BISC220 Lecture 1 & 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:55 PM on 1/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
where do you find protons?
clustered in nucleus
2
New cards
what’s the charge of a proton?
positive charge
3
New cards
where do you find neutrons?
clustered in nucleus
4
New cards
what’s the charge of a neutron?
neutral charge
5
New cards
where do you find electrons?
scattered around nucleus in valence shells
6
New cards
what’s the charge of an electron?
negative charge
7
New cards
what’s a valence shell?
outermost regions of an atom where electrons can exist
8
New cards
how many electrons needed to fill innermost valence shell?
2
9
New cards
how many electrons needed to fill all valence shells after the innermost shell?
8
10
New cards
when is an atom considered unstable?
when valence shells are incomplete
11
New cards
what are ions?
atoms with an electrical charge
12
New cards
what do ions do?
signal and maintain balance of bodily fluids in biology
13
New cards
what are isotopes?
atoms that have an uneven number of neutrons relative to the number of protons
14
New cards
what happens to isotopes overtime?
they’re radioactive, so they decay overtime and emit energy
15
New cards
what’s an isomer?
compounds that share the same chemical formula, but may vary in structural arrangement
16
New cards
what are the different types of isomers?
structural, geometric, enantiomers
17
New cards
what’s a structural isomer?
they exhibit different arrangements of the atoms that make up the compound
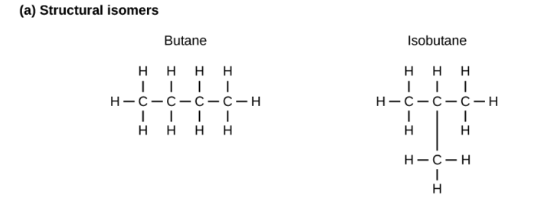
18
New cards
what’s a geometric isomer?
they exhibit different angle/orientation based on the presence of single or double covalent bonds
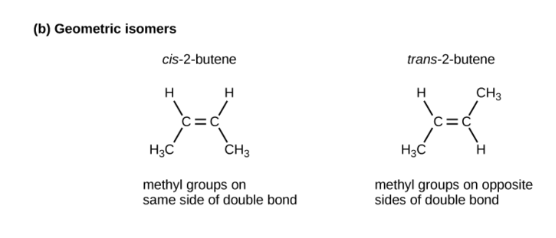
19
New cards
what’s an enantiomer?
“mirror images” of one another. particularly useful in pharmacology
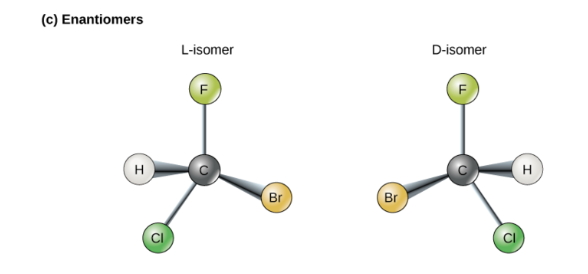
20
New cards
elements most important to biology
CHONPS: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
21
New cards
what’s an ionic bond?
metal (usually a cation) and nonmetal (usually an anion) elements form a bond. metal donates an electron to the nonmental, relationship typically uneven.
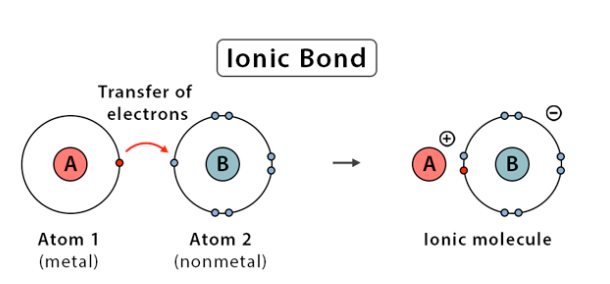
22
New cards
what are common examples of ionic bonds?
sodium chloride (NaCl, table salt), sodium hydroxide (NaOH, bleach)
23
New cards
what’s a covalent bond?
two nonmetals bond. sharing of electrons, relationship somewhat equal
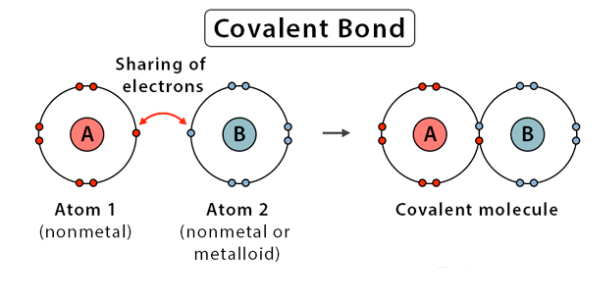
24
New cards
what are common examples of covalent bonds?
