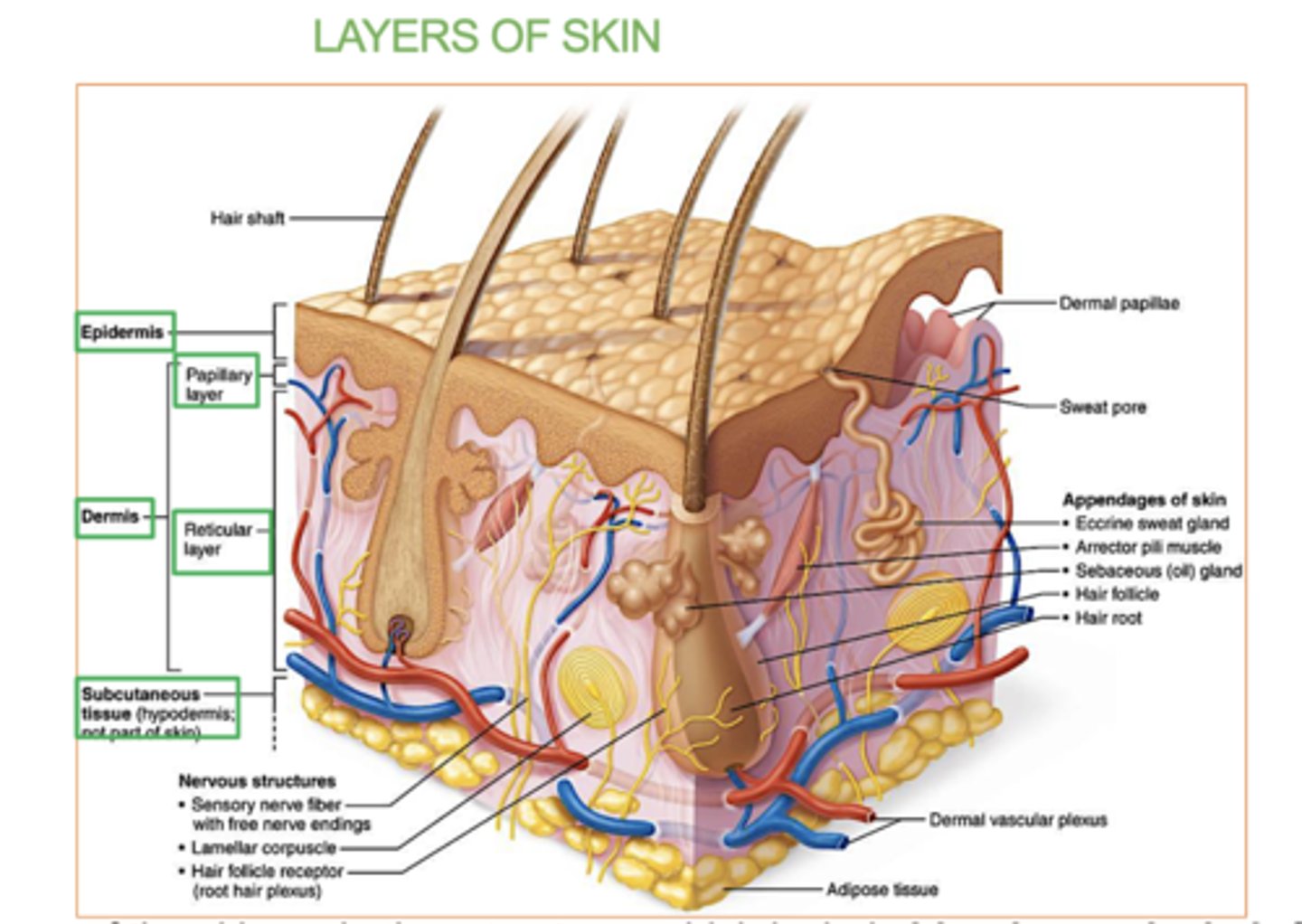
Hypodermis
deepest layer of skin, made of fat and connective tissue.
-
It insulates the body, stores energy, and cushions organs for protection.
(Not a part of the skin, but usually studied with the skin .
Adipose connective tissue (subcutaneous fat)
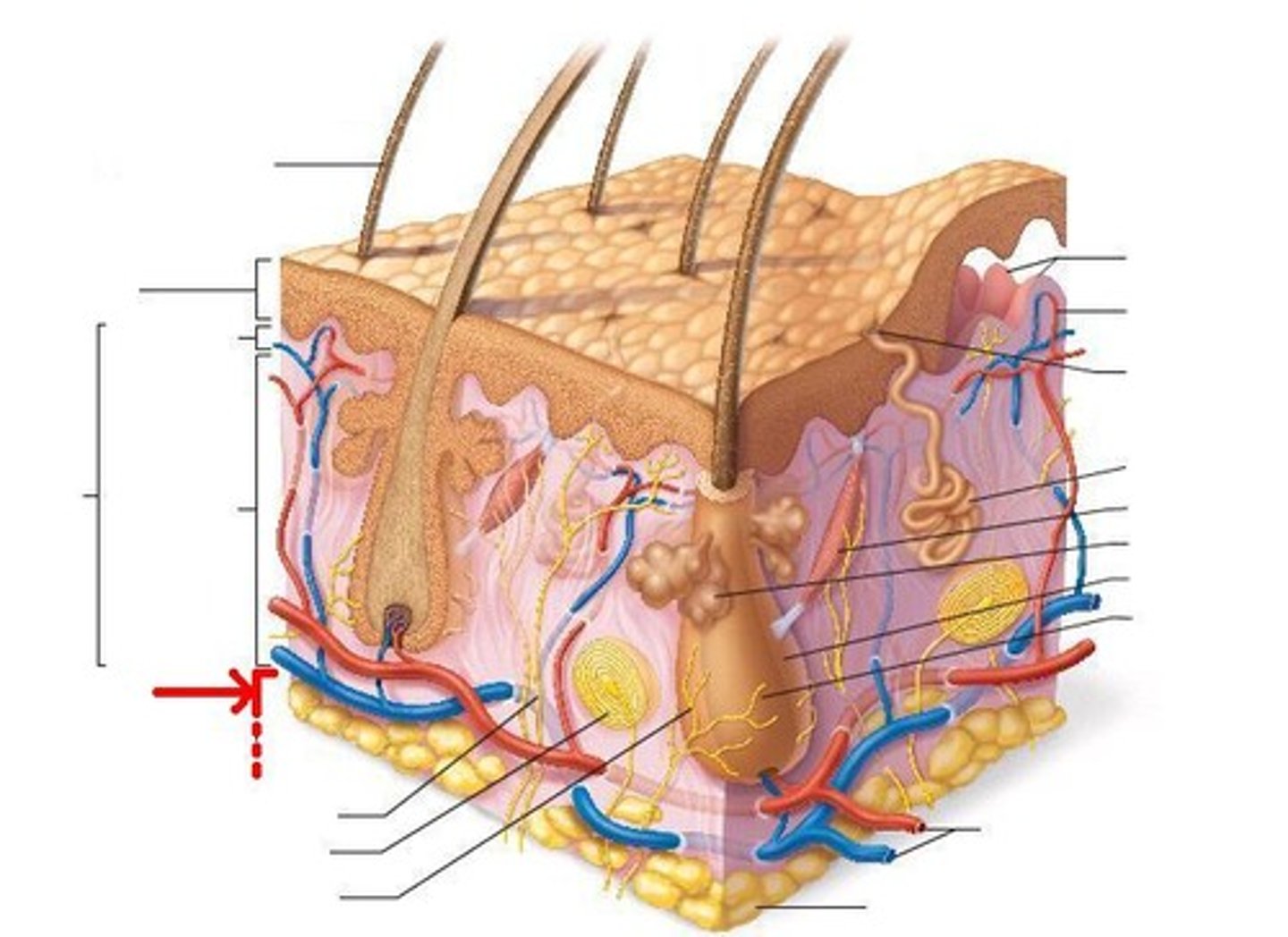
Which structure/layer of the skin is mostly fat and connective tissue?
The hypodermis (adipose fat tissue) - subcutaneous fat
deepest layer of skin, made up of mostly fat and connective tissue
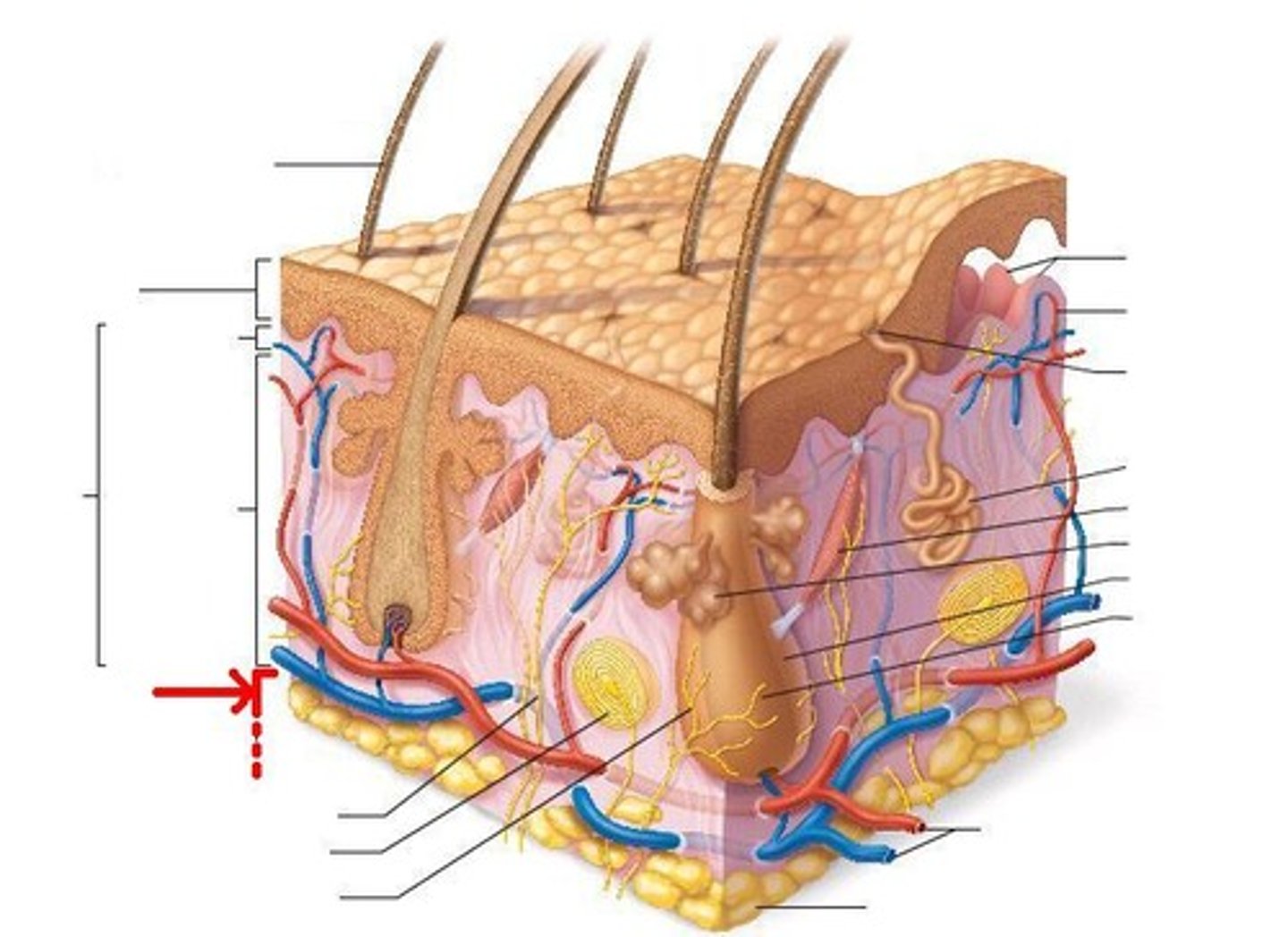
another name for the hypodermis layer?
(the tissue that it's made up of)
subcutaneous tissue
the deepest layer of skin, made up of fat and connective tissue.
