Topic 3 - Membranes - Biology 241 - University of Calgary
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:44 AM on 10/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
• Molecules that tend to repel, not absorb, or not dissolve/mix with or by water.
Hydrophobic
2
New cards
• Molecules that tend to be attracted to, absorb, or dissolve/mix with or by water.
Hydrophilic
3
New cards
• Triglycerides.
• Phospholipids.
• Sterols.
• Phospholipids.
• Sterols.
What are the three main biological lipids?
4
New cards
• Energy storage.
What is the function of triglycerides?
5
New cards
• Hydrocarbon chain.
• Carboxyl group at the end of the chain.
• Carboxyl group at the end of the chain.
What makes up a fatty acids structure? (2)
6
New cards
• Cannot absorb anymore hydrogen atoms in its carbon chain; commonly found in animal fats.
• No double bonds.
• No double bonds.
Saturated Fatty Acid (2)
7
New cards
• Can absorb additional hydrogen atoms; found in vegetable oils.
• Has a double bond.
• Has a double bond.
Unsaturated Fatty Acid (2)
8
New cards
• 3 fatty acids.
• Glycerol anchor.
• Glycerol anchor.
What makes up a triacylglycerols structure? (2)
9
New cards
• Charged molecule.
• Phosphate.
• Glycerol.
• 2 fatty acids.
• Phosphate.
• Glycerol.
• 2 fatty acids.
What makes up a phospholipids structure?
10
New cards
• Charged molecule.
• Phosphate.
• Glycerol.
• Phosphate.
• Glycerol.
What makes up a phospholipids head group?
11
New cards
• 2 fatty acids.
What makes up a phospholipids tails?
12
New cards
• False.
A phospholipids head groups repels water, true or false?
13
New cards
• True.
A phospholipids tails repel water, true or false?
14
New cards
• Tight packing between them.
• Less fluidity.
• Restricted movement.
• Less fluidity.
• Restricted movement.
What are the characteristics of saturated phospholipid fatty acid tails?
15
New cards
• Looser packing between them.
• More fluidity.
• More movement.
• More fluidity.
• More movement.
What are the characteristics of unsaturated phospholipid fatty acid tails?
16
New cards
• Regulates transport in and out of the cell.
What does the cell membrane do?
17
New cards
• Membrane.
Which part of a cell is commonly known for the following:
• Communication
• Chemical Reactions
• Communication
• Chemical Reactions
18
New cards
• Selective.
What type of permeability do membranes have?
19
New cards
• Allows some molecules to pass through the membrane.
Selective Permeability
20
New cards
• Yes.
Is it possible for lipids and proteins to coexist in a membrane?
21
New cards
B) Laterally.
Which way do lipids and proteins diffuse in a membrane?
A) Diagonally
B) Laterally
C) Horizontally
D) They don't diffuse across the membrane
A) Diagonally
B) Laterally
C) Horizontally
D) They don't diffuse across the membrane
22
New cards
• Protein.
Transport involves what types of channels and carriers?
23
New cards
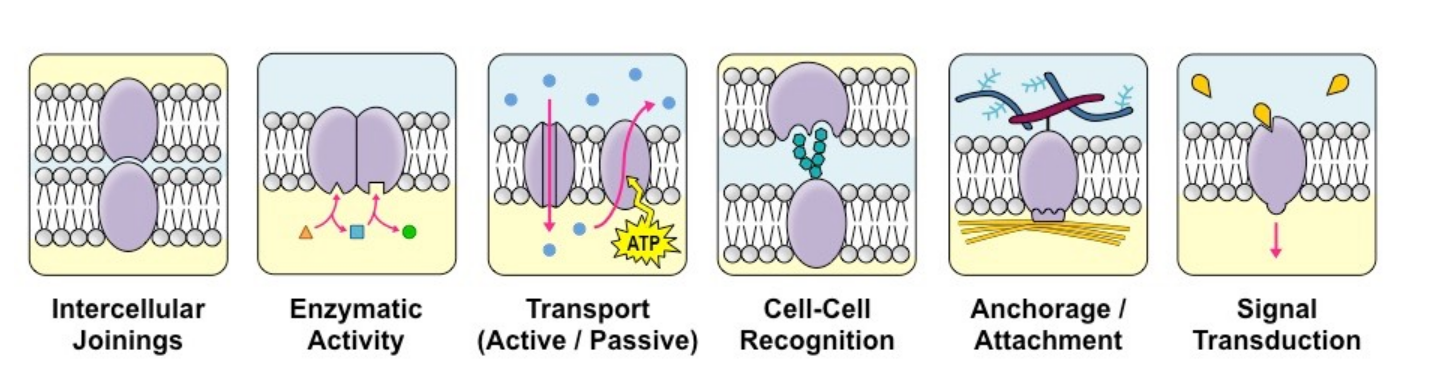
• Involves enzymes and the binding of substrates to enzymes.
