Chapter 8 - Skeletal System: Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
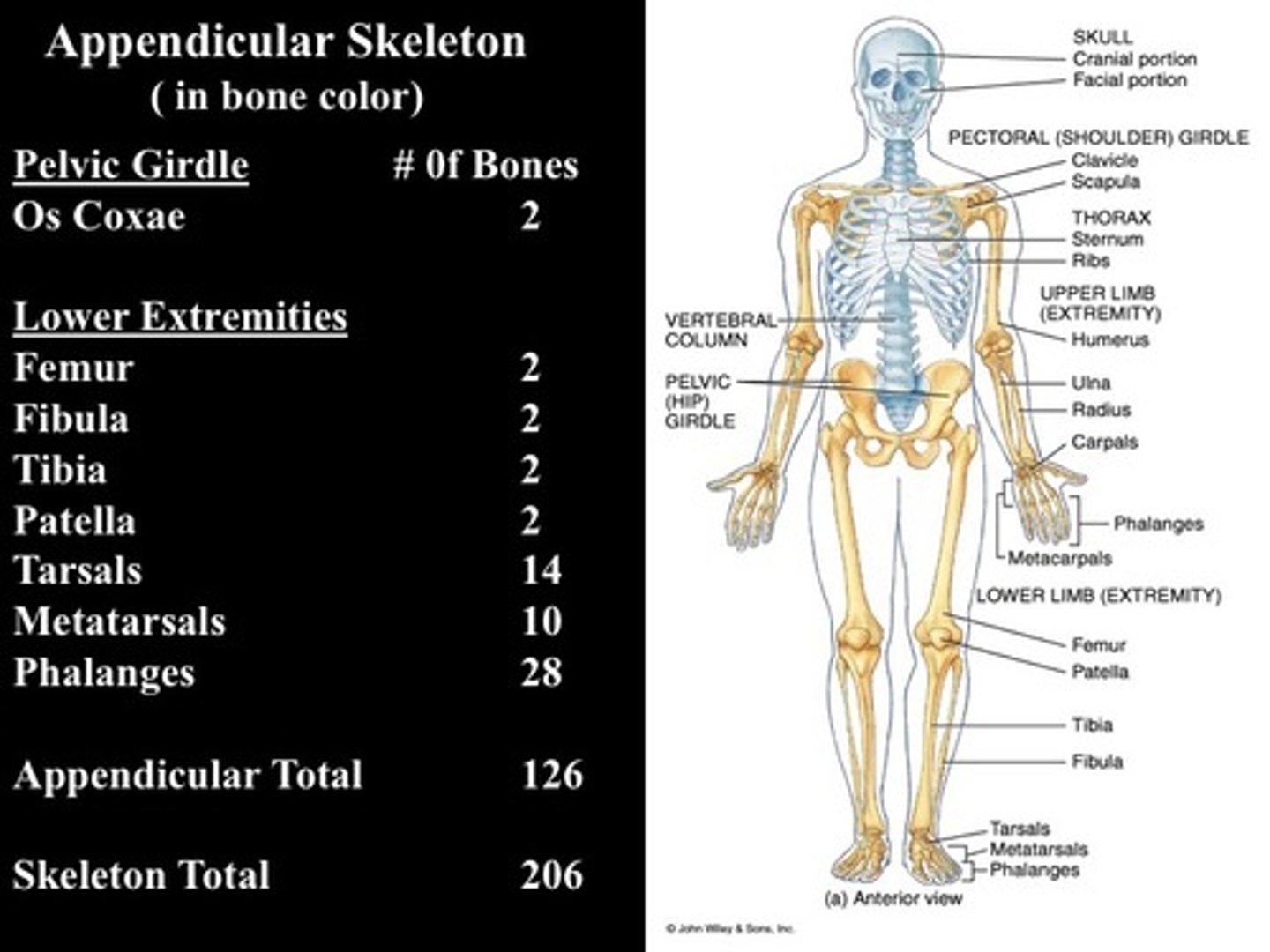
Appendicular Skeleton
-includes 126 bones:
>pectoral girdle (4)
>upper limbs (60)
>pelvic girdle (2)
>lower limbs (60)
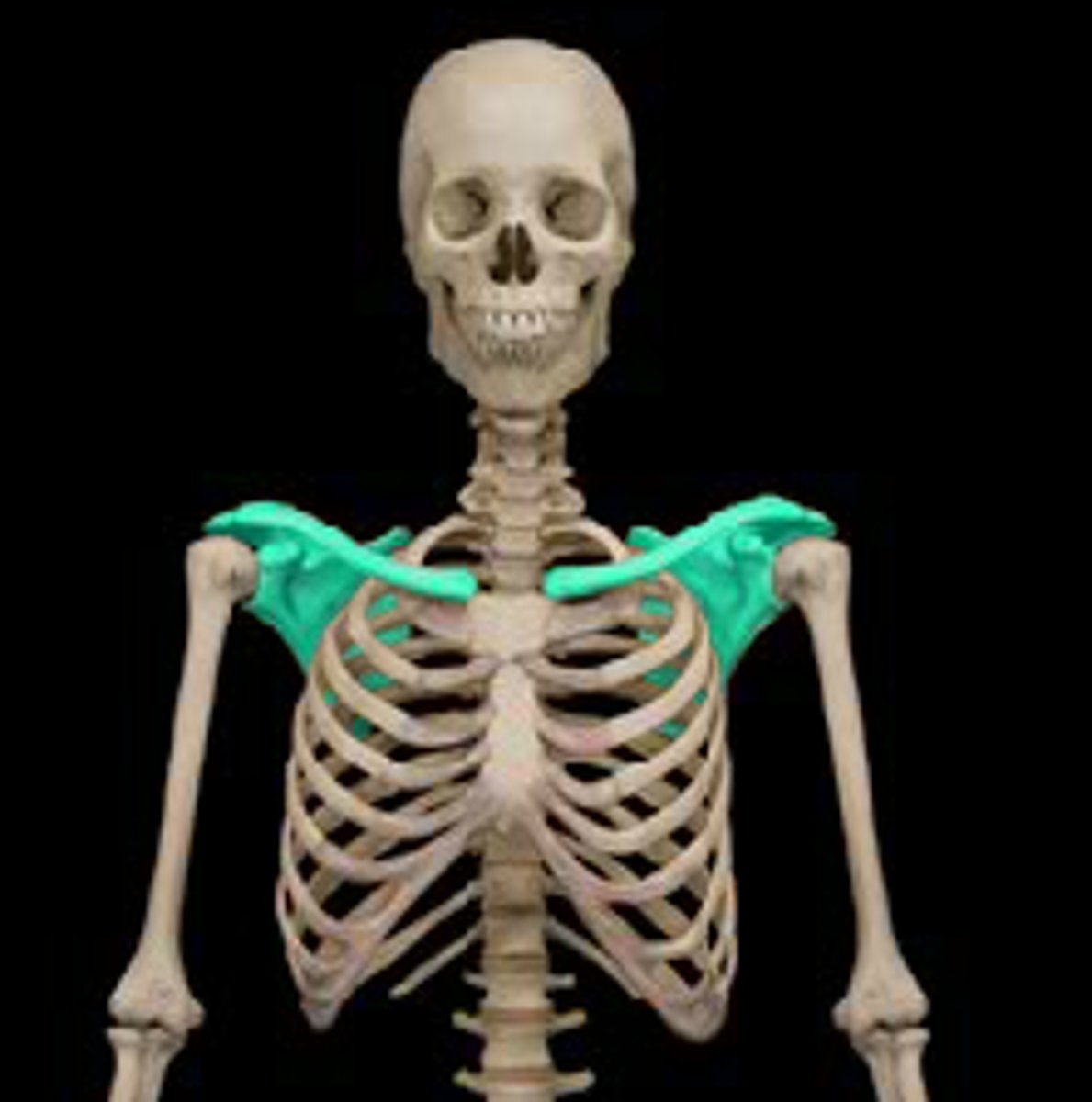
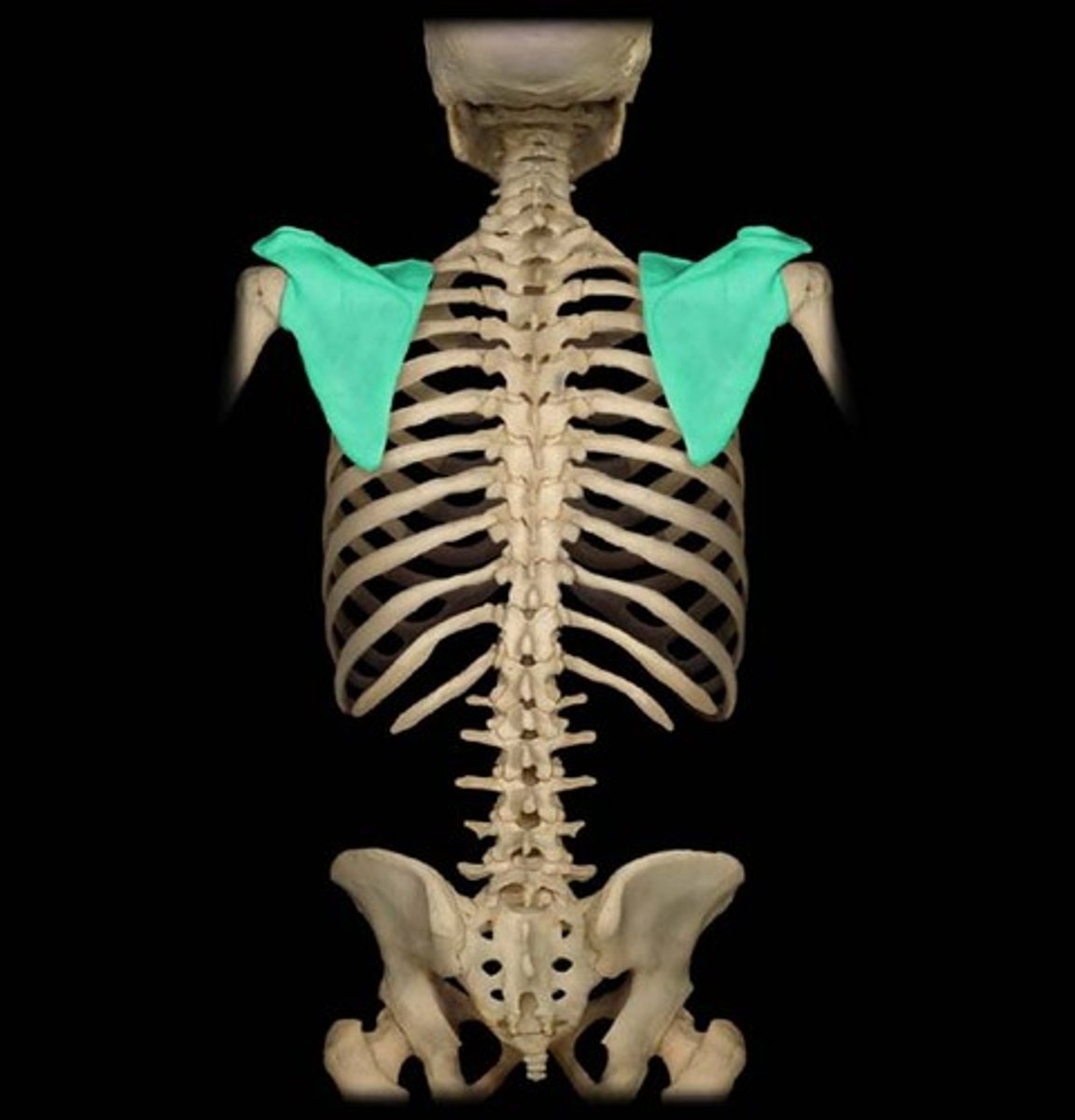
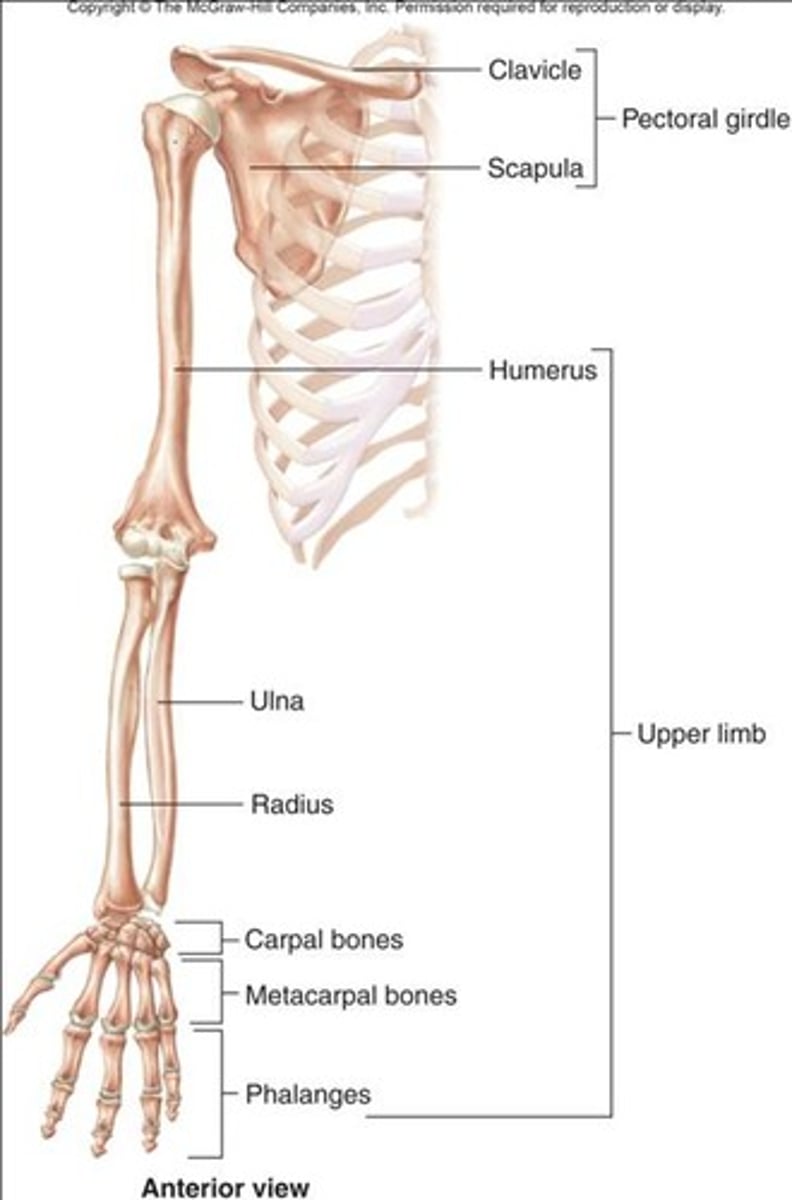
The pectoral girdle
-Consists of clavicle and scapula
-Articulates the upper limbs with the trunk
