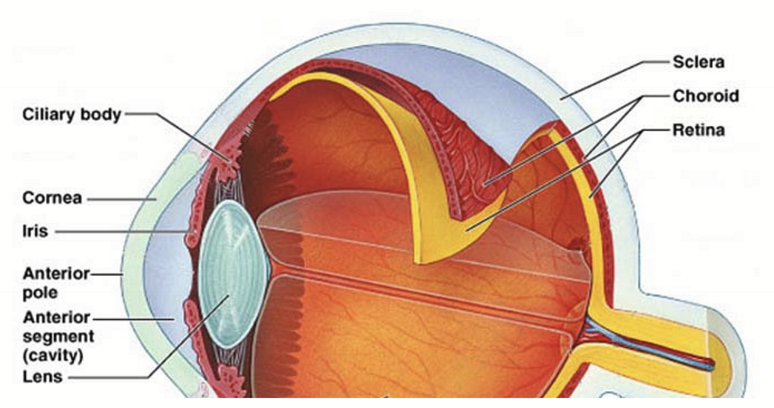
11. Choroid
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Choroid characteristics
Very vascular
Located between the sclera and retina
extends from the optic nerve head to the
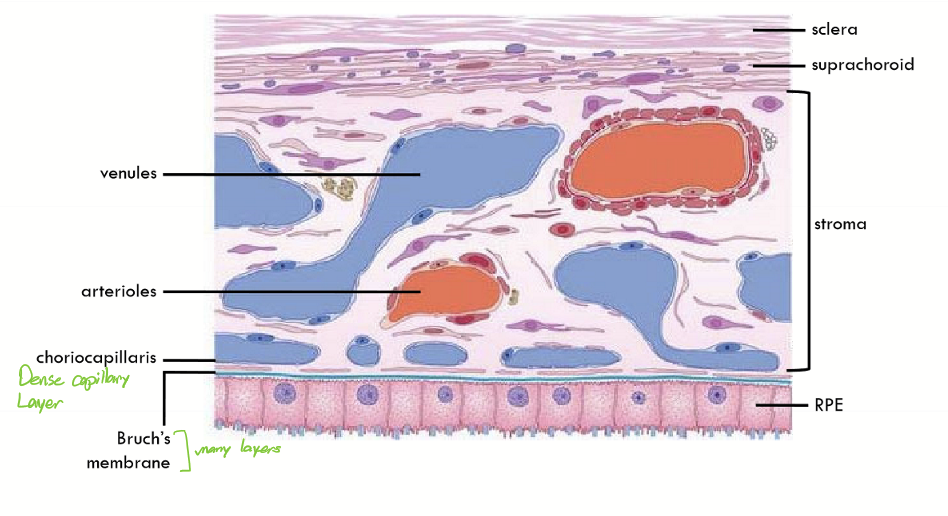
Choroid layers from external to internal
Suprachoroid
Stroma
choriocapillaris
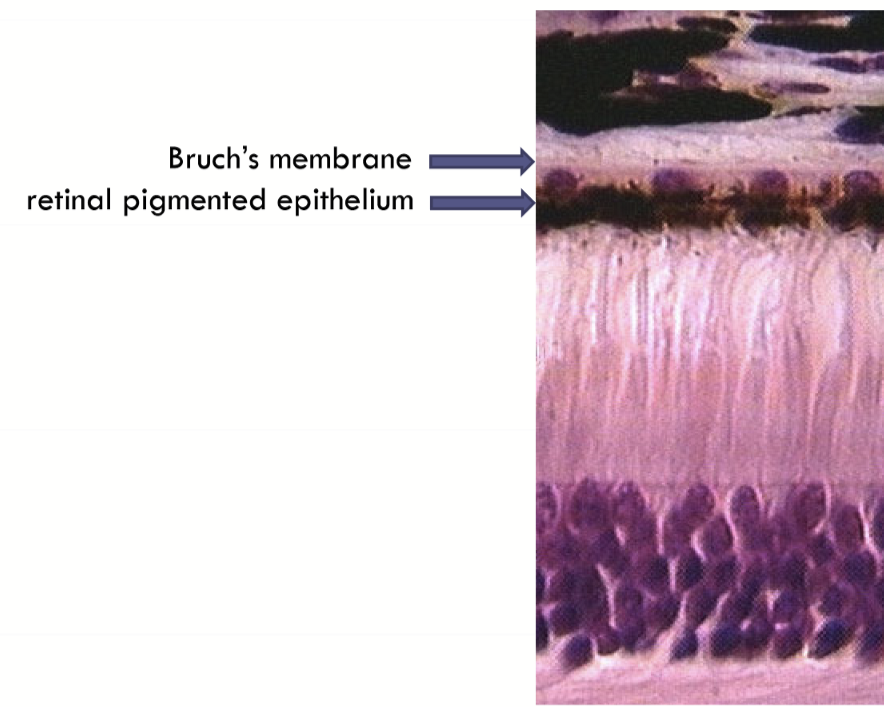
Bruch’s membrane
RPE
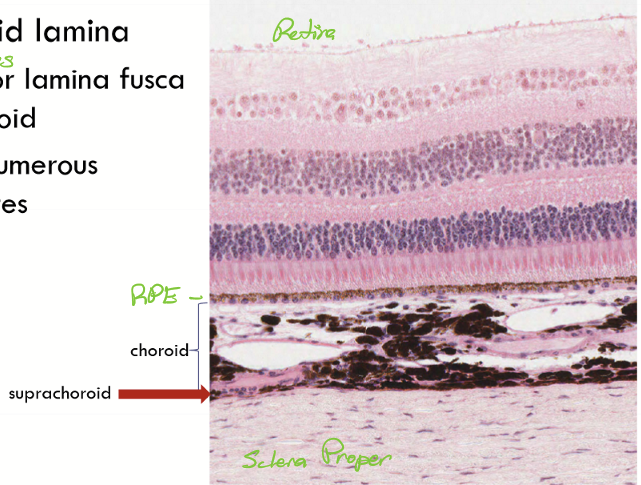
Suprachoroid lamina
posterior lamina fusca or epichoroid are old names for itcontains numerous melanocytes
