GCSE Physics AQA - Waves
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
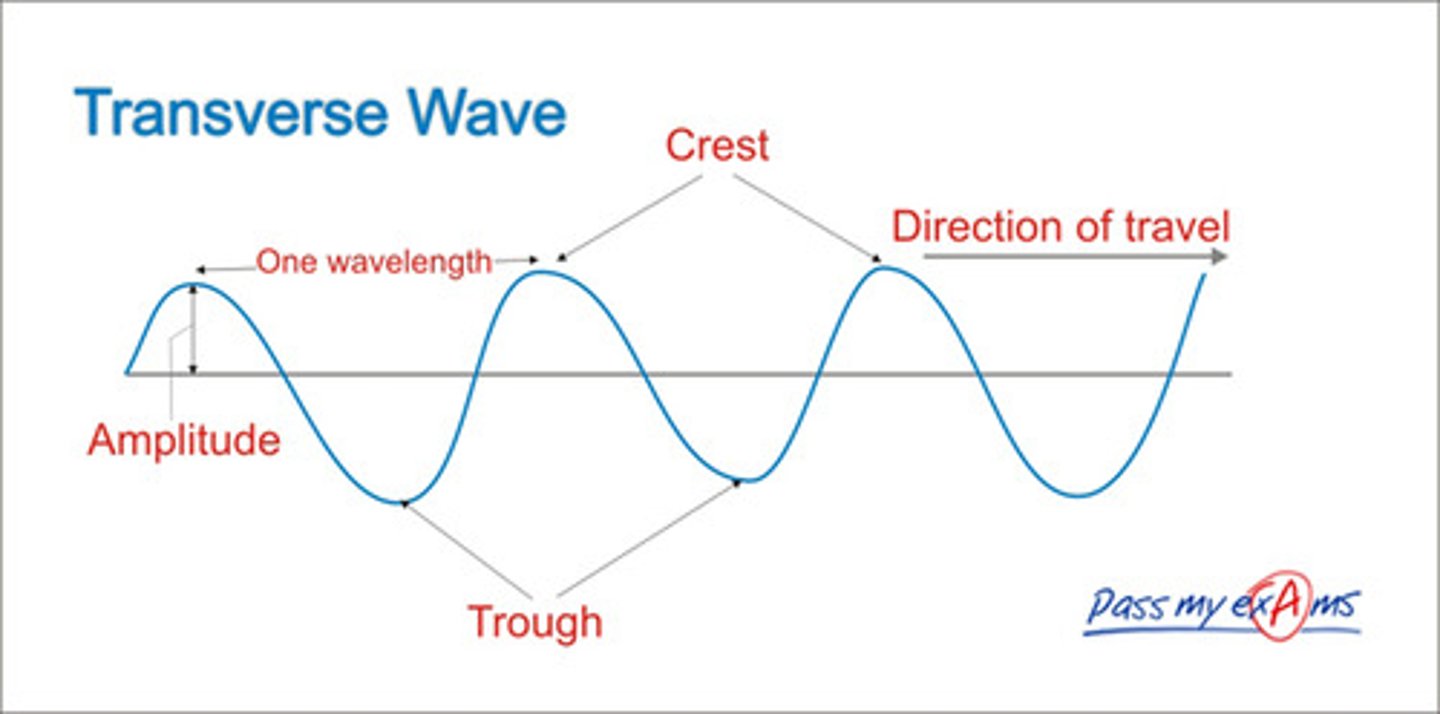
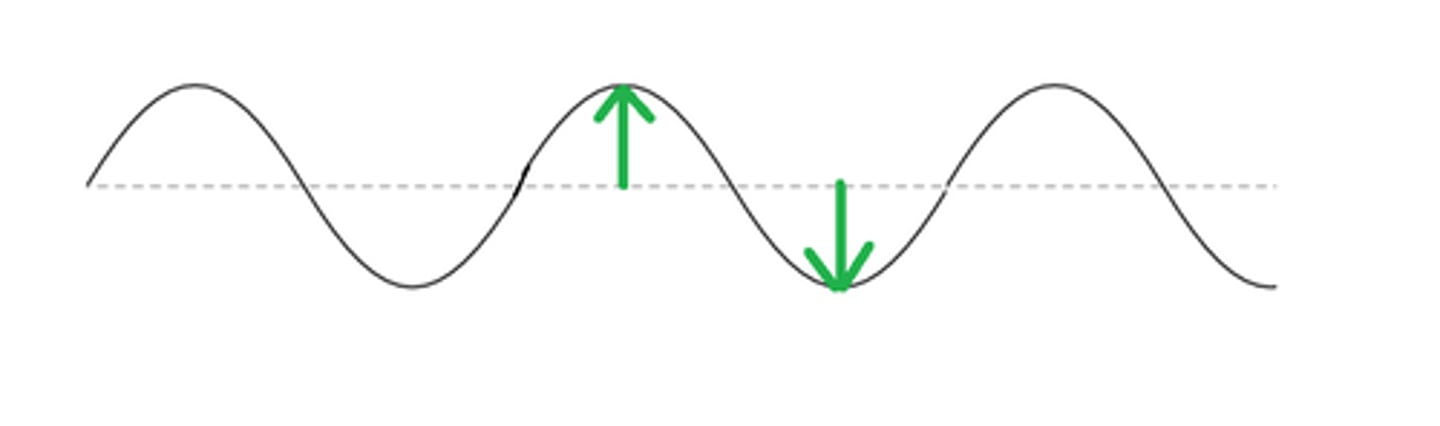
Transverse waves
The vibrations are at right angles to the direction of travel.
