Electromagnetic Spectrum
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Properites of Electromagnetic Waves
They are all transverse waves (oscillate in planes perpendicular to each other)
They can travel in a vacuum (they do not require a medium to travel)
They travel at the same speed (3.0×10^8)
They transfer energy from one place to another
They all obey the general wave equation
When they travel from one medium to another their speed and wavelength change
They obeys the law of reflection and refraction
They do not carry any electric charges
They produce a charge when accelerated
Ionising waves are those with a higher frequencies and hence higher energies
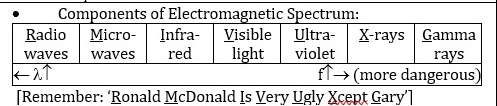
Components of electromagnetic spectrum
Radio → Gamma (frequency ^)
Uses of component of Electromagnetic Spectrum

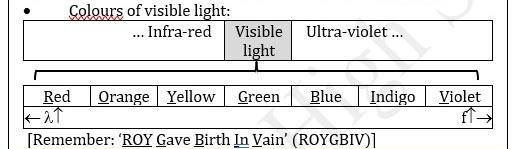
Visible light range
Red → Violet (f^)
Ionisation
The process where one or more electrons are removed from a neutral atom by the action of radiation
Ionising radiation
extremely high frequency EM waves such as X-rays and gamma rays have high energy and can penetrate our bodies more easily than high energy particles that do not penetrate as deeply.
A large portion of our exposure to ionising radiation comes from natural sources in our environment, such as radon gas from the ground, medical exposure, gamma rays from the Earth, cosmic rays, and food and water.
Ionisation harms living cells, resulting in destruction or modification of living tissues. As the charged ion will not behave in the same way as the original atom or molecule, the ion may hinder chemical reactions that affect certain cell processes
Depending on the scale of such disruptions and the specific biological system affected, the result could be cell death, mutations leading to diseases and organ failure.
The exposure to strong ionising electromagnetic radiation such as UV light causes heating effects. The over-exposure to UV light can have harmful effects such as skin cancer and premature aging.
Non-ionising radiation
EM Waves with energy too little to produce ionisation such as visible light, infra-red radiation, microwaves and radiowaves