Common Media and Biochemical Tests Objectives
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Describe the importance of plate reading to the bacterial culture examination process.
Characteristics and form of bacterial colonies
Compare with direct examination
Distinctive patterns can distinguish some pathogens and facilitate presumptive identifications
Blood Agar
Composition: Tryptic Soy Agar base with 5% sheep blood. TSA is a nutritive media that provides casein and soy peptones for source of nitrogen and amino acids
Clinical Utility: Grows fastidious organisms and can help differentiate them by hemolytics
MacConkey agar
Composition: crystal violet dye, bile salts, lactose, and neutral red (pH indicator)
Clinical Utility: isolate and identify gram-negative bacteria
Sorbitol MacConkey (SMAC)
Composition: Peptone 20.0; sodium chloride 5.0; bile salts No. 3 1.5; sorbitol 10.0; crystal violet 0.001; neutral red 0.03; agar-agar 15.0.
Clinical Utility: used to identify and isolate Escherichia coli 0157:h7 (EHEC)
Chocolate Media
Composition: added hemoglobin and a supplementary growth factor (e.g., KoEnzyme Enrichment).
Clinical Utility: isolation and cultivation of fastidious bacteria, particularly Haemophilus influenzae, Brucella Spp., and Neisseria species
Modified Thayer Martin (MTM)
Composition: hemoglobin, which provides the X factor (hemin), and GCHI Enrichment, which provides the V factor, vitamins, amino acids, coenzymes, and dextrose. Vancomycin and colistin are selective agents that inhibit gram-positive cocci and gram- negative bacilli, respectively
Clinical Utility: isolation of pathogenic Neisseria from specimens containing mixed flora of bacteria and fungi.
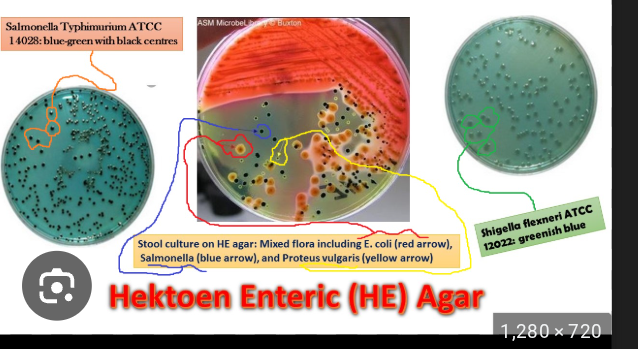
Hektoen Enteric (HE) Agar
Composition: Peptone base with bile salts, lactose, ferric ammonium citrate, bromthymol blue, and acid fushion
Clinical Utility: Able to isolate & differentiate Salmonella (black from hs2) & Shigella (Blue) from other enterics
Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate (XLD) agar
Composition: Similar to HE agar but contains different xylose as carbohydrate source and lysine for nitrogen
Clinical Utility: Salmonella sp will turn black, Shigella sp will be colorless (lack of xylose ferm), Any remaining non-pathogens will be orange (ferm of xylose)
Campy Blood Agar
Composition: Agar base, sheep blood, vancomycin, polymyxin b, trimethoprim, nystatin
Clinical Utility: primary isolation of. Campylobacter jejuni from stool specimens
Colistin-nalidixic acid (CNA) agar
Composition: an agar base with nutrients (peptones, starch, sodium chloride), the selective and differential antibiotics colistin and nalidixic acid, and typically 5% sheep blood
Clinical Utility: isolation and identification of gram-positives, inhibits growth of gram-negatives
Anaerobic blood agar
Composition: a basal agar with peptones, yeast extract, and agar as a base, supplemented with sheep blood for growth factors and hemolysis observation, and specific anaerobic growth stimulants like Hemin and Vitamin K
Clinical Utility: Isolation and cultivation of anaerobic bacteria
Lim/Group B Selective broths
Composition: Takes a streptococcal supportive media and adds colistin, nalidixic acid, and yeast extract
Clinical Utility: Selectively grows Group B Streptococci from the material Genitourinary tract to avoid neonatal sepsis, any growth seen can be subculture to BAP to determine if Group B strep is present
Staphylococci
Streptococci
Diptheriods
Enterics
Yeast
small, visible clusters of cells that are often creamy-white to pinkish in color, with a smooth, moist, or slightly rough surface texture
Catalase
Purpose of test:Detects if the organism can break down hydrogen peroxide into water and carbon dioxide
clinical utility: differentiates Staph (+) and Strep (-)
Reagents: Hydrogen Peroxide
