AP MACRO UNIT 5
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
demand-pull economics
occurs when increased demand for goods and services outstrips the economy's ability to produce them, leading to higher prices and a general increase in the cost of living.
Goal of fiscal and monetary policy
change AD to achieve full employment output
fiscal policy
change gov spending, influence consumer spending by changing tax rates
monetary policy
change interest rates to influence interest sensitive spending
why cant fiscal policy fix staglfation
because increasing AD increases inflation
SRPC
shows the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment
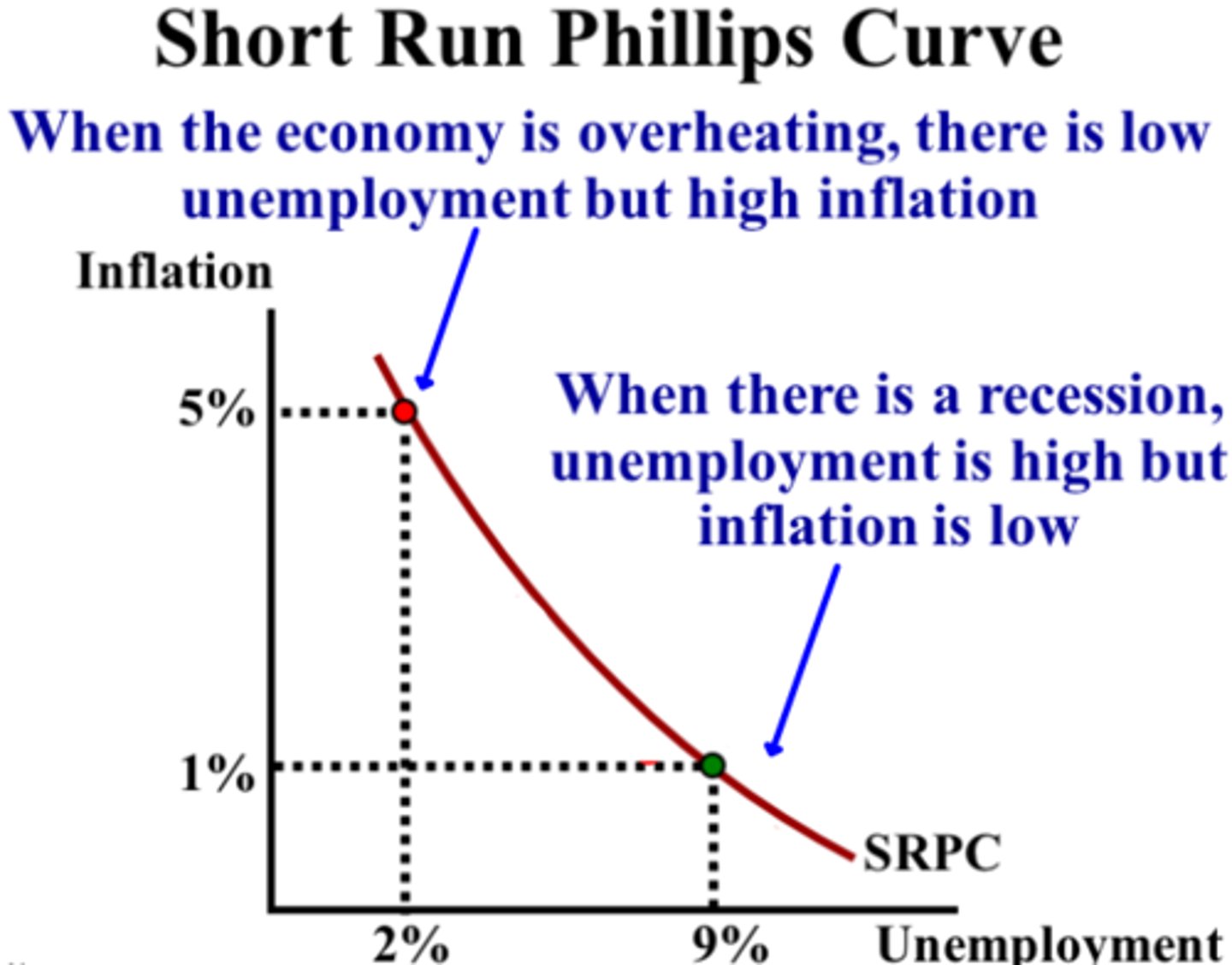
stagflation
-if there is stagflation, unemployment is up and inflation is up
-causes SRPC to shift right
LRPC
shows there is no tradeoff between inflation and unemployment
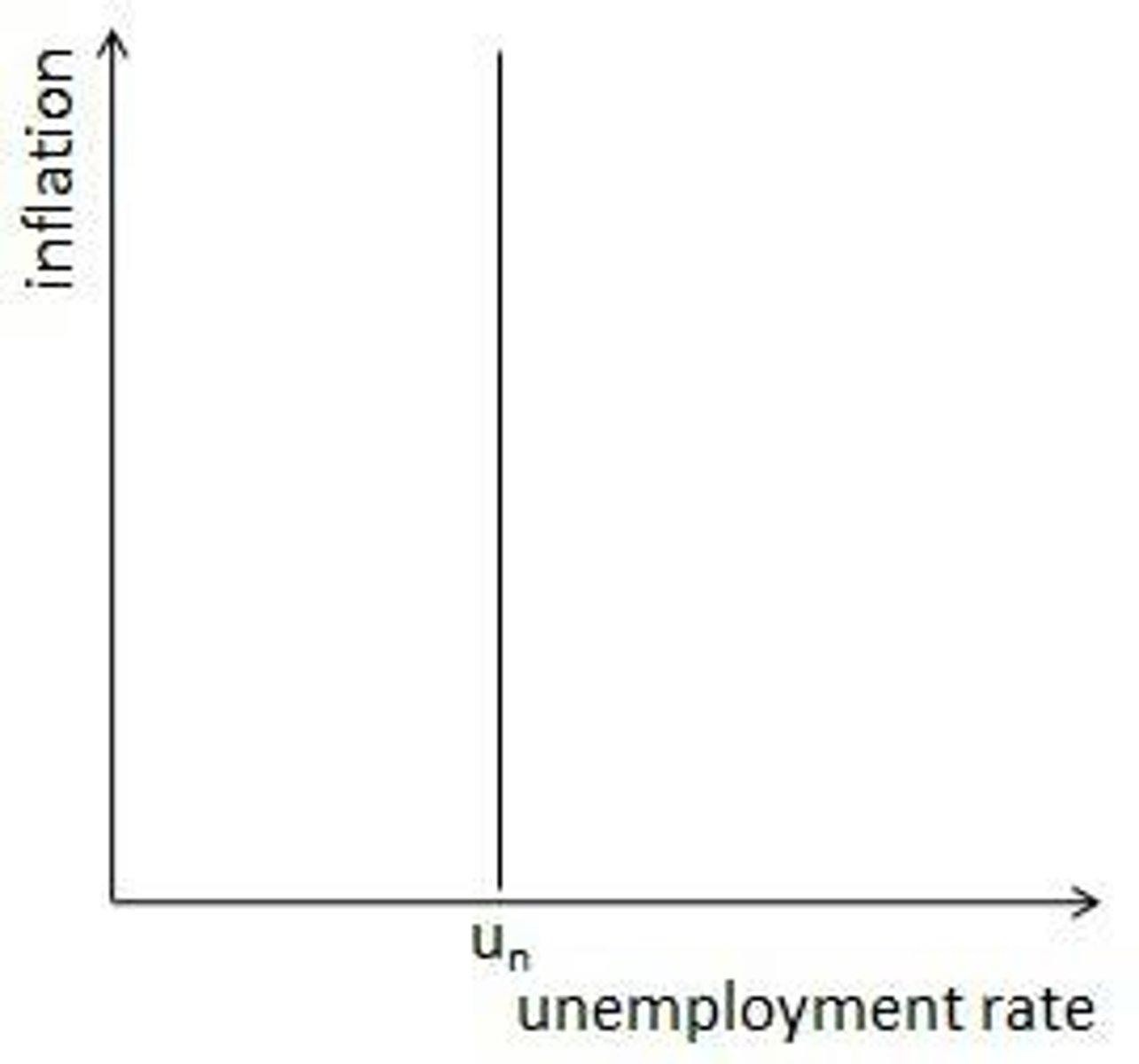
in the long run...