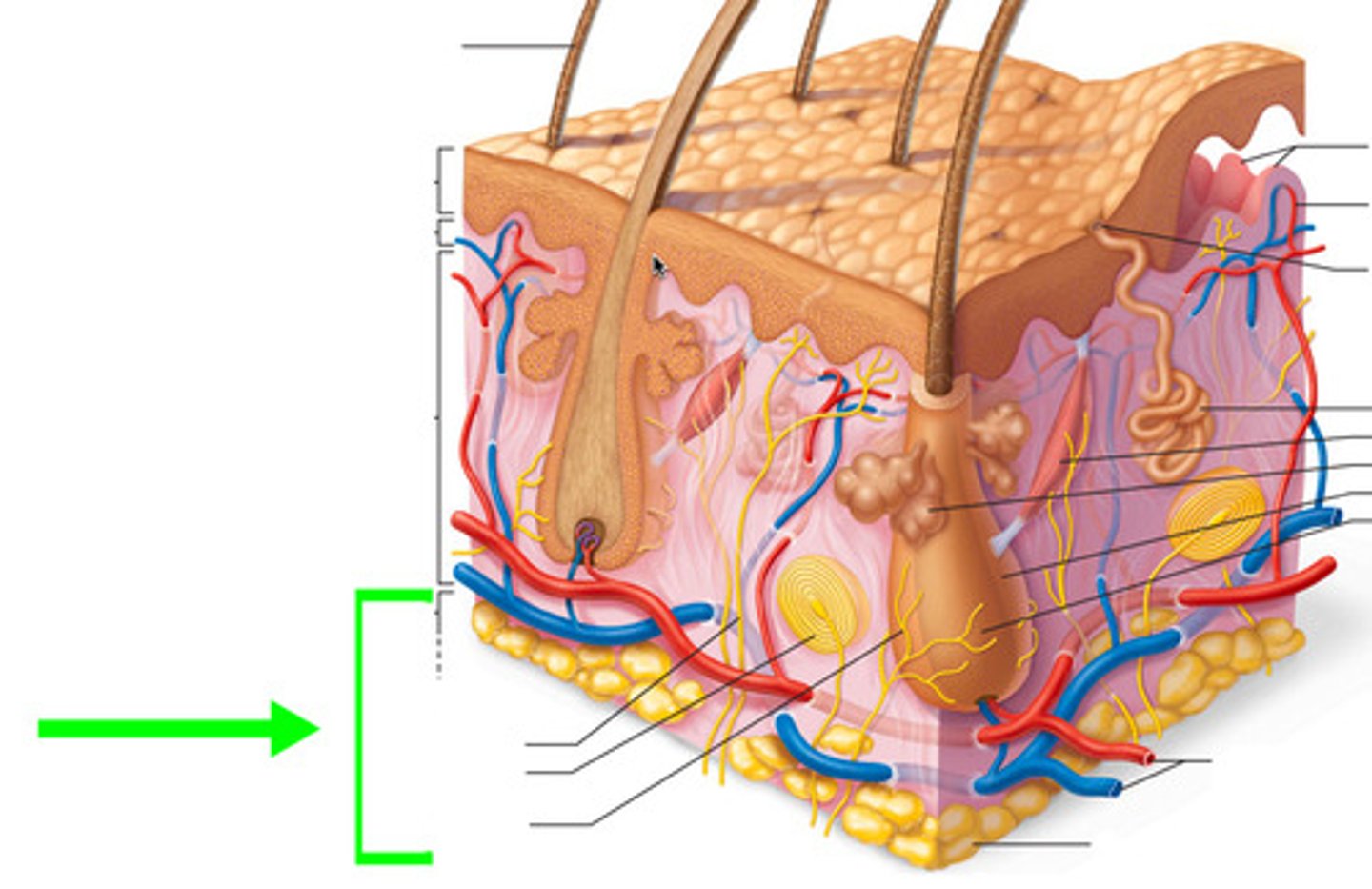
What's the name of the tissue that makes up the papillary layer?
Areolar connective tissue
Whats the name of the tissue that makes up the reticular layer?
Dense irregular connective tissue
Where do you find thick skin?
on palms and soles, fingers and toes
what does thick skin have & not have?
sweat glands, but no hair follicles or sebaceous (oil) glands
ex- palms, soles, fingertips, toes
if the epidermis is thicker i it considered thick or thin skin?
thick skin
Where do you find thin skin?
rest of the body except the palm, soles, fingers and toes.
which skin possesses hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands?
Thin or Thick skin?
Thin skin
5 layers of the Epidermis : from deep to top
(newest to oldest)
From deep to top:
Stratum basale: Single layer of stem cells with few melanocytes and Merkel cells.
Stratum spinosum: Keratinocyte attachments appear spiny. Few dendritic (Langerhans) cells.
Stratum granulosum: Granular keratinocytes.
Stratum lucidum: Only in thick skin. No nucleus or organelles.
Stratum corneum: Dead keratinocytes flaking away.
stratum basale
deepest layer of epidermis
-where stem cells divide to produce new keratinocytes. It also contains melanocytes (which produce melanin) and Merkel cells (touch & pressure receptors).
This layer is responsible for renewing the skin.
Stratum spinosum
2nd deepest layer of the epidermis
-layer of the epidermis where keratinocytes are connected by spiny projections.
It contains dendritic (Langerhans) cells that help with immune defense.
Stratum granulosum
3rd deepest layer of the epidermis (closer to surface)
- layer of the epidermis where keratinocytes begin to die and form granules of keratin.
(Granular keratinocytes)
Stratum lucidum
4th layer of the epidermis (deep to top, so super close to surface)
- A thin, clear layer of dead keratinocytes
found only in thick skin (like the palms and soles)
No nucleus or organelles
Stratum corneum
outermost layer of the epidermis
-made up of dead, flattened keratinocytes
The cells in this layer constantly shed and are replaced by new ones from deeper layers.
5 Cell types of the epidermis (deep to top)
1. Stem cells: Cells that divide to make new skin cells (keratinocytes) - Stratum basale
2. Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color and protects against UV radiation - Stratum basale
3. Merkel (Tactile) cells: Cells that act as touch and pressure sensors
- Stratum basale
4. Keratinocytes: Skin cells that produce keratin, a protein that helps protect the skin
- Found in Stratum basale, Stratum spinosum, and Stratum granulosum
5. Dendritic (Langerhans) cells: Immune cells that fight off harmful pathogens or toxins (phagocytosis)
-Stratum spinosum
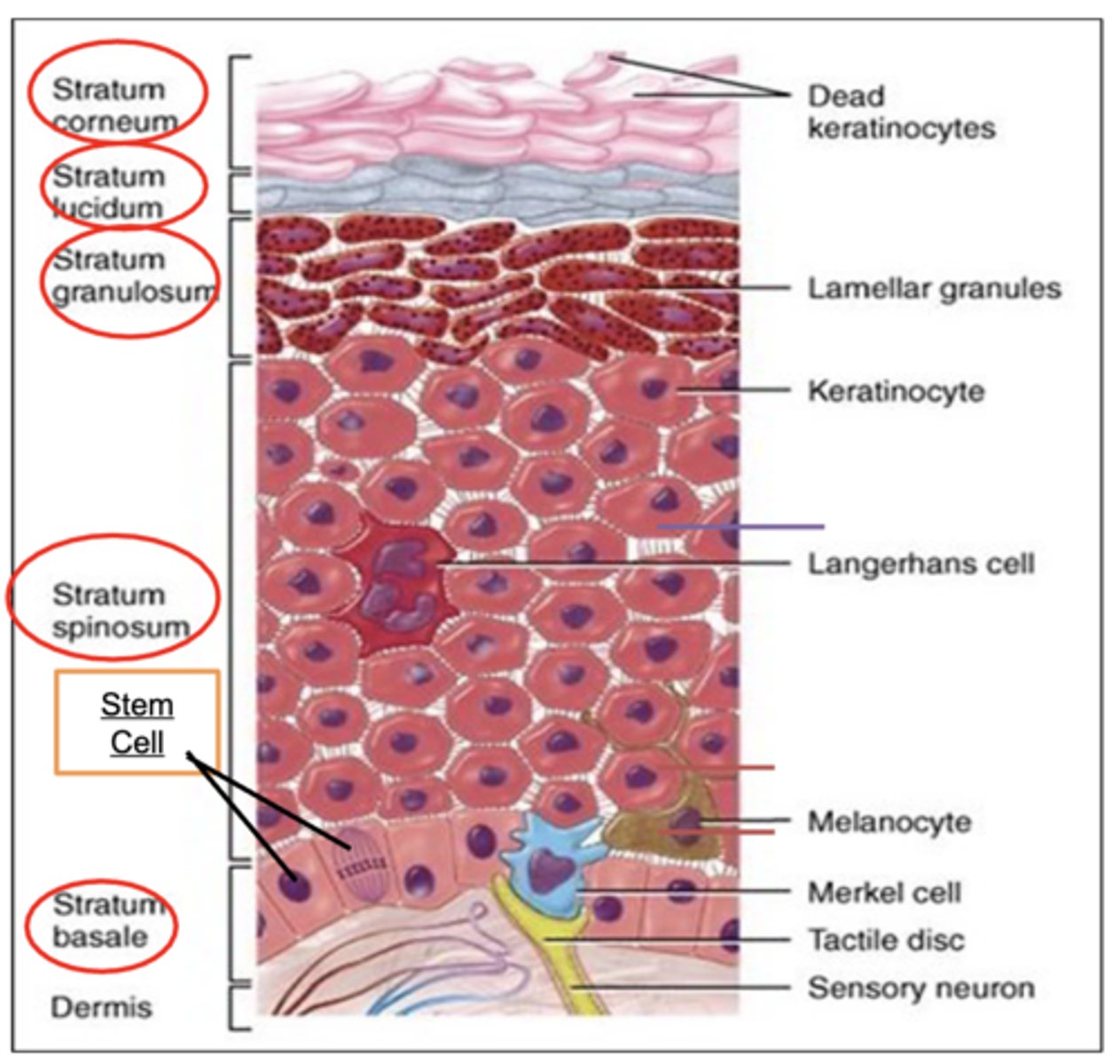
In which layer of the epidermis are each of these cell types :
Stem cells:
Melanocytes:
Merkel cells:
Keratinocytes:
Dendritic (Langerhans) cells
Stem cells: Stratum basale
Melanocytes: Stratum basale
Merkel cells: Stratum basale
Keratinocytes: All layers (mostly in stratum basale, spinosum, and granulosum)
Dendritic (Langerhans) cells: Stratum spinosum
stem cells
Found in the stratum basale
- Stem cells divide to produce new keratinocytes.
These new skin cells move up through the layers of the epidermis as they mature.
Melanocytes
Found in the stratum basale
-produce/create melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
Melanin also helps protect the skin from UV radiation by absorbing and dispersing sunlight.
Merkel cells
found in the stratum basale
- act as touch receptors.
They are involved in sensing light touch and pressure, helping with the skin's ability to detect tactile stimuli.
Keratinocytes
the main cells in the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). They produce keratin, a tough, protective protein .
Found in the stratum basale, stratum spinosum, and stratum granulosum layers
( they move upward as they mature and form the skin's protective barrier)
(most abundant cells in the epidermis)
Dendritic (Langerhans) cells
Immune cells found in the stratum spinosum (2nd deepest layer)
- help protect the skin by identifying and fighting off harmful pathogens or toxins through phagocytosis.
