Biotech Final Study Guide
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Volume Range and tip size of p100
VR: 100 - 1000
TS: 1000
Volume Range and tip size of p200
VR: 20 - 200
TS: 200
Volume Range and tip size of p20
VR: 20 - 200
TS: 200
Volume Range and tip size of p10
VR: 0.5 - 10
TS: 10
DNA Stands for...
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid
Where are DNA and RNA found?
packed tightly within chromosomes within the nucleus.
DNA is made of...
repeating subunits called nucleotides
Three parts of a nucleotide
PHOSPHATE
DEOXYRIBOSE (sugar)
BASE (A,T,G,C)
Base-pairing Rule
Adenine <==> Thymine
Guanine <==> Cytosine
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
DNA is "naked"
"circular" chromosome
Eukaryote DNA
Eukaryotic DNA is wound around histone proteins and organized into "supercoiled" linear chromosomes found in the nucleus
Eukaryote
organism whose cells contain a nucleus
Is E. coli gram positive or gram negative?
gram negative
Parts of E. Coli cells that have Genes
Genome (or chromosome)
Plasmid
DNA Plasmid
separate from the bacterial chromosome
replicates independently
the part that gets changed in genetically engineered E coli
transferable and mobile - similar to a memory stick
3 main Plasmid parts
ORI - Origin of replication - Ensures plasmid replicates independently and effectively
TRAIT GENE - This is the DNA code that enables the engineered E coli to make something new
SELECTION GENE - Allows the engineered E coli to grow in the presence of a selection agent e.g. an antibiotic
DNA Replication
the process of making a copy of DNA (cell division)
DNA Transcription
the process by which DNA makes template of RNA with the use of polymerase
SEMI-CONSERVATIVE
half of the old strand is saved
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer using the parental DNA strand as a template.
Flow of information in a cell
DNA-->RNA-->Protein
CONSERVATIVE
the DNA is left unchanged
Where does prokaryotic transcription occur?
transcription occurs in the cytoplasm
Where does eukaryotic transcription occur?
nucleus
DNA vs. RNA
deoxyribose sugar vs. ribose sugar, thymine vs. uracil
double strand vs. single strand
How does RNA make a protein?
RNA tells the ribosomes what protein to build.
Every 3 letters (AAA) specifies a single amino acid.
Proteins are made of many amino acids.
Non- polar amino acids have...
+ charge
Polar amino acids have...
- charge
4 levels of protein structure
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Primary Protein Structure
sequence of amino acids
Secondary Protein Structure
occurs when the sequence of amino acids are linked by hydrogen bonds
Protein is not active yet
Tertiary Protein Structure
Tertiary structure occurs as the protein finishes folding
Proteins are usually functional at this point.
Hydrophobic collapse is the major driving force behind formation of the tertiary structure.
Hydrophobic Collapse
Occurs as the hydrophobic amino acids collapse away from the water and into the interior of the tertiary structure of the protein.
Quaternary Structure
Quaternary structure occurs when multiple proteins come together to form a protein complex.
Not all proteins are involved in quaternary structures.
Substrate
Reactant that is changed by the enzyme
Active Site
Where the substrate binds.