site of smooth muscle stars
small space
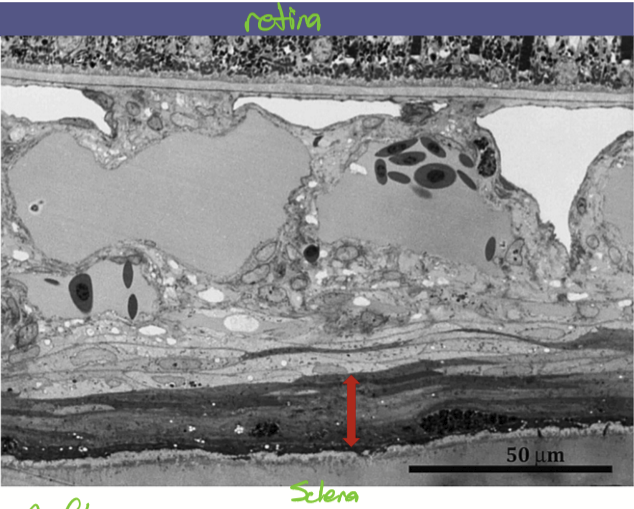
What is found in the suprachoroid lamina?
Nerves and blood vessels
contains the perichoroidal or suprachoroidal space
contains diagonal collagen fibrous sheets
fastens the choroid to the sclera
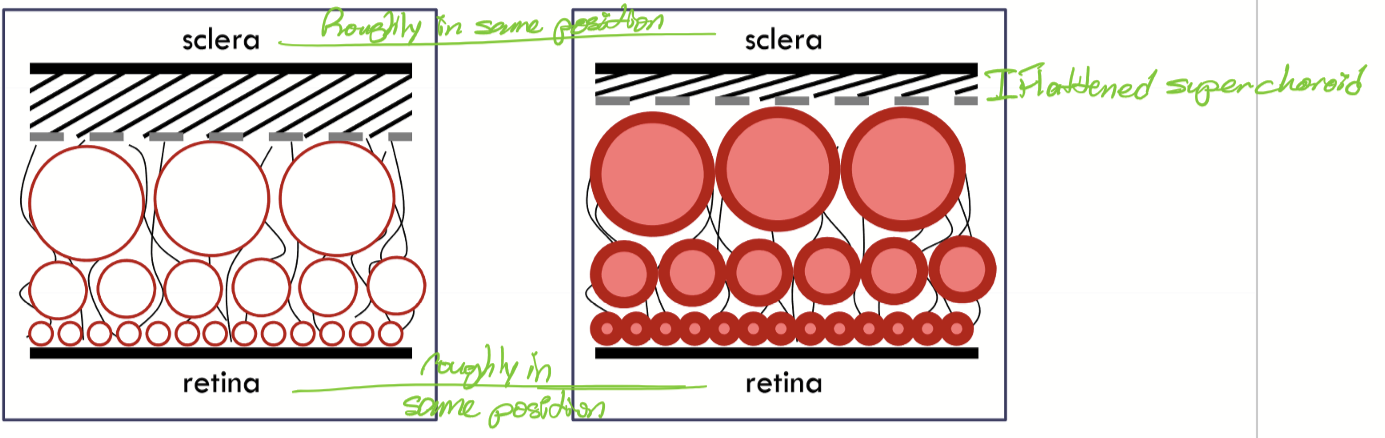
Why are the collagen fibrous sheets diagonal in the suprachoroid?
To accomodate for changes in thickness within the choroid stroma
Stroma of choroid
Widest layer and is the vessel layer.