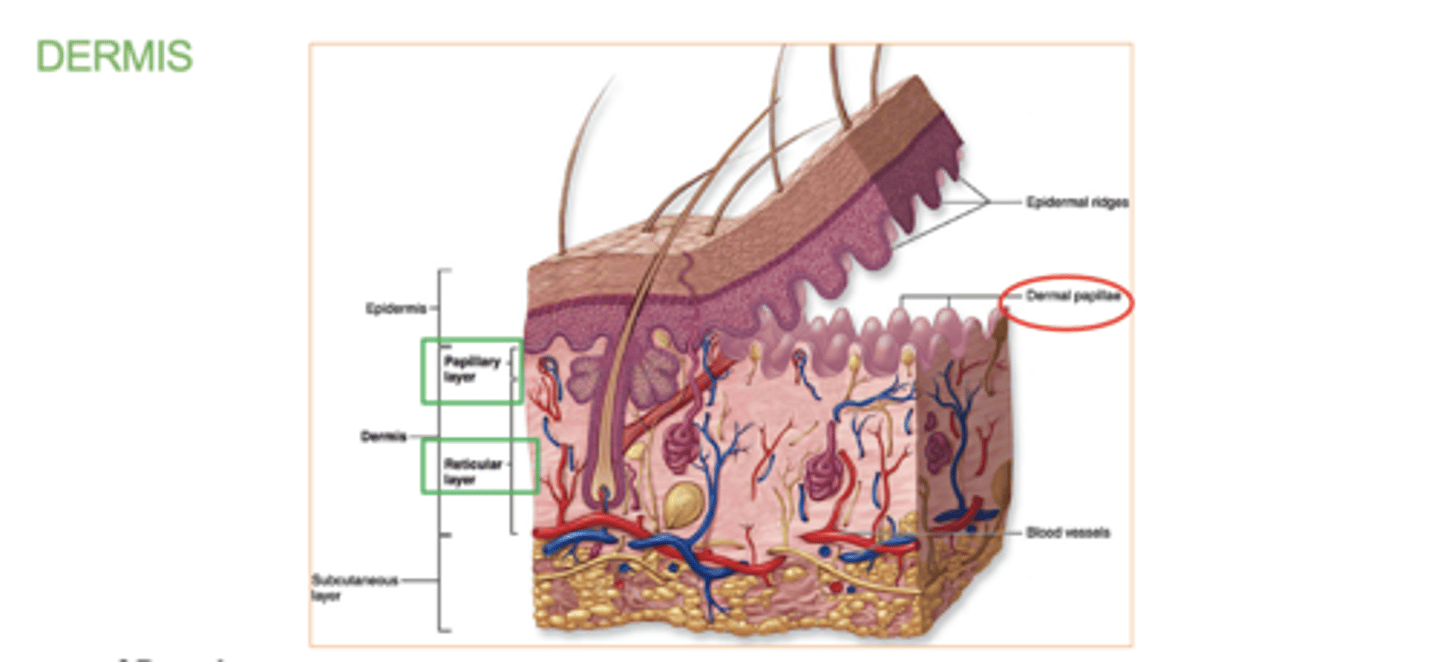
2 Layers of the dermis
1. papillary layer
2. reticular layer
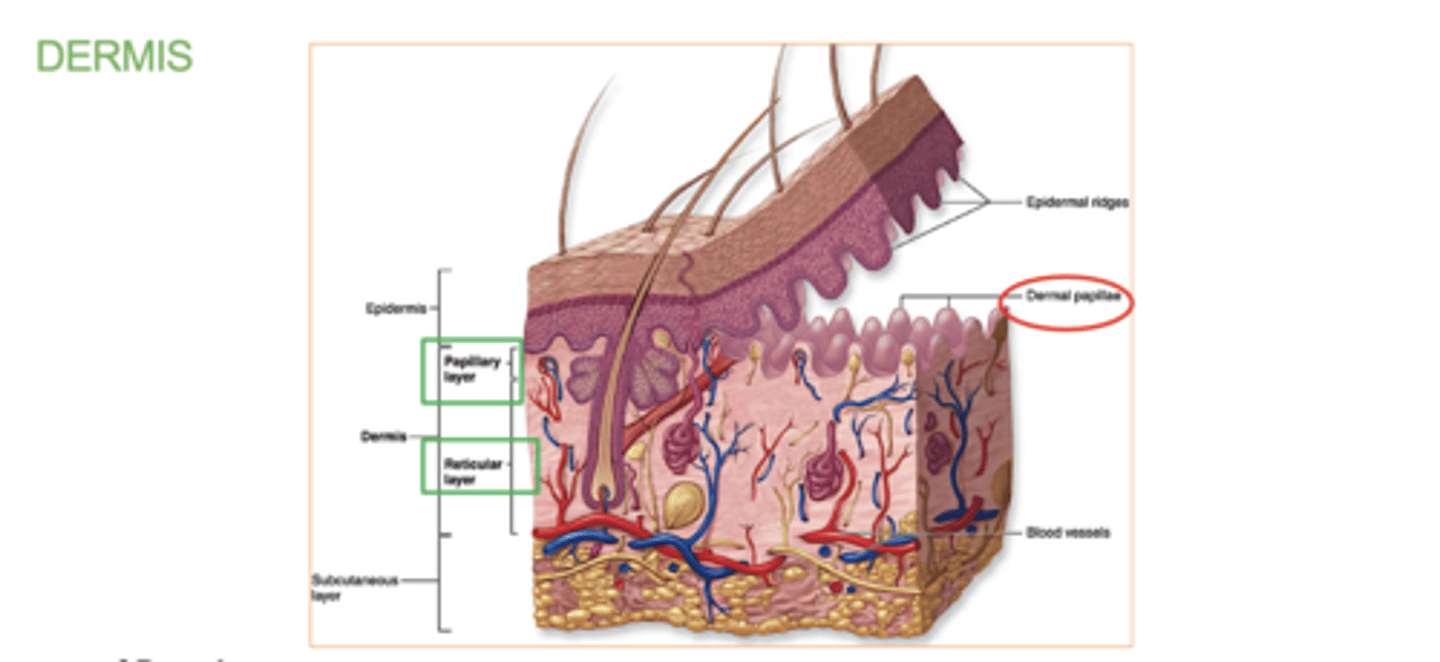
papillary layer
outer layer of the dermis, directly beneath the epidermis
- contains the dermal papillae
( upward fingerlike projections of the dermis. responsible for fingerprints)
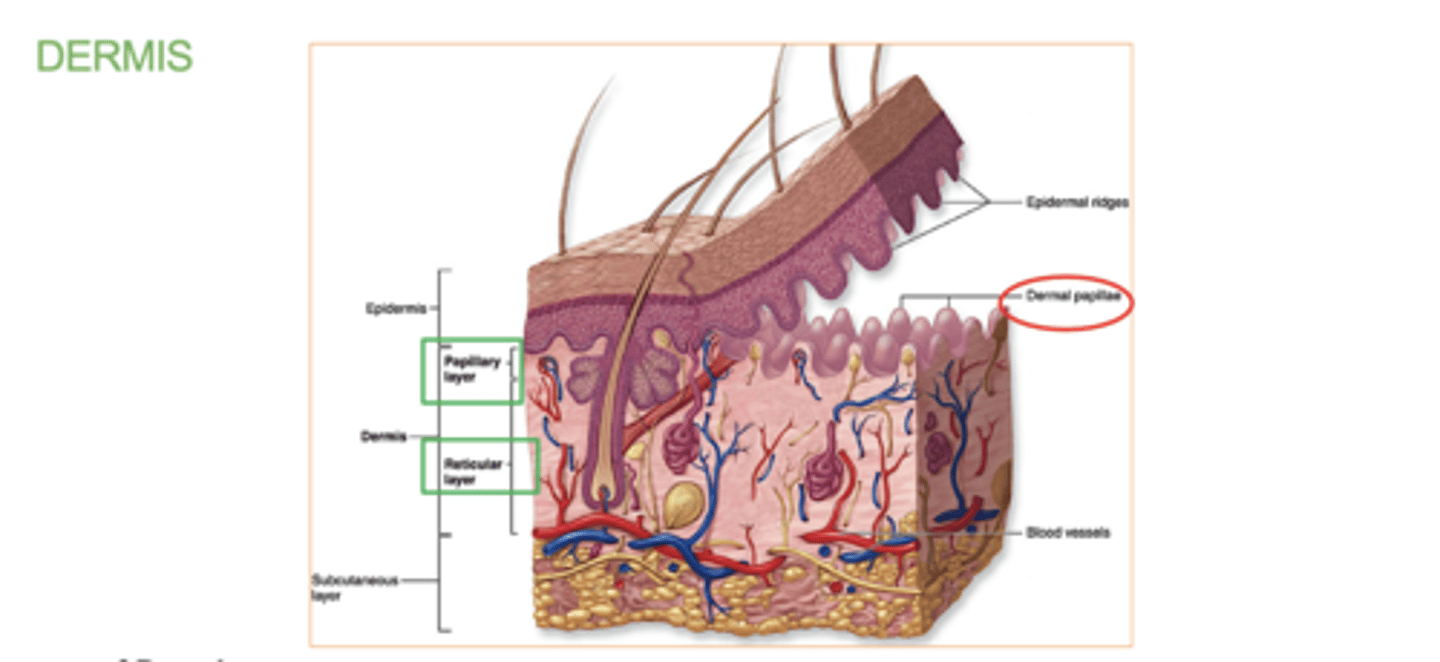
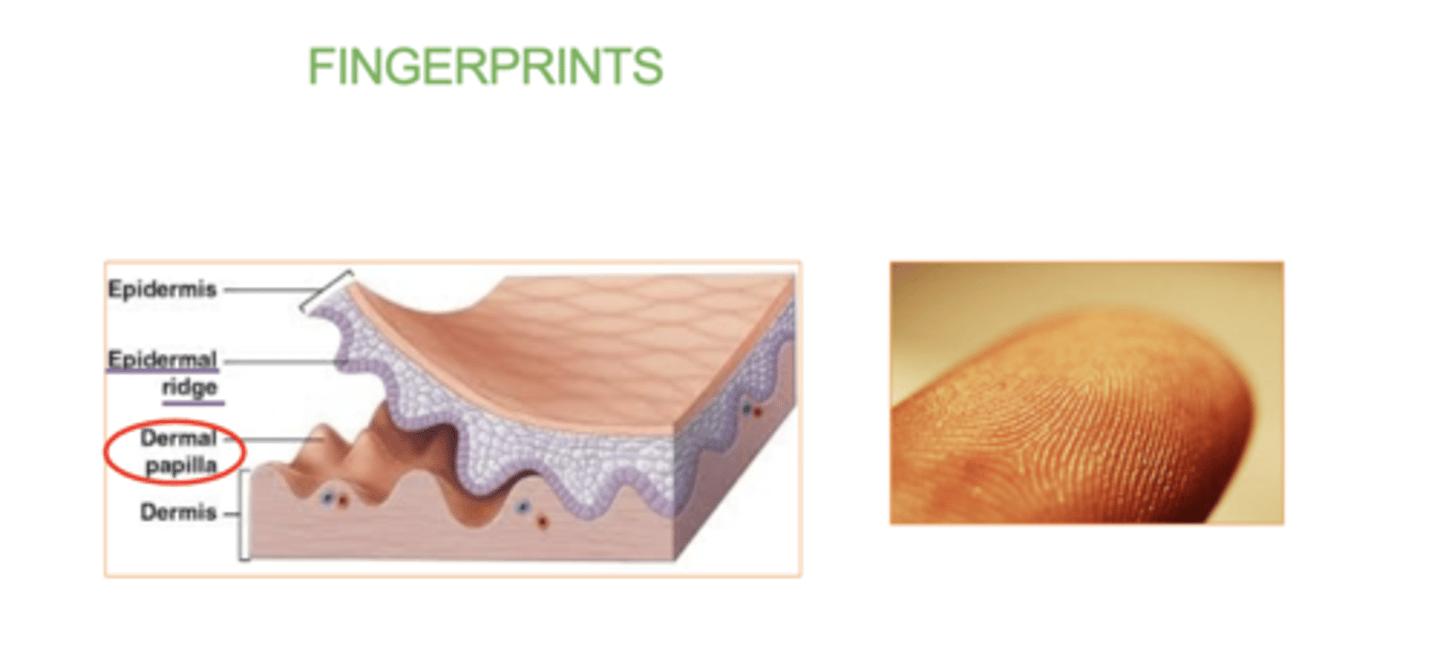
What is the dermal papillae ?
(dermis layer)
those upward fingerlike projections of the dermis.
They fit into epidermal ridges on fingertips that leave fingerprints.
