AP Bio Unit 4: Cell Communication and Cell Cycle
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Types of signaling
Juxtacrine, autocrine, paracrine, endocrine
Juxtacrine
direct contact
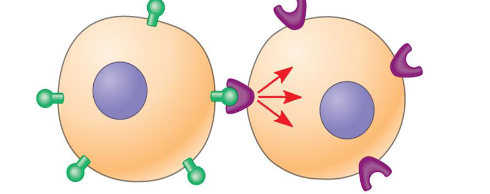
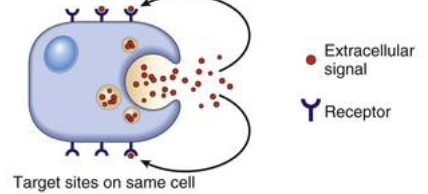
Autocrine
targets self
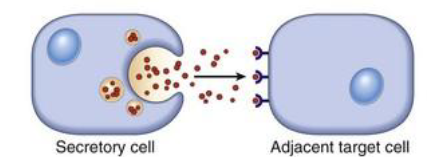
Paracrine
local/ nearby
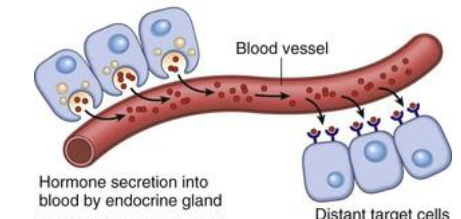
Endocrine
long distance
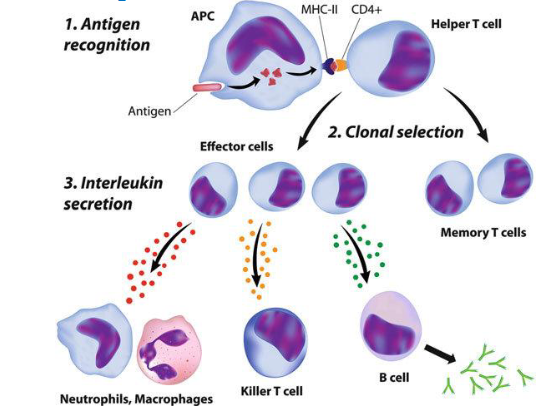
Juxtacrine signaling (immune system)
Ligand on one cell binds with a receptor on another
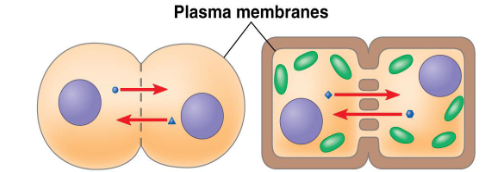
Juxtacrine signaling (gap junctions, plasmodesmata)
Cells share particles through small pores that link their cytoplasms together
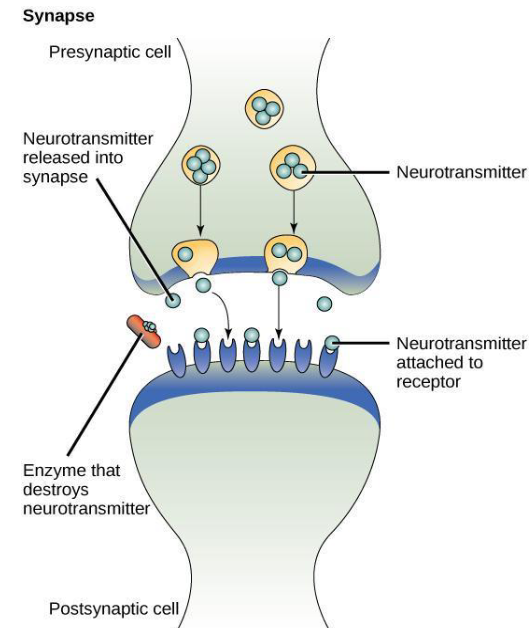
Local (paracrine) signaling
Cells secrete ligands to nearby cells where they initiate a response. ex: neurotransmitters (synapses)
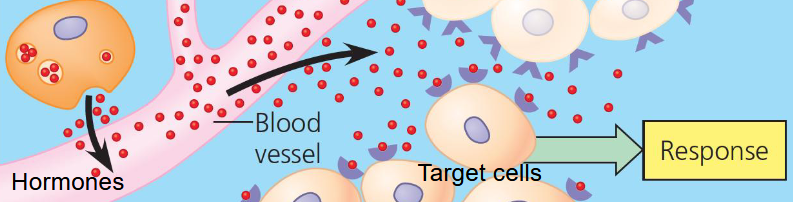
Long distance (endocrine) signaling
Produce ligands called hormones
Hormones travel through bloodstream to target cells
Slower but a long-lasting effect
Steps of cell signaling
reception
transduction
response
Reception
Binding between signal molecule (ligand) + specific receptor. Receptor protein changes shape and initiates a transduction signal.
