6. Endo/Repro Exam 2: Male Genitalia Pathology (Dr. Griffin)
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What is a complete or partial failure of testes to descend into scrotal sac?
cryptorchidism

What phase of crytorchidism?
Abdomen to lower pelvis by the 3rd month of gestation
1st

What phase of cryptorchidism?
Inguinal canal to scrotum within the last 2 months intrauterine
2nd

Where is the most common site of cryptorchidism?
inguinal canal
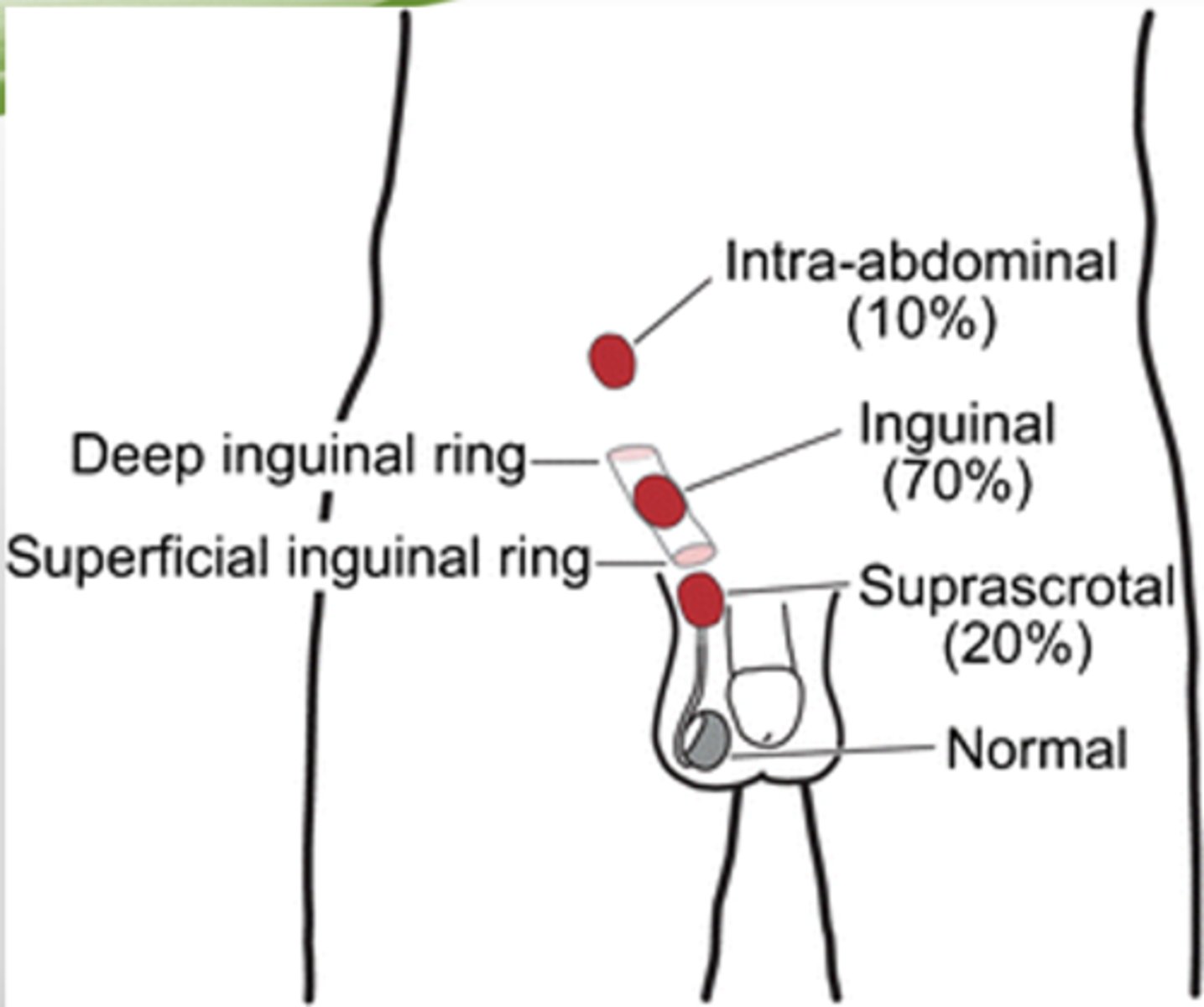
T/F: In cryptorchidism, Testes may arrest anywhere along the pathway of descent
True

T/F cryptorchidism is unilateral in most cases
true (25% bilateral)

T/F: Cryptorchidism can be established with certainty after birth
False (asymptomatic - only after 1 year b/c descent is not always complete at birth)

If cryptorchidism is bilateral what can happen?
sterility (undescended testes - atrophic, can still happen if unilateral)

Cryptochordism has a 3-5x increased risk for what?
testicular cancer

How can cryptorchidism be corrected?
Surgery

When is surgery recommend to correct cryptorchidism to decrease likelihood of atrophy, infertility, and testicular cancer?
By 18 months