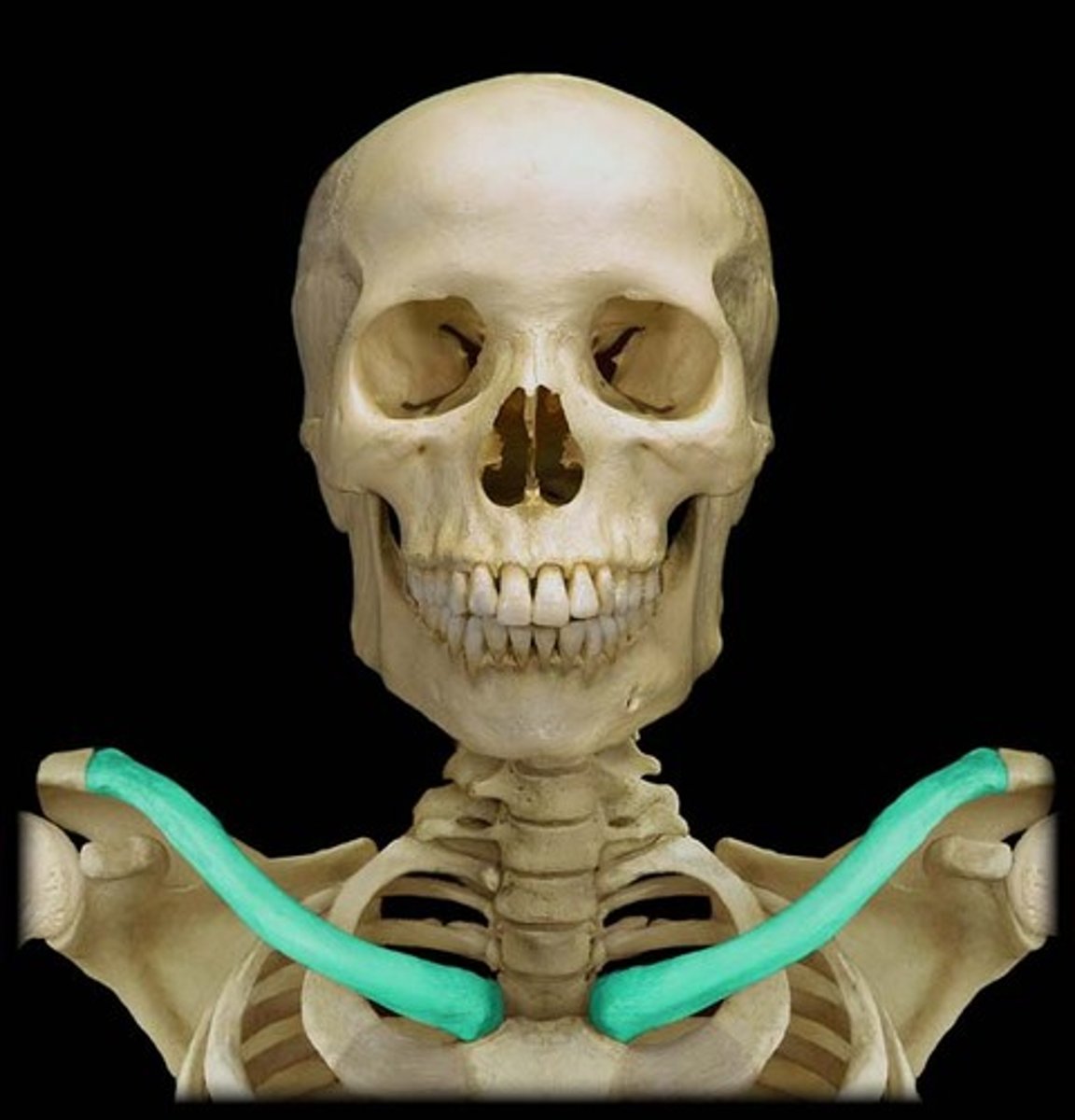
Clavicle & scapula
-Position the shoulder joint
-Help move the upper limb
-Provide a base for muscle attachment
Clavicle
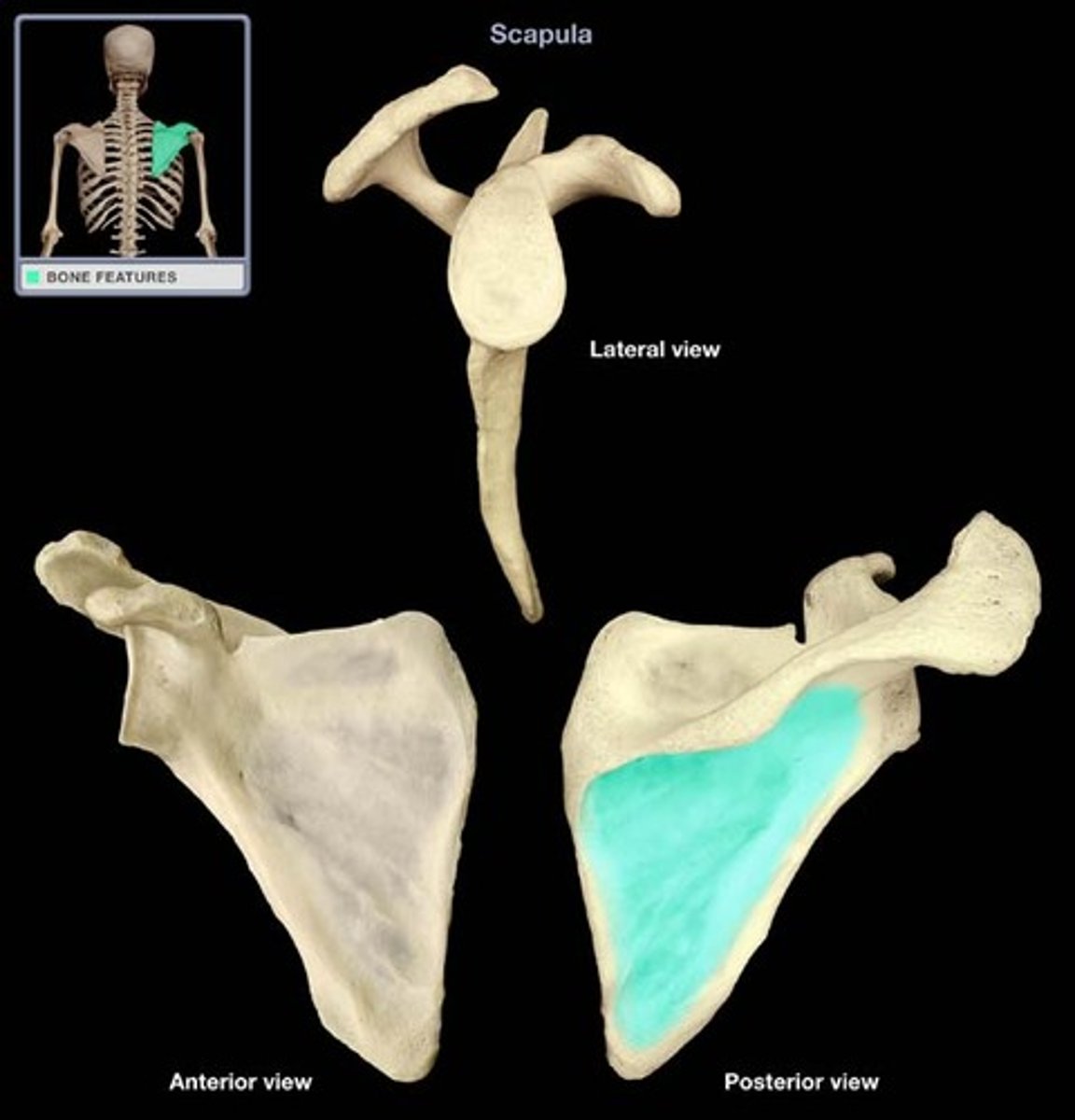
Scapula
Right scapula
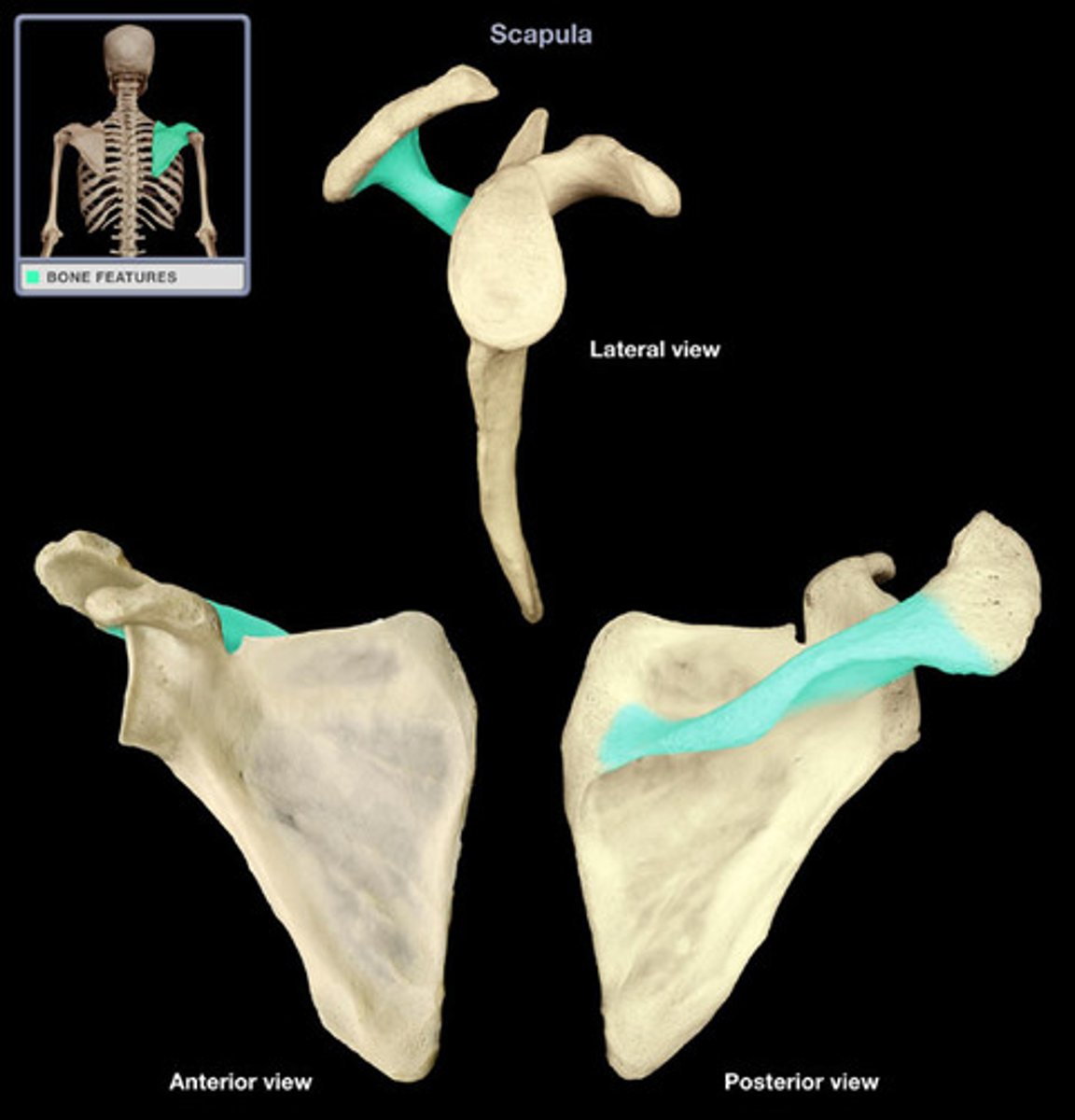
2 scapula markings
-Coracoid process
-Acromion
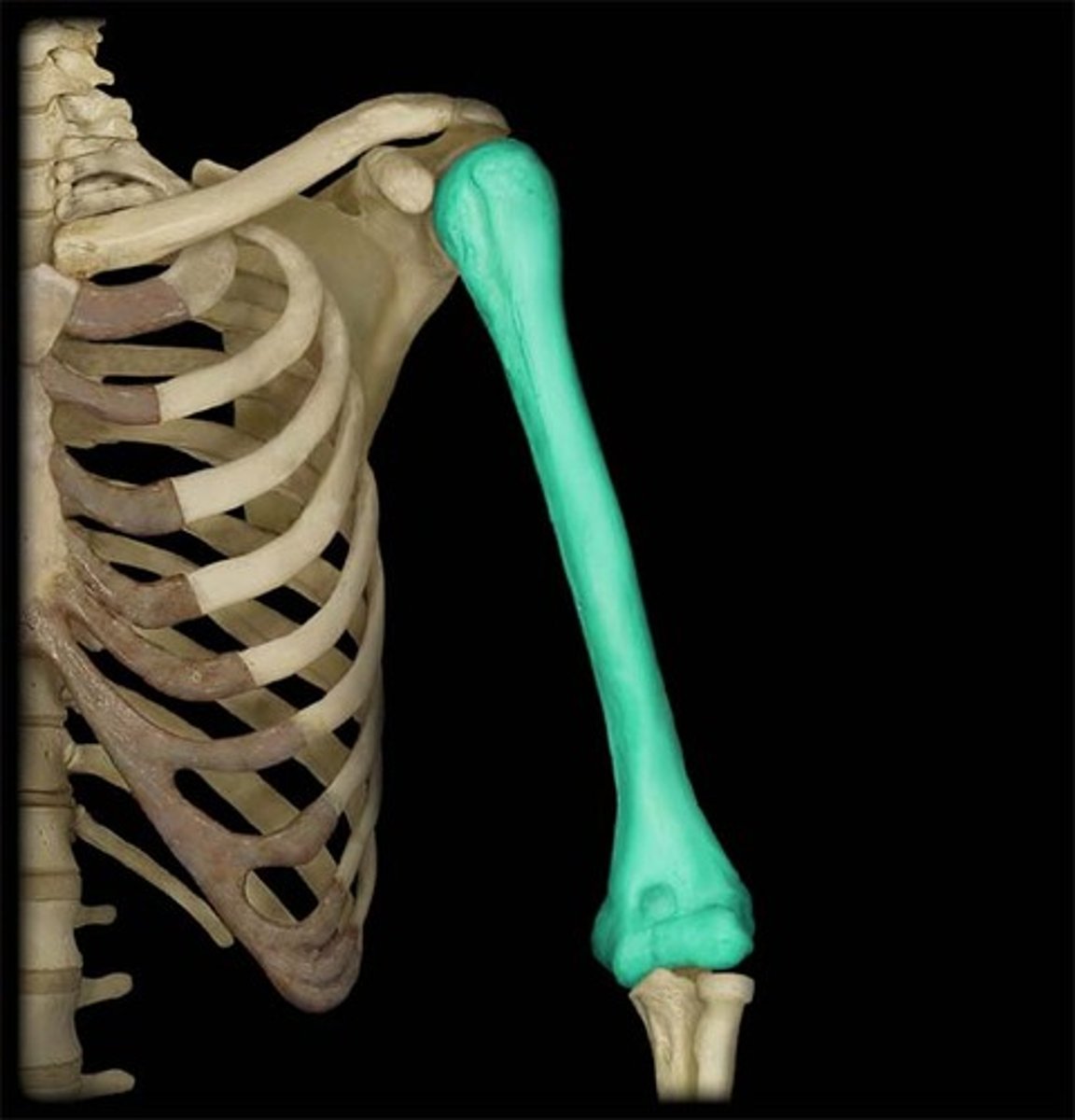
The upper limbs
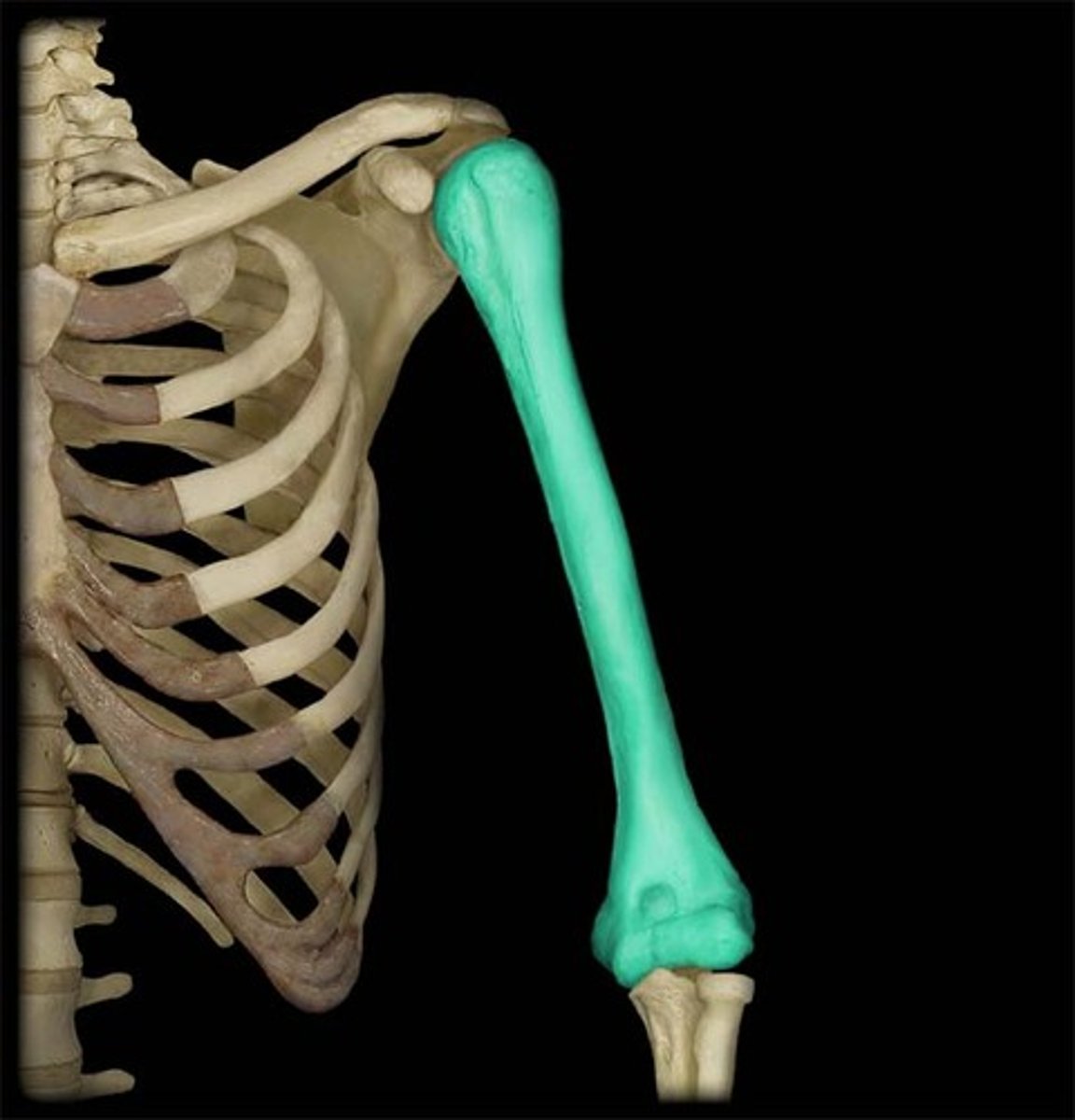
-Scapula articulates with the humerus at the glenohumoral joint