Limitations: do not use colonies from blood containing agar since rbcs pseudoperoxidase activity of heme
Coagulase
Purpose of test: detects if the organism can convert soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin in a plasma sample
Clinical Utility: Differentiates Staph aureues (+) from couagulase negative staph (-)
Reagents: Fibrin-containing plasma
Limitations: Other organisms besides s.aureus can be positive
Oxidase
Purpose of test: Detects the presence of a cytochrome oxidase that will catalyze the transport of electrons between electron donors in the bacteria
Clinical Utility: Aids in the differentiation of Neisseria, Moraxella, Campylobacter, and Pasteurella species
Reagents:methyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride, in water
Limitations:
(O/F) Tests
Purpose of test: If the organisms utilize carbohydrates aerobically or anaerobically
Clinical Utility: understanding organism metabolism
Reagents:
Limitations:
TSI and KIA slants
Purpose of test: Aims to determine a microorganism’s ability to ferment various sugars, produce H2S, and/or produce gas
Clinical Utility: Used to differentiate enterics from other GNB’s and also differentiate among the enterics
Reagents:Agar contains peptones, 1% Lactose, 1% sucrose, and 0.1% glucose along with sodium/ferrous thiosulfate (reagent in media), and phenol red
Limitations:
Methyl Red/Voges-Proskauer
Purpose of test: MR: Detects acid end product detection from ferm of glucose VP: Test is used to determine if an organism produces acetylmethyl carbinol from glucose fermentation.
Clinical Utility: Historically used to differentiate enterics, Now used to differentiate Actinobacteria
Reagents: Both: media containing peptones and glucose
MR detection uses methyl red pH detector
VP detection uses alpha-napthol/KOH detector combo
Limitations: Can not be both MR and VP pos
Phenylalanie deaminase (PAD)
Purpose of test: To determine the ability of an organism to oxidatively deaminate phenylalanine to phenylpyruvic acid.
Clinical Utility: Used to differentiate Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella orgs
Reagents: Agar contains nutrients and phenylalanine After incubation, 10% Ferric Chloride - if positive will turn black
Limitations:
Pyrrolidonyl arylamidase (PYR)
Purpose of test: pyrolidonyl arylamidase activity in Streptococcus spp, Enterococcus spp., some coagulase-negative staphylococci, and some Enterobacteriaceae
Clinical Utility: identify group A and D strep (+)
Reagents: N, N-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde to look for red color (+)
Limitations:
Bile-Esculin
Purpose of test: Can the organism hydrolyze esculin in the presence of bile
Clinical Utility: Used to differentiate Streptococci bovis - negative and Enterococci - positive
Reagents: Nutritive agar with esculin and bile with ferric salt
Limitations:
Salt Tolerence
Purpose of Test: Can the organism survive and grow in a 6.5% salinity?
Clinical Utility: Used to differentiate enterococci from Group D strep and Aerococcus spp
Reagents: Brain-heart infusion broth (nutritive media) with 6.5% NaCl solution
Limitations:
Amino Acid decarboxylase
Purpose of test: Determines what amino acids an organism can decarboxylate. Mainly use arginine, ornithine, and lysine as the amino acid
Clinical Utility: Differentiate decarboxylase producing Enterobacteriaceae from other GNB’s.
Reagents: The agar media contains nutrients, the amino acid being assessed, and a pH indicator. Decarboxylation raises pH causing purple color (+)
Limitations:
Lysine Iron Agar (LIA)
Purpose of the Test: Determines if an organism can decarboxylate or deaminate lysine and if it can form H2S
Clinical Utility: Used to differentiate enterics and other GNB’s
Reagents: lysine, peptones, a small amount of glucose, ferric ammonium citrate, and sodium thiosulfate.
