Chemistry I: Lesson 7: Acids and Bases
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
CRB Before the more broad definitions of acids and bases were developed, Arrhenius created the simplest definition of acids and bases. Explain what Arrhenius acids and bases are, and how they are related to water.
Arrhenius acids are compounds that will, in an aqueous solution, ionize to produce Hydrogen ions (H+). Arrhenius bases, likewise, will ionize to form hydroxide ions (OH-).
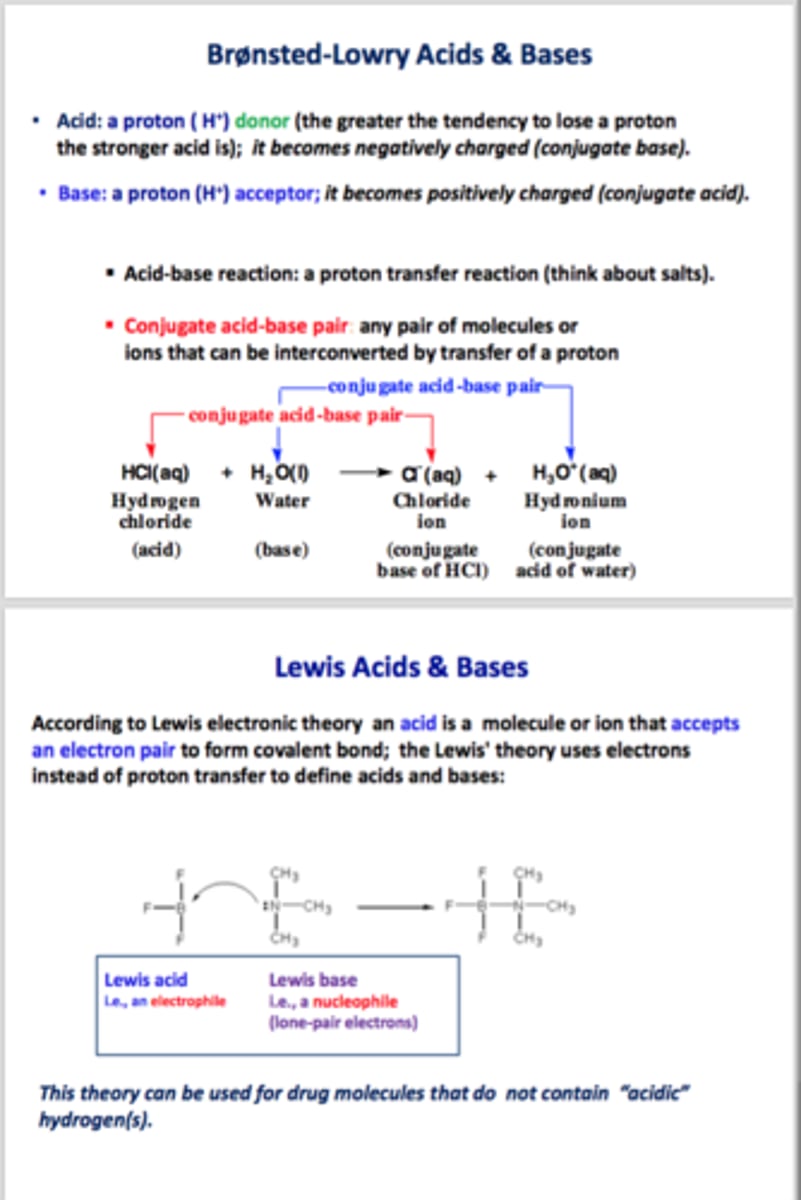
Define a Bronsted-Lowry base vs. Bronsted-Lowry acid?
Define a Lewis base vs. Lewis acid?
A Bronsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor, and a Bronsted-Lowry acid is a proton donator.
A Lewis base is an electron donator, and a Lewis acid is an electron acceptor.