-Greater and lesser tubercles are muscle attachment sites
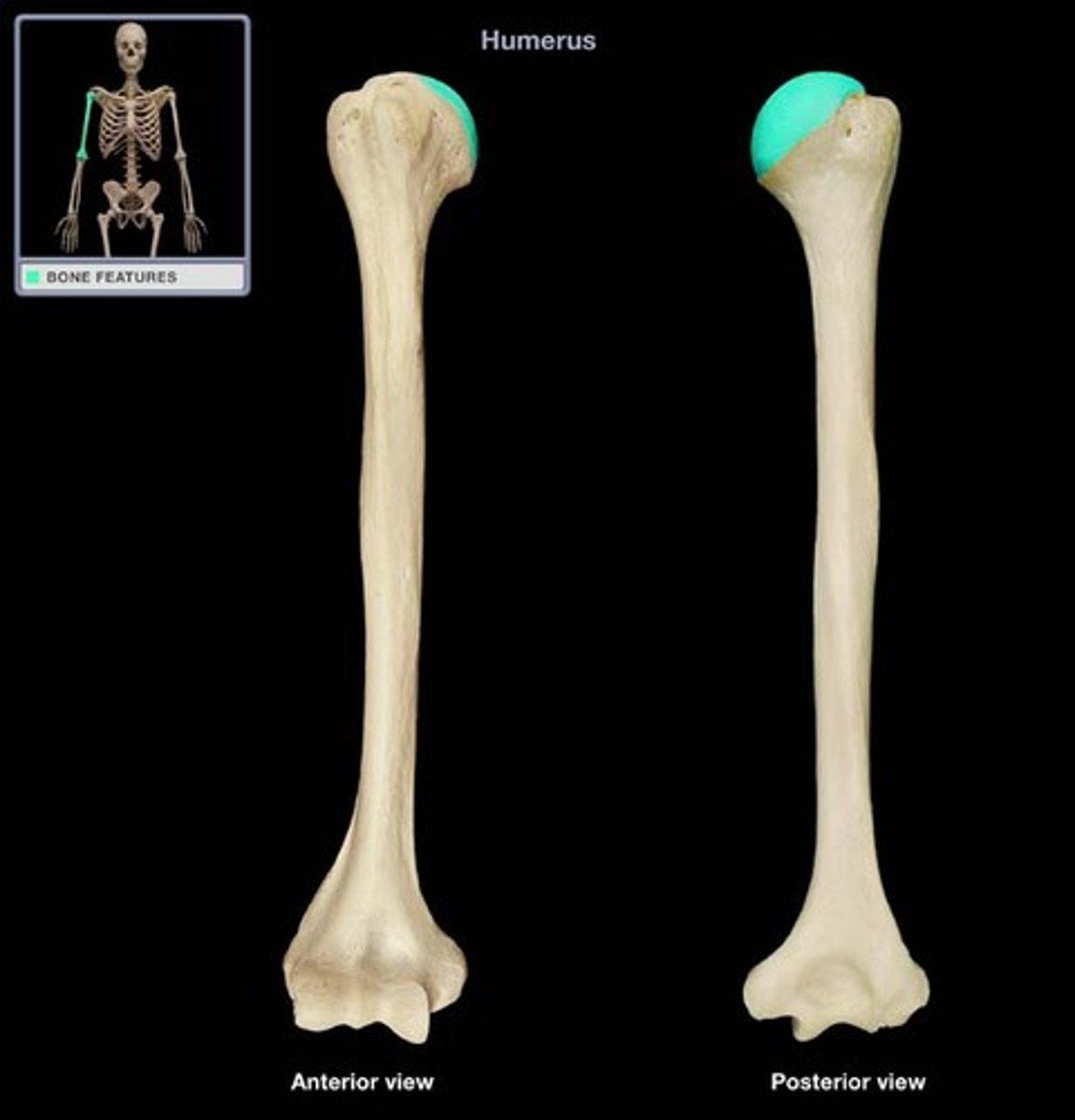
Humerus
-Articulates with radius and ulna
-Elbow joint
Right humerus
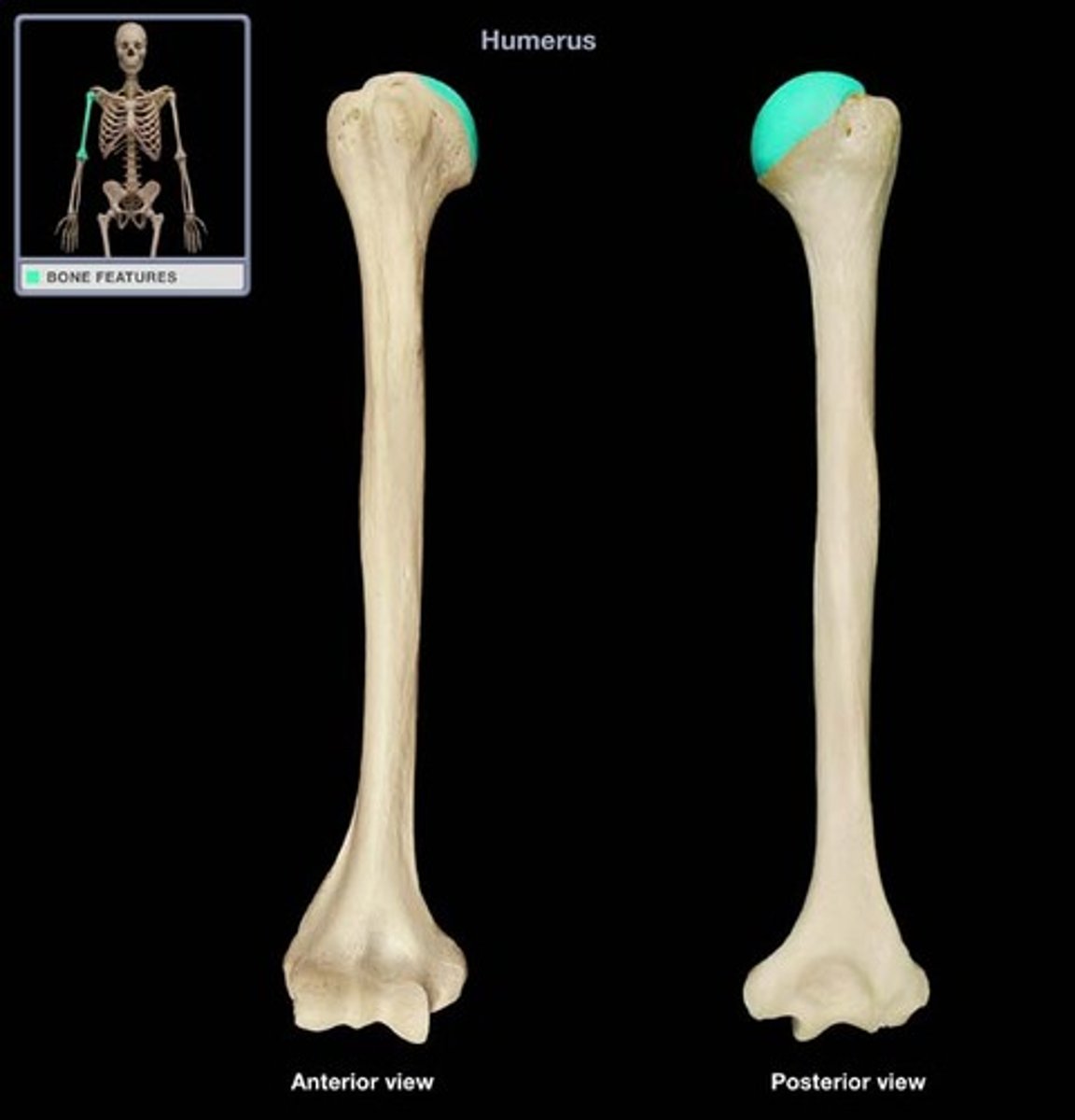
Left humerus
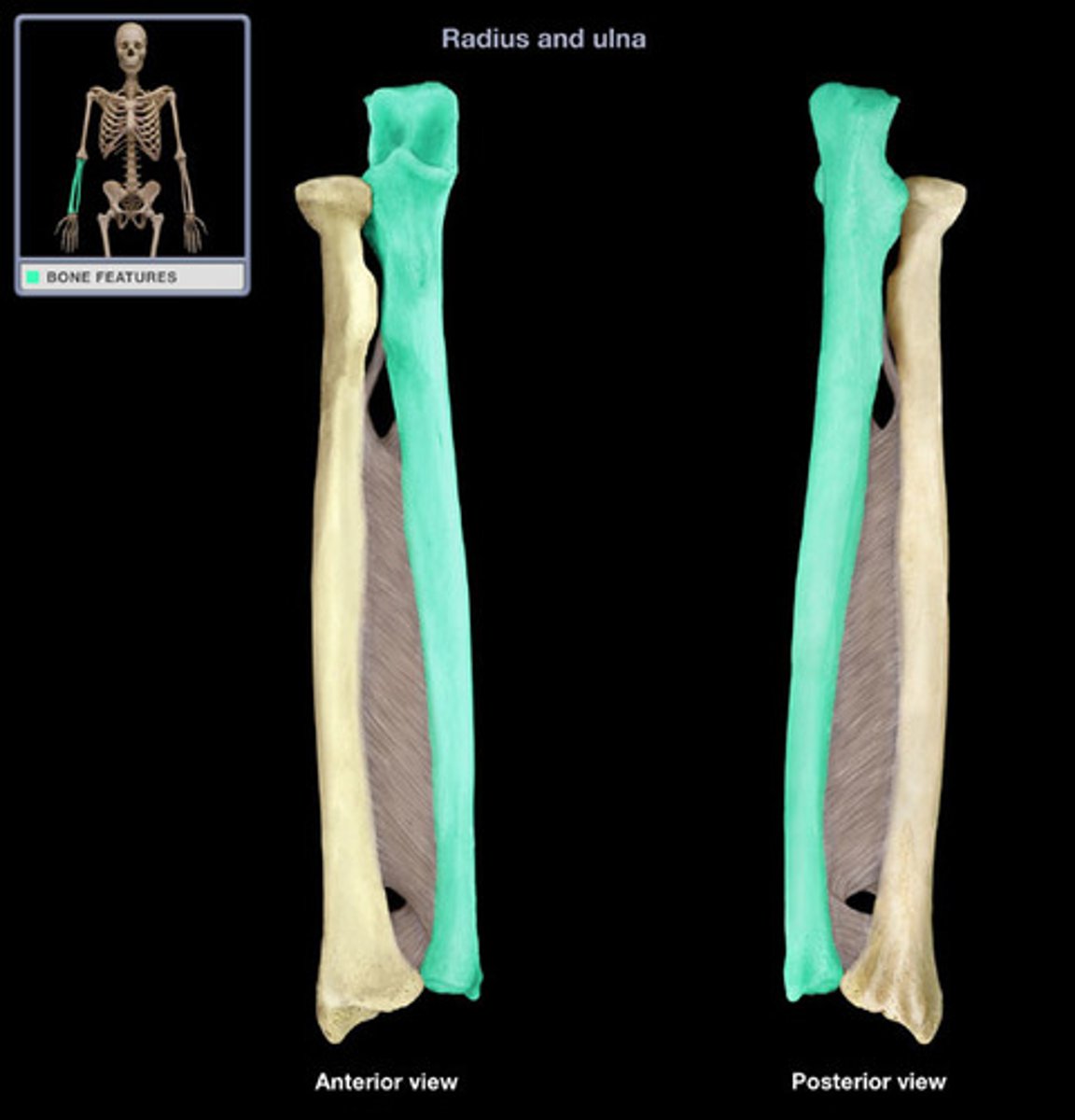
Radius and ulna

Right radius
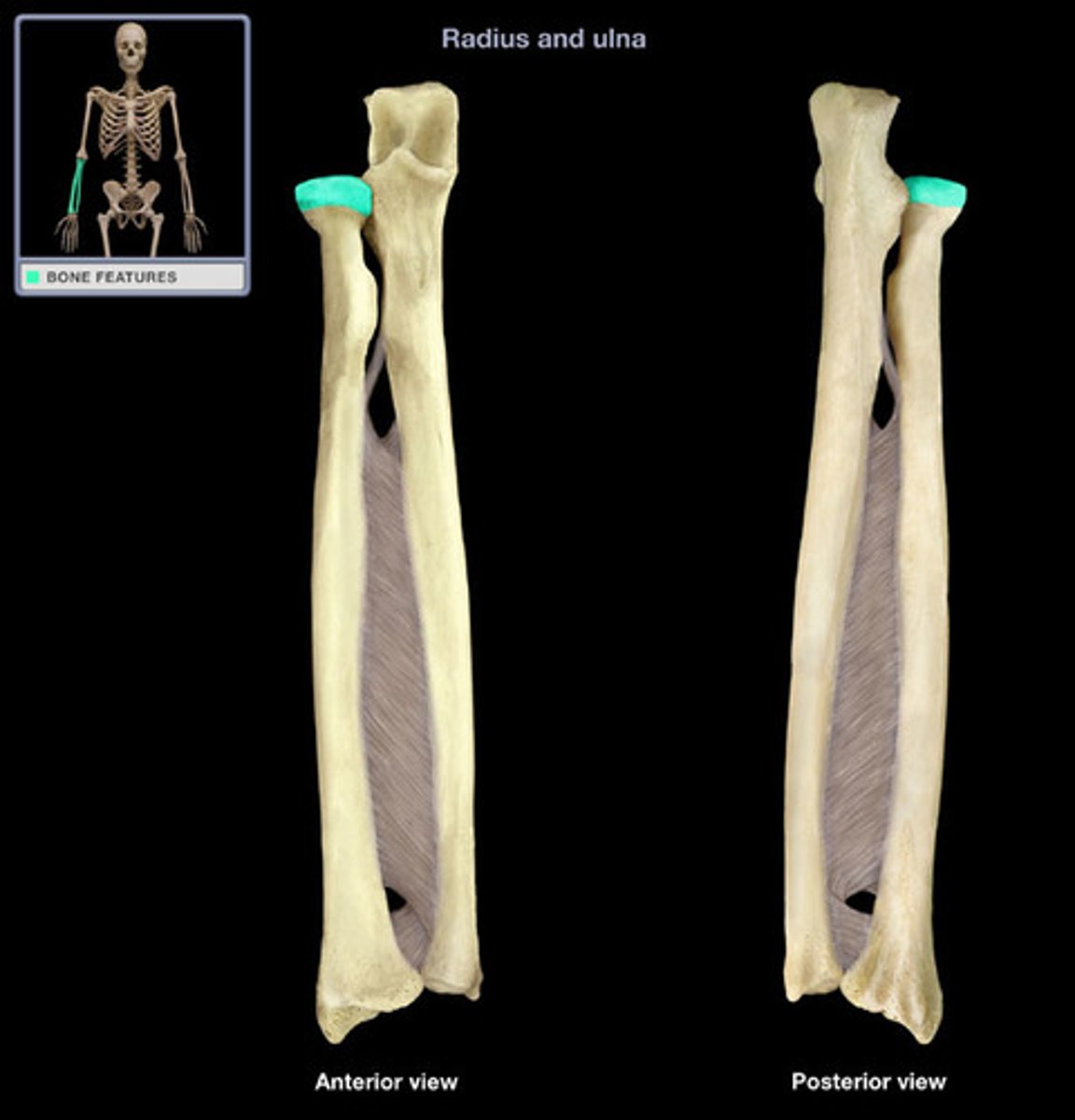
Right ulna
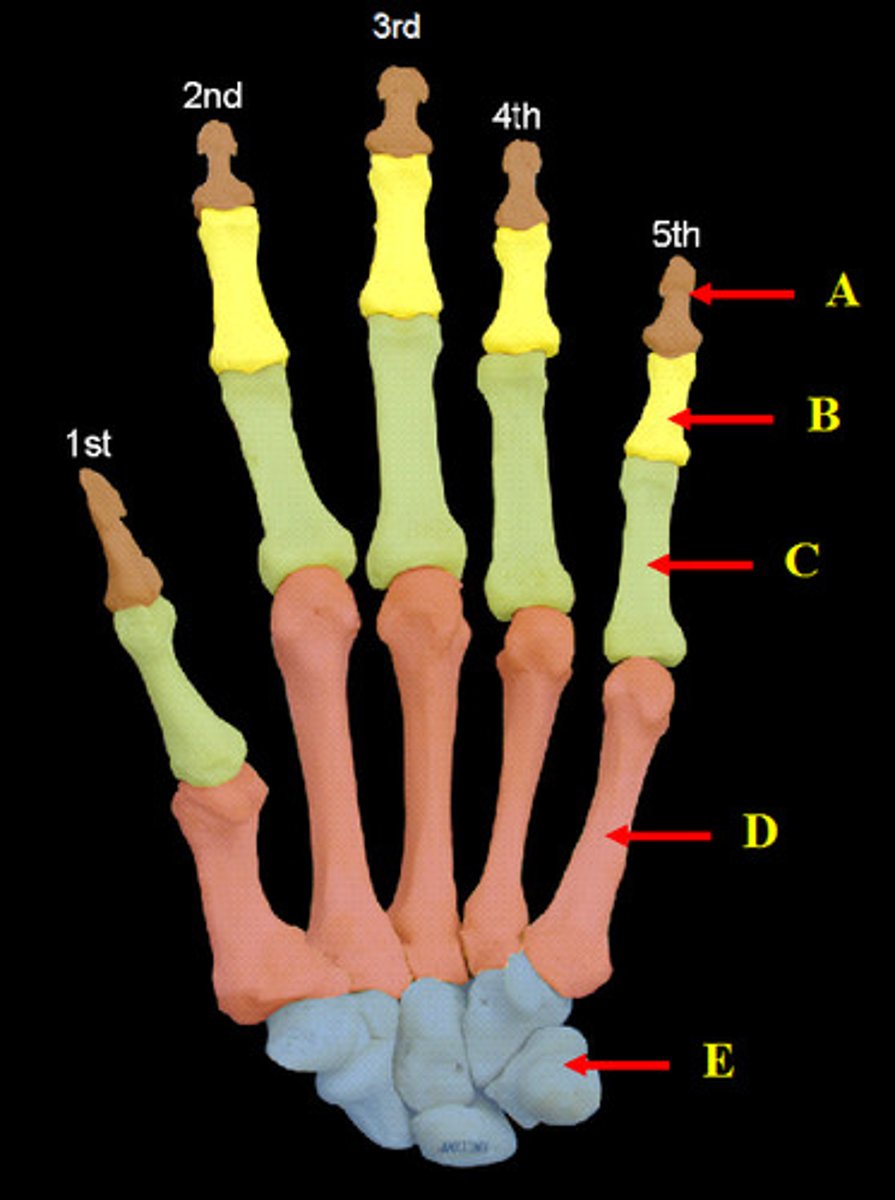
Carpal bones and hand
-Carpus forms wrist
>Two rows of short bones