Dihydrogen oxide (H2O, water), methane (CH4)
25
New cards
why can hydrogen form hydrogen bonds?
hydrogen is the smallest element on Earth, so it can form special transient bonds
26
New cards
what are the properties of water?
1. water is polar
2. universal solvent
3. high heat capacity
4. high heat of vaporization
5. high cohesion + adhesion
6. less dense as a solid than as a liquid
27
New cards
how does hydrogen affect pH?
more hydrogen ions (H+)- more acidic (pH
28
New cards
what’s a monomer?
a single chemical unit, or a building block for a larger molecule
29
New cards
what’s a polymer?
a molecule that consists of several monomers bound together
30
New cards
what are carbohydrates?
a class of macromolecules that are commonly known as sugars. Composed of CHO. Some carbohydrates are known as saccharides.
31
New cards
MIGHT NEED TO KNOW?
TYPES OF POLYSACCHARIDES
32
New cards
MIGHT NEED TO KNOW?
PROTEIN STRUCTURE OF AMINO ACIDS (TABLE IN SLIDES)
33
New cards
what are lipids?
class of macromolecule that are commonly known as fats. composed exclusively of CH. not water soluble because their chemical structure makes them a nonpolar covalent molecule.
34
New cards
can nonpolar molecules dissolve in polar molecules?
no. e.g nonpolar molecules can’t dissolve in water, a polar molecule. “like dissolves like”.
35
New cards
what are 3 common lipids?
triglyceride, phospholipid, steroid
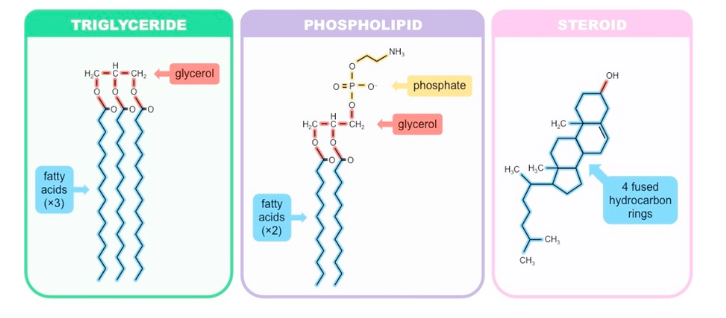
36
New cards
what is the structure of a saturated fatty acid?
CHO, no double bonds
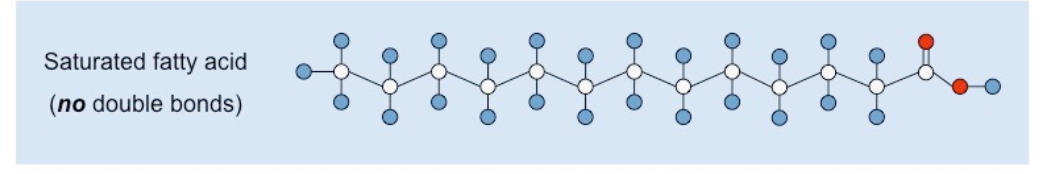
37
New cards
what is the structure of an unsaturated trans fatty acid?
CHO, double bond, H atoms opposite
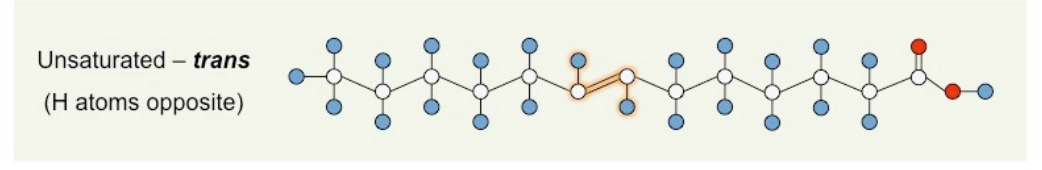
38
New cards
what is the structure of an unsaturated cis fatty acid?
