IB Biology Topic 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
Totipotent
Stem cell type, present in morula, can become any human cell and placenta
2
New cards
Pluripotent
Stem cell type, inner cell mass, can become any human cell
3
New cards
Multipotent
Stem cell type, can become a few closely-related types of cell
4
New cards
Unipotent
Stem cell type, regenerate, can only become their associated cell type
5
New cards
Regenerative Medicine: Leukaemia
* Hematopoietic Stem Cells → Bone marrow stem cells that circulate in the blood stream
* Leukaemia → White blood cells mutate and stop functioning
* Stem Cell Therapy → Chemo/Radiation destroy malfunctioning leukocytes and bone marrow stem cells, replace with healthy hematopoietic stem cells from matching donor
* Leukaemia → White blood cells mutate and stop functioning
* Stem Cell Therapy → Chemo/Radiation destroy malfunctioning leukocytes and bone marrow stem cells, replace with healthy hematopoietic stem cells from matching donor
6
New cards
Regenerative Medicine: Stargardt’s Disease
* Inherited macular(photoreceptor) degeneration causing central vision loss
* Stem Cell Therapy → Embryonic stem cells are used to produce Retinal Pigment Epithelial cells to slow or stop photoreceptor loss
* Stem Cell Therapy → Embryonic stem cells are used to produce Retinal Pigment Epithelial cells to slow or stop photoreceptor loss
7
New cards
Stem Cell Source: Embryonic
Advantages
* Can be obtained from excess IVF embryos
* Almost unlimited growth potential + pluripotent
* Less chance of genetic damage
Disadvantages
* Embryo destruction
* Higher risk of tumour development
* Not genetically identical to patient
* Can be obtained from excess IVF embryos
* Almost unlimited growth potential + pluripotent
* Less chance of genetic damage
Disadvantages
* Embryo destruction
* Higher risk of tumour development
* Not genetically identical to patient
8
New cards
Stem Cell Source: Umbilical
Advantages
* Umbilical cord discarded
* Easily obtained and stored
* Unlikely to develop into tumour + less genetic damage
* Genetically identical to patient
Disadvantages
* Limited quantities available
* Reduced growth potential
* Limited capacity to differentiate(only blood cells unless induced)
* Umbilical cord discarded
* Easily obtained and stored
* Unlikely to develop into tumour + less genetic damage
* Genetically identical to patient
Disadvantages
* Limited quantities available
* Reduced growth potential
* Limited capacity to differentiate(only blood cells unless induced)
9
New cards
Stem Cell Source: Adult Somatic
Advantages
* Adult patient can give consent
* Unlikely to develop into tumour
* Genetically identical to patient