CRB Which of the following compounds can behave as a Bronsted-Lowry acid but not a Lewis acid?
(A) I2
(B) H2O
(C) HF
(D) None of the above
(D) None of the above
To be a Bronsted-Lowry acid, the compound must have a Hydrogen to donate. To be a Lewis acid, the compound must be able to accept an electron pair.
Any correct answer must have a Hydrogen to donate, and cannot be able to accept any electron pairs. Formally, this is not possible, since donating the Hydrogen means accepting the electron pair that used to make up the covalent bond with the Hydrogen.
Since all Bronsted-Lowry acids are Lewis acids, no compound can be a correct answer.
The acid ionization constant is also known as the:
(A) Acid association constant
(B) Acid dissociation constant
(C) Acid solubility constant
(D) Acid precipitation constant
(B) Acid dissociation constant
The acid ionization constant is also known as the acid dissociation constant (Ka).
Write the acid dissociation constant expression for the following reaction: HA <-> H+ + A-
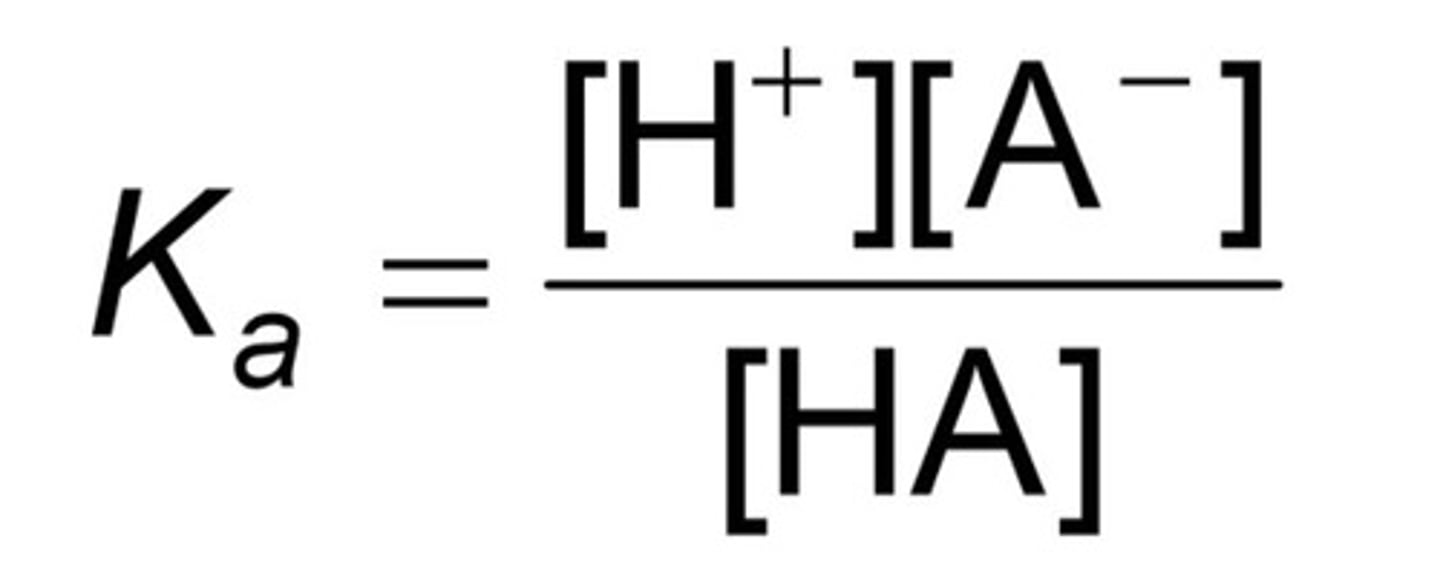
Which is a stronger base, H2O or Cl-, in the following reaction: H2O + HCl <-> H3O+ + Cl-
H2O is a stronger base than Cl- because Cl- is the conjugate base of a strong acid, making it a very weak base.
