APH CH 11 endocrine system
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Nervous
Cells
Neurons
Endocrine
Cells
Glandular epithelium
Nervous
Chemical
Neurotransmitters
Endocrine
Chemical
Hormones
Nervous
Response
Receptors on postsynaptic cell
Endocrine
Response
Receptors on target cell
Nervous
Speed
Seconds
Endocrine
Speed
Seconds to hours
Nervous
Duration
Very brief unless neuronal activity continues
Endocrine
Duration
May be brief or last for days - years even if secretion ceases
Endocrine system
Includes cells, tissues, and organs collectively called endocrine glands that secrete hormones
2 main types of glands
Exocrine and Endocrine
Exocrine Glands
Secrete fluid to the outside of the body
Ex: Sweat glands, salivary glands, mammary glands and sebaceous glands
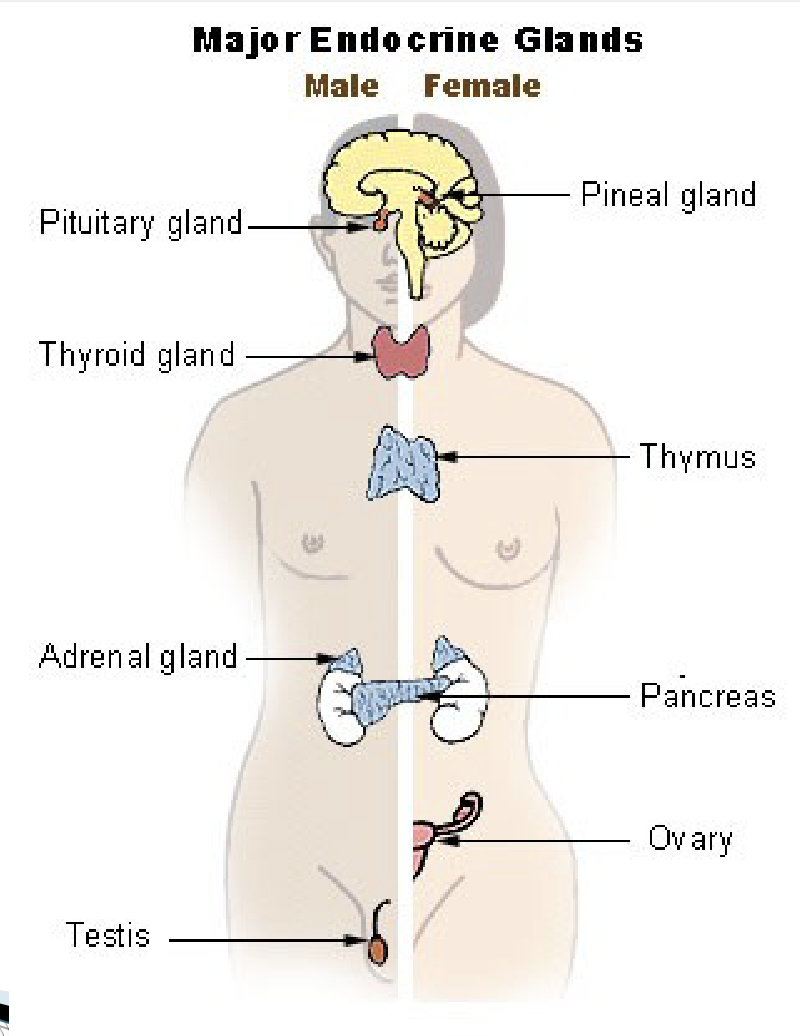
Endocrine glands