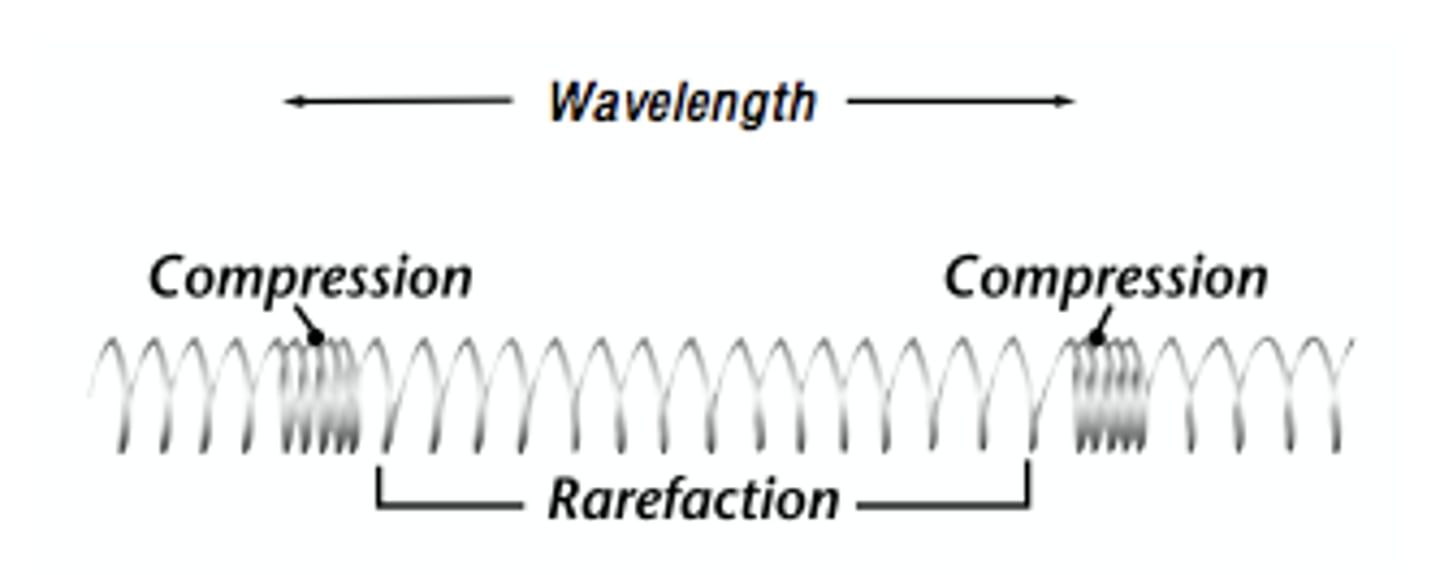
Longitudinal waves
The vibrations are along the same direction as the direction of travel.
Examples of transverse waves
Light and other types of electromagnetic radiation, as well as water waves and S waves (a type of seismic wave).
Examples of longitudinal waves
Sound waves and waves in a stretched spring, and P waves.
Equation linking time, period and frequency
Period = 1/frequency
Equation linking wave speed, frequency and wave length
Frequency = wave speed/wave length
The range of human hearing
20 to 20,000 hertz.
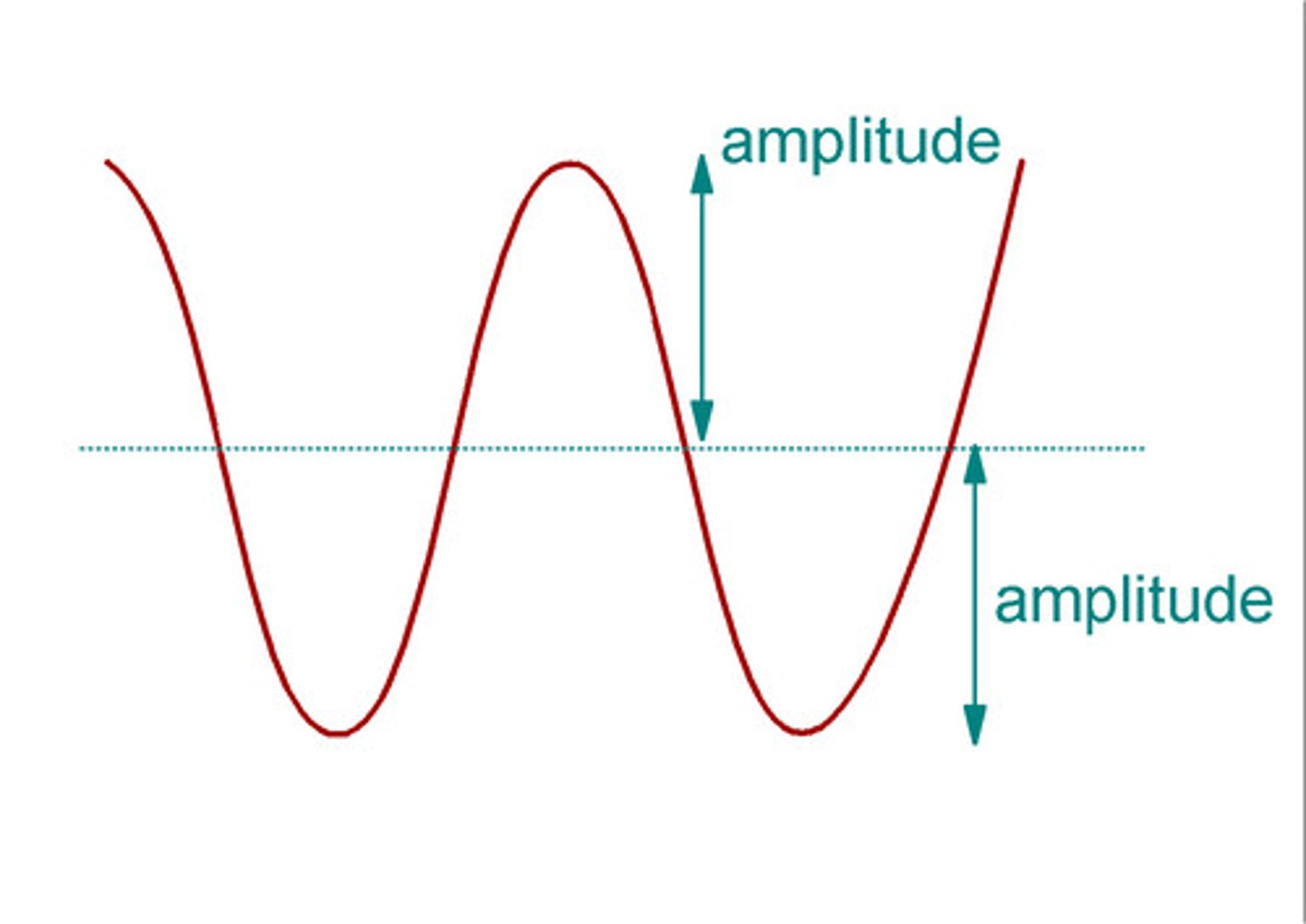
Amplitude
The maximum displacement of points on a wave, from a crest or trough to the middle.
