HUG Unit 1 Thinking Geographically Vocab
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Time Distance Decay
The farther two places/things are from each other, the less interaction and relation they have together.
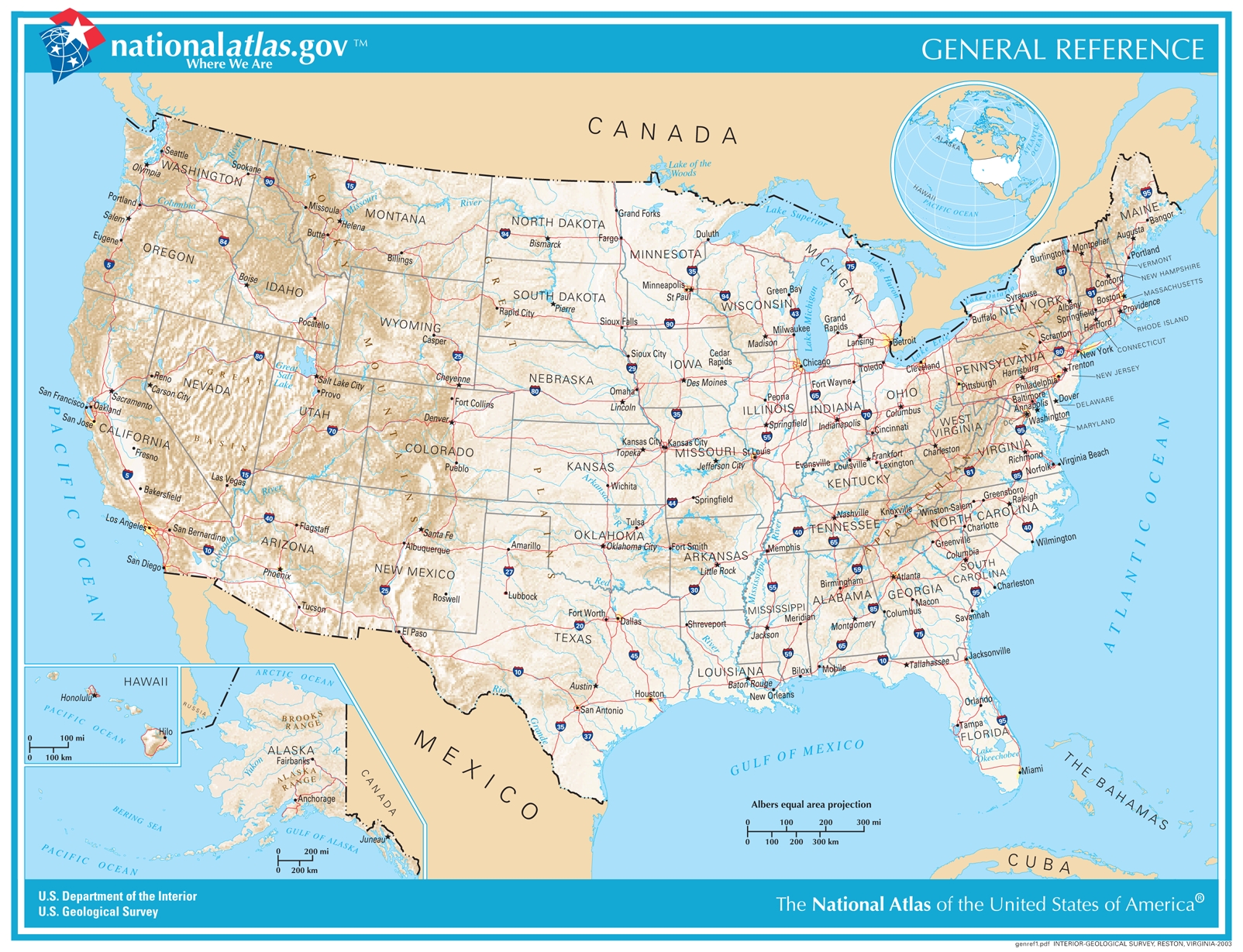
Reference Map
The general location of places, potentially including natural and man-made.
