Lecture 1
1/83
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
How do scientists classify organisms
Based on their anatomy, morphology, evolutionary history, features of embryological development, and genotype
What’s the order of classification
Domain - Kingdom - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species
Whitaker R.H 1969
Classified living organisms according to the nature of their cellular structure, and their feeding pattern
Five kingdoms
Monera
Protista
Fungi
Plantea
Animalia
Subkingdoms of Animalia
Mesozoa
Parazoa
Eumetazoa
Features of Eumetazoa
Includes the rest of the animal kingdom
Multicellular with specialized cells
Clear original tissue
The structure of the body Ranges from simple to complex images
Features of Mesozoa
Very small and simple animals characterized by their slender body and lateral symmetry
Kingdom Mesozoa contain on phylum which is ?
Phylum:Mesozoa
What kind of animals are in the kingdom Mesozoa
Parasites
The parasites (Mesozoa) infect what kind of animals
Marine invertebrates
The Lateral symmetry of Mesozoa
Consists of an outer layer of ciliated digestive cells and is surrounded by an inner layer made up of reproductive cells
An example of Mesozoa
Rhoplura
Features of Parazoa
Reproduces sexually or asexually
Radially symmetrical or asymmetrical
Made up 2layers
Non specialized cells
Have different colors
Hardly any clear tissue
No digestive system
No nervous system or sensory cells
What the phylum of kingdom Parazoa
Phylum:Porifera
Where are Porfera found ?
Most in marine water and a few in freshwater
What are Spongocoel