Composed of connective tissue, fibroblasts, APCs, and melanocytes
Blood vessels are arranged in layers
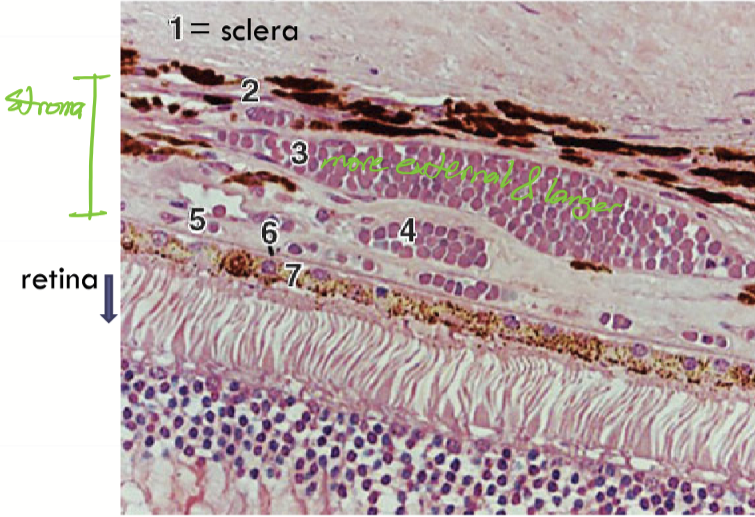
Layers of blood vessels in the choroid stroma
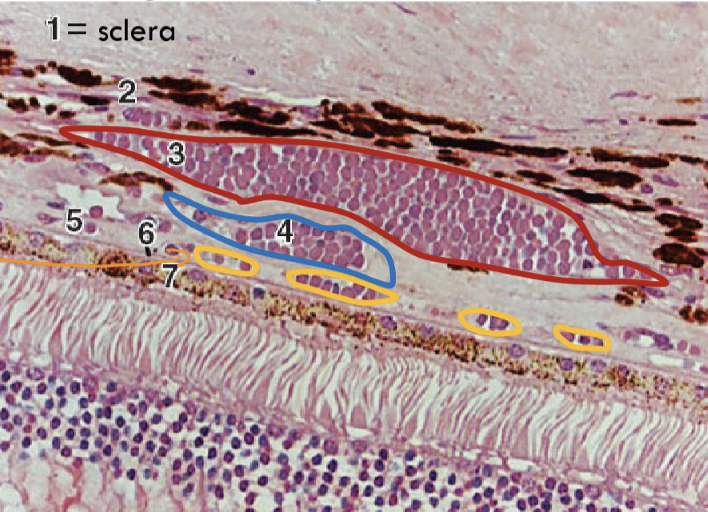
Haller’s Layer, more external and larger (3)
Sattler’s layer, more internal and smaller (4)
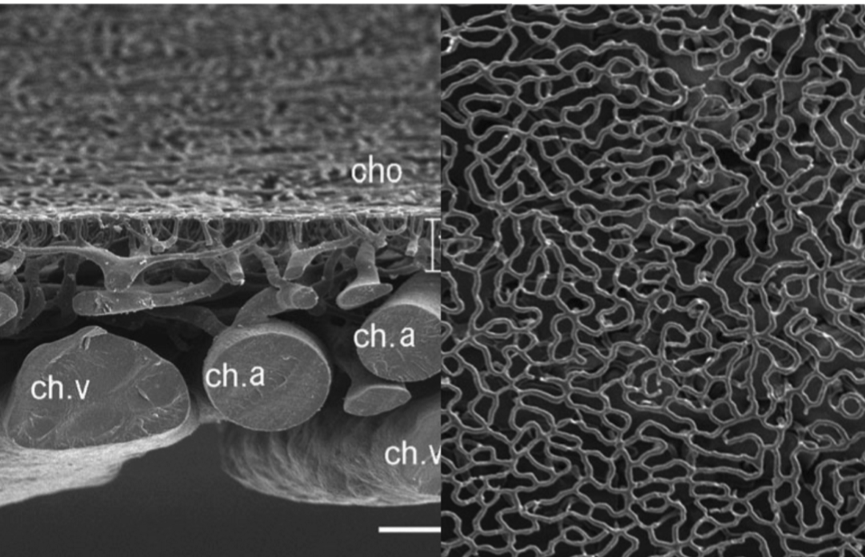
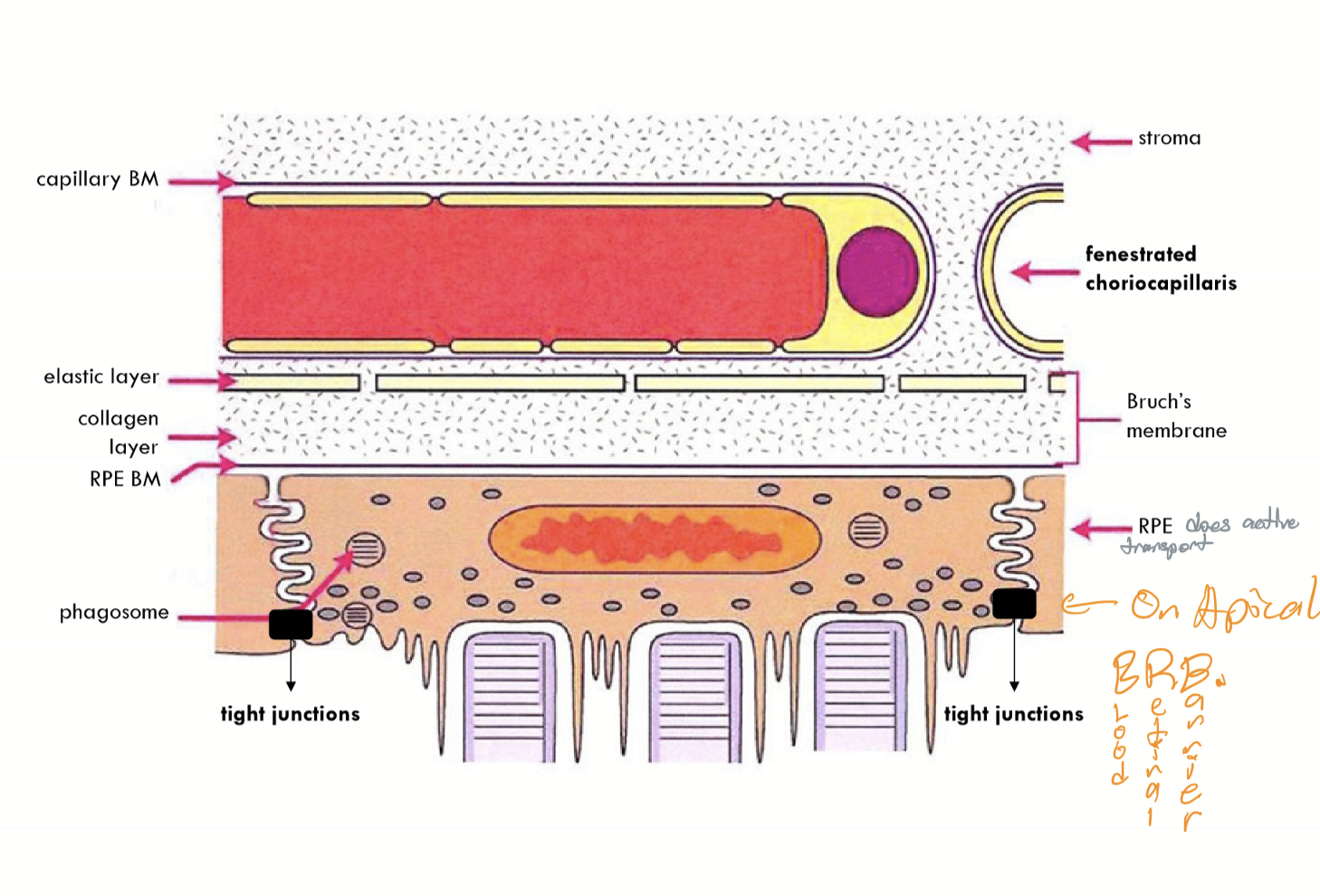
Choriocapillaris