-Five metacarpals
-Four fingers have three phalanges
-Pollex (thumb) has two phalanges
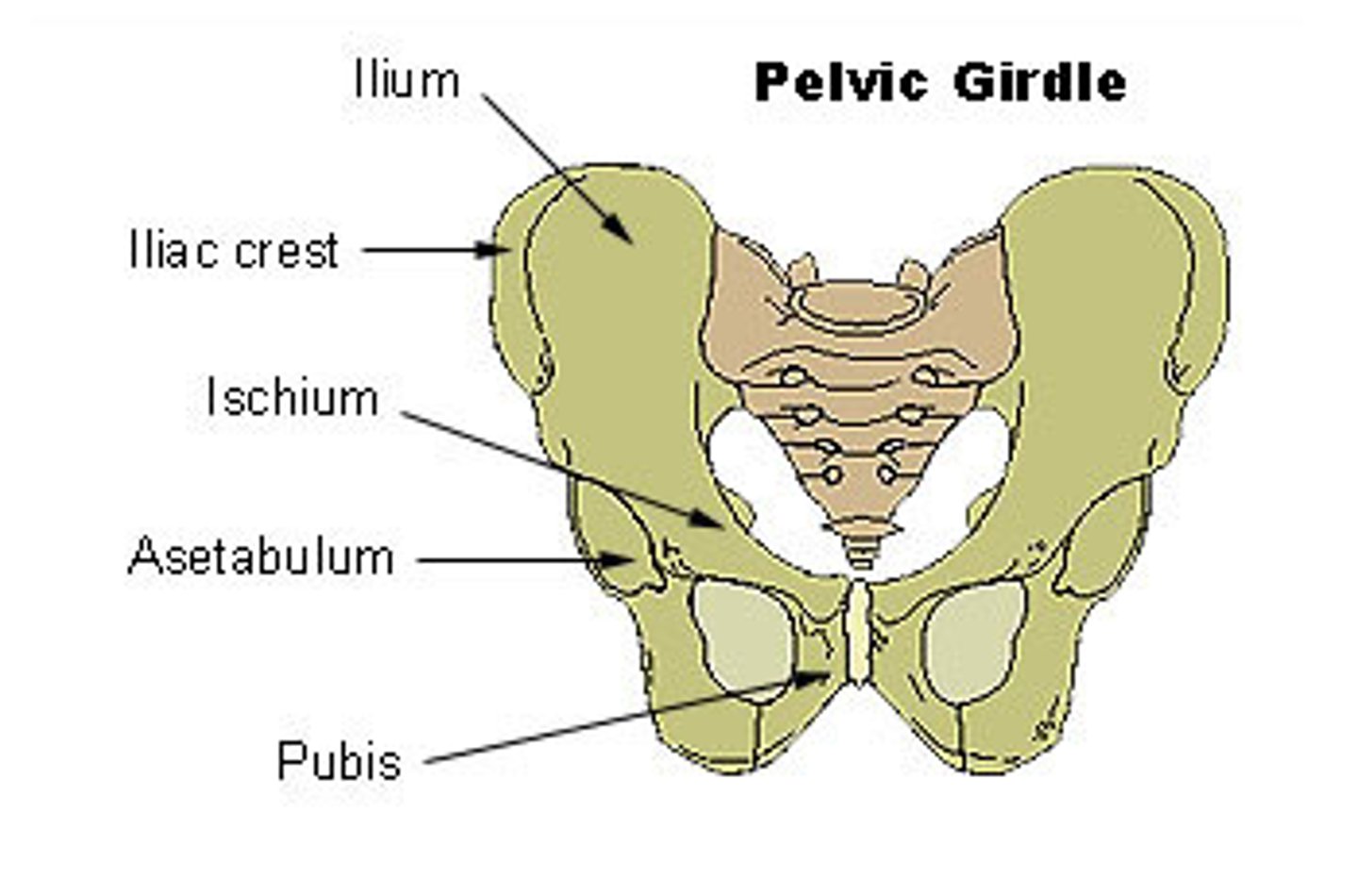
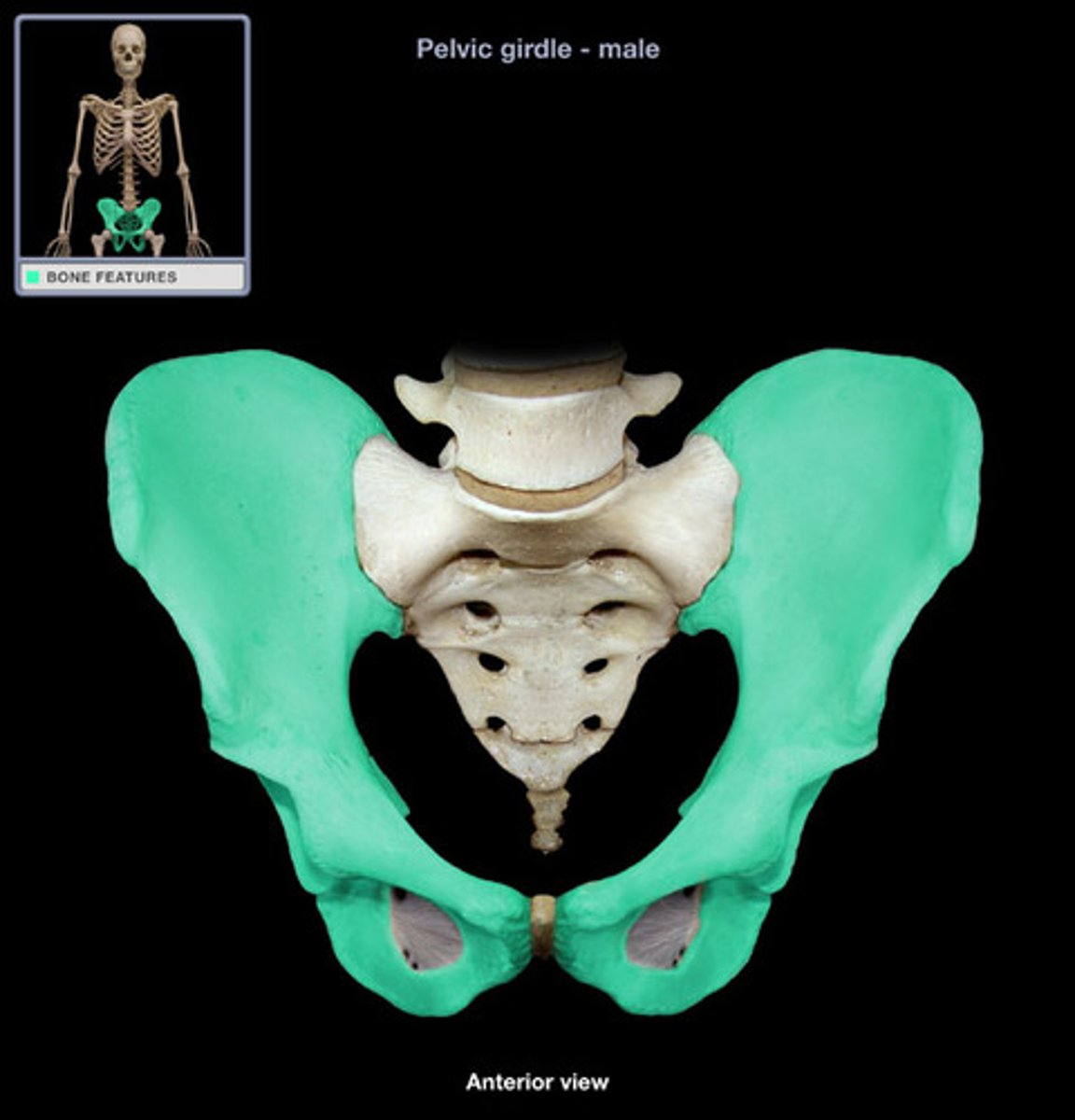
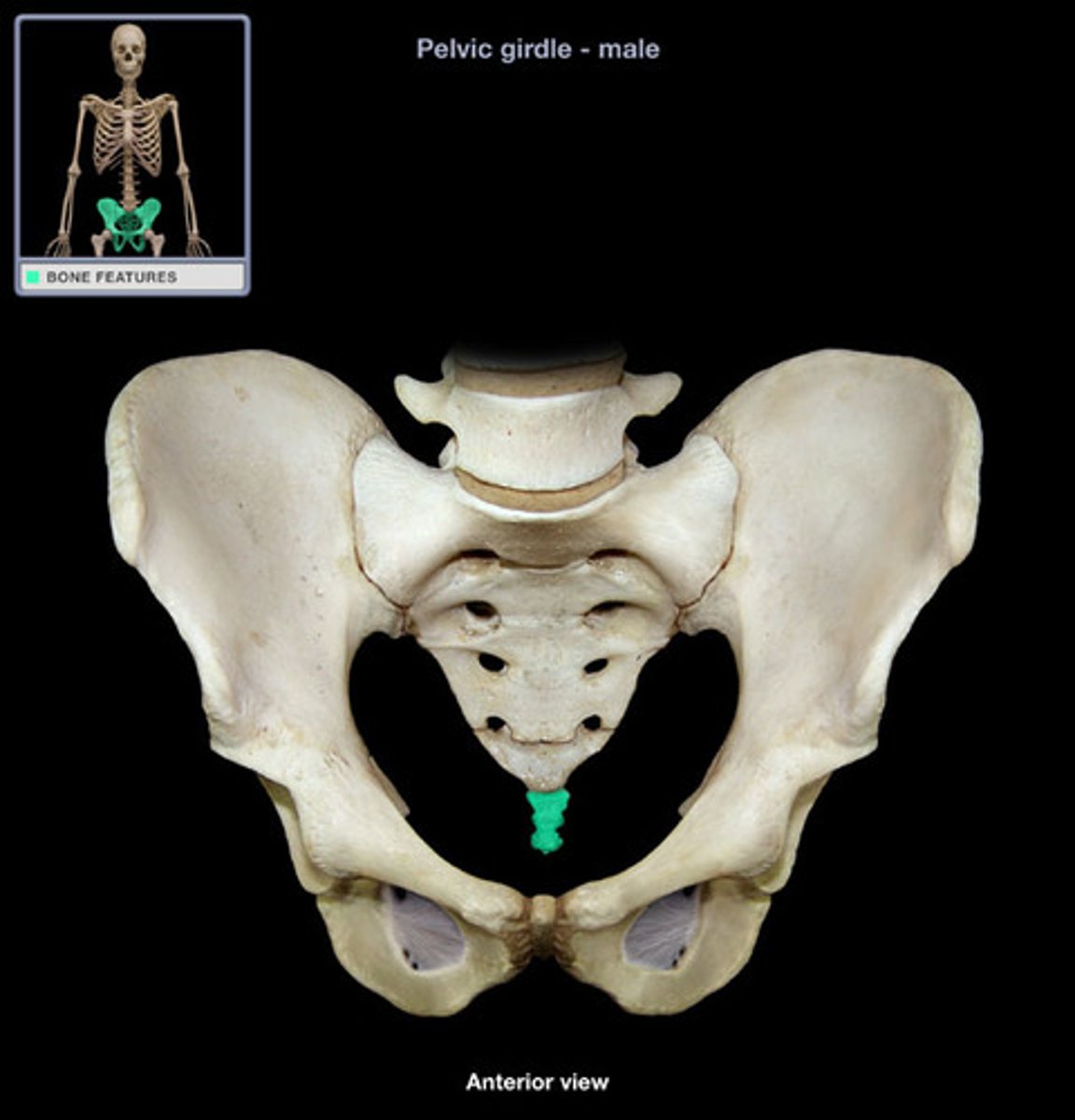
Pelvic girdle
-More massive than the pectoral girdle
-Consists of two os coxae
>Fusion of ilium, ischium and pubis
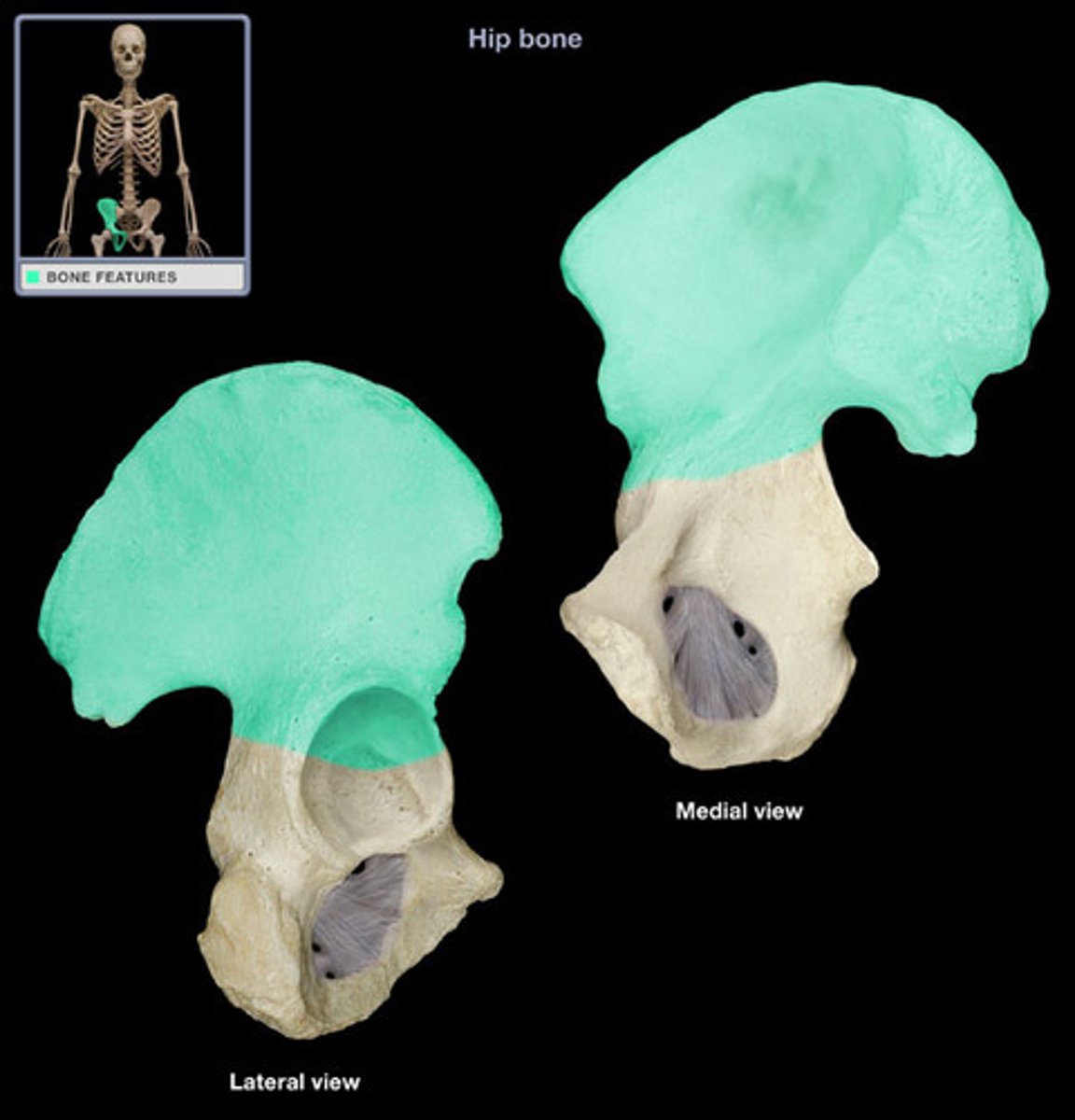
The os coxae
Right os coxae
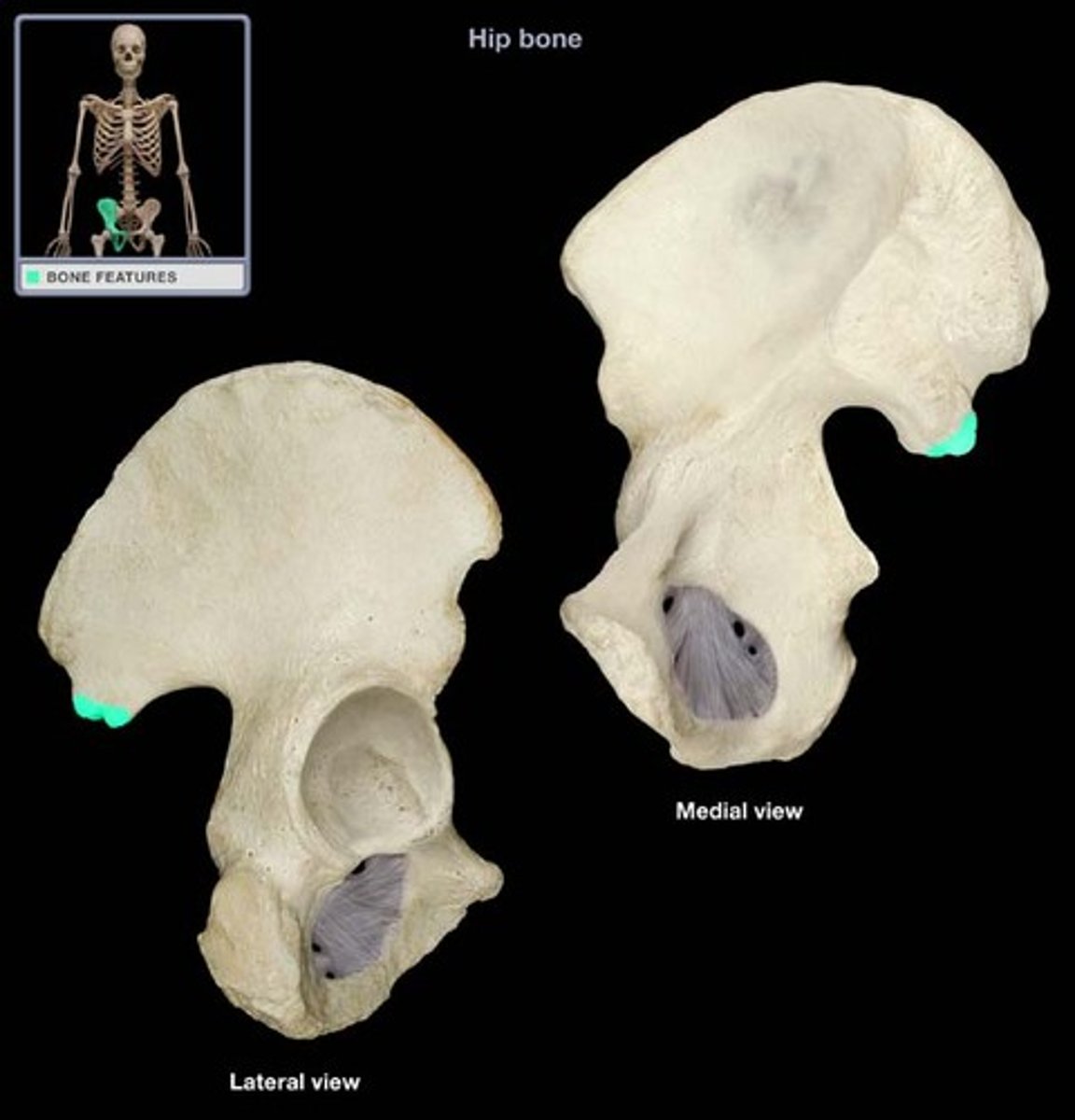
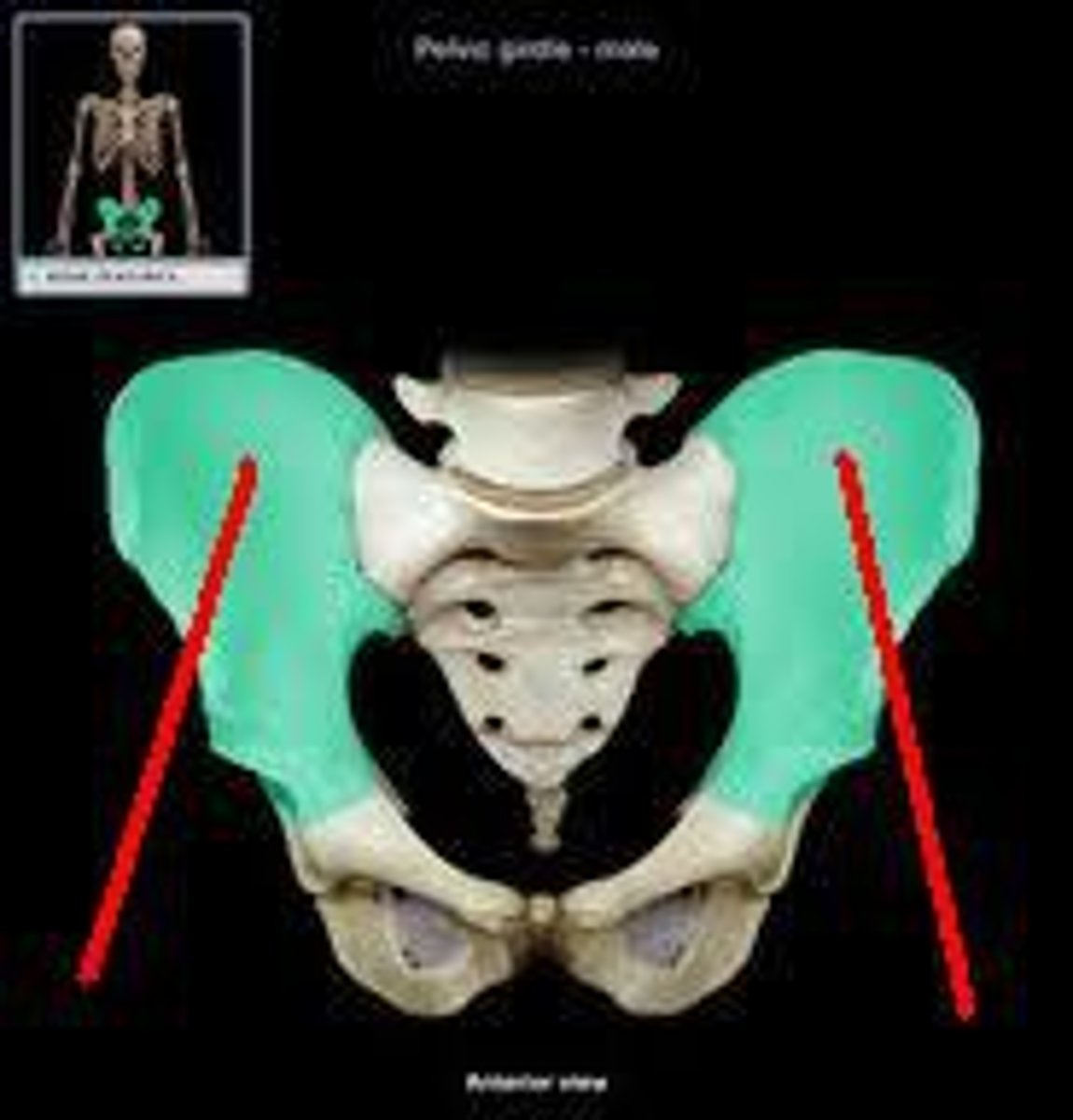