Central cavities
What are the different shapes of Porifera
Branched, and irregular
How does digestion occur in Porifera
Interceptor and holozoic nutrition
How does respiration and excretion occur in Porifera
By simple diffusion
What are sponges made up of?
A system of tiny pours and canals that make up a filter feeding system
Sponge Anatomy
They have numerous tiny pores that allow water flow into the body and a large opening to allow water to flow out
small cells that line the canals of a sponge with flagella
Ostia
Numerous tiny pores that allow water to flow into the body
Oscula
one to several large openings that allow water to flow out of the sponge
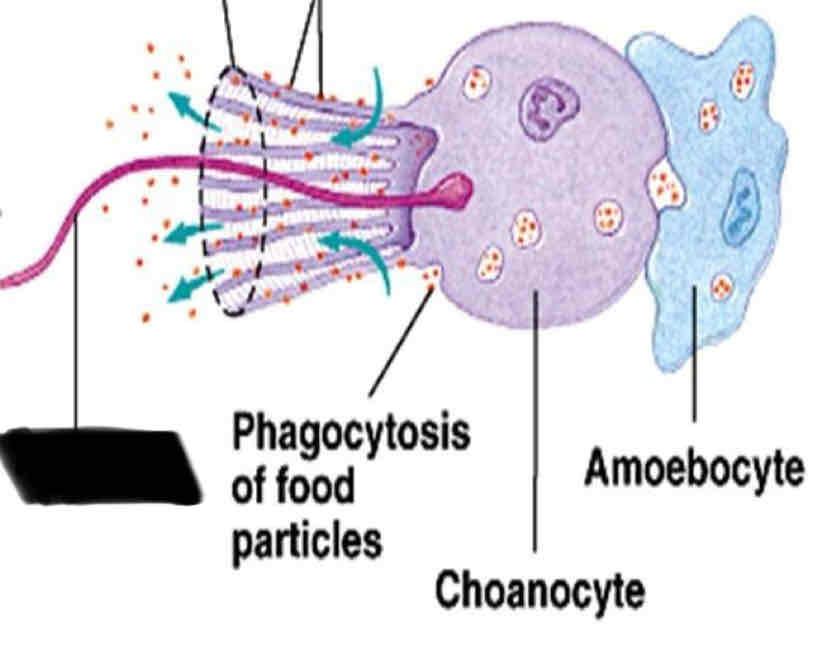
Chanocytes
Small cells that line the canal of a sponge with flagella
function of Chanocyte
Maintain the floor water through the canal
trap food particles
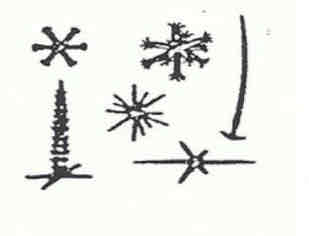
Siliceous spicules (Hexactinellida)
Siliceous spicules (Demospongiae)
Spongin

Calcareous Spicules
Classes of Phylum: Porifera
Hexactinellidae
Calcarea
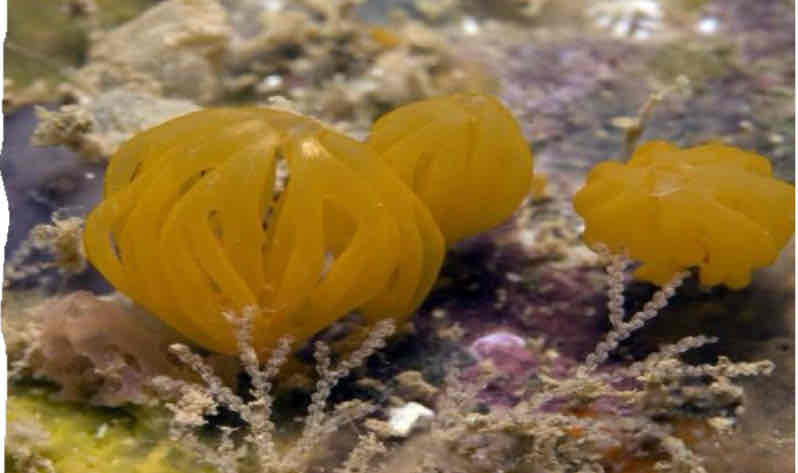
Demospongiae
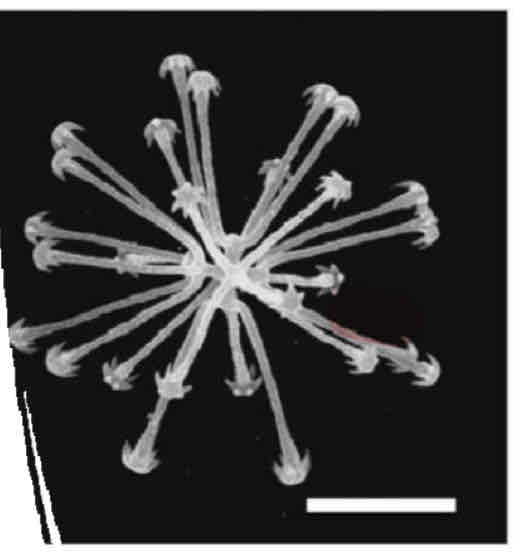

Hexactinellidae
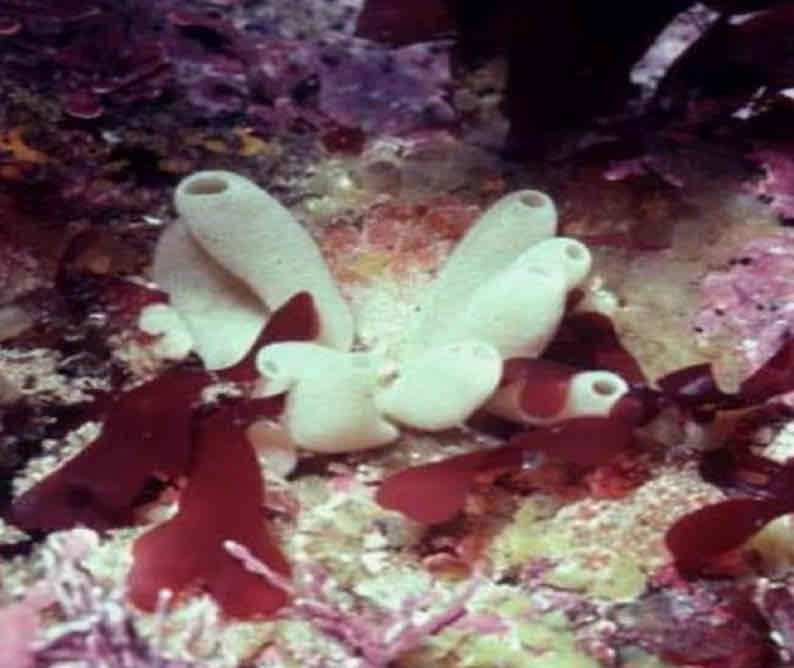

Calcarea

Calcarea
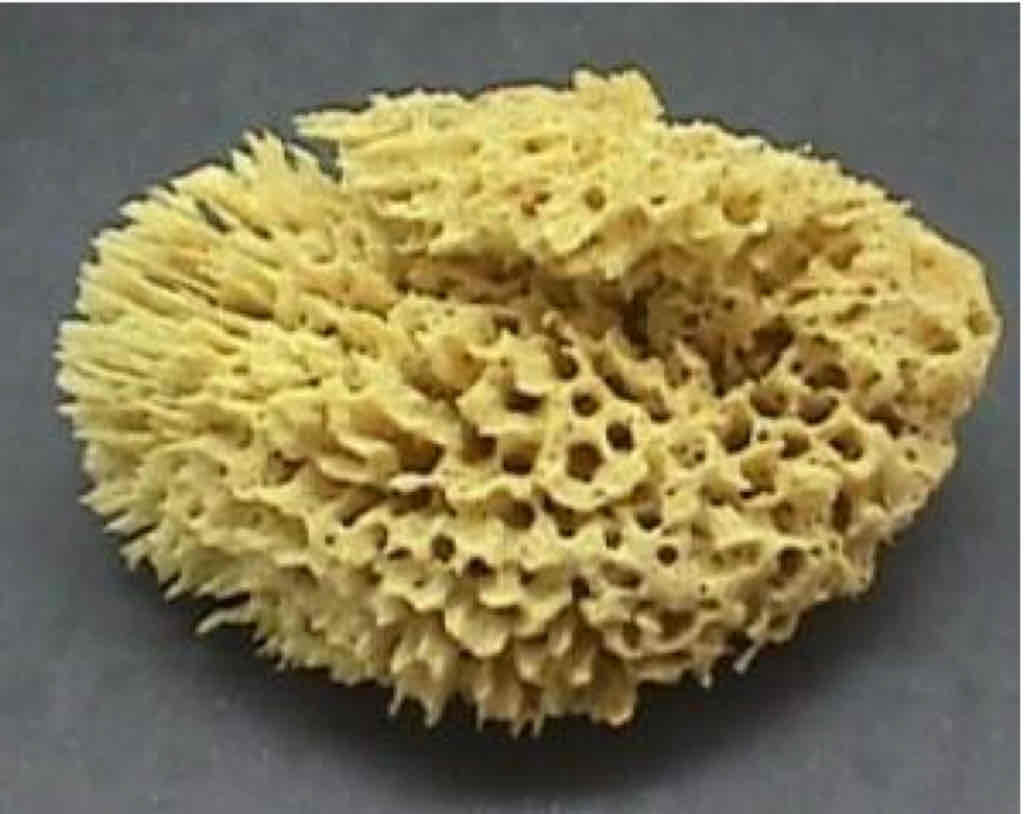

Demospongiae
The three types of canal systems
Asconoid
Synonoid
Leuconoid
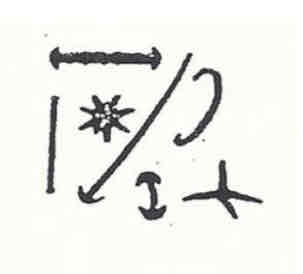
Asconoid
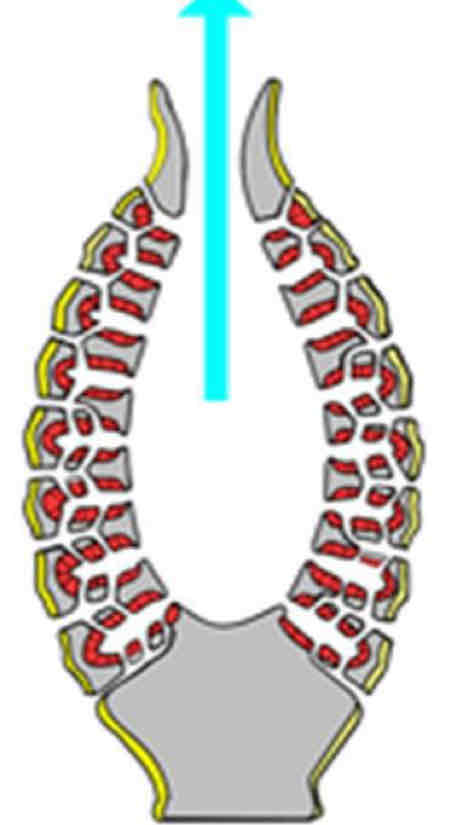
Syconoid
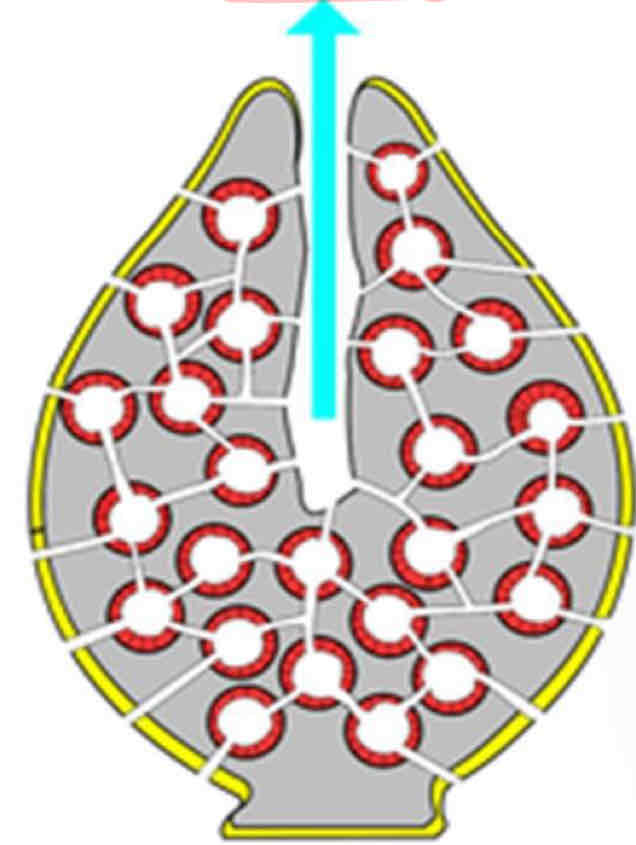
Leuconoid
Asconoid features
Has the simplest body plan
Grows in colonies
Small and shaped like a tube