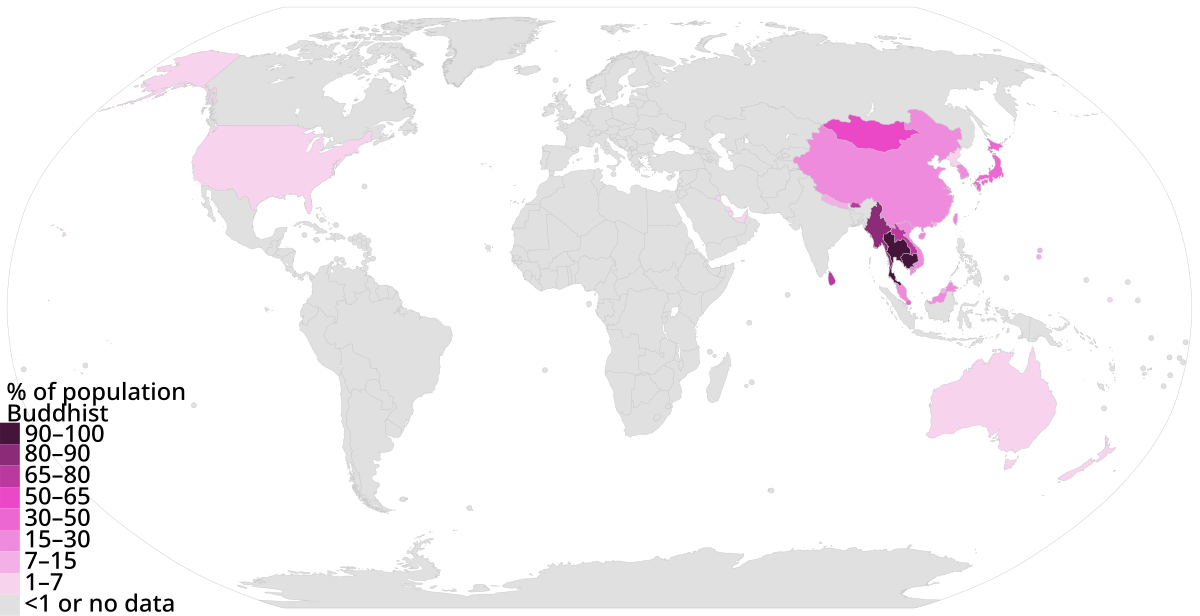
Thematic Map
A map that visually shows a pattern throughout one idea/topic with one color of different shades, with relationships occasionally
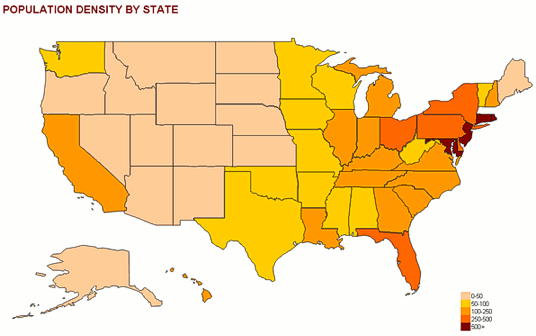
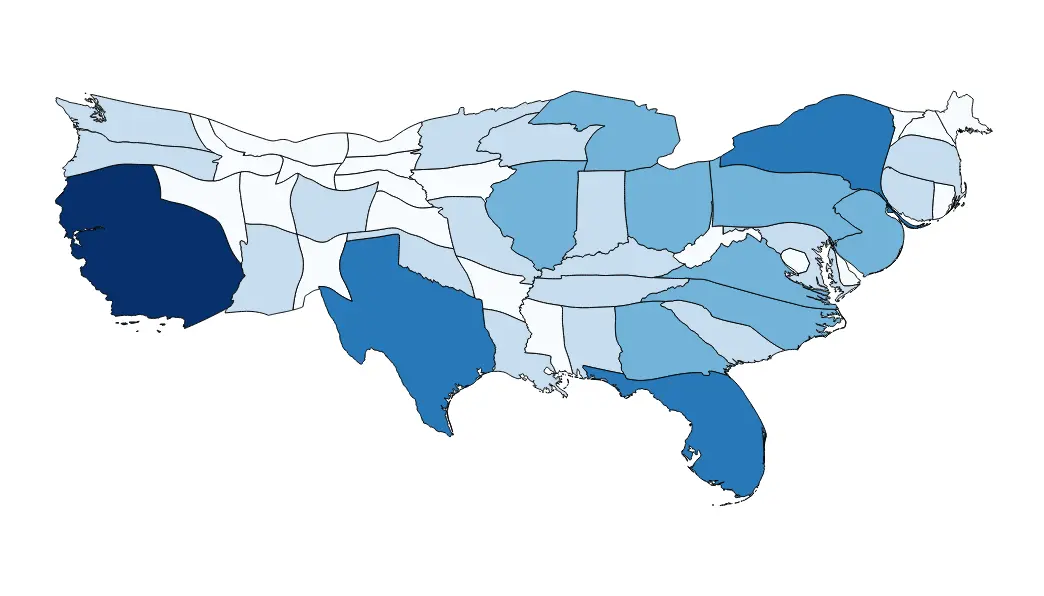
Choropleth Map
A map that visually represents data using different colors to show different values throughout one area.