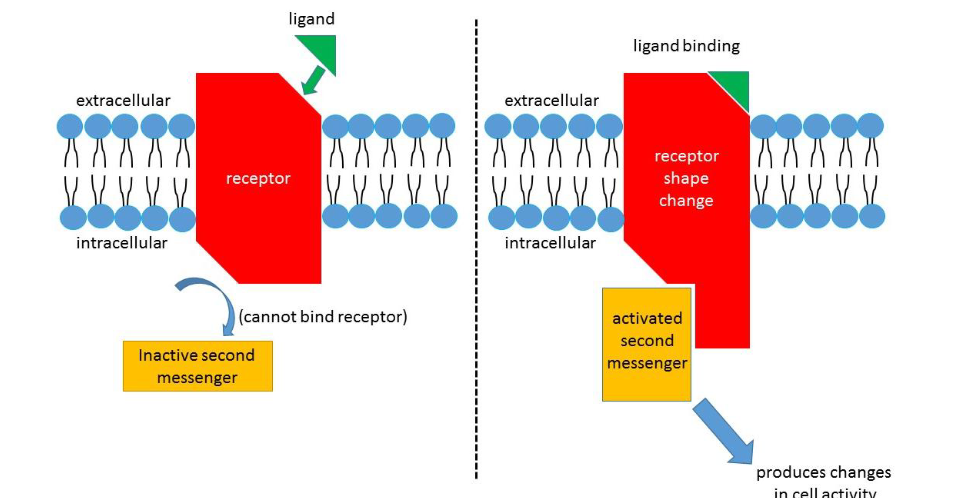
Membrane surface receptors
for ligands that can’t pass through (hydrophilic or very large)
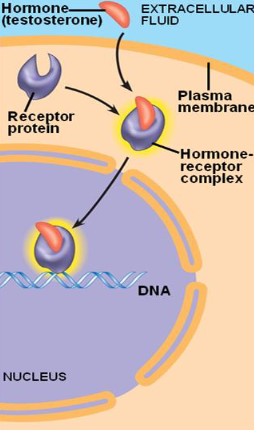
Intracellular receptors
for small or hydrophobic ligands that can pass through the membrane
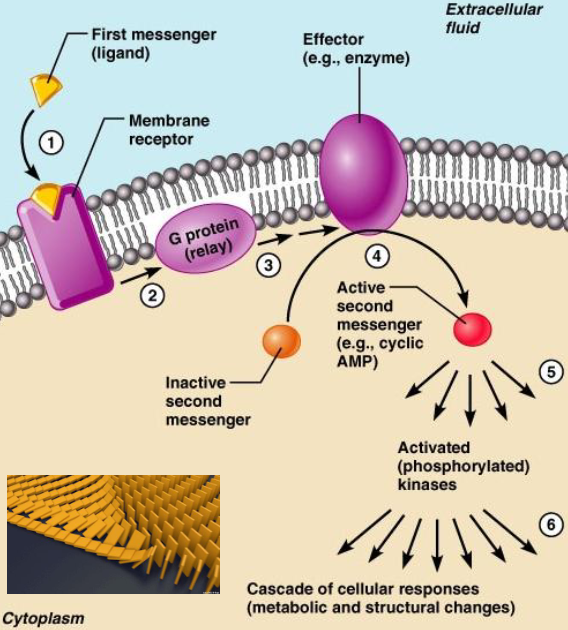
Transduction
Conversion of signal reception into cellular response. Second messengers are triggered to amplify the signal (ex: cAMP). Creates a cascade that mobilizes many more molecules.