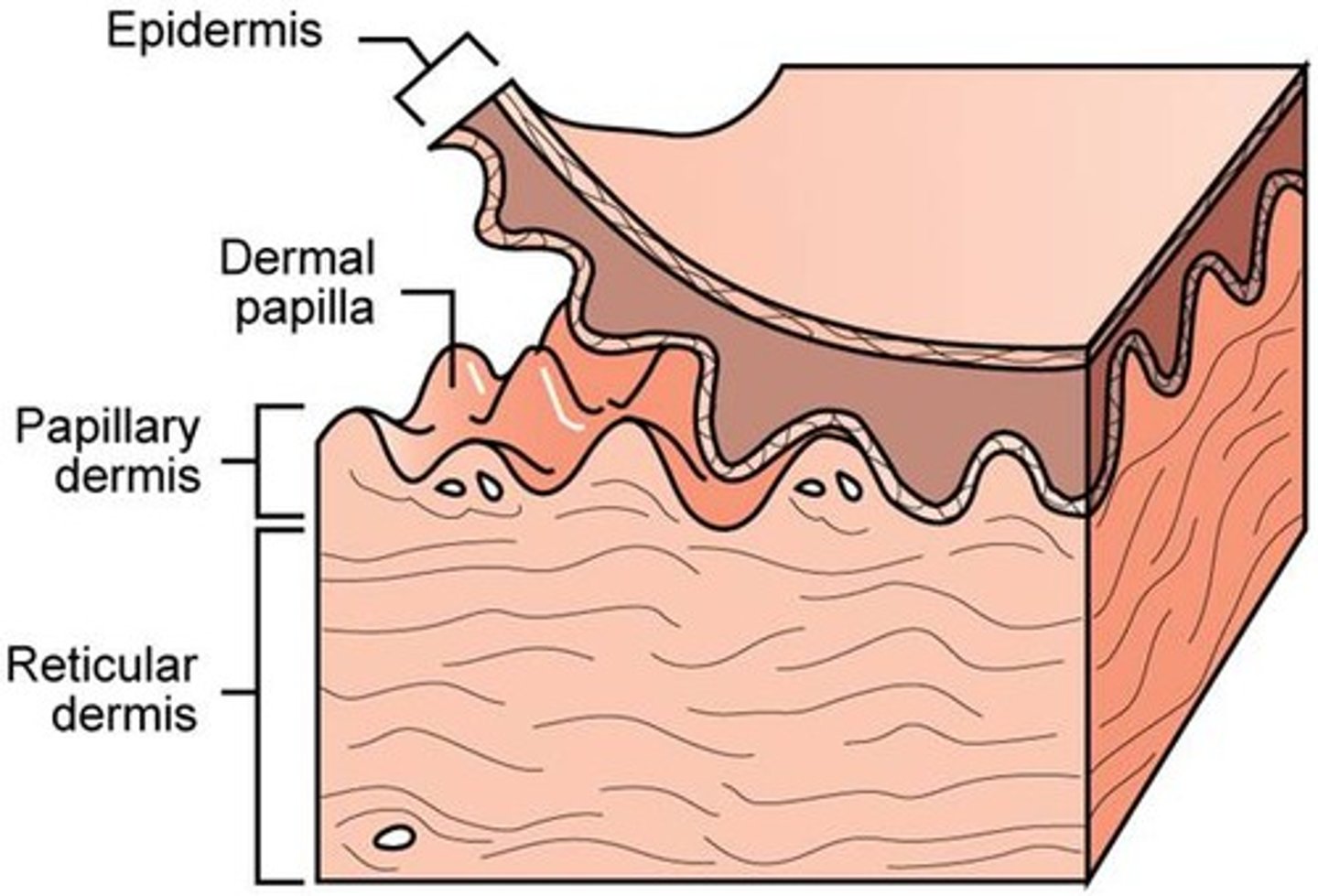
reticular layer
Deeper & thicker layer of the dermis that supplies the skin with oxygen and nutrients.
Dense irregular CT
________ papillae and _________ ridges from fingerprints.
Dermal, epidermal.
which comes first /top layer the papillary layer or reticular layer?
papillary layer.
located just below the epidermis.
which comes second/bottom layer the papillary layer or reticular layer?
The reticular layer .
located beneath the papillary layer.
4 Structures in the dermis
(not layers, structures)
1. Meissner’s corpuscles- touch receptor
2. Free nerve endings- pain, temperature
3. Pacinian corpuscles - (pressure receptors)
4. Sweat and sebaceous- (oil) glands
(Hair bulbs are located in the dermis but they originate from epidermis)
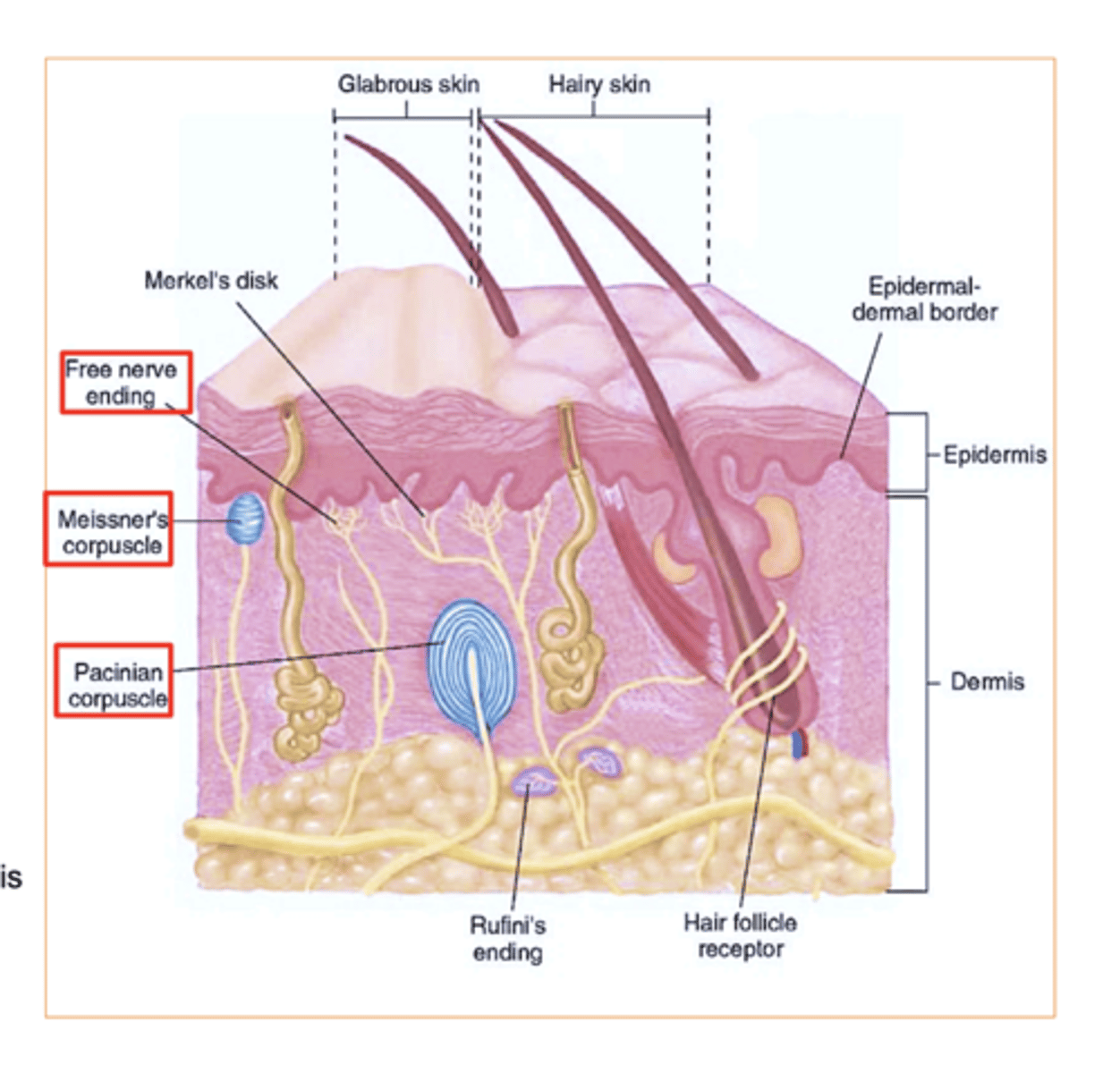
Pressure receptor in dermis?
Pacinian corpuscles
Where is the Meissner's corpuscles?
In the papillary layer of the dermis!
Where are the Free nerve endings?
come all the way from the bottom of the dermis (reticular layer) up to the papillary layer of the dermis!
the 2 main touch receptors in our skin :
Merkel cells (epidermis) : Located in the stratum basale.
Meissner's corpuscles (dermis/ papillary layer): Located in the papillary layer of the dermis.
What's melanin produced by?
melanocytes
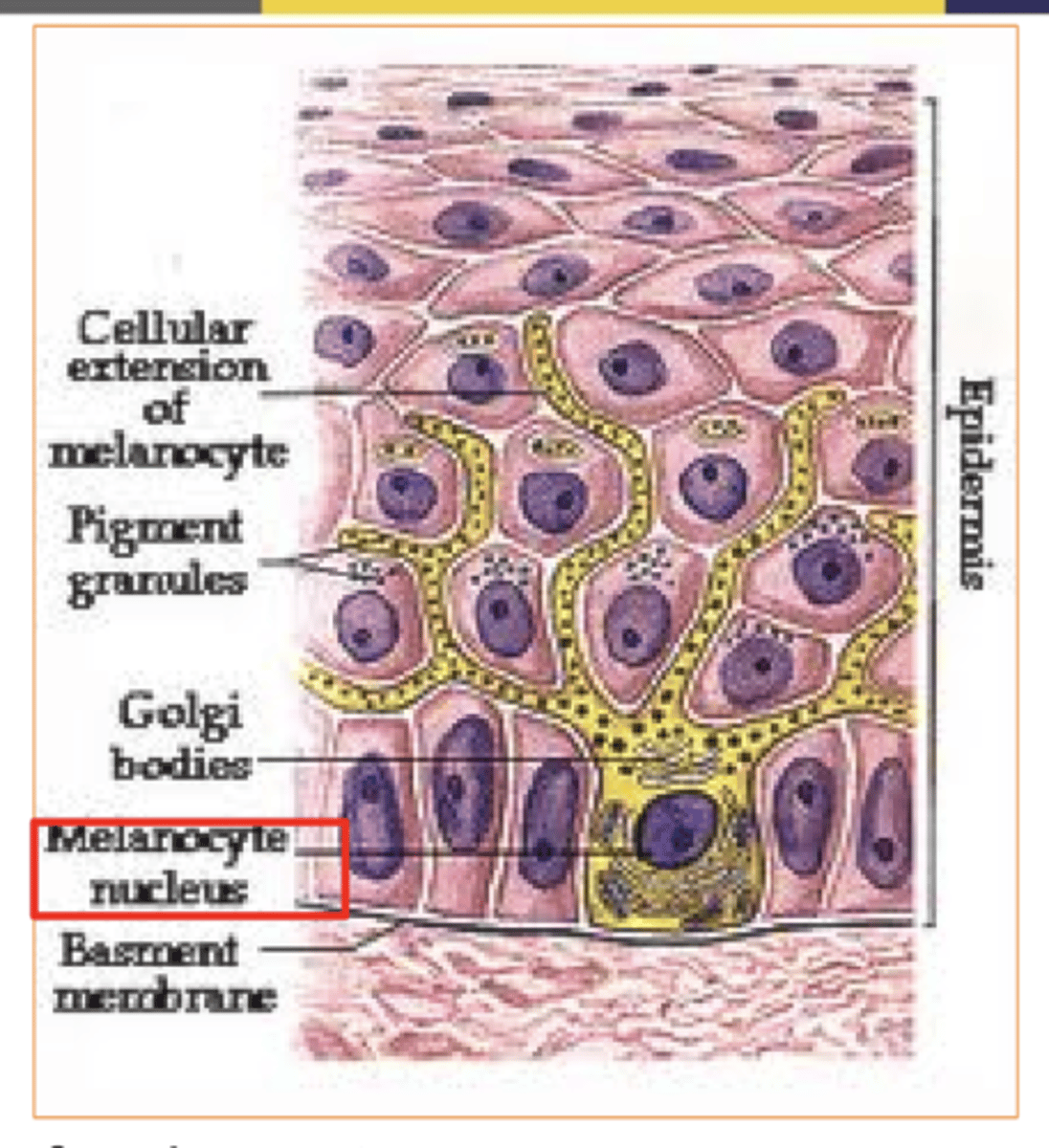
what's melanin?