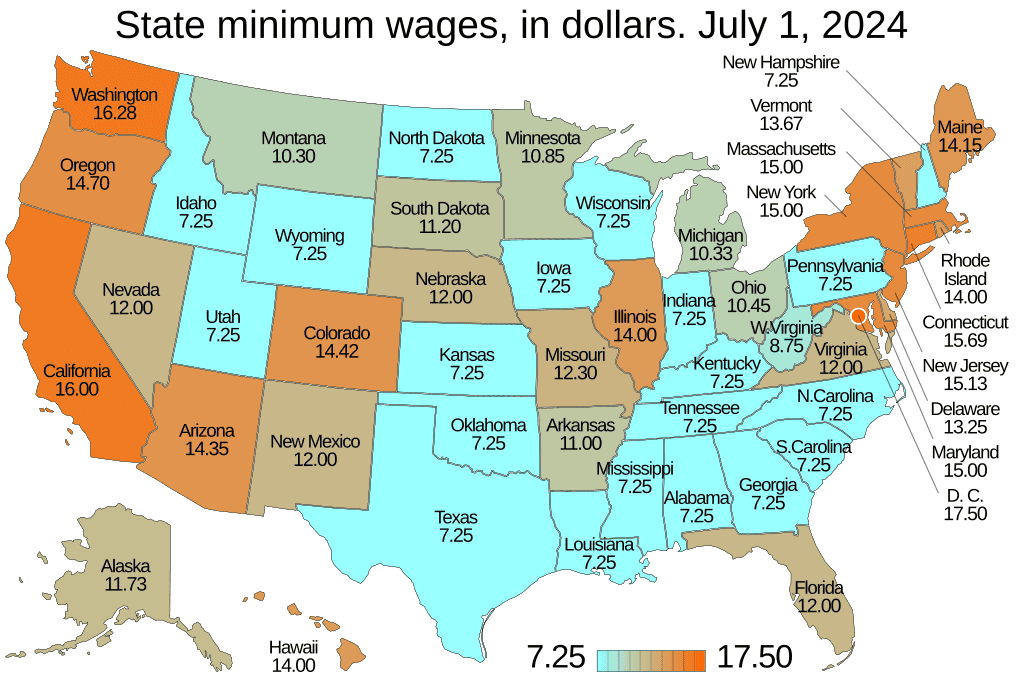
Cartogram
A map that distorts geographic land into a different shape so that the area is proportional to the data value instead of reality, like population or birth rates.
Map projection
Shows the earth on a flat surface while distorting some proportions of the surface in order to attempt to represent the 3d surface of the earth
The 4 main types of Map Projections
Goode, Peters, Mercator, Robinson
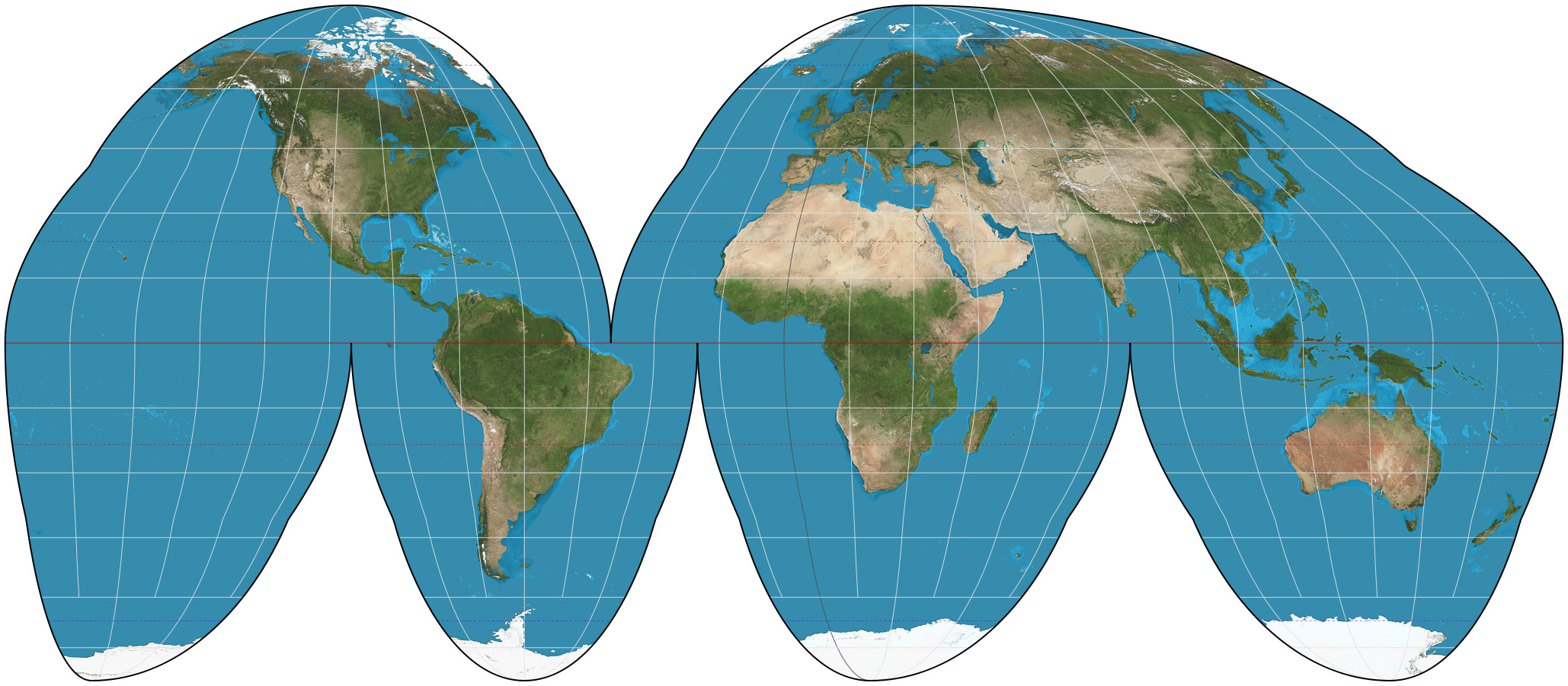
Goode Homolosine
Pros: Size and shape
Cons: Disrupts oceans and divides antarctica apart, navigation
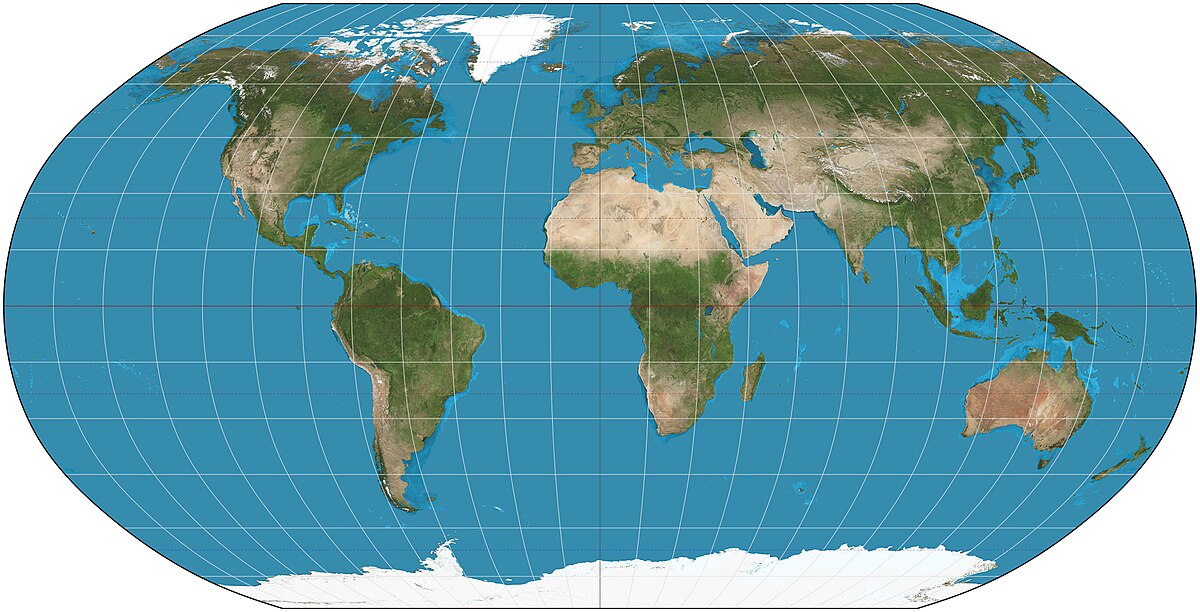
Robinson
Pros: Best of all worlds, aesthetic appeal
Cons: A compromise of all distortions, so is all slightly off direction, distance, size, and shape