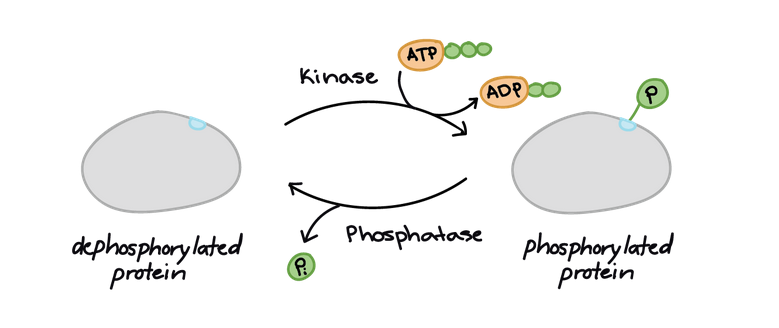
Kinases
enzymes that phosphorylate other molecules and activate them
Phosphorylation cascade
occurs during transduction and amplifies the signal
Phosphorylation
addition of a phosphate group to one or more sites of a protein. acts as a switch.
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
small molecule made from ATP. used as a second messenger.
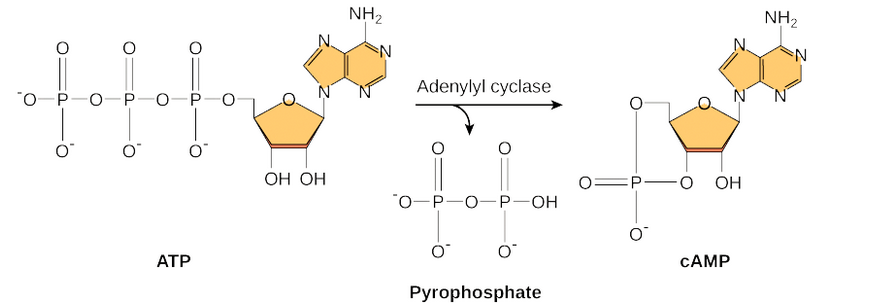
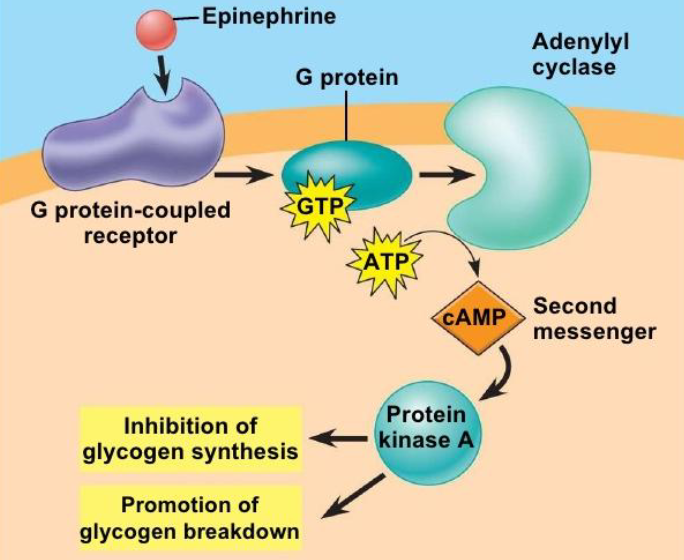
G-coupled protein receptors

Response
Signal transduction pathways lead to regulation of cellular activities. Occurs in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Many pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins by turning genes on/off in the nucleus.
G proteins (guanine nucleotide-binding proteins)
act as molecular switches in cells. transmit signals. bind the GTP and GDP.
