Comprehensive Anatomy Test #3 (Upper Limb, Skull/Face, Neck, Nose/Oral Cavity/Mouth, Eye/Ear, and Brain/CN)
1/1023
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1024 Terms
pectoral girdle
the upper limb is connected to the axial skeleton via this
medial (sternal) end
end of the clavicle that is triangular
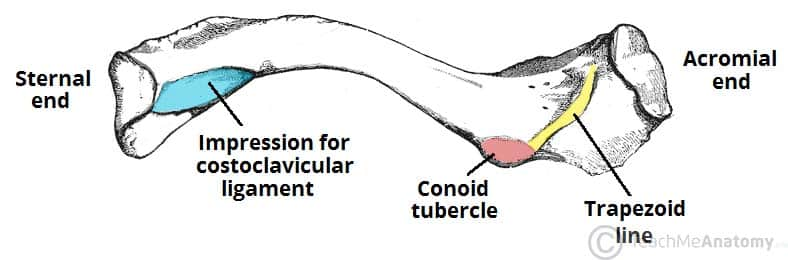
lateral (acromial end)
end of the clavicle that is flattened
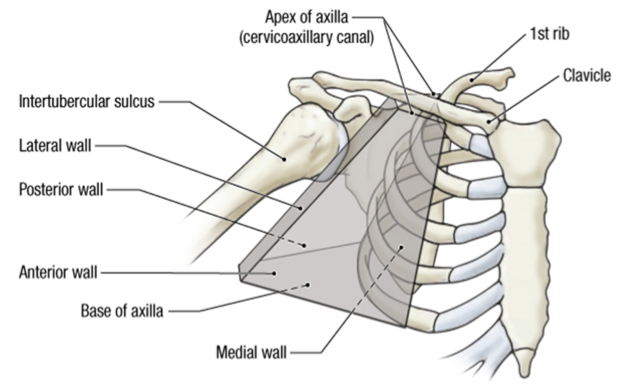
cervico-axillary canal
bony boundary for the passageway into the upper limb
2nd-7th ribs
ribs that the scapula lay over
ulna
arm bone that does NOT articulate with the carpals
ulna
arm bone that works in the elbow
radius
arm bone that rotates to pronate/supinate
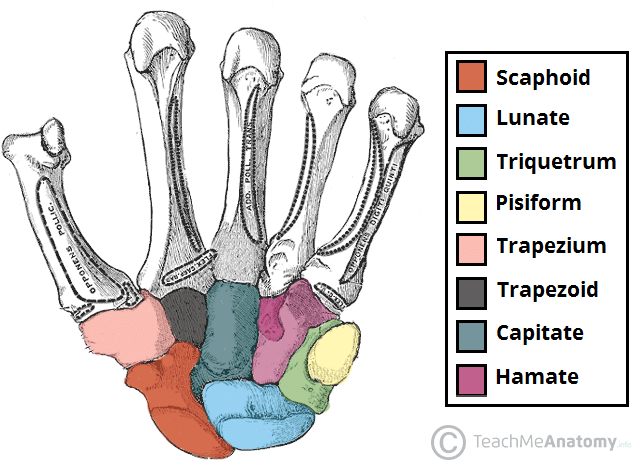
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform
proximal carpals (lateral to medial)
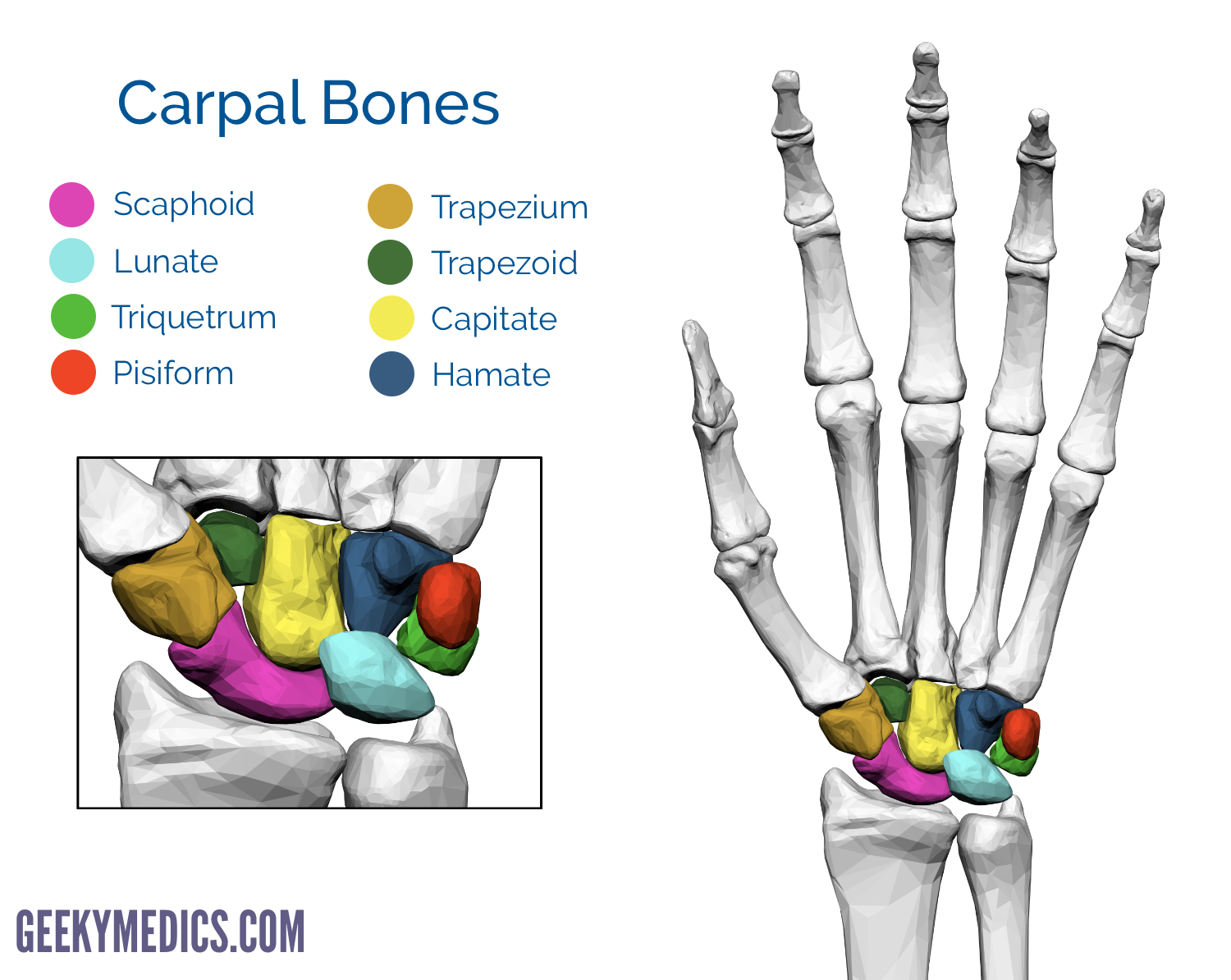
trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
distal carpals (lateral to medial)
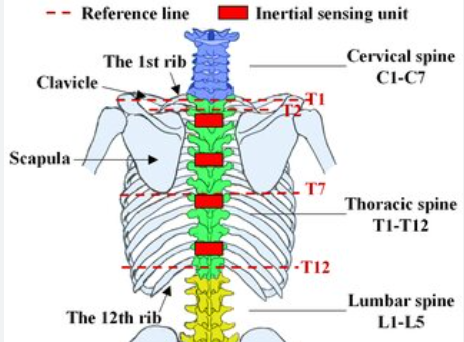
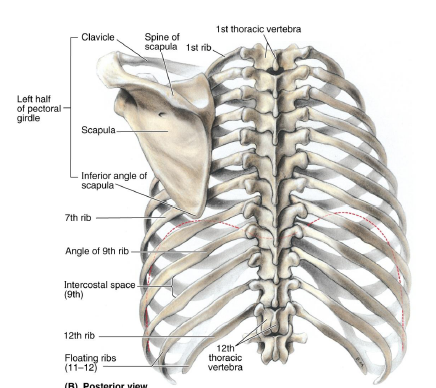
T2
superior angle of the scapula lies at
T3
medial end of scapular spine is at
