CardioPulm Peat and Gold Standard Conditions (copy)
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What position would a patient be in for drainage of upper lobes, anterior segments?
Supine w/ pillows under knees
What position would a patient be in for drainage of upper lobes, posterior segments?
Patient leans 30 degrees forwards w/ pillow cushion
What position would a patient be in for drainage of lower lobes, anterior basal segments?
Sidelying, head down, pillows under knees OR legs elevated higher than head
What position would a patient be in for drainage of lower lobes, posterior basal segments?
Prone, head down, pillow under hips
What is the respiratory term that describes the maximal volume of air a patient can forcefully expire after taking in a maximal inspiration?
Vital Capacity
What is the respiratory term that describes the maximal volume of air that can be inhaled after a normal tidal exhalation?
Inspiratory Capacity
What is the respiratory term that describes the amount of air inspired or expired during normal breathing?
Tidal Volume
What is the respiratory term that describes the volume of air still remaining in the lungs after a maximal forced expiration?
Residual Volume
The medical record indicates that a patient is orthopneic. Prior to placing the patient in bed, the physical therapist assistant should:
Check pt’s RR
Which of the following interventions is CONTRAINDICATED for a patient who has heart failure with lower extremity edema?
Ankle pumps in supine position with the legs elevated
The patient is MOST likely to have which of the following abnormal breath sounds during auscultation of the lung fields?
Discontinuous crackles (rales)
What is pleural rub?
An adventitious breath sound heard in the lower lateral chest areas, which may indicate pleural inflammation
What are continuous wheeezes caused by?
Results from airway restriction due to obstruction or bronchospasm
What are Bronchovesicular?
Normal breath sounds heard over the junction of the mainstem bronchi and segmental bronchi produced by the turbulence of airflow between the airways
Which value is MOST appropriate to assess the patient's exercise intensity level?
Rate of Perceived Dyspnea Scale
Which of the following signs and symptoms should the patient be advised to monitor prior to discharge home?
Rapid weight gain and tachypnea
Which measurement tool provides the BEST indicator of functional ability for a patient who has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
6 minute walk test
Which activity would be CONTRAINDICATED for a patient who had a myocardial infarction 3 days ago?
Iso exercises for LEs
An increase up to how many beats per min is an acceptable range to continue exercise?
10-20 bpm
A patient reports leg pain with walking that is relieved with rest. Which system is the MOST likely source of this condition?
Arterial; presents with delayed venous filling, dependent rubor, pain with walking that is relieved with rest, and increased pallor in the limb when elevated
Which position is appropriate for drainage of superior segments of lower lobes?
Supine w/ 2 pillows under hips and bed flat
A patient's recent spirometry shows a forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC) ratio of 60%. Which of the condition is the MOST likely cause of this spirometry result?
Asthma
Which type of respiratory condition is associated with compromised flow rates?
Obstructive; asthma, copd, emphysema, bronchitis
Which type of respiratory condition is associated with compromised lung volumes and capacities?
Restrictive; sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, radiation fibrosis
Which physiological effect involving the pulmonary system DECREASES during exercise?
Airflow resistance; in response to increased oxygen needs with exercise, the airways dilate, resulting in decreased airway resistance
Which of the following physiological effects involving the pulmonary system INCREASES during exercise?
Mucus transport, tissue oxygen extraction, minute ventilation (TV x RR)
Which findings is MOST easily interpreted from an electrocardiogram (ECG) output graph?
Effect of sympathetic nervous system stimulation on the heart
Which heart valves are responsible for preventing backflow into ventricles during DIASTOLIC phase?
Pulmonary and Aortic
Which heart valves are responsible for prevention of backflow into ventricles during SYSTOLIC phase?
Mitral and Tricuspid
Which intervention is BEST to improve long-term ventilation for the patient?
Strengthening the accessory muscles of respiration
What is recommended the MOST for a patient who is taking beta-blockers?
Change positions SLOWLY
A patient who has atherosclerosis in the lower extremities reports lower extremity pain that is worse at night. Which sleeping position would be BEST for the patient?
Supine with legs lower than the head to assist with blood circulation to legs
Which clinical manifestation is MOST likely to occur in a patient who has right-sided heart failure?
Pitting Edema; Peripheral Edema
Which clinical manifestation is MOST likely to occur in a patient who has left-sided heart failure?