the pigment that gives our skin its color
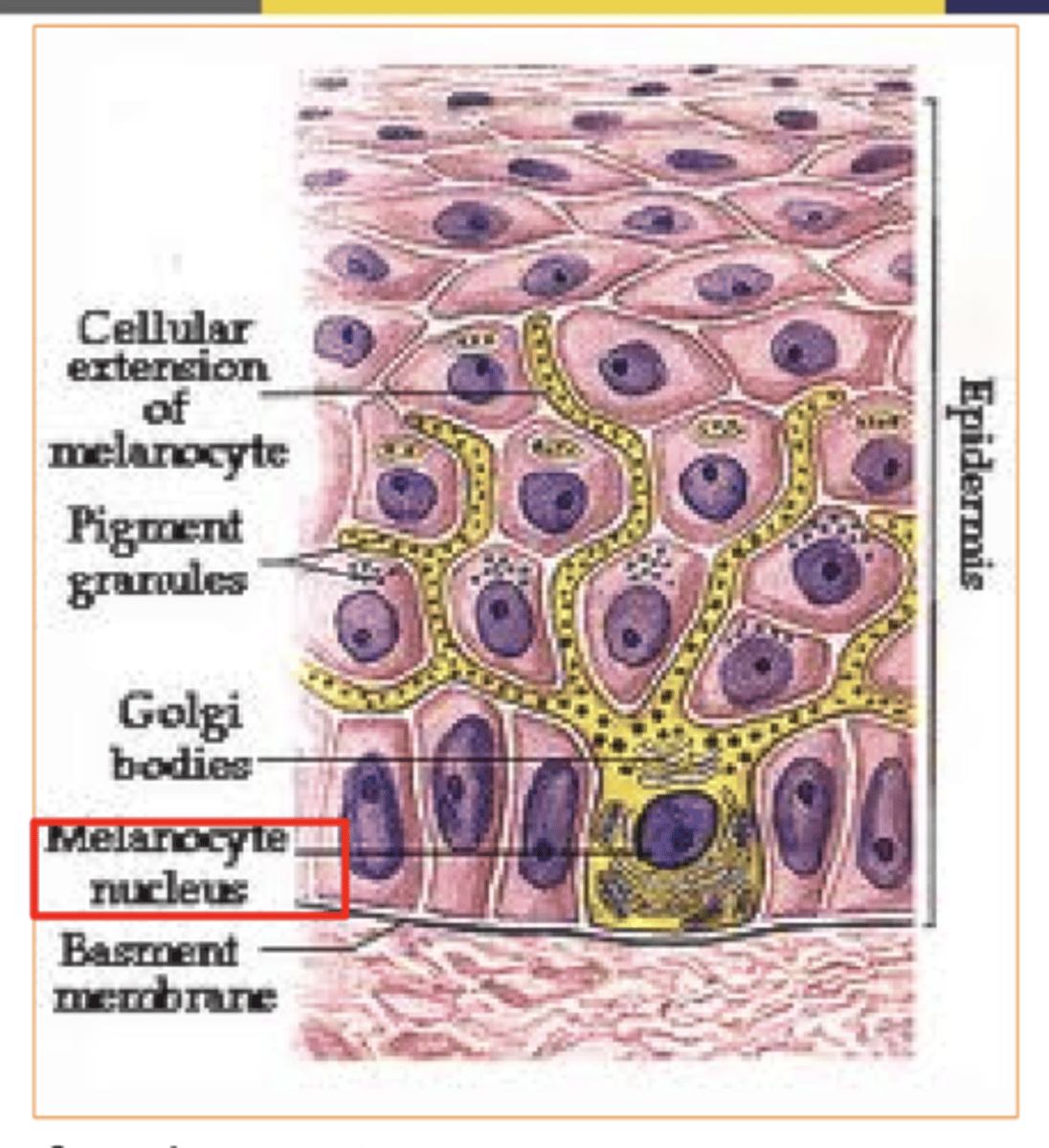
People of different skin color have the ______ number of melanocytes.
same/different
same
Dark skinned people produce _____ quantities of melanin, & melanin breaks down more ______.
Greater/lesser
slowly/rapidly
Dark-skinned people produce greater quantities of melanin, melanin breaks down more slowly.
light skinned people produce ______ melanin, & melanin break down more ______.
Greater/less
slowly/rapidly
Light-skinned people produce less melanin, melanin breaks down more rapidly.
Amount of melanin also varies with exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays of sunlight?
true or false
true.
what are 2 factors that can affect skin color?
Hemoglobin & Carotene
Whats hemoglobin?
The red pigment of red blood cells.
Adds reddish to pinkish hue to skin
Whats carotene?
The yellow pigment acquired from egg yolks and yellow/orange vegetables.
3 abnormal skin colors/conditions
Pallor, Jaundice, Cyanosis

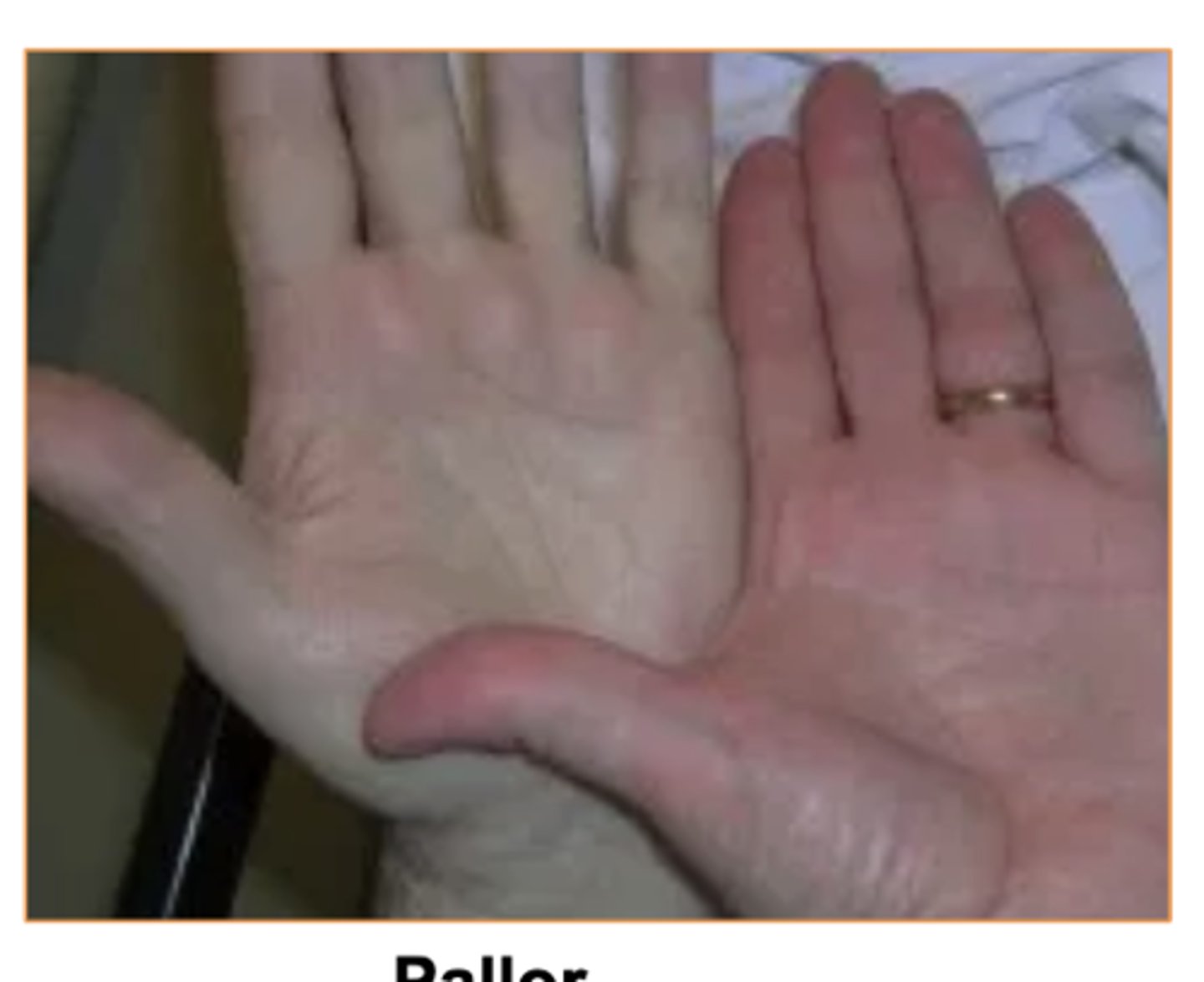
Whats Pallor?
decreased blood flow to skin
Some causes- Emotional stress, low blood pressure, circulatory shock, cold, anemia
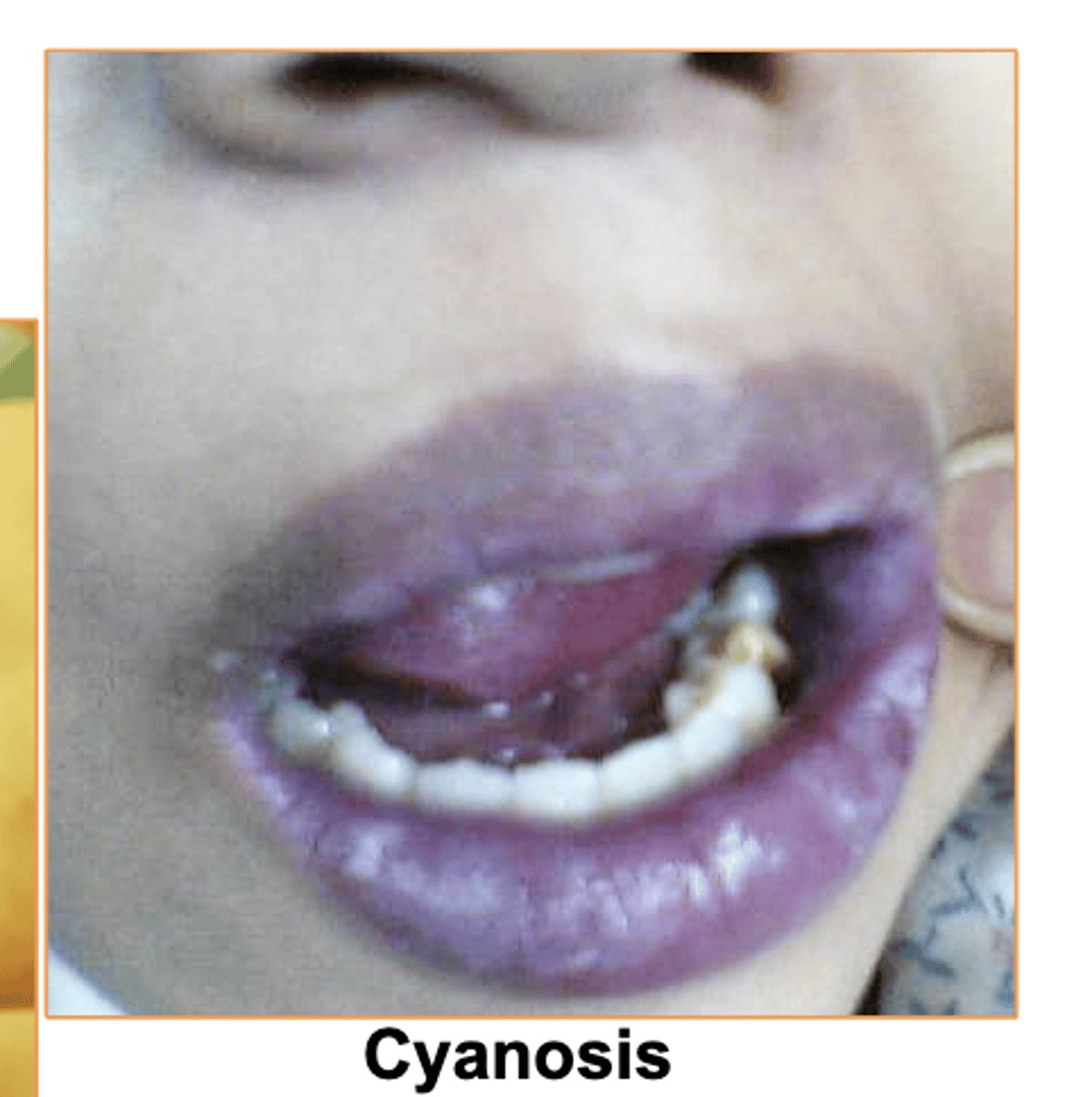
Whats Cyanosis?