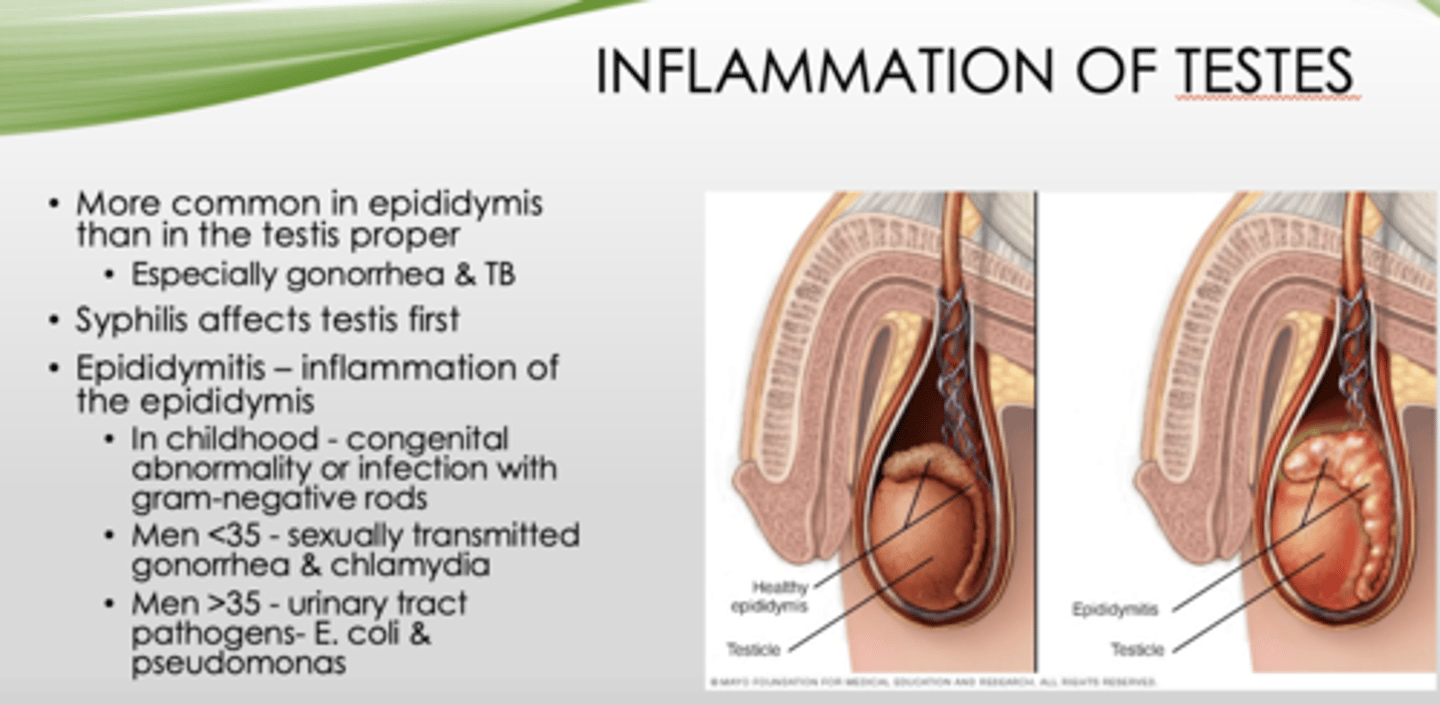
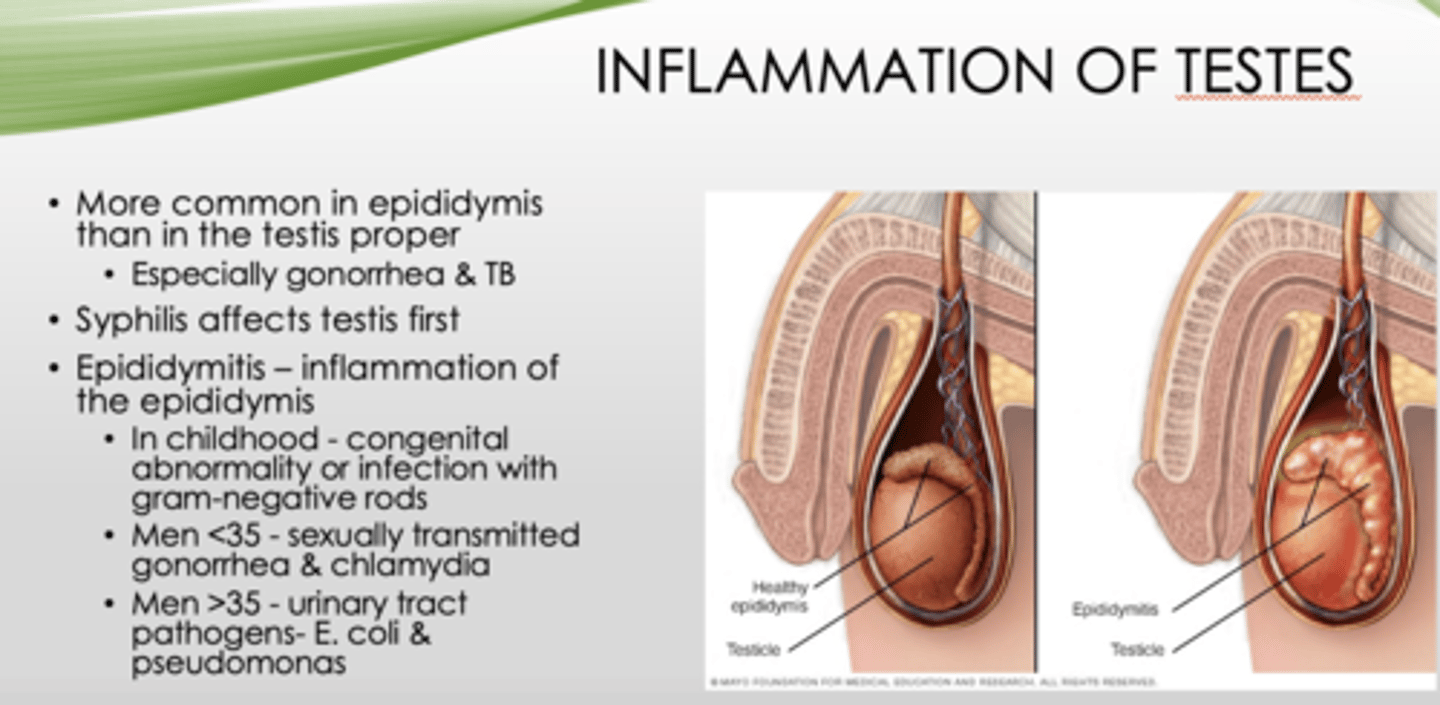
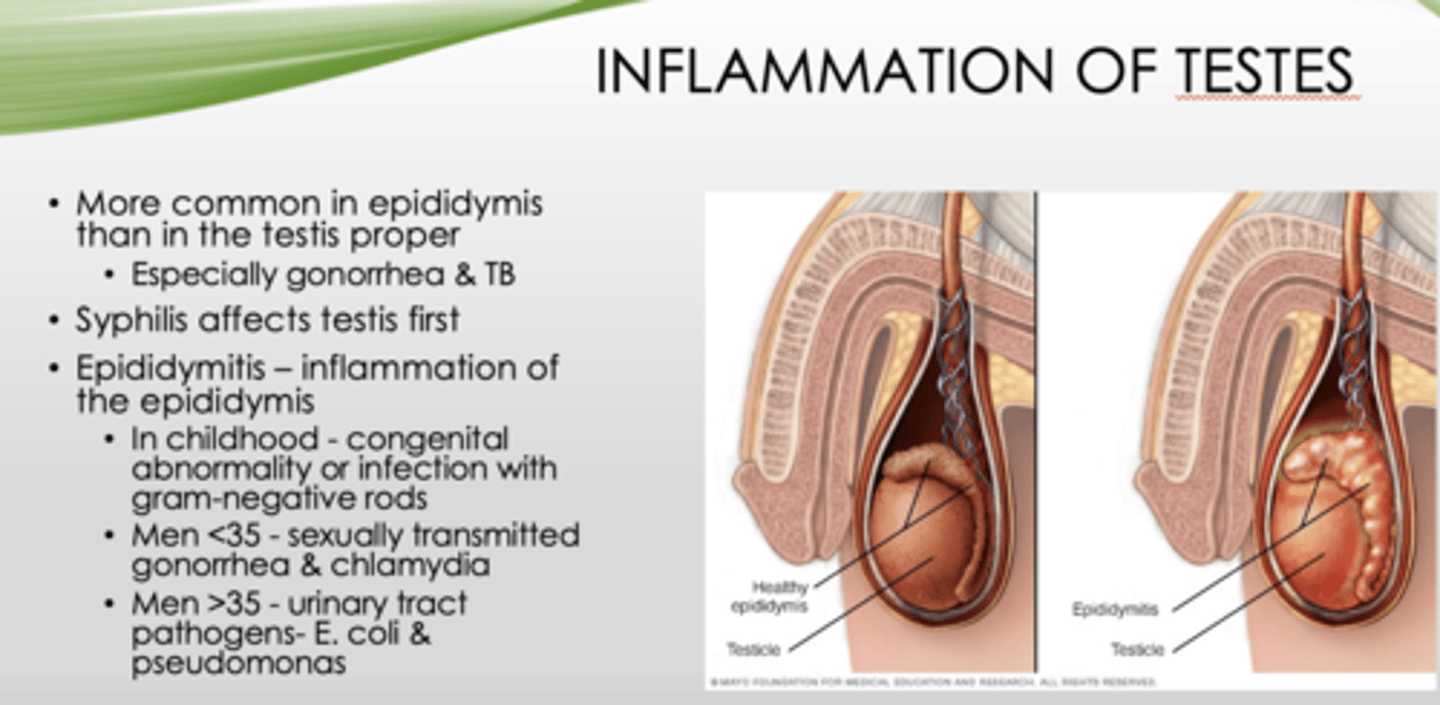
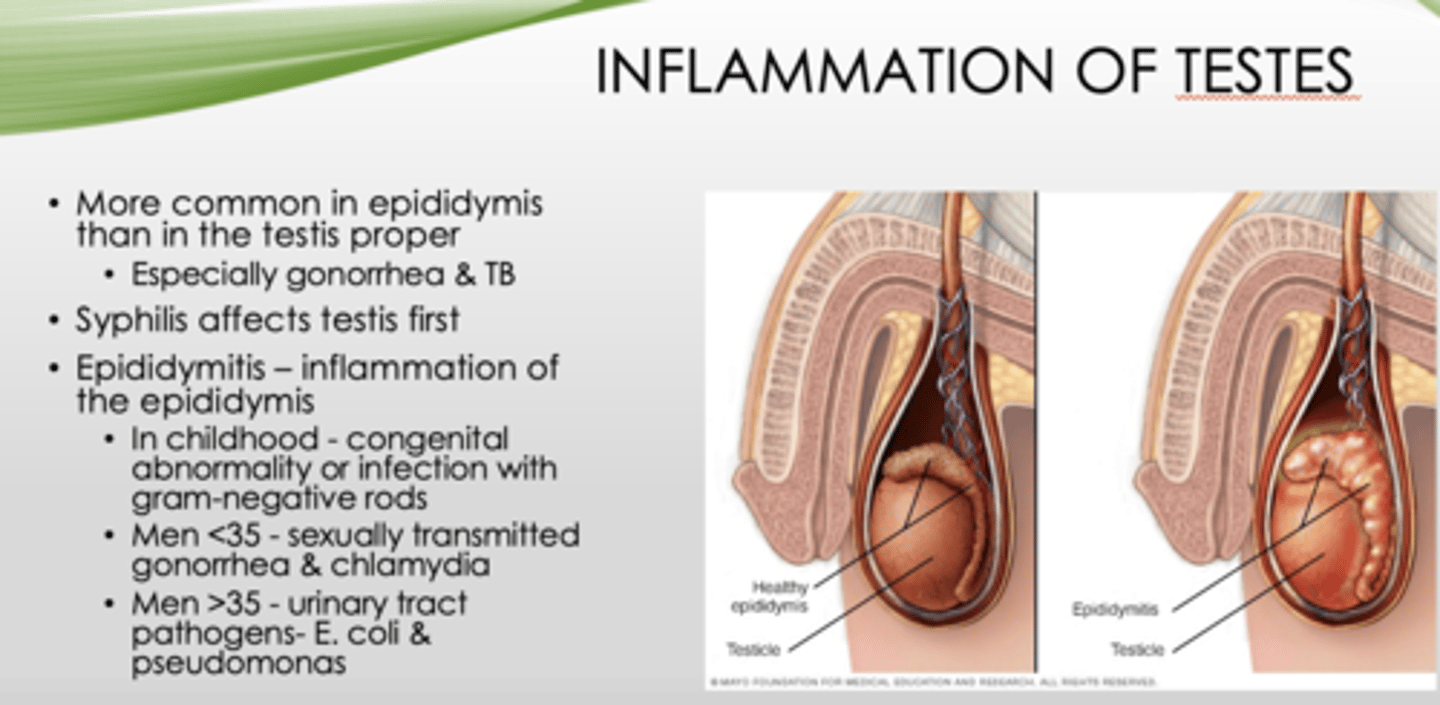
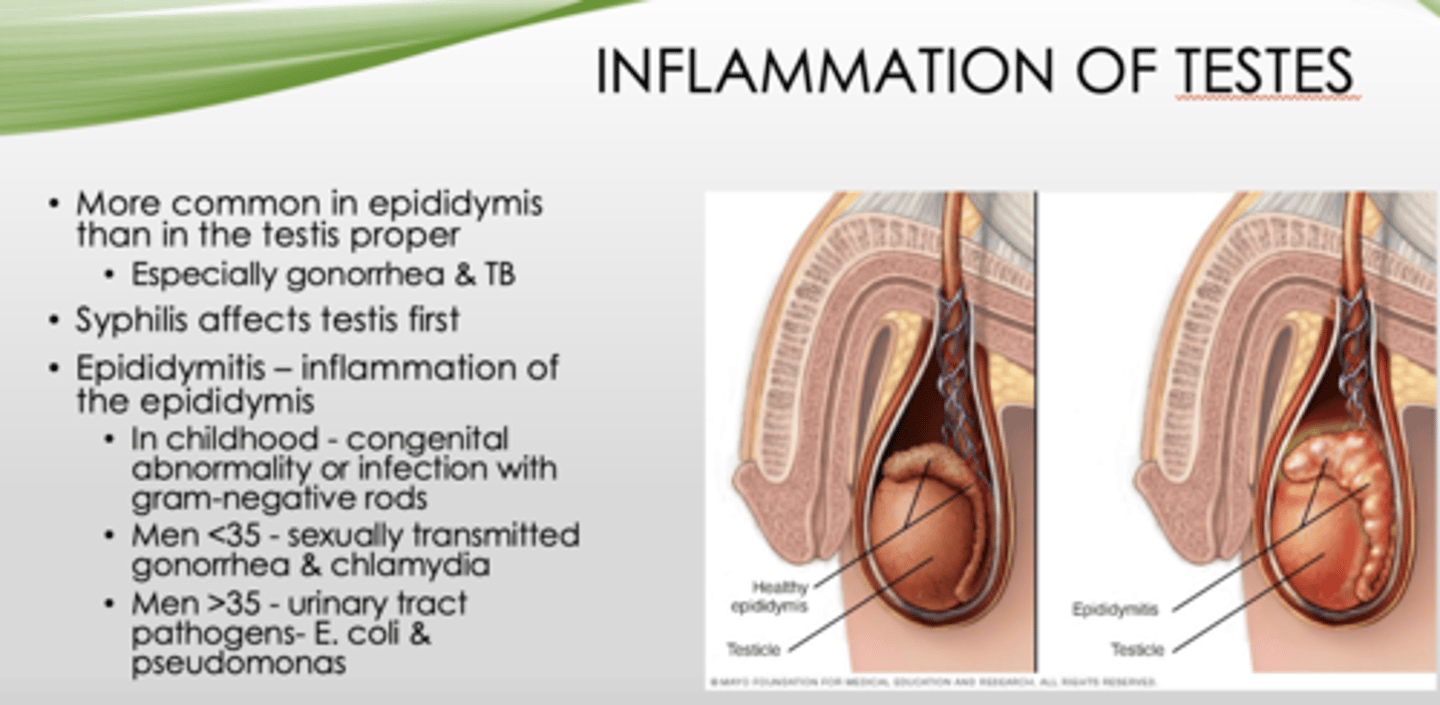
Inflammation of testes is more common where?
epididymis (than testis proper, especially gonorrhea & TB)
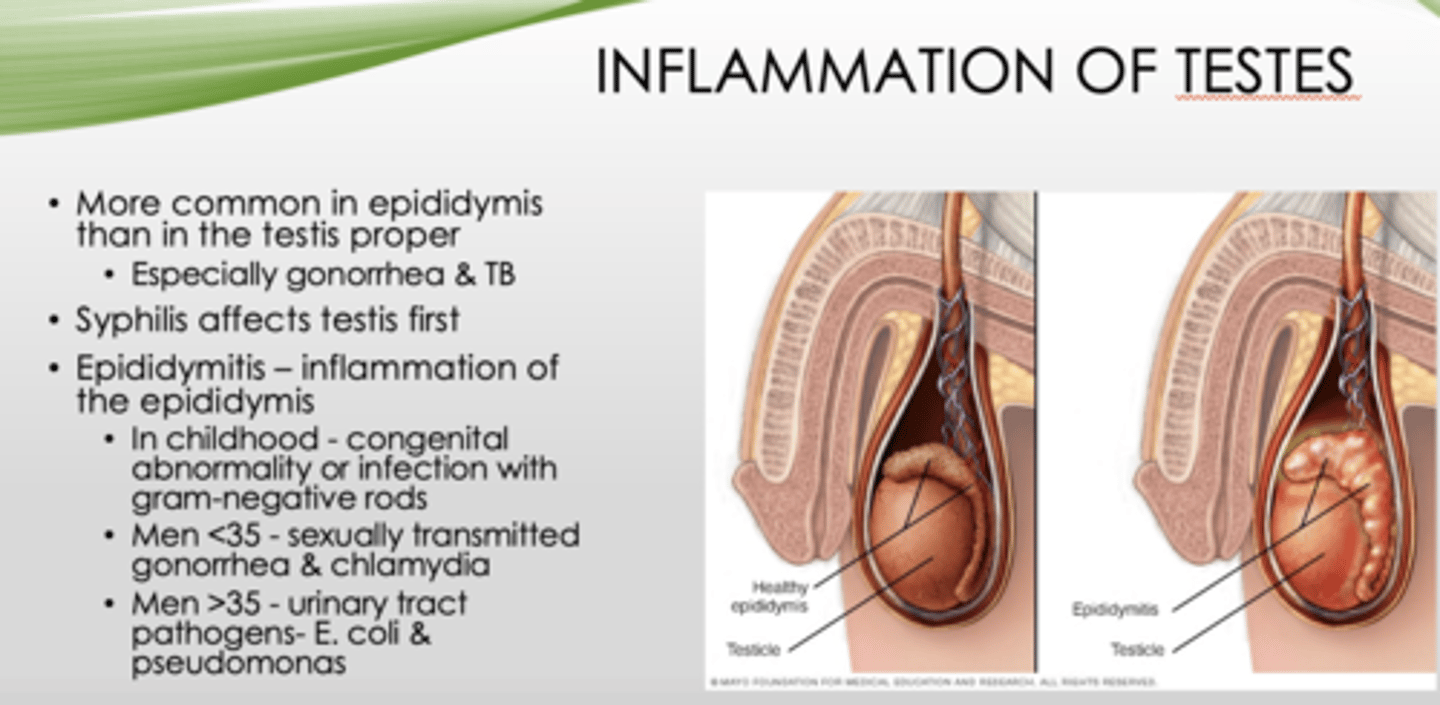
What affects testis first?
Syphillis
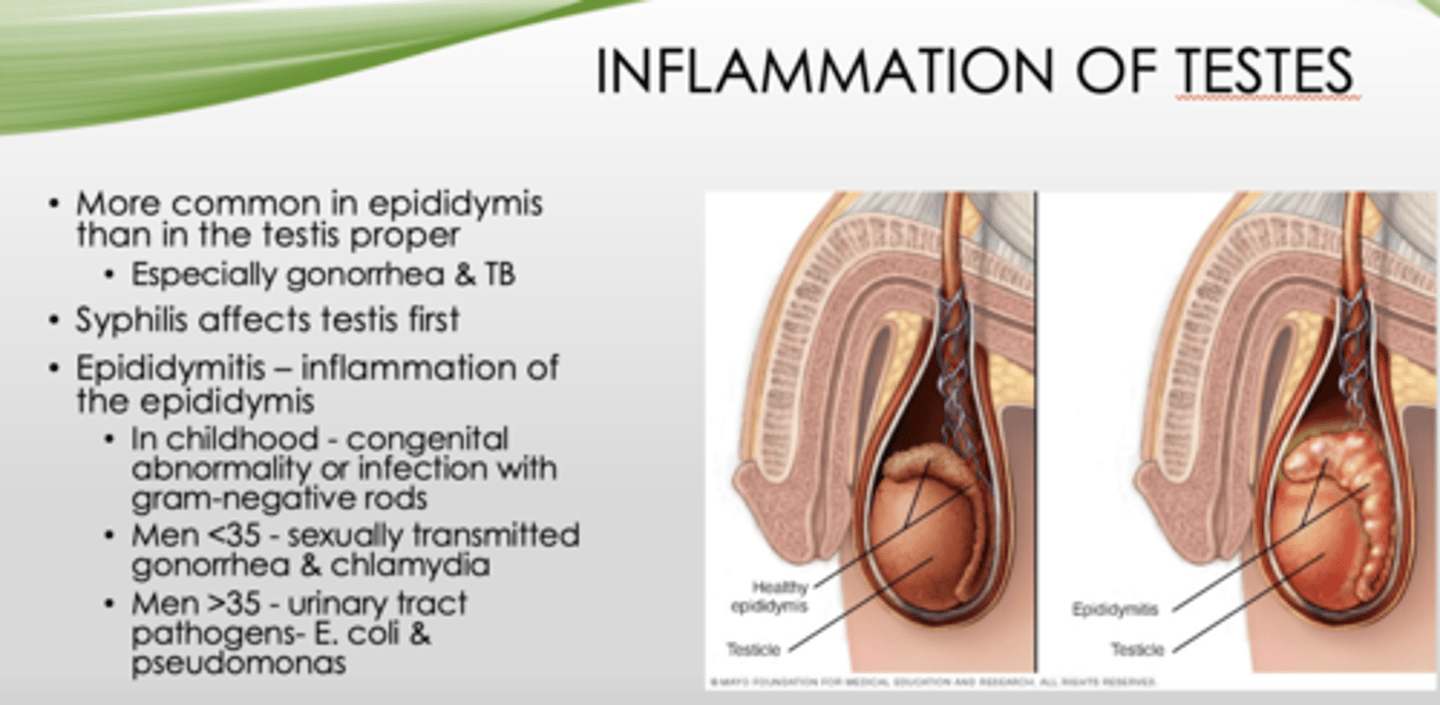
What is inflammation of the epididymis?
epididymitis
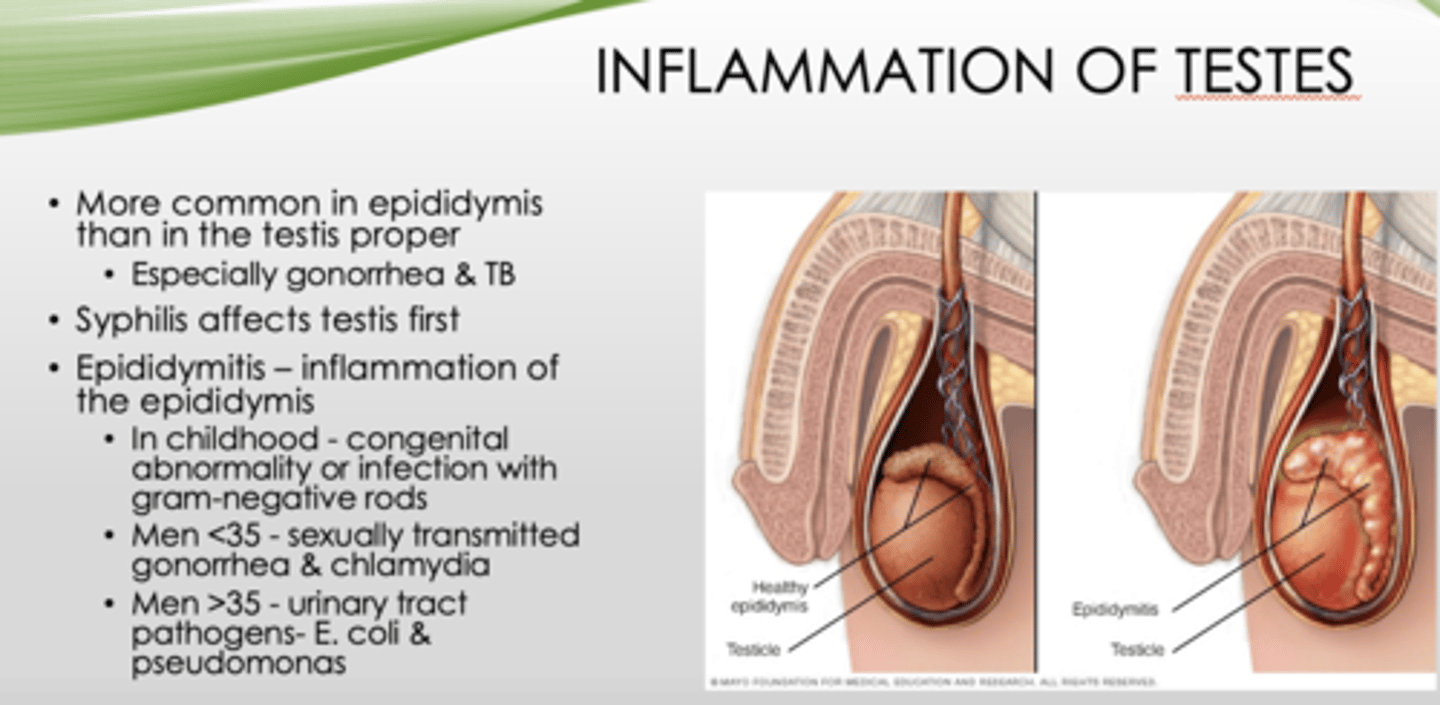
Epididymitis in children is most likely caused by what?
congenital abnormality/infection with gram-negative rods

