Life on Earth
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is an ecosystem?
It consists of all the organisms living in a particular habitat
What is a species?
An organism that can interbreed to product fertile offsprings
What is biodiversity?
It’s the range of living things in an ecosystem
What is population?
It’s the total number of a single species in an ecosystem
What is the definition of community?
All of the organisms living in an ecosystem
What is the definition of a producer?
Is the plant that being the food chain by making their own energy
What is a consumer?
An orangish that must consume other organisms to gain energy to survive
What the definition of a herbivore?
An organism that only eats plant
What’s a carnivore?
An organism that only eats animals
What is an omnivore?
An organism that eats both plant and animals
What is the definition of a predator?
It’s an organism the hunts, kills and eats other animals for food
What the definition of a prey?
An organism that predators kills for food
What the definition of a niche?
The role an organism play in its community
When does interspecific competition occur?
It occurs amongst individuals of DIFFERENT species for a few of the resources the both require
When does intraspecific occur?
Occurs amongst individuals of the SAME species and is for ALL resources required
What competition is more intense interspecific or inraspecific?
Intraspeific
What the definition of a biotic factor?
Their living factors the affect the distribution of organism
What is the definition of an abiotic factor?
Their non-living factors affect the distribution of organisms
What is an indicator species?
They’re species the by there absent or present can indicate the level of pollution
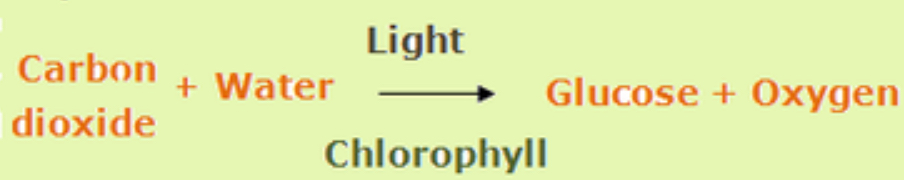
What is the photosynthesis word equation?
Carbon dioxide + water ——light energy + chlorophyll——> glucose + oxygen
What is photosynthesis?
It’s the process by which green plant make their own food
What are the stages called in photosynthesis?
Stage 1 - Light dependent stage
Stage 2 - Carbon fixation
What is the definition of stage 1 of photosynthesis?
It’s the light energy from the sun then is trapped by the chlorophyll in the chloroplasts and is converted into chemical energy with is used to generate ATP
What is water split into?
It’s split in to hydrogen and oxygen
What is the definition of stage 2 of photosynthesis?
It’s the series of enzyme - controlled reactions which is use hydrogen and ATP which carbon dioxide to produce sugar
Stage 2 of photosynthesis is controlled by what?
By enzymes
What do plants do with the glucose made during photosynthesis?
Used immediately in respiration
Converted in to starch for storage
Cellulose for structure
What is cellulose for?
Build long chains of cellulose for
Structure
What are the 3 limiting factors of photosynthesis?
Temperature
Carbon dioxide concentration
Light intensity
How much energy is passed on to an organism?
Only 10%
How much of the energy if lost?
90%
How is the energy is lost?
Heat
Movement
Indigested waste
how are nitrates dissolve?
In the soil water and adsorbed through the roots
What does nitrates produce?
Amino acids
What does nitrates synthesis into?
Into plant protein
What happen there is to much fertiliser?
it can leach into fresh water adding excess nitrates
What happens when algal populations increases?
Can cause algal bloom
What can algal bloom reduce?
Light levels reaching the water killing aquatic plants
Dead plants and algae can provide what?
Plenty food for bacteria
The more bacteria the more of what is used up?
Oxygen
Leaching can results in what?
Biodiversity decreasing
Why do farmers spray pesticides on to crops?
To increase crop yield by protecting the crops by killing pests
What is a mutation?
It’s a random change to genetic material (DNA)
What are the source of new alleles?
Mutations
What are the 3 types of mutations?
Advantageous
Disadvantageous
Neutral
What environmental factors can increase the rate of mutations?
UV rays
X-rays
What is the definition of adaptation?
Is an inherited characteristic that makes an organism well suited to survival in its environment
What does new alleles produced by?
Mutation can result in plants and animals becoming better adapted to their environment
Variation within a population can be a result in what?
To make it possible for a population to evolve overtime
What is natural selection?
The best adapted individuals in a population survive to reproduce passing on the favourable alleles the confer the selective advantage
Natural selection or survival of the fittest occurs when?
There are selection pressures
Initial population is separated by?
An isolation barrier
What is the definition of geographical?
Features such as rivers or mountains ranges isolate groups
What is ecological?
Isolated by such things as occupying different habitats
What is behavioural?
A population barriers caused by different in timing location that prevent members of the population from mating