Unit of frequency
Hertz (Hz)
What wavelength is measured in
Metres (m)
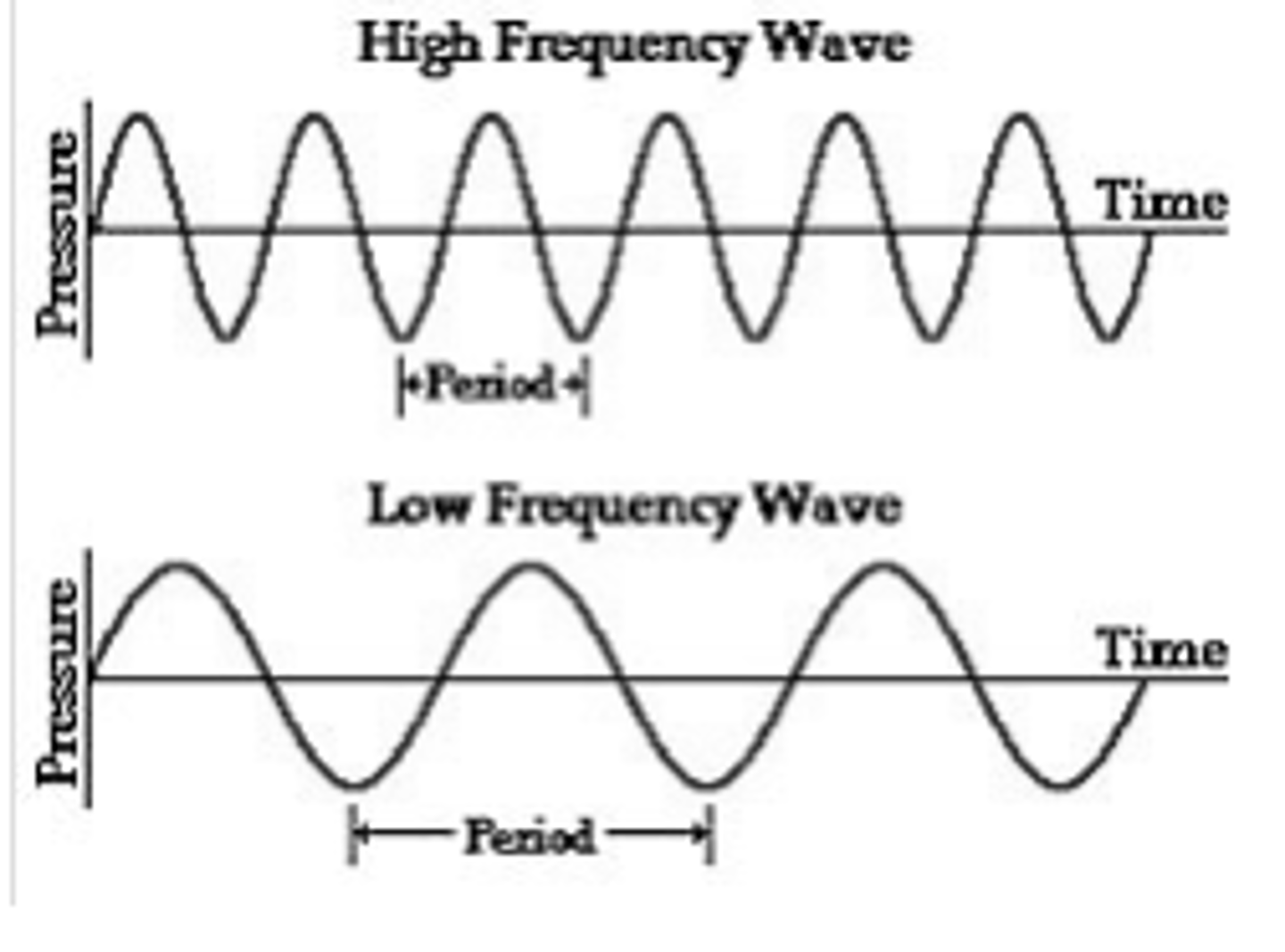
The frequency of a wave
The number of waves passing a point in a certain time.
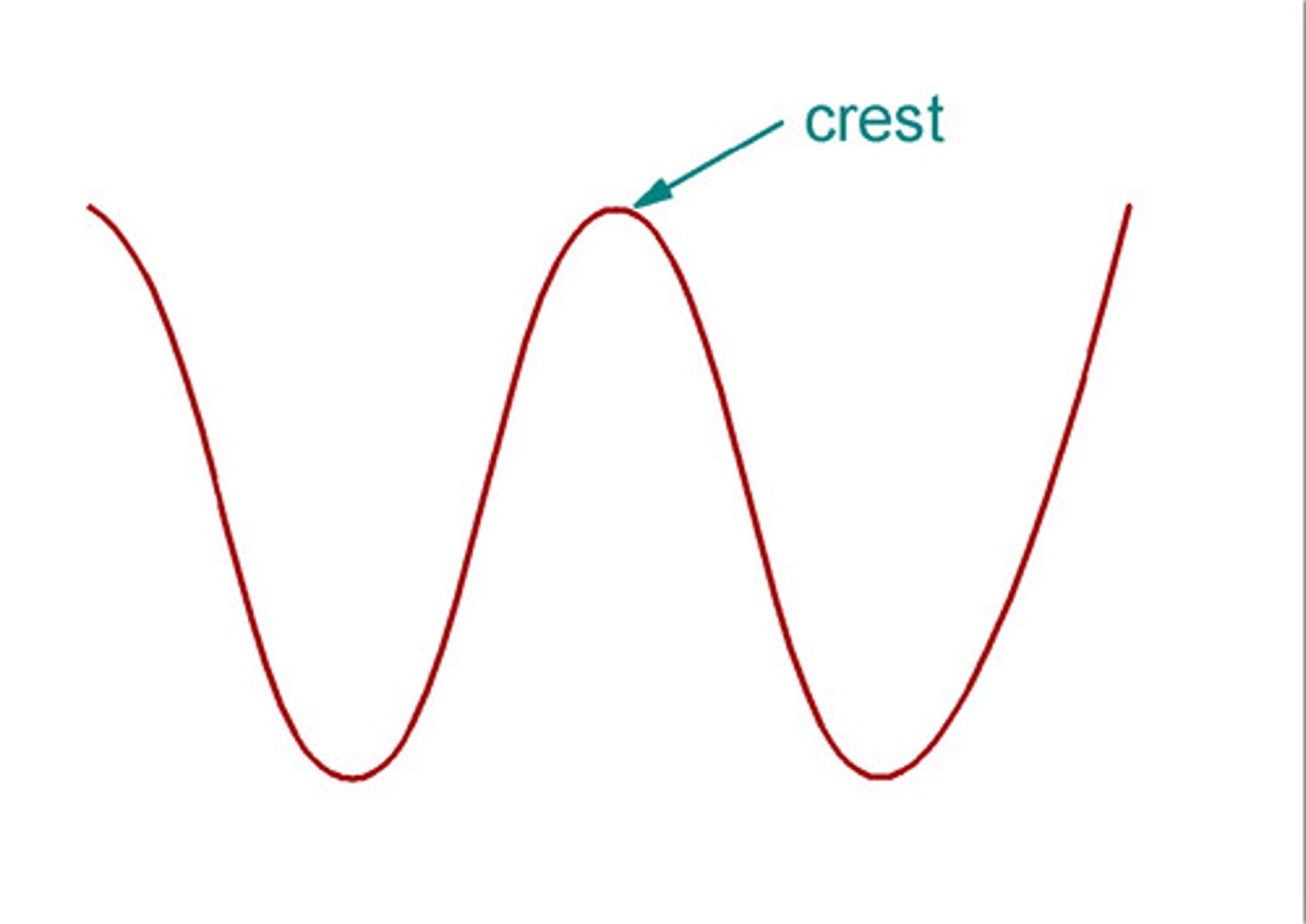
Crest
The highest point on a wave.