Enzymatic Activity
24
New cards
• Involves a hormone that binds to a receptor.
Signal Transduction
25
New cards
• Attachment points for cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix.
Attachment/Recognition
26
New cards
• Junctions - Connect and join two cells together.
• Enzymes - Fixing to membranes localizes metabolic pathways.
• Transport - Facilitated diffusion and active transport.
• Recognition - Markers for cellular identification.
• Attachment - Attachment points for cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix.
• Transduction - Receptors for peptide hormones.
JETRAT
• Enzymes - Fixing to membranes localizes metabolic pathways.
• Transport - Facilitated diffusion and active transport.
• Recognition - Markers for cellular identification.
• Attachment - Attachment points for cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix.
• Transduction - Receptors for peptide hormones.
JETRAT
(I found this online and thought it would help to remember the different types of membrane protein functions)
27
New cards
• Short fatty acid tails.
• Unsaturated fatty acids.
• Higher temperature.
• Sterols.
• Unsaturated fatty acids.
• Higher temperature.
• Sterols.
What factors increase the fluidity of a membrane?
28
New cards
• They change the strength of van der Waals forces.
How do short fatty acid tails increase a membranes fluidity?
29
New cards
• Sterols.
What factor both increases and decreases the fluidity of a membrane?
30
New cards
• To prevent freezing, sterols stop phospholipids from packing too tightly together.
• To prevent melting, sterols fill in gaps between phospholipids.
• To prevent melting, sterols fill in gaps between phospholipids.
How do sterols regulate membrane fluidity (for both preventing freezing and melting)?
31
New cards
• More solutes can pass through the bilayer more quickly.
If fluid membranes are "leaky" what happens?
32
New cards
• Fewer solutes are able to pass through the membranes more slowly.
Why are viscous membranes better barriers?
33
New cards
• Small, uncharged, barely polar molecules.
What can diffuse across a lipid bilayer?
34
New cards
• Large, charged, polar molecules.
• Ions.
• Ions.
What cannot diffuse across a lipid bilayer? (2)
35
New cards
• Maintain homeostasis.
• Cells live in dynamic environments.
• Allows for concentrations of molecules on the inside that are different from the outside.
• Transport of molecules is regulated by cells.
• Cells live in dynamic environments.
• Allows for concentrations of molecules on the inside that are different from the outside.
• Transport of molecules is regulated by cells.
Why do cells need a selective barrier? (4)
36
New cards
• An area of high concentration distributes evenly to an area of lower concentration.
Diffusion
37
New cards
• The concentration gradient (high in entropy).
Where does the energy in diffusion come from?
38
New cards
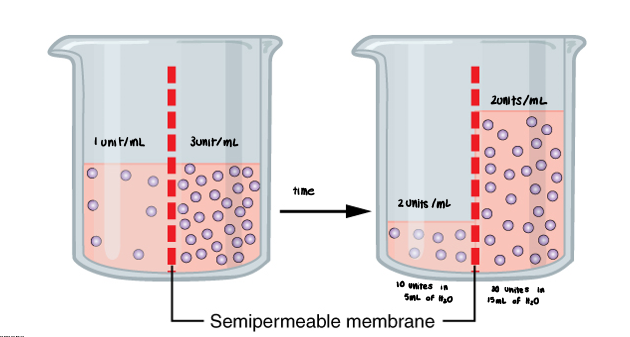
• Diffusion of water from a low solute to a high solute.
Osmosis
39
New cards
• Capability of a solution to modify the volume of cells by altering their water content.
Tonicity
40
New cards
• No net movement of water, causing the cell to not change in size or shape.
Isotonic Conditions
41
New cards
• Water diffuses out of the cell, causing shrinkage.
Hypertonic Conditions
42
New cards
• Water diffuses into the cell, causing swelling.
Hypotension Conditions
43
New cards
• Transport of a solute through diffusion.
Passive Transport: Simple Diffusion
44
New cards
• Moves down or with its concentration gradient.
• Powered by potential energy in the concentration of the gradient.
