Amino Acids Clinical Chemistry
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
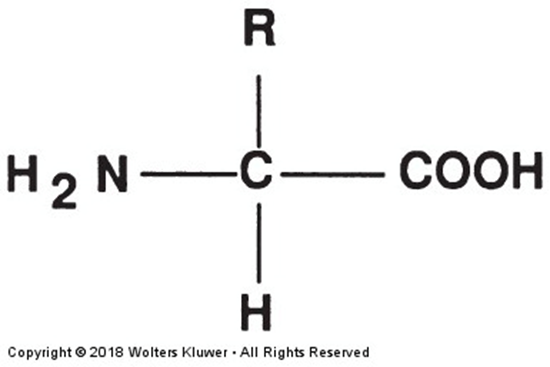
what makes up an amino acid?
carboxyl group
amine group
R-group (differentiates)
what amino acids are ketogenic? (converted into Acetyl CoA => ketones)
leucine
lysine
what amino acids are both glucogenic AND ketogenic?
phenylalanine
isoleucine
tyrosine
tryptophan
what amino acids are glucogenic? (can be converted into glucose)
alanine, glycine, threonine, cysteine, serine, arginine, proline, histidine, glutamine, glutamate, valine, methionine, threonine, asparagine, aspartate
what is a non-essential amino acid
amino acids the body can build itself
what is an essential amino acid
amino acids the body CANNOT build itself - must be obtained through dietary intake
what are the 10 essential amino acids
phenylalanine
valine
threonine
tryptophan
isoleucine
methionine
histidine
arginine
leucine
lysine
what is a neutrally charged amino acid called?
zwitterion/ampholyte
when an amino acid is placed in an alkaline solution, does it become an anion, a cation, or a zwitterion?
anion due to de-protonation of carboxyl and amine groups
when an amino acid is placed in an acidic solution, does it become an anion, a cation, or a zwitterion?
cation due to both carboxyl and amine groups being protonated
An amino has a pI of 4.8. What buffer pH would you need for this protein to occur as a zwitterion with no net charge?
pH of 4.8
An amino has a pI of 5.4. What buffer pH would you need for this protein to occur as a zwitterion with a positive net charge?
any pH < 5.4 (more acidic)
what are some characteristics of renal aminoaciduria
increased urine AA levels
normal plasma AA levels
caused by a malfunction in renal reabsorption of AA
can be acquired or congenital
what are some characteristics of overflow aminoaciduria
increased urine AA levels
increased plasma AA levels
caused by a build up of AA with normal renal clearance
can be acquired or congenital
what is secondary aminoaciduria
a defect in renal tubular transport mechanism
what is primary aminoaciduria
congenital enzyme defect that inhibits the body’s ability to metabolize certain AA
causes buildup of toxic AA and AA byproducts in blood and urine
what is phenylketonuria (PKU)
Absence of phenylalanine hydroxylase
Mousy odor of the urine
Causes significant brain damage
seen typically in babies
what are the 2 types of tyrosinemia
type I: furmarylacetoacetate acid hydrolase (FAH) deficiency
cabbage-like odor in infants
type II: tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT) deficiency
what is maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
absence or reduction of alpha-ketoacid decarboxylase
odor of maple syrup or burnt sugar in the urine, breath, and skin
what is isovaleric acidemia
absence of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase
sweaty feet odor of urine due to build up of isovaleric acid
what is homocystinuria
absence of cystathionine-beta-synthetase
what is alkpatonuria
absence of homogentisic acid oxidase
urine will appear darkened after exposure to light
what is cystinuria
absence of carrier protein that helps in reabsorption of cysteine, lysine, ornithine, and arginine
causes buildup of AA in urine and renal calculi formation
what 2 tests can be used for AA acid analysis
blood or urine
what are some of the criteria that must be met for an AA analysis of a peripheral blood sample?
Heparinized plasma (heparin as anticoagulant)
Patient should fast for 6-8 hours
NO WHITE CELLS OR PLATELETS OR HEMOLYSIS!!!
The sample must be deproteinized within 30 minutes and immediately run or frozen
what are some of the criteria that must be met for an AA analysis of a urine sample?
a random void is acceptable for qualitative analysis. However, a 24-hour urine is needed to complete quantitative testing
what is the dye used to stain AA during a TLC analysis
ninhydrin