Single layer of anastamosing fenestrated capillaries.
Has a discontinuous basement membrane.
Capillaries have a wider lumen (3-4 times)
Pericytes
wrap around the capillary and are involved with blood flow & communicate with endothelium of blood vessel
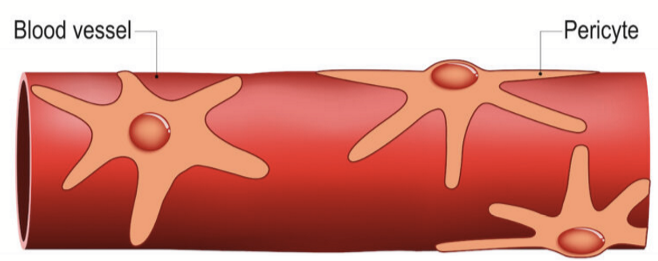
Choriocapillaries is densest where?
Foveal region
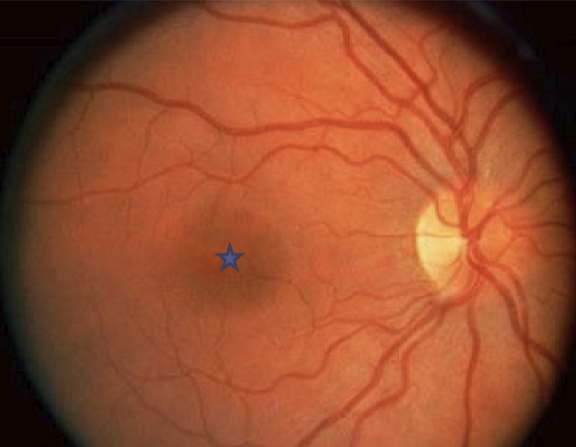
Where is high arteriole to venule ratio? What benefit does this ratio have?