Illium
-Largest hip bone
-Within acetabulum, fused to the ischium (posteriorly) and the pubis (anteriorly)
-Pubic symphysis limits left to right
Right illium
The pelvis
-Composed of the os coxae, sacrum and coccyx
-Subdivided into the false (greater) and true (lesser) pelvis
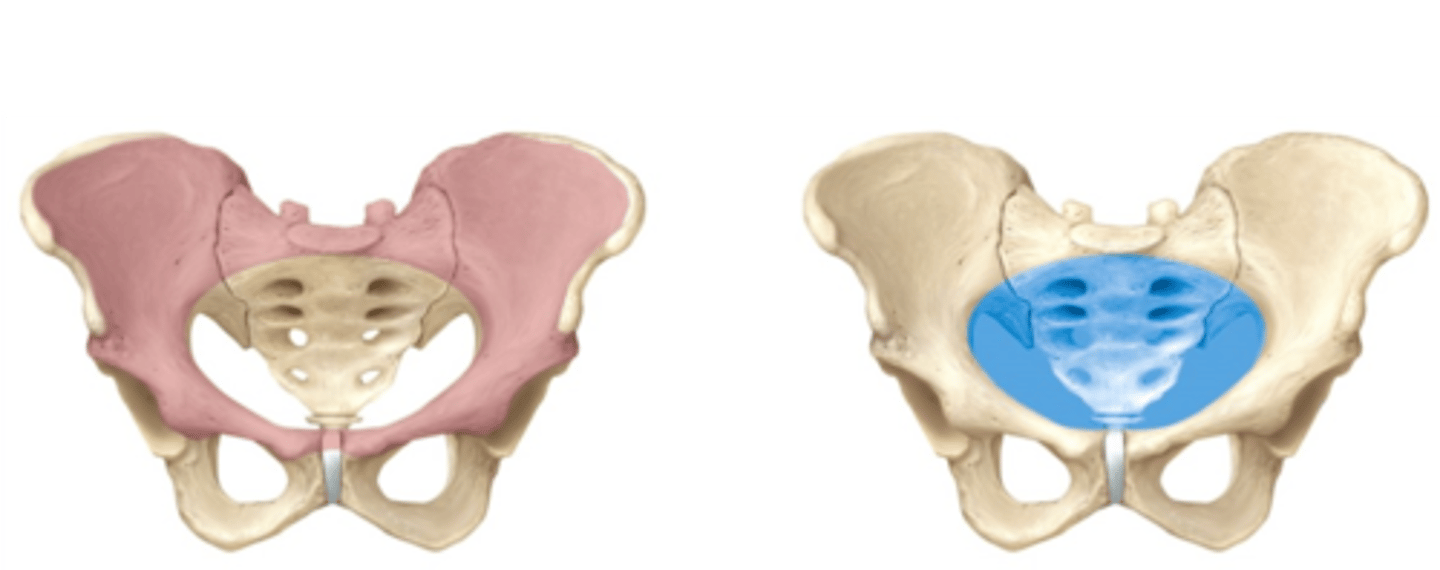
False (greater) pelvis
True (lesser) pelvis
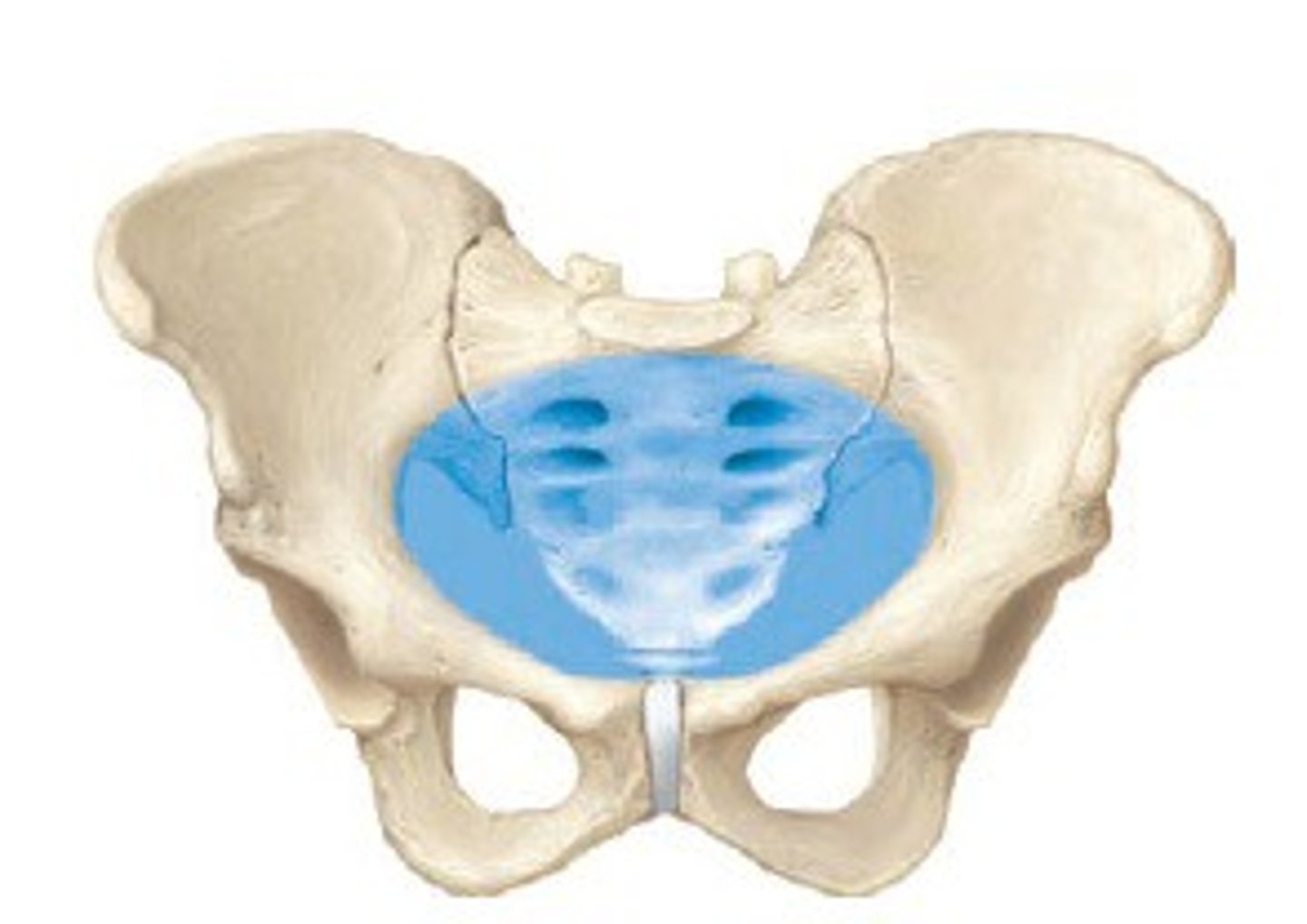
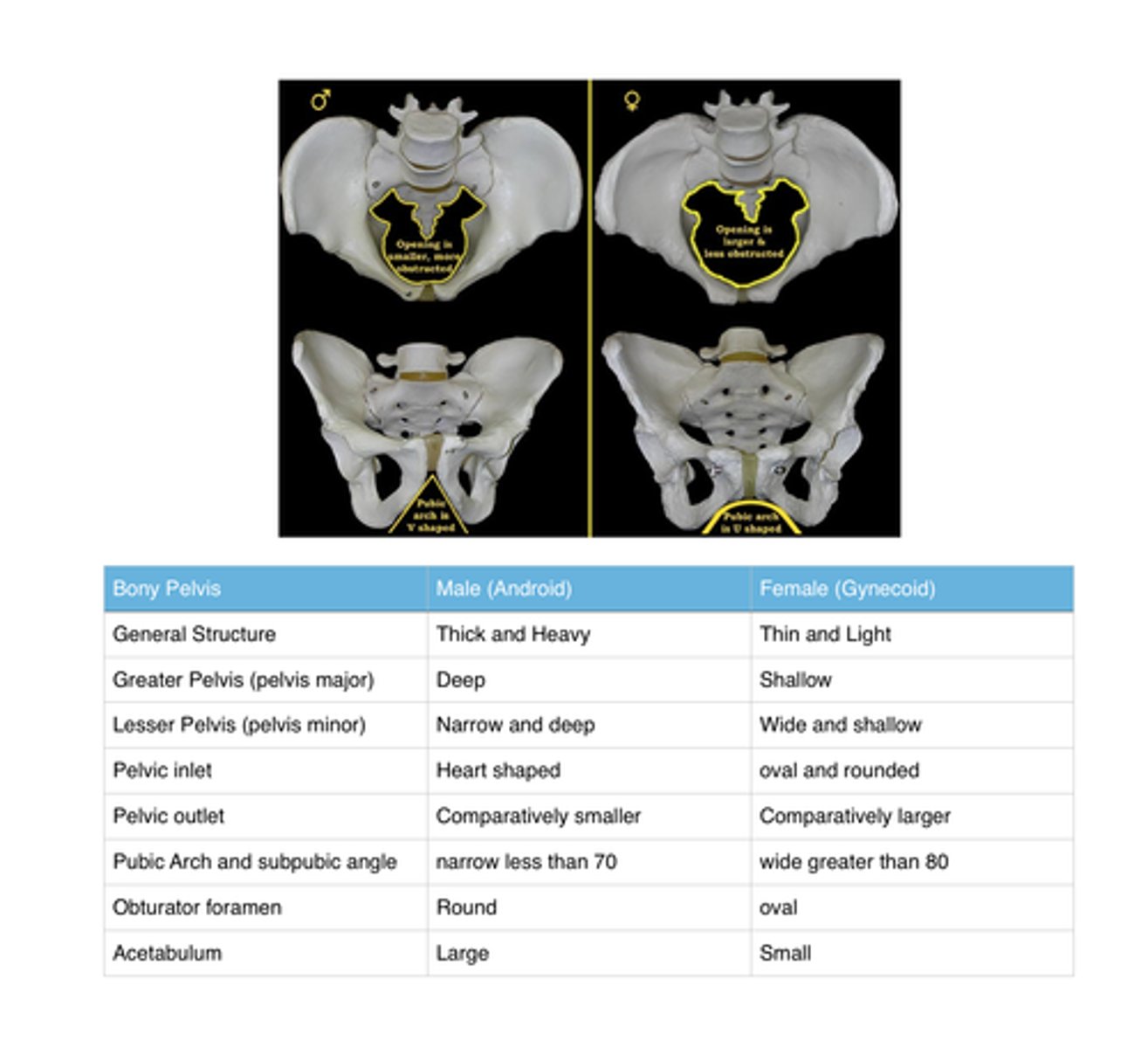