bluish discoloration from deficiency of oxygen
Some causes- Airway obstruction (drowning or choking) andlung diseases (emphysema
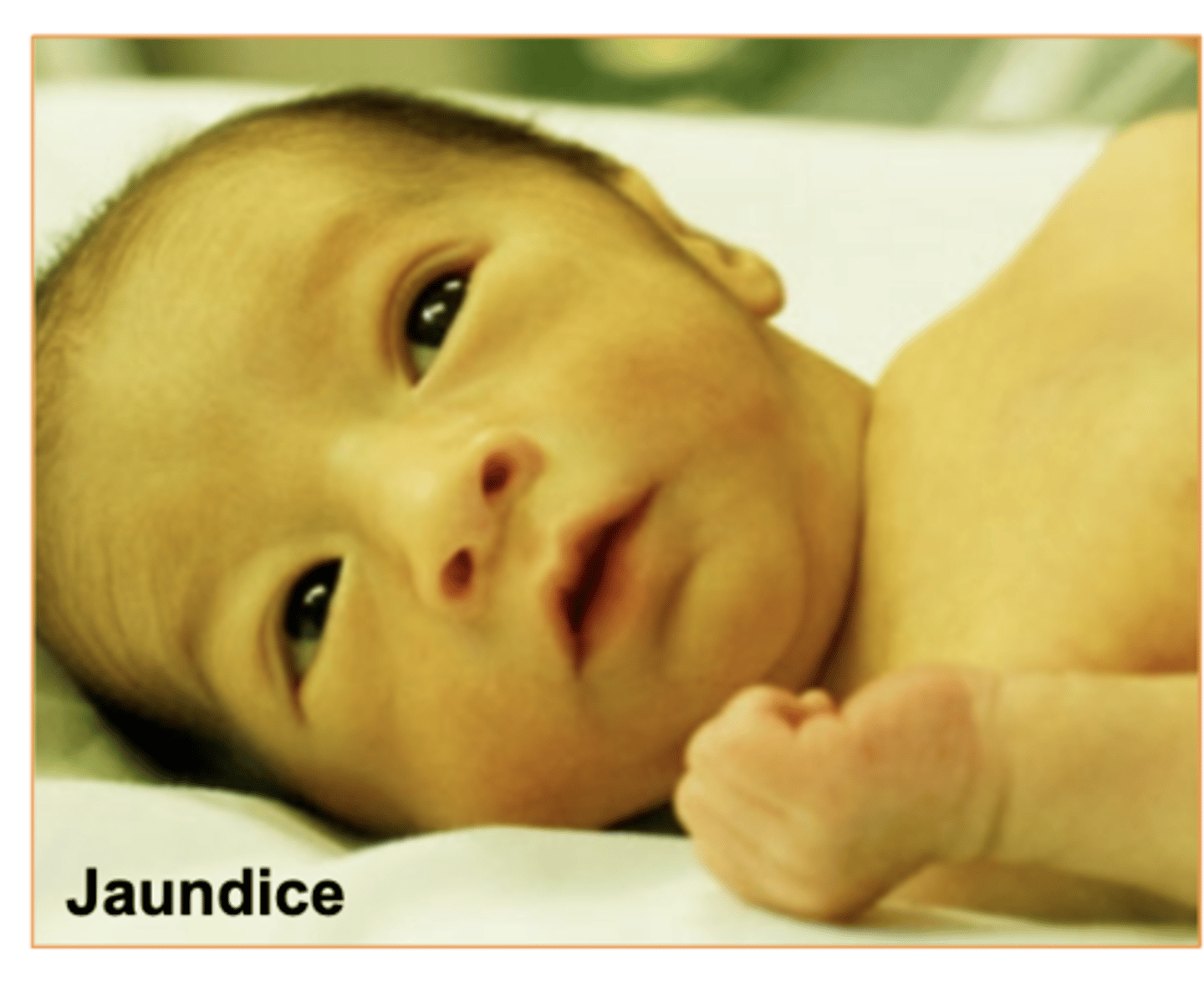
Whats Jaundice?
yellowish discoloration of skin and sclera due to excess of bilirubin in blood
Some causes- Cancer, hepatitis,compromised liver function.
(common in babies when they're first born)

Whats bilirubin?
a yellow substance produced when red blood cells/hemoglobin breaks down.
It is processed by the liver and excreted in our poo/pee.
High levels of bilirubin can cause jaundice, which makes the skin and eyes look yellow.
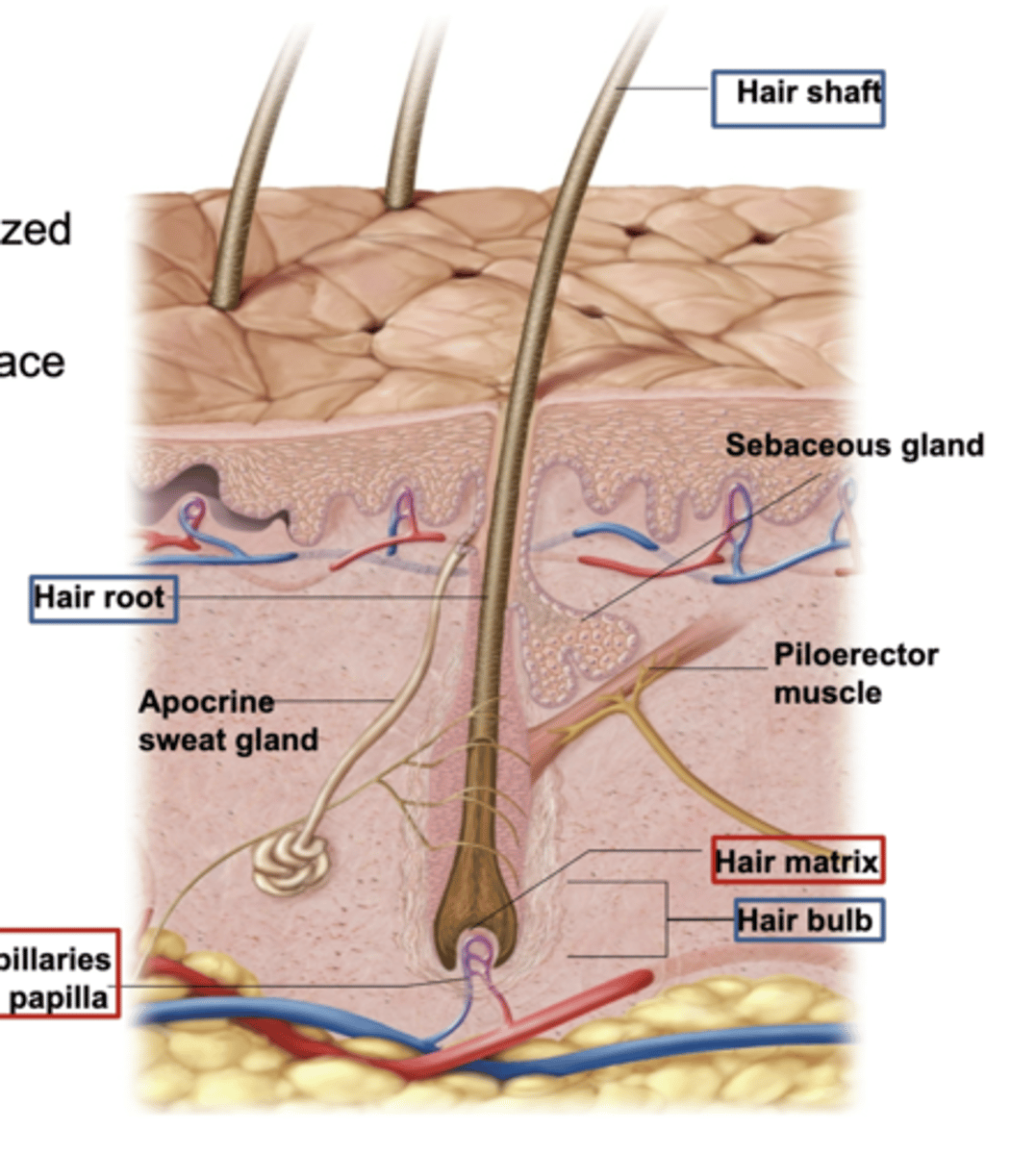
3 Hair Structures
Hair Shaft
Hair root
Hair bulb (contains - Matrix & Papilla)
Hair is an ________ structure.
epidermis/dermis
epidermis
What are hair follicles made of (which type of cells) and where do they originate from?
keratinized cells and they originate in dermis.
Hair shaft :
The visible part of the hair that extends above the skin's surface.
It is made of keratinized cells
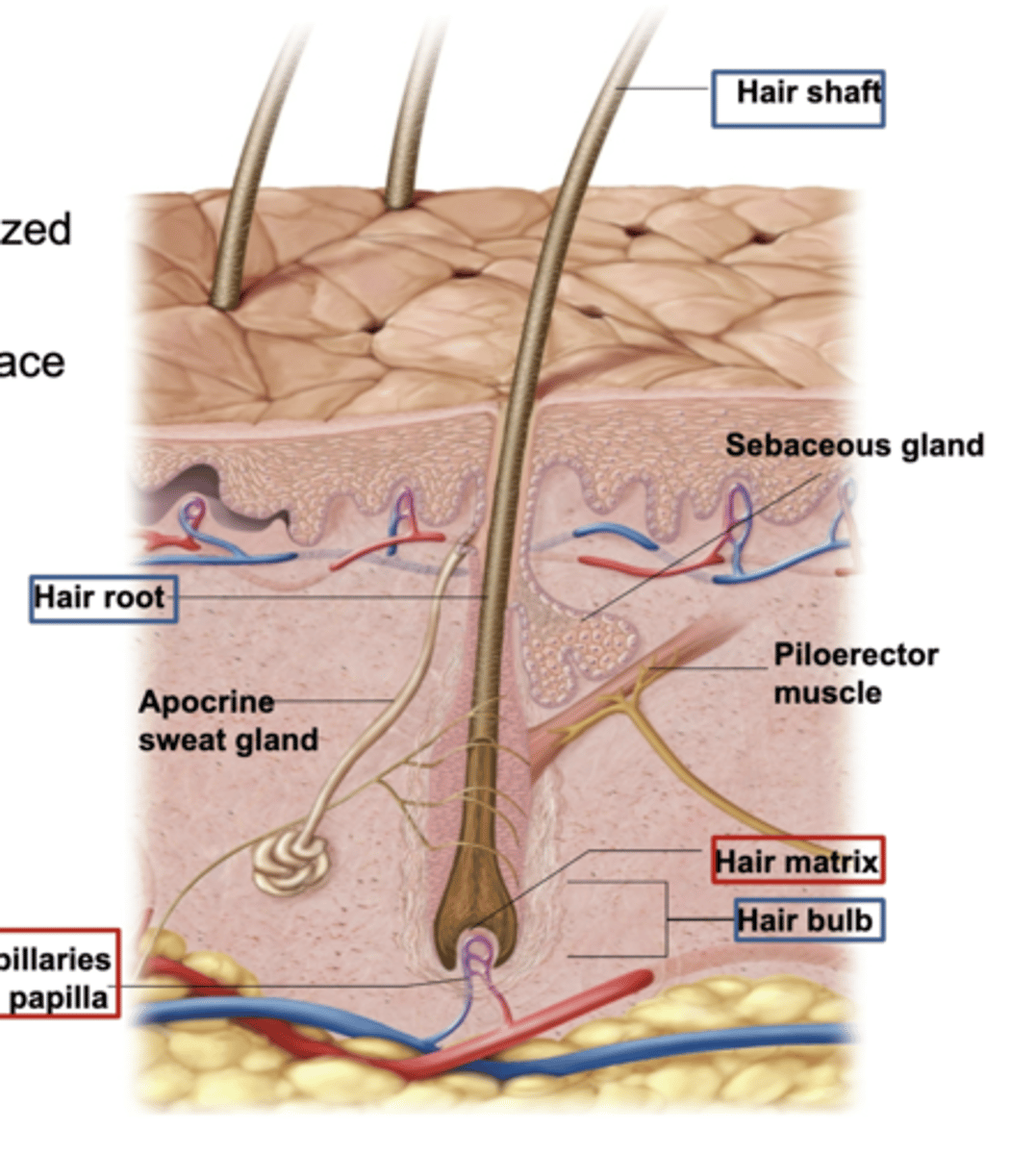
Hair root:
The part of the hair located below the skin's surface
anchored in the hair follicle
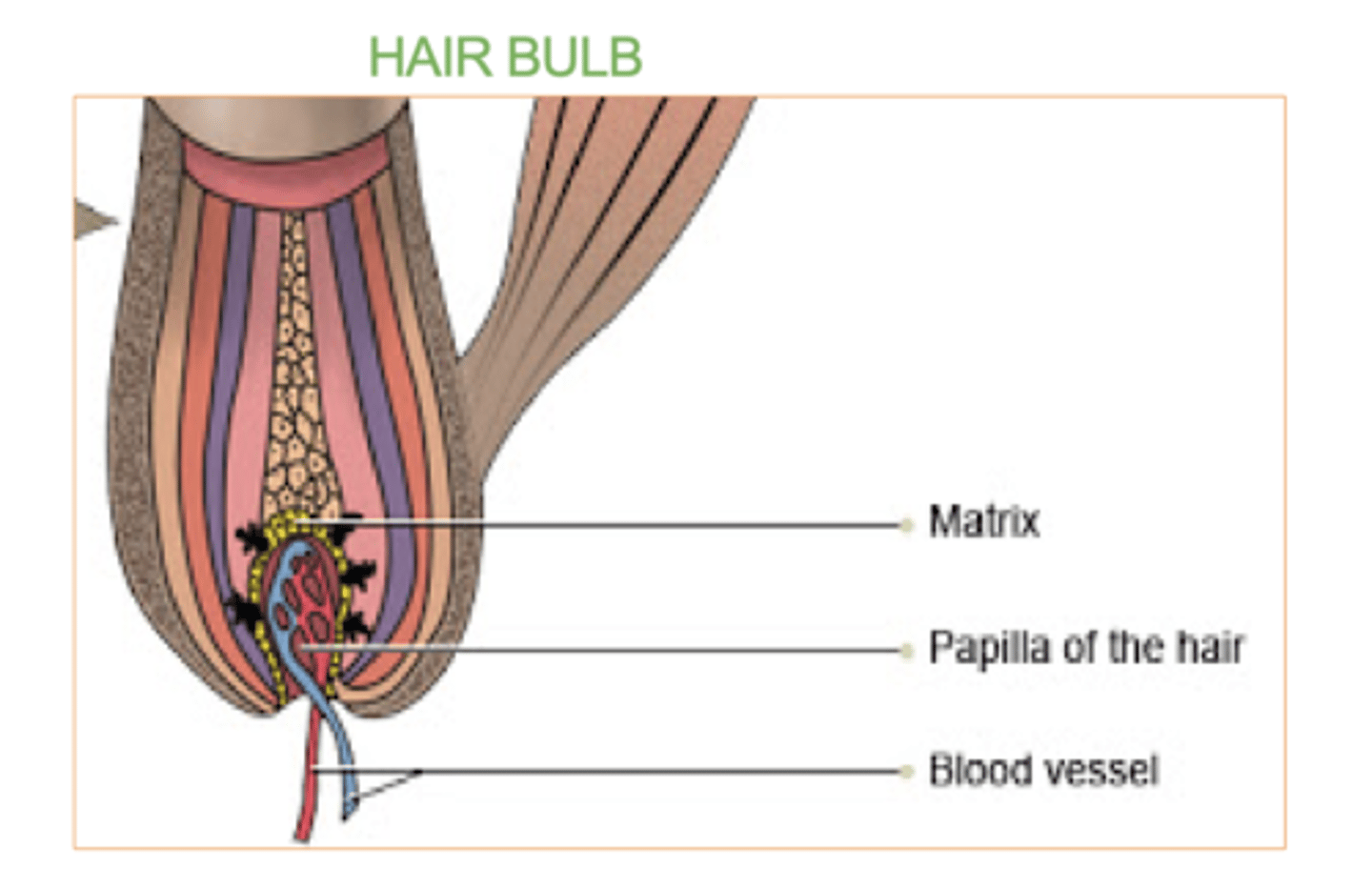
Hair bulb:
The rounded, base part of the hair root located deep in the hair follicle.
