Unit 1 Ocular Anatomy
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Christiaan Huygens
Wave Theory Of light
Sir Isaac Newton
light was made up of tiny particles
James Clerk Maxwell
Light is an electro magnetic wave
Leon Foucault
Speed of light
Max Planck
Quantum Theory
Albert Einstein
Photo electric effect
Frequency formula
Speed/wavelength
Long wavelength
Low Frequency
Short wavelength
High frequency
Foot Candle (historical)
light from a single candle falling on a surface 1 foot away; Amount of light that reaches a surface area.
Foot Candle (current)
a unit of illumination equal to one lumen per square foot
Luminous Flux
quantity of energy of light emitted per second in all directions.
Lux
is the unit of illuminance and it is an indication of how much light is incident on a surface
Concave
diverging
Convex
converging
Index of refraction formula
speed of light in air/speed of light in substance
Snells law formula
n1 sin ɵ1 = n2 sin ɵ2
Light entering a prism
towards the base
Prism Formula
C/D
Convex Lens
Base to Base
Concave lens
Apex to Apex
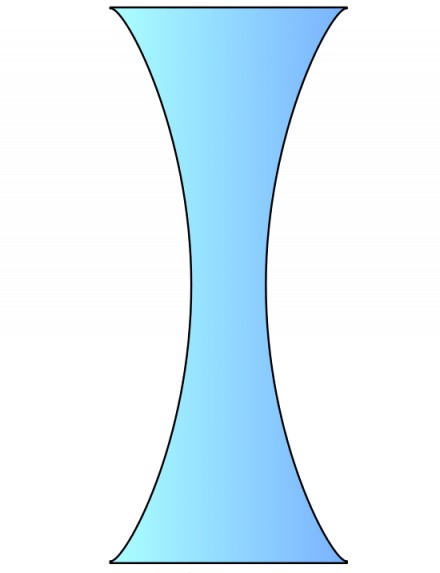
Concave or Convex
Concave
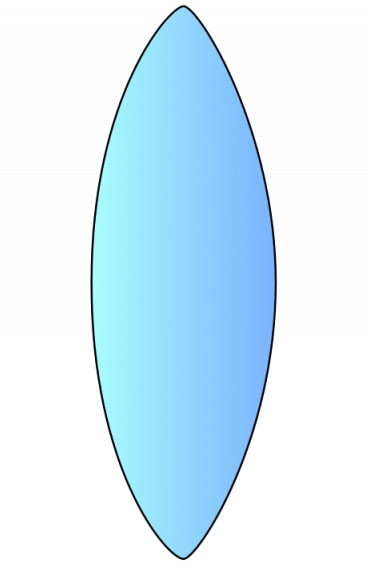
Concave or Convex
Convex
Focal Length Formula
1/f
Convex Lens properties
Plus power, Magnified, Behind the Lens, Real & inverted.
Concave Lens Properties
Minus power, Minified, Infront of lens, Virtual and Upright.
(+3.00)-2.00 ×180
Spherical Power
+3.00(-2.00)x180
Cylinder Power
+3.00-2.00(x180)
Axis
Emmetropia
Images from distance objects are formed at the central retina
Ametropia
Images from distance objects are focused either in front of or behind the retina, in one or both the meridian. Refractive error present.
Myopia
Light rays focus in front of the retina & corrected with diverging or minus lenses. Eye is longer.
Hyperopia
The eye is shorter so the focal point for parallel light rays lands behind the retina. Corrected with plus or converging lenses.
Astigmatism
When parallel rays of light do not come to a single point focus on the retina. Corrected with coronoid of strum
Anisometropia
A condition in which the two eye have unequal refractive errors
Aniseikonia
A difference in image size and/or shape seen by both eyes
Accomodation
Eye changes its power to focus on near objects
Amplitude of accommodation
measures the closest point that the eye can focus
Presbyopia
Loss of accommodation associated with aging
Latent hyperopia
Amount of hyperopia that can be overcome with accommodation