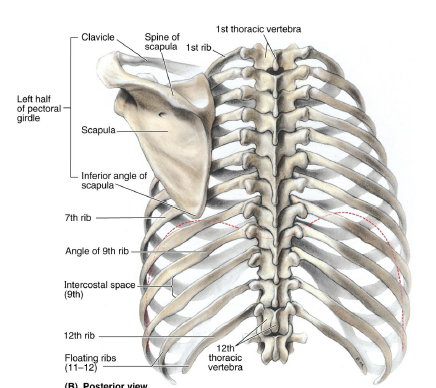
T7
inferior angle of scapula is at
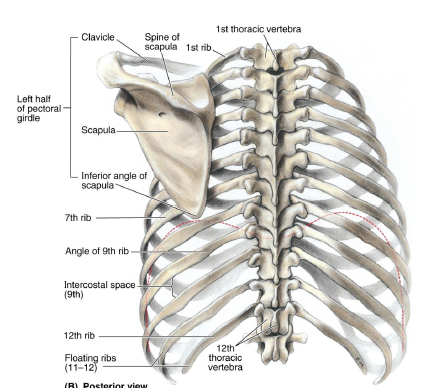
T3-T7
medial border of scapula runs along this range of ribs
FOOSH or direct fall on the shoulder
clavicle fracture most common mechanism
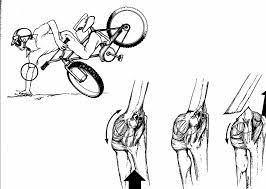
drop
in a clavicle fracture, the shoulder will ____ because the trapezius cannot lift the lateral fragment to compensate for the sternocleidomastoid pulling the medial fragment superior
clavicle fracture
SCM pulls medial fragment superior in the mechanism of this injury
clavicle fractures
trapezius can’t lift the lateral fragment causing the shoulder drop in to this clavicle
clavicle fractures
greenstick fracture is this type of fracture, most commonly found in children
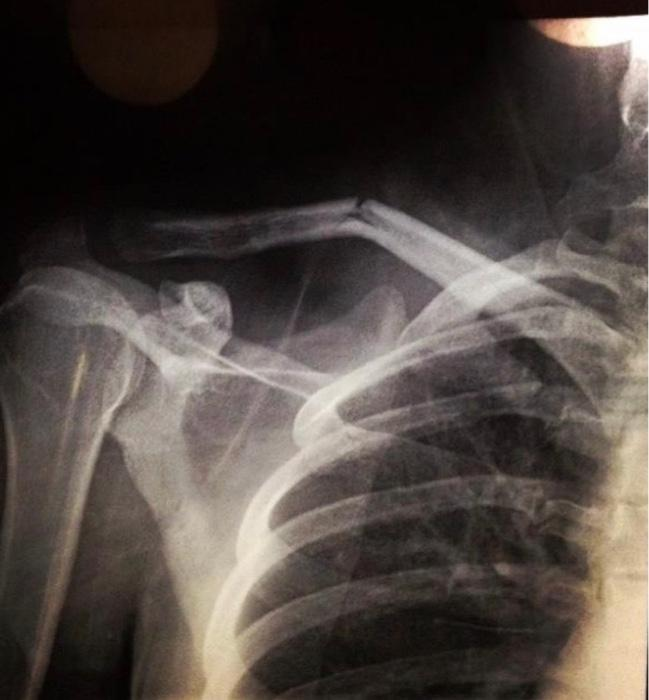
rare
scapular fractures are
scapular fractures
fractures don’t usually require surgery due to support of multiple muscles that hold scapula in place
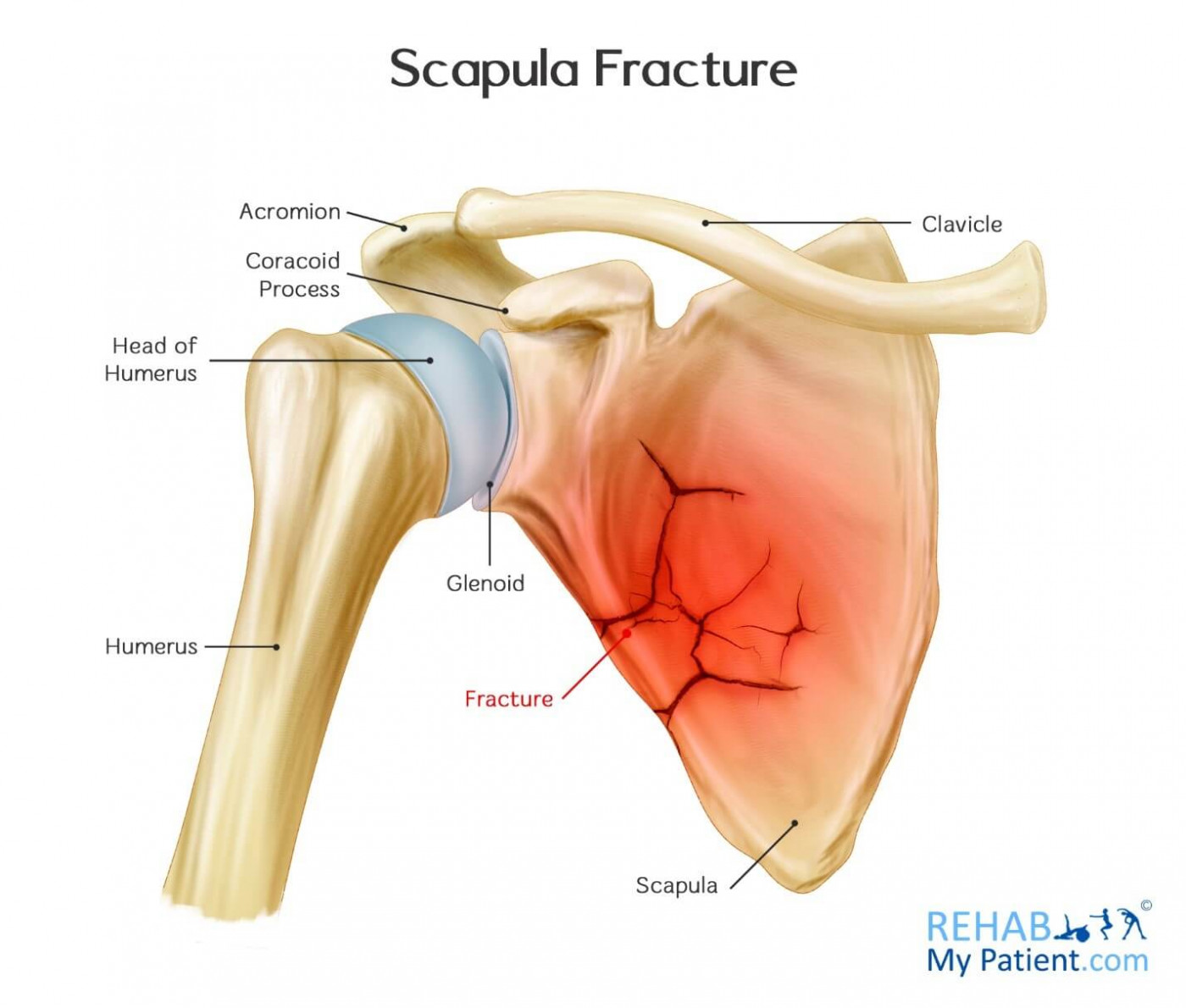
scapular fracture
results from severe trauma like a pedestrian vs car
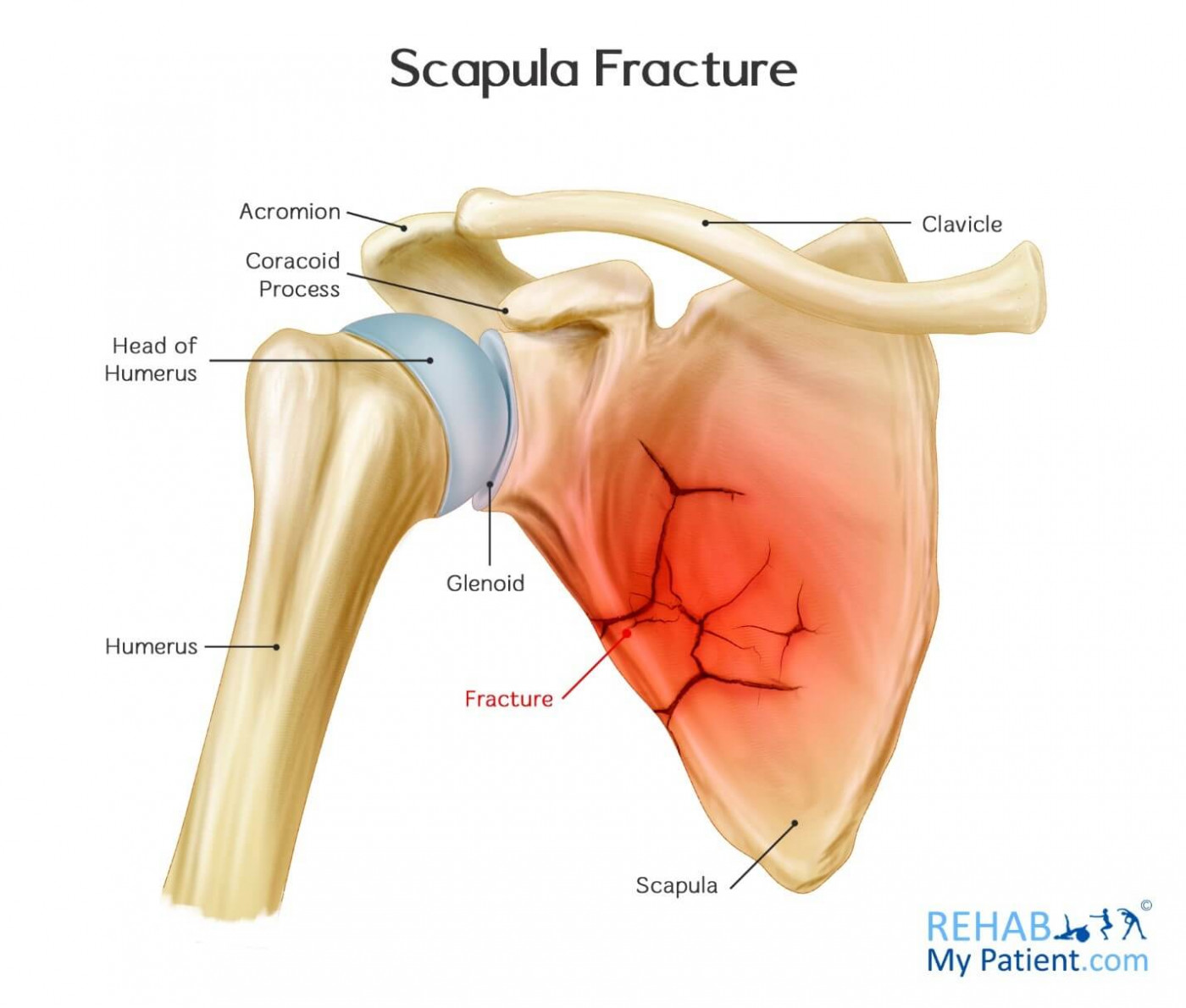