1. AS increases as workers accept lower wages and production costs fall
2. PL decreases, Y returns to full employment output
how does a change in AD affect the phillips curve
increased AD leading to higher inflation and lower unemployment, and vice versa. increase PL
a change in AD causes a ____ along the SRPC
movement
how does a change in AS affect the phillips curve
If aggregate supply increases, then the Phillips curve shifts to the left. If it decreases, it shifts to the right.
inflationary expectations
there is a direct and constant relationship between the expected rate of inflation and the nominal IR
if inflation is expected
interest rates will rise and decrease SRAS, causing stagflation
if we expect deflation
monetary is ineffective because nominal IR are zero bound which causes a liquidity trap. banks will not lend if nominal IR are below 0%
what does inflation result from
increasing the MS too quickly for a sustained period of time
when the economy is at full employment...
changes in MS have no effect on RGDP in the wrong run... only changes PL
monetarism theory
steady growth of the MS causes steady growth in GDP
Quantity Theory of Money Equation
M x V = P x Y
M- money supply
V- velocity
P- PL
Y-output
... so in the LR the growth rate of M determines the growth rate of P
another way to write quantity theory of money equation
V= (P x Y)/M
P x Y- real gdp
why are budget deficits a "necessary evil"
forcing a balanced budget would not allow congress to stimulate the economy
budget balance =
tax revenues - (gov spending + gov transfers)
budget surplus
tax revenue is greater than gov spending and transfers in a year
budget deficit
tax revenue is less than gov spending and transfers in a year
the accumulation of annual budget deficits
the national debt
the government must pay interest on its debt, which...
-accelerates debt growth
-prevents using those funds for other things
-can lead to crowding out
-increases IR for citizens on loans
crowding out
a decrease in investment that results from government borrowing
-Government usually starts borrowing a budget deficit. (This increases money demand and therefore, the interest rate which then decreases private investment.) ● May cause a lower rate of physical capital accumulation & less economic growth in the long-run
when governments borrow to finance deficit spending...
1. the demand for loanable funds increases
2. the IR rises
3. I decreases
4. the increase in gov spending may be offset by the decrease in investment
crowding out in the SR and LR
-SR: leads to decreased interest sensitive spending
-LR: leads to a lower rate of physical capital accumulation and less economic growth
expansionary fiscal policy
increases IR, but expansionary monetary policy decrease IR
-increases AD curve in SR (fixes recessionary gap & creates a budget deficit).
why might the government increase spending?