Contains the Matrix & the Papilla.
What's the hair matrix?
Where the cells rapidly divide. (group of rapidly dividing cells)
These cells produce new hair cells, which become keratinized and form the hair shaft as they move upward.
It also contains melanocytes, which give hair its color.
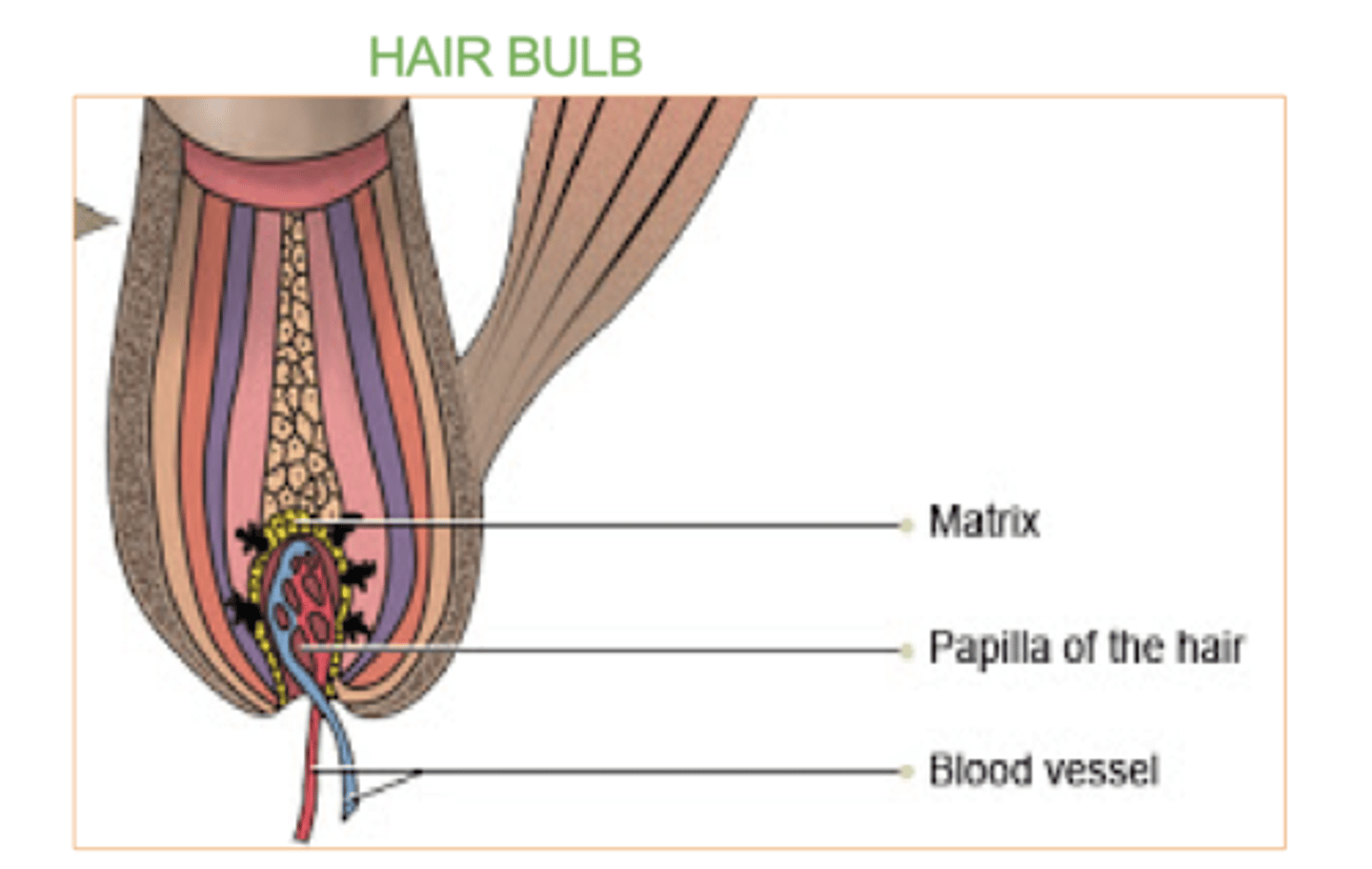
What's the hair papilla?
what supplies nutrients and signals needed for hair growth.
It contains blood vessels and nerves.
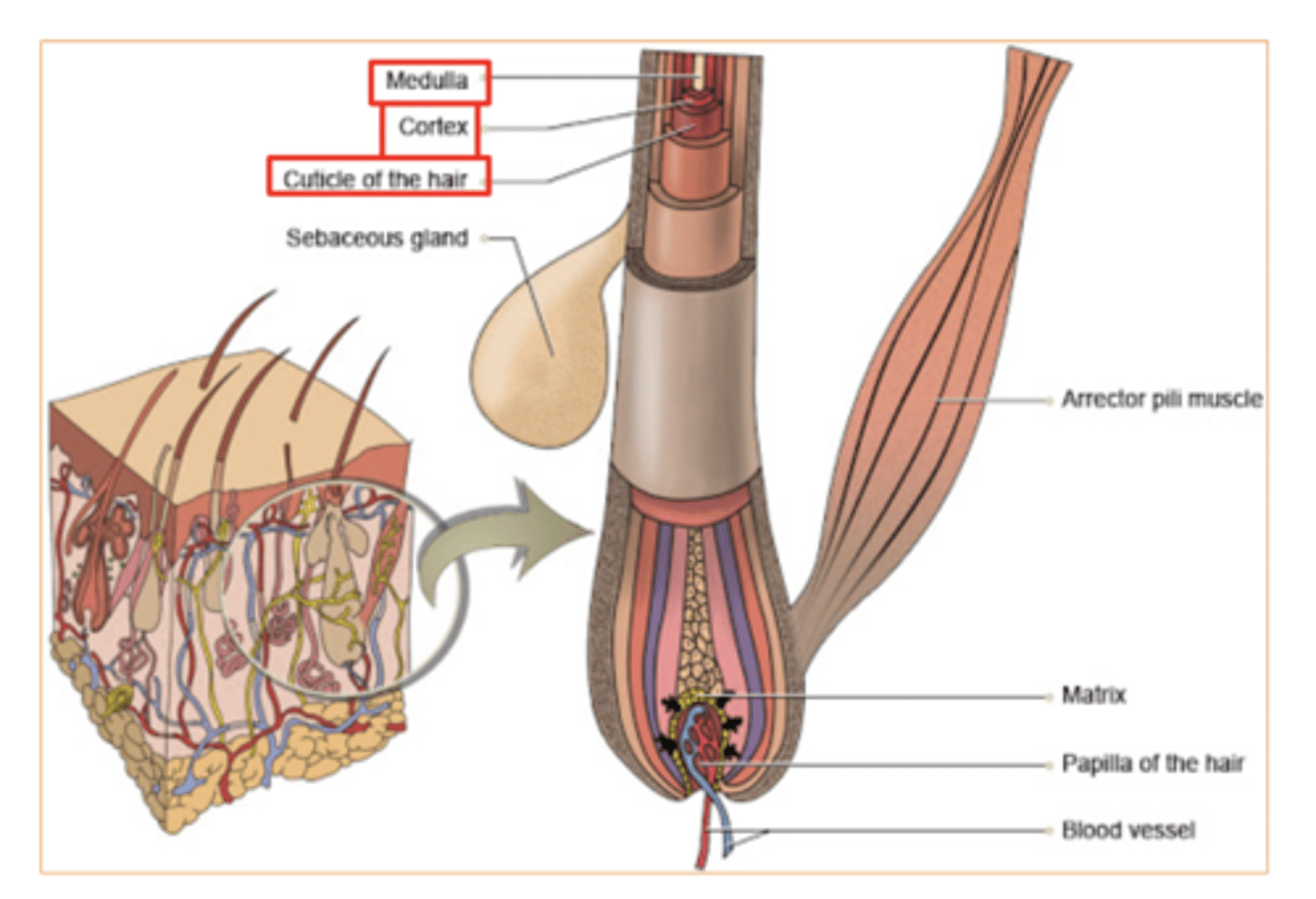
3 layers of the hair root from inside out?
Medulla
Cortex
Cuticle
What are hair receptors ?
nerve fibers that wrap around each hair follicle.
-allows you to feel pain
They detect hair movement, allowing the body to sense even the slightest touch, such as a breeze or an insect on the skin.