Disadvantages
* Reduced growth potential
* Difficult to obtain
* Multipotent unless induced
* Genetic damage can occur
* Adult patient can give consent
* Unlikely to develop into tumour
* Genetically identical to patient
Disadvantages
* Reduced growth potential
* Difficult to obtain
* Multipotent unless induced
* Genetic damage can occur
10
New cards
Resolution + Electron Microscopes
Shortest distance between two points that can be distinguished
Better resolution than light microscopes(200nm vs 1nm) as light waves are too large to fit through smaller gaps, can see organelles
Better resolution than light microscopes(200nm vs 1nm) as light waves are too large to fit through smaller gaps, can see organelles
11
New cards
Ultrastucture
All structures of a biological specimen that are ≥0.1nm in their smallest dimension
12
New cards
Binary Fission
* DNA replicated semi-conservatively
* 2 DNA loops attach to the membrane
* Membrane elongates and pinches off(cytokinesis)
* Asexual, produces two identical daughter cells
* 2 DNA loops attach to the membrane
* Membrane elongates and pinches off(cytokinesis)
* Asexual, produces two identical daughter cells
13
New cards
Compartmentalisation Benefits
* Efficiency of metabolism → substrates and enzymes can be localised and concentrated
* Localised conditions → pH etc. can be kept at differents levels
* Toxic/damaging substances can be isolated → digestive enzymes stored in lysosomes
* Numbers and locations of organelles can be changed based on cell requirements
* Localised conditions → pH etc. can be kept at differents levels
* Toxic/damaging substances can be isolated → digestive enzymes stored in lysosomes
* Numbers and locations of organelles can be changed based on cell requirements
14
New cards
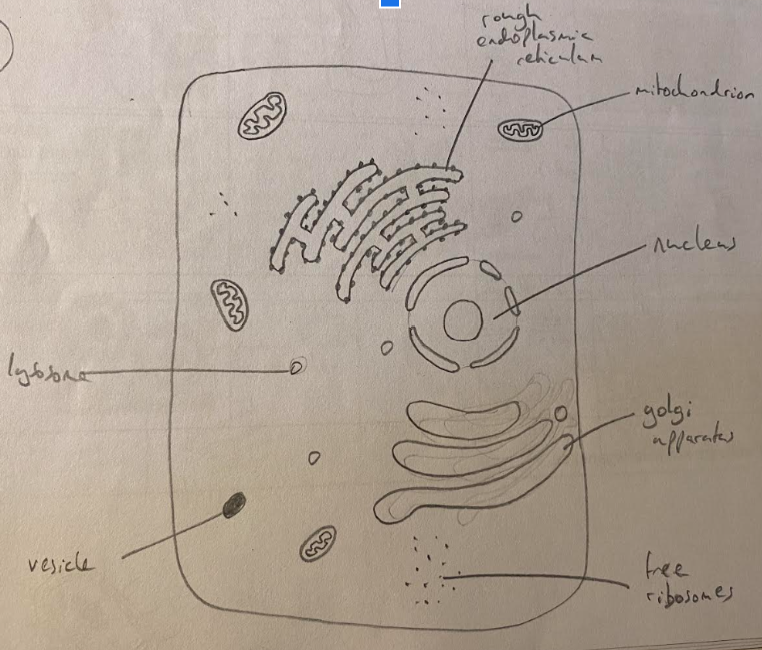
Generalised Animal Cell(7)
* Vesicle
* Lysosome
* Nucleus
* Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
* Golgi Apparatus
* Ribosomes
* Mitochondrion
* Lysosome
* Nucleus
* Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
* Golgi Apparatus
* Ribosomes
* Mitochondrion
15
New cards
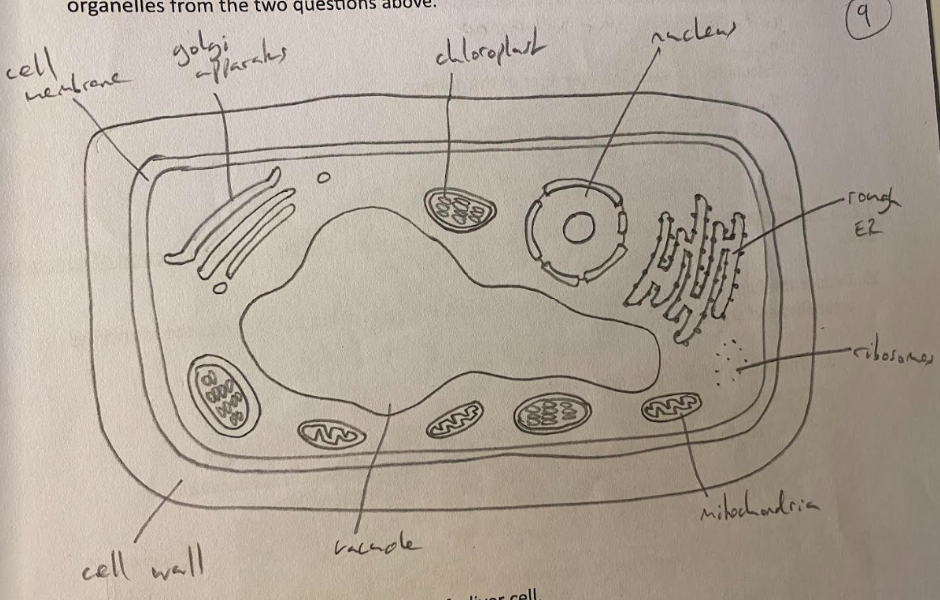
Generalised Plant Cell(9)
* Nucleus
* Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
* Golgi Apparatus
* Ribosomes
* Mitochondrion
* Vacuole
* Cell Membrane
* Cell Wall
* Chloroplast
* Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
* Golgi Apparatus
* Ribosomes
* Mitochondrion
* Vacuole
* Cell Membrane
* Cell Wall
* Chloroplast
16
New cards
Davson-Danielli Model
Proposed membrane ‘sandwich’ of phospholipids inside proteins, falsified
Issues:
* Freeze-etching → freeze sample then cut to reveal irregular surfaces and transmembrane proteins