• A greater concentration gradient = greater rate of movement.
• Powered by potential energy in the concentration of the gradient.
• A greater concentration gradient = greater rate of movement.
What are the characteristics of passive transport (simple diffusion)? (3)
45
New cards
• Involve protein carriers to help carry large/charged/polar molecules into and out of the membrane.
Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion
46
New cards
• Moves down with the concentration gradient.
• Direction of transport is reversible.
• Rate of transportation depends on concentration gradient.
• Substrate specific.
• Direction of transport is reversible.
• Rate of transportation depends on concentration gradient.
• Substrate specific.
What are the characteristics of passive transport (facilitated diffusion)? (4)
47
New cards
• Bind a single solute and transport it across the lipid bilayer.
Carrier Proteins
48
New cards
• Form hydrophilic channels in the membrane which water and ions can move across.
Channel Proteins
49
New cards
• They move solutes away from equilibrium (low energy state).
How do cells establish a concentration gradient?
50
New cards
• ATP.
In order for cells to establish a concentration gradient, what molecule is needed?
51
New cards
• Involves specific protein pumps that cross the membrane and moves solutes up (against) their concentration gradient.
Primary Active Transport
52
New cards
• ATPO.
What does the transporter pump use in primary active transport?
53
New cards
• Chemical gradients.
• Electrochemical gradients.
• Electrochemical gradients.
What types of gradients do transporter pumps generate? (2)
54
New cards
• Specific protein pumps that move solutes up their concentration gradient.
• Powered by the energy released as different solutes move down its concentration gradient.
• Powered by the energy released as different solutes move down its concentration gradient.
Secondary Active Transport Pumps (2)
55
New cards
• Both solutes move in the same physical direction.
Symporters
56
New cards
• Solutes move in opposite physical direction.
Antiporters
57
New cards
• Having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts.
Amphiphatic
58
New cards
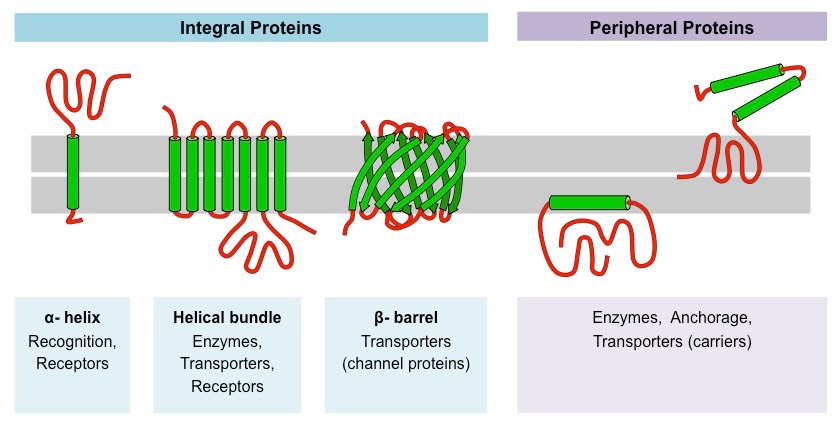
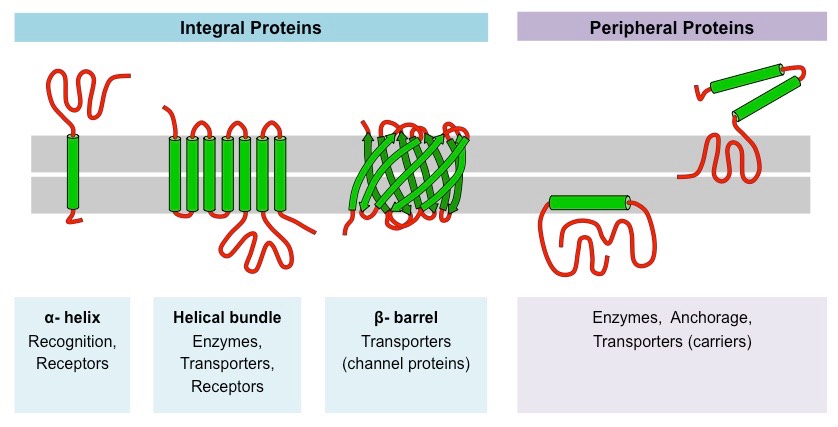
• A type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane.
Integral Proteins
59
New cards
• Interact with the surface of the lipid bilayer of cell membranes.
Peripheral Proteins