BIO 325 Topic 16 Human Genome
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is Polymorphism?
Places in the genome where DIFF people have DIFF base-pair sequences
SNP- Single nucleotide polymorphism
SSR- Simple sequence repeat
SNP
Simple Nucleotide Polymorphism
SNPS are mostly neutral
alleles
1 bp, present ever 10bp
300 million SNP loci in a human genome
SSR
Simple Sequence Repeat
SSRs are used to solve crimes in DNA profiles
1-10 bp repeat unit
longer repeats caused by slipped misprint in DNA
Common variants that don’t affect gene function
SNP: Introns, synonymous codons
SSR: outside genes
Rare variants that affect gene function
SNP: promotoer/splice junctions, codons
SSR: in trinucleotide repeat genes
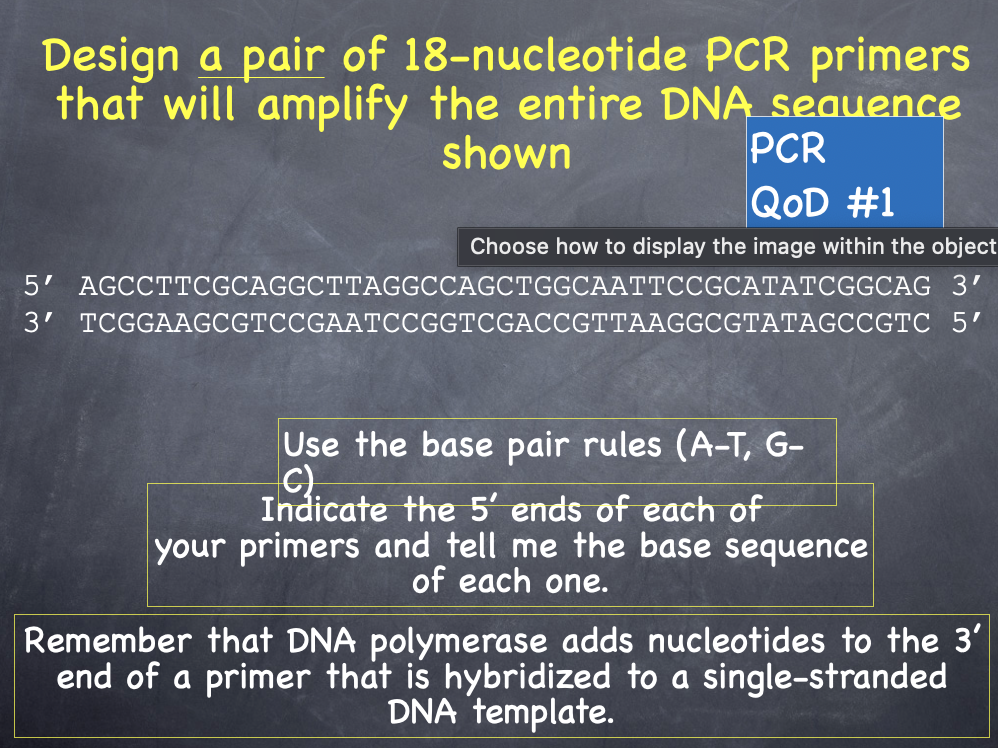
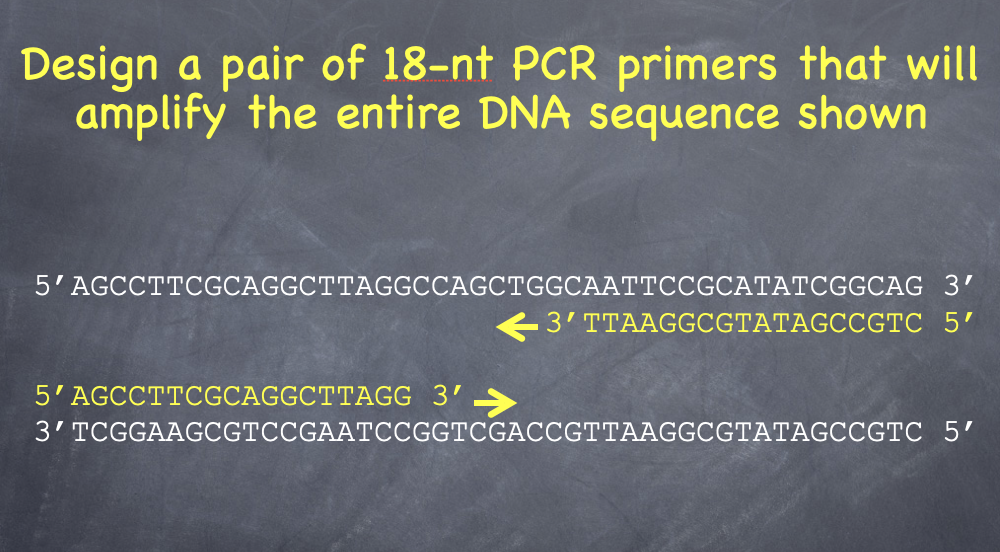
What is PCR and what does it do?