Matches the shape and chemical properties of the substrate
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
When the enzyme and substrate are bound together
Enzyme
biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in the body so they go fast enough to maintain homeostasis
What is the difference between cells and bacteria in the context of this experiment? (Canvas IT Lab)
cells are not colorful, bacteria are
When labeling your plates, S. stands for (Canvas IT Lab)
Selective
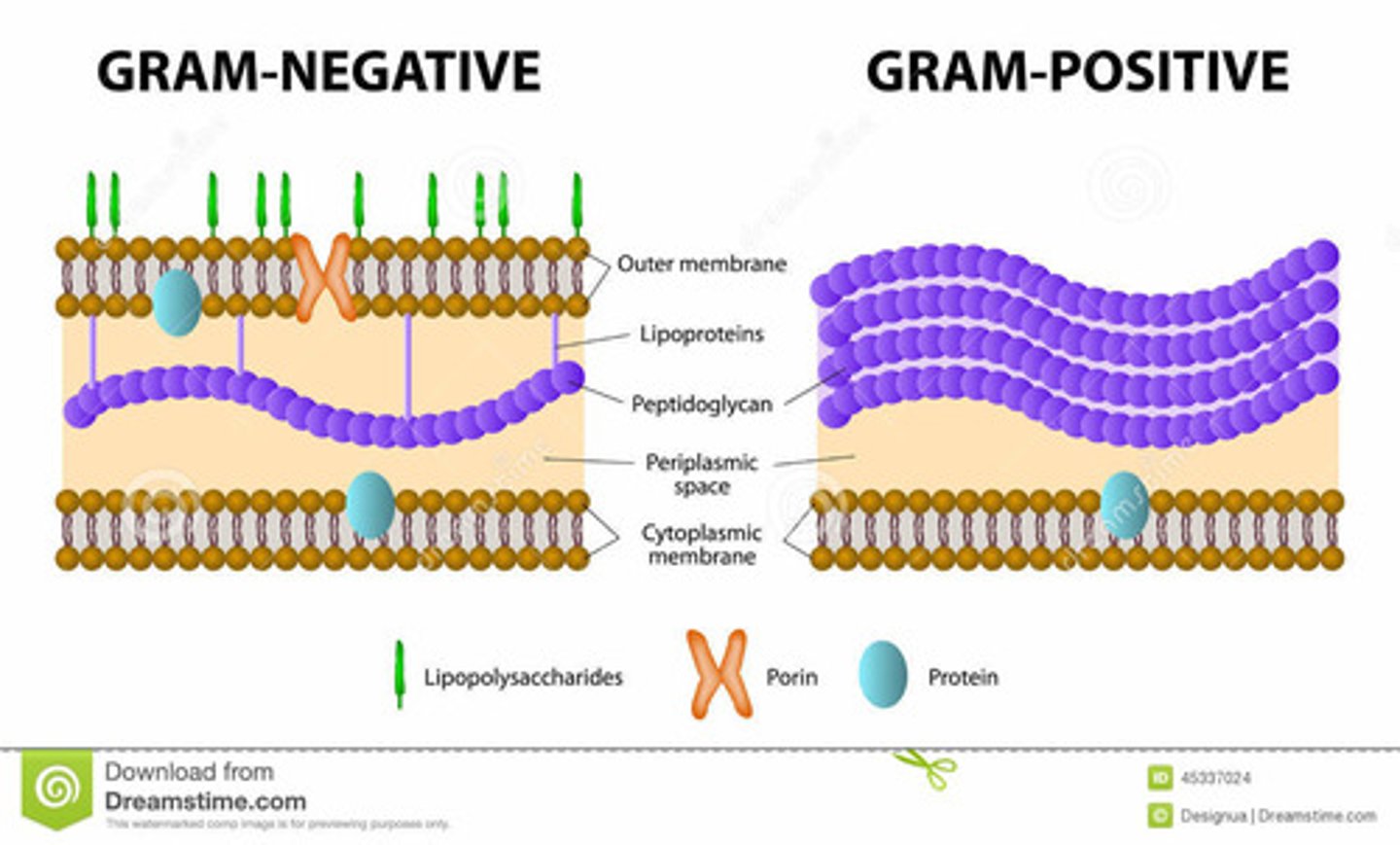
Gram-Positive cell wall vs Gram-Negative cell wall
Gram-Positive has no cell wall, but a thicker Peptidoglycan Layer, which Gram-Negative has thin Peptidoglycan Layer but thick cell wall.
Which is Gram-Positive cell wall and which is Gram-Negative
Left is Gram-Negative and right is Gram-Positive
5 basic Modes Antibiotic can take against bacterial cells
1) Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis.
2) Inhibition of Protein Synthesis (Translation)
3) Alteration of Cell Membranes.
4) Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis.
5) Breakdown of Enzymes
Narrow spectrum antibiotics
Effective against specific bacteria (ex. only Gram-Positive or only Gram-Negative)
Broad spectrum antibiotics
affect a broad range of gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria
How do bacteria reproduce?
Asexually (binary fission)
Key Steps in the Gram Stain Process
1) Crystal Violet (Primary Stain)
2) Iodine (Mordant)
3) Alcohol (Decolorizer)
4)Safranin(Secondary/Counter Stain):
Why is the Gram Stain Important?
The Gram stain helps microbiologists figure out what type of bacteria they're dealing with. This is super important because different bacteria types are affected differently by antibiotics.
What color is gram positive bacteria stained?
purple
What color is gram negative bacteria stained?
pink
Point mutations
chemical changes in just one base pair of a gene
Silent mutation
alters a base but does not change the amino acid
Frameshift Mutations
base pair insertions and deletions