What is the most common cause of epididymitis in men under 35?
STI (gonorrhea, chlamydia)
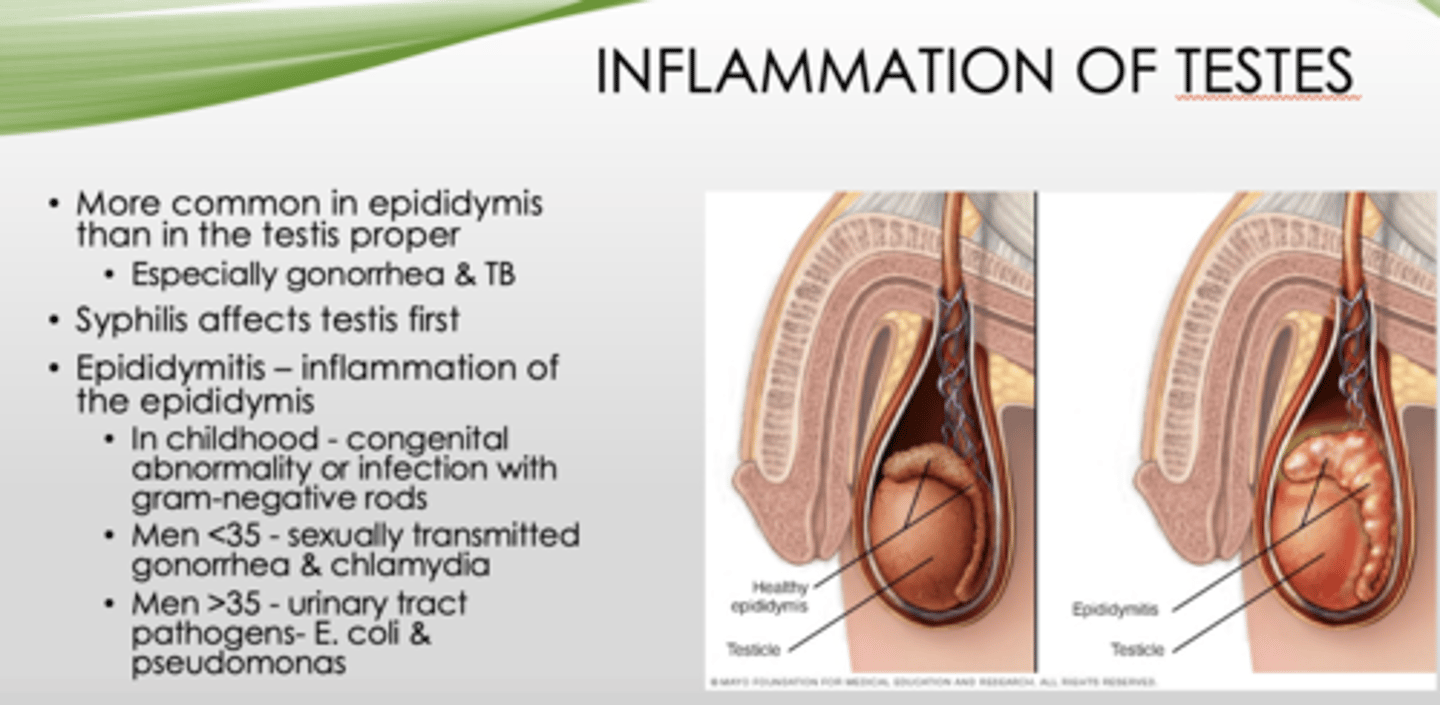
What is the most common cause of epididymitis in men over 35?
Urinary tract pathogens (E Coli and pseudomonas)
What is the inflammation of one or both testicles?
orchitis
What can orchitis be caused by in 20-30% of cases?
mumps
T/F: Orchitis does NOT lead to sterility
False
Nonspecific epididymitis and orchitis usually begin as what?
UTI that spread to the testes via the spermatic cord
Mumps is what type of infection?
viral
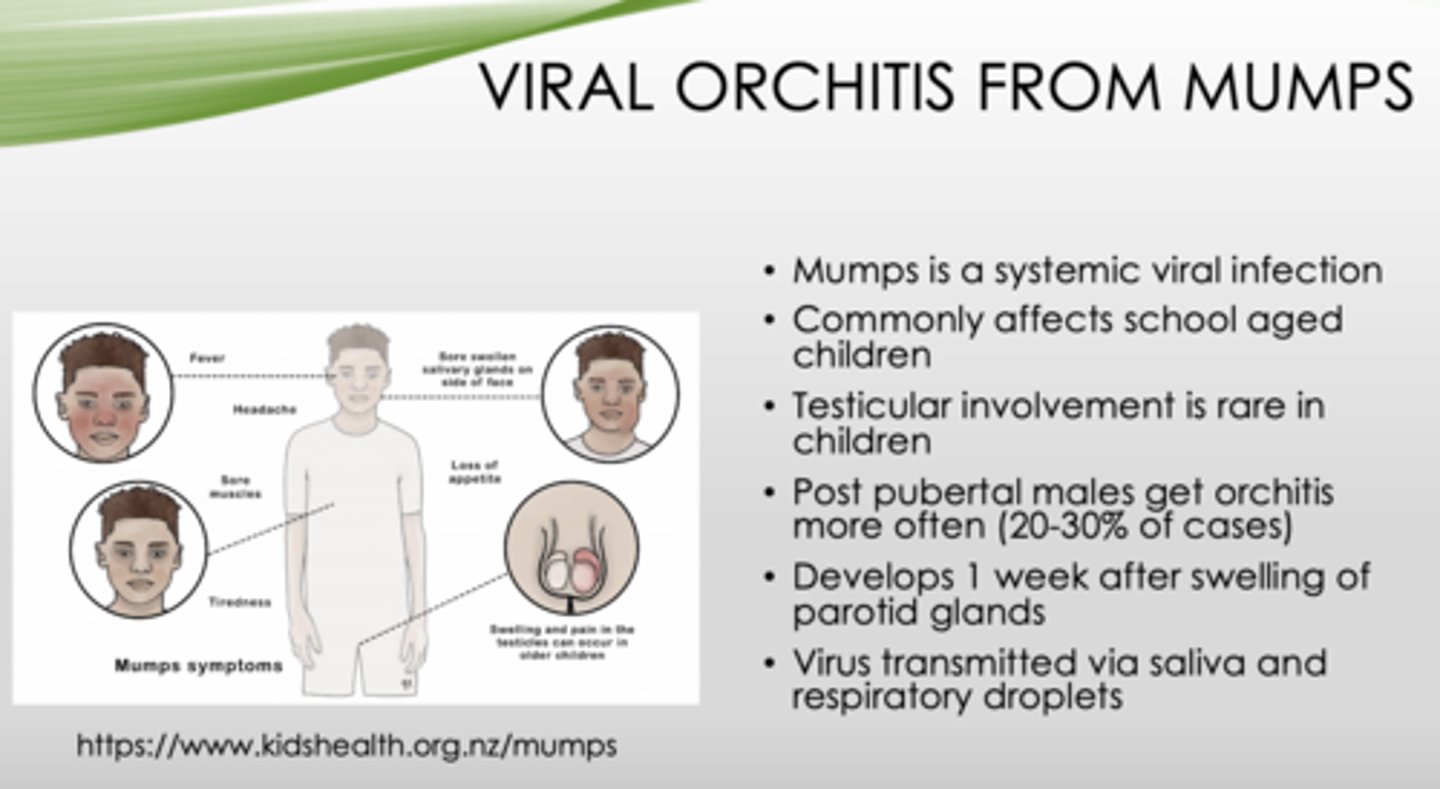
What population do mumps typically affect?
School aged children
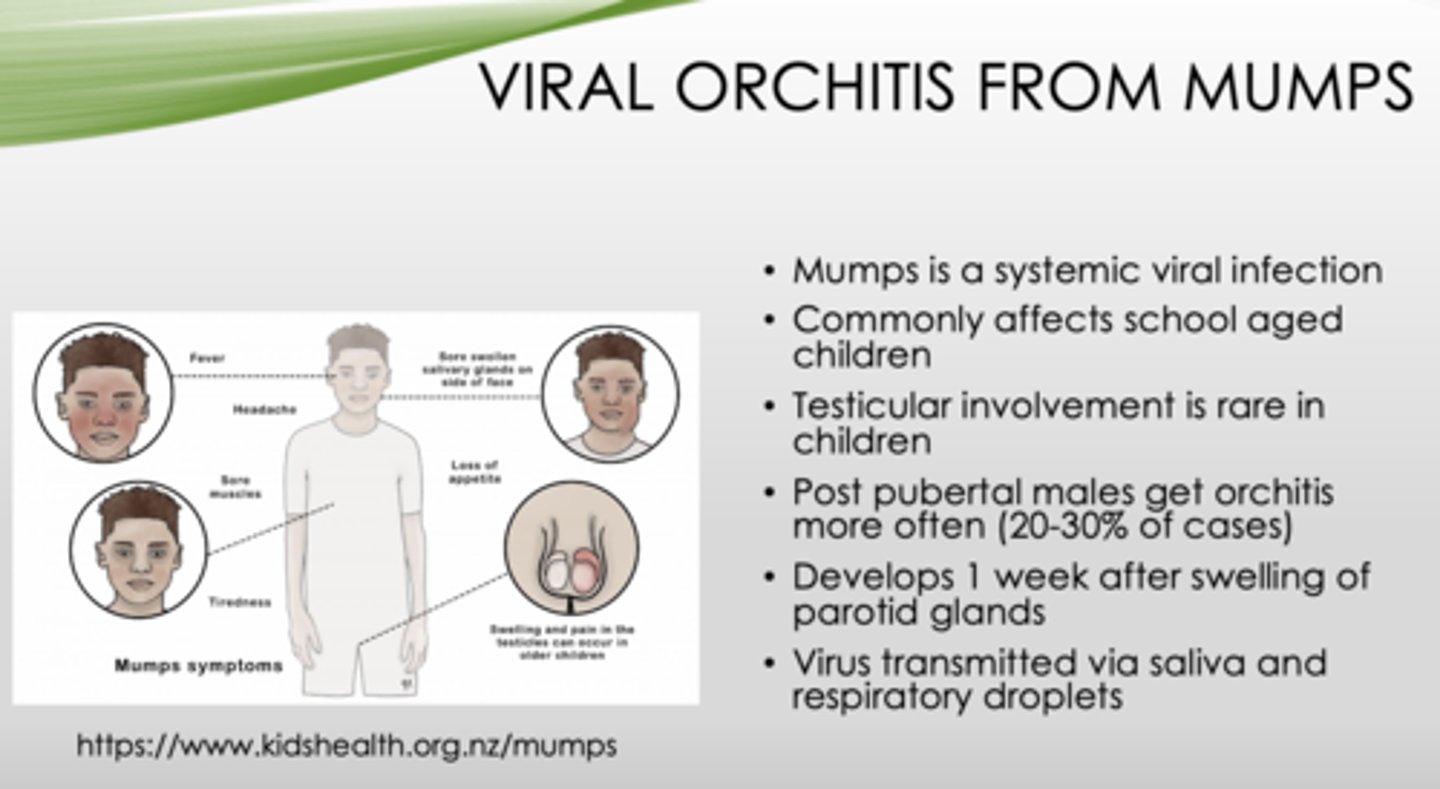
T/F: Testicular involvement in mumps in common in children
false (RARE)
Which population is at highest risk of developing orchitis as a complication of mumps?
Post-pubertal males
How long does it take for orchitis to occur after swelling of the parotid gland (in mumps)?
1 week
How are mumps transmitted
Via saliva and respiratory droplets
What are the two types of testicular tumors?
- Germ cell
- Sex-cord-stromal

What are the two categories of testicular tumors?
- Seminomas
- Non-seminomatous

95% of testicular germ cell tumors in post-pubertal males are all malignant or benign?
malignant

Is family history important for germ cell tumors?
Yes! (Brothers of patients with a germ cell tumor have an 8-10x increased risk)

Where is the lifetime risk highest for testicular germ cell tumors?
- Northern Europe
- New Zealand

Where is the lifetime risk lowest for testicular germ cell tumors?
- Africa
- Asia