release hormones into the bloodstream
Ex: pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal gland and pancreas, pineal gland, thymus gland, testis, and ovary
Functions of glands and their hormones
a) Regulate metabolic processes
b) Control rates of certain chemical reactions
c) Aid in transport of substances across the membrane
d) Regulates water and electrolyte balance
e) Reproduction, development, and growth
Endocrine glands secrete substances called _______ into the internal environment
hormones
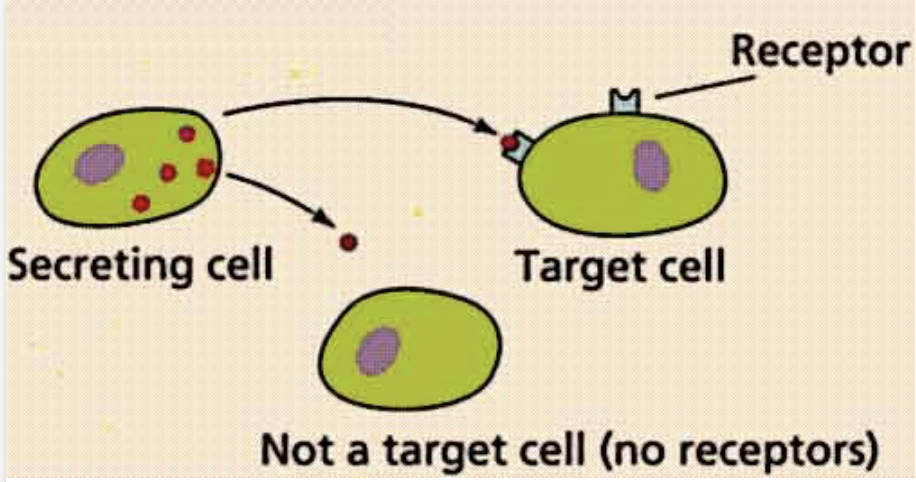
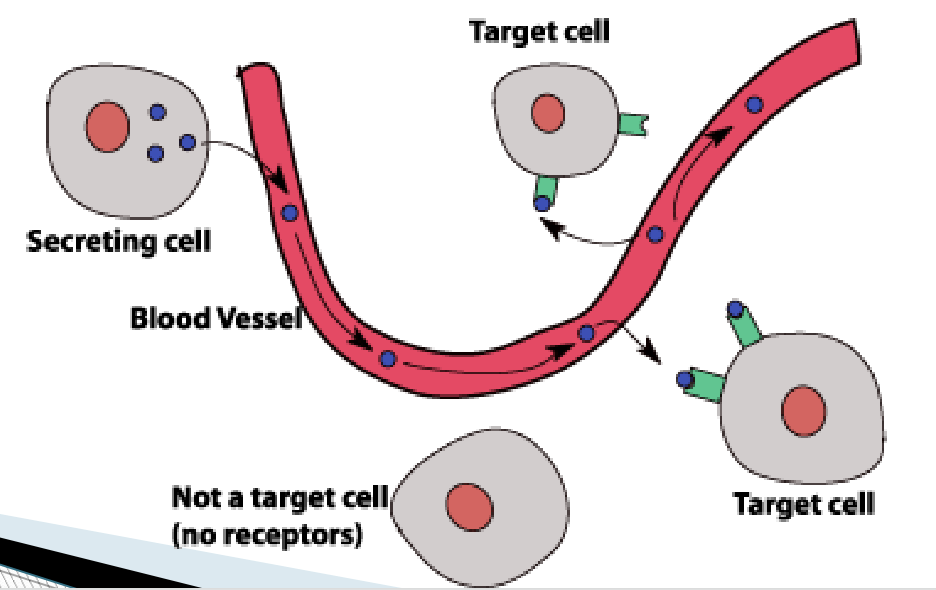
Hormones diffuse from the interstitial fluid into the blood stream, and act on cells called
target cells
Only target cells with specific protein or __________ binding sites can respond to a hormone
glycoprotein
Hormones and target cells are like
“locks and keys” or “puzzle pieces”