Wavespeed
How far the wave travels in a certain time. (Sometimes called the velocity of a wave).
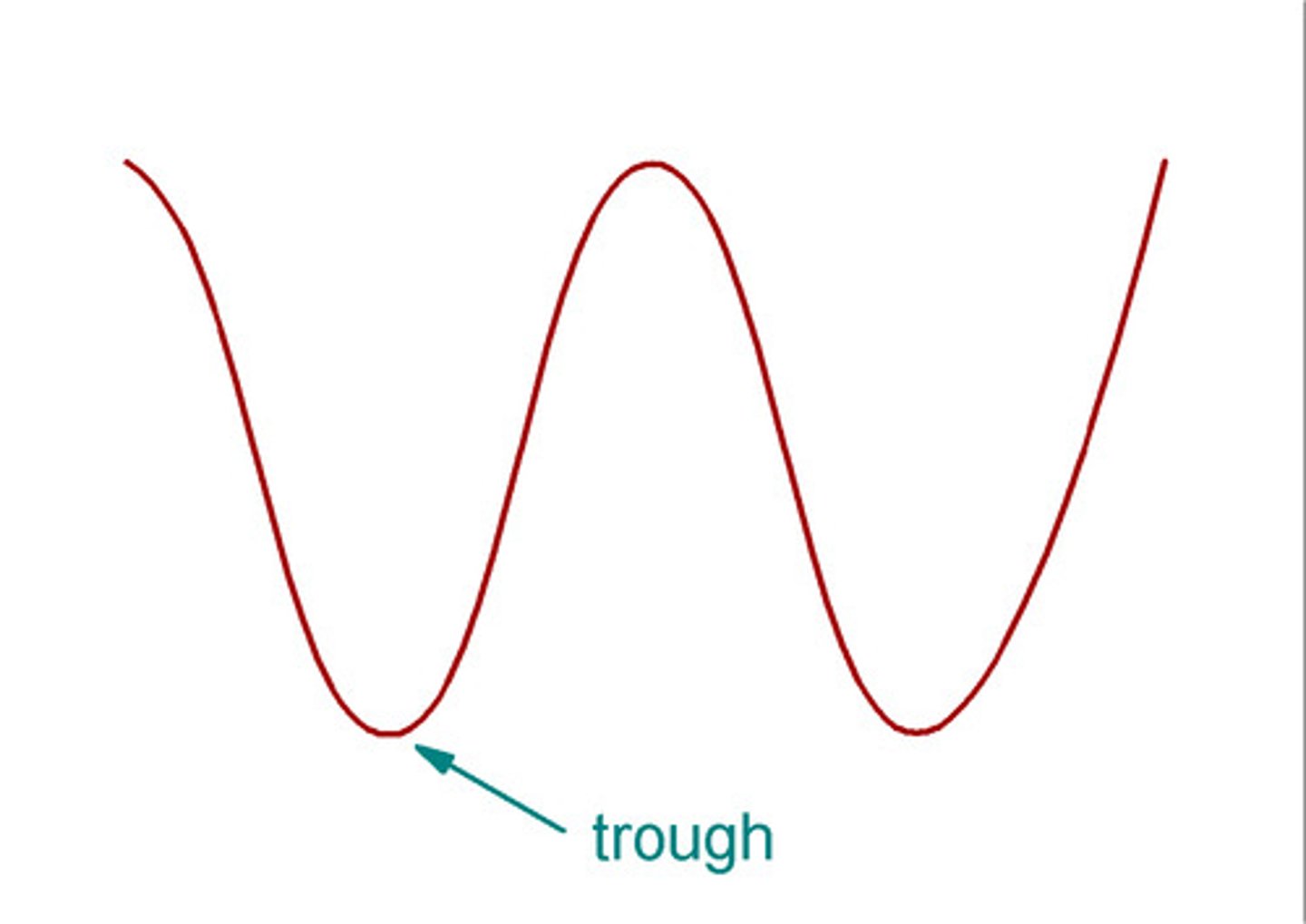
Trough
The lowest point of a wave.