What type of tumor arises from sertoli and leydig cells?
sex-cord-stromal

Are sex-cord-stromal tumors are usually benign or malignant?
Benign

What is the most common type of germ cell tumor?
seminoma
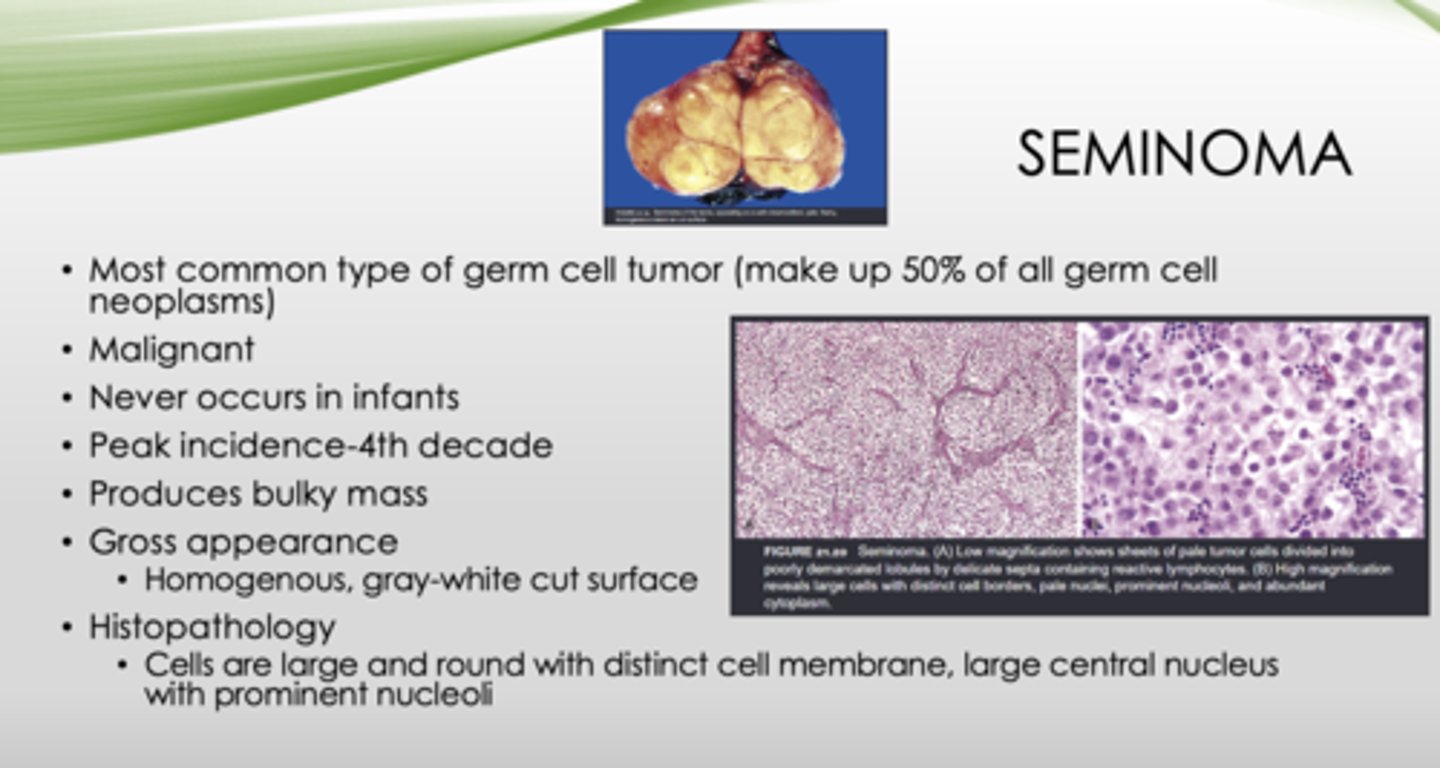
Is a seminoma malignant or benign?
malignant
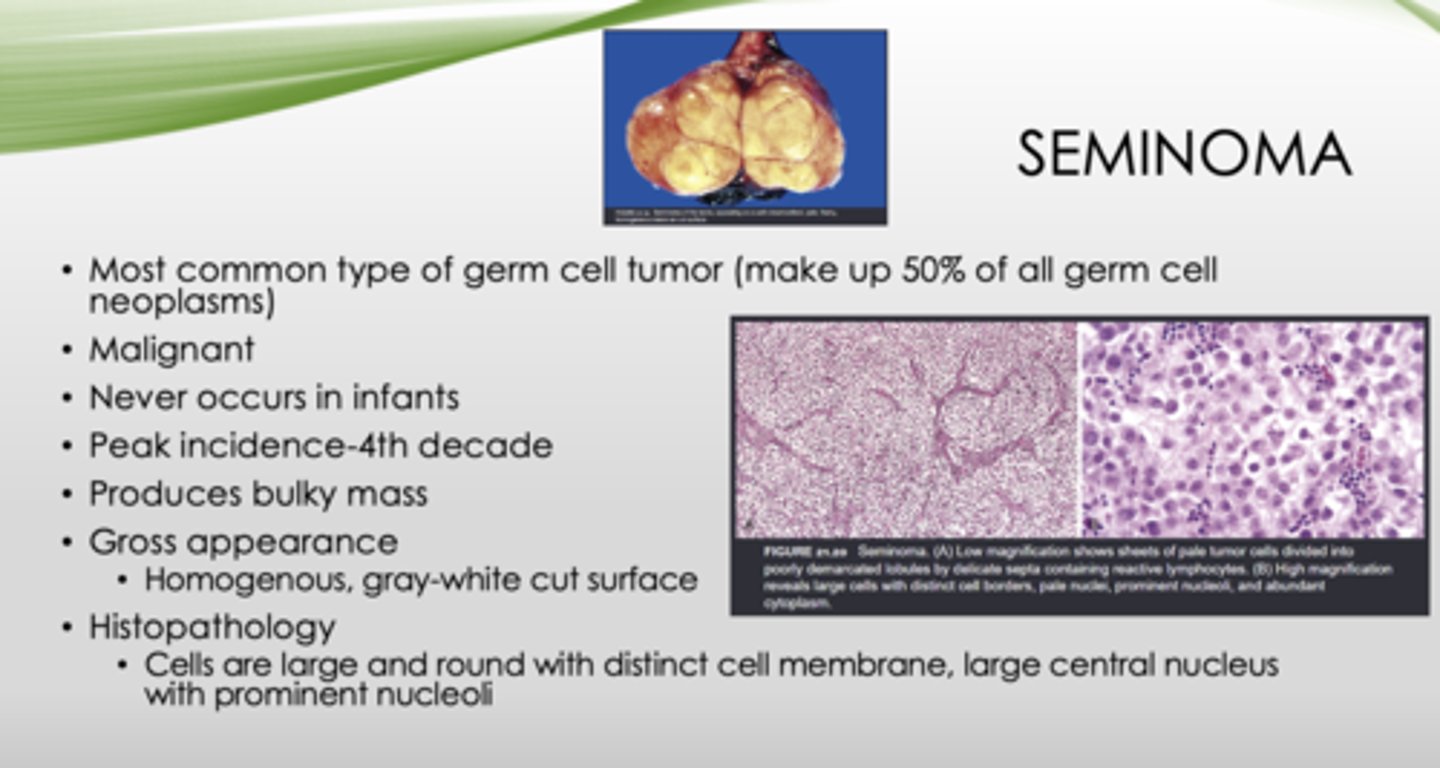
T/F: Seminomas never occur in infants
true
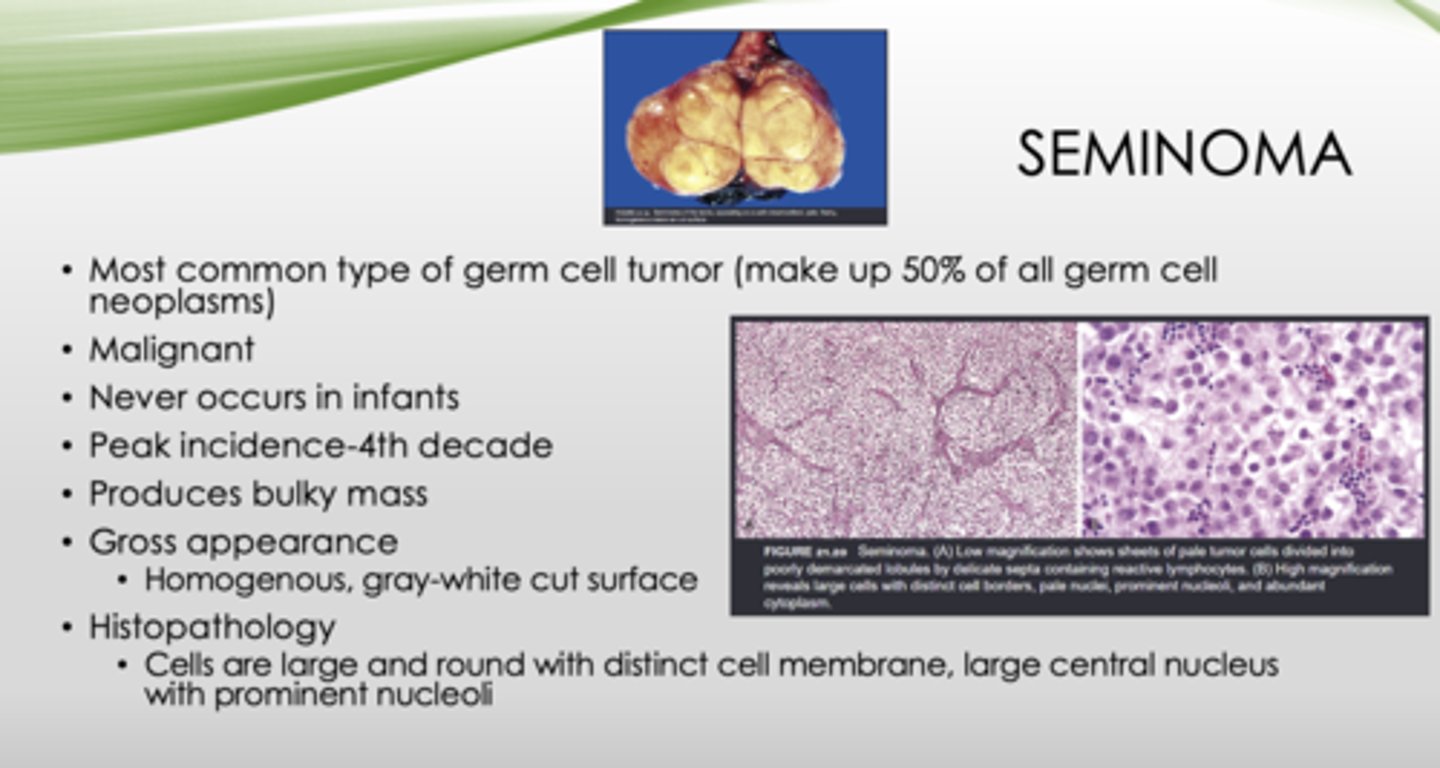
What is the peak incidence of seminomas?
4th decade
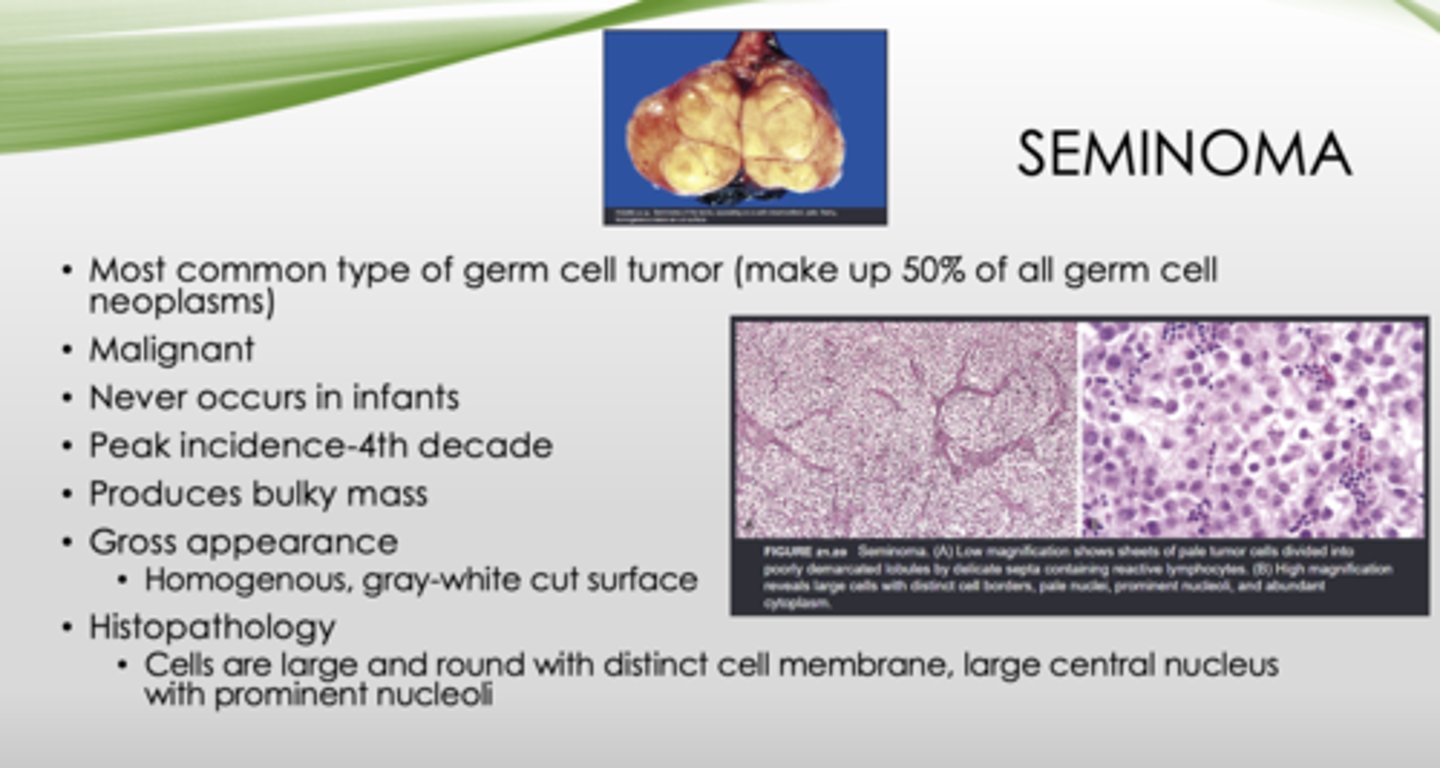
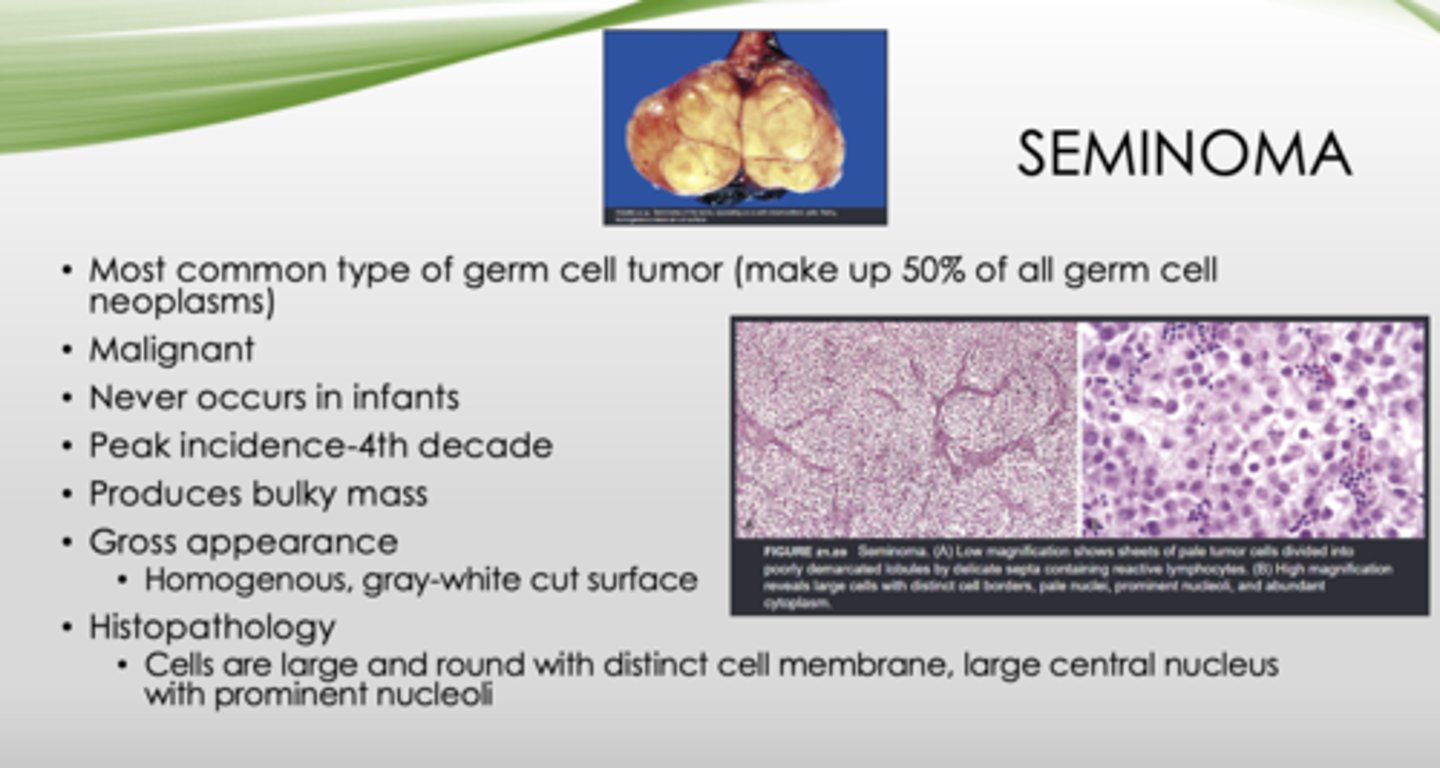
This is the gross appearance of what?
Homogenous, gray-white cut surface
seminomas
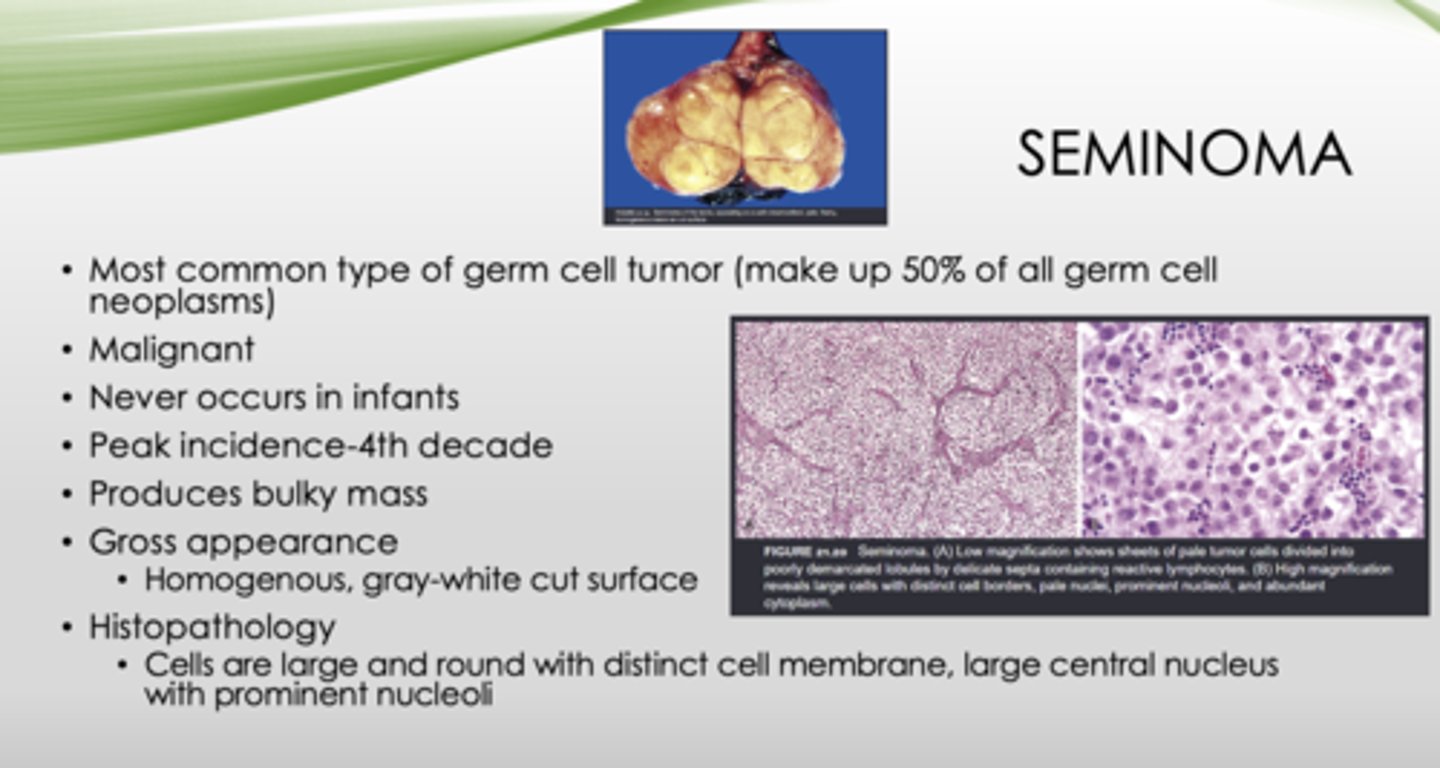
This is the histopathology of what?
Cells are large and round with distinct cell membrane, large central nucleus with prominent nucleoli
