10Biology Unit 1: Genetics
1/60
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Heredity
Passing on traits from parents to offspring
Heritable Trait
A trait which can be inherited
Variation
Differences in genetic profiles in a population
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
How many chromosomes are there
46 (23 pairs)
Homologous pairs of chromosomes
consist of two chromosomes the same size and with the same genes
Haploid cells
A cell containing only one set of chromosomes (gametes).
Diploid cells
Cells containing the full set of chromosomes (body cells)
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA Structure
Double helix
What is DNA made from
Sugar phosphate backbone of deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases
Nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
What are the base pairs
Adenine - Thymine
Guanine - Cytosine
What are nitrogenous bases bound to
Deoxyribose sugar
What is a nucleotide made from
one phosphate, one deoxyribose sugar, one nitrogenous base
codon
triplet of bases
Allele
Different forms of a gene
Dominant Gene
A gene that is expressed in the offspring whenever it is present
Recessive Gene
Gene that is hidden when the dominant gene is present
Homozygous
Having two forms of the gene
Heterozygous
Having two different forms of the gene
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup
Phenotype
Actual trait resulting from genetic makeup
Sex determination
An individual's sex is determined by sex chromosomes from each parent
Sex linked genes
Females: XX Males: XY
Where are sex linked genes located
on the sex chromosomes
Pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
Autosomal dominant
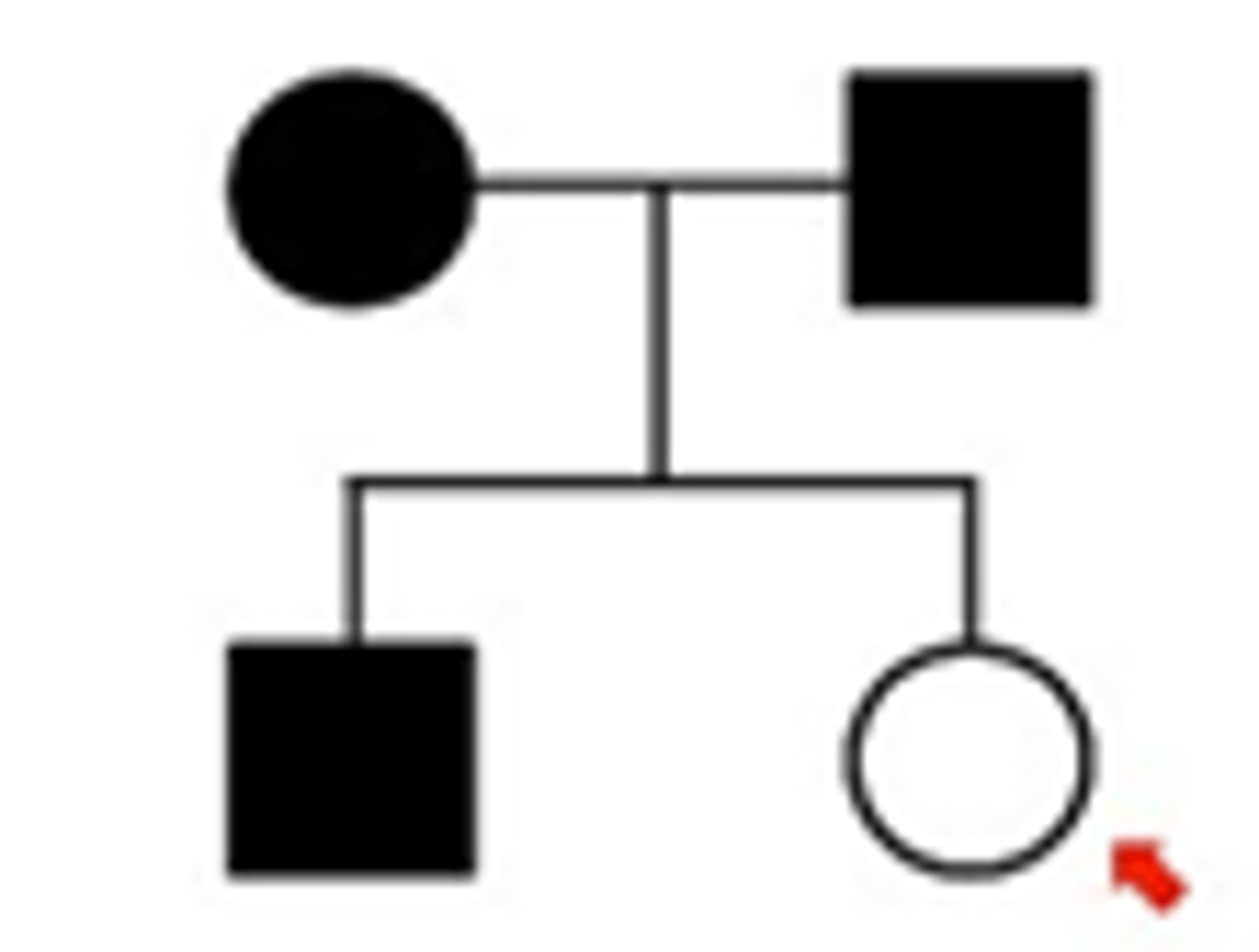
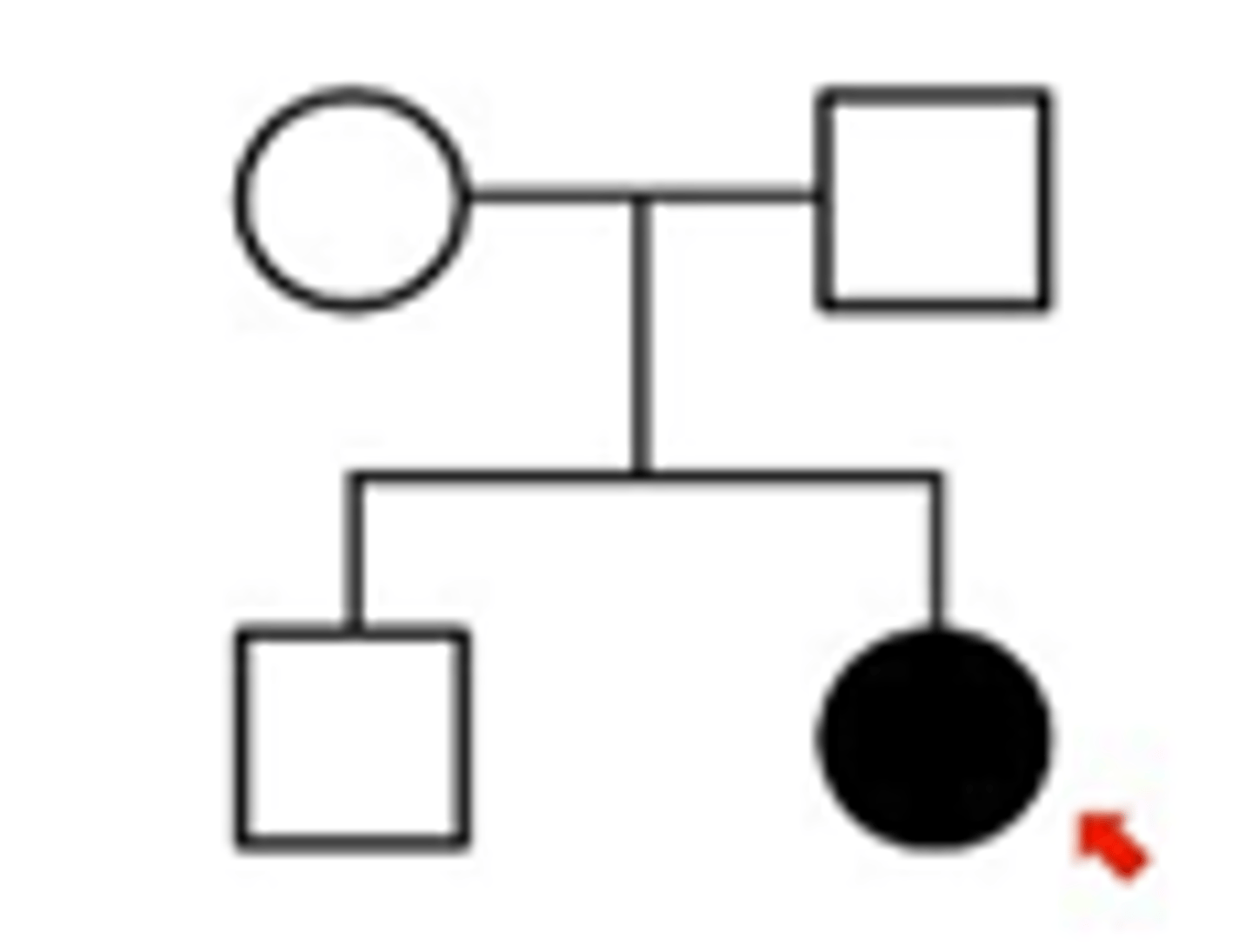
Autosomal Recessive

X-Linked dominant
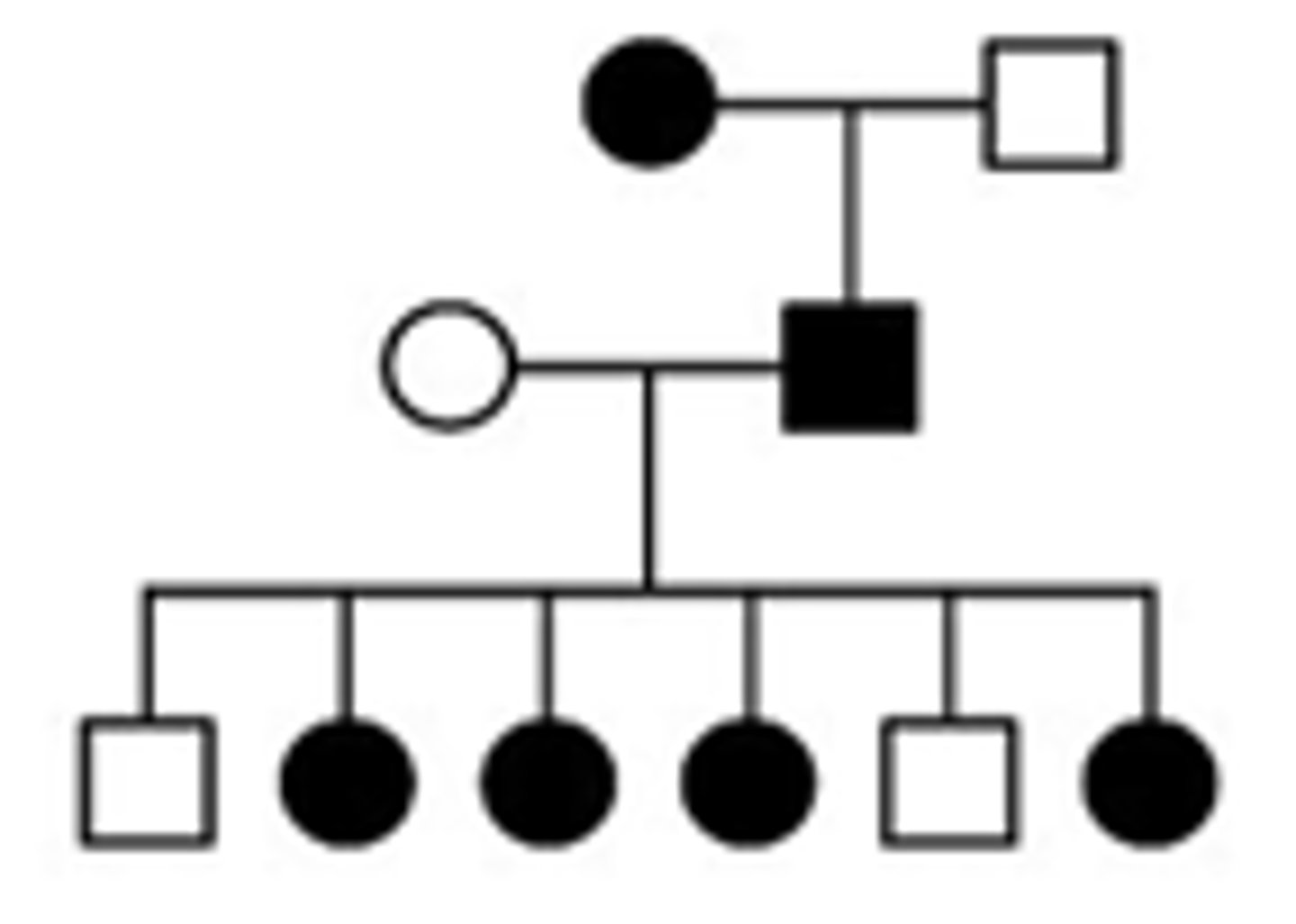
X-Linked recessive
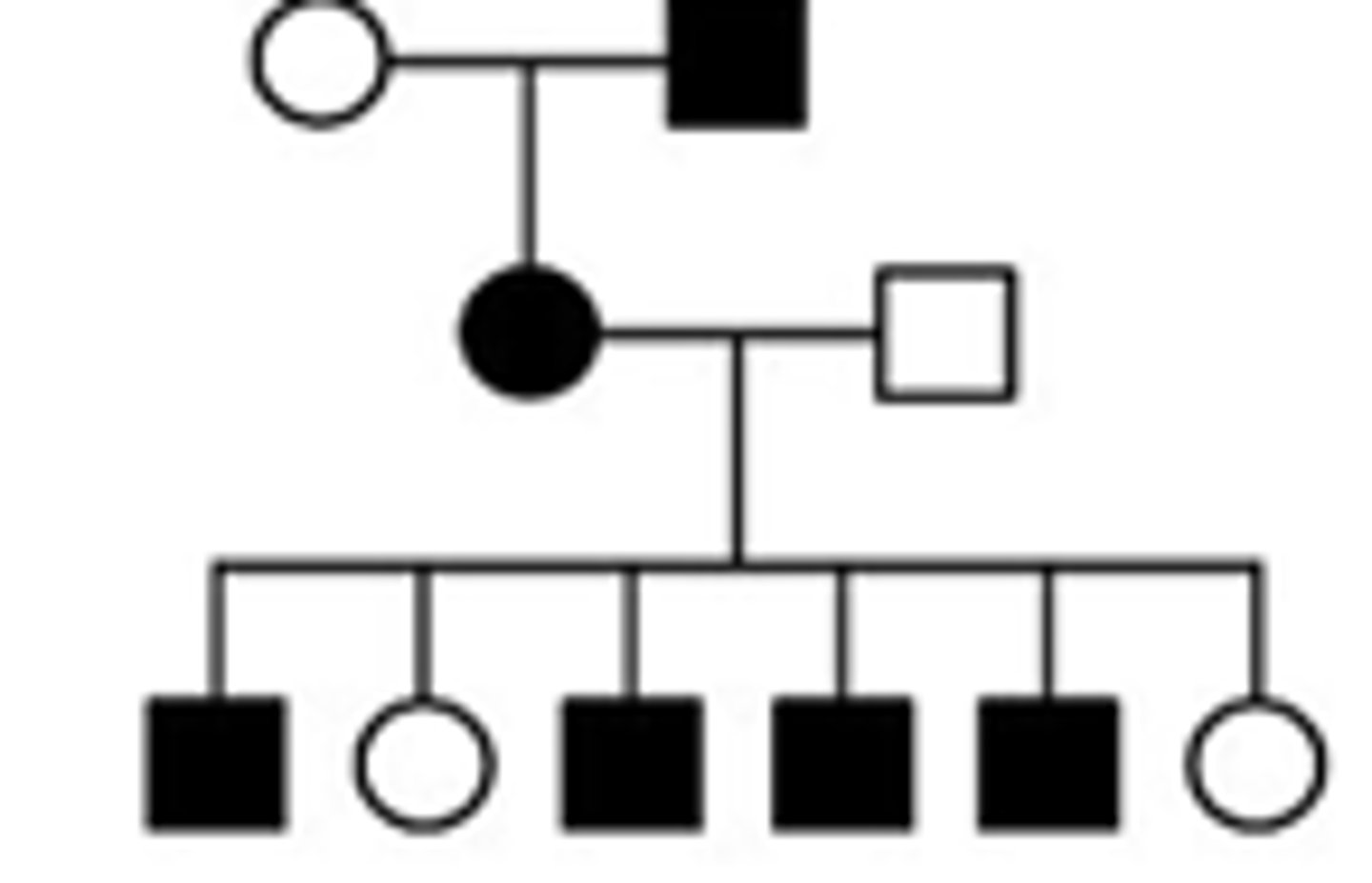
Fertilisation
The process of combining the male and female gamete, producing a zygote
Asexual reproduction
- Does not involve sex cells or fertilisation
- only 1 parent required
- genetically identical offspring
Sexual reproduction
the production of new organisms by the combination of genetic information of two individuals of different sexes
Asexual reproduction advantages
Saves energy, no time needed to find a mate