scapular fractures
patients will almost always have rib fractures and pulmonary contusions
humeral fractures
commonly occur at the surgical neck of the humerus
FOOSH
radial and ulnar fractures mechanism of injury
Colles fracture; dinner fork
distal 2 cm transverse fracture of radius with dorsal displacement and will have this type of_____ deformity
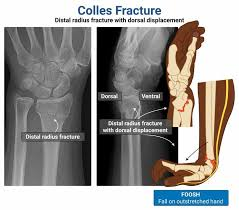
Colles fracture
dorsal displacement of radius (distal 2 cm transverse fracture)
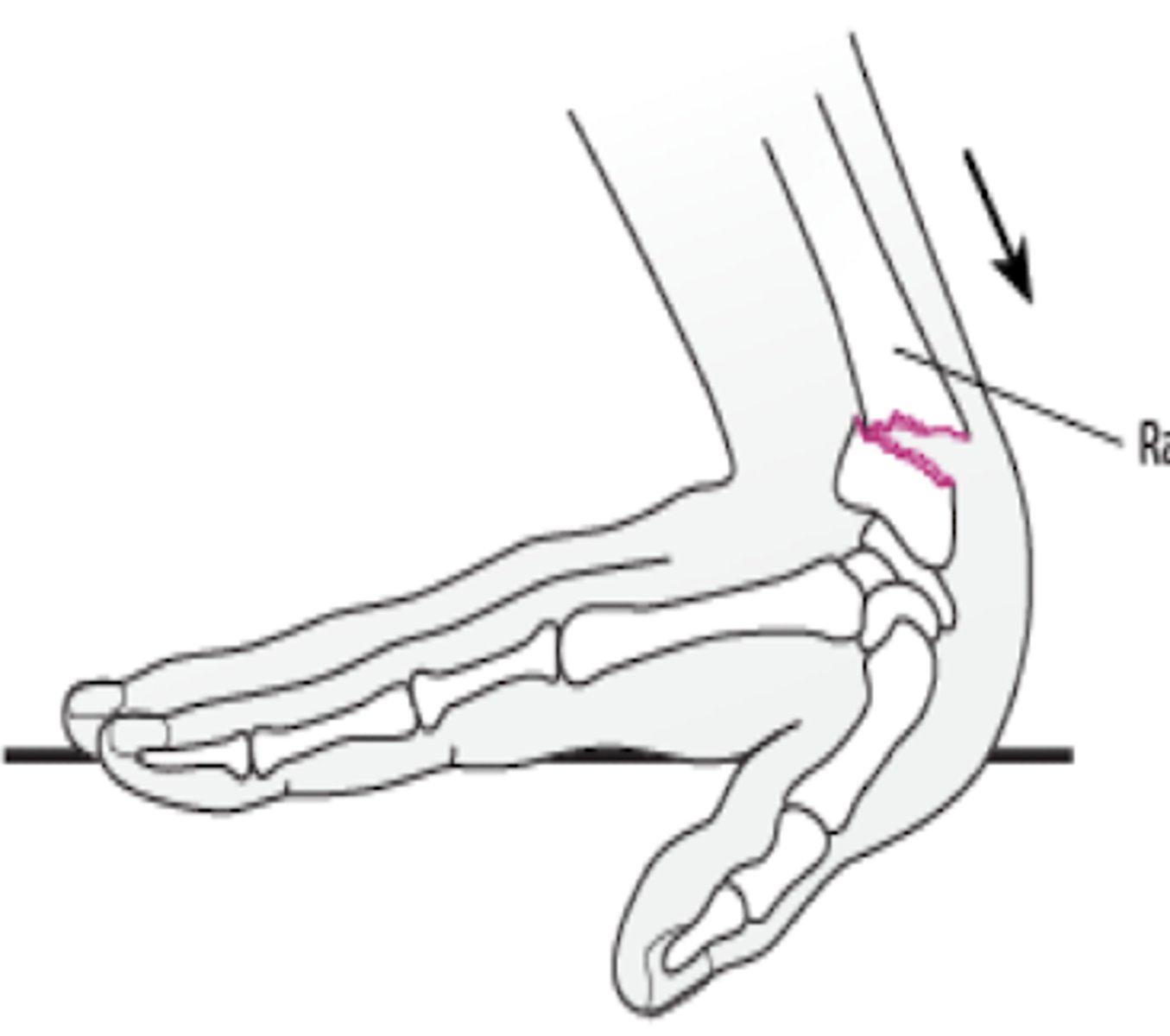
Smith fracture
volar displacement of radius (distal 2 cm transverse fracture)
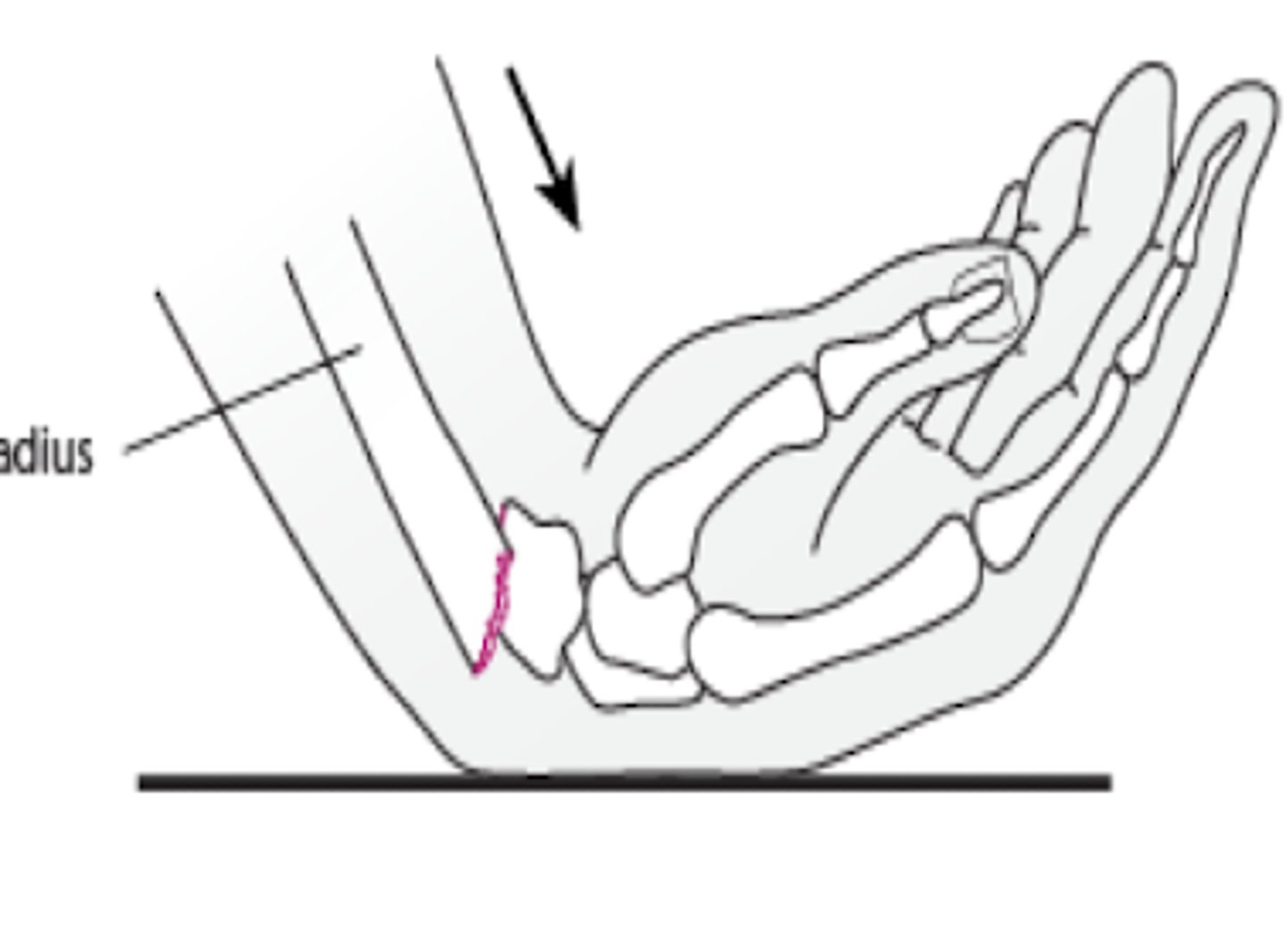
Smith fracture
volar displacement of radius
Scaphoid fracture
may result in avascular necrosis
scaphoid fracture
commonly misdiagnosed as a sprained wrist (doesn't show on X ray)
scaphoid fracture
million dollar break, results in snuffbox tenderness
Scaphoid fracture
commonly occurs when the patient falls on the palm with the thumb abducted
results in snuffbox tenderness
radial artery
artery affected in Scaphoid fracture
pectoral fascia
invests pectoralis major muscle, continuous with the abdominal fascia; joins the axillary fascia in the armpit