seminoma
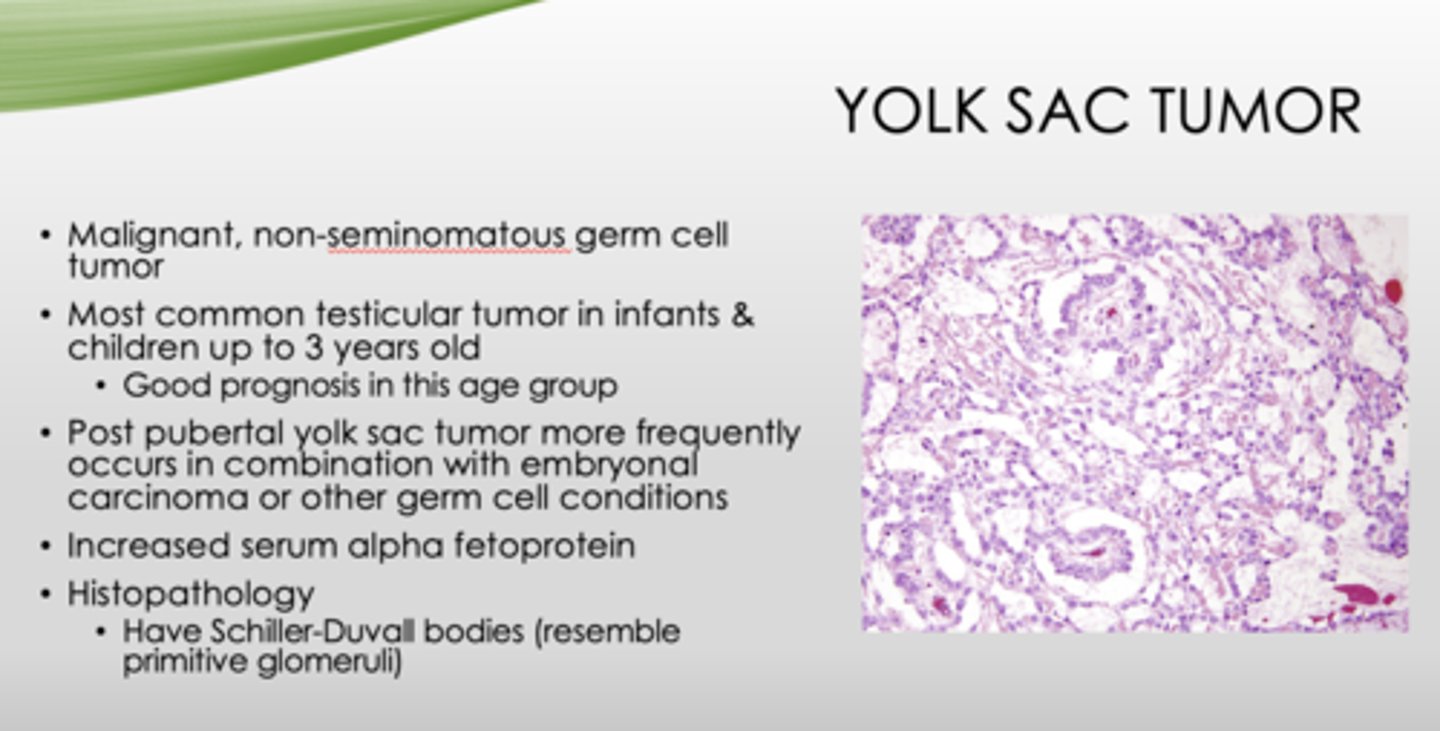
What is a malignant, non-seminomatous germ cell tumor?
yolk sac tumor
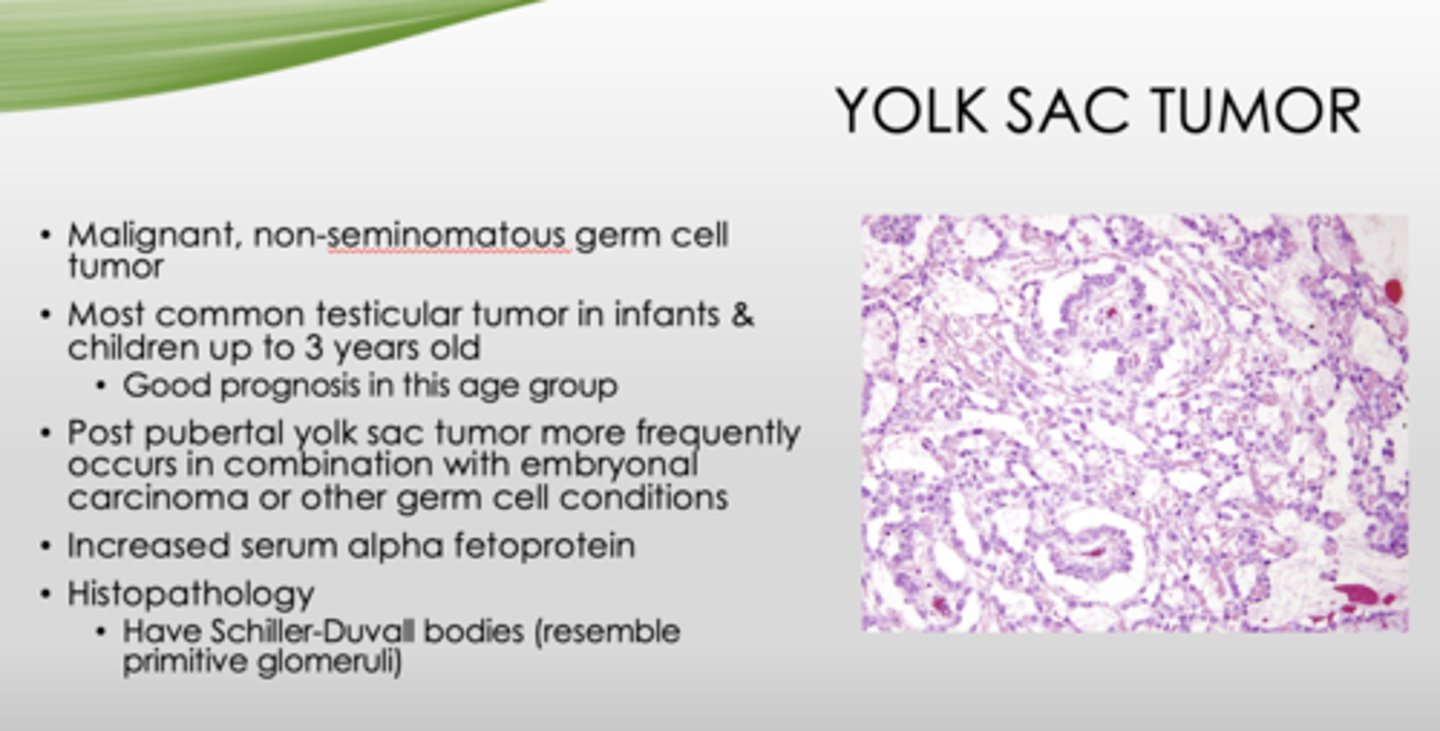
What is the most common testicular tumor in infants and children up to 3 years old (good prognosis in this age group)?
yolk sac tumor
What tumor more frequently occurs in combination with embryonal carcinoma or other germ cell conditions?
post-pubertal yolk sac
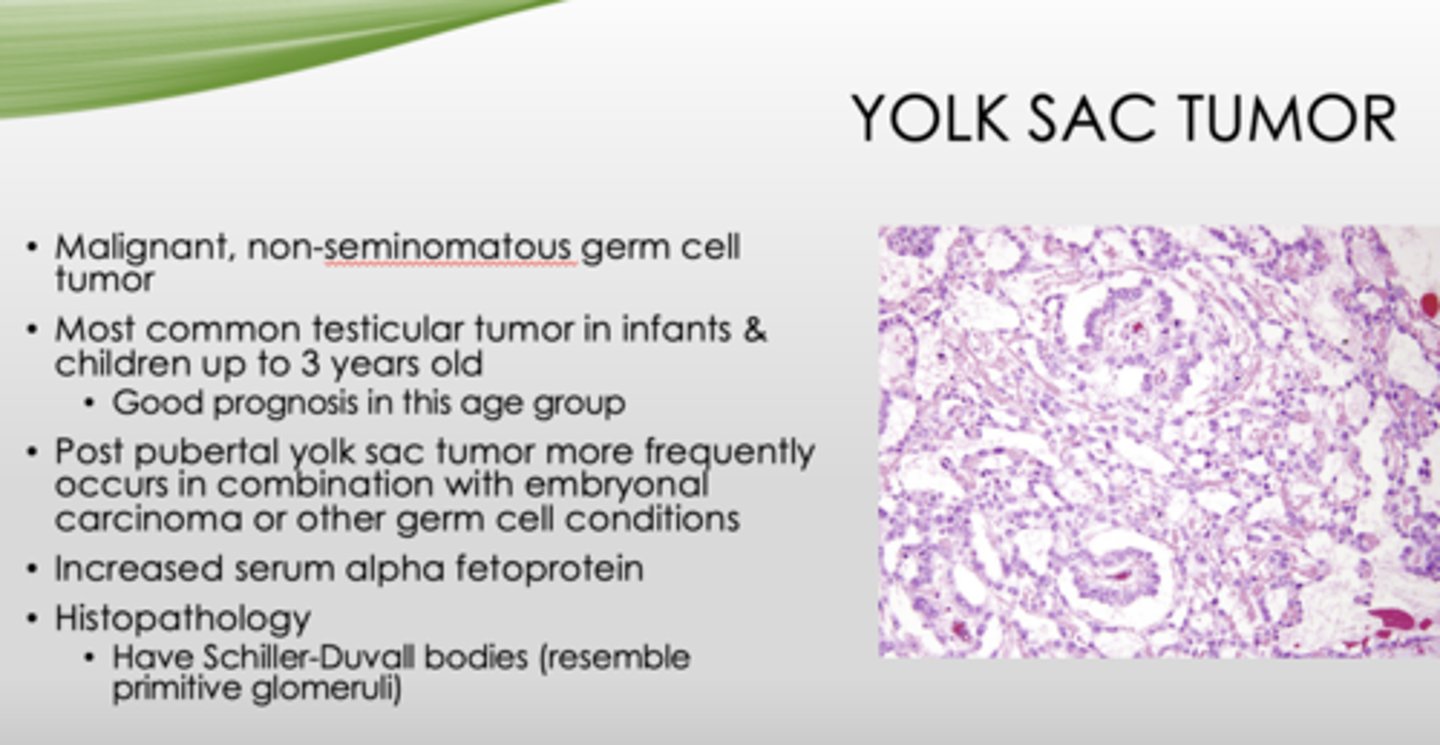
What type of tumor has serum alpha fetoprotein?
yolk sac tumor
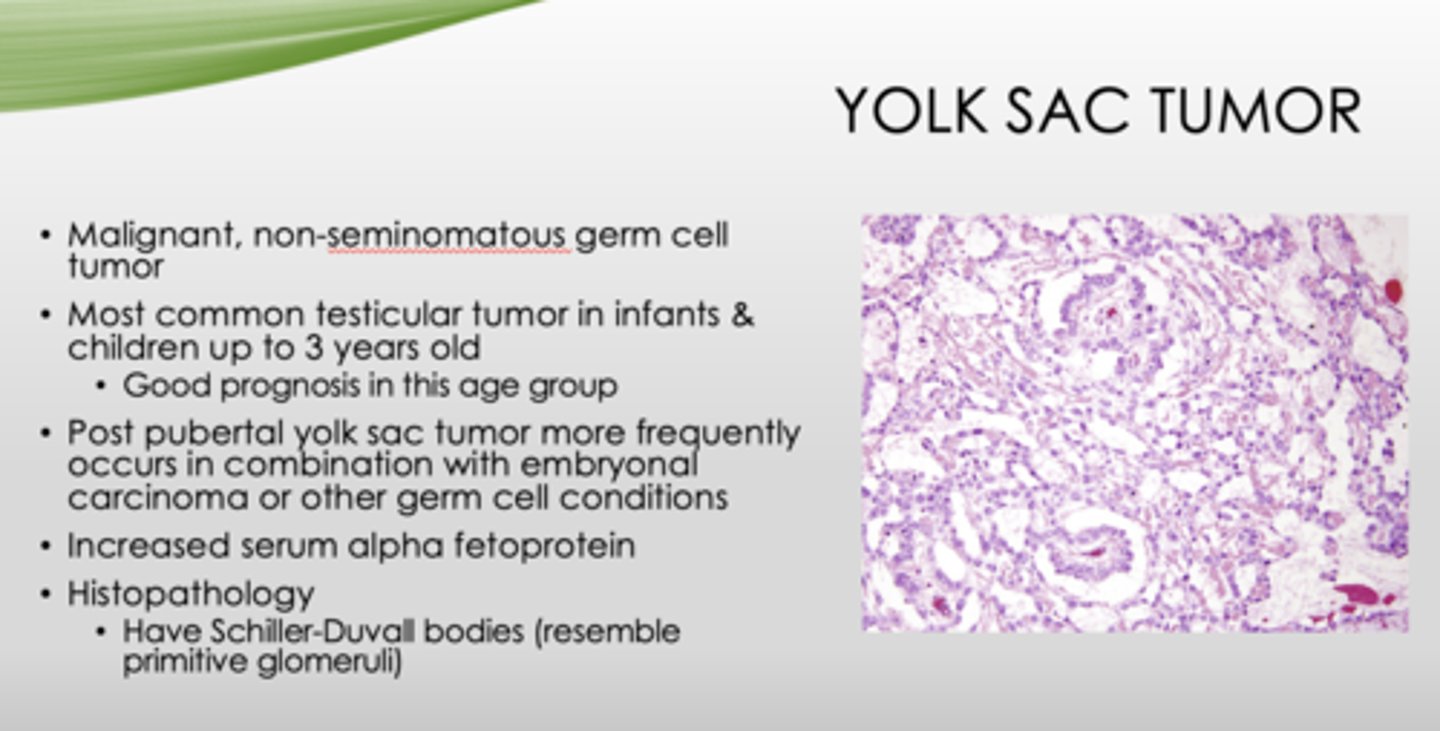
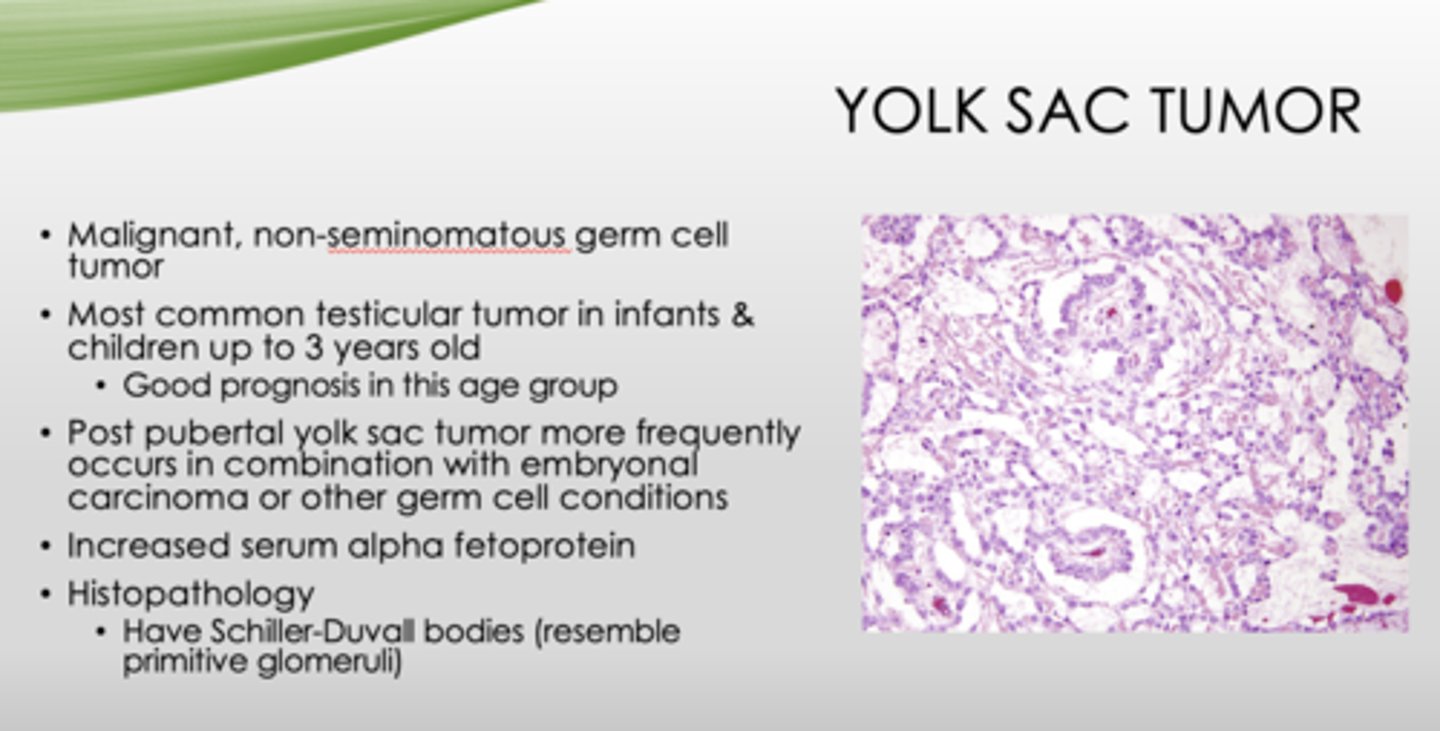
What is the key histopathology in yolk sac tumors?
Schiller-Duvall bodies (resemble primitive glomeruli)
What are the two types of sex-cord tumors?
- Leydig
- Sertoli