True or false? The larger the Ka value, the weaker the acid.
False. The larger the Ka value, the STRONGER the acid.
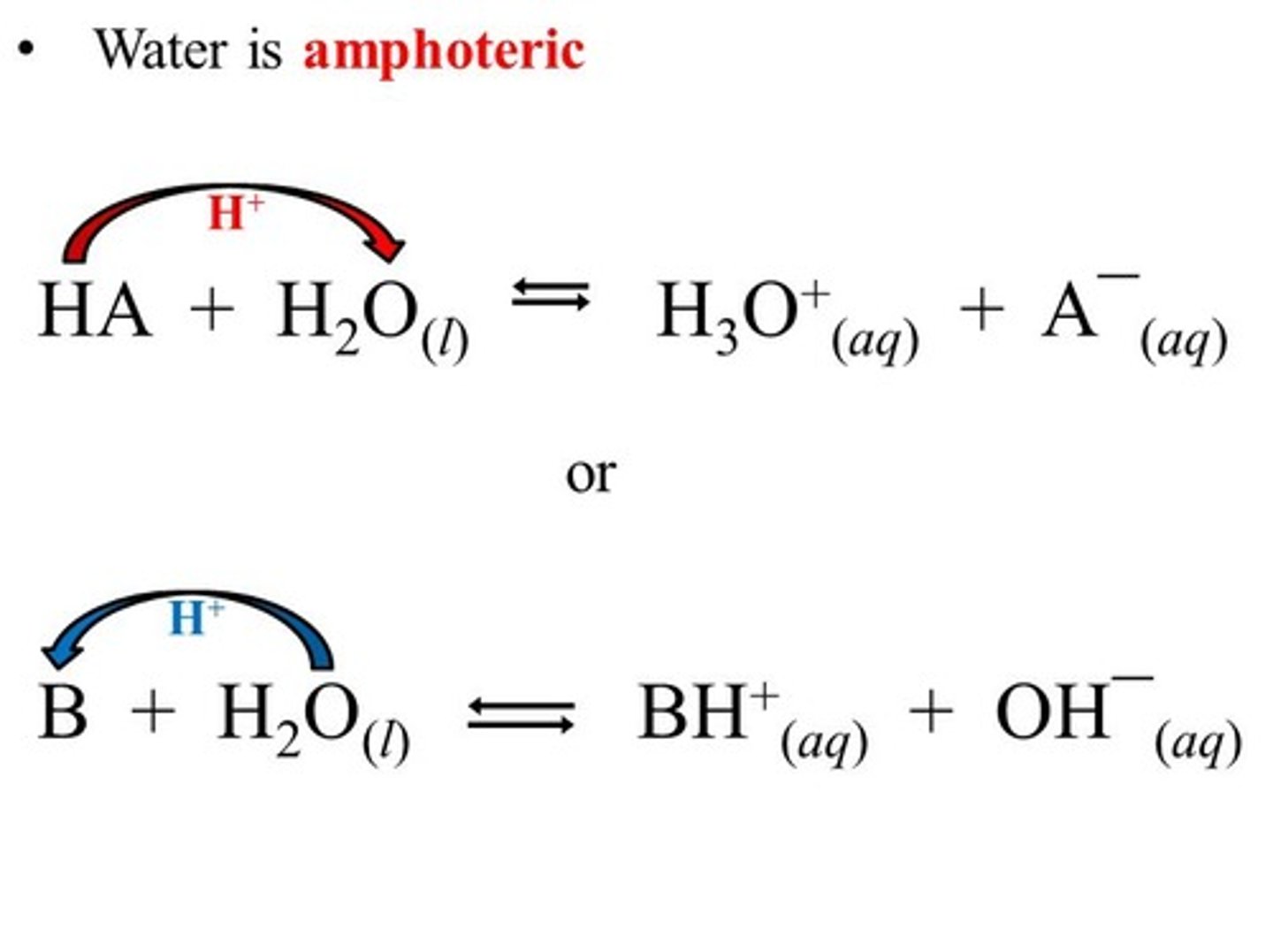
What does it mean to say that water is amphoteric?