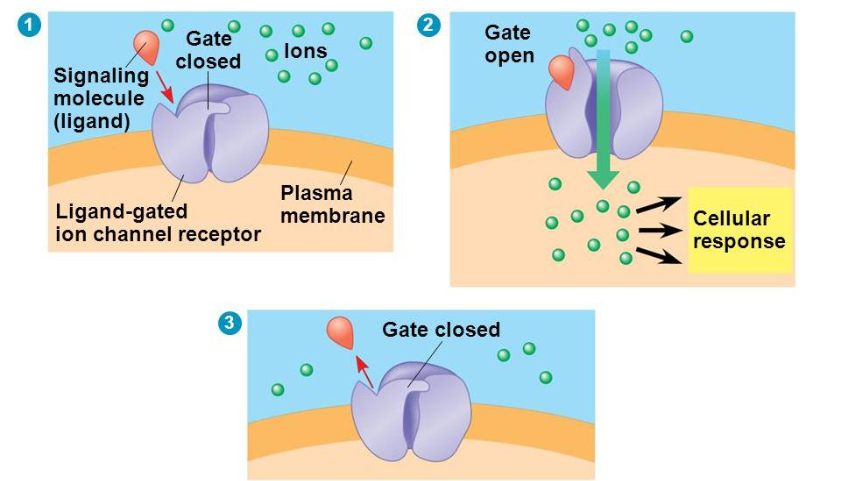
Ligand-gated channels
These proteins act as both receptors and channels. When the appropriate ligand is bound, solutes are allowed through the protein channel.
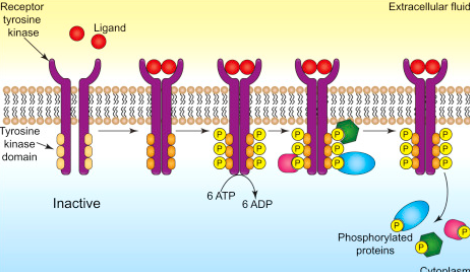
Enzyme and enzyme-linked receptors
These receptors are either enzymes or enzyme linked proteins (interact directly with enzymes). Trigger the intracellular production of second messenger cyclic GMP. ex: tyrosine kinase (TK) receptors.
Nitric oxide (NO)
gas that acts as a ligand
Peptide (protein) ligands
largest and most diverse class of water-soluble ligands. ex: growth factors, insulin, certain neurotransmitters.
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
Cell division purpose
repair, replace cells, growth, immune response (B and T cells), asexual reproduction
Mitosis
process of replicating the nucleus before a parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Short phase of cell cycle. Results in two nuclei, not two cells.
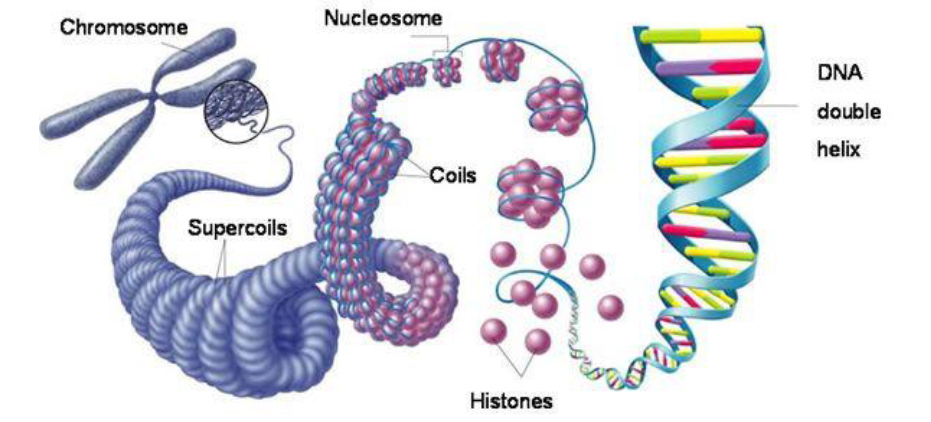
Chromosomes
molecules of DNA. Compact and organized in eukaryotes. DNA is tightly wrapped around proteins. Each has millions of base pairs and thousands of genes.