clavipectoral fascia
deep to the pectoral fascia; encloses subclavius and pectoralis minor
brachial fascia
covers the arm and extends to the antebrachial fascia of the forearm
cephalic and basilic veins
primary superficial veins of the upper limb
cephalic vein
lateral superficial vein
clavipectoral triangle
point at which the cephalic vein dives to join the axillary vein
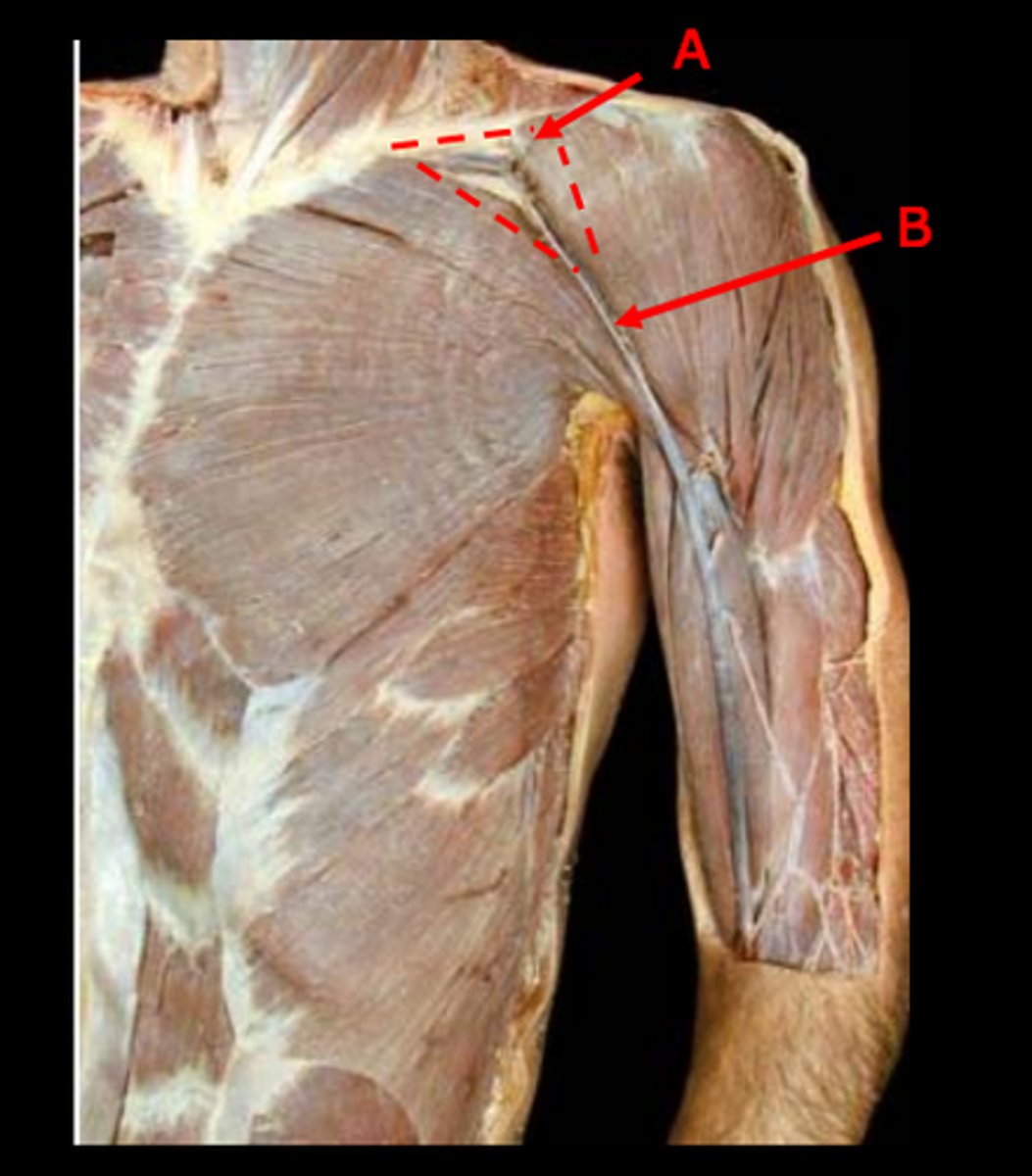
cephalic vein
vein that ascends lateral to biceps brachii, inferior to deltoid
median cephalic and basilic vein
alternative venous drainage to the medial cubital vein in about 30% of people
basilic vein
medial superficial vein is termed
brachial
the basilic vein dives deep in the ____ region
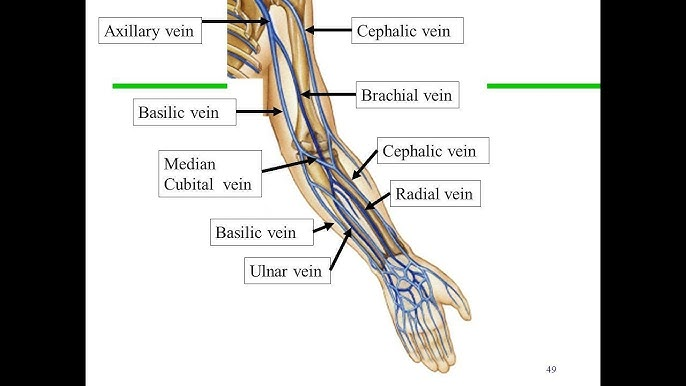
median cubital vein
vein that connects the cephalic and basilic veins
ulnar, radial, and brachial
primary deep veins of the upper limb
deep veins
veins that go through the antecubital fossa separately
brachial vein
the ulnar and radial veins fuse into this vein
deep veins
ulnar, radial, brachial veins
lymphatic