To say that water is amphoteric means that water can act as both an acid and a base.
CRB Two identical amphoteric compounds can react with each other to form an acid and a base. What is this process called?
(A) Ionization
(B) Propionation
(C) Single-displacement reaction
(D) Autoionization
(D) Autoionization
Autoionization is where two identical molecules react with one another to form an acid and base.
What is the relationship between Ka and Kw?
Kw (the autoionization constant of water) is the Ka (acid dissociation constant) for water.
What is the value of Kw?
1 ⋅ 10^-14
The concentration of [H3O+] in a solution is 4.30 ⋅ 10^-4 M. What is the concentration of [OH-] in this solution?
(A) 4.30 ⋅ 10^-4 M
(B) 8.76 ⋅ 10^-5 M
(C) 1.22 ⋅ 10^-10 M
(D) 2.33 ⋅ 10^-11 M
(D) 2.33 ⋅ 10^-11 M
Kw = [H3O+][OH-]
1 ⋅ 10^-14 = (4.3 ⋅ 10^-4)[OH-]
(1 ⋅ 10^-14)/(4.3 ⋅ 10^-4) =
[OH-]
[OH-] = approx. .25 ⋅ 10^-10 -> 2.5 ⋅ 10^-11 (actual: 2.33 ⋅ 10^-11)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What is the pH when you have a [OH-] concentration equal to 9.84⋅10^-8 M?
(A) 8.67
(B) 7.92
(C) 6.99
(D) 5.43
(C) 6.99
Kw = [H3O+][OH-]
1⋅10^-14 = [H3O+](9.84⋅10^-8)
(1⋅10^-14)/(9.84⋅10^-8) = [H3O+]
[H3O+] = approx. .1⋅10^-6 -> 1⋅10^-7 (actual: 1.02⋅10^-7)
pH = -log( 1⋅10^-7)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Name the 7 Strong Acids