Chromosome structure
Chromatin
the name of the material made from DNA and protein
Gene
segment of DNA that codes for a specific trait
Single chromatid chromosome (unduplicated)

Double chromatid chromosomes
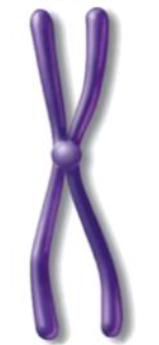
Chromatid
a chromosome copy
Number of centromeres equals
number of chromosomes
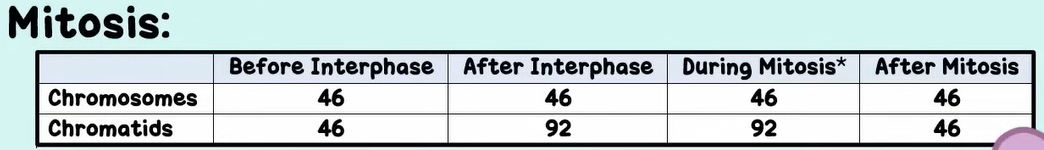
Interphase (chromosome numbers)
Before interphase occurs there are 46 chromosomes and after interphase duplication there are still 46 chromosomes but they each have two chromatids (or two copies of information). There are 92 chromatids after duplication.
Two identical chromatids
one is an exact copy of the other and each contains one DNA molecule
Centromere
constricted point of the chromosome
DNA molecule
long string like DNA molecule formed into a compact structure by proteins called histones
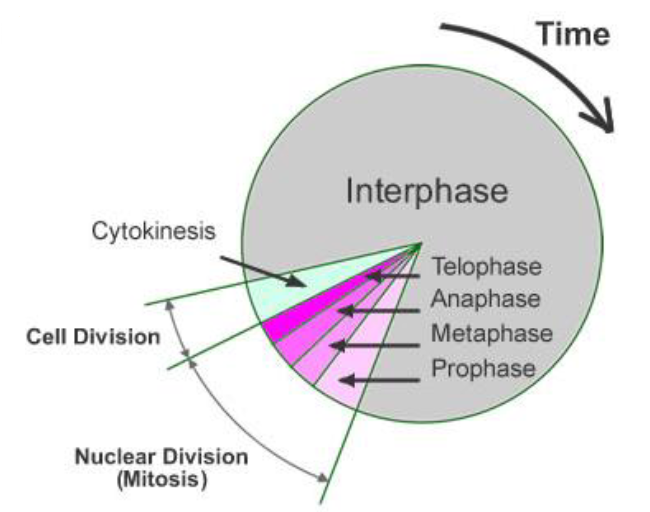
Cell cycle phases
Interphase - cell grows, DNA replicated
Nuclear division - mitosis
Cell division - cytokinesis
Interphase
majority (90%) of cell’s life
Interphase phases
Gap 1 (G1)
S phase
Gap 2 (G2)
Gap 1
most growth occurs, organelles replicate, cell makes proteins and enzymes for replication
S phase
DNA replicates (single chromosomes become double)
