Biology C1.1- enzymes and metabolism
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
enzymes description
are catalysts
3D proteins that speed up chemical reactions
interact with substrates and substrate molecules
control the rate of reactions
metabolism
complex network of interdependent and interacting reactions occurring in living organisms
anabolic reactions
“build up”
build macromolecules
require energy input to occur
anabolic reaction examples
condensation reactions, photosynthesis
catabolic reactions
“break down”
break down macromolecules into monomers
release energy as they occur
catabolic reaction examples
hydrolysis, oxidation reaction, digestion
what living organisms are dependent on
C - carbon
O- oxygen
H - hydrogen
metabolic pathway
cells make things in steps and each step needs an enzyme
substrate goes into enzyme 1 → intermediate 1
intermediate 1 goes into enzyme 2 → intermediate 2
intermediate 2 goes into enzyme 3 → final product
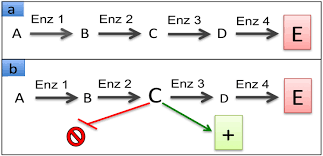
what happens when there is too much product
the product goes back and blocks enzyme 1 which stops the whole pathway so the cell doesnt waste energy
how you get more control over reactions
chemical changes in living things often occur with a number of stages
describing metabolic pathways
cycle / chain of enzyme catalysed reactions
chemical change from 1 molecule to another
not often happening in large jumps'
sequence of small steps
small steps = metabolic pathways
are enzymes globular
yes
enzyme structure
tertiary
active site
region / area of an enzyme surface that has a specific shape, composed of a few amino acids with complimentary base pairing
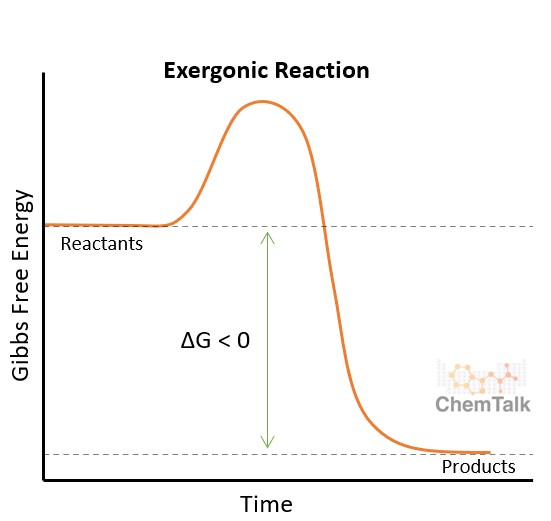
exergonic
release energy