CHO, double bond, H atoms same side, bent configuration
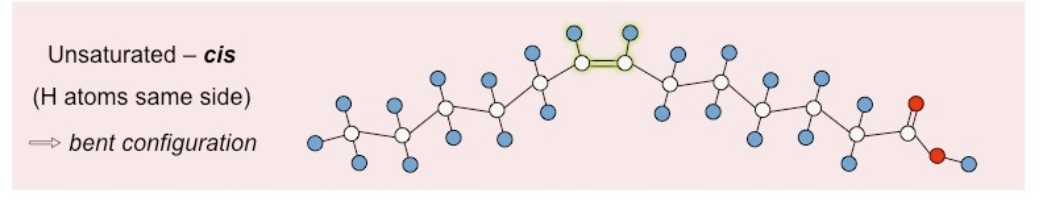
39
New cards
what are proteins (peptides)?
largest and most important class of macromolecules. CHON minimum elements required, sometimes contains S
40
New cards
what’s the monomer for proteins?
amino acids. can bind together to form polymer (polypeptide)
41
New cards
how many naturally occurring amino acids important for life on Earth are there?
20
42
New cards
what are the different types of protein structure?
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
43
New cards
what is primary protein structure?
polypeptide chain

44
New cards
what is secondary protein structure?
alpha helix + beta sheets produced by hydrogen bonds forming within the polypeptide
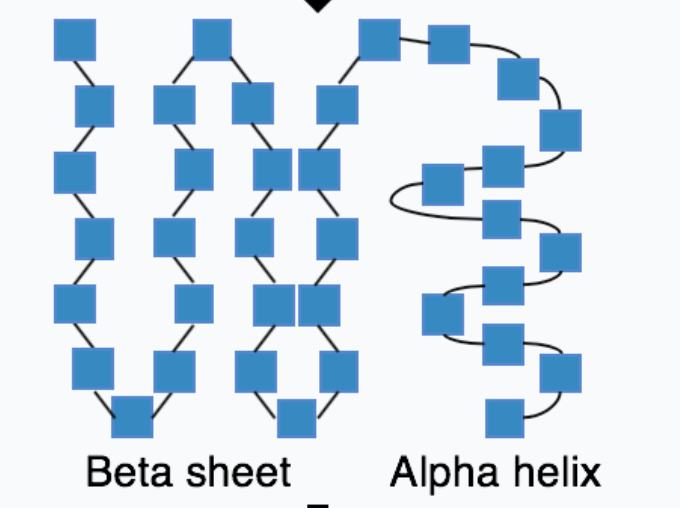
45
New cards
what is tertiary protein structure?
3D overall fold of the protein containing secondary structures
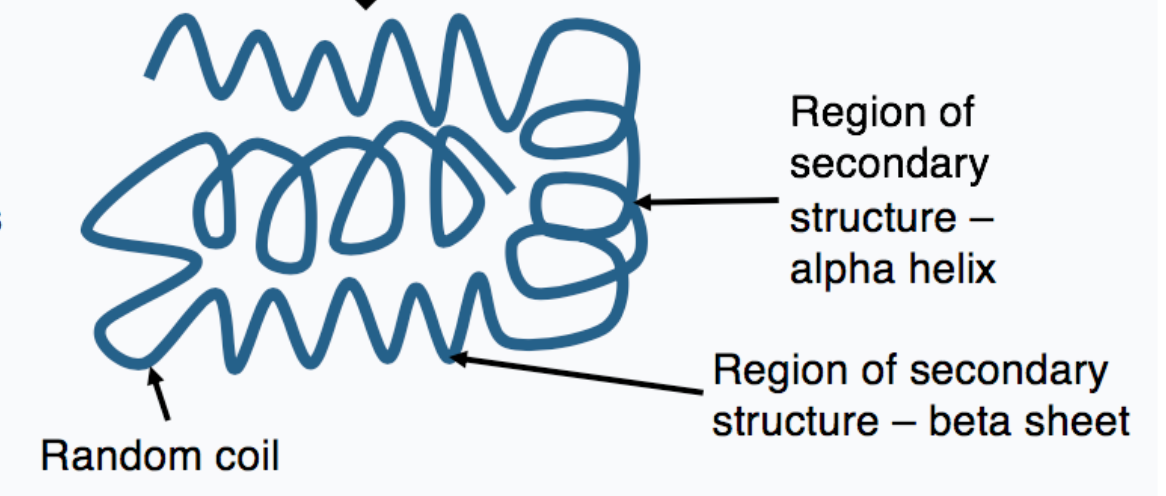
46
New cards
what is quaternary protein structure?