CRB During digestion, the contents of the stomach are near a pH of 2, but in the duodenum the pH is raised to about 6. How many times more acidic (Higher [H+]) is the chyme in the stomach than the chyme in the duodenum?
(A) 4
(B) 10,000
(C) 100
(D) 40
(B) 10,000
Because there is a pH difference of 4, the difference in [H+] is a factor of 10^4, which is equal to 10,000.
Calculate the pH of a 4.56 ⋅ 10^-3 M solution of HClO4?
(A) 3.46
(B) 3.03
(C) 2.34
(D) 1.95
(C) 2.34
HClO4 is a strong acid, so treat its concentration as [H+]
[H3O+] = 4.56 ⋅ 10^-3
pH = -log(4.56 ⋅ 10^-3)
pH = approx. 2.5 (actual: 2.34)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
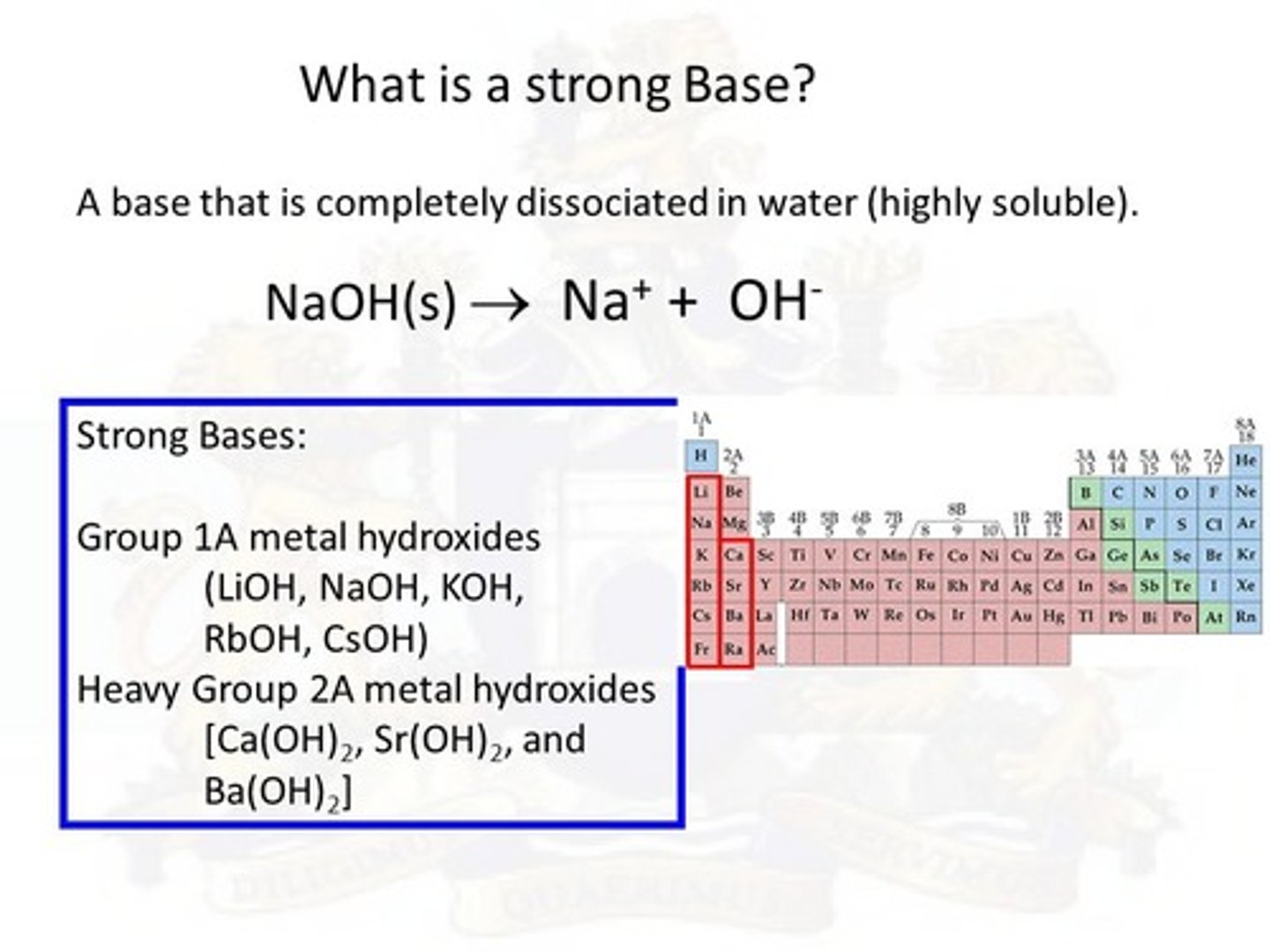
Strong bases are formed from which two groups of the periodic table mixed with OH?
Groups 1A and 2A
What is pKw in terms of pH and pOH?
pKw (14) = pOH + pH
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
Calculate the pH of a 7.45 ⋅ 10^-6 M solution of Ba(OH)2?
(A) 9.17
(B) 7.34
(C) 4.83
(D) 3.98
(A) 9.17
[OH-] = 7.45 ⋅ 10^-6 x 2
[OH-] = 14.9 ⋅ 10^-6 OH-] = 1.49 ⋅ 10^-5
pOH = -log([OH-])
pOH = -log(1.49 ⋅ 10^-5)
pOH = approx. 5 (actual: 4.83)
pKw = pH + pOH
14 = pH + 5
pH = 9 (actual: 9.17)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Which of the following is the strongest base?