Polymerase chain reaction, repeats cycles of DNA synthesis of a target region exponentially
PCR Components:
Dna Sample
Primers
Nucleotide bases
Mix buffer
Per tube
Taq polymerase
• 7. Thermal cycler
PCR steps:
Denaturing DNA
Primers hybridize
• 3. Extension (synthesize new strand)
PCR rules:
20 nt base sequences at each end to performance PCR
Primers can be ~1000 bp apart
INSTAPOLL:
If a double-stranded DNA molecule is amplified by PCR, how many double-stranded DNA molecules will exist after FOUR cycles?
16
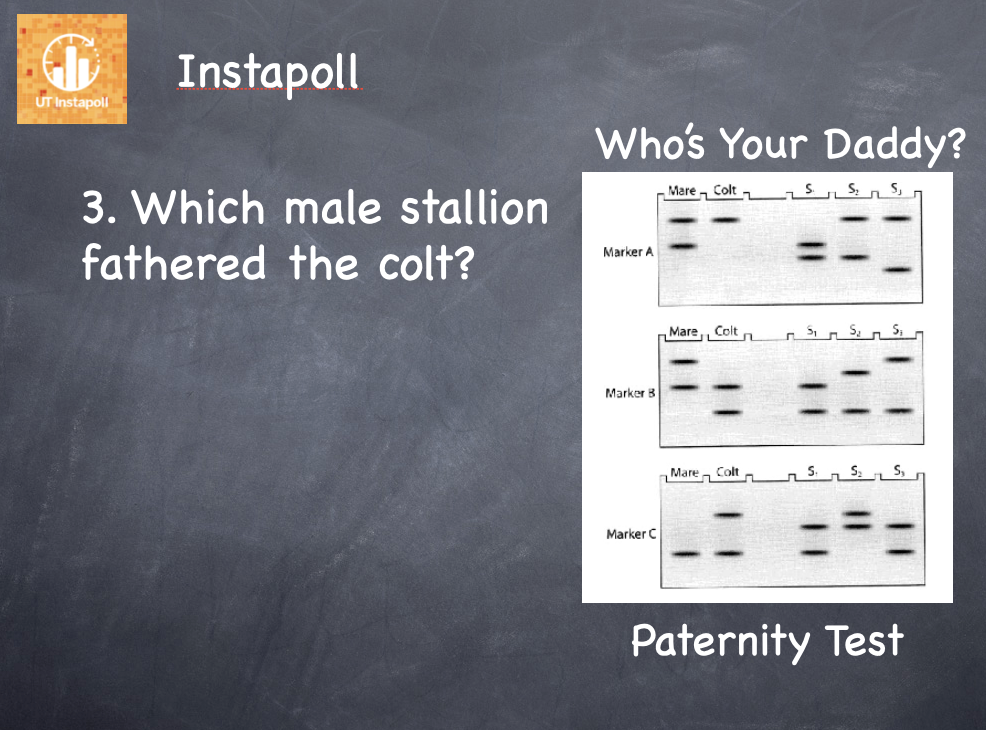
Stallion 2