Steroids -
made from cholesterol (lipids); water insoluble
Anabolic steroids -
synthetic substances related to the male sex hormones (androgens)
Ex: estrogen, and testosterone
Corticosteroids -
drugs closely related to cortisol, a hormone which is naturally produced in the adrenal gland. Act on the immune system by blocking the production of substances that trigger allergic and inflammatory actions
Non- steroids -
made from amino acids
Ex: insulin, Growth hormone, epinephrine
Negative Feedback Loop
Mechanism used by the Endocrine System that is activated to correct an imbalance in order to correct itself
Negative Feedback Loop
Excess of a particular hormone may shut off its production
Negative Feedback Loop
Excess or lack of a hormone may signal the production of another
Negative Feedback Loop
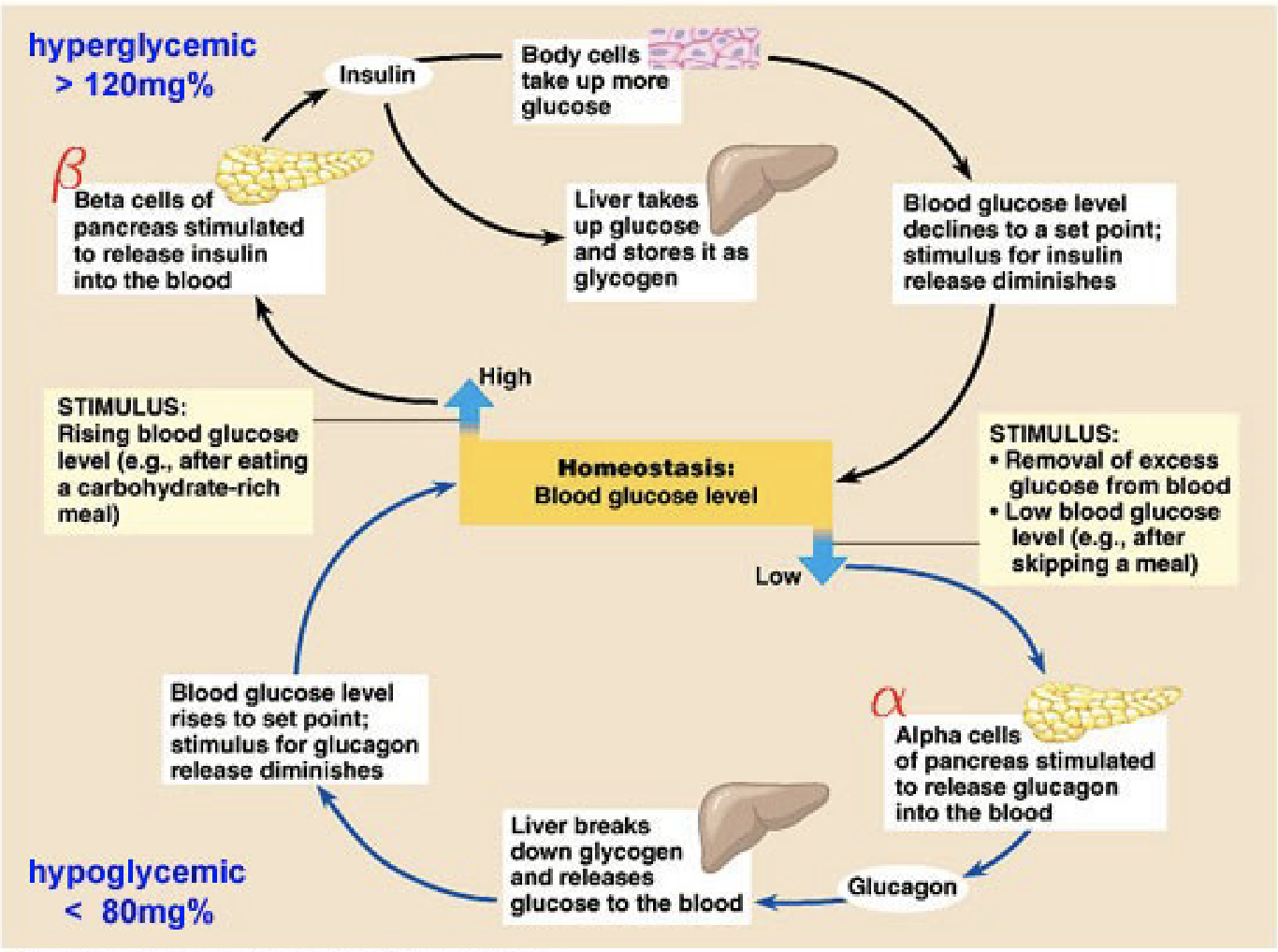