In the macula and peripapillary area. It is more resistant to eschemic event due to high number of arterioles.
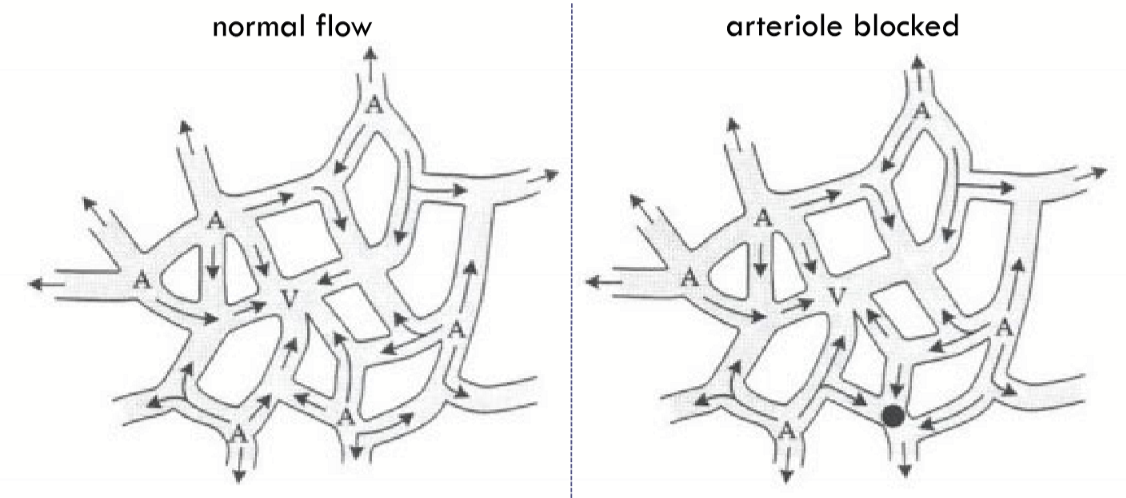
Where is low arteriole to venule ratio? What benefit does this ratio have?
In the equitorial and peripheral areas. It is more resistant to ischemic events due to high number of venules.
Bruch’s Membrane Composition
Basement membrane of choriocaillaris
Outer collagenous zone
elastic layher
inner collagen zone
basement membrane of retinal pigment epithelium
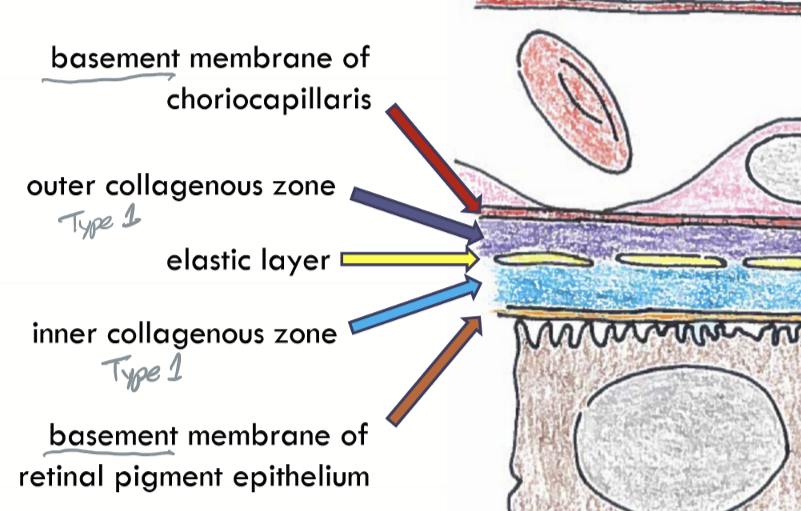
Where does Bruch’s membrane taper?
In pars plana
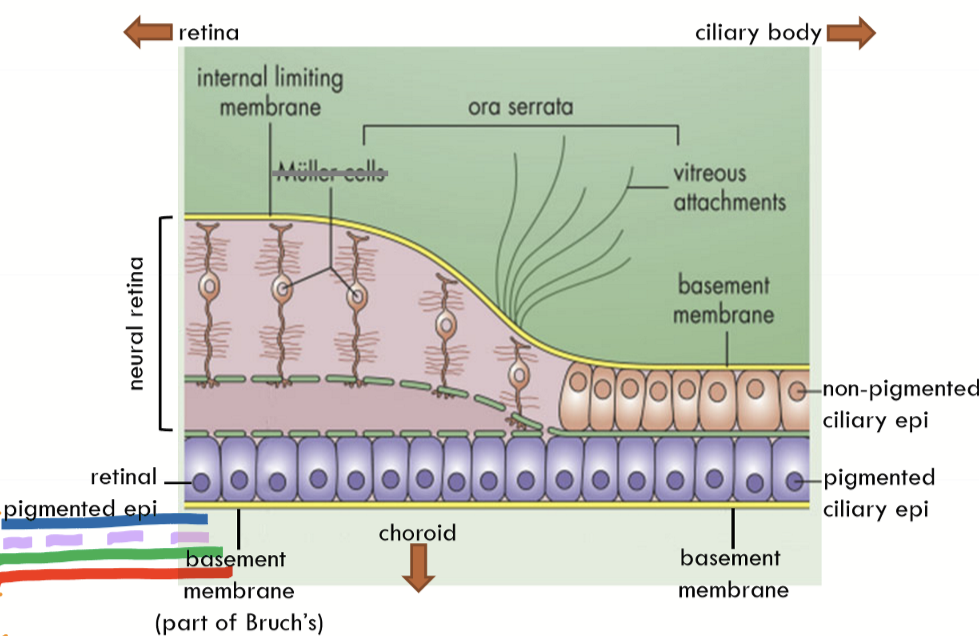
What is the neural retina continuous with?