What are the differences between male and female pelvis
- Pubic arch is wider in females
Lower limbs
-Femur is the longest bone in the body:
>Articulates with the tibia at the knee
-Patella is a large sesamoid bone
-Fibula parallels tibia laterally
Femur
Patella
Tibia
"Shin"
Fibula
Tarsus
-Has seven tarsal bones
-Pattern of metatarsal bones and phalanges parallels that of the hand
>All toes have three phalanges except the hallux (two phalanges)
The ankle bones are AKA...
Malleoli
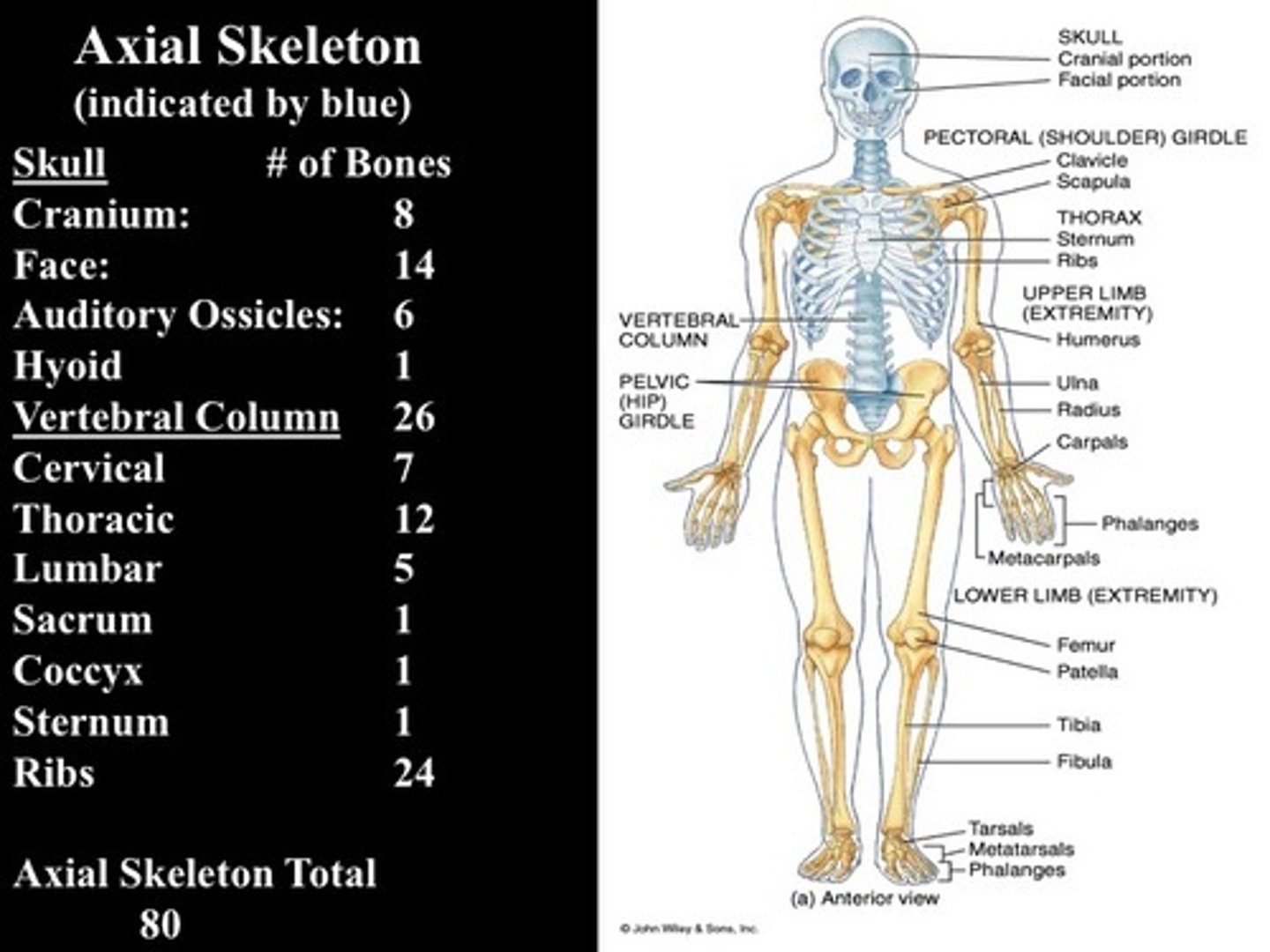
Axial Skeleton
-includes 80 bones
>Skull and associated bones (29)
>Thoracic cage (25)
>Vertebrae column (26)
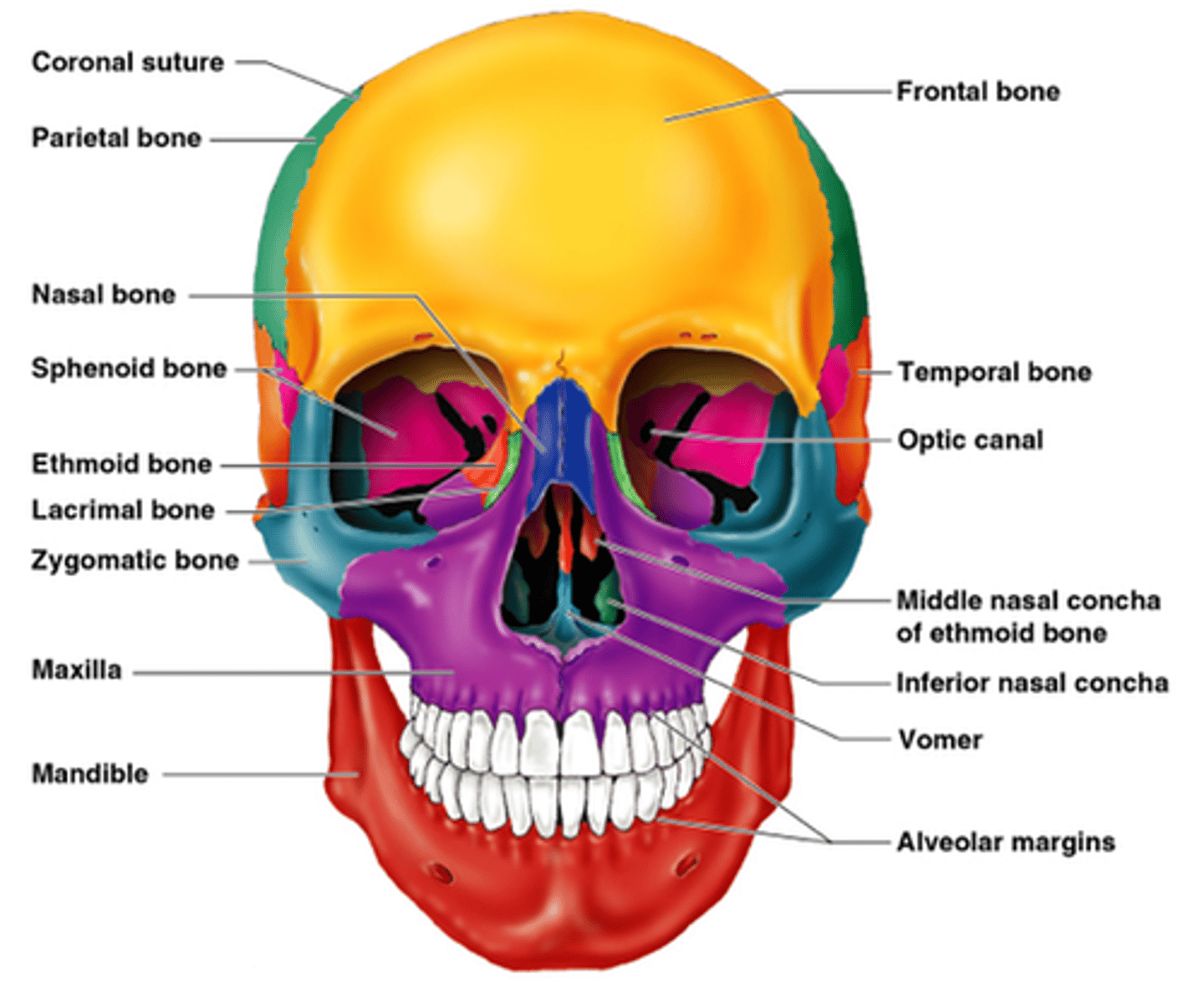
Skull
-Consists of the cranium and the bones of the face
-The cranium encloses cranial cavity
-Facial bones surround and protect the entrances to the respiratory and digestive tracts
Facial bones
Maxillary bones
Mandible
Palatine bones
Nasal bones
Vomer
Inferior nasal conchae