Asexual reproduction disadvantages
Low genetic variability, can be wiped out by a single change in the environment
Sexual reproduction advantages
highly genetically diverse, better adaptation to changing environment
Sexual Reproduction disadvantages
Energy costly, time needed to find a mate
Role of the cell cycle
Growth and development, repair and replacement, asexual reproduction
Interphase
Cell prepares for division by growing, replicating DNA and producing organelles
Prophase
Chromosomes condense, spindle fibres form, and the nuclear envelope breaks down
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's metaphase plate, attached to spindle fibres
Anaphase
Sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase
Chromatids reach the ends, nuclear envelope and chromosomes de-condense
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm divides, forming two separate daughter cells
Prophase 2
A new spindle forms around the chromosomes, nuclear envelope breaks down again
Metaphase 2
Chromosomes line up individually along the equator of each cell, spindle fibres attach to each chromatid
anaphase 2
sister chromatids separate ad move to opposite poles of the cell, each chromatid is considered a separate chromosome
Telophase 2
Chromosomes reach the poles and begin to decondense, nuclear envelopes re-form around each set of chromosomes
cytokinesis 2
the 2 cells divide again, producing 4 genetically unique gamete cells
Mutation
change in DNA code, therefore can alter the protein product
where do mutations occur
in one of the parental gametes
causative agents - induced mutations
x rays, uv radiation, nuclear radiation, chemical substances (mutagenic agents)
non causative agents - spontaneous mutation
occurs more frequently with age
How does DNA code for proteins
proteins are made from amino acids and each codon codes for one amino acid
chromosomal mutations
the individual inherits the wrong number of chromosomes or large parts of chromosomes are altered via crossing over
point substitution mutation
The replacement of one nucleotide by another in the DNA
Frameshift Mutation
An insertion or deletion of one or more bases has occurred, resulting in the disruption of subsequent codons
Inversion mutation
Chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of the chromosome is reversed end to end