multi-subunit complex where each unit is a distinct polypeptide chain
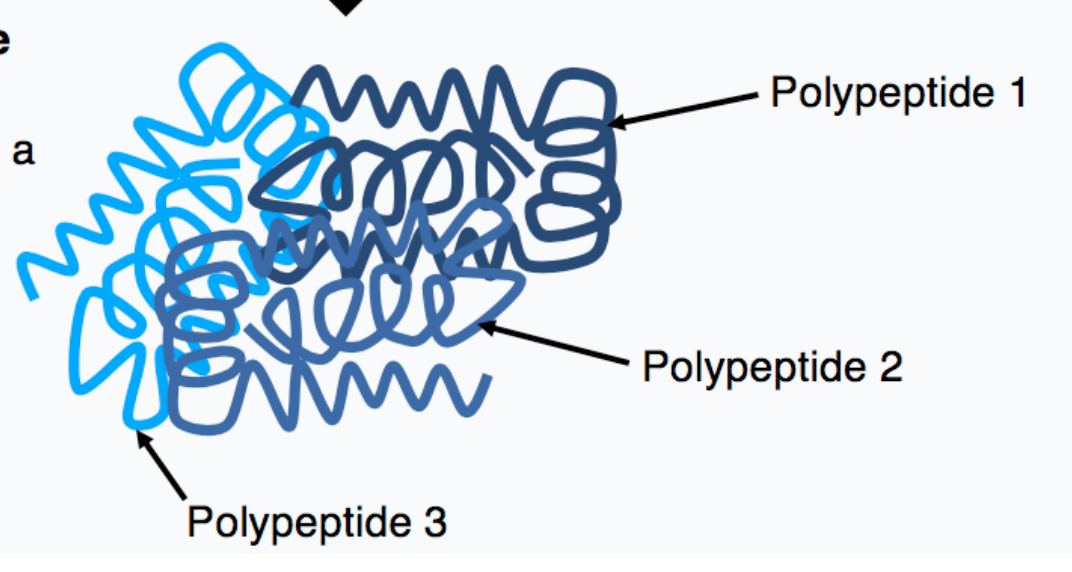
47
New cards
what’s an enzyme?
a special type of protein that performs a catalytic function- reduces the energy threshold required for a specific reaction to occur, allowing the reaction to proceed at a faster rate. can be anabolic or catabolic.
48
New cards
what are nucleic acids?
a group of macromolecules that include several important, high-energy compounds for cells, including Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). CHONP.
49
New cards
what is a nucleotide?
a common monomer for nucleic acids consisting of a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group (PO4-), and a sugar (typically ribose)
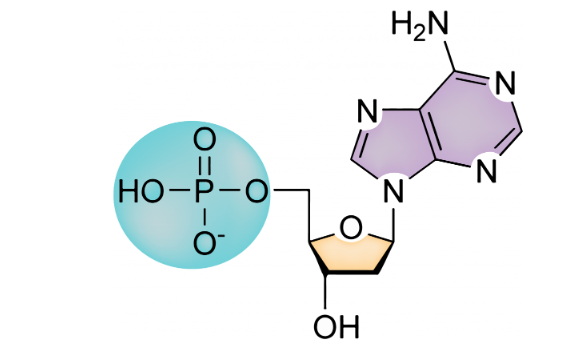
50
New cards
Compare DNA & RNA
DNA: double stranded, Thymine, No oxygen on sugar
RNA: single stranded, Uracil, Oxygen on sugar
RNA: single stranded, Uracil, Oxygen on sugar
51
New cards
what is the central dogma of biology?
Genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to Polypeptide through transcription and translation