Which sex-cord tumor?
- Occurs between ages of 20-60
- 5-10% are malignant
- Testicular swelling and/or gynecomastia
- Increase in androgens, estrogens, corticosteroids
leydig cell tumor

Which sex-cord tumor?
- Presents as a testicular mass
- Can have gynecomastia as initial finding
- Up to 10% can be malignant
sertoli cell tumor

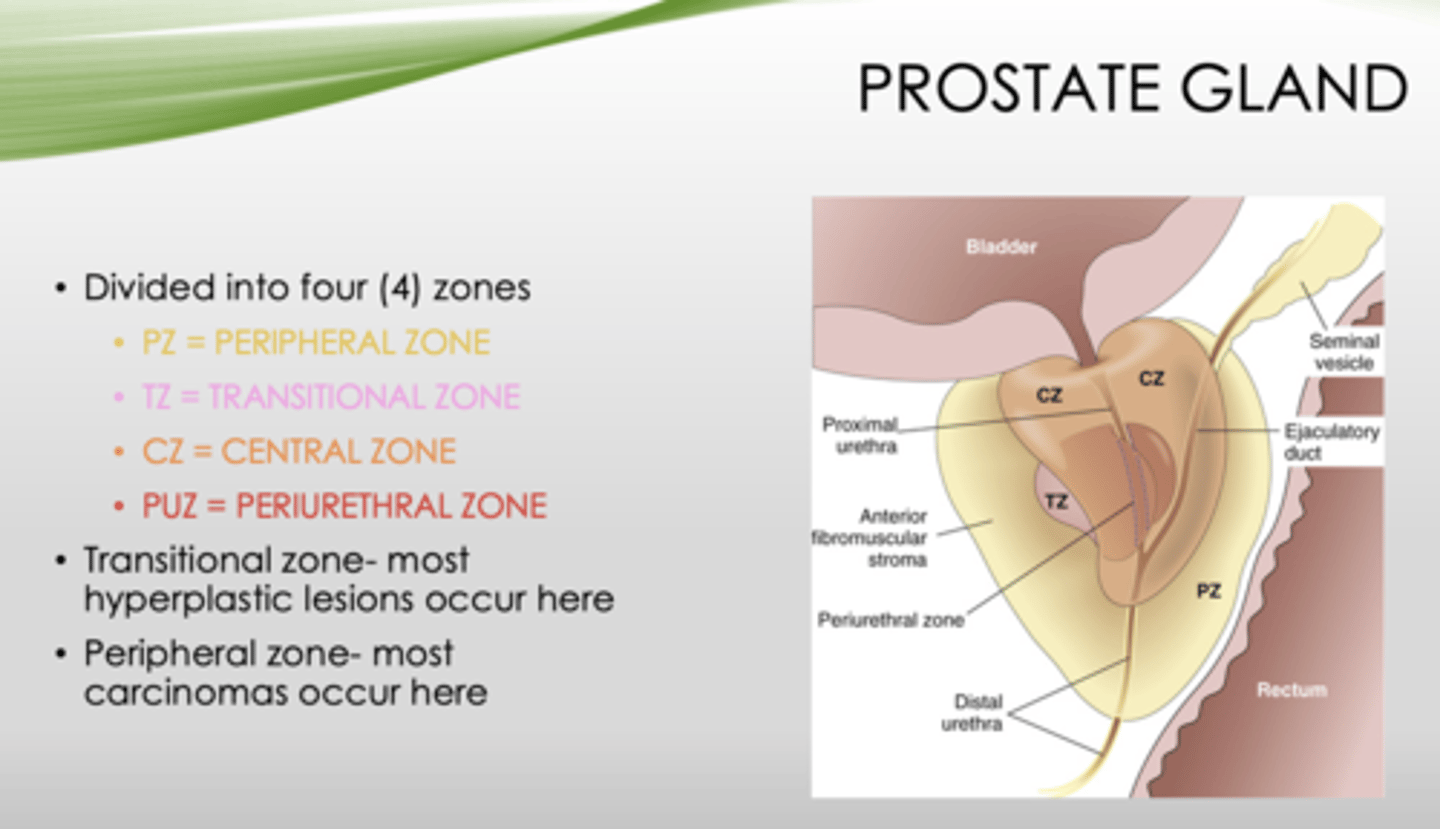
What four zones is the prostate gland divided into?
- Peripheral zone
- Transitional zone
- Central zone
- Periurethral zone

Which zone of the prostate gland has the most hyperplastic lesions?
transitional zone
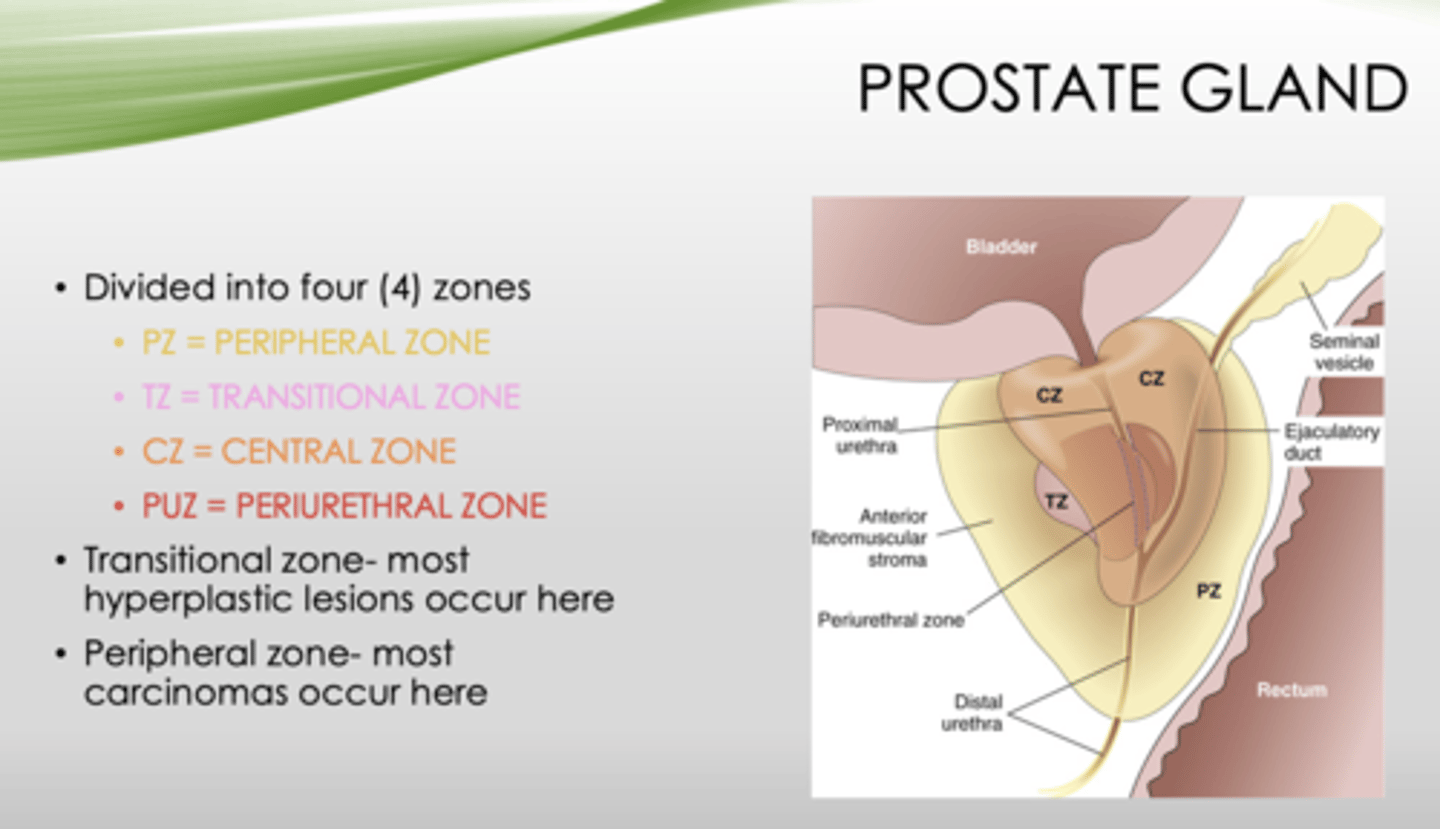
Which zone of the prostate gland has the most carcinomas occur?
peripheral zone
What is the most common bacteria that causes prostatitis?
E. coli

Acute or chronic prostatitis?
- Can cause urinary tract infections
- Associated with fever, chills, dysuria
- Prostate is tender & boggy
acute

Acute or chronic prostatitis?
- Usually associated with recurrent urinary tract infections bracketed by asymptomatic periods
- Presenting symptoms include low back pain, dysuria, and perineal and suprapubic discomfort
chronic

What condition?
- Signs and symptoms same as chronic bacterial
- No history of recurrent urinary tract infections
- Etiology is unknown, unsure if prostate is even related
- Prominent finding - pain during or after ejaculation
- Diagnosis of exclusion
chronic abacterial prostatitis (chronic pelvic pain syndrome)

Define the following
A medical diagnosis that's made by ruling out other possible conditions through examinations and tests
Diagnosis of exclusion

Histologic evidence of BPH is found in up to _____% of men by the age of 80
90%

What is the common cause of BPH?
prostate enlargement

What condition?
- Proliferation of stromal and glandular structures
- Cause of urinary obstruction
- Not premalignant
- Large discrete nodules on periurethral region
- Begins in transition zone
- Can encroach on lateral walls of urethra to compress to a slit-like orifice
BPH

T/F the etiology of BPH is unknown but studies show androgens may play a role
true

These are symptoms of what?
- Increased urinary frequency
- Nocturia
- Dysuria
- Difficulty starting and stopping
BPH