Gap 2 (G2)
more cell growth, DNA checked for errors and repaired, final prep for mitosis
G0
the phase in the cell cycle in which the cell is neither dividing nor preparing for division
Mitosis and cytokinesis
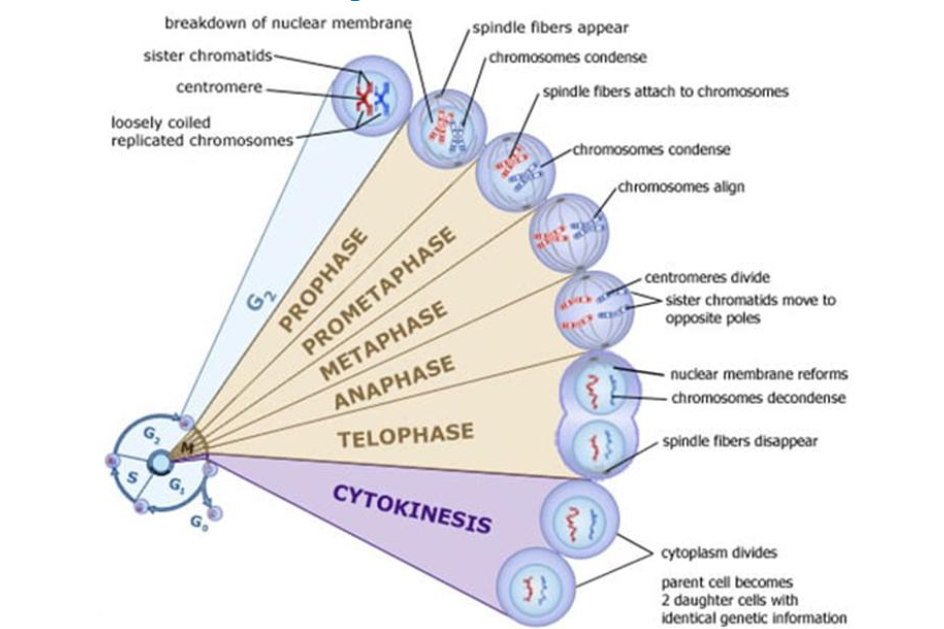
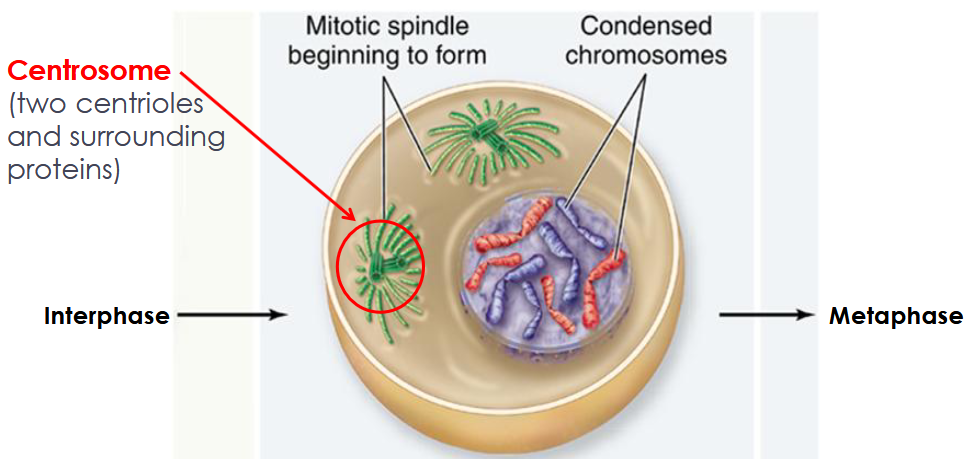
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible, chromosomes appear as two sister chromatids held together at the centromere, nuclear envelope breaks down
Kinetochores
protein structures that allow microtubules to attach to the centromere
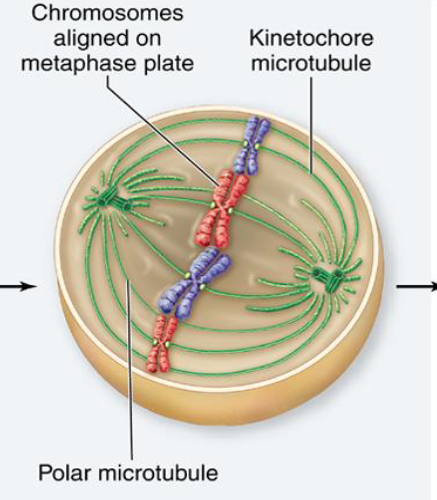
Metaphase
All chromosomes are aligned at equator of the cell (______ plate), chromosomes are attached to opposite poles and are under tension
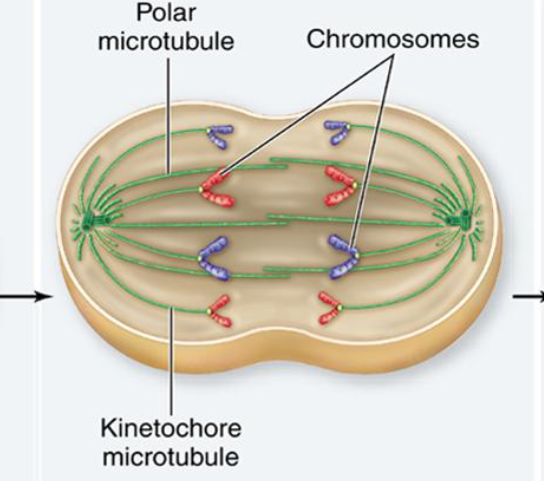
Anaphase
Sister chromatids are separated, chromatids are pulled by microtubules to opposite poles
Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms, nucleolus reforms, spindle breaks down, chromosomes uncoil, cytokinesis begins, 2 identical nuclei formed by the end
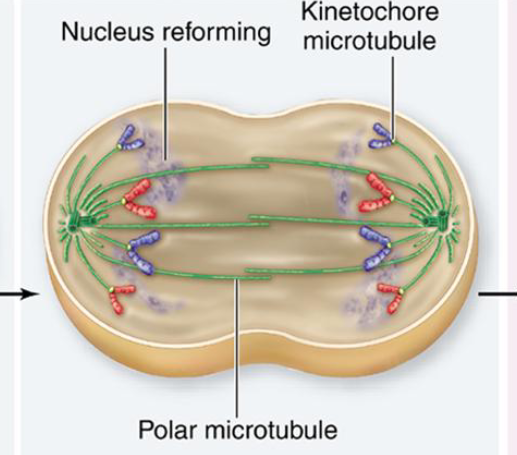
Cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm. forms two identical cells. cell plate (dividing cell wall) forms in plant cells.