(A) F-
(B) CH3O-
(C) CH3COO-
(D) NO3-
(B) CH3O-
CH3OH is a very weak acid, so its conjugate base will be extremely strong.
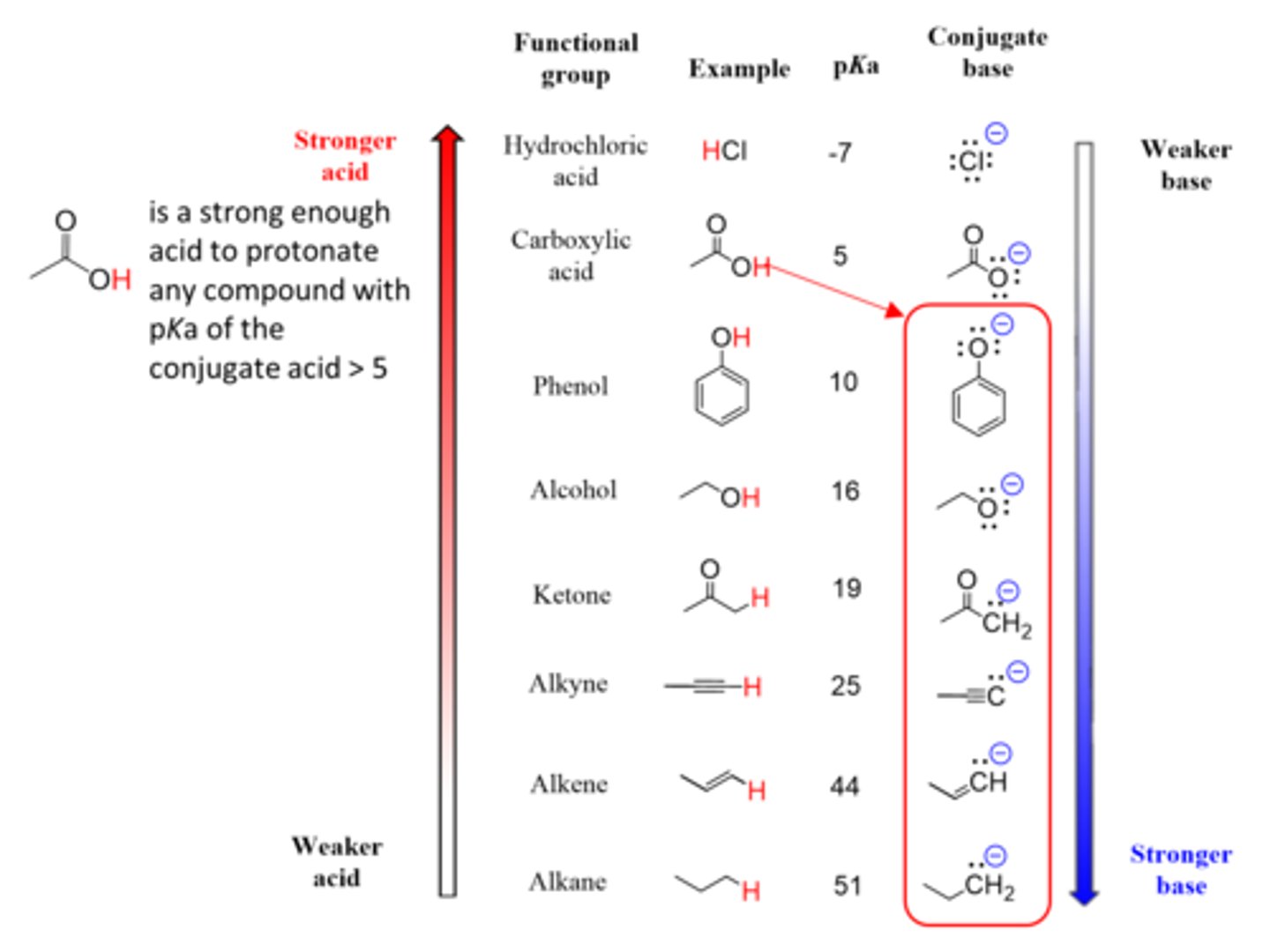
What is the pKa of acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 ⋅ 10^-5)?