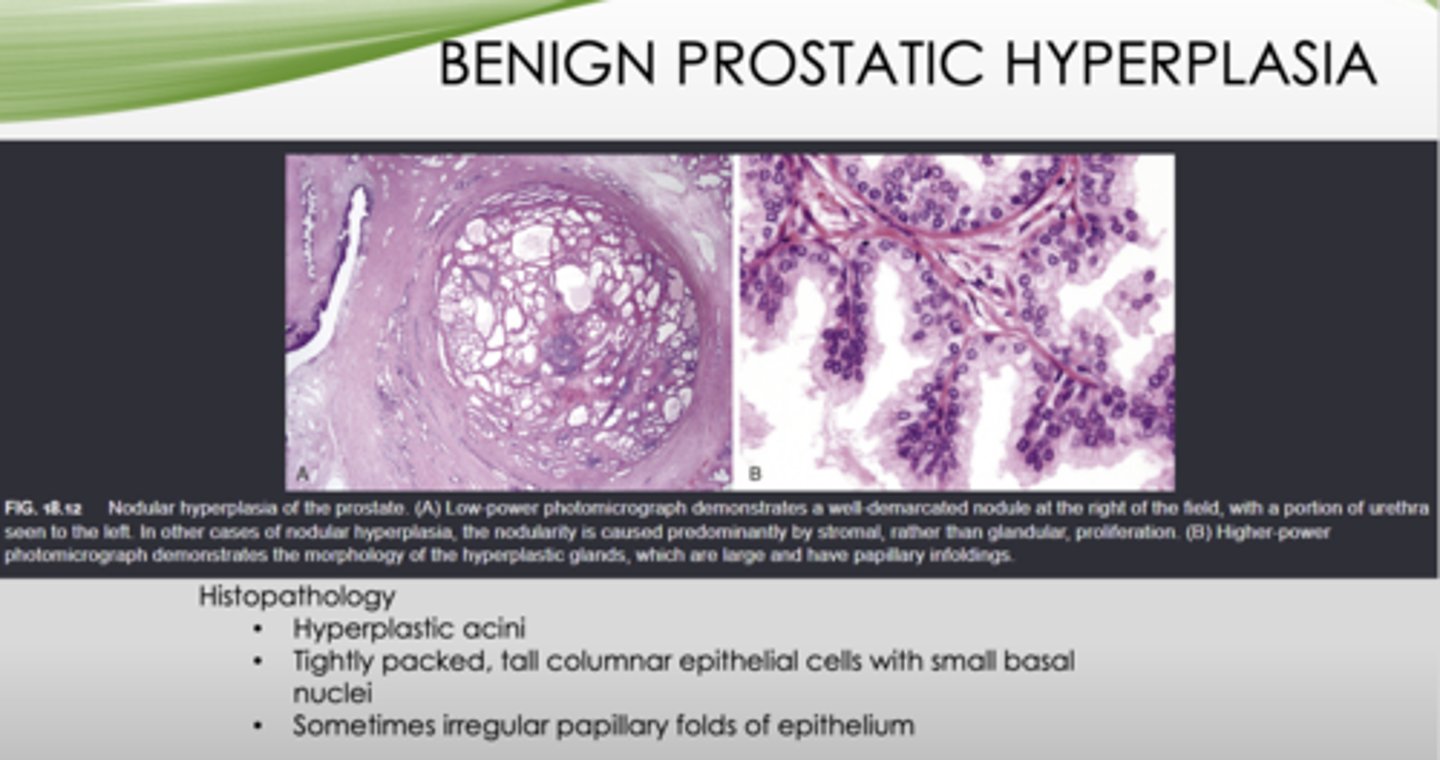
This is the histopathology of what?
- Hyperplastic acini
- Tightly packed, tall columnar epithelial cells with small basal nuclei
- Sometimes irregular papillary folds of epithelium
BPH
What is the most common cancer in men?
Prostate (adenocarcinoma)

What is the etiology of prostate cancer?
- Age (Incidence increases as one gets older)
- Race
- Family history
- Hormones
- Environment
- Androgens play role

Where does prostate cancer arise?
In peripheral zone-posterior aspect

What can be palpated on a rectal exam?
prostate cancer (adenocarcinoma)

This is the histopathology of what?
- Adenocarcinoma- glandular formation, lined by single layer of cuboidal or columnar epithelium
- Glands are smaller & crowded than benign prostate
- Basal cells not seen
prostate cancer (adenocarcinoma)

What condition can metastasize via lymphatics and hematogenous spread (mandible/maxilla)?
prostate cancer (adenocarcinoma)

The following is the grading system for what disease?
- Gleason system (based on glandular pattern of differentiation)
- Grade 1 - most well-differentiated
- Grade 5 - poorly-differentiated-no glandular differentiation
- More than one pattern with 2 scores given
- First number is most dominant pattern
Prostate cancer (adenocarcinoma)

What is measured to diagnose and manage prostate cancer?
PSA (prostate-specific antigen)

What is the treatment for prostate cancer?
- Surgery
- Radiation
- Hormonal manipulation

What is abnormal urethral opening on ventral surface of penis due to malformation of urethral groove/canal?
hypospadias

What is abnormal urethral opening on dorsal surface of penis due to malformation of urethral groove/canal?
epispadias

What other congenital abnormalities can hypospadias and epispadias be associated with?
- Failure of normal descent of testes
- Inguinal hernia

With abnormal openings of the penis, what can be a result?
- UT obstruction
- UTI

What condition?
- Local inflammation of the glans penis and overlying prepuce, respectively
- Caused by candida albicans, anaerobic bacteria, pyogenic bacteria
- Most cases result from poor hygiene in uncircumcised males
- Balanitis
- Balanoposthitis

Define the following:
Accumulation of desquamated epithelial cells, sweat, debris
Smegma