more energy is released when chemical bonds form its products then is needed to break the bonds in the reactants
exothermic reactions
product has less energy than the reactants of an experiment
exergonic graph
endergonic graph
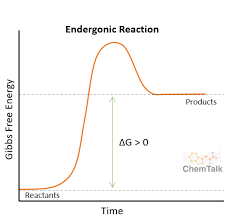
endergonic
takes in energy
more energy is needed to break the bonds in the reactants than is released when the product is formed
endothermic reaction
product has more energy than the reactants of an experiment
induced fit theorey
explains the broad specifity of enzyme activity
needing to be similar enough to work
imrpovement of lock and key method
ATP
adenine TRI phosphate
energy currency of a cell
ADP
adenine DI phosphate
looses a phosphate
activation energy
energy storage molecule
energy necessary to destabalise the existing bonds in a substrate so the reaction can proceed
lowering the activation energy = increased chemical reactions = bonds broken easier
ATP functions
supplying energy - needed to synthesize large molecules
supplying energy for mechanical work - muscle action
collision theorey
substrates entering with a minimum rate of motion (kinetic energy)
that will provide the energy necessary for the reaction to occur
enzymes dont provide this energy, they just lower it
ways of overcoming the energy barrier and increasing the rate of reactions
increase energy of the reacting molecules which increase the rate of collisions
lowering the activation energy so bonds can break more easily
thermodynamic reaction examples
exergonic, endergonic
intracellular enzymes
enzymes that occur within a cell
extracellular enzymes
enzymes that occur outside a cell
do groups of enzymes work together in incremental steps inside and outside the cell
yes
linear pathway
happens in a fixed sequence