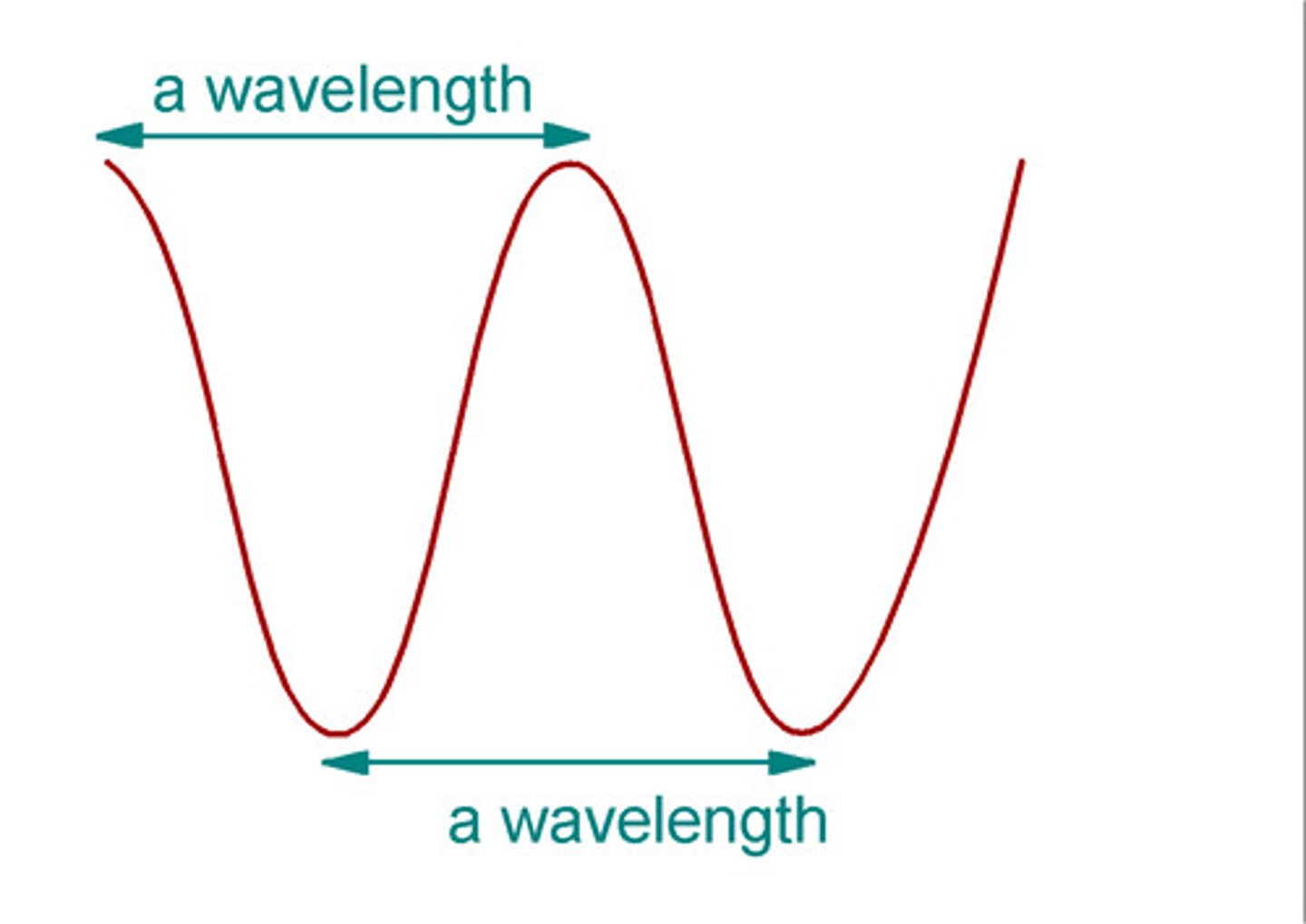
Wavelength definition
The distance from any point on one wave to the same point on the next wave along.
Where on a wave the wavelength is found
From the top of a crest to the top of the next crest, or from the bottom of a trough to the bottom of the next trough.
Where on a wave the amplitude is found
The vertical distance between the middle of a wave and the crest.
Equation for magnification
magnification = image height/ object height
Time period
How many seconds it takes for one complete wave to pass in a given point.
The unit for time period
Seconds (s)
4 types of wave behaviour
-Interference
-Reflection
-Refraction
-Diffraction
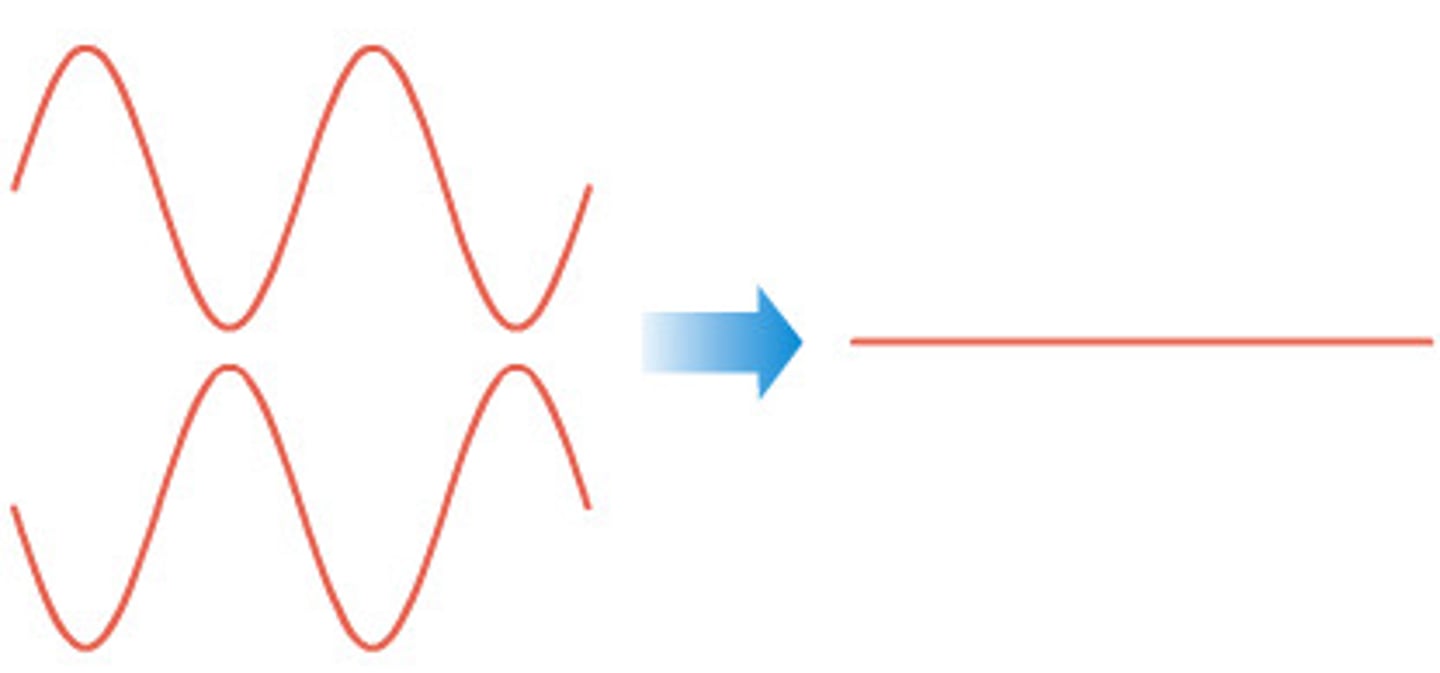
Interference of waves
When two waves overlap.