Limitations
OF Sugars
Purpose of the Test: Determines if an organism oxidizes or ferments sugars
Clinical Utility: Differentiate various organisms
Reagents: Agar-based stab media with nutrients and the sugar of interest with pH indicator
Limitations
Indole
Purpose of Test: Determines if an organism can decompose tryptophan to indole
Clinical Utility:Used to differentiate various enterics
Reagents:organism is incubated in a tryptophan broth and allowed to incubate then Kovac’s reagent (p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde) is added to determine if pink color (+) forms
Limitations
Hippurate Hydrolysis
Purpose of Test: Determines if an organism can hydrolyze Hippuric acid into glycine and benzoic acid
Clinical Utility: Used to identify Group B strep, Campylobacter jejuni, Listeria monocytogenes, Gardnerella vaginalis
Reagents: Prepare a heavy inoculum of isolated organism to a test tube and add disk with Hippurate into it. After 2 hour incubation add nihydrin reagent and look for purple color change to occur (+)
Limitations:
Nitrate Reduction
Purpose of Test: Determines if organism reduces nitrate as terminal electron acceptor in anaerobic metabolism
Clinical Utility: to differentiate various enterics by other by products being produced
Reagents: Broth contains nutrients and nitrate.Sulfanic acid is added after incubation to detect nitrites and then alpha-naphthylamine to give a red precipitate
Limitations: When negative must add zinc powder to reduce any lingering nitrate. If pink after zinc: negative. If not pink after zinc: all nitrate was already used and thus a positive test
H2S Production
Purpose of Test: Determines if an organism can reduce sulfur into H2S
Clinical Utility: Differentiates various enterics
Reagents: Nutrient-rich media with Sodium thiosulfate.
Limitations
Citrate Utilization
Purpose of Test: Determines if an organism can use citrate as a sole source of energy - use as carbon source
Clinical Utility: Differenitiate varius enterics
Reagents: Agar contains no carbohydrates and no carbon sources besides sodium citrate. Bromothymol blue pH indicator is present. When citrate is broken down (energy used), ammonium salts that are formed and converted to ammonia. The alkaline pH shift causes color change from green to blue (+)
Limitations
Urease
Purpose of Test: Determines if an organism can produces the enzyme urease - lowers Ph
Clinical Utility: Enterics
Reagents: Agar contains no carbohydrates and no carbon sources besides Urea. Phenol red pH indicator is present. When urea is broken down, ammonium salts that are formed and converted to ammonia. The alkaline pH shift causes color change from yellow to pink (+)
Limitations: Prolonged incubation= false positive
Butyrate Esterase
Purpose of test: detect enzyme butyrate esteraste
Clinical Utility: Identify Moraxella Catarrhalis
Reagents: Pad impregnated with bromo-chloro-indolyl butyrate has isolated colony placed onto it. Hydrolysis releases indoxyl which oxidizes and forms a violet color
Limitations
Bile Solubilty
Purpose of test: detect if the organism autolysis occurs when exposed to bile salts
Clininical Utility: Identify Strep Pneumo
Reagents: Prepare a suspension of organism and then add sodium deoxycholate
Examine for clearing of turbidity after 15 minutes
Limitations
The principle and utility of hybridization-based detection systems in medical microbiology
Principle: The formation of hydrogen bonds between single strands of RNA or DNA that are complementary - Target - Sequence that will be identified - Probe - Single-stranded RNA or DNA oligonucleotide labeled with a reporter chemical, radionucleotide, or fluorescent particle.
Utility: Deteermines recognition of the target sequence at the 5’ or 3’ end
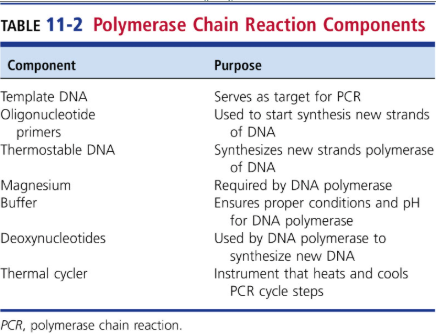
The principle and utility of PCR detection systems in medical microbiology
PCR: Denaturing, Primer Annealing, Primer Extension
The principle and utility of MALDI-TOF technology
Useful for identifying microorganisms in clinical microbiology laboratories
Identification can occur in minutes from isolated colonies
They are separated by their mass-to-charge ratio.