each step converts the substrate into a product which becomes the substrate for the next enzyme
clear start and end point
if one enzyme stops working, the whole pathway is affected
linear pathway example
glycolysis
cyclic pathway
arranged in a loop
starting molecule is regenerated at the end so the pathway is continued repeatedly
each step is controlled by a specific enzyme
cyclic pathway example
krebs cycle in respiration and calvin cycle of photosynthesis
cyclic pathway drawing

linear pathway drawing
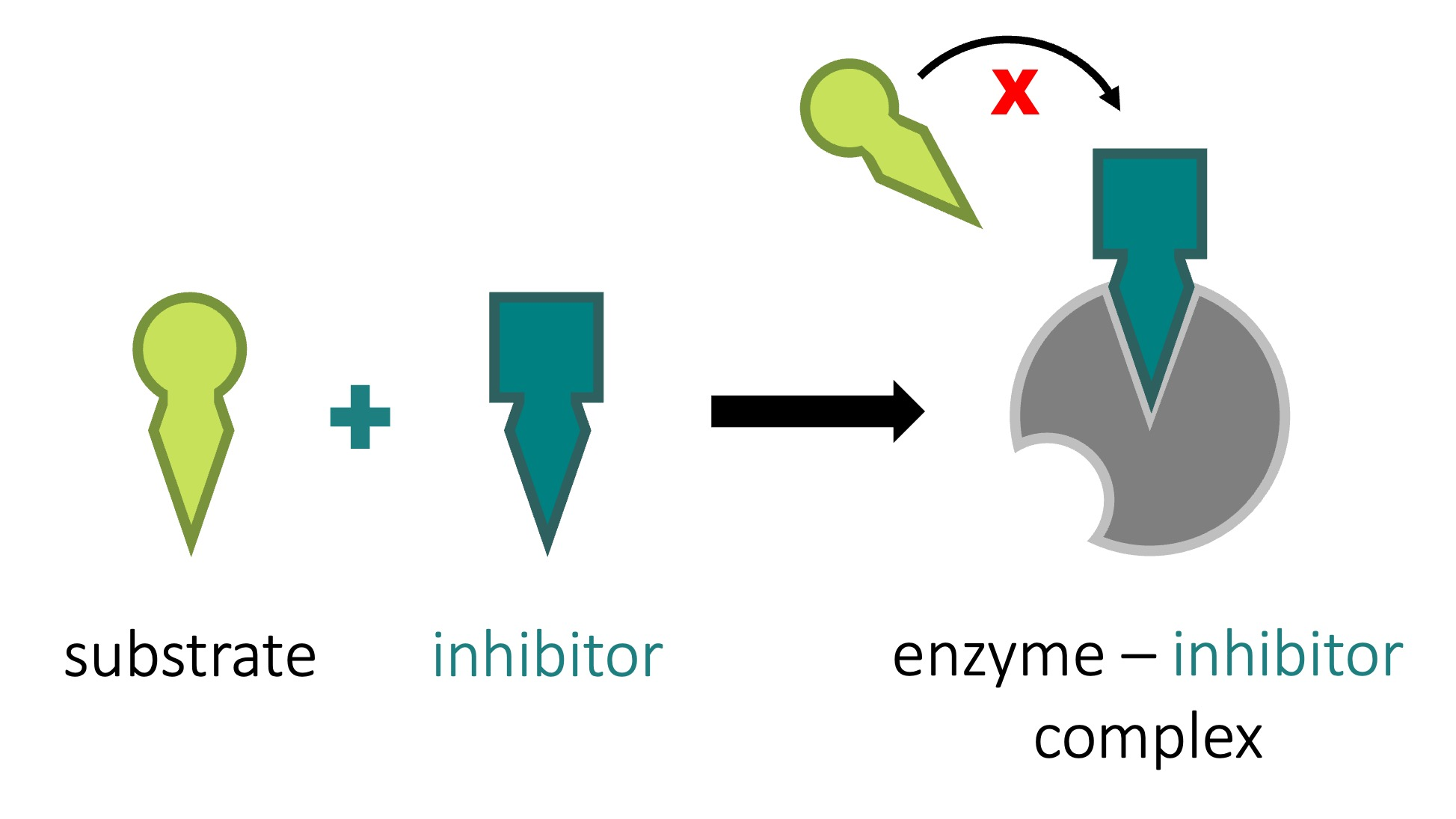
inhibitor
a molecule that binds to an enzyme and slows down / stops the enzymes function
enzymes can be inhibited by other molecules
inhibition can either be competitive or non competitive
competitive inhibition drawing
non competitive inhibition drawing
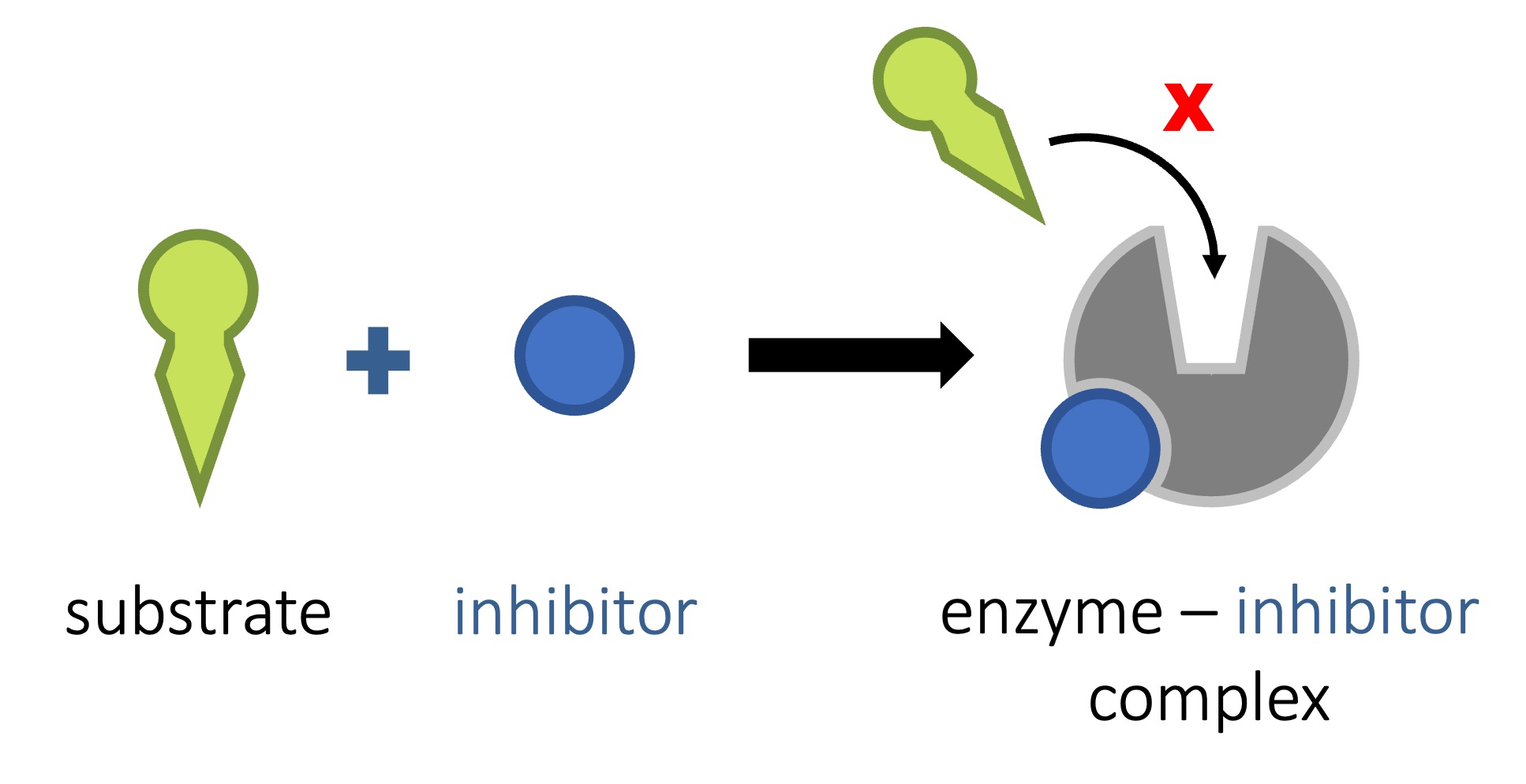
competitive inhibition
the inhibitor fits into the active site and prevents the substrate from entering
non competitive inhibition
inhibitor fits into an allosteric site which causes a change in the active site so the substrate cant attach to react
allosteric site
other site
non competitive inhibition example
cyanide ions blocking cytochrome oxide in oxidation
competitive inhibition example
O2 competing with CO2
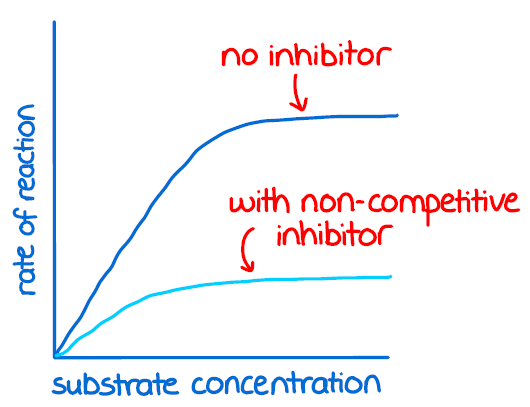
non competitive inhibition graph
as the concentration of inhibitors increase, the rate of reaction decreases and fewer functional active sites are available for a reaction
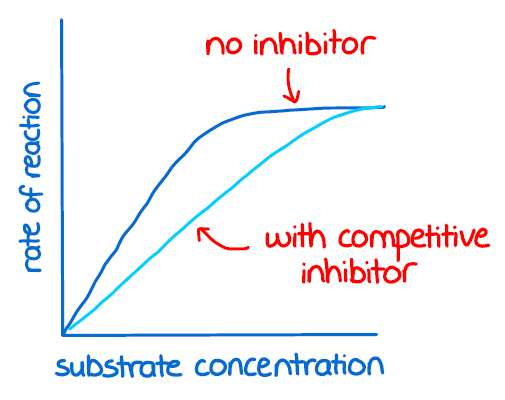
competitive inhibition graph
same maximum rate will be achieved. if there is more inhibitor, the faster it will take to reach the maximum rate but no number of enzymes have changed
competitive inhibition consequenses
high levels of cholesterol means blockages in blood vessels which can lead to cardiovascular disease