SOB, Cough, Pulmonary edema
A patient has been immobilized in a knee extension brace due to a patellar fracture for the past 2 weeks. The patient has no significant medical history. When sitting up, the patient exhibits acute dyspnea, tachycardia, and a decrease in oxygen saturation levels. Which condition is MOST likely causing the symptoms?
Pulmonary Embolism
What are the clinical manifestations of pneumonia?
Cough and Fever
What are the signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension?
Dizziness, light-headedness, pallor, and diaphoresis
What are the initial symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or emphysema?
Coughing, sputum production, and increased dyspnea
Which position would be BEST for diaphragmatic strengthening exercises
Semi-reclined
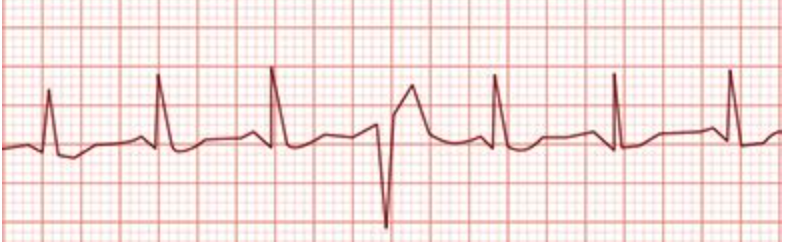
During gait training with a patient, a physical therapist assistant notices the change in the electrocardiogram shown in the photograph. Which action should the assistant take?
Continue w/ treatment; pt has exhibited one premature ventricular contraction (PVC). If experiencing more frequently or in couplets/triplets, then stop treatment, and document only. If occuring in succession, indicating a possible conversion to ventricular tachycardia, then activate emergency medical system.
Which of the following interventions is MOST appropriate to reduce the risks associated with bed rest for a patient who has a documented lower extremity deep vein thrombosis and has reached therapeutic levels of the prescribed anticoagulant?
Frequent Ambulation
Which of the following provides a noninvasive way for a physical therapist assistant to measure oxygen saturation in arterial blood?
Pulse Ox
A patient is performing a cardiovascular conditioning exercise and reports that the activity is "somewhat hard." This report BEST corresponds to which numeric score on the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion Scale?
13/20
A patient is performing a cardiovascular conditioning exercise and reports that the activity is "light." This report BEST corresponds to which numeric score on the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion Scale?
11/20
A patient is performing a cardiovascular conditioning exercise and reports that the activity is "hard." This report BEST corresponds to which numeric score on the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion Scale?
15/20
A patient is performing a cardiovascular conditioning exercise and reports that the activity is "very hard." This report BEST corresponds to which numeric score on the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion Scale?
17/20
Which of the following activities would be MOST effective to achieve a metabolic equivalent (MET) level of 8 METs?
Jogging on level ground at 5 miles/hour (8 km/hour)
Which of the following activities would be MOST effective to achieve a metabolic equivalent (MET) level of 5-6 METs?
Gardening
Which of the following activities would be MOST effective to achieve a metabolic equivalent (MET) level of 1.5-2 METs?
Completing light housework, such as sweeping
Which of the following activities would be MOST effective to achieve a metabolic equivalent (MET) level of 5-6 METs?
Walking on a level treadmill at 4 miles/hour (6.4 km/hour)
When monitoring the vital signs of a patient who is taking a beta-blocker, which of the following effects would MOST likely be observed during exercise?
Lower than normal increase in heart rate
Which of the following values BEST represents the appropriate rating of perceived exertion for a patient to achieve 70% of the maximum heart rate?
13/20
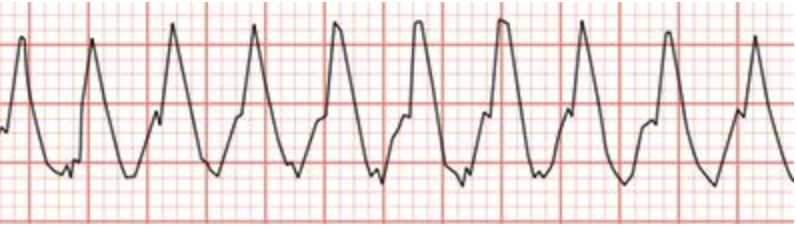
A patient who has cardiomyopathy reports light-headedness during treatment. The physical therapist assistant observes the rhythm shown in the photograph. Which of the following responses is MOST appropriate for the assistant?
