Unit 3 - Economic Models: Trade-Offs and Trade
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
In general, the higher the degree, the higher the salary. So why aren’t more people pursuing higher degrees?
Choices and tradeoffs
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
A diagram that shows the productively efficient combinations of two products that an economy can produce given the resources it has available.
Productive efficiency
when it is impossible to produce more of one good or service without decreasing the quantity produced of another good or service
Productively inefficient
inside the PPF curve, and thus not all resources are being used.
Infeasible
Any combinations outside the frontier
Outward shift of the PPF
-An increase in factors of production
-Better technology
An increase in factors of production
resources used to produce goods and services.
Better technology
the technical means for producing goods and services.
Factors of production
Land, labor, physical capital, human capital
Land
includes natural resources, such as mineral deposits, oil, natural gas, water, and actual land acreage.
Labor
is the mental and physical abilities of the workforce.
Physical capital
is manufactured items used to produce other goods and services.
Human capital
is the educational achievements and skills of the labor force (which increase labor productivity).
What does PPF show?
tradeoff between devoting social resources to healthcare and devoting them to education
PPF is downward sloping, meaning:
the only way society can obtain more education is by giving up some healthcare.
The Slope of PPF
the opportunity cost (of good on the x-axis)
Not all resources
are suited to every task
When does opportunity cost
as you apply resources to tasks for which they are ill-suited and leave other areas neglected.
Law of diminishing returns
as additional increments of resources to producing a good or service are added, the marginal (additional) benefit from those additional increments will decline.
Marginal Analysis
Examining the benefits and costs of choosing a little more or a little less of a good.
Law of diminishing marginal utility
as a person receives more of a good, the marginal (additional) utility from each additional unit of the good declines
Utility
satisfaction, usefulness, or value one obtains from consuming goods and services.
Sunk Cost
costs that were incurred in the past and cannot be recovered.
The lesson of sunk costs
The lesson of sunk costs is to ignore the past errors and make decisions based on what will happen in the future.
Why is sunk costs not an opportunity cost?
Sunk costs exists whether you make your choice or not, so it is not an opportunity cost.
When weighing costs and benefits, a good decision maker ignores
Sunk Costs
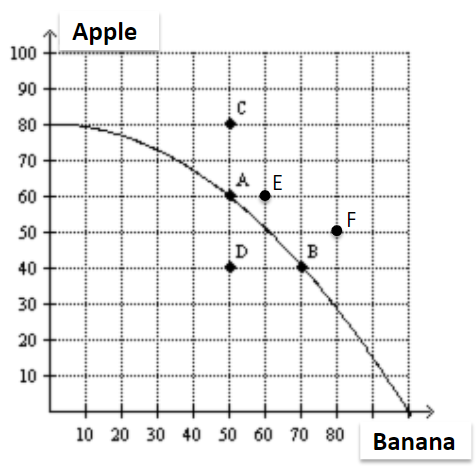
It is possible for this economy to produce:
a. 60 apples and 60 bananas. (E)
b. 60 apples and 50 bananas. (A)
c. 80 apples and 50 bananas. (F)
d. All of the above.
B
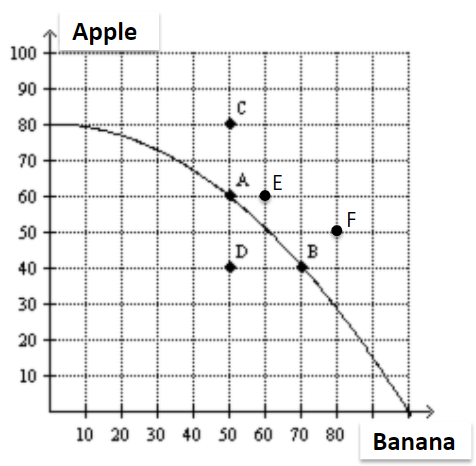
Inefficient production is represented by which point(s)?
a. A, B
b. C
c. C, D
d. D
D
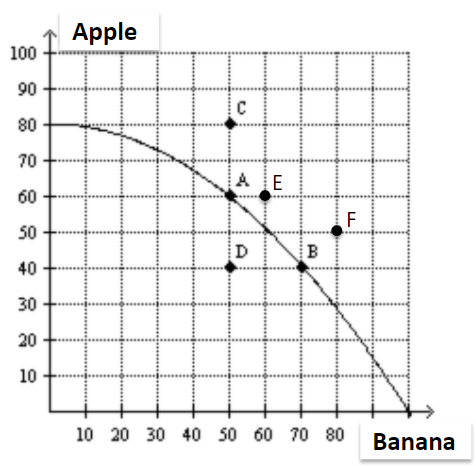
It is not possible for this economy to produce at point
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
C
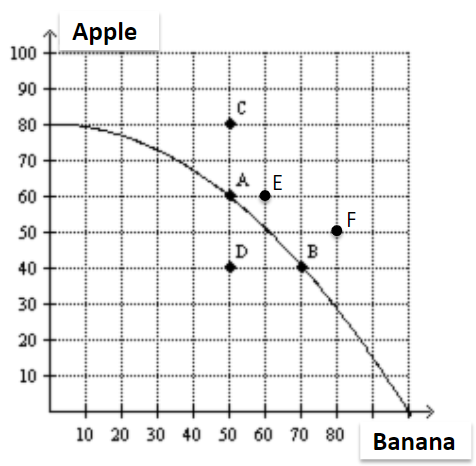
The opportunity cost of this economy moving from point A to point B is
a. 20 apples.
