Chapter 6: Interest Rates and Bond Valuation
1/78
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Coupon
the stated interest payment made on a bond
Face value
the principal amount of a bond that is repaid at the end of the term (aka par value)
Coupon rate
the annual coupon divided by the face value of a bond
Maturity
specified date on which the principal amount of a bond is paid
Yield to maturity (YTM)
the rate required in the market on a bond
Interest rate risk
the risk that arises for bond owners from fluctuating interest rates is called interest rate risk
Current yield
a bond’s coupon payment divided by its closing price
Bond yields
the return an investor receives from holding a bond until it matures, encompassing interest payments and any capital gains or losses
Cash flow
the money that flows into and out of an investment, including interest payments, principal repayments, and sale proceeds
General expression
for the relationship between bond prices and yields, reflecting the required return by investors
Equity securities
financial instruments that represent ownership in a company, giving shareholders voting rights and potential dividends
Debt securities
financial instruments representing borrowed money that must be repaid with interest, often taking the form of bonds or loans
Creditor
an entity or individual that lends money or extends credit, expecting repayment with interest
Lender
an individual or entity that provides funds to borrowers with the expectation of repayment, usually with interest
Debtor
an individual or entity that borrows money or takes on debt, agreeing to repay the principal amount along with any interest incurred
Borrower
an individual or entity that receives funds from a lender and is obligated to repay the borrowed amount with interest
Unfunded debt
debt that does not have cash backing or reserves set aside to cover it, often representing future obligations without current financial resources allocated
Bond
a fixed-income instrument that represents a loan made by an investor to a borrower, typically corporate or governmental, with a set interest rate and repayment terms.
Indenture
written agreement between the corporation (the borrower) and its creditors (aka deed of trust)
Registered form
the registrar of a company records who owns each bond, and bond payments are made directly to the owner of the record
Bearer form
a bond issued without record of the owner’s name; payment is made to whomever holds the bond
Collateral
general term that means securities that are pledged as security for payment of debt
Mortgage securities
secured by a mortgage on the real property of the borrower; providing collateral for lenders in case of default.
Debenture
an unsecure bond for which no specific pledge of property is made
Note
used for such instruments if the maturity of the unsecured bond is less than 10 or so years from when the bond is originally issued
Unsecure bond
A bond that is not backed by any specific assets, relying solely on the creditworthiness of the issuer for repayment.
Secure bond
a bond backed by collateral or specific assets that can be claimed by bondholders in case of default.
Seniority
indicates preference in position over other lenders in the repayment hierarchy in case of liquidation or bankruptcy
Subordinated
All debts or claims that are ranked below senior debts in terms of repayment priority during liquidation or bankruptcy.
Sinking fund
an account managed by the bond trustee for the purpose of repaying the bonds
Call provision
agreement giving the issuer the option to repurchase a bond at a specific price prior to maturity
Call premium
the amount by which the call price exceeds the par value of the bond
Deferred call provision
bond calls provision prohibiting the company from redeeming the bond prior to a certain date
Call protected bond
bond during period in which it cannot be redeemed by the issuer
Protective covenant
a part of the indenture limiting certain actions that might be taken during the term of the loan, usually to protect the lender’s interest
Positive covenant
specifies an action that the company agrees to take or a condition the company must abide by
Junk bond
a high-yield bond that carries a higher risk of default compared to investment-grade bonds.
Corporate bonds
debt securities issued by corporations to raise funds for various purposes
Government bonds
debt securities issued by a government to support government spending and obligations
Municipal
bonds issued by local or state governments to finance public projects, often with tax benefits for investors
Aftertax yields
the yields on investments after accounting for taxes, reflecting the actual return to the investor.
Zero coupon bonds
a bond that makes no coupon payments, and thus is initially prices at a deep discount
Floating-rate bonds
bonds with variable interest rates that adjust periodically based on market conditions
Inflation-linked bonds
bonds where the interest payments and the principal value are adjusted for inflation to protect investors from inflation risk.
Structured notes
bonds that are based on stocks, bonds, commodities, or currenciesCo
Convertible bond
can be swapped for a fixed number of shares of stock any time before maturity at the holder’s option
Put bond
allows the holder to force the issuer to buy the bond back at a stated price
Sukuk bond
an Islamic financial certificate similar to a bond, but compliant with Sharia law, representing ownership in a tangible asset or project.
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS)
a type of securitized financial instrument that represents claims to the cash flows from pools of mortgage loans, providing investors with a stream of income backed by real estate.
Catastrophe bonds (CAT)
bonds issued to cover insurance companies against natural catastrophes
Bid price
the price a dealer is willing to pay for a security
Asked price
the price a dealer is willing to take for a security
Bid-ask spread
the difference between the bid price and the asked price; represents the dealer’s profit
Bellwether bond
a bond issued by a company with a strong credit rating that serves as a market benchmark for other bonds.
Clean price
the price of a bond net of accrued interest; this is the price that is typically quoted
Dirty price
the price of a bond including accrued interest, also known as the full or involved price. this is the price the buyer actually pays
Real rates
interest rates or rates of return that have been adjusted for inflation
Nominal rates
interest rates or rates of return that have not been adjusted for inflation
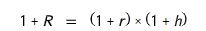
Fisher effect
the relationship among nominal returns, real returns, and inflation (1 + R = ( 1 + r ) x ( 1 + h ))
Term structure of interest rates
the relationship between nominal interest rates on default-free, pure discount securities and time to maturity; that is, the pure time value of money
Nominal interest
rates that include inflation expectations
Default-free, pure discount bonds
bonds that pay no interest but are sold at a discount to face value, with the face value paid at maturity.
Inflation premium
the portion of a nominal interest rate that represents compensation for expected future inflation
Interest rate risk premium
the compensation investors demand for bearing interest rate risk
Upward-sloping term structure
a graphical representation showing that longer-term interest rates are higher than shorter-term rates, indicating higher returns for longer maturities.
Downward-sloping term structure
a graphical representation indicating that longer-term interest rates are lower than shorter-term rates, reflecting expectations of declining rates or economic contraction.
Default risk premium
the portion of a nominal interest rate or bond yield that represents compensation for the possibility of default
Taxability premium
the portion of a nominal interest rate or bond yield that represents compensation for unfavorable tax status
Liquidity premium
the portion of a nominal interest rate or bond yield that represents compensation for lack of liquidity
Treasury yield curve
a graph that shows the relationship between interest rates and the maturity dates of Treasury securities, indicating the yields of these securities at different maturities.
CoCo bond
coupon payments; which are a type of bond that can be converted into equity if certain conditions are met, typically used by banks to increase their capital.
NoNo bond
zero coupon bonds that do not make periodic interest payments and are sold at a discount to their face value.
How bonds are bought and sold
Bonds can be bought and sold in the primary market during their initial issuance and in the secondary market where existing bonds are traded among investors.
Bond price reporting
refers to the process of providing current prices for bonds in the market, including their yield and any changes due to interest rate fluctuations, helping investors make informed trading decisions.
Why we say bond markets have little to no transparency
Bond markets are often considered to have little to no transparency because of the lack of publicly available information on pricing and trading volumes, making it difficult for investors to assess market conditions and the true value of bonds.
What are bid and ask prices
Bid and ask prices are the terms used to describe the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask) for a bond in the market.
Real rate of interest
the compensation investors demand for forgoing the use of their money
Rate of inflation
the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, subsequently eroding purchasing power.