statins
act as drugs and competitive inhibitors
combine with the active site of an enzyme
essential catalyzing the biosynthesis of cholesterol within the liver
isoleucine
essential for amino acids
as concentration increases, some of it binds to the allosteric site
acts as non competitive
then the pathway is turned off
end product of isoleucine
usually involves the allosteric site
usually reversable when toxins and poisons are involved
substrate combines with an allosteric site
penicillin
irreversible inhibitor which binds to transpeptidase (makes bacteria cell walls)
inactivates transpeptidase by bonding to a particular chemical group at the active site
defensive cell wall prevents bacterial reproduction
why arent humans effected from penicillin
dont have cell walls
the change from penicillin
some satin bacteria have become resistant to penicillin due to mutation
penicillinase attacks molecular structure of penicillin by breaking specific bonds
how to treat satins
scientists change the structural makeup of penicillin to produce variants that arent inactivated by penicillinase
what allows them to produce an enzyme called penicillinase
some satins of bacteria have become resistant to penicillin due to mutation
denaturation
structural change in proteins active site that results in a loss of its biological properties
enzymes depend on the shape of their active site to function
factors affecting enzyme activity
high temperatures, extreme pH, concentration of the substrate
process of denaturation
causes the active site of an enzyme to change shape since the bonds are broken and that enzyme wont work anymore

how the spread of a reaction can be measured
how fast the substrate disappears
how fast the product is formed