A single large opening
Where are Asconoid found
Only on Calcarea
Synconids features
Water expelled through one large osculum
Radial canals, along the sides of the body tube
Where are sycononids found
Mostly found in Calcarea and some in Hexactinellidae
Radial Canals
Choanocytes line individual canals
Example of syconoids
Sycon
Example of Asconoid
Leucosolenia
Leuconoids features
Most complex body plan
No spongocoel
Much greater body size
Where are leuconoids found
In all 3 classes
Example of Leuconoid
Euspongia
Leuconoid
Syconoind

Ascondnoid
Leucosolenia kingdom
Animalia
Leucosolenia subkingom
Parazoa
Leucosolenia Phylum
Porifera
Leucosolenia Class
Calcarea
Leucosolenia characteristics
The body wall is transparent with many tiny pores and surrounded by numerous triradiate spicules within the wall
The three layers of Leucosolenia are
The inner layer (enclosed cell layer)
Medium jelly
The outer layer or epidermis
The outer layer of Leucosolenia consist of
Disc cell and formaina cell
What does the medium jelly of Leucosolenia consist of?
Old cell, Muscle cells, gradular cells, and gum cells
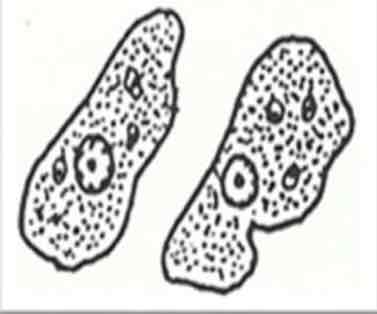
Amoebic cell (old cells)
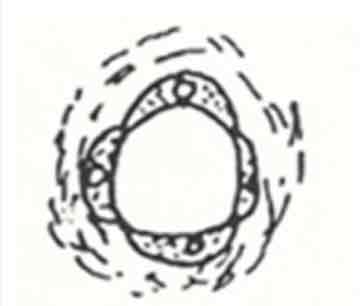
Mycocytes
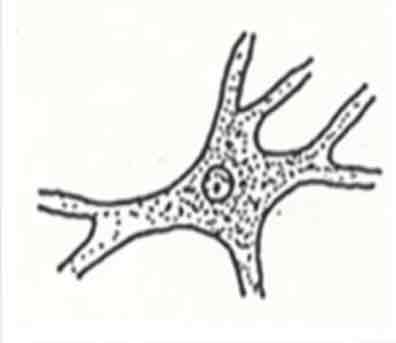
Collencyte
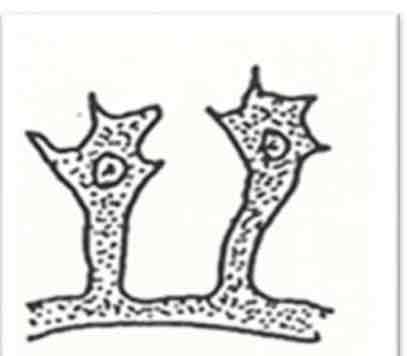
Gland cells
What are the colors of asexual reproduction in sponges?
Budding
Renewal
Gemmules
What are GEMMULES
Configure circus or internal budding
Where are GEMMULES found
In freshwater sponges
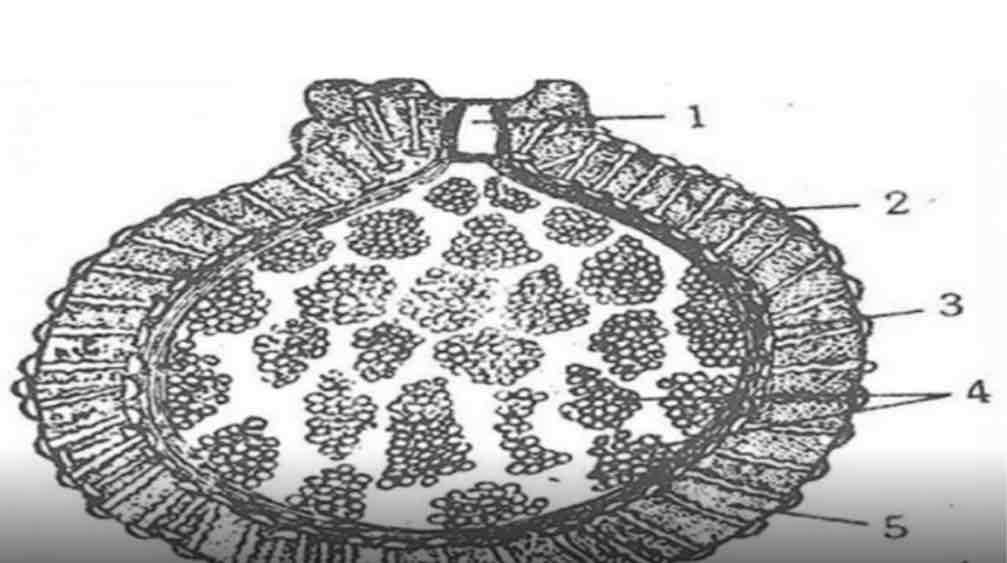
GEMMULES
What are sponge larva called?