b. 20 bananas.
c. 20 apples and 20 bananas.
d. 60 apples.
A
Theory of Comparative Advantage
It makes sense to produce the things you’re especially good at producing… and buy everything else from others.
When different countries have different opportunity costs…
It makes sense to specialize and trade.
A country has a comparative advantage in producing a good or service if…
its opportunity cost of producing the good or service is lower than other countries’.
An individual has a comparative advantage in producing a good or service if…
his or her opportunity cost of producing the good or service is lower than for other people.
Through specialization and trade, two countries…
produce more and consume more than if they were self-sufficient
Absolute Advantage
-When one country can use fewer resources to produce a good compared to another country;
-When a country is more productive compared to another country.
Comparative Advantage
When a country can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost in terms of other goods.
Mutually Beneficial Trade
Even when one country has an absolute advantage in all goods and another country has an absolute disadvantage in all goods, both countries can still benefit from trade.
What does trade allow each country to do?
To take advantage of lower opportunity costs in the other country.
What do gains from international trade, on both sides, result from?
Pursuing comparative advantage and producing at a lower opportunity cost.
If Texia specializes in food, it can produce 1,000 units of food and 0 units of clothing this year. If it specializes in clothing, it can produce 500 units of clothing and 0 units of food. This year Urbania can produce either 500 units of food and 0 units of clothing or 200 units of clothing and 0 units of food. (assume linear production possibility frontiers)
_______has the absolute advantage in the production of clothing and ________has the absolute advantage in the production of food.
Texia; Texia
Texia; Urbania
Urbania; Texia
Urbania; Urbania
1
If Texia specializes in food, it can produce 1,000 units of food and 0 units of clothing this year. If it specializes in clothing, it can produce 500 units of clothing and 0 units of food. This year Urbania can produce either 500 units of food and 0 units of clothing or 200 units of clothing and 0 units of food. (assume linear production possibility frontiers)
_______has the comparative advantage in the production of clothing and ________has the comparative advantage in the production of food.
Texia; Texia
Texia; Urbania
Urbania; Texia
Urbania; Urbania
2
If a country specializes according to its own comparative advantage and then trades with other nations:
it will operate at a point inside its production possibilities frontier.
it can consume at a higher level than the domestic production possibilities frontier.
its production possibilities frontier will shift or rotate inward.
it can consume at the same level as the domestic production possibilities frontier.
2
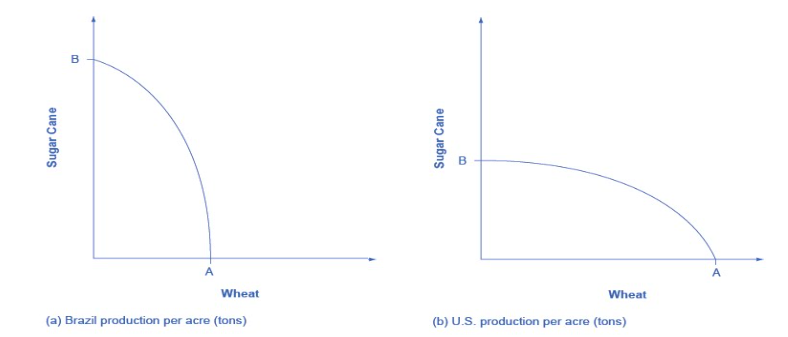
Explain opportunity costs and comparative advantages
The US’ PPF is flatter than the Brazil’s PPF:
The opportunity cost of wheat in terms of sugar cane is lower in US than in Brazil. The US has comparative advantage in wheat
The opportunity cost of sugarcane in terms of wheat is lower in Brazil. Brazil has comparative advantage in sugar cane.
