Economies of Scale
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Economies of scale
Financial advantages that come from increasing production leading to reduction in average unit costs.
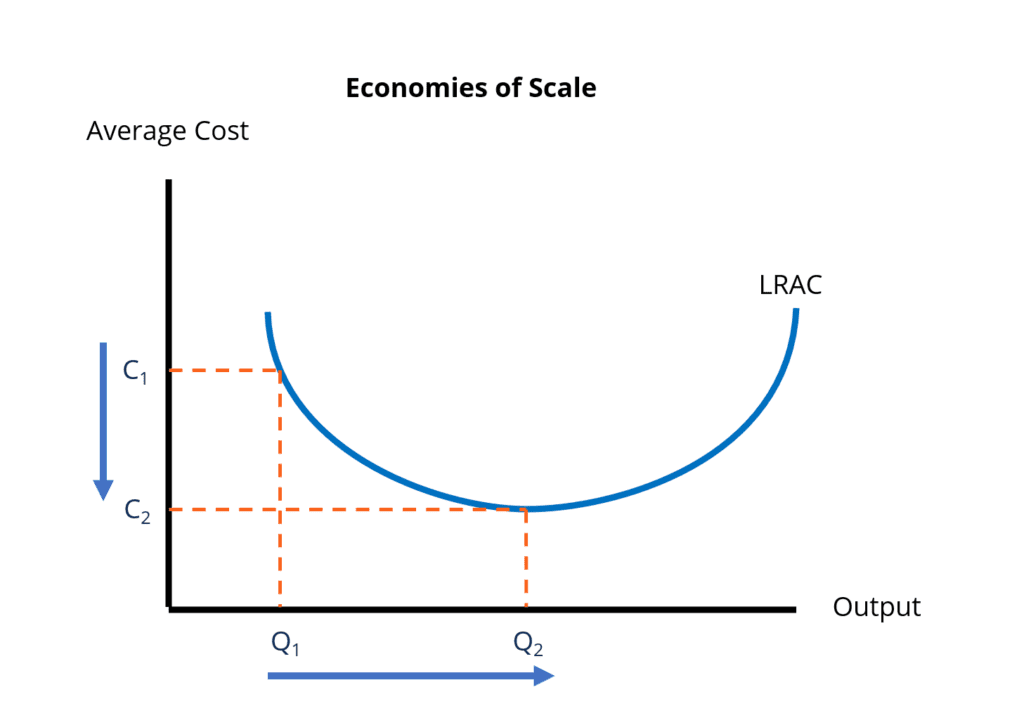
Describing economies of scale diagram
As quantity increases, average costs decreases
Happens until MES (minimum efficient scale), a point that shows the output level where firm achieves its lowest average cost per unit
In some cases, diseconomies of scale may occur and average costs begin to rise again, could be caused by inefficiencies in management or lack of communications.
Internal economies of scale
The reduction of average unit costs and increase of cost savings due to the growth of a business.
How many internal economies of scale are there?
9.
Technical economies of scale
As a business gets bigger, it can purchase more advanced machinery and equipment to perhaps replace workers on a production line.
Increased dimensions economies of scale
When large businesses expand their physical size of a production facility or storage space. This increases capacity and output, leading to lower average costs.
Purchasing economies of scale
When large businesses can buy raw materials or products in bulk leading to lower per-unit costs due to discounts from suppliers.
Division of labour economies of scale
The breaking of production into separate tasks in production to increase efficiency and potentially reduce average costs.
Financial economies of scale
Large businesses having better lending terms, lower rates of interest and better terms with suppliers. This makes it easier for large firms to raise capital and profitability.
Managerial economies of scale
When larger businesses hire more specialised management workers, increasing efficiency of the business and reducing costs.
Marketing economies of scale
Cost savings made by large businesses as they spread advertising costs over more products, getting discounts when investing in more advertisement.
Risk-bearing economies of scale
When large businesses are more likely to take risks with new products as they have more products to spread the risks and market fluctuations over.
Research and development economies of scale
As R&D typically requires high fixed costs (such as specialised equipment and workers), larger businesses can make most of their fixed costs through the development of new products and improve their existing offerings. This also reduces average costs as they spread their fixed costs over more products and the potential increased profitability.
External economies of scale
When costs fall as entire industries or regions experience cost savings due to factors outside individual firms.
E.g. as prices of computer chips fall, computer manufacturers in whole industry reduce their costs
Benefits of geographical external economies of scale
Local skilled labour force is available
Highly specialist - local firms can supply parts or services
Good transportation network
Excellent reputation for producing particular good
Overall benefit of internal / external economies of scale
Creates lower unit costs that cause an improvement in efficiency and production leading to higher profit margins. This can also feed through to consumers by lowering of prices.