(A) 5.54
(B) 5.13
(C) 4.74
(D) 4.13
(C) 4.74
pKa = -log(Ka)
pKa = -log(1.8 ⋅ 10^-5)
pKa = approx. 4.82 (actual 4.74)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What is the pH of a 4.65 ⋅ 10^-4 M solution of acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 ⋅ 10^-5)?
(A) 7.86
(B) 6.02
(C) 4.89
(D) 4.08
(D) 4.08
Ka = ([CH3COO-][H3O+])/[CH3COOH]
1.8 ⋅ 10^-5 = x^2/4.65 ⋅ 10^-4 - x (but x is so little that we can disregard it), making our equation:
1.8 ⋅ 10^-5 = x^2/4.65 ⋅ 10^-4
(1.8 ⋅ 10^-5)(4.65 ⋅ 10^-4) = x^2
approx. 90 ⋅ 10^-10 = x^2
approx. 1 ⋅ 10^-4 = x
pH = -log(1 ⋅ 10^-4)
pH = approx. 4 (actual: 4.08)
CRB In terms of acids and bases, define a neutralization reaction.
A neutralization reaction is where an acid and a base react to form a salt. Oftentimes, water is also a product of these reactions.

CRB For a polyvalent or polyprotic acid or base, the same molecule can act as an acid or base multiple times. Using the example of H2SO4, explain the concept of gram equivalent weight.
H2SO4 is a diprotic acid, so half of a mole of H2SO4 can donate as many H+ as a mole of a normal acid (like HCl). The gram equivalent weight is how much of the polyprotic acid is needed to act like a 1N acid, and in this example, is equal to half of the molecular weight of H2SO4.
Polyvalent or polyprotic acids and bases are able to act as an acid or base multiple times per one molecule. To account for this, acids’ strengths are often measured in terms of normality (N), where an acid with the strength of 1 N will donate 1 mole worth of H+ per liter of acid added. how much 1 M HCl would need to be added to a solution to have the same effect as adding 0.300 L of 2.5 N acid?
0.75 L
Lewis’s theory of acids covers many different compounds that cannot be considered Bronsted-Lowry acids. Which of the following is a Bronsted-Lowry acid, but not a Lewis acid?
A) I2
B) None of the above
C) HF
D) H2O
None of the above. Any correct answer must have a hydrogen to donate, and cannot be able to accept any electron pairs. Formally, this is not possible, since donating the hydrogen means accepting the electron pair that used to make up the covalent bond with the hydrogen. Since all Bronsted-Lowry acids are Lewis acids, no compound can be a correct answer.
Over time, multiple theories describing acids and bases have been developed to accommodate new findings. Whose definition of acids and bases relies on the ionization of water into H+ and OH-, respectively?
The Arrhenius definition of acids and bases states that they are compounds that, when in aqueous solutions, will ionized water to form H+ and OH-.
A researcher prepares a solution with an OH- concentration of 10-8 M by adding a weak electrolyte. Which of the following did the researcher likely add to the solution?
A) NaOH
B) HCl
C) NH3
D) H2CO3
D) H2CO3.
A weak electrolyte does not fully dissociate in solution, but will dissociate somewhat. Weak acids and bases are often examples of weak electrolytes. The solution has less [OH-] than regular water. This means that it is an acidic solution, and an acid was added. H2CO3 is a weak acid, and therefore a weak electrolyte, making it the best answer.
Weak acids partially react with water to form hydronium, or H3O+. There are several ways to represent the degree to which a weak acid (HA) reacts. Which of the following is not one of those ways?
A) [H3O+][A-]/[HA]
B) pH
C) Acid ionization constant
D) Acid dissociation constant
B) pH