Cell cycle checkpoints
G1, G2, M (Mitotic)

Cyclins
proteins that control cell cycle checkpoints. increases in the concentration of _____ proteins are triggered by both external and internal signals. turn on Cdks.
Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
phosphorylate other proteins that advance the cell cycle past a checkpoint
Cell cycle negative control
Some regulatory pathways halt the cell cycle. ex: p53 tumor suppressor protein
p53 tumor suppressor protein
If damaged DNA is detected before G1, it halts the cell cycle and recruits enzymes to repair the DNA (activates Cdk inhibitor, cyclin complex inactivated). Can trigger apoptosis to prevent replication.
Cell cycle loss of control
mutations of regulatory genes can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and possibly cancer

Tumor
a mass of irregular cells
Benign tumor
cells grow only locally and cannot spread by invasion or metastasis
Malignant (cancer) cells
invade neighboring tissues, enter blood vessels, and metastasize to different sites
Metastasis
when cancer spreads via the blood or lymphatic system
Contractile ring (animals)
cell division occurs when a band of cytoskeletal fibers contract inward and pinch the cell in two. The indentation produced as it contracts inward is called the cleavage furrow.
Examples of cells in G0
neurons that conduct signals, liver cells that store carbohydrates
24 hours
cell cycle length (typical, human cells)
Mitotic spindle
forms in prophase. made of microtubules, strong fibers that are part of the cell’s “skeleton”. it organizes the chromosomes and moves them around during mitosis. grows between the centrosomes.
Prophase condensation
makes it easier to pull apart chromosomes
Spindle checkpoint
before anaphase, cell checks that all chromosomes are at the metaphase plate with kinetochores correctly attached to the microtubules
Motor proteins
molecular machines that can “walk” along microtubule tracks and carry chromosomes or other microtubules
broken down, reappear, decondense
In cytokinesis, the mitotic spindle is _____, nuclear membranes and nuclei _______, and chromosomes ______
Genome
a cell’s set of DNA
Histones
a group of basic (positively charged) proteins that form “bobbins” around which negatively charged DNA can wrap
Negative
charge of DNA
Positive
charge of histones
Decondensed
chromatin is ______ for most of the life of the cell and exists and long, thin strips. Can be easily accessed by proteins and other cellular machinery when in this state.
Circular
bacterial chromosomes are typically…
Cohesins
sisters chromatids are attached by proteins called…
G1 Checkpoint
checks for:
cell size - large enough?
nutrients - enough energy?
growth factors/molecular signals - receiving positive ques?
DNA damage - is any DNA damaged?
G2 Checkpoint
Checks for:
DNA damage - is any DNA damaged?
DNA replication - DNA completely copied during S phase?
M checkpoint
spindle checkpoint is also known as…
Types of cyclins
G1, G1/S, S, and M cyclins. Promotes the events of each phase.
Maturation-promoting factor (MPF)
adds phosphate tags to several different proteins in the nuclear envelope, resulting in its breakdown. activates targets that promote chromosome condensation and other M phase events.
Anaphase-promoting complex/ cyclosome (APC/C)
causes M cyclin destruction which takes the cell out of mitosis