Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation
1/224
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
What is x-ray imaging used for?
detecting broken bones
finding breast tumors
screening for osteoporosis
What are the light areas in x-ray imaging?
dense structures
What are the dark areas in x-ray imaging?
hollow air-containing organs
What are the drawbacks of x-ray imaging?
radiation exposure
2D images
What is a Computed Tomography (CT) scan?
a computerized reconstruction of a series of x-ray images that provide detailed cross-sectional pictures of scanned body regions
What is a Computed Tomography (CT) scan used for?
images of bone, soft tissues, and blood vessels
What is the drawback of a Computed Tomography (CT) scan?
more radiation exposure than x rays
What is Digital Subtraction Angiography?
digitally subtracting images from before and after injection of an x-ray-absorbing contrast agent that yields very clear images of blood vessels
What is Digital Subtraction Angiography used for?
detecting blood vessel abnormalities such as blockages in the arteries that supply the heart
What are the drawbacks of Digital Subtraction Angiography?
time-consuming and expensive
adverse reactions to the contrast medium can occur
How do Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans work?
they use gamma rays that are emitted by radioactively tagged tracer molecules that are injected into the body
What are Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans used for?
detecting the spread of cancer
monitoring the response to cancer treatment
may help diagnose Alzheimer’s
What are the drawbacks of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans?
radiation exposure
relatively poor image resolution
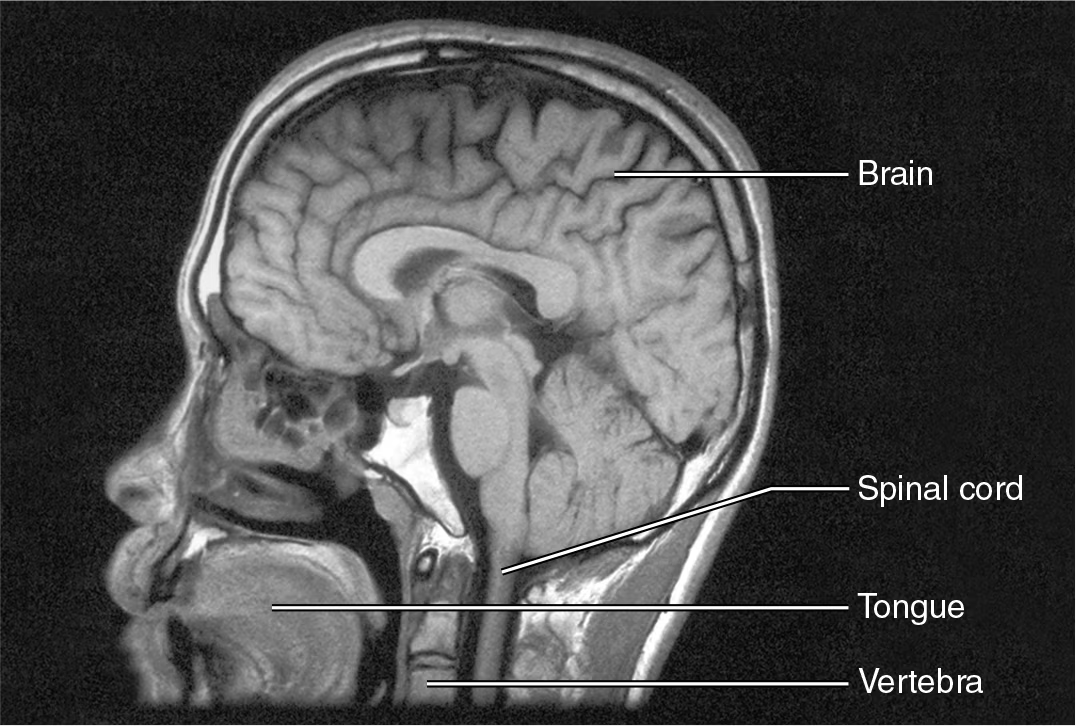
How does Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) work?
it uses powerful magnets and radio waves to image the location of hydrogen atoms in the body, distinguishing body tissues based on water content and producing high-contrast images of soft tissues
What does a functional MRI (fMRI) do?
tracks blood flow into various parts of brain
What is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) used for?
imaging of brain, spinal cord and nerves detect abnormalities
fMRI allows visualization of the activity in specific brain regions
What are the drawbacks of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)?