* Structure of membrane proteins → Membrane proteins were discovered to be insoluble in water and varied in size, not able to form a uniform and continuous layer around the outer surface of a membrane
* Fluorescent antibody tagging → showed they were mobile and not fixed in place, demonstrated that the membrane proteins could move and did not form a static layer
Issues:
* Freeze-etching → freeze sample then cut to reveal irregular surfaces and transmembrane proteins
* Structure of membrane proteins → Membrane proteins were discovered to be insoluble in water and varied in size, not able to form a uniform and continuous layer around the outer surface of a membrane
* Fluorescent antibody tagging → showed they were mobile and not fixed in place, demonstrated that the membrane proteins could move and did not form a static layer
17
New cards
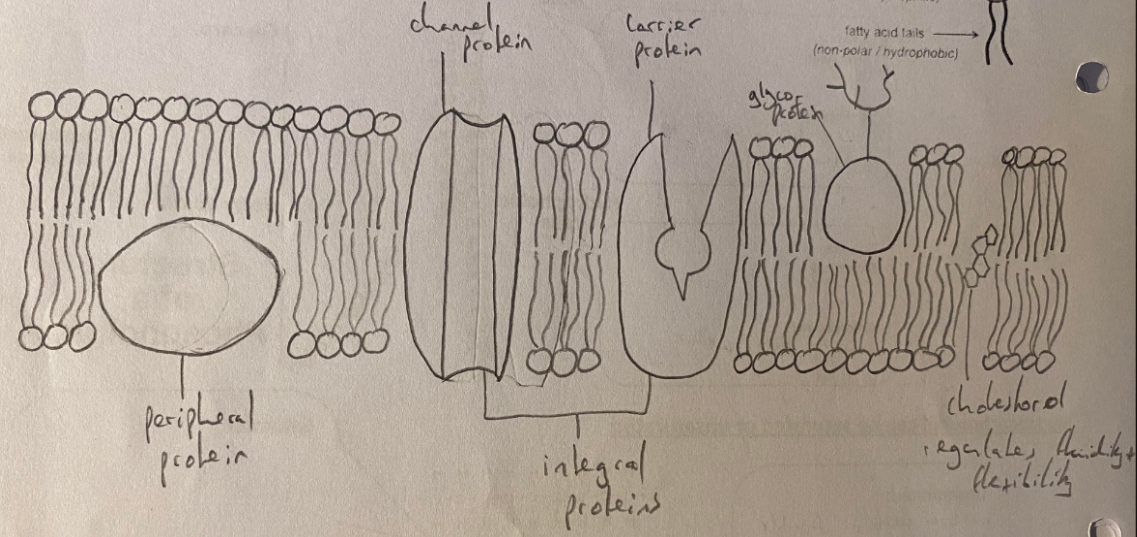
Membrane Proteins(9)
Proteins embedded either permanently or temporarily in the membrane
Types:
* Integral Proteins → permanently attached, typically span the bilayer
* Peripheral Proteins → temporarily attached by non-covalent interactions, associate with one surface of the membrane
* Junctions → Connect cells together
* Enzymes → Catalyse reactions at the membrane level, localise metabolic pathways
* Active Transport → Carriers, bind to substances on one side of the membrane then change shape to transport them to the other side, protein pumps
* Passive Transport → Channels, some proteins have a pore/channel that allows passive transport of substances
* Cell to Cell Recognition → Certain proteins help the cell in recognising the difference between itself and other cells, important for immune response
* Anchorage → Attachment points for cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
* Receptors → Proteins that extend through the cell membrane to send information into or out of the cell
Types:
* Integral Proteins → permanently attached, typically span the bilayer
* Peripheral Proteins → temporarily attached by non-covalent interactions, associate with one surface of the membrane
* Junctions → Connect cells together
* Enzymes → Catalyse reactions at the membrane level, localise metabolic pathways
* Active Transport → Carriers, bind to substances on one side of the membrane then change shape to transport them to the other side, protein pumps
* Passive Transport → Channels, some proteins have a pore/channel that allows passive transport of substances
* Cell to Cell Recognition → Certain proteins help the cell in recognising the difference between itself and other cells, important for immune response
* Anchorage → Attachment points for cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