Ex: Blood Sugar Regulation
Pancreas (insulin, glucagons)
Increased sugar levels stimulates the beta cells to produce insulin and inhibits production of glucagons
Low sugar levels stimulates glucagons to be release from the alpha cell which increase sugar level in the body
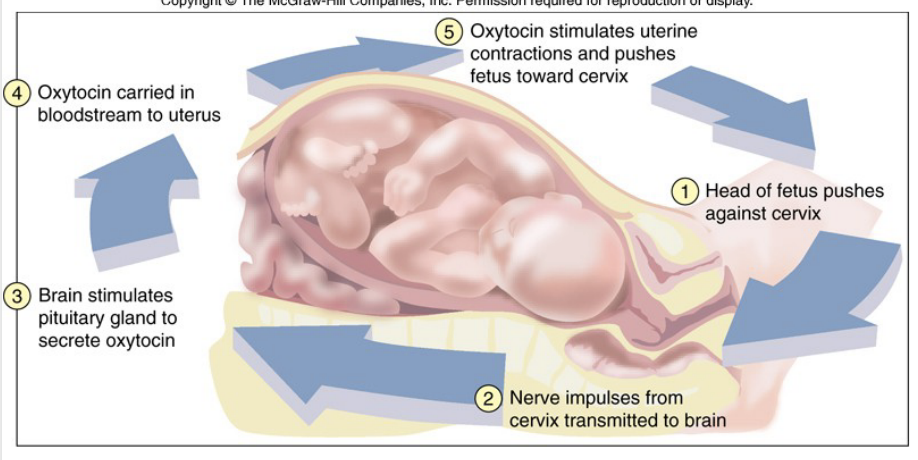
Positive Feedback Loop
Process by which changes cause additional similar changes; moving away from “normal”
Positive Feedback Loop
Ex: Stretching of the uterine tissue causes the hypothalamus to signal the posterior pituitary gland to release oxytocin. Oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions. Uterine contractions stimulates more powerful contractions stimulating the release of more oxytocin... Etc...
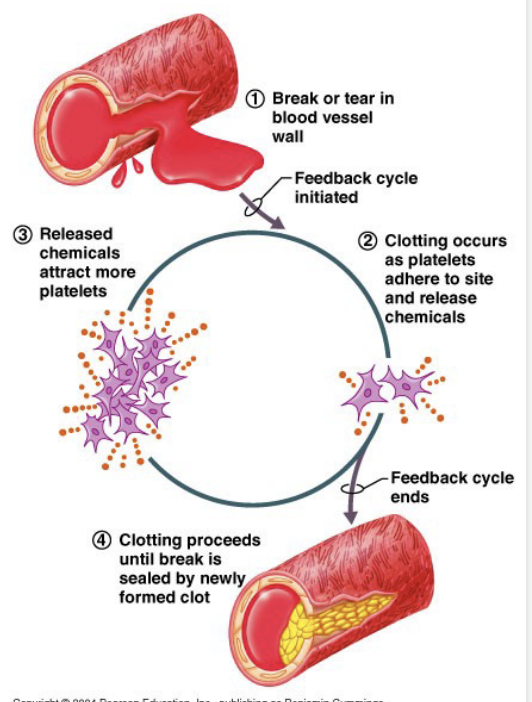
Positive Feedback Loop
Ex: Blood clotting to minimize bleeding