Amphiblastula
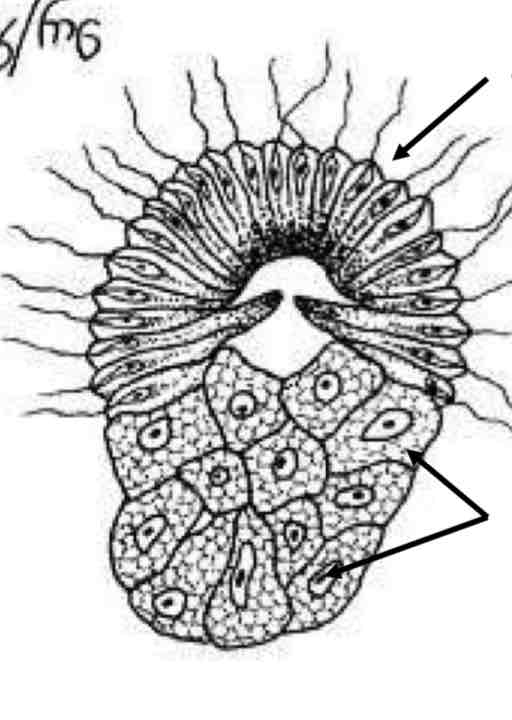
Amphiblastula
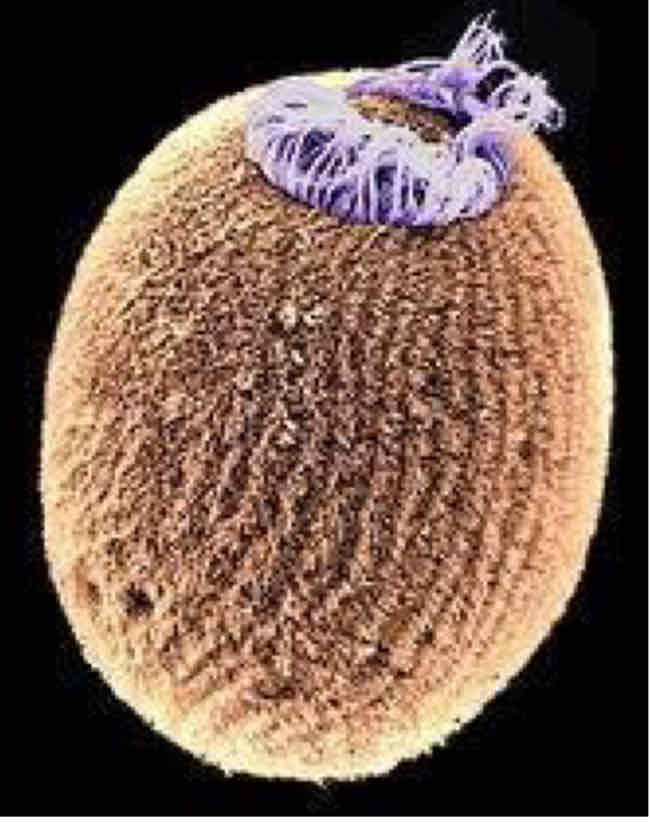
Amphiblastula
What are the uses of sponges commercially
Washing
Mattress manufacturing