* Receptors → Proteins that extend through the cell membrane to send information into or out of the cell
18
New cards
Cholesterol in the Membrane
Regulates fluidity and flexibility of the membrane based on temperature
19
New cards
Fluid-Mosaic Model
Singer-Nicholson
20
New cards
Membrane Transport: Simple Diffusion
* Down conc. gradient
* A concentration gradient, small non-polar molecules
* Oxygen, carbon dioxide
* A concentration gradient, small non-polar molecules
* Oxygen, carbon dioxide
21
New cards
Membrane Transport: Facilitated Diffusion
* Down conc. gradient
* Concentration gradient, transmembrane proteins, large polar molecules
* Oxygen in blood, glucose
* Concentration gradient, transmembrane proteins, large polar molecules
* Oxygen in blood, glucose
22
New cards
Membrane Transport: Osmosis
* Area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration
* Concentration gradient, aquaporin (both simple + facilitated)
* Exclusively water
* Concentration gradient, aquaporin (both simple + facilitated)
* Exclusively water
23
New cards
Membrane Transport: Active Transport
* Against conc. gradient
* Integral protein pumps, ATP
* Sodium-potassium pumps
* Integral protein pumps, ATP
* Sodium-potassium pumps
24
New cards
Membrane Transport: Endocytosis
* Out of cell
* Inward pouching of plasma membrane, forming a vesicle
* Inward pouching of plasma membrane, forming a vesicle
25
New cards
Membrane Transport: Exocytosis
* Into cell
* Vesicle joins plasma membrane, releasing contents
* Vesicle joins plasma membrane, releasing contents
26
New cards
Isotonic
Same osmolarity, no change to tissues in these solutions
27
New cards
Hypertonic
Higher osmolarity, tissue would become dehydrated
28
New cards
Hypotonic
Lower osmolarity, tissue would have increased turgor pressure
29
New cards
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Active Transport and Facilitated Diffusion
1. Three sodium ions bind to intracellular sites on the pump
2. A phosphate group is transferred to the pump via the hydrolysis of ATP
3. The pump undergoes a conformational change, moving sodium out of cell
4. Two potassium binding sites are exposed on the extracellular surface
5. The phosphate group is released, pump returns to its original conformation
6. Potassium moves into cell
1. Three sodium ions bind to intracellular sites on the pump
2. A phosphate group is transferred to the pump via the hydrolysis of ATP
3. The pump undergoes a conformational change, moving sodium out of cell
4. Two potassium binding sites are exposed on the extracellular surface
5. The phosphate group is released, pump returns to its original conformation
6. Potassium moves into cell