drainage that passed through cubital lymph nodes and humeral axillary lymph nodes
cervical plexus
shoulder cutaneous innervation is from this plexus
C6
thumb dermatome
C7
middle finger dermatome
C8
pinky finger dermatome
the pectoralis major
this muscle of the pectoral and scapular region has two heads
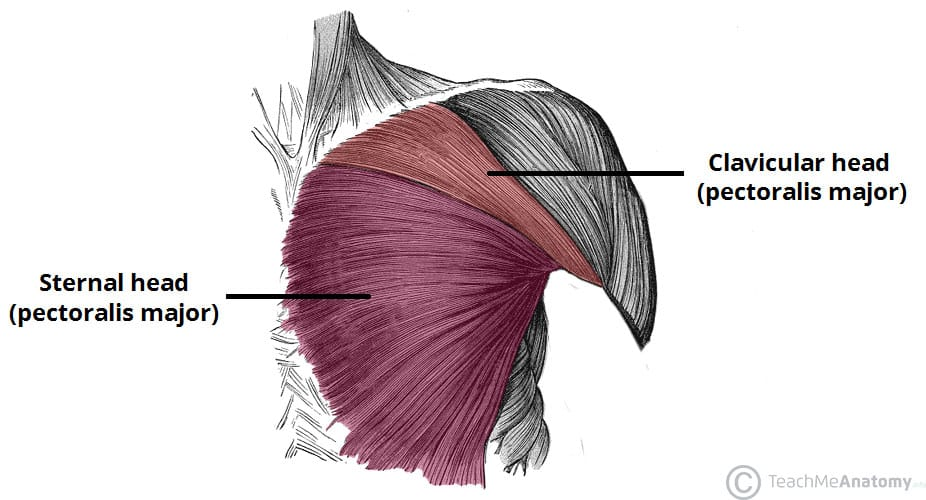
clavicular and sternocostal
pectoralis major two heads
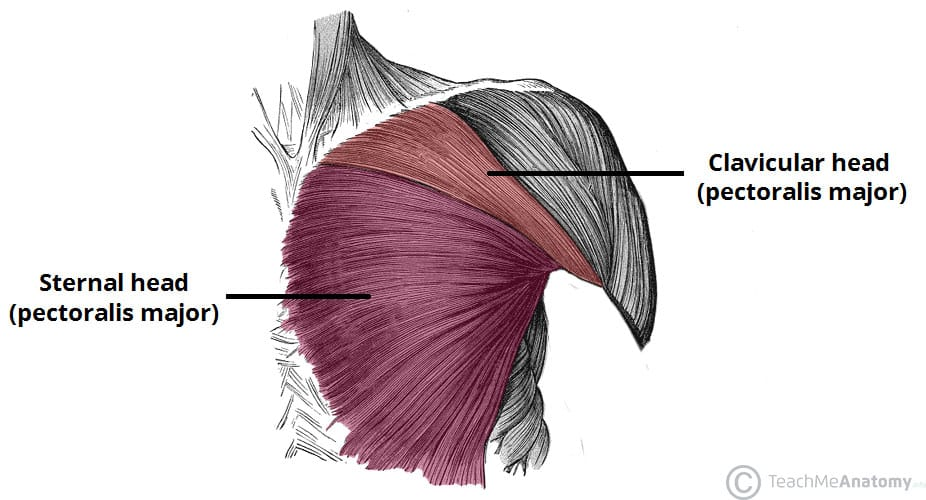
anterior
pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, subclavius, serratus anterior
_______ axio-appendicular muscles move the pectoral girdle; what are their names
posterior; superficial, deep, scapulohumeral
______ axio-appendicular muscles attach the appendicular skeleton to the axial skeleton; name the three groups
trapezius, latissimus dorsi
superficial posterior axio-appendicular muscles
levator scapulae, rhomboids
deep posterior axio-appendicular muscles
deltoid, teres major, rotator cuff
scapulohumeral muscles
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
rotator cuff muscles
triangle of auscultation
small gap in musculature allowing great access to lung sounds
latissimius dorsi, scapula, trapezius