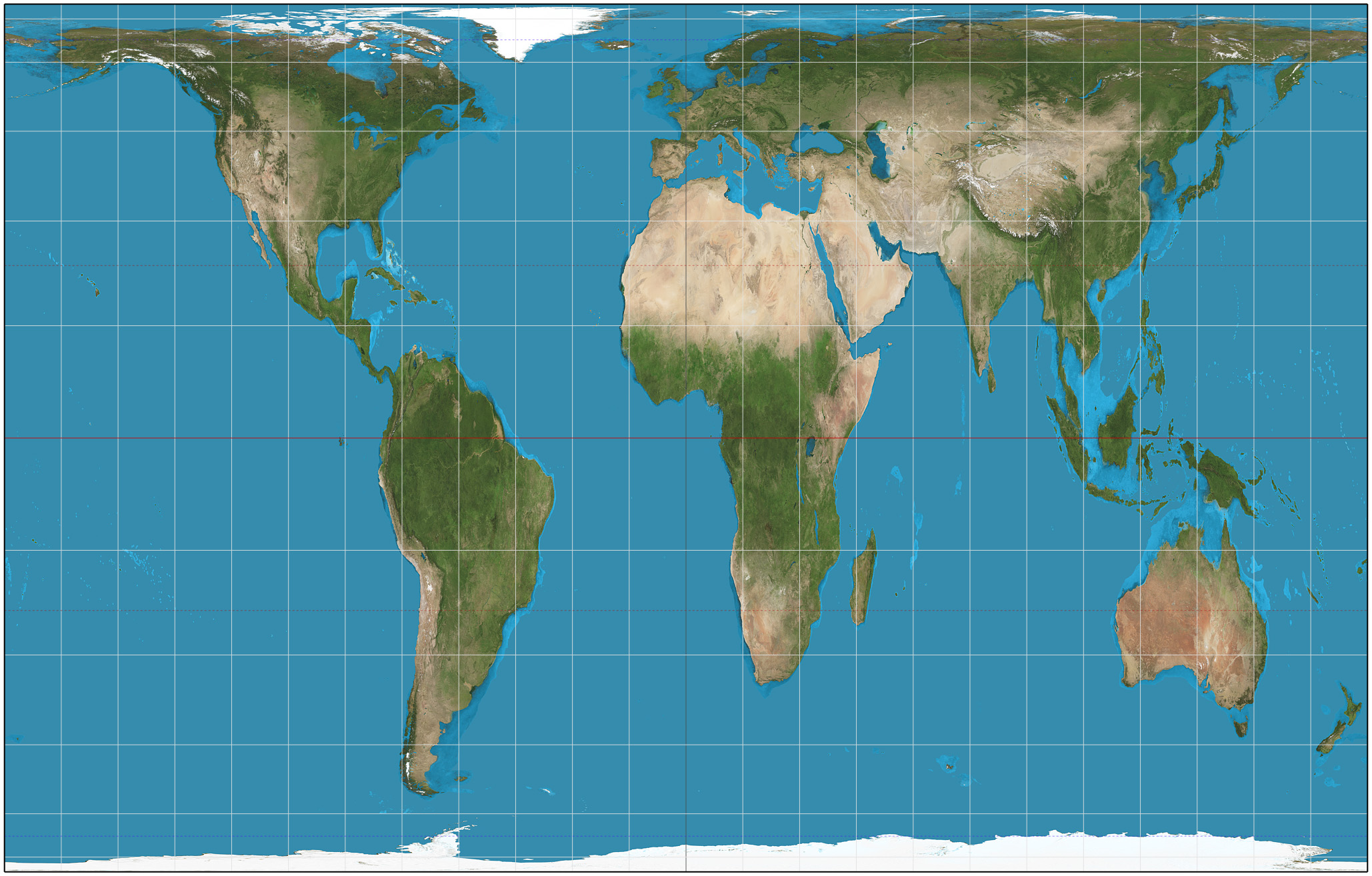
Mercator
Pros: Navigation and shape
Cons: Size
Ex. Greenland is huge and Africa is small
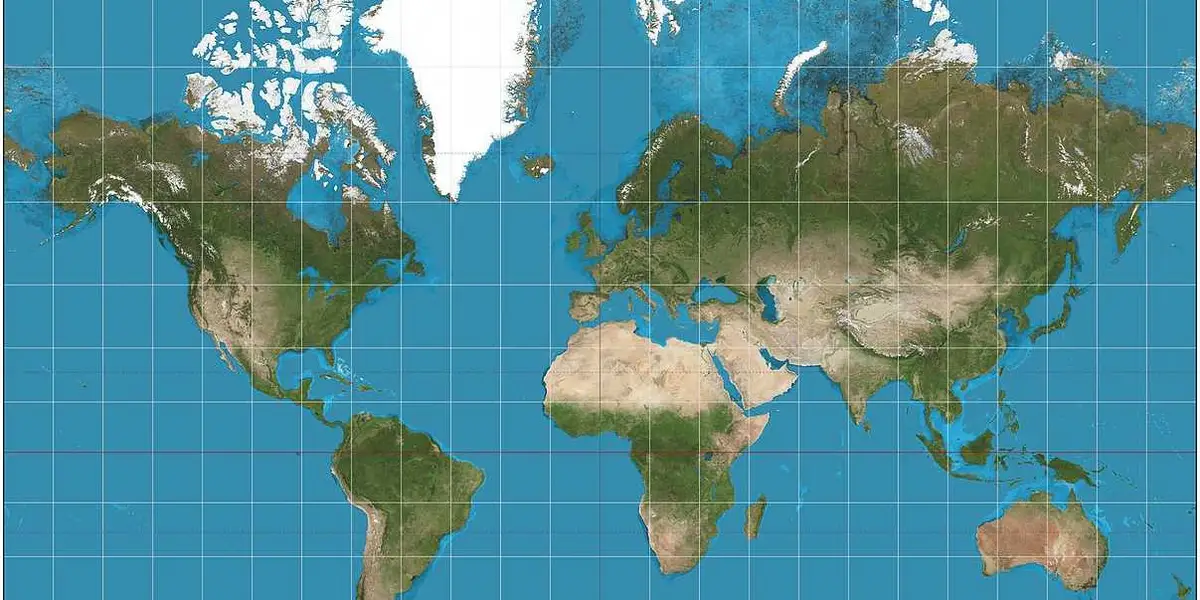
Peters
Pros: Size (besides antarctica)
Shape & Navigation
Lands are distorted and elongated

Cultural Landscape
The visual imprint of human activity on the natural environment, reflecting values, culture, religion, etc.
Diffusion
The process where an idea, religion, or movement spreads from the origin to other areas over time.
Expansion Diffusion
When ideas and practices spread from the birthplace to other areas nearby, increasing the number of people under the concept.
Relocation Diffusion