more expensive and much slower than CT scans
cannot be used in patients with most types of metal implants
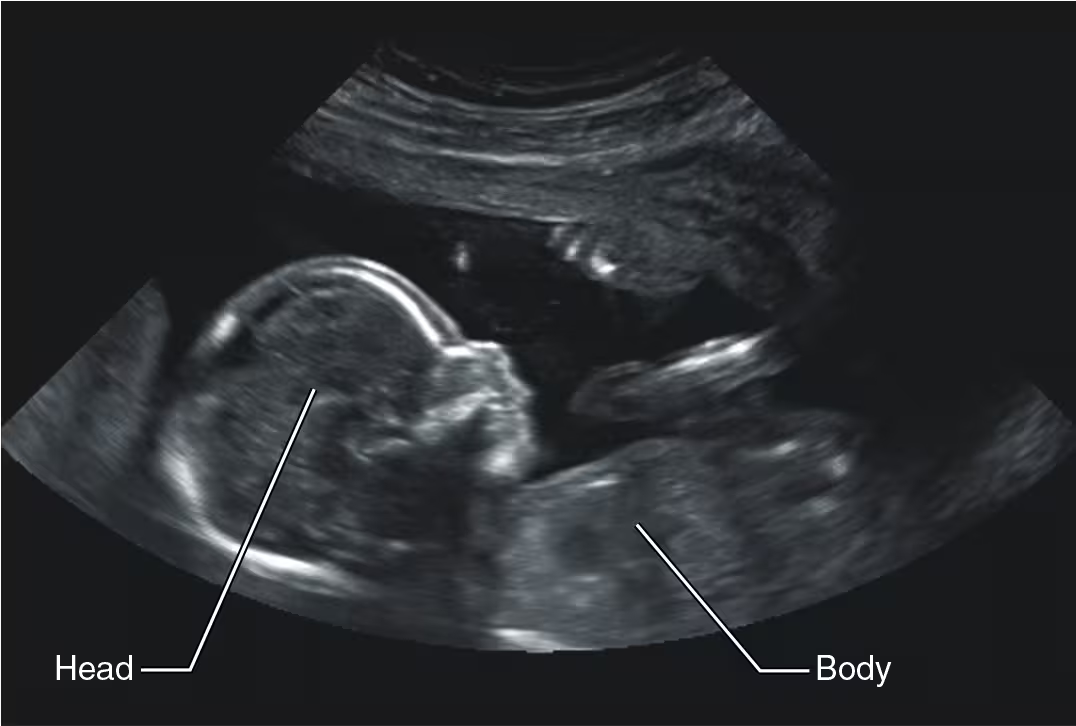
How does ultrasound imaging work?
it uses high-frequency sound waves that reflect off of the body’s tissues
What is ultrasound imaging used for?
monitoring a fetus during pregnancy
diagnosing abdominal or pelvic disorders
detecting atherosclerosis and heart valve disorders
What is the drawback of ultrasound imaging?
images tend to be lower resolution
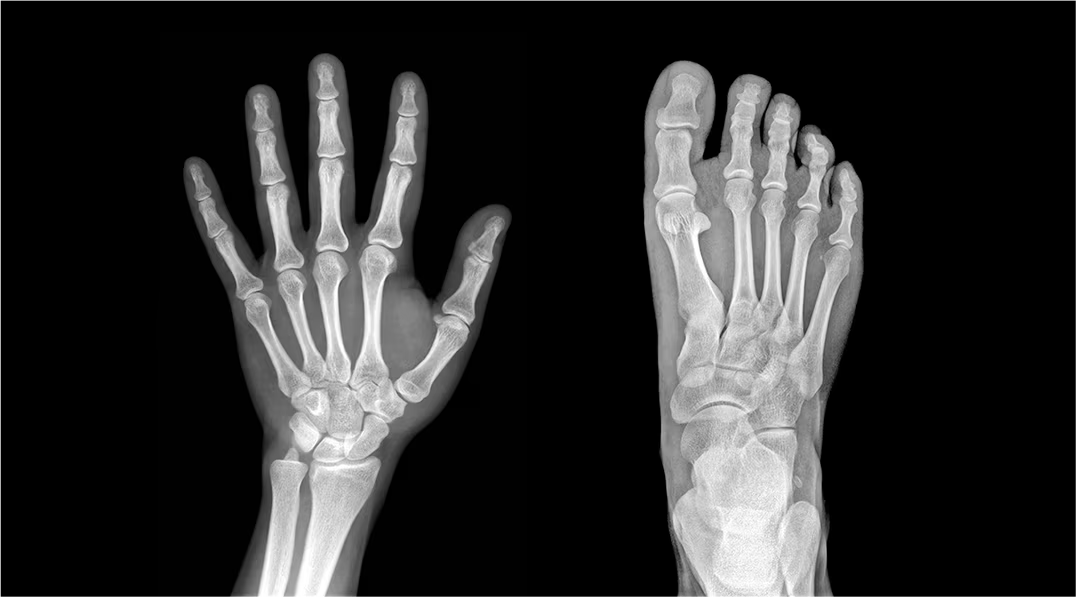
x-ray imaging
CT scan
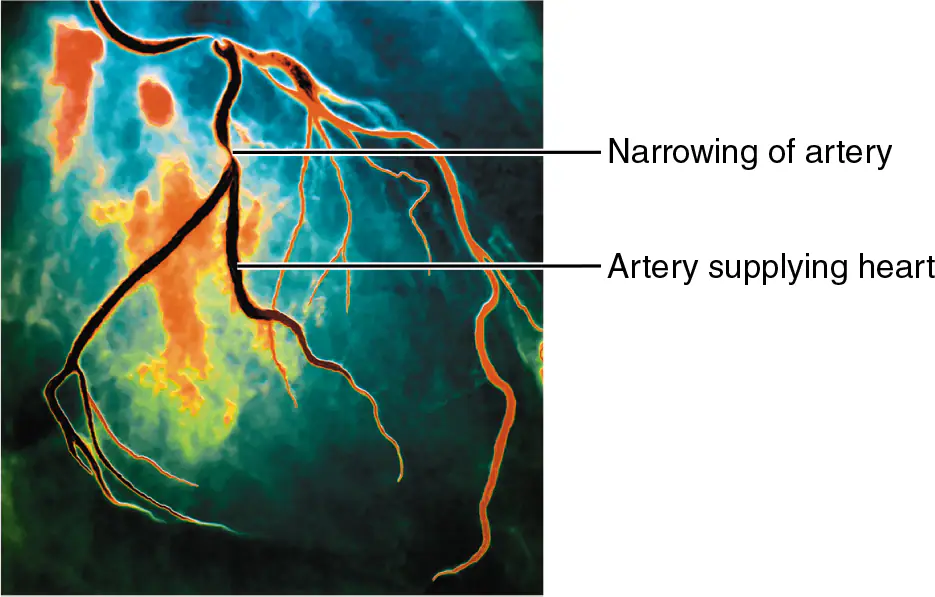
digital subtraction angiography
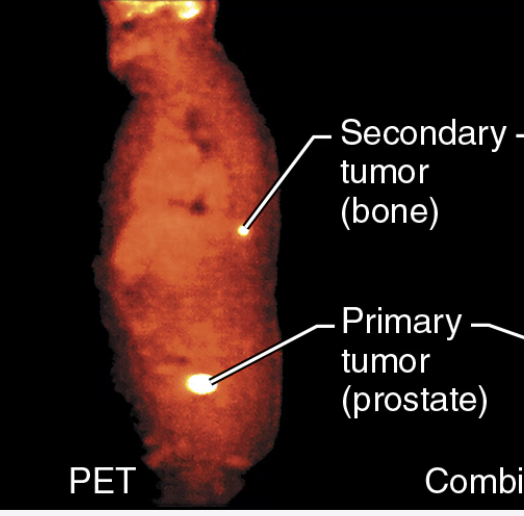
PET scan
MRI
ultrasound imaging
Why do we rarely see extreme anatomical variations from person to person?
because they are incompatible with human life
What are the functions of the integumentary system?
forms the external body covering
protects deeper tissues from injury
houses cutaneous receptors and sweat and oil glands
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
protects and supports body organs
provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement
serves as location where blood cells are formed
stores minerals
What are the functions of the muscular system?
allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion and facial expression
maintains posture
produces heat
What are the functions of the nervous system?
serves as the fast-acting control system of the body
responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands
What are the functions of the cardiovascular system?
transports blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, etc., via blood vessels
pumps blood via the heart
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood
disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream/houses white blood cells (lymphocytes) involved in immunity
its immune response mounts the attack against foreign substances within the body
What are the functions of the digestive system?
breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells
eliminates indigestible foodstuffs as feces
What are the functions of the urinary system?
eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body
regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood
What are the specific functions of the male reproductive system?
testes produce sperm and male sex hormone
male ducts and glands aid in delivery of sperm to the female reproductive tract
What are the specific functions of the female reproductive system?
ovaries produce eggs and female sex hormones
the remaining female structures serve as sites for fertilization and development of the fetus
mammary glands produce milk for the newborn