borders of the triangle of auscultation; have patient protract to increase size
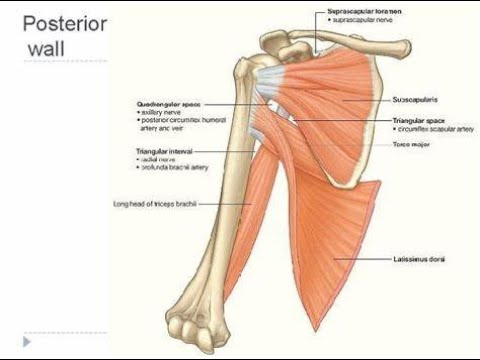
axillary nerve
the __________ wraps posteriorly around the surgical neck of the humerus and is commonly injured because of fractures and IM shots
axillary nerve
the ______ is injured if symptoms pertain to the deltoid or skin on the outside of the arm
pectoralis major and minor, fascia
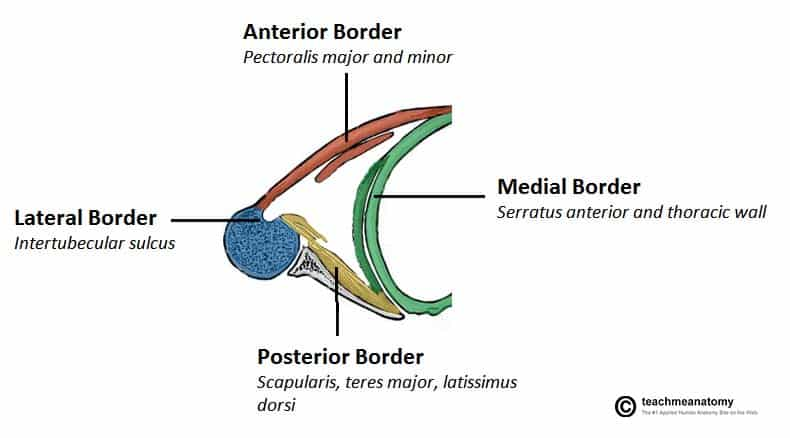
axilla anterior wall is comprised of these muscles
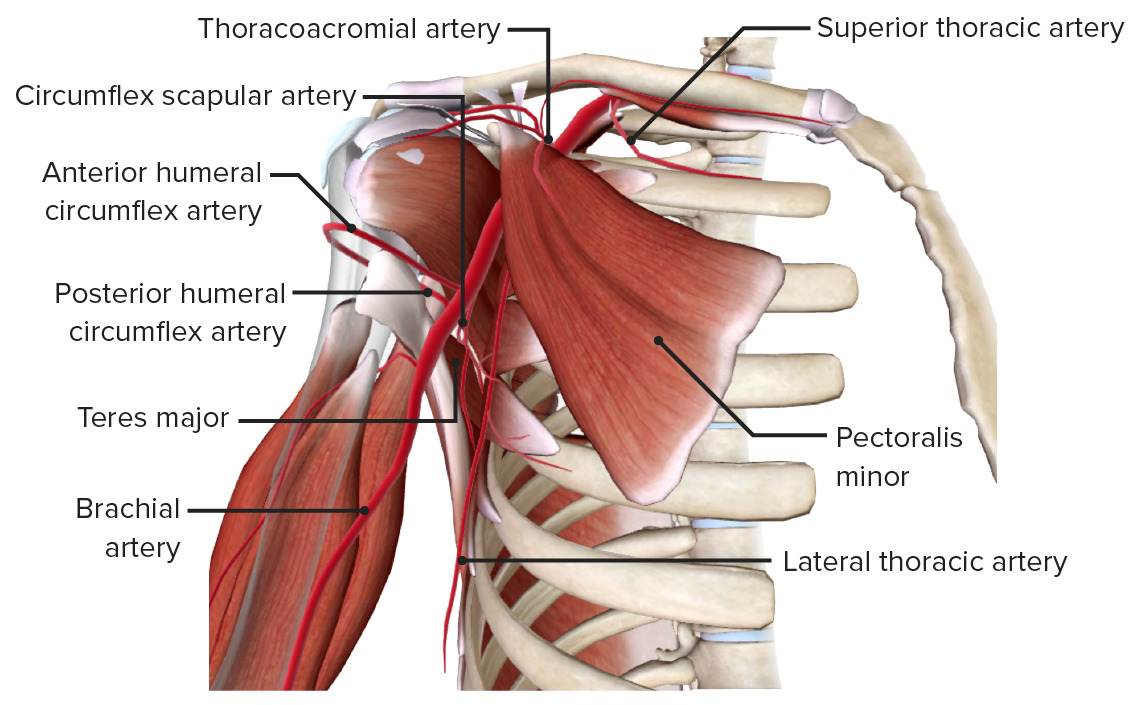
scapula, subscapularis, teres major, and latissimus dorsi
axilla posterior wall muscles
thoracic wall (ribs 1-4 and intercostals)
axilla medial wall
humerus
axilla lateral wall contains this singular bone
cervico-axillary canal
the apex of the axilla is also known as the
1st rib, clavicle, superior edge of scapula
boundaries of the cervico-axillary canal/apex of the axilla
teres major
landmark at which the axillary artery turns into the brachial artery
1st rib
landmark at which the subclavian artery turns into the axillary artery
C5-C8 and T1 spinal nerves
