Lecture 6: Membranes and Transport
1/33
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
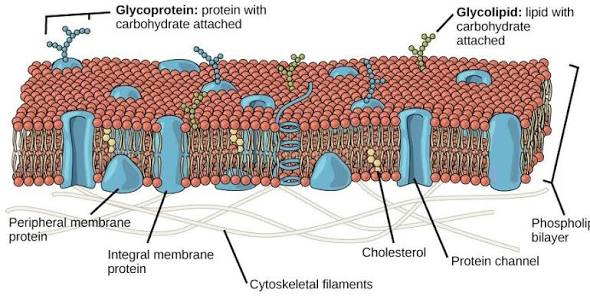
important features of membrane structure
fluid mosaic model, phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates
membrane components
primarily phospholipids; carbohydrates; proteins
how does a phospholipid bilayer form?
spontaneously
why does phospholipid bilayer form spontaneously?
amphipathc structure
amphipathic
polar/nonpolar sides
how is phospholipid bilayer held together?
hydrophobic interactions (van der waals)
what do membrane proteins do?
determine many membrane functions
transmembrane
span membrane
can membrane proteins move?
some membrane proteins can move, some cannot
functions of membrane proteins
transport; enzymatic activity; signal transduction; cell-cell recognition; intercellular joining; attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM)
carbohydrates
polysaccharides attached to protein or lipid
glycoprotein
polysaccharide attached to protein
glycolipid
polysaccharide attached to lipid w
function of carbohydrates in membrane components
cell identification (blood types A, B, O) f
fluid mosaic model
membrane components can move laterally within one layer of the membrane (lipids, proteins, carbs); plasma membrane moves dynamically, changing constantly, moving; not rigid, fluid; different parts come together, freely moving structure
passive transport
does not use metabolic energy (ATP); moves with the gradient like a bike downhill
active transport
does use metabolic energy (ATP);moves against the gradient like bike uphill; low concentration to high concentration
parts of passive transport
simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
diffusion
tendency for molecules of a substance to fill available space; small gases (O2, CO2, N2); small nonpolar molecules (including hydrocarbons); small polar uncharged molecules (including H2O)
dynamic equilibrium
no net movement at equilibrium; different substances diffuse independently
osmosis
diffusion of H2O across selectively permeable membrane
“salt sucks”
water diffuses from lower → higher [solute] or from higher → lower [H2O]
(high salt concentration draws water out of cells)
tonicity
ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose H2O
isotonic solution
[solute] outside cell = [solute] inside cell
(no net H2O movement)
hypertonic solution
[solute] outside cell > [solute] inside cell
hypotonic solution
[solute] outside cell < [solute] inside cell
what cannot diffuse directly across a membrane?
large molecules (just too big); not-small polar molecules (hydrophilic e.g. glucose); ions (charged—even H+)
facilitated diffusion
large molecules or ions (H+, Ca+2, Na+)
transport proteins
channel proteins → (ie: ion channel)
carrier proteins →
specific to what each protein is transporting
how is active transport facilitated?
proteins (carriers or pumps) or bulk transport of molecules
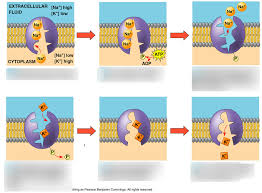
sodium potassium pump
3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in; establishes electrical gradient
exocytosis
vesicle fuses with plasma membrane to release contents from cell → primary mechanism for growing plasma membrane; waste, proteins, and secretory products “out”
endocytosis
material taken into cell by forming vesicles derived from plasma membrane
phagocytosis
cell engulfs large particle (non-specific); “cellular eating”
pinocytosis
ingestion of fluid and dissolved material (non-specific); “cellular drinking”