Zygomatic bones
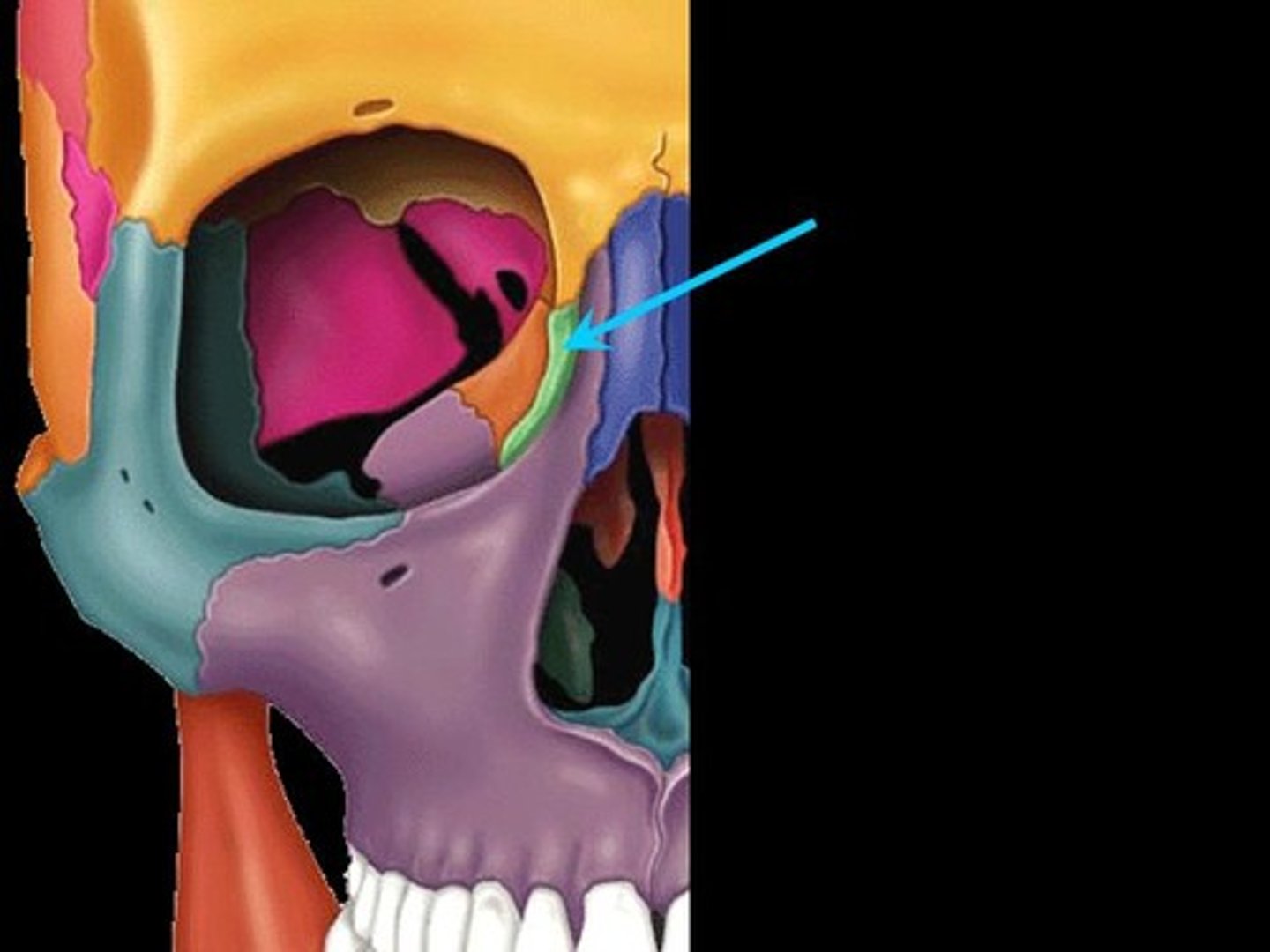
Lacrimal bones
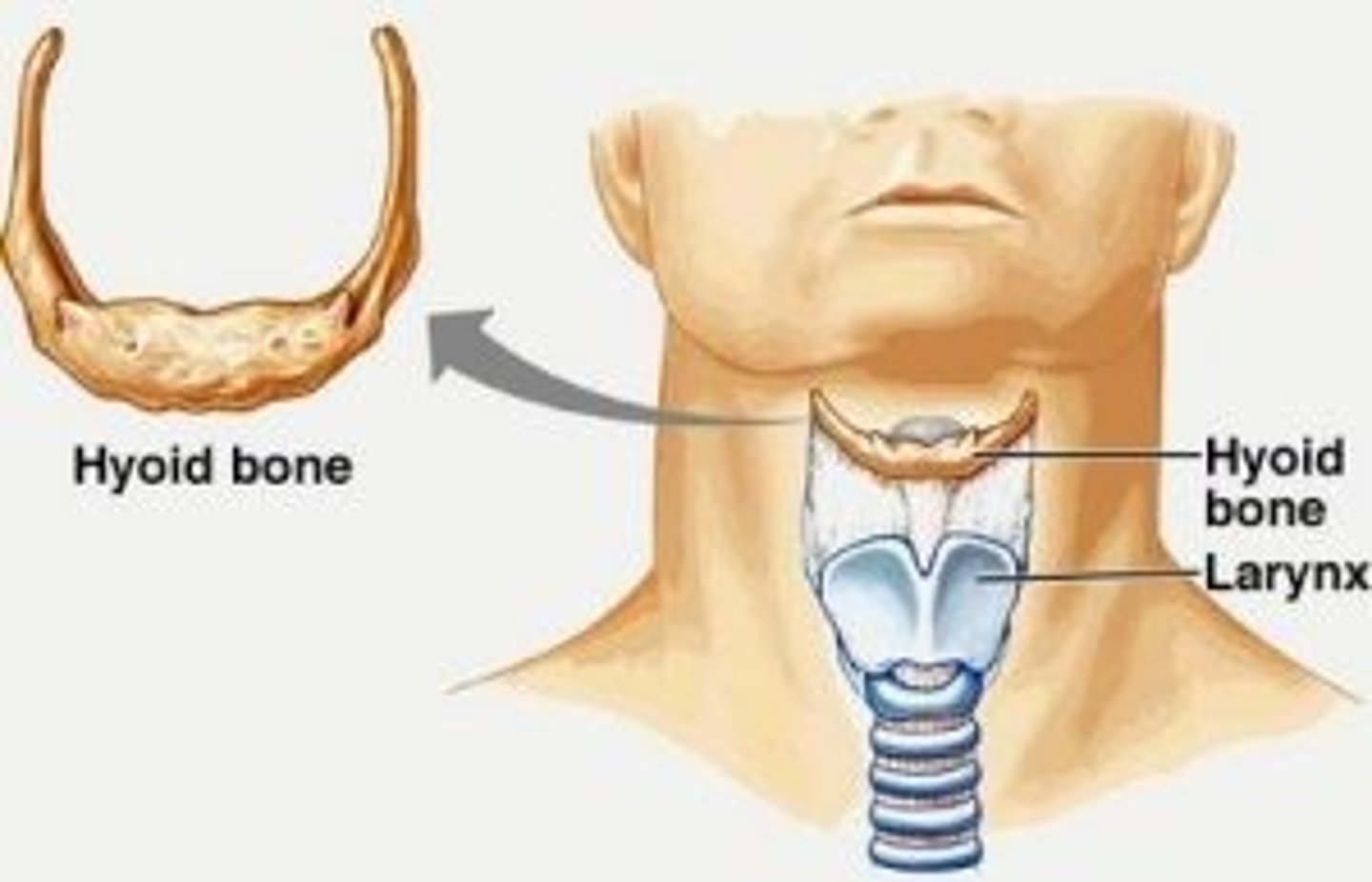
Hyoid
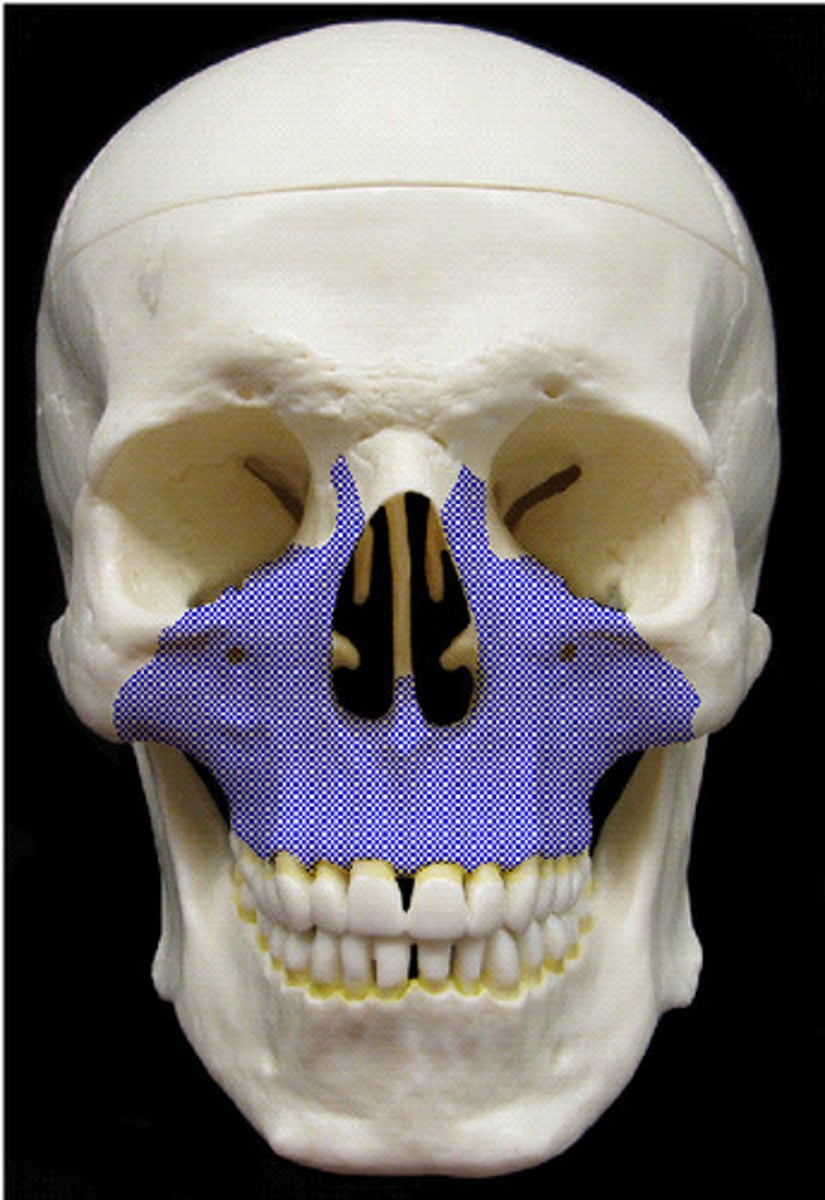
Maxilla
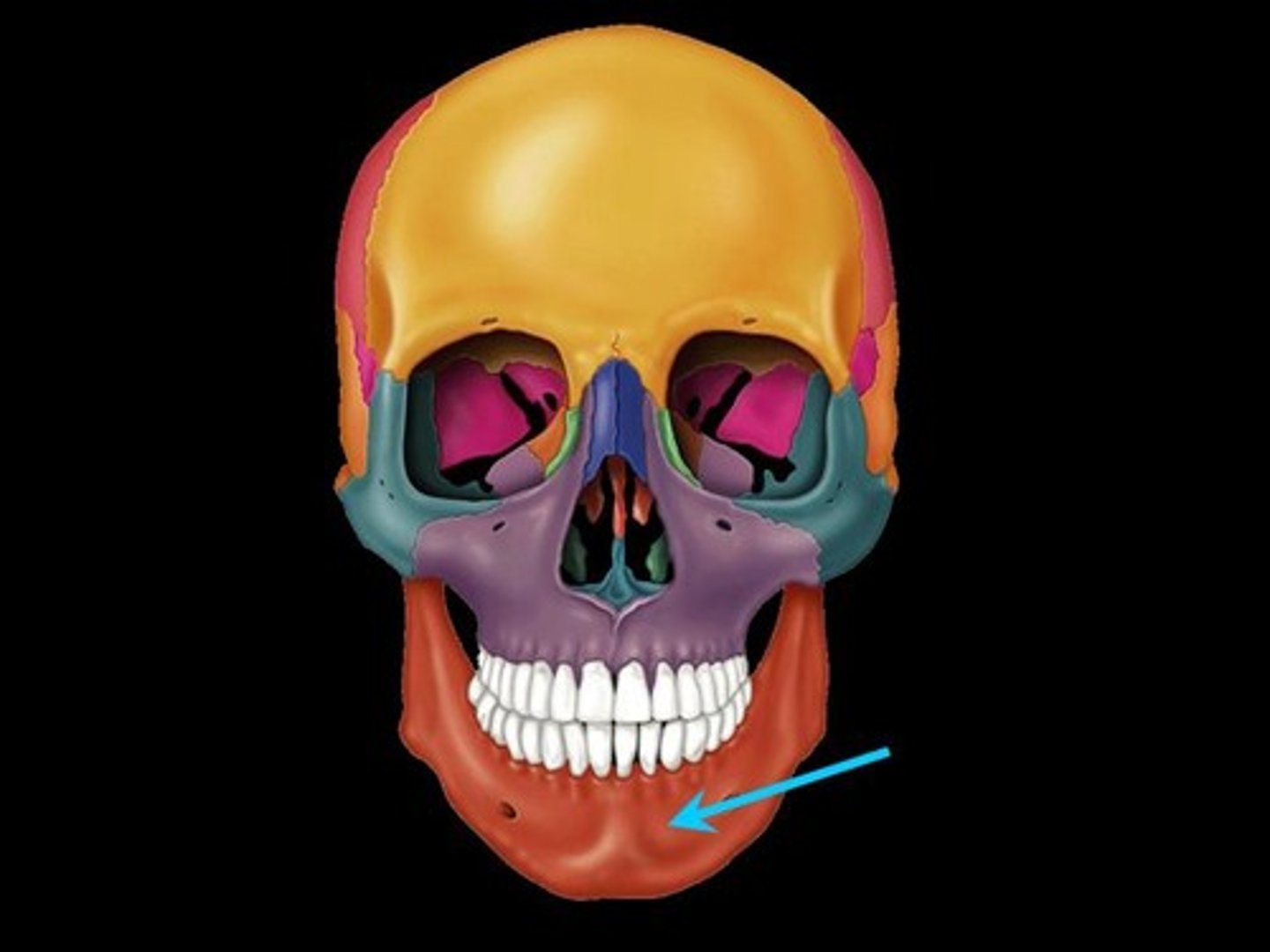
Mandible
Palatine bones
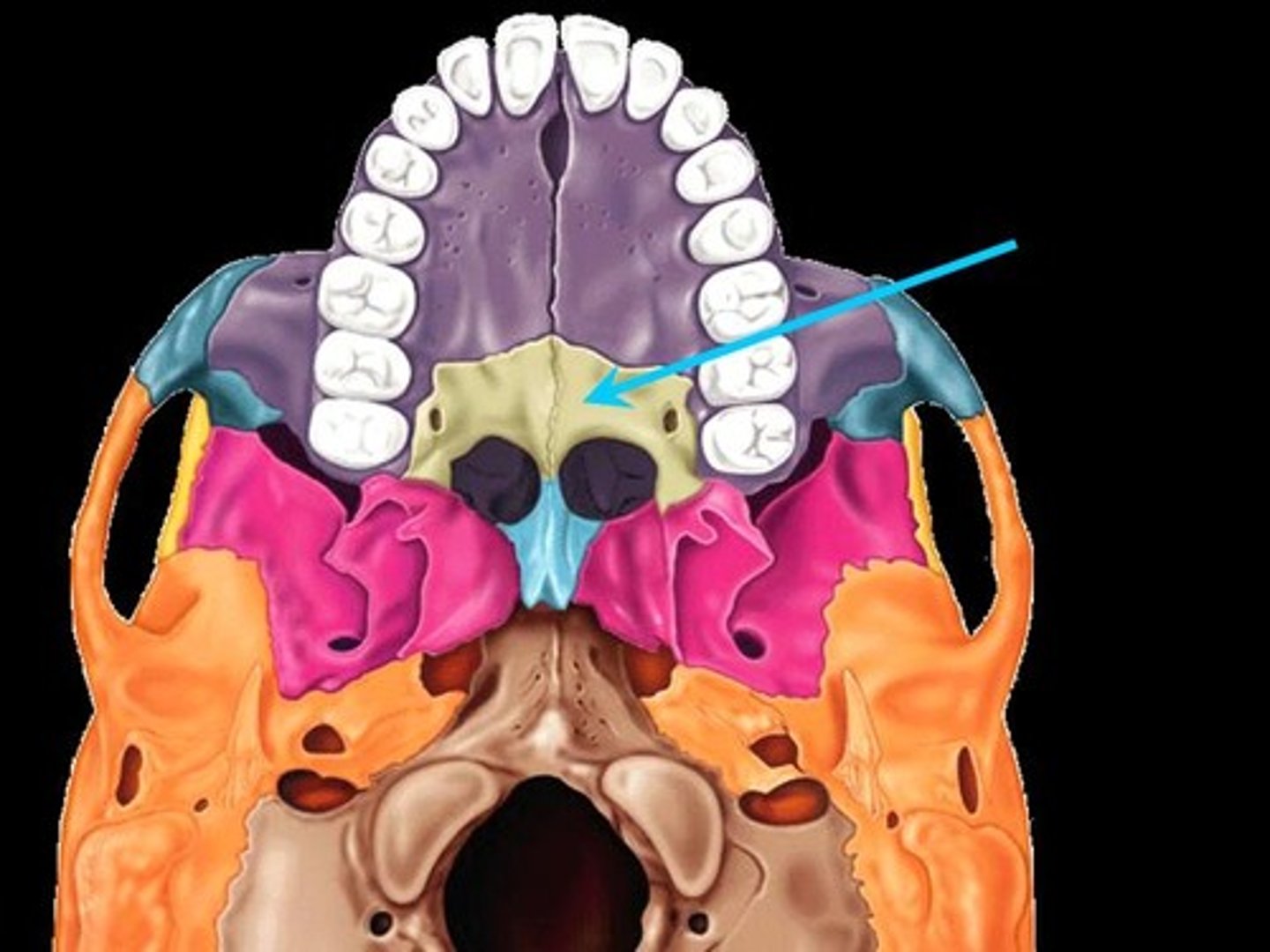
Nasal bones
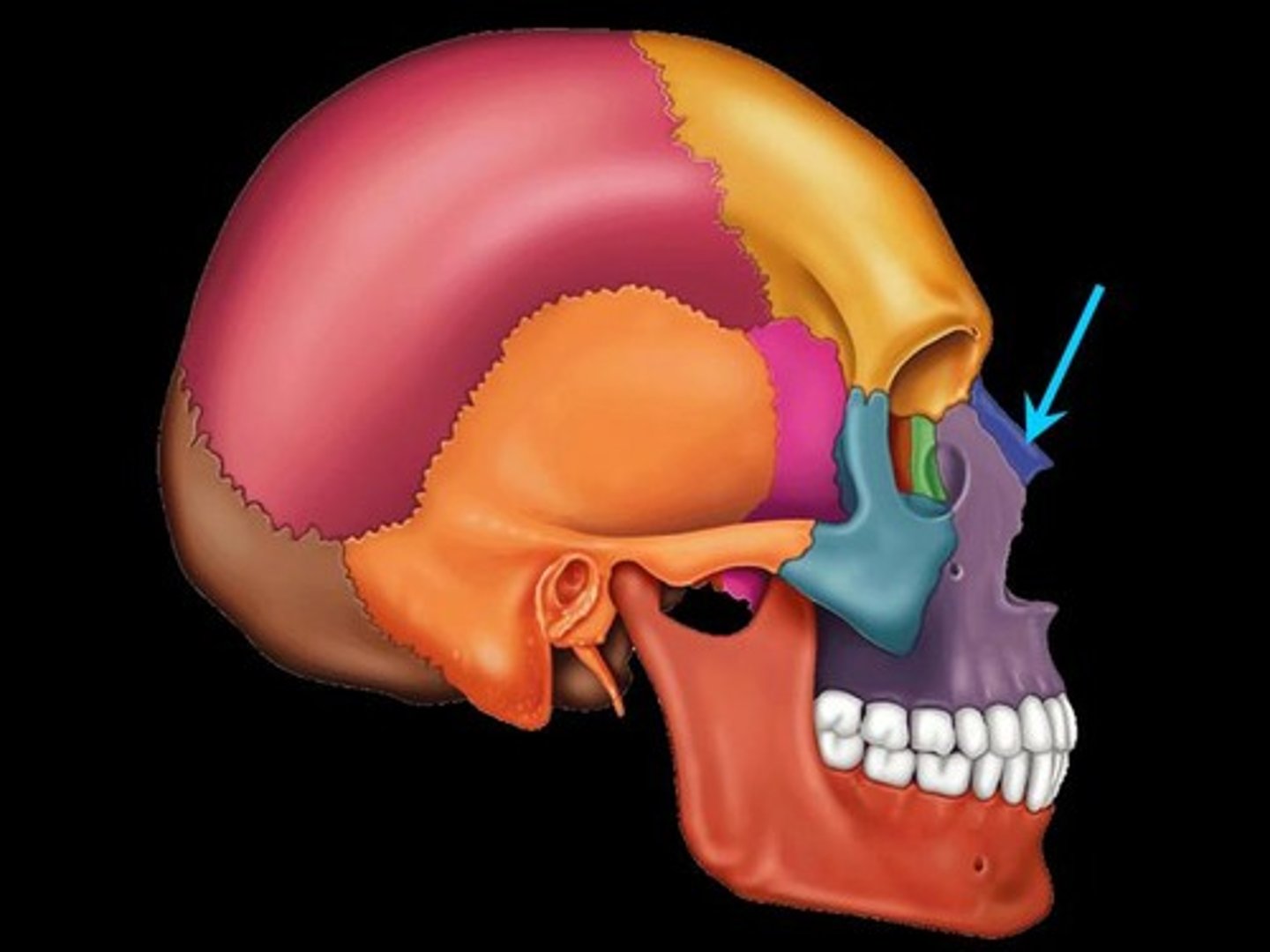
Vomer
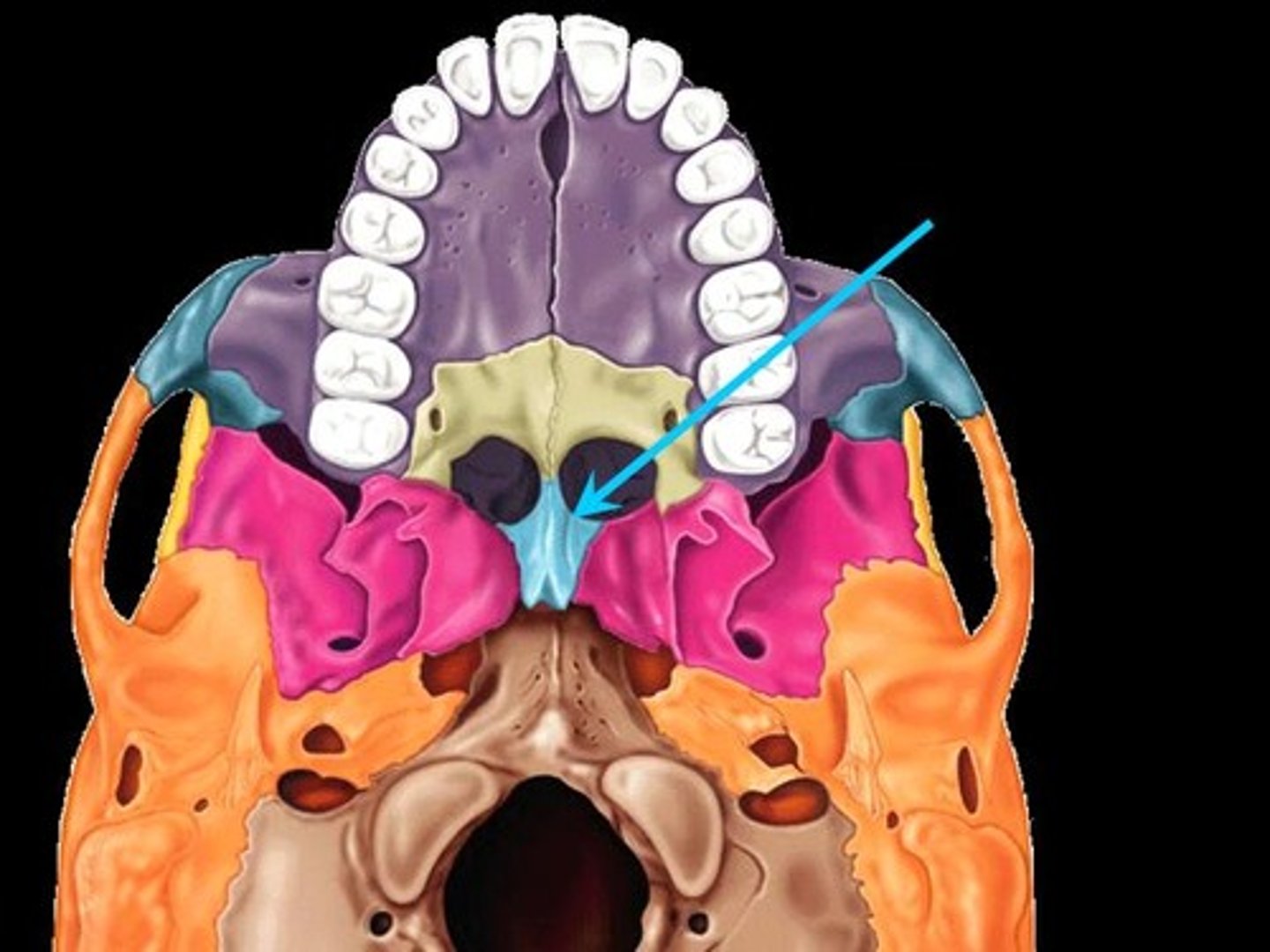
Inferior nasal conchae
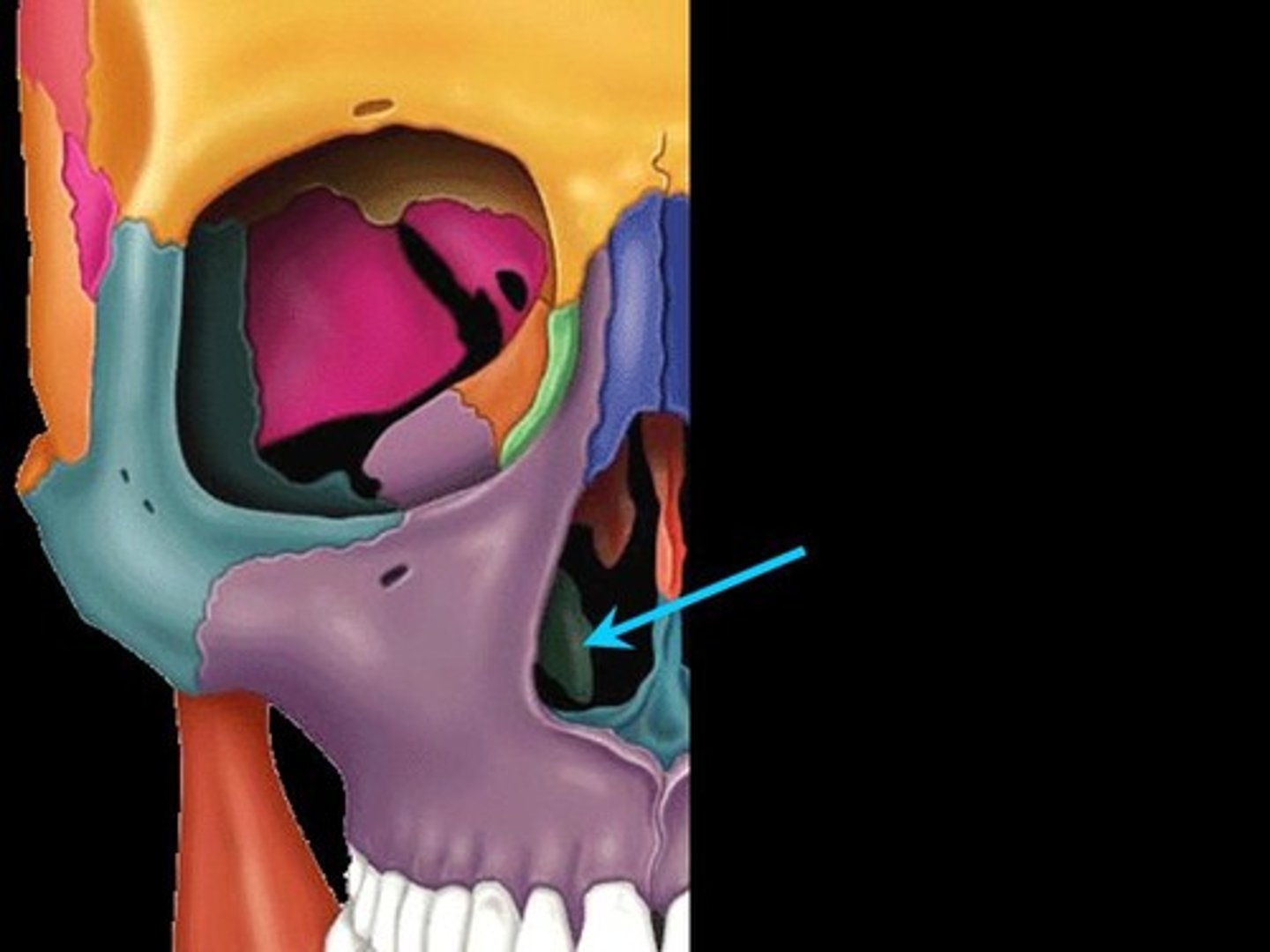
Zygomatic bones