roots of the brachial plexus
superior (C5, C6), middle (C7), inferior (C8, T1)
trunks of the brachial plexus
anterior and posterior
each trunk of the brachial plexus divides into _____ and _____ divisions
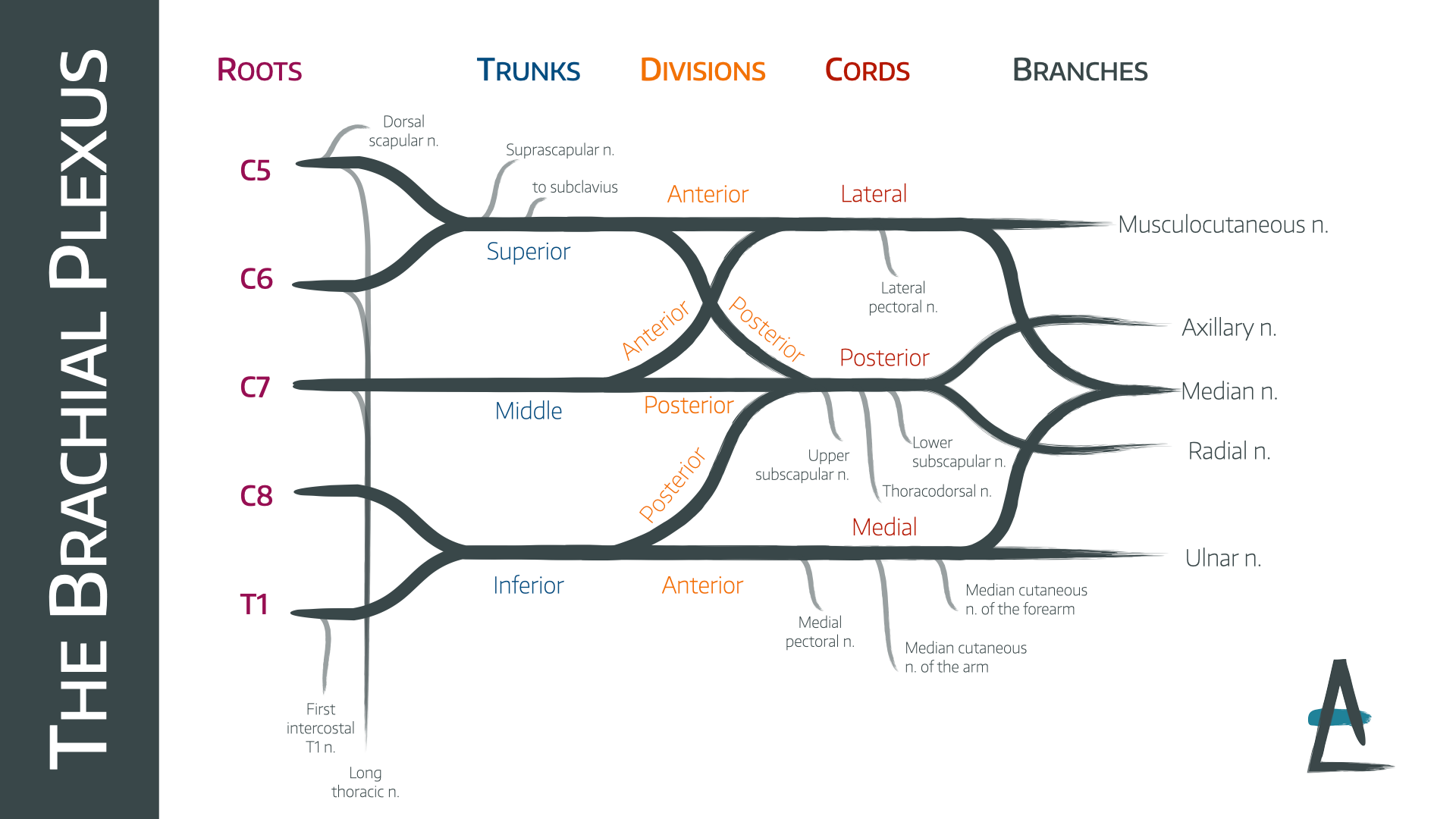
anterior division (of brachial plexus)
this part of the brachial plexus supplies the anterior upper limb (flexors)
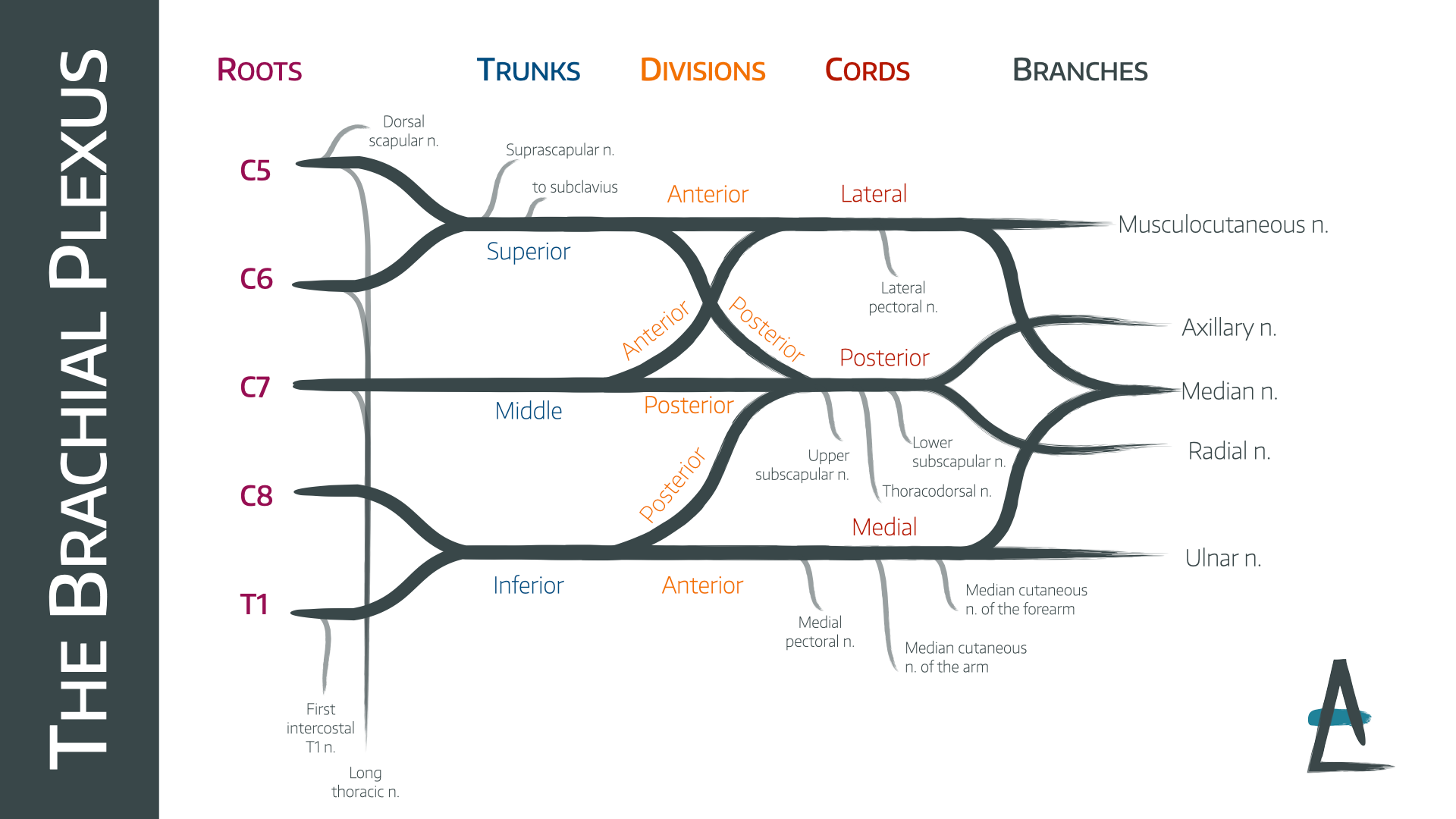
posterior division (of brachial plexus)
this part of the brachial plexus supplies the posterior upper limb (extensors)
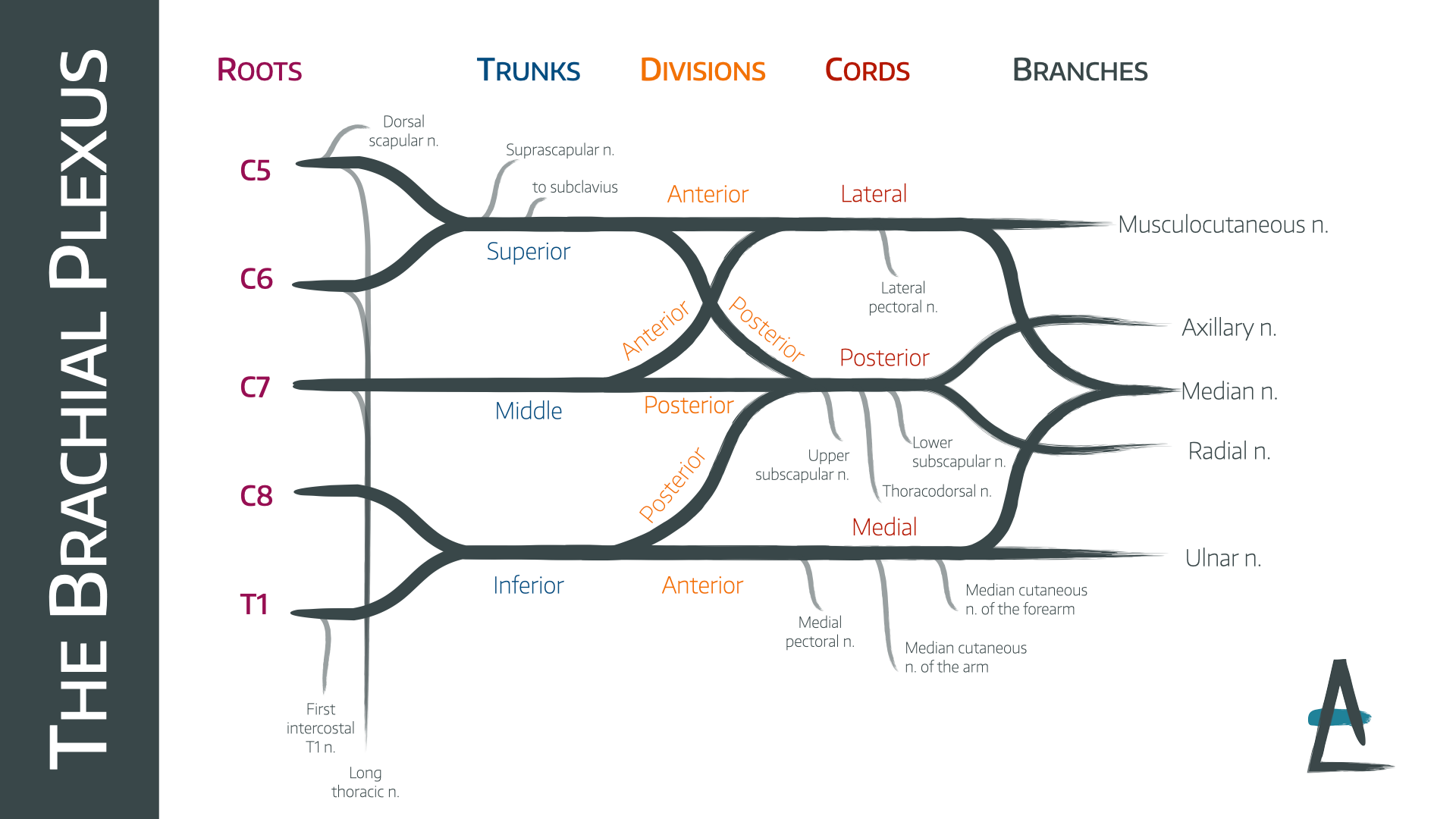
lateral cord
anterior divisions of superior and middle trunks form the _____
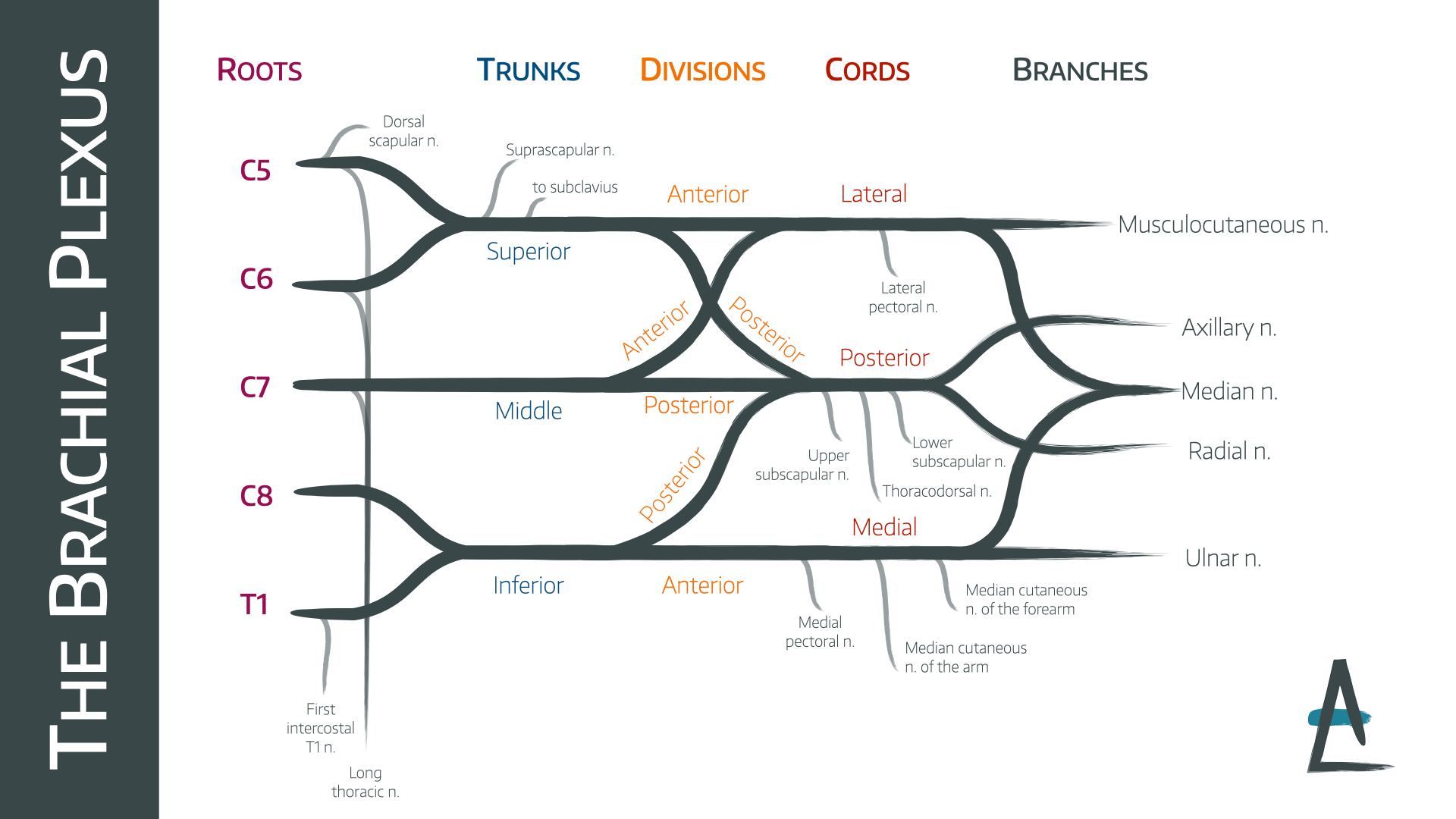
medial cord
anterior division of the inferior trunk forms which cord _________
posterior cord
posterior divisions from all 3 trunks form which cord
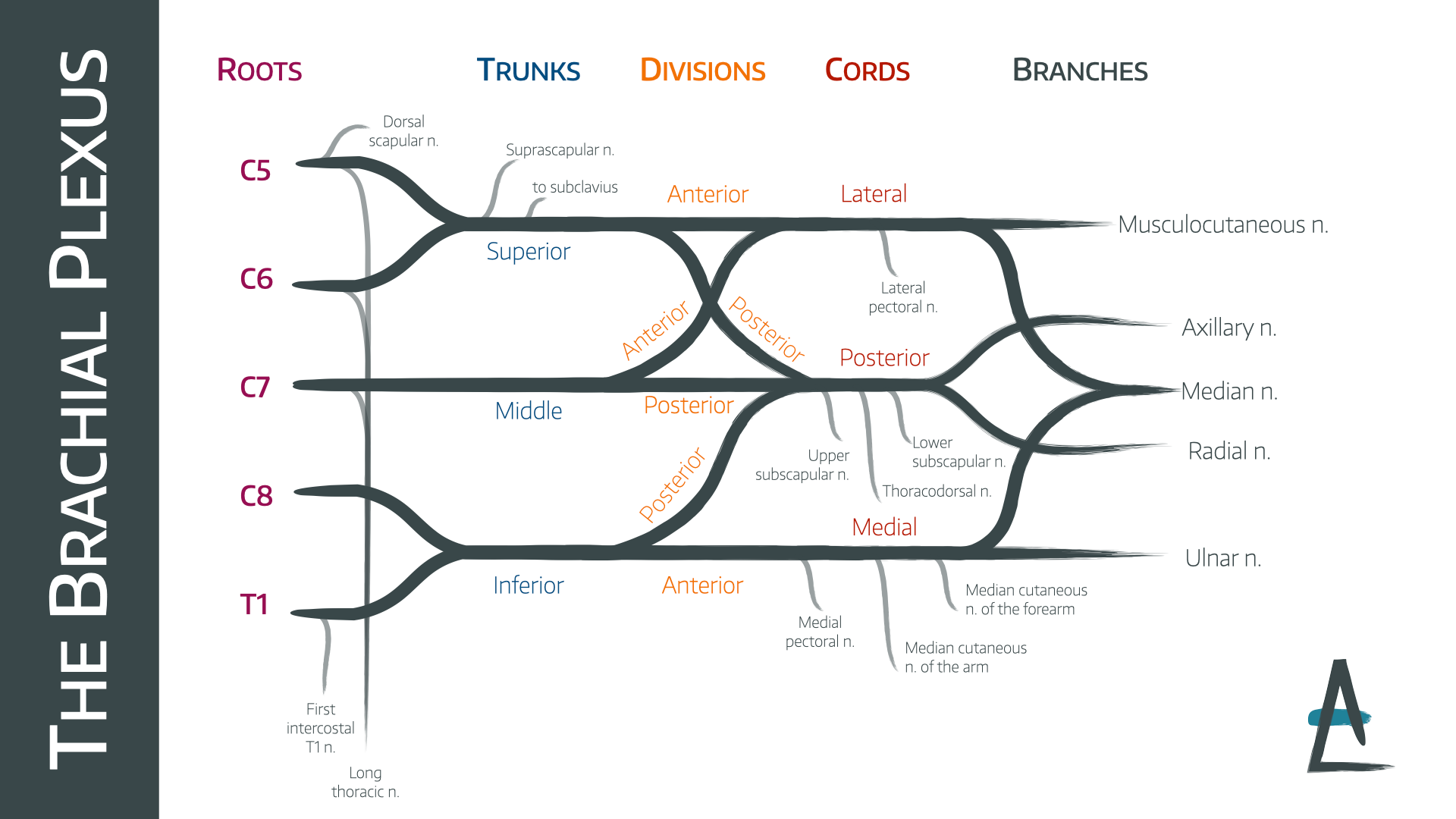
cephalic vein
excessive enlargement of the axillary lymph node may obstruct _______ flow of this superficial vein
long thoracic and thoracodorsal
2 veins at risk in an axillary lymph node dissection
increase
brachial plexus injuries usually result from excessive ____ in angle between neck and shoulder
biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis
3 flexors of the arm
musculocutaneous nerve
the flexors of the arm are supplied by
triceps brachii
extensor of the arm
radial nerve
the extensor of the arm (triceps brachii) is supplied by
anconeus
supplemental muscle to triceps brachii
brachial artery
main arterial supply to the arm
cubital fossa
landmark at which the brachial artery ends
radial and ulnar
the brachial artery splits into the ________ arteries
median bicipital groove
palpations of the brachial artery are felt in the _______; also a great place to feel pulse of babies and take BP
median
the brachial artery accompanies the _______ nerve
brachial artery (dividing to radial and ulnar arteries), deep veins, biceps brachii tendon, median nerve, radial nerve, superficial veins
cubital fossa contents
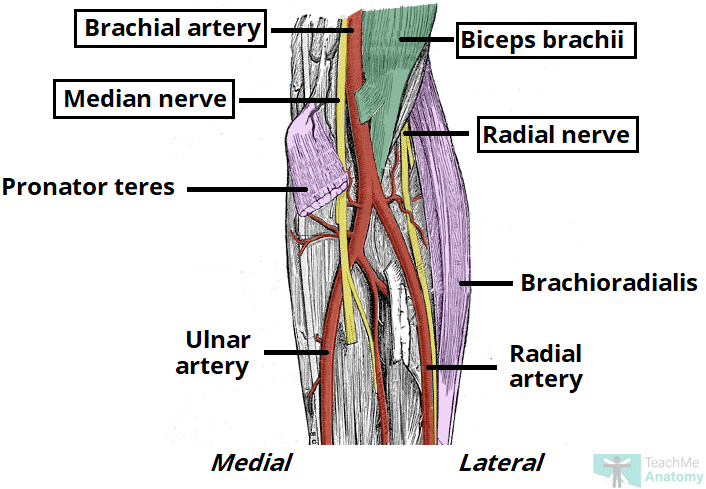
line connecting medial and lateral epicondyles
superior boundary of cubital fossa
pronator teres
medial boundary of cubital fossa
brachioradialis
lateral boundary of cubital fossa
flexors and pronators
anterior muscles of forearm actions