Stuffed toys
Medical purposes of sponges
Antimicrobial compounds have been found on sponges like antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral
Enclosed cell layer (the inner layer) contains
Choancyte and flagella
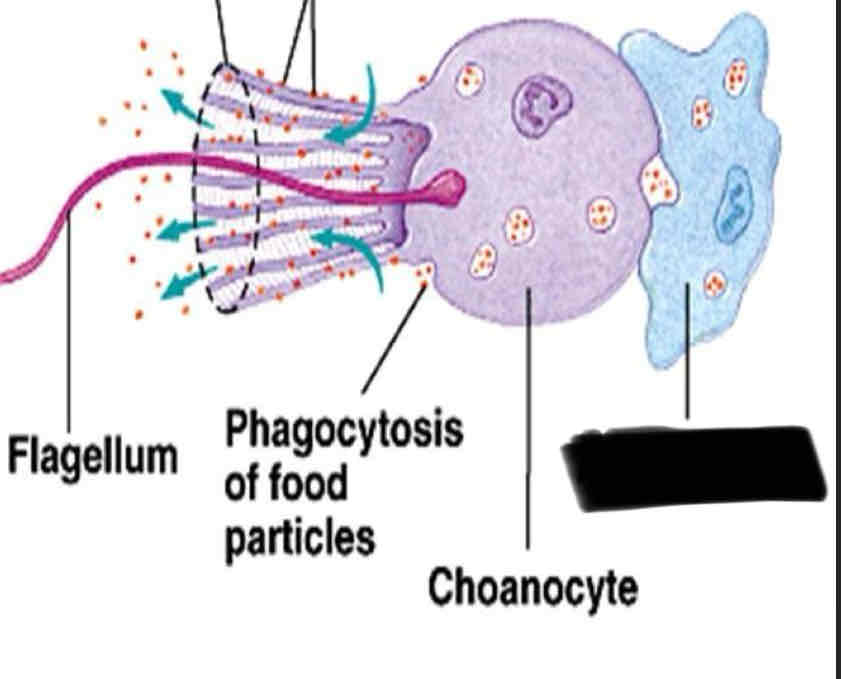
Amoebocyte
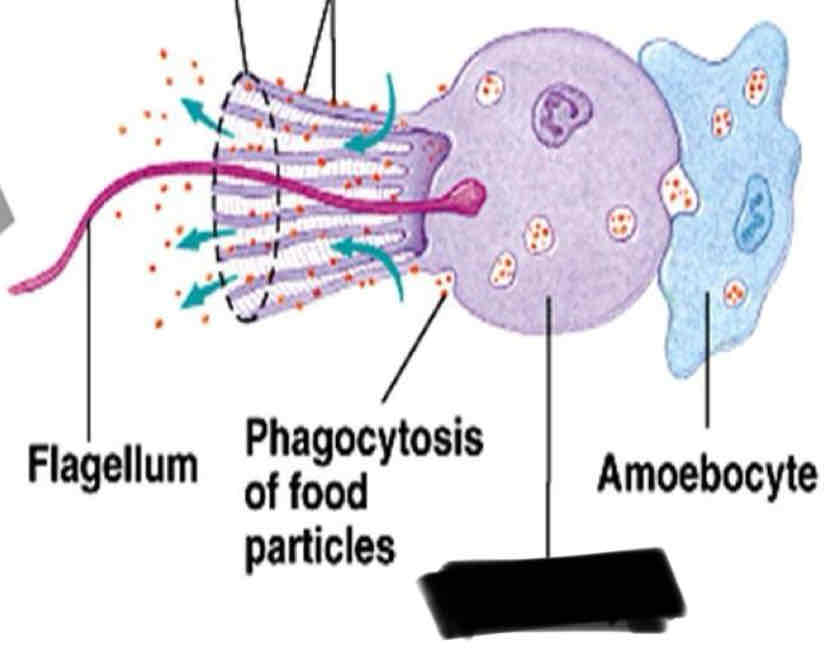
Choanocytes
Flagellum
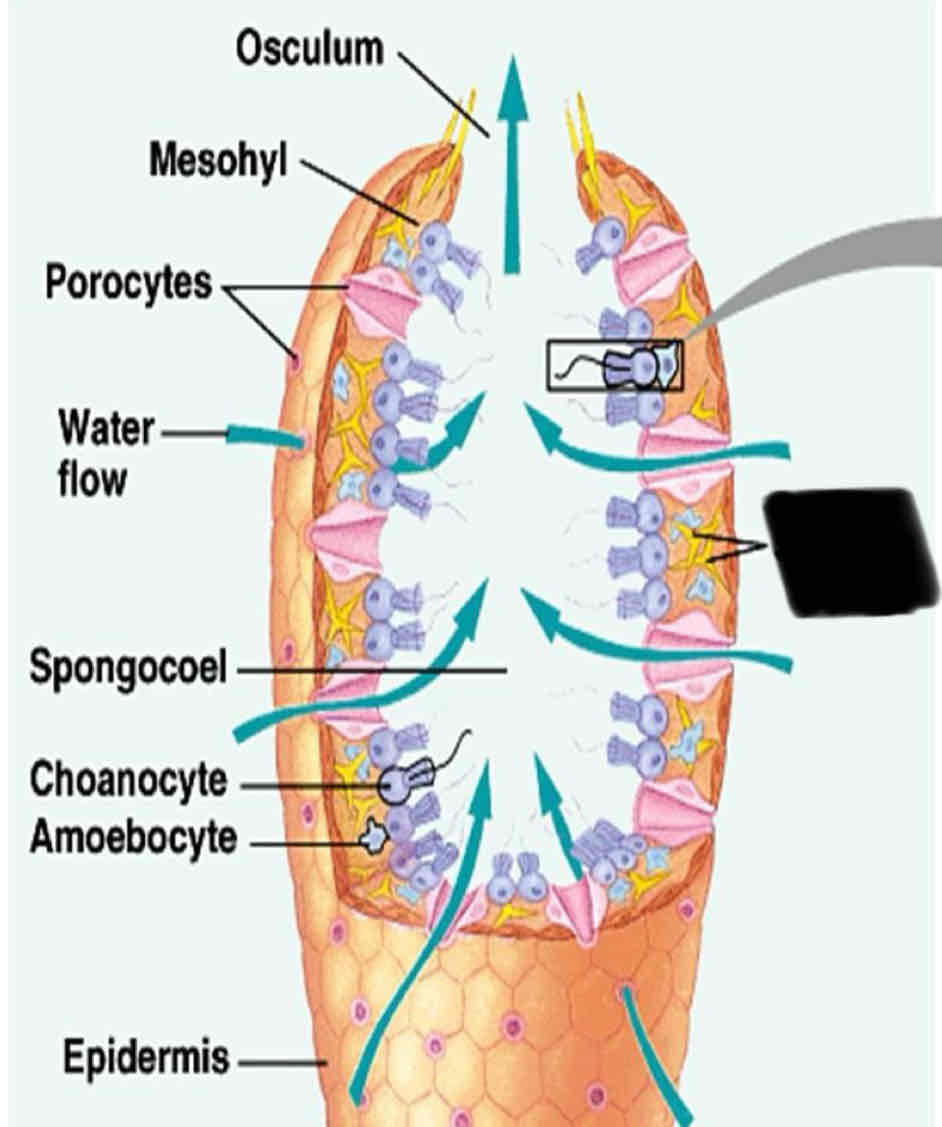