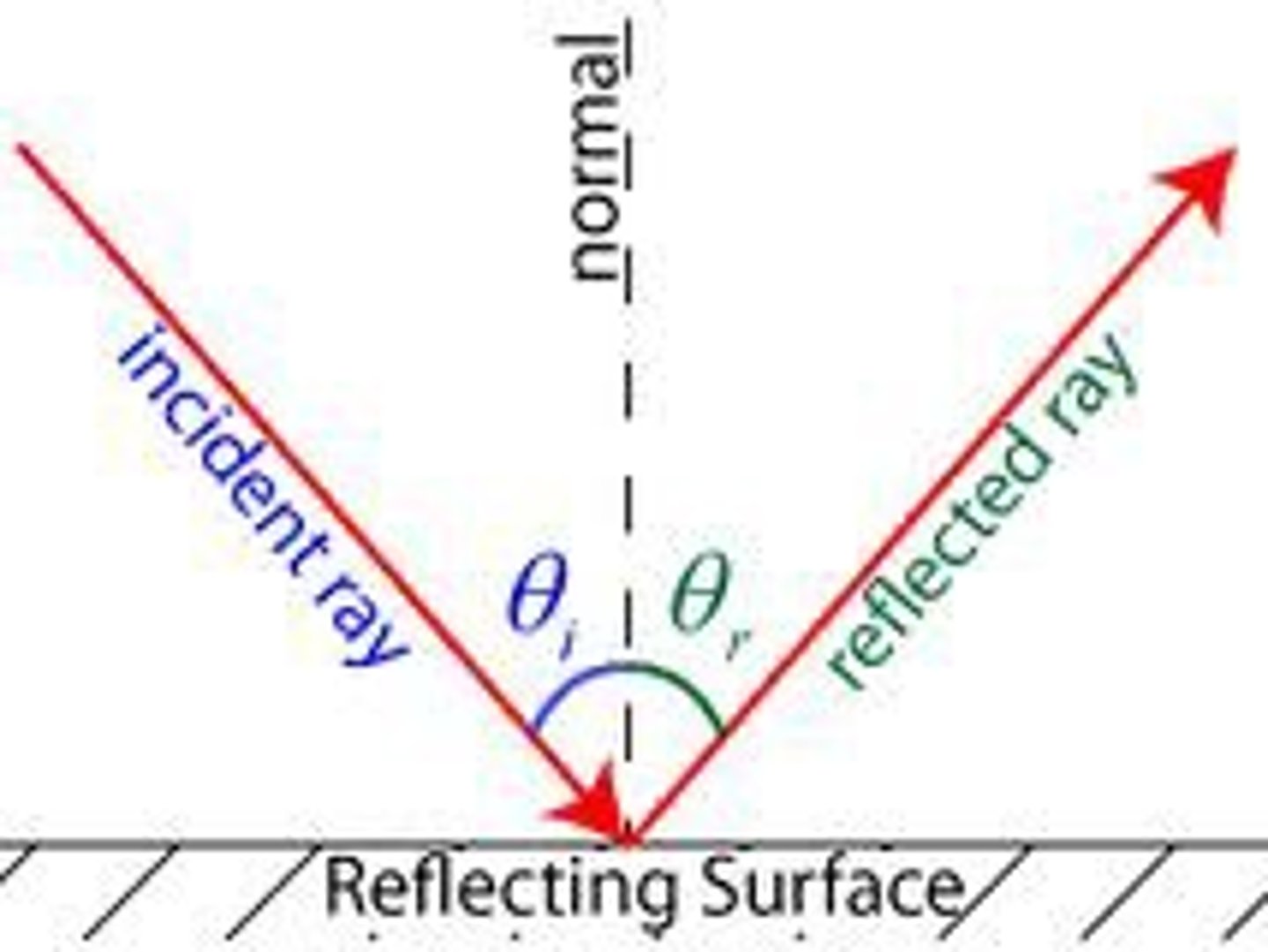
Reflection of waves
When a wave bounces back from a surface instead of passing
through it.
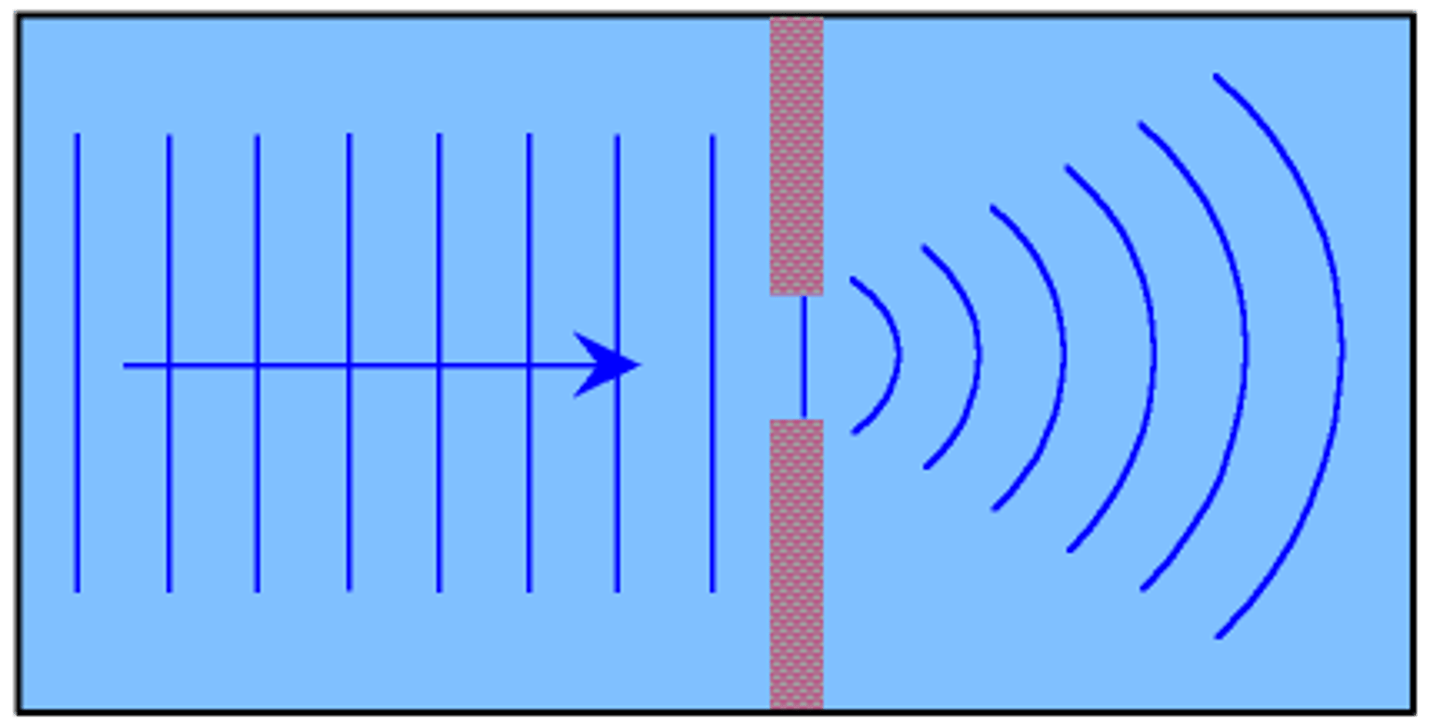
Diffraction of waves
The spreading out of waves when they pass through a gap, or around an obstacle.