What are the two types of penile intraepithelial neoplasia (carcinoma in situ of penis)?
- Undifferentiated
- Differentiated
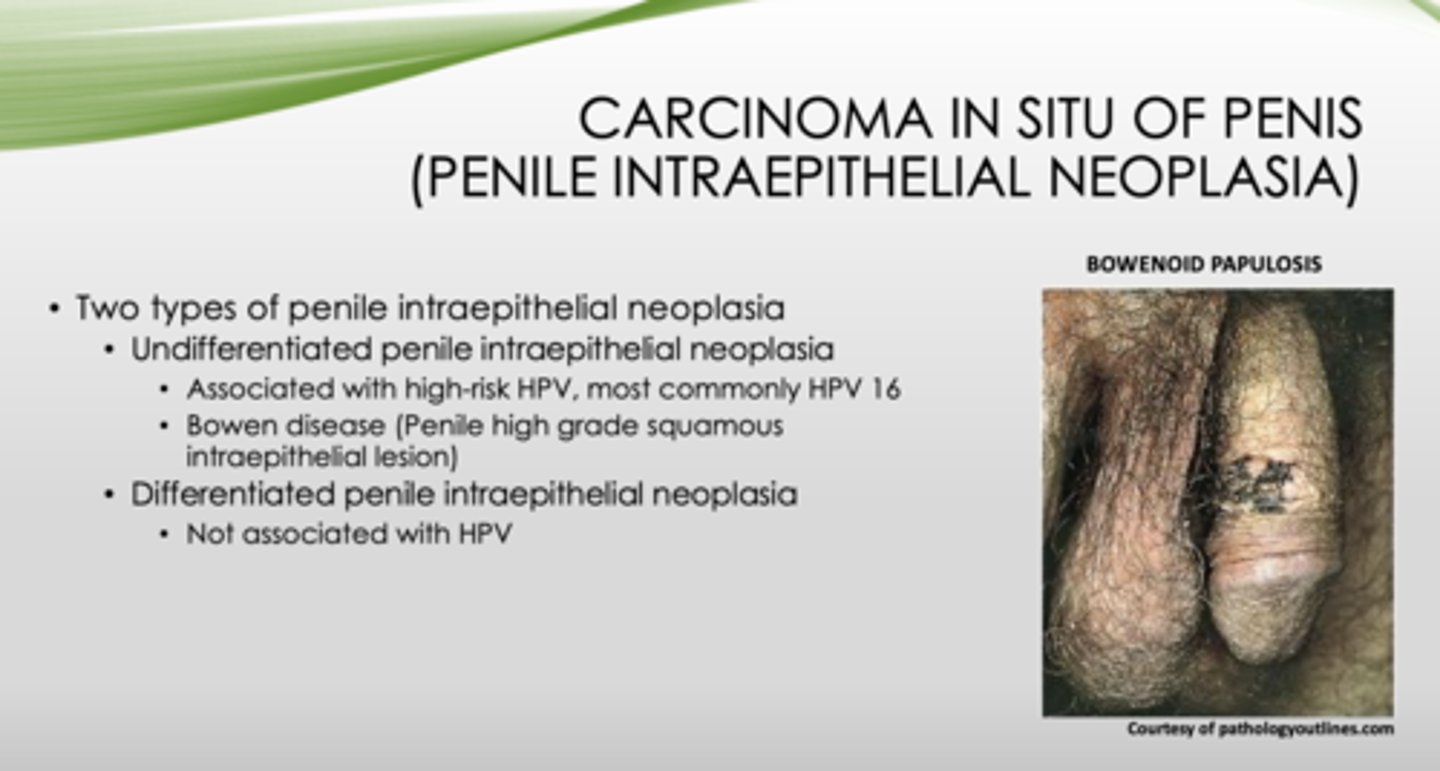
Which type of penile intraepithelial neoplasia is associated with high-risk HPV and bowen disease (penile high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion)?
undifferentiated
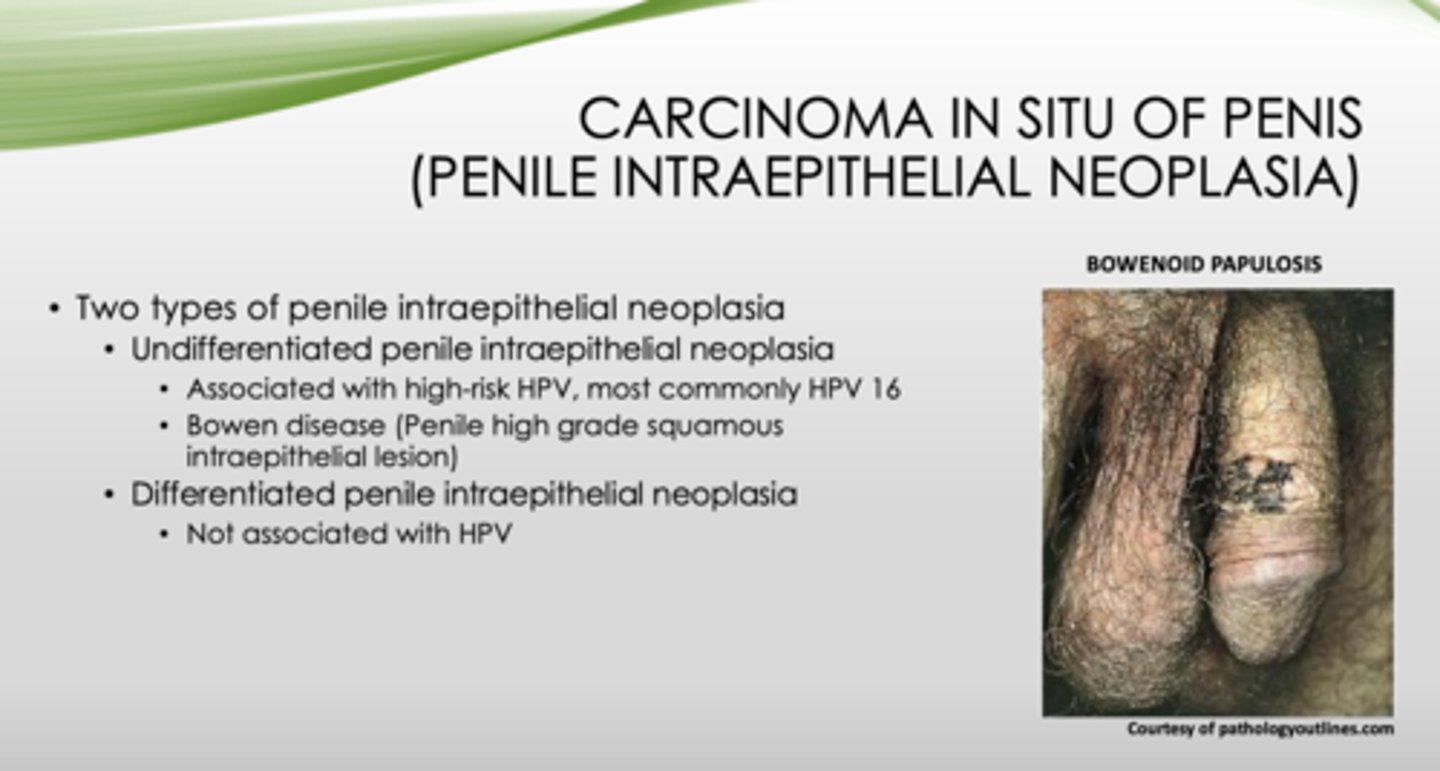
Which type of penile intraepithelial neoplasia is not associated with HPV?
differentiated
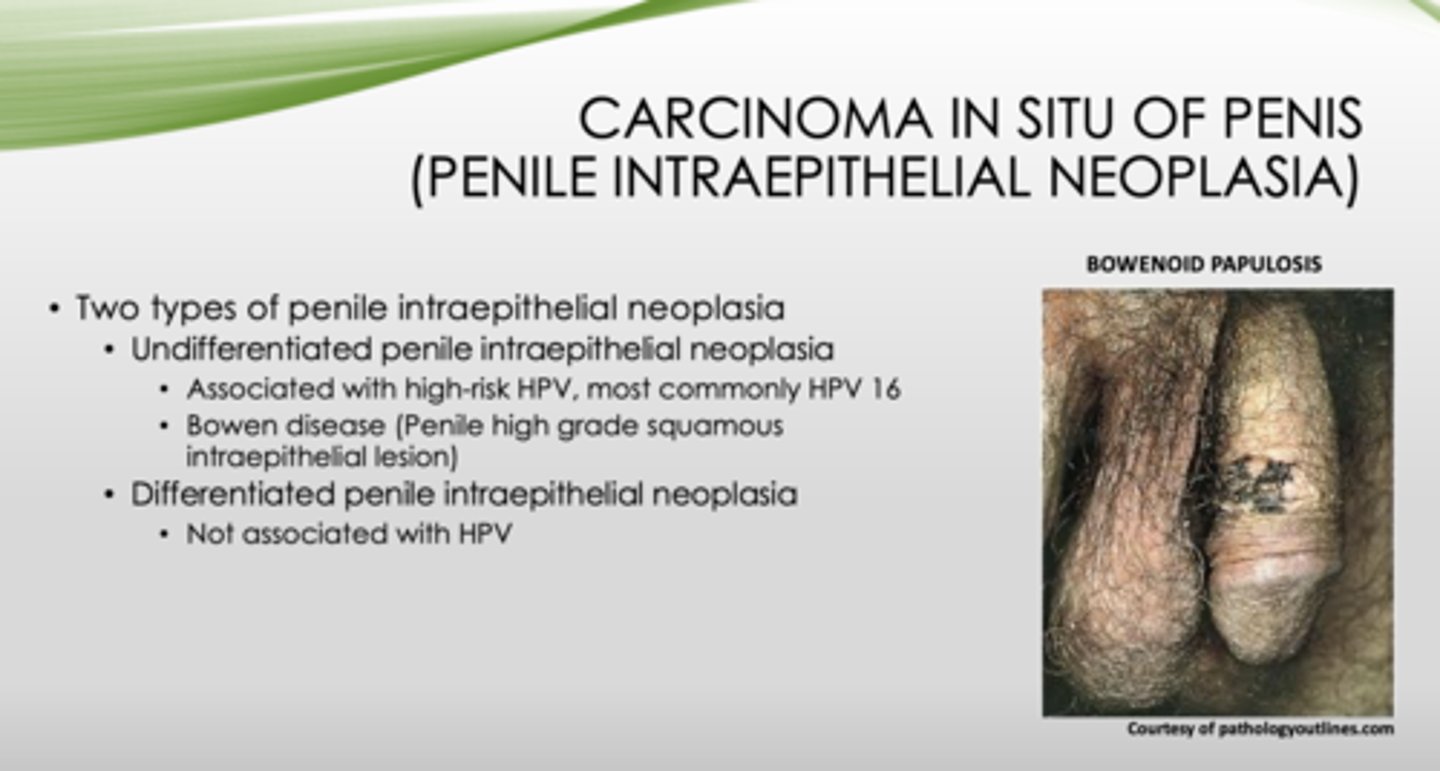
Bowenoid papulosis or Bowen disease?
- Involves sexually active adults
- Affects younger age than Bowen disease
- Presents as multiple, reddish-brown papules
- Small number may transform into SCC
- Usually regresses spontaneously
Bowenoid
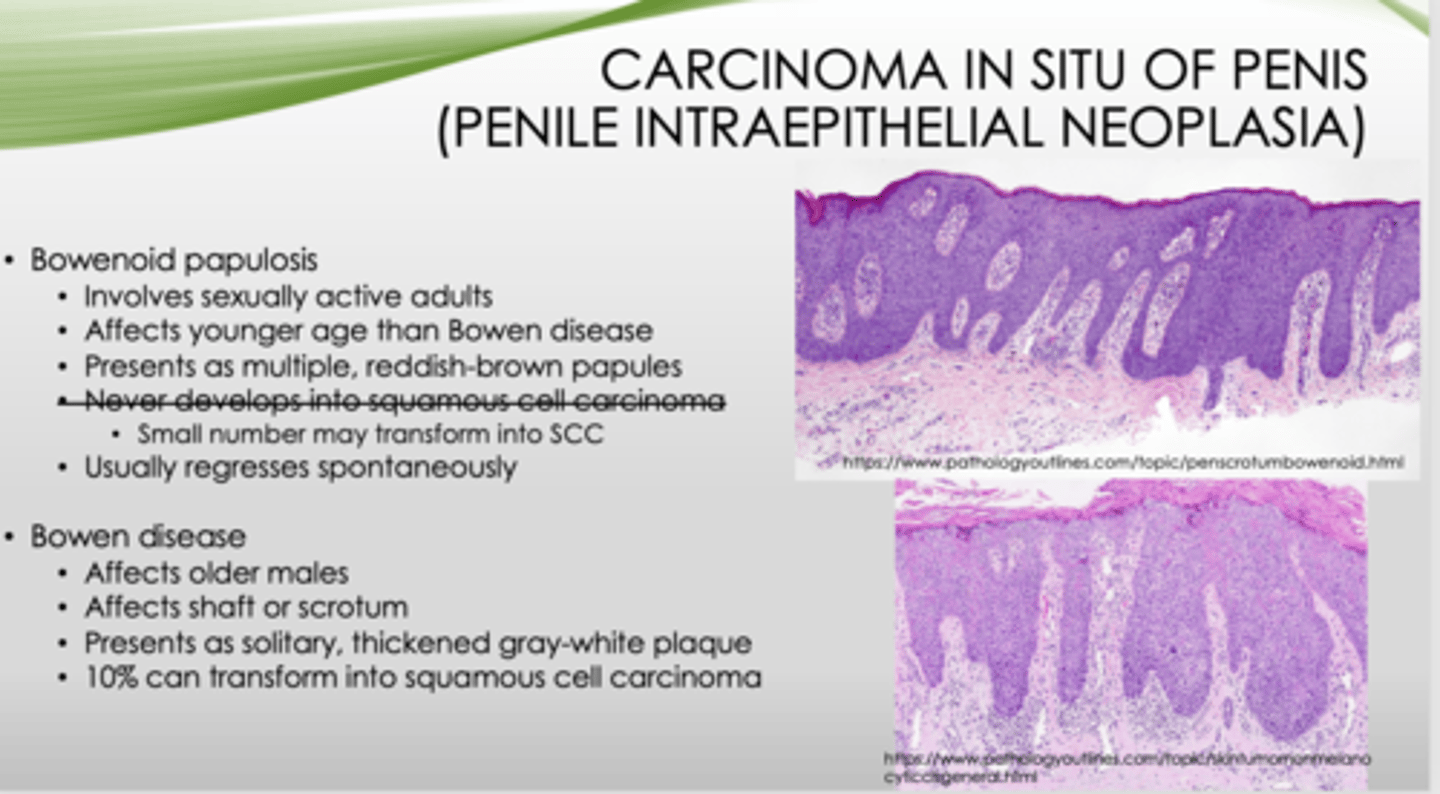
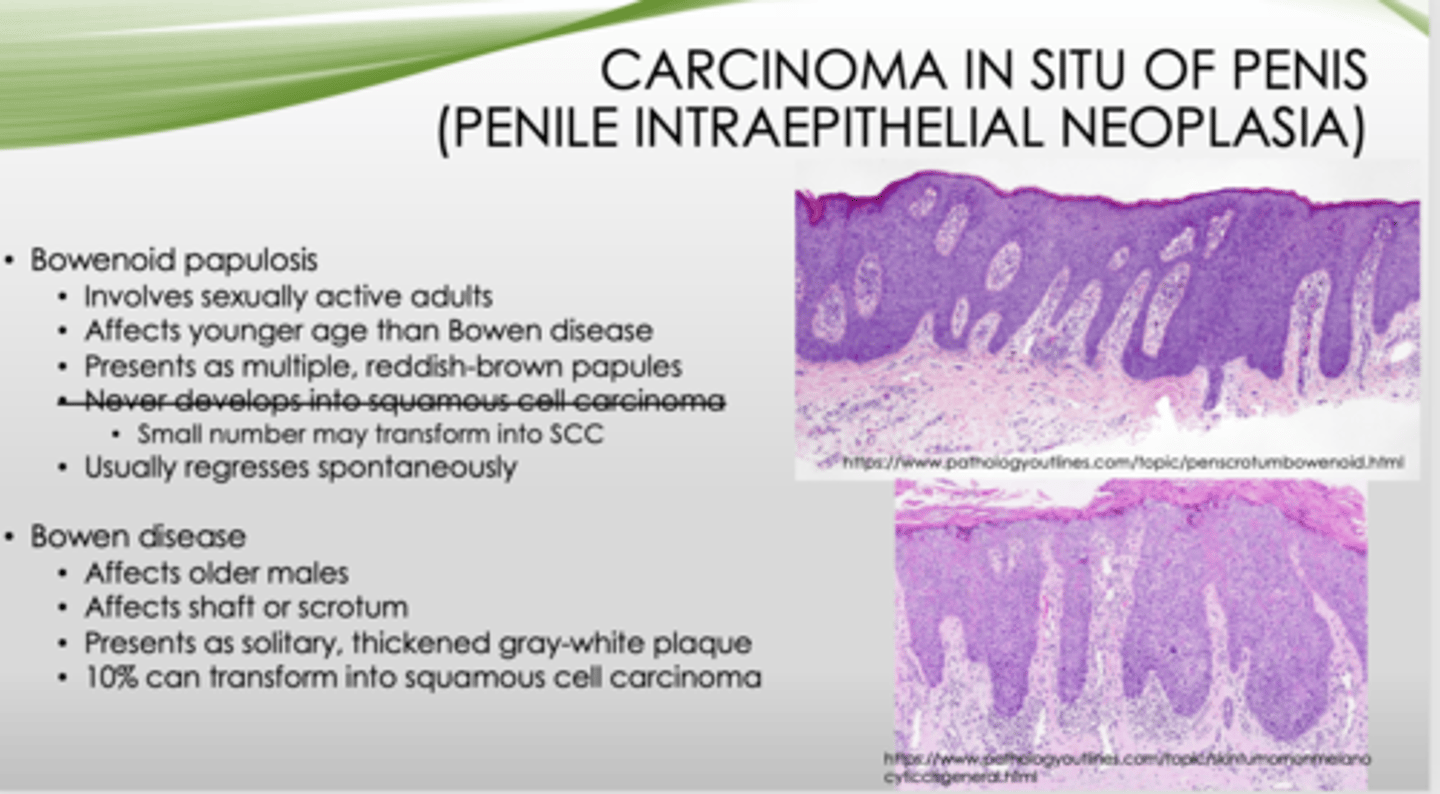
Bowenoid papulosis or Bowen disease?
- Affects older males
- Affects shaft or scrotum
- Presents as solitary, thickened gray-white plaque
- 10% can transform into squamous cell carcinoma
Bowen
What type of cancer is uncommon in the US?
squamous cell carcinoma
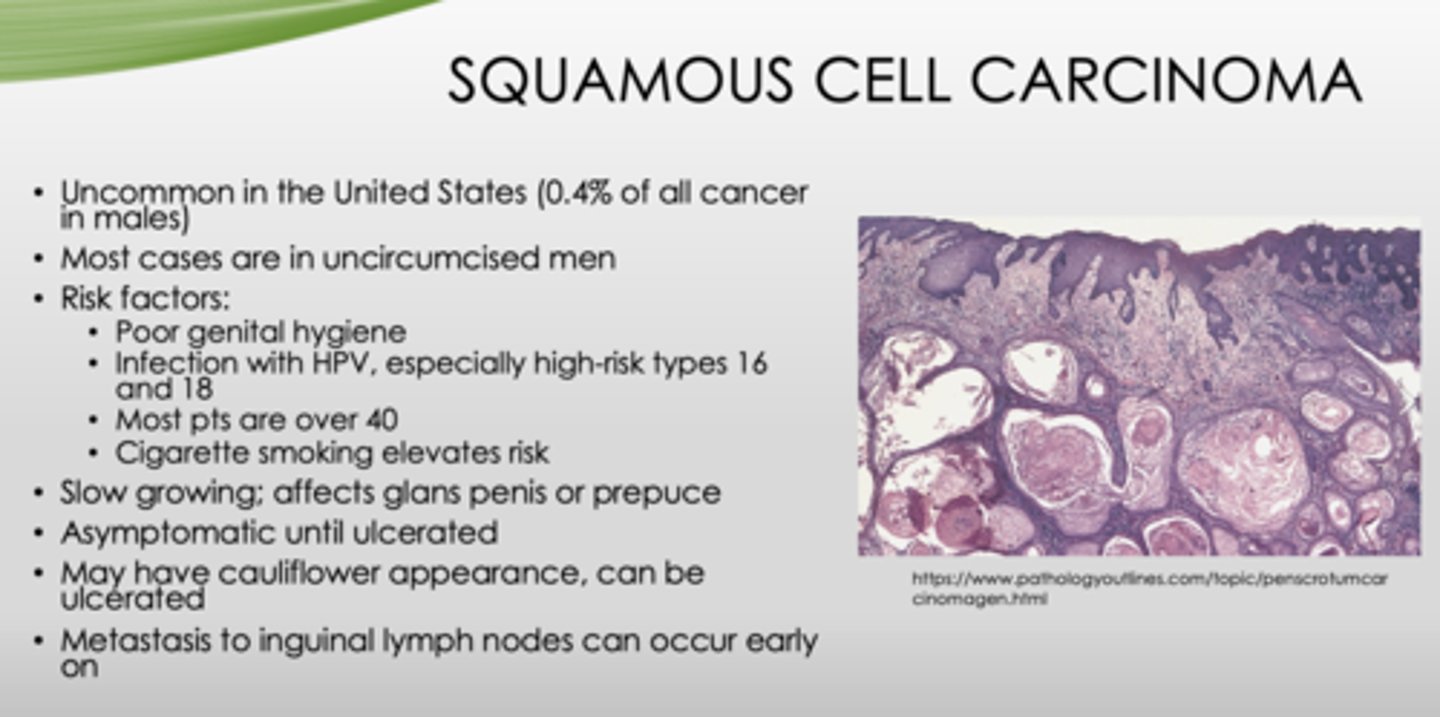
These are risk factors for what?
- Poor genital hygiene
- Infection with HPV, especially high-risk types 16 and 18
- Most pts are over 40
- Cigarette smoking elevates risk
squamous cell carcinoma
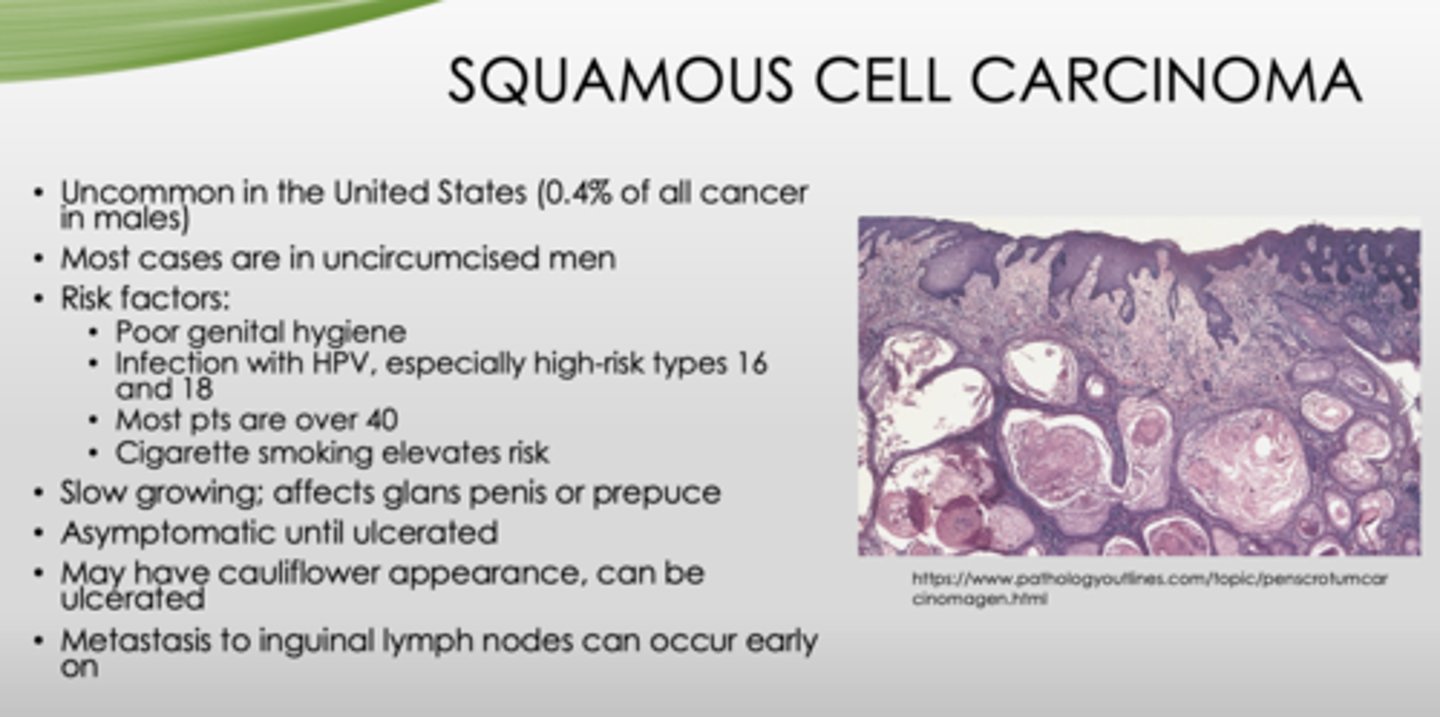
What condition?
- Most cases in uncircumcised men
- Slow growing; affects glans penis or prepuce
- Asymptomatic until ulcerated
- May have cauliflower appearance, can be ulcerated
- Metastasis to inguinal lymph nodes can occur early on
squamous cell carcinoma