When people with an idea or practice migrate to another location, spreading that concept to their new, found homeland.
Natural Resources
Materials from earth that are used to benefit & profit the world

Environmental determinism
A belief that the physical environment shapes humanities cultures and the way they are mainly, that humans are only a product of the atmosphere

Possibilism
A view that any physical environment has many different ways for societies to develop with many opportunities, and humans finding ways to overcome challenges in their surroundings.
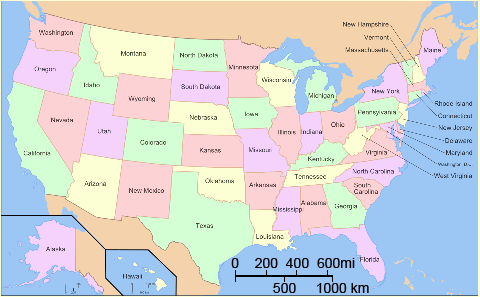
Map scale
A key on a map to show the real life distance on a smaller scale to fit. Example: 1 inch on the map equals 100 real miles
Data Aggregation
Summarizing a collection of amounts of data into a more comprehensive state
Spatial Perspective
To understand the world by explaining and identifying the why, when, how, where things are the way they are. To explain the uses of space
Time-Space compression
The idea that technological advancements are making everything seem quicker and distances shorter, “shrinking the world”

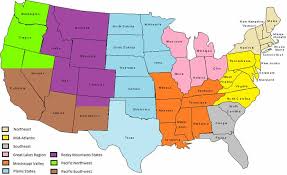
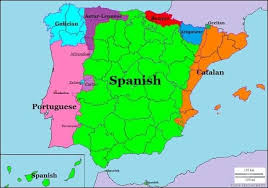
Formal Region
An area where people who have traits like language or religion in common live together
Functional Region
An area that is organized to function socially, politically, economically, and culturally all on its own.

Perceptual/Vernacular Region
An area defined by people's beliefs and views rather than the official stance.