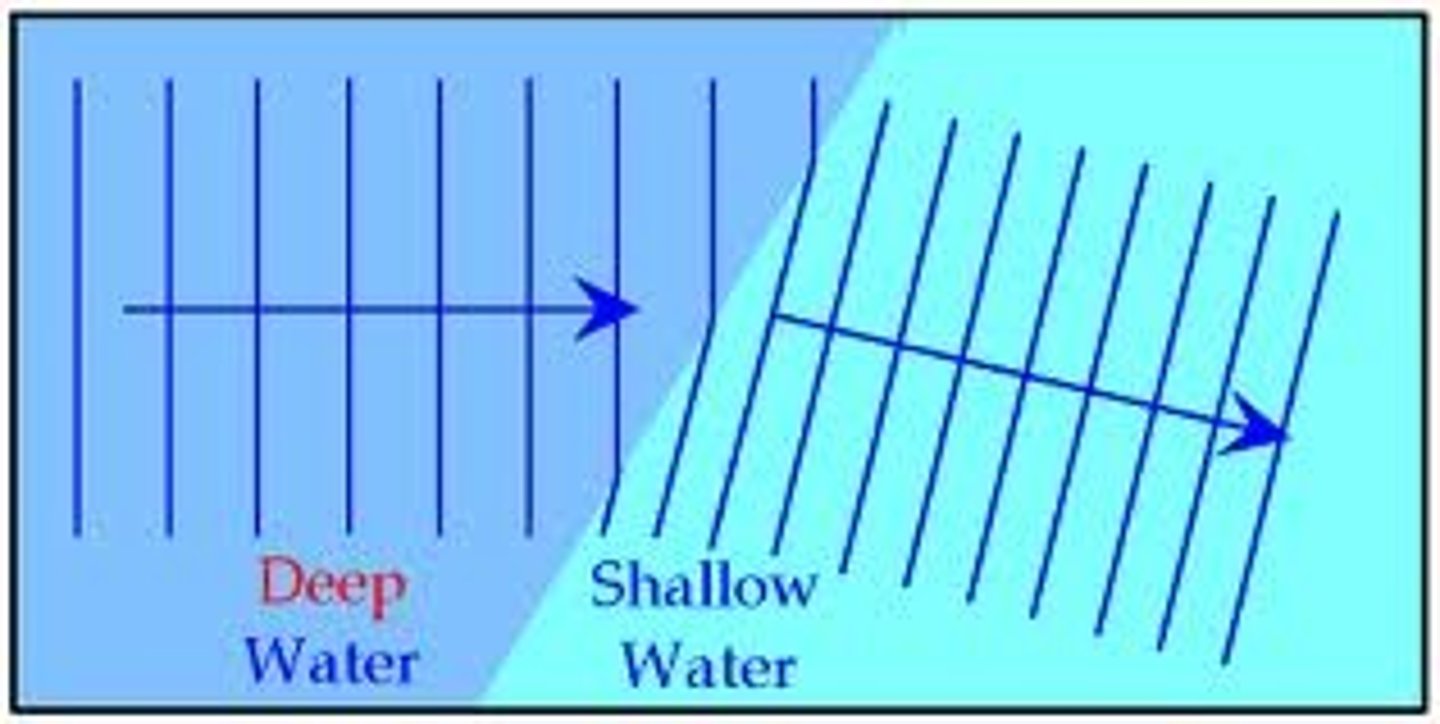
Refraction of waves
The change in direction of waves that occurs when waves travel from one medium to another.
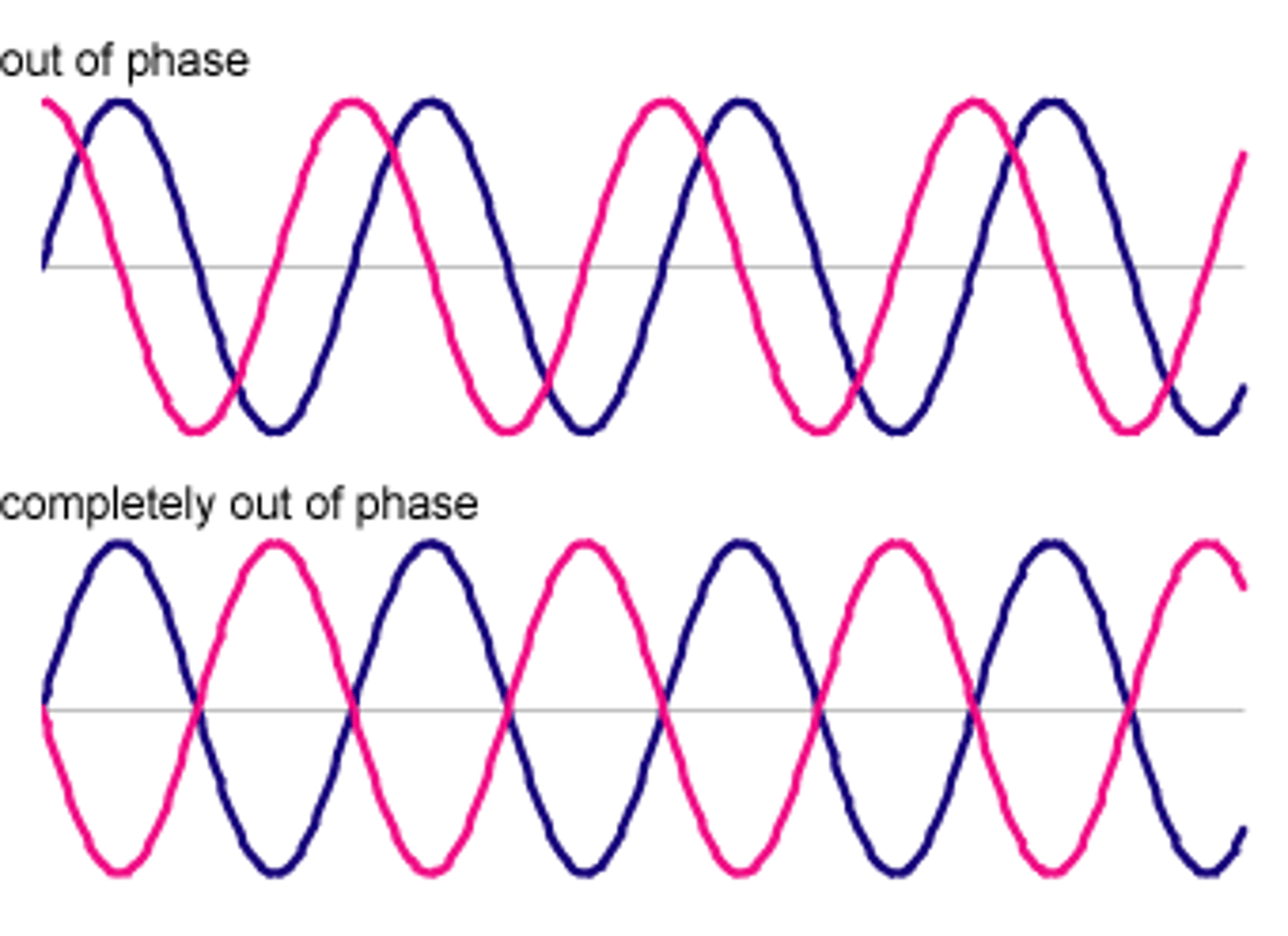
In phase
Points on a wave which are a whole number of wavelengths apart.