Spicules
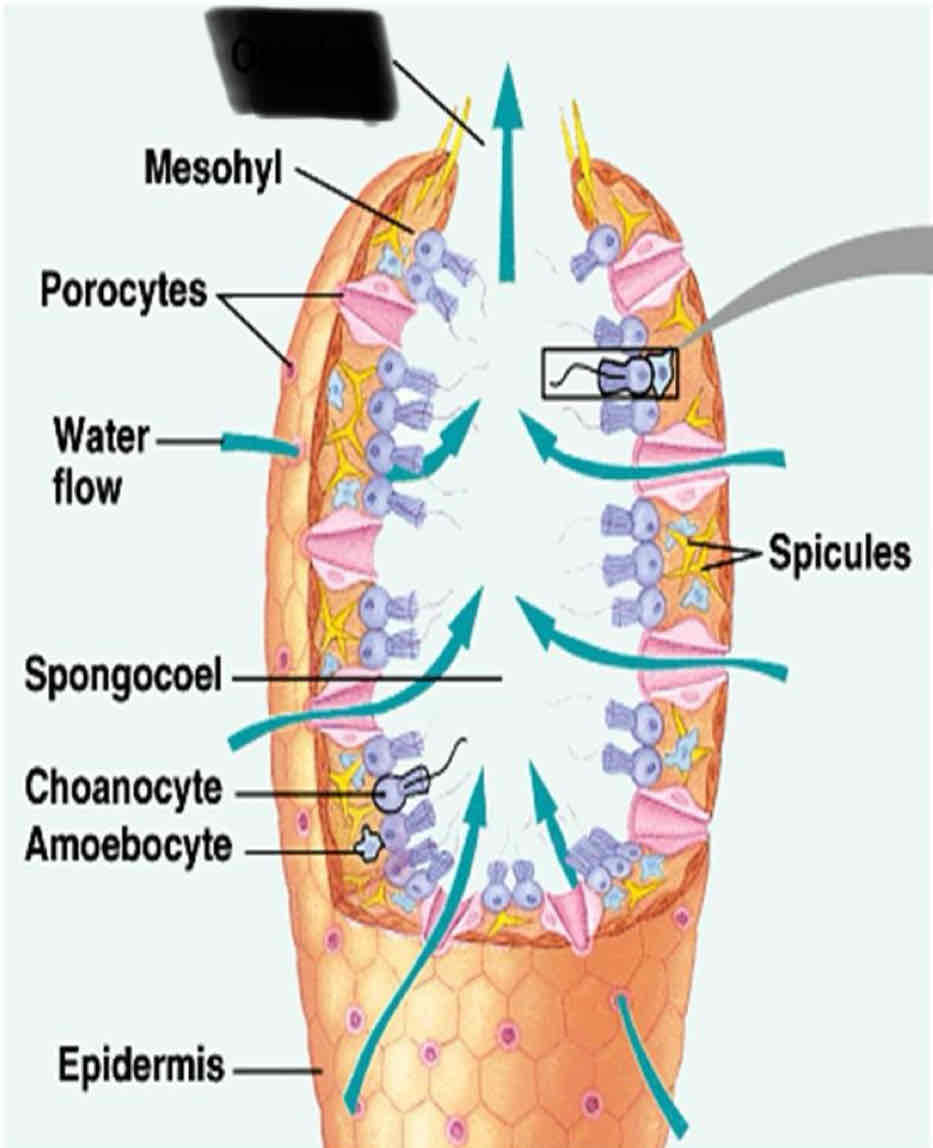
Osculum
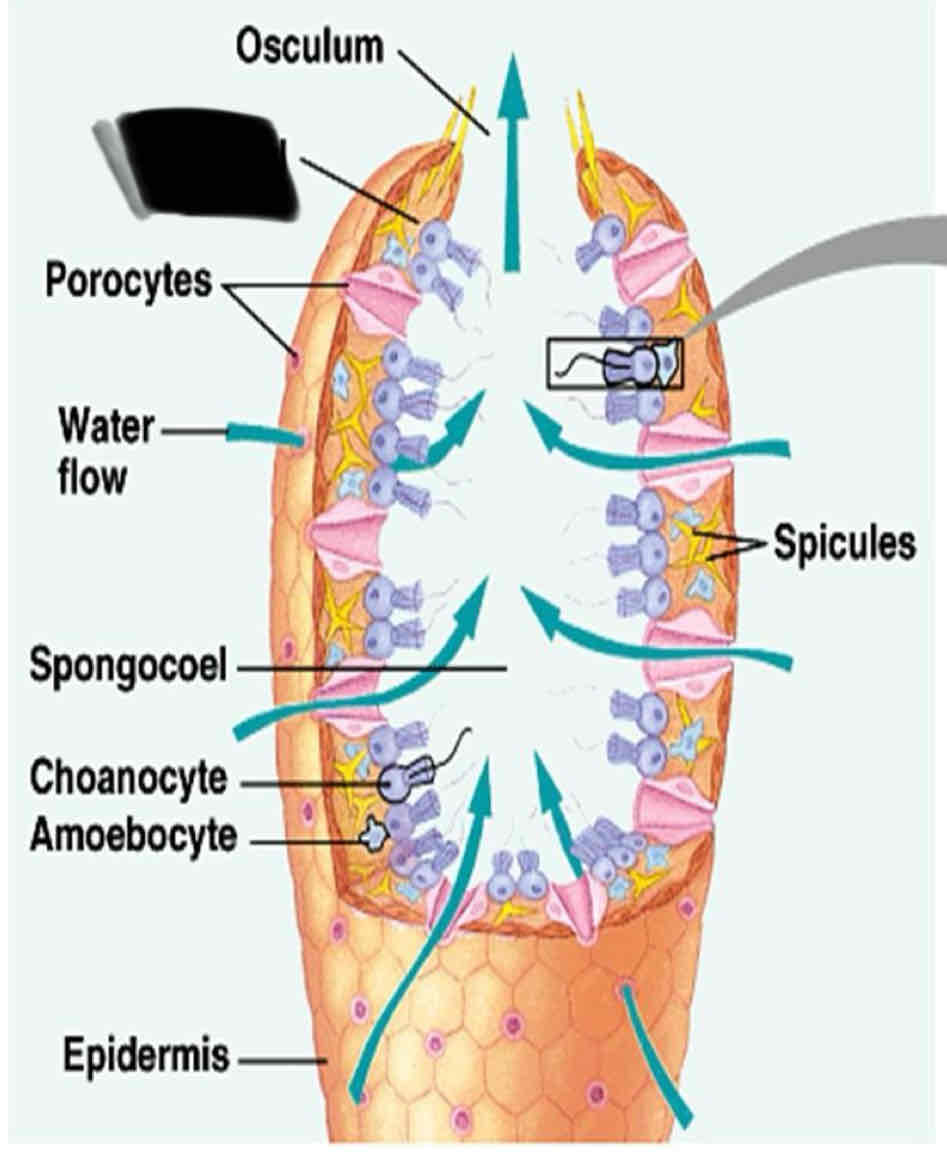
Mesohyl
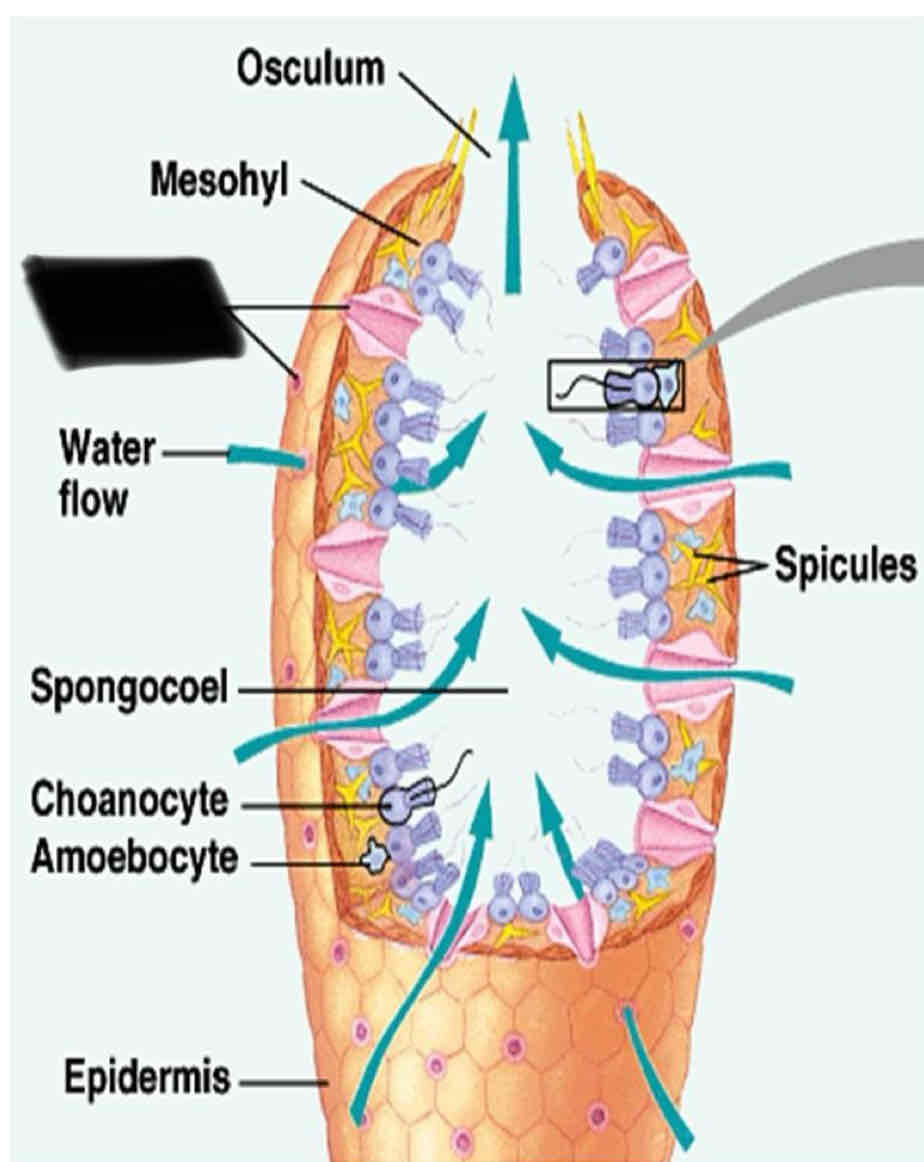
Ostia