Non-pigmented ciliary epithelium
Innervation of the Choroid
both divisions of autonomic nervous system.
Sympathetic is for vasoconstrictgion.
parasympathetic is for vasodilation ish
Some autoregulation
Function of choroid
absorbs stray light
thermoregulation
removes wastes
blood supply to part of the retina (photoreceptors highly metabloic)
Degeneration of Bruch’s membrane
Drusen
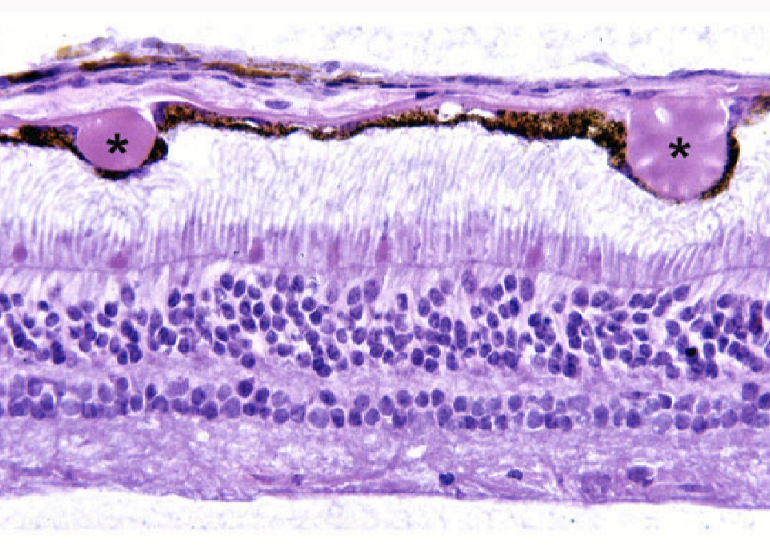
Drusen
nodule outer to RPE basement membrane
collection of BM-like material in inner collagenous zone
seen as a yellow-white dot with ophthalmoscope