They may be trying to use fiscal policy to close arecessionary gap by shifting AD to the right
economic growth
measured as the growth rate in RGDP per capita over time
RGDP per capita =
RGDP/population
-also measures labor productivity
-increase in LP increase RGDP
-both measure economic growth
the aggregate production function
a hypothetical function that shows how productivity (real GDP per worker) depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker as well as the state of technology
-aggregate employment and aggregate output are directly related
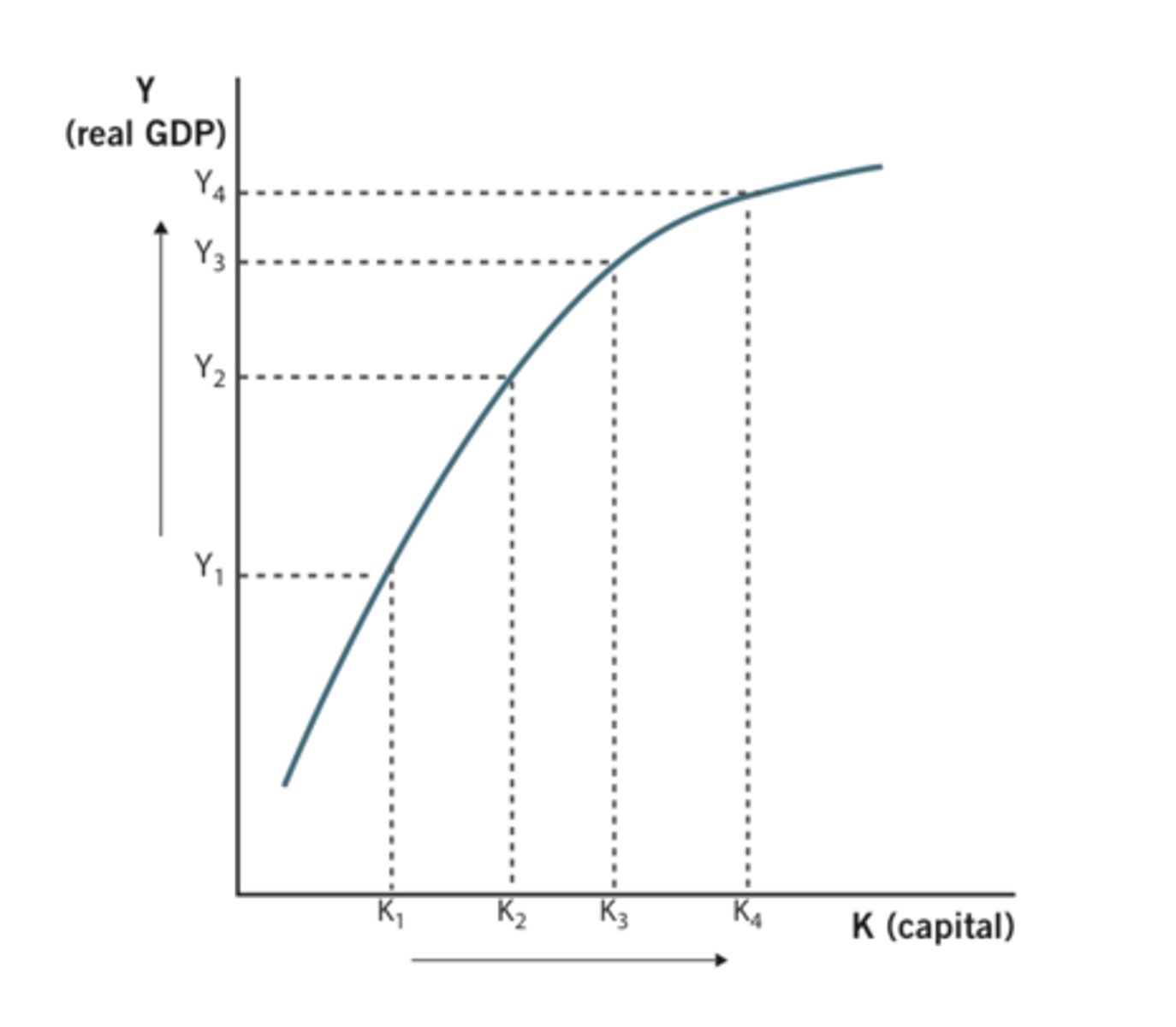
productivity is determined by the...
1. lvl of tech
2. stock of physical capital\
3. human capital
if investment increases, what happens in the short run and long run?
In the short run, increased investment boosts aggregate demand, leading to higher output and potentially inflation. Long-run effects include increased capital stock, shifting the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right, and potentially higher long-term economic growth
what shows economic growth
a right shift of LRAS, increase potential GDP/output, and outward shift of PPC
-ONLY INVESTMENT IN PRODUCER RESOURCES LEADS TO LR ECONOMIC GROWTH!!!!!
the role of the gov in promoting economic growth
1. Adding to Physical Capital
• Increase and improve infrastructure
• Encourage high rates of private saving and investment
2. Adding to Human Capital
• Increase and improve education
• Increase the labor force participation rate (LFPR)
3. Adding to Technology
• Government research and development programs
supply side fiscal policy
discretionary fiscal policy to promote economic grwoth that affects AD, SRAS, LRAS, and potential output
in the private market, the gov should provide incentives for households and business to
1. work (increases output)
2. save (increases investment)
3. invest (increases productivity)
...decreasing income tax rates, offering investment tax crdits, and reducing regulation
in the public market, gov spending should include
education and infrastructure
contractionary fiscal policy
decreases AD curve in short-run (fixes expansionary gap & creates a budget surplus
expansionary monetary policy
increases AD (helps fix recessionary gaps
contractionary monetary policy
decreases AD (helps fixes expansionary gap
in the short run, gov deficits can...
cause an inflationary gap and raise interest rates which can delay economic growth.
government deficits
Occur when governments spend more than they receive in tax revenues
how does expansionary monetary policy cause inflation
it stimulates spending and demand, potentially outpacing the economy's ability to produce goods and services, thus driving up prices.
supply-side fiscal policy
When producers focus on employing contractionary fiscal policies to foster increased production
● Affects AD, SRAS, & potential output in the short-run