Recognize that a medical emergency is occurring; activate the emergency medical response system, pt experiencing ventricular tachycardia
A patient who demonstrates decreased lung sounds, an increased anteroposterior chest diameter, and a decreased excursion of the diaphragm would MOST likely have a diagnosis of
Emphysema
If the heart rate of a patient 3 days post two-vessel bypass surgery increases from 60 bpm to 90 bpm during endurance exercises, the physical therapist assistant should
let the patient rest for 3 minutes and then take the pulse
Which vital sign measurements is the SAFEST blood pressure response to exercise?
Increase in systolic blood pressure of 10 mm Hg
What is an abnormal increase in blood pressure and is unsafe to proceed with exercise?
20-30 mmHG systolic, more than 10mmHg diastolic
Which of the following signs is MOST likely to result from upper airway obstruction and narrowing of the glottis or trachea?
Stridor sounds
What are crackles (rales)?
A rattling or bubbling sound that occurs secondary to secretions in the air passages of the respiratory tract that obstruct the airway
A patient has been experiencing postural hypotension when moving from supine to sitting position. To reduce the risk of hypotension, which of the following actions should be implemented prior to treatment?
Elevate the head of the bed
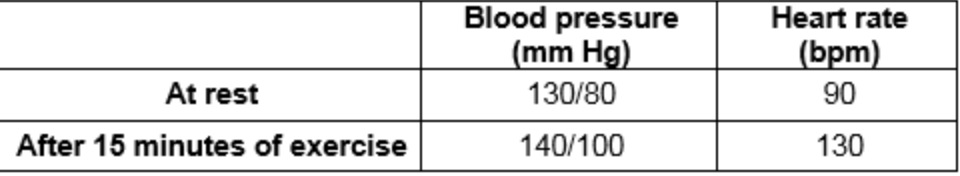
A 60-year-old patient is in outpatient cardiac rehabilitation 2 weeks post myocardial infarction. After the patient exercises for 15 minutes on a stationary bicycle, vital signs are remeasured. The results are shown in the table. Which of the following changes is MOST appropriate?
Decrease intensity of exercise due to increase of HR
When monitoring the vital signs of a person who has mitral valve prolapse, which of the following findings is MOST likely to be observed
Tachycardia
Compared with healthy individuals, a patient who has restrictive pulmonary disease is MOST likely to have which of the following changes in lung volumes or capacities?
Decreased inspiratory reserve volume and decreased vital capacity
Which respiratory measurements would be affected as a result of restrictive lung diseases?
Decrease in vital capacity, functional residual capacity, reserve volume, and total lung capacity
A patient with a recent history of immobilization has a new onset of unilateral leg swelling with dependent edema. This condition is MOST likely due to
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Which of the following interventions would MOST improve outcomes for a patient who has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
Cessation of smoking
Which of the following tests is MOST likely to identify the presence of peripheral artery disease?
Girth Measurements
Which of the following interventions is MOST appropriate to prevent the occurrence of a deep vein thrombosis in a patient who has a complete C6 spinal cord injury?
Passive range of motion exercises to the lower extremities
The results of a patient's spirometry test reveal a tidal volume of 500 mL, residual volume of 1300 mL, and vital capacity of 4600 mL. The patient MOST likely has which of the following conditions?
Cystic Fibrosis
In sarcoidosis, which lung volumes will be affected?
All lung volumes will be decreased
Which lung volumes will be affected by obstructive lung diseases?
Elevated Tidal Volume, Reserve Volume, or Vital Capacity
Which of the following value ranges is considered NORMAL for ejection fraction of the heart?
55% to 75%
Which of the following resting physiological measurements decreases with age?
Cardiac Output
A patient is performing a graded walking program for chronic arterial insufficiency. Leg pain has been increasing during graded walking over the past several days as the distance and speed have been increased. Which of the following modifications should be made to the patient's activity?
Walk at slower pace
A patient has muscle wasting due to use of a medication for chronic pulmonary disease. Which of the following medications MOST likely caused the patient's muscle wasting?
Prednisone (Deltasone)
Which of the following conditions is MOST likely to produce cough, fever, dyspnea, bronchial breath sounds, and mild hypoxia?