The Law of reflection (2 rules)
1) The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
2) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane.
Cause of refraction
Sound waves and light waves change speed when they pass across the boundary between two substances with different densities, such as air and glass. This causes them to change direction.
P-waves (P stands for primary)
They arrive at the detector first, they are also longitudinal waves.
S-waves (S stands for secondary)
They arrive at the detector of a seismometer second, they are transverse waves.
Electromagnetic waves
Transverse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber.
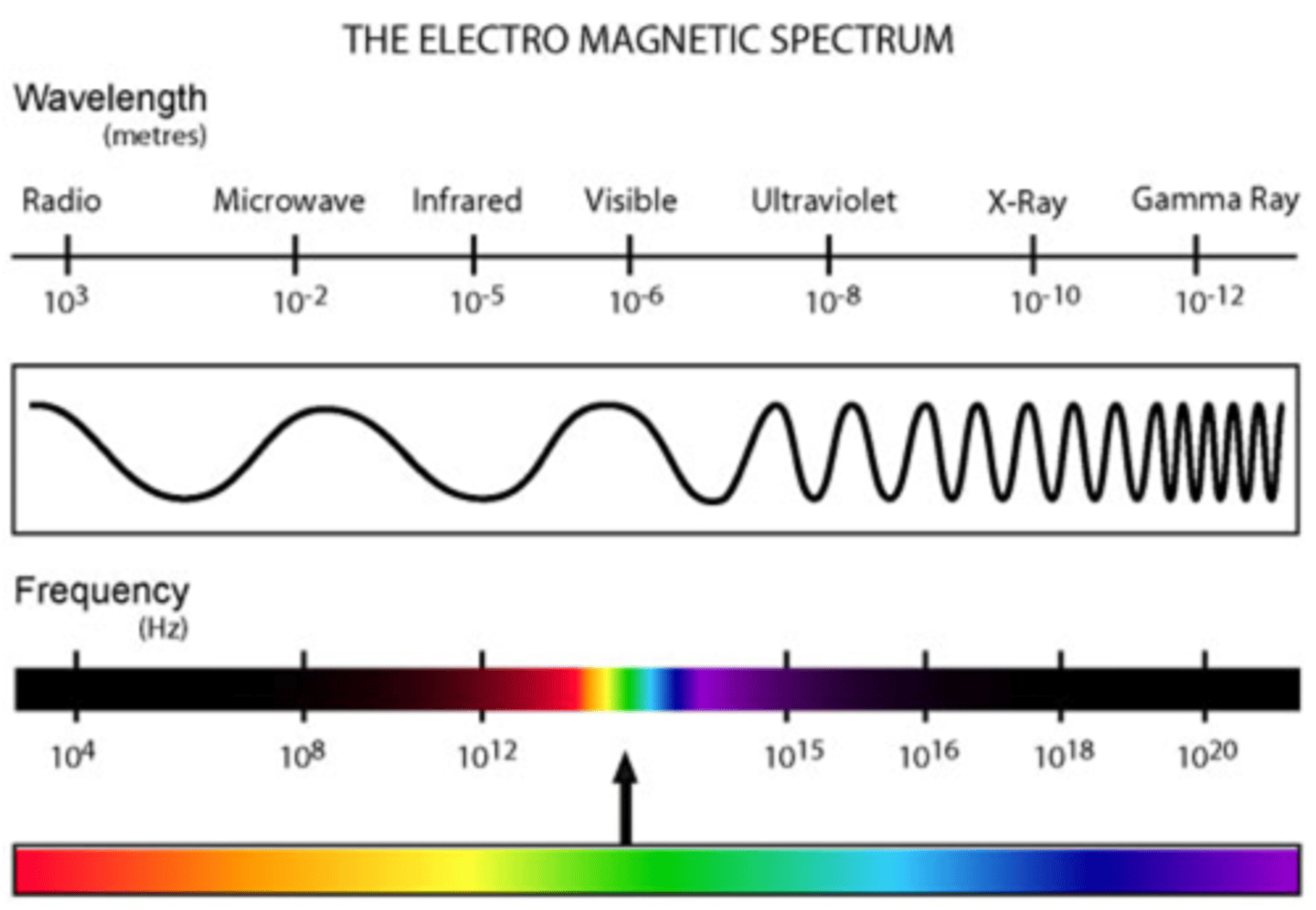
Electromagnetic wave spectrum
Ion
Electrically charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons.
Ionising radiation
Alpha, beta and gamma radiation are all examples of this, can break molecules into smaller fragments. Damages substances and materials, including those in the cells of living things. The ions themselves can take part in chemical reactions, spreading the damage.
Dose
It is the energy of ionising radiation absorbed per unit mass of any material.
Unit of dose
gray (gy)
- gray per second
- gray per hour
- gray per year