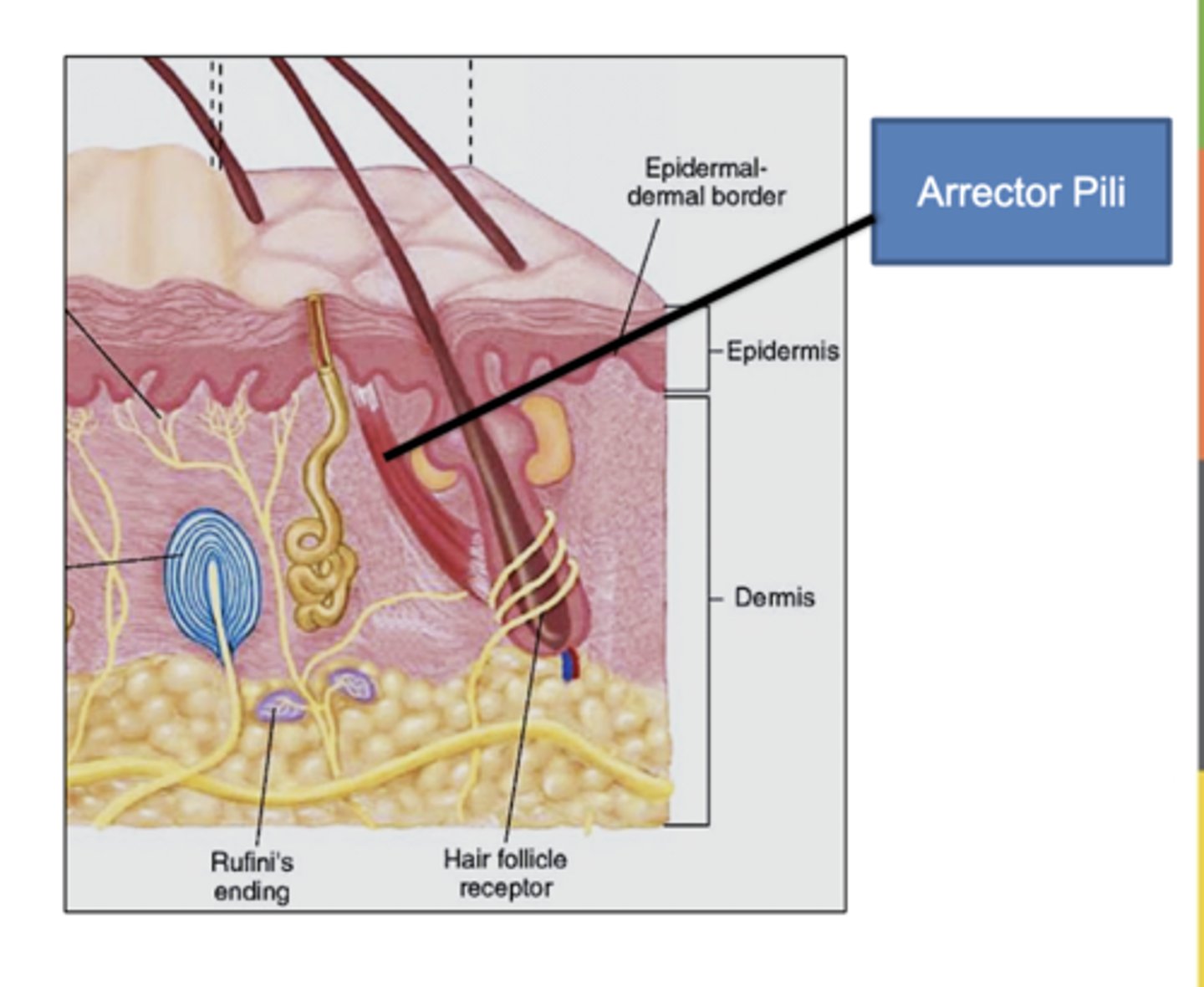
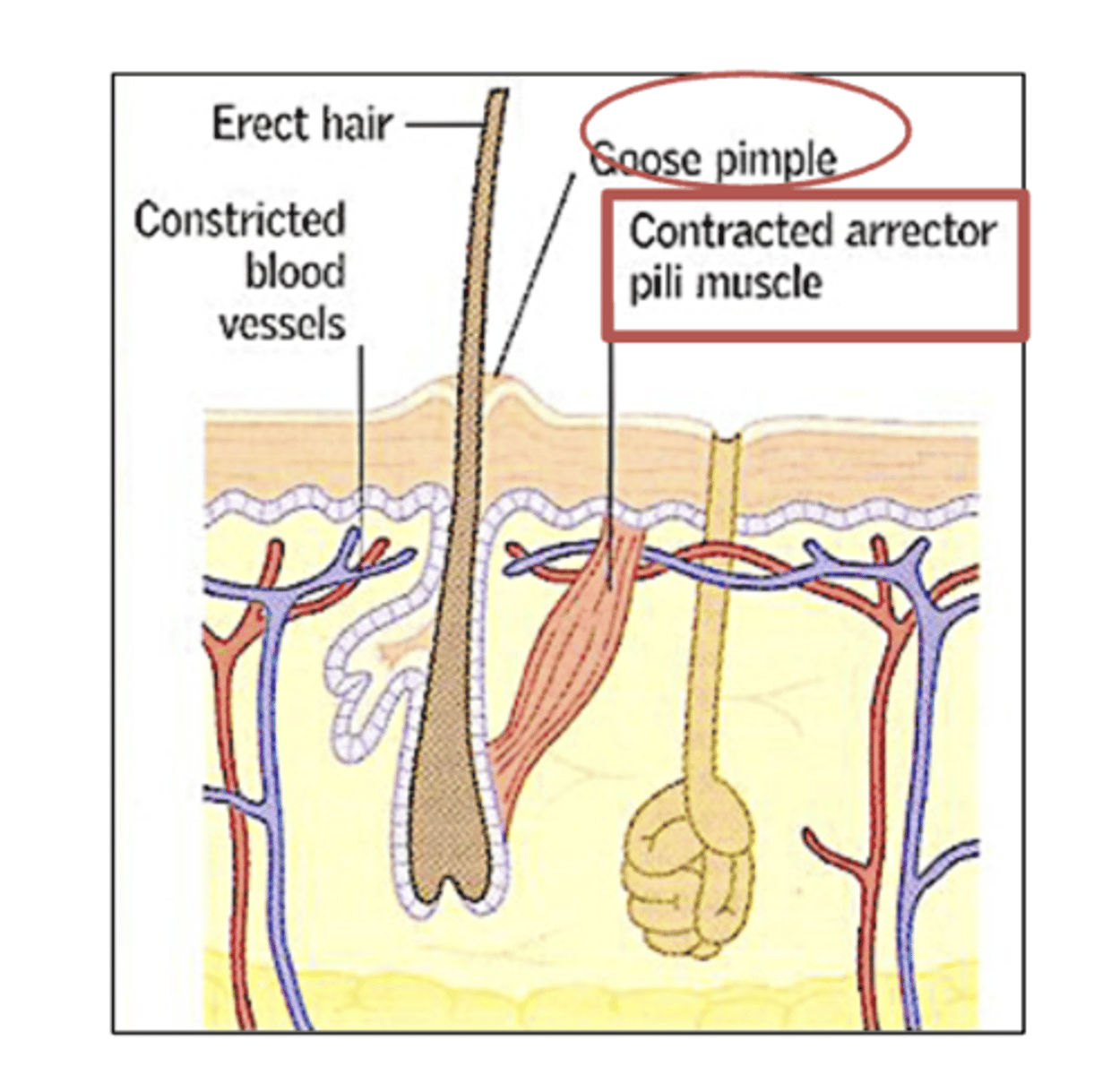
what Is Piloerector muscle (arrector pili)?
Bundles of smooth muscle cells that cause the hairs to erect
EX- Goose bumps
2 skin glands
Sudoriferous (sweat) glands
sebaceous glands (secret sebum)
sudoriferous glands produce
sweat
sweat which helps regulate body temperature and remove waste.
2 main types of Sudoriferous (sweat) glands
Eccrine & Apocrine
Eccrine (sweat) gland:
one of the 2 Sudoriferous (sweat) glands
open directly onto the skin's surface through pores in the epidermis.
They are found all over the body and help cool the body by releasing sweat when you're hot or exercising.
Apocrine (sweat) gland-
release sweat into hair follicles
mainly in areas like the armpits and groin.
These glands become active during puberty and are triggered by stress or emotions.
Sweat is mostly ______ and _________. It is slightly acidic which inhibits overgrowth of bacteria.
water/oil
bacteria/minerals
Sweat is mostly water and minerals. It is slightly acidic which inhibits overgrowth of bacteria
What does sweat help do in our skin since its slightly acidic?
it stops the overgrowth of bacteria .
what do the Sebaceous glands secrete?
sebum
primarily secreted through hair follicles, but can also be secreted through normal skin pores.
Through what do Sebaceous glands secrete sebum?
primarily secreted through hair follicles
( but can also be secreted through normal skin pores )
Through what do eccrine glands secrete sweat?
through ducts that open directly through a pore in the epidermis
NOT a hair follicle
Through what do Apocrine glands secrete sweat?
through hair follicle pores.
infection of sebaceous glands causes acne.
True or false
true
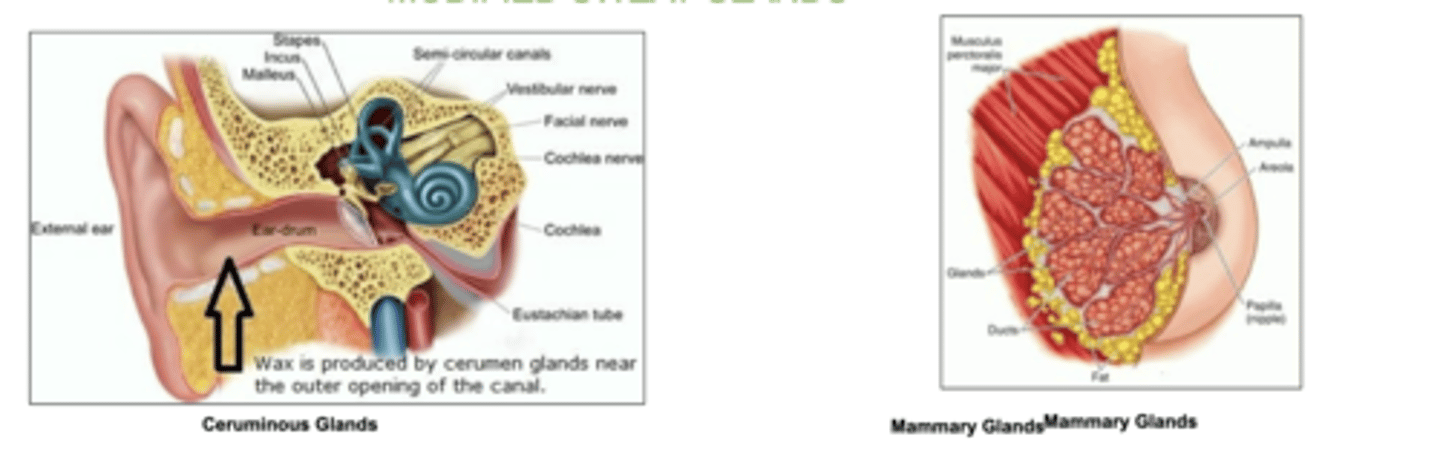
2 examples of modified sweat glands
wax-producing ceruminous glands (ear)
mammary glands of the breast (milk)
Which layer does the sudoriferous (sweat) glands come from?
The reticular layer in the dermis.
Which layer does the sebaceous glands come from?
the reticular layer in the dermis
2 structures in the papillary layer (dermis)
Meissner's corpuscles (touch receptor)
&
Free nerve endings (pain, temp)
2 structures in the reticular layer (dermis)
Pacinian corpuscles (pressure receptor)
&
Sudoriferous (sweat) Glands
Sebaceous glands (secrete sebum primarily through hair follicles)
3 nail structures
Body
Root - (contains nail matrix)
Cuticle
The nail is an accessory structure of the integumentary system.
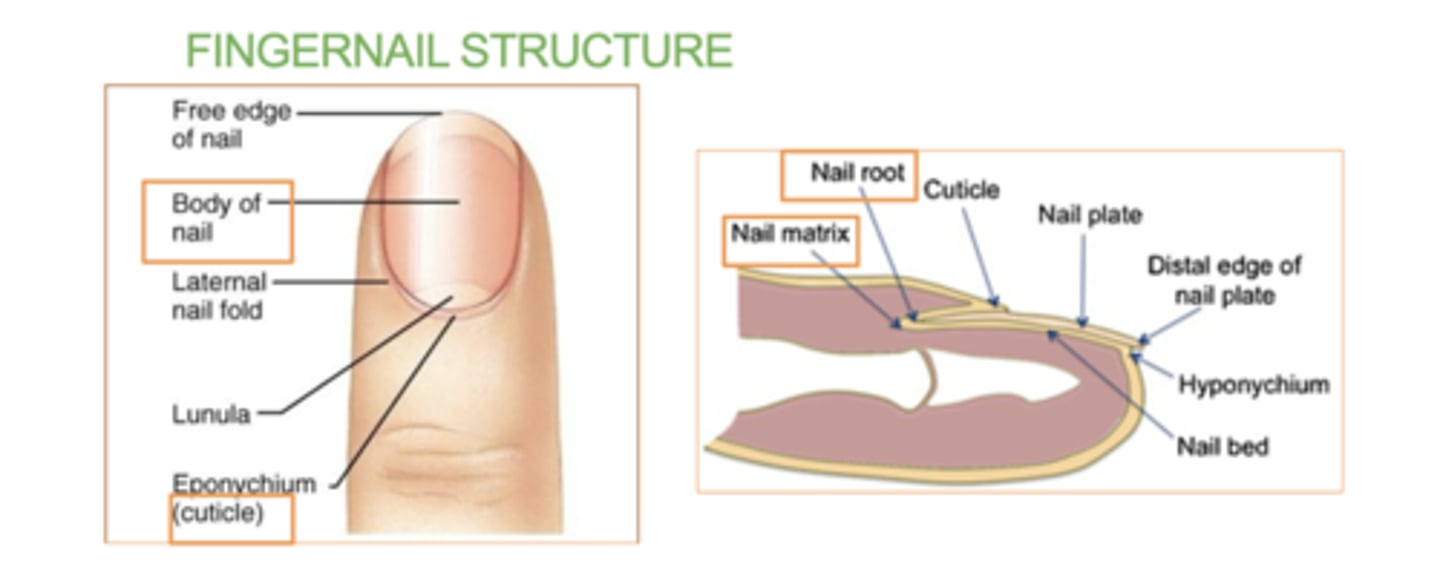
The nail is an accessory structure of the _________ system, formed from the stratum _________ and made up of layers of ________ , which gives it strength and durability.
Integumentary system
corneum
keratin