Pneumonia
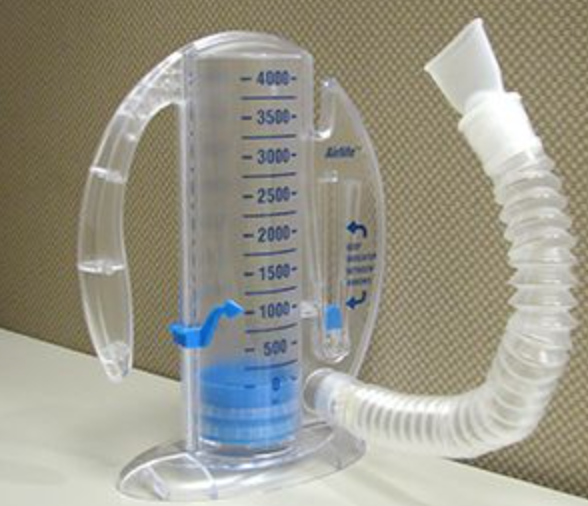
Which of the following rationales BEST explains the use after surgery of the device shown in the photograph?
To facilitate lung expansion through sustained inspiratory effort
Which of the following findings would indicate the need to discontinue exercise in a patient who had a coronary artery bypass graft?
Systolic blood pressure of 270 mm Hg
A patient with arterial insufficiency should be instructed to:
inspect the legs and feet daily
Which of the following signs and symptoms would occur FIRST in the course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
Dyspnea during exertion
Common etiologies for CHF:
Arrythmias (A-fib), pulmonary embolism, hypertension, valvular heart disease, myocraditis, unstable angina, renal failure, medical induced problems, high salt intake, severe anemia
CHF occurs when:
Decrease in cardiac output, impaired left ventricular contraction, abnormalities in skeletal metabolism
What are the clinical presentations with CHF?
Tachycardia, venous congestion, high catecholamine levels, and decrease cardiac output
With CHF, a patient can present with:
S3 gallop, exertional dyspnea, SOB, pulmonary edema, nocturnal dyspnea, orthopnea, sudden weight gain
Medical management for CHF includes?
Diuretics (diuril, lasix), nitrates (nitrostat), cardiac glycosides, analgesics, and angio-statin converting enzyme inhibitor agents (capoten, vasotec)
Etiology of Cystic Fibrosis
It is caused by an autosomal recessive genetic disorder located on long arm of chromosome 7. It causes an abnormality on the CFTR protein that allows sodium chloride to pass through to pass through plasma membrane of the epithelial cell.
What are early symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis?
Persistent cough, salty skin, sputum production, wheezing, poor weight gain, recurrent infections
What are the levels of sodium and chloride that indicate cystic fibrosis?
Amounts greater than 60 mEq/l (normal levels is around 40 mEq/l)
What lung volumes are INCREASED with Cystic Fibrosis?
Increased Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) and Residual Volume (RV)
What lung volumes are DECREASED with Cystic Fibrosis?
Decreased Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV1) and Forced Vital Capacity (FVC)
Pharmacological interventions for Cystic Fibrosis include:
Treatment of infections, thin mucus secretions, replace pancreatic enzymes, reduce inflammation, and assist with breathing. Flutter or Pep Valve.
Physical Therapy interventions for Cystic Fibrosis include:
Chest PT: Postural drainage, percussion, vibration, breathing and assistive cough techniques, and ventilatory muscle training
Posture training, Thorax Mob, Breathing exercises
What are the 3 types of Emphysema?
Centrilobular, Paraseptal, and Panlobular
What structures are affected in Centrilobular emphysema?
Bronchioles
What structures are affected by Paraseptal Emphysema?
Alveoli ducts/Alveoli Sacs
What structures are affected in Panlobular Emphysema?
Bronchioles, Alveoli
Etiology of Emphysema:
Chronic bronchitis, lower respiratory infections, cigarette smoking, genetics
Clinical presentations of Emphysema include:
Most often diagnosed until 55-60 years old. Increased RR, persistent cough, wheezing, difficulty breathing esp during expiration, cor pulmonale (R sided heart failure), severe dyspnea, cyanosis, and increased used of accessory muscles.
What additional findings are found within a patient with Emphysema?
Barrel Chest, rounded shoulders due to tight pectorals, utilizes pursed lip breathing for ventilation, increased anxiety, insomnia, depression, claustrophobia.
Pharmacological Interventions for Emphysema include:
Bronchodilation, Improved oxygenation, and ventilation. Drugs include bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory agents (pulmicort, aerobid), mucolytic expectorants (mucinex), mast cell membrane stabilizers, and antihistamines.