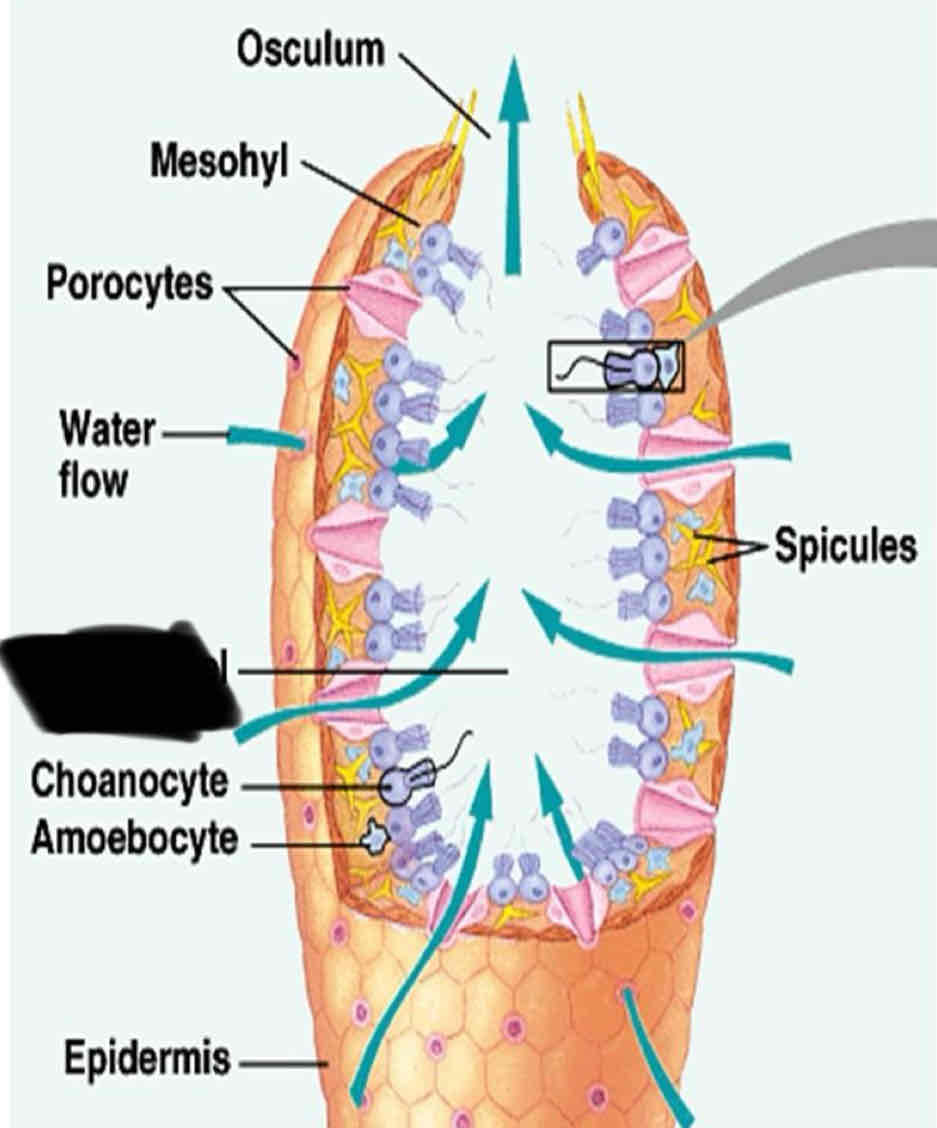
Spongocoel
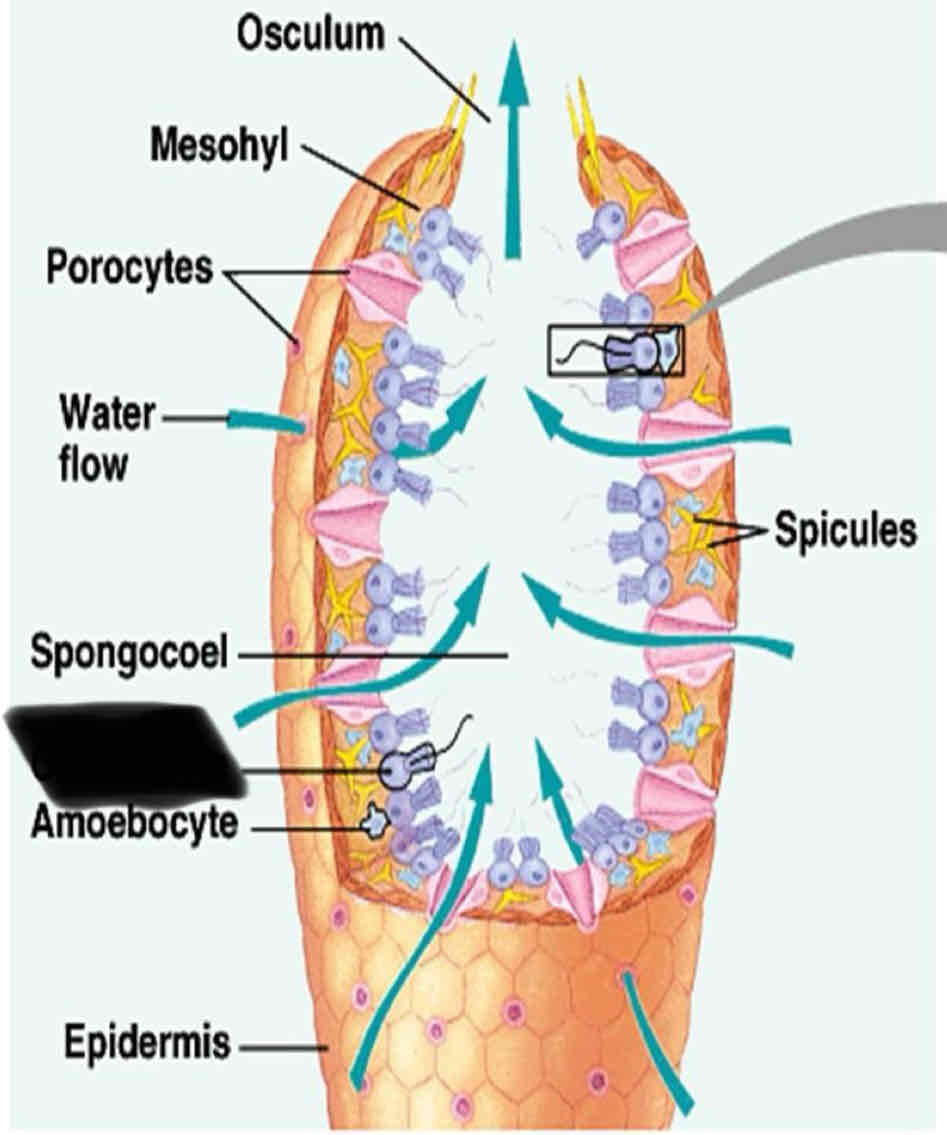
Choanocytes
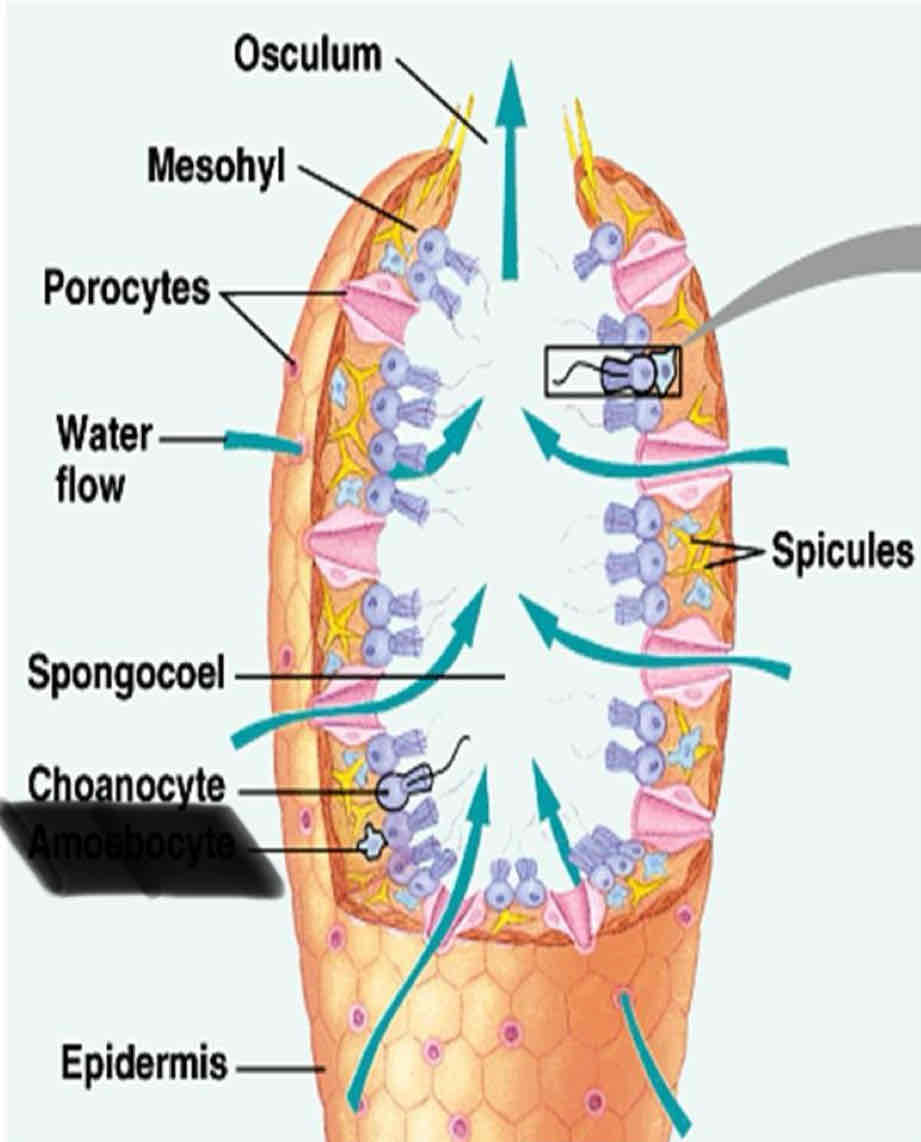
Amoebocyte
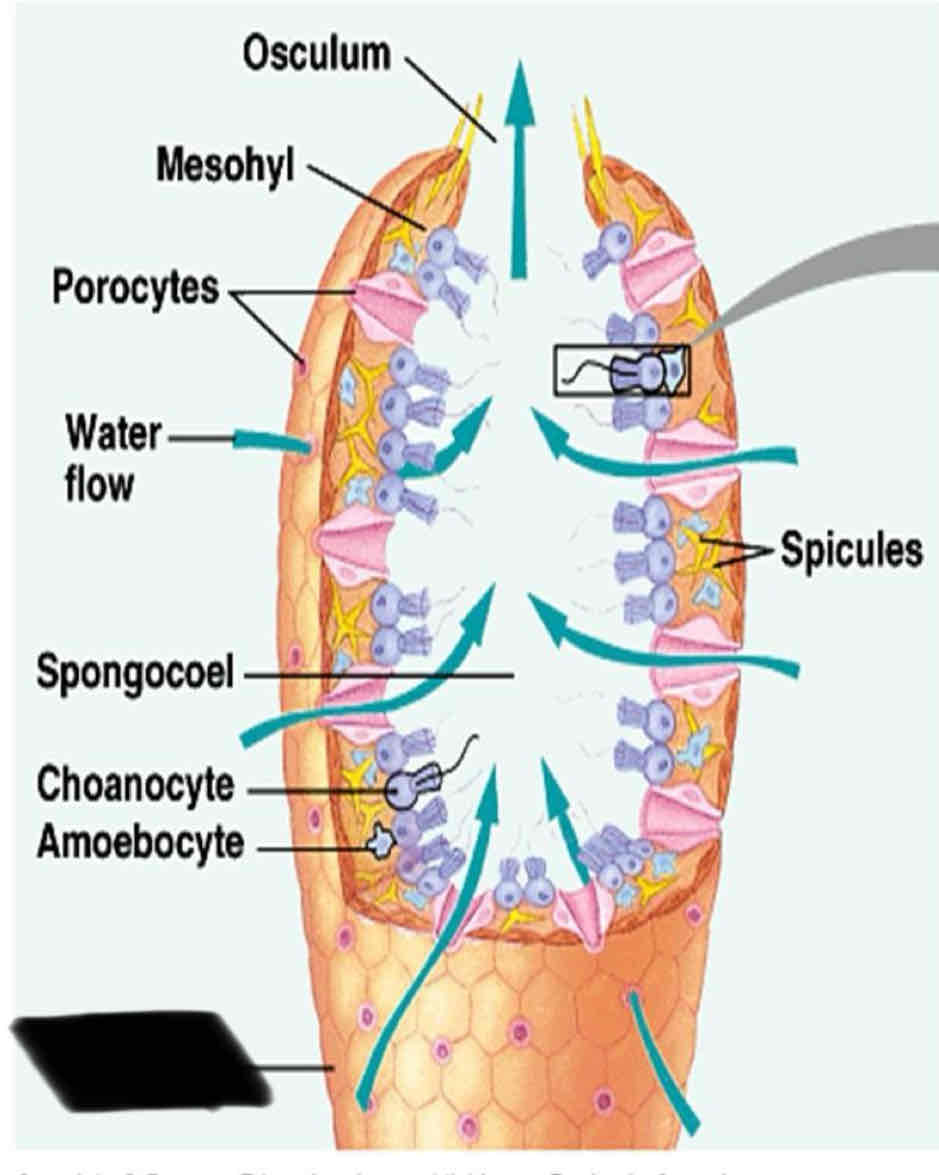
Epidermis