Occurs in older individuals
does not cause vision loss, but increases risk of AMD
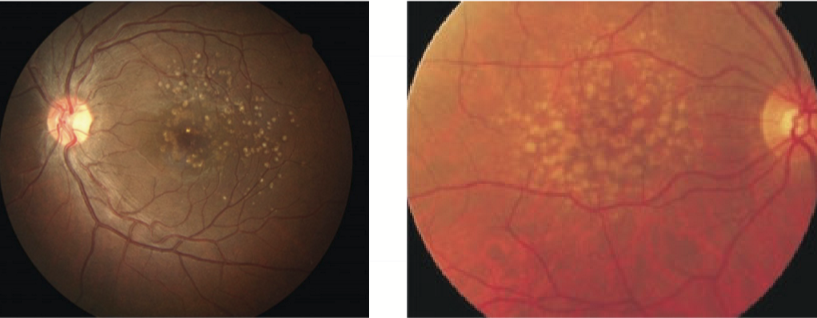
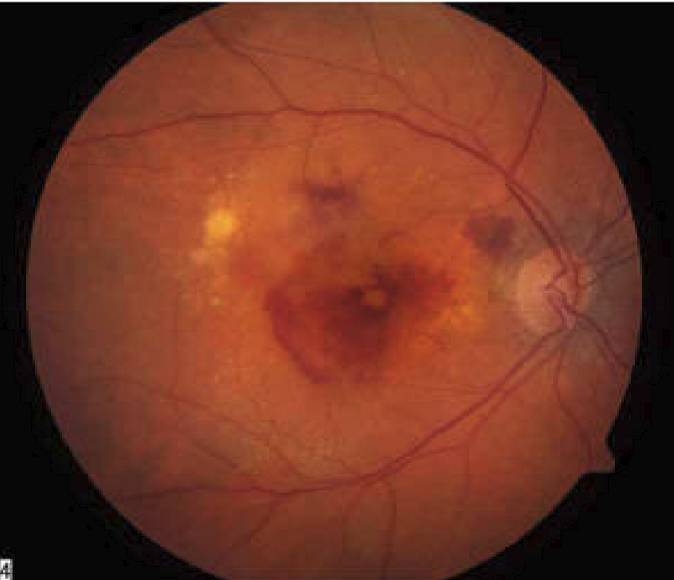
Age related maculoar degeneration (AMD)
common cause of blindness in western countries
pathology associated with both the choroid and the retina
can involve drusen deposition, RPE atrophy, vision loss
can involve neovascularization
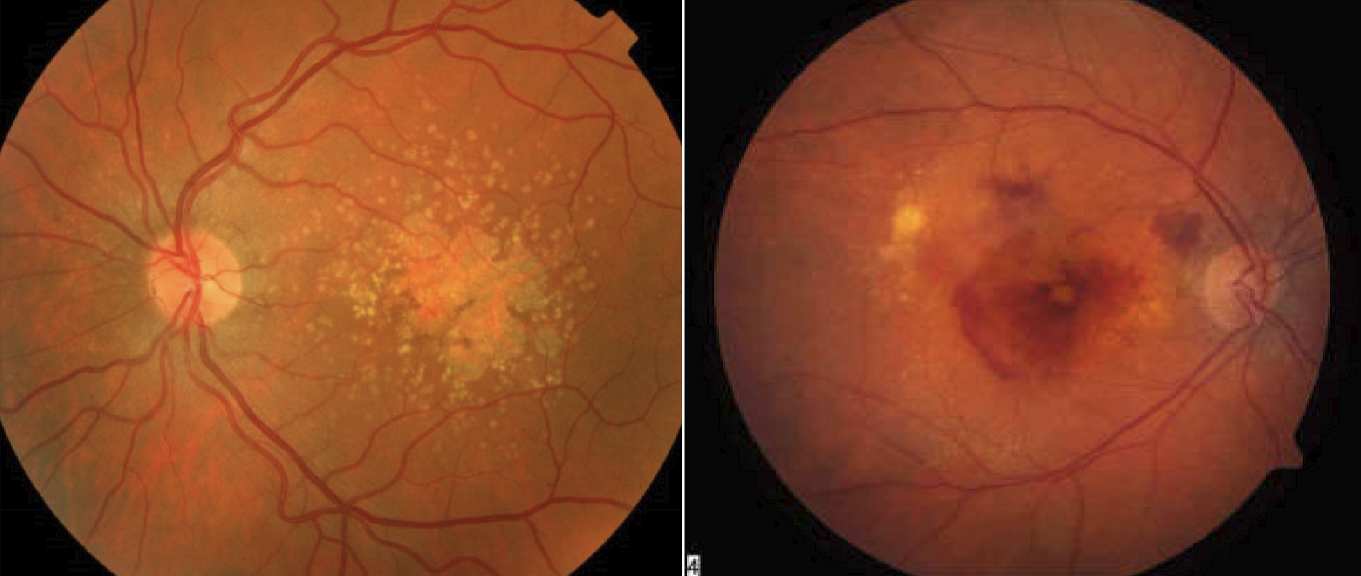
Types of AMD
geographic atrophy AMD
wet AMD
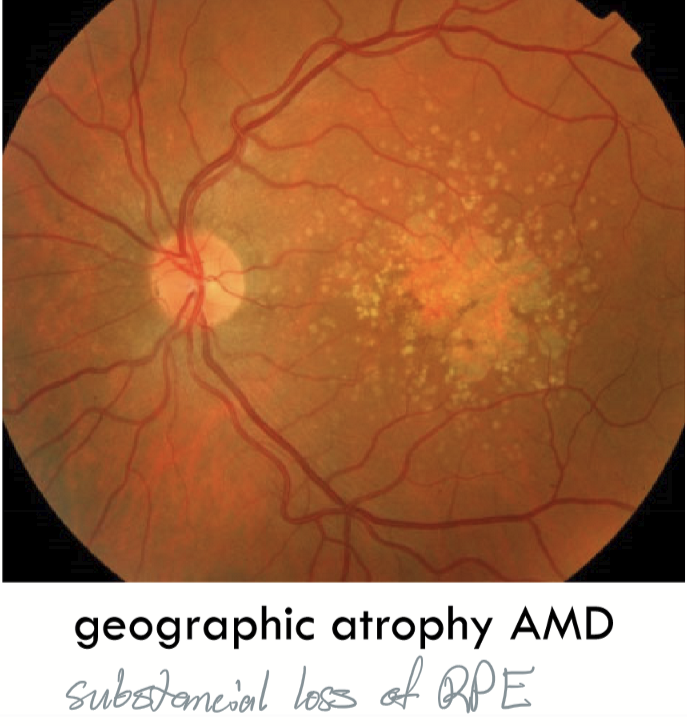
Geographic atrophy AMD
Substancial loss of RPE due to poor nutrient exchange