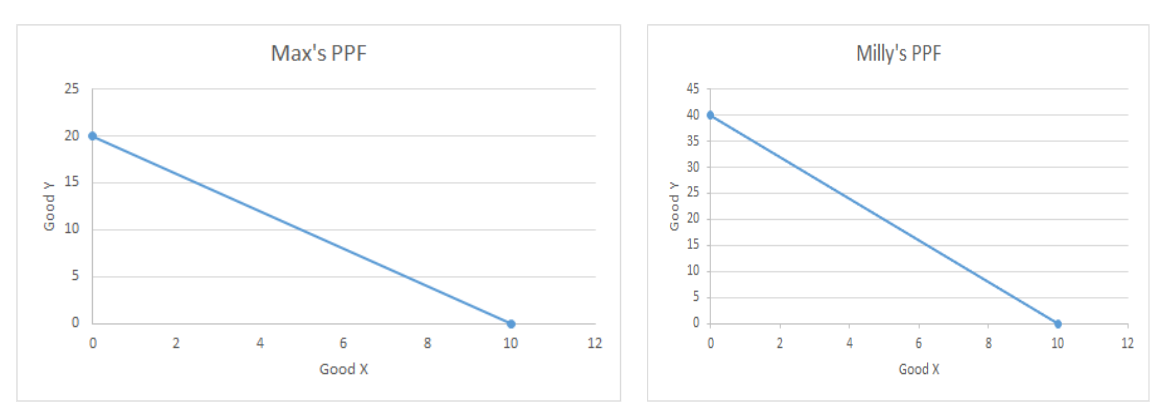
Who has absolute advantage in Y? X?
Y: Milly, X: Neither
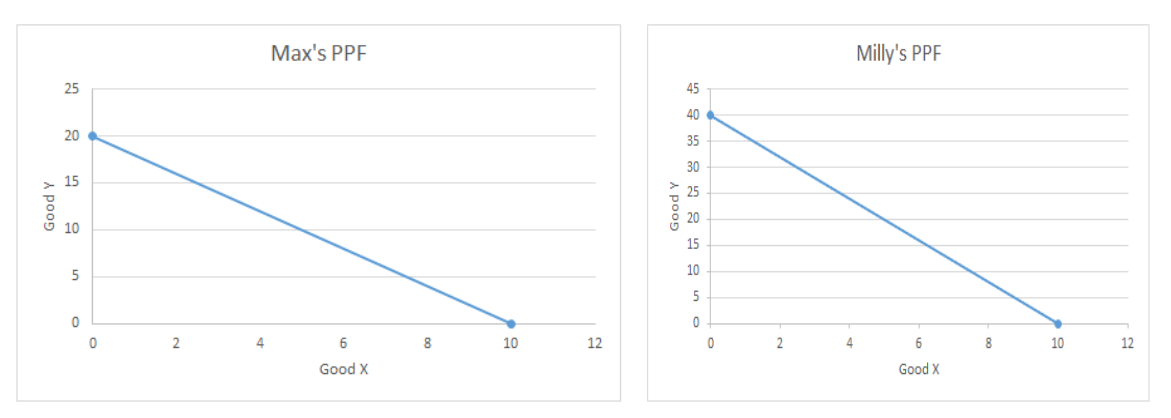
Who has comparative advantage in Y? X?
Y: MIlly, X: Max
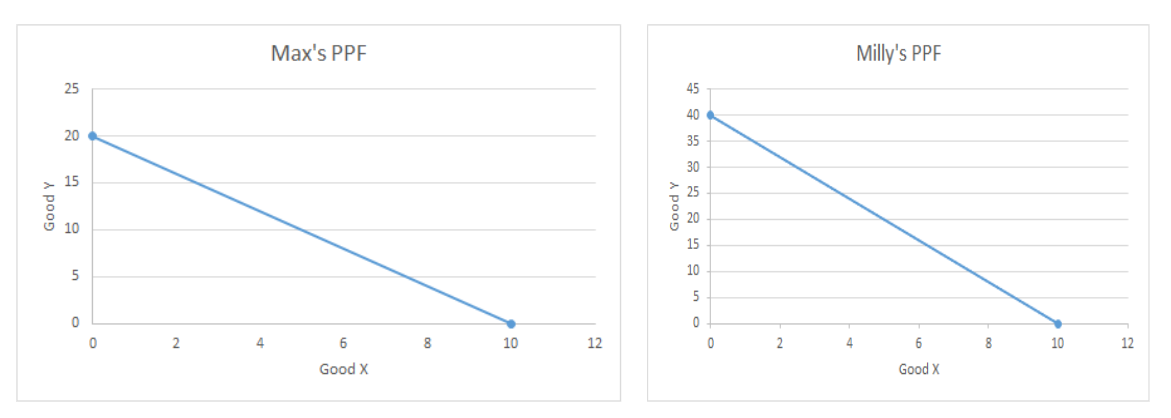
In terms of trade of 5x for 25y is proposed, will max be better off? Milly?
Max!