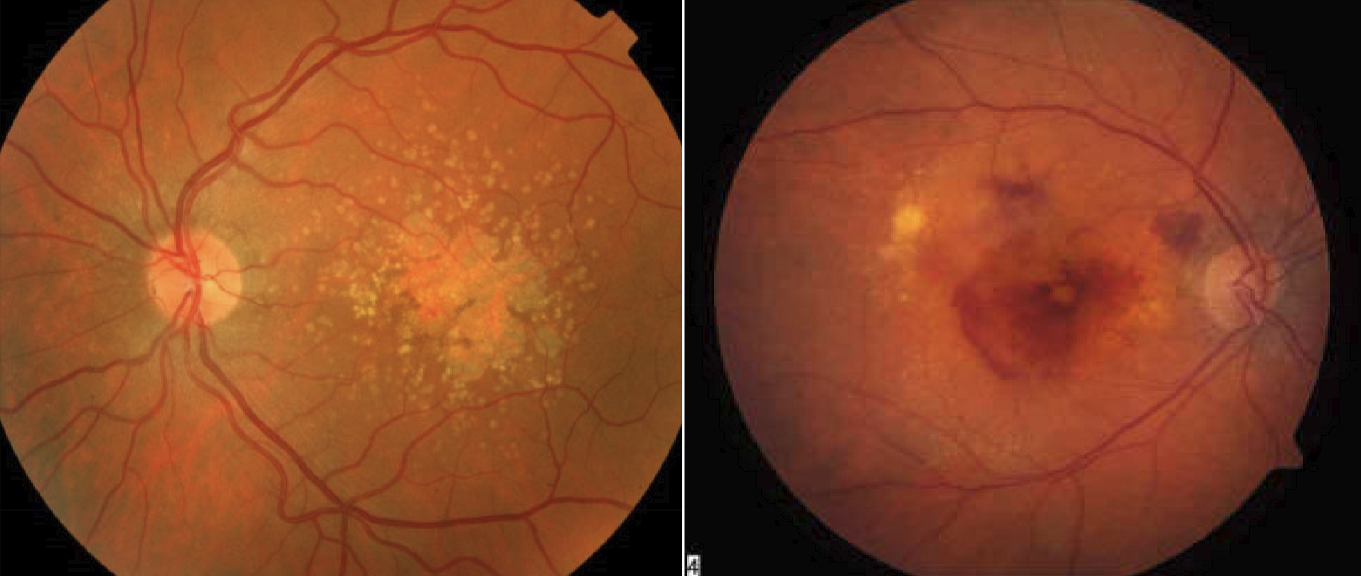
wet AMD
neovascularization from hypoxic event. Blood is toxic to neurons and kills the retinas
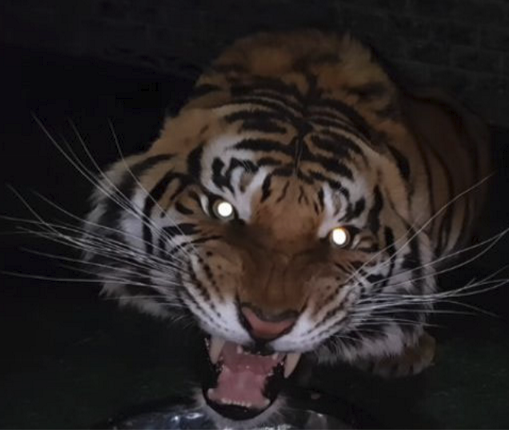
Tapetum lucidum
Present in the stroma (sattler’s layer). Various in color, size, reflective material.
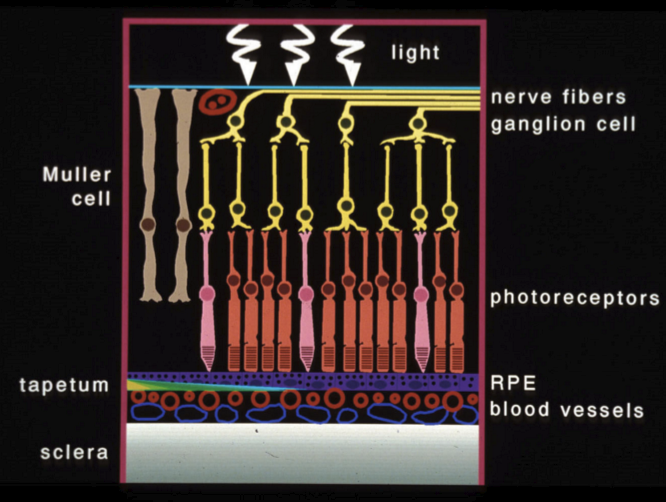
Tapetum lucidum function
Increase sensitivity to light in dark environments by reflecting certain wavelengths back to retina.
cats have light detection threshold 7x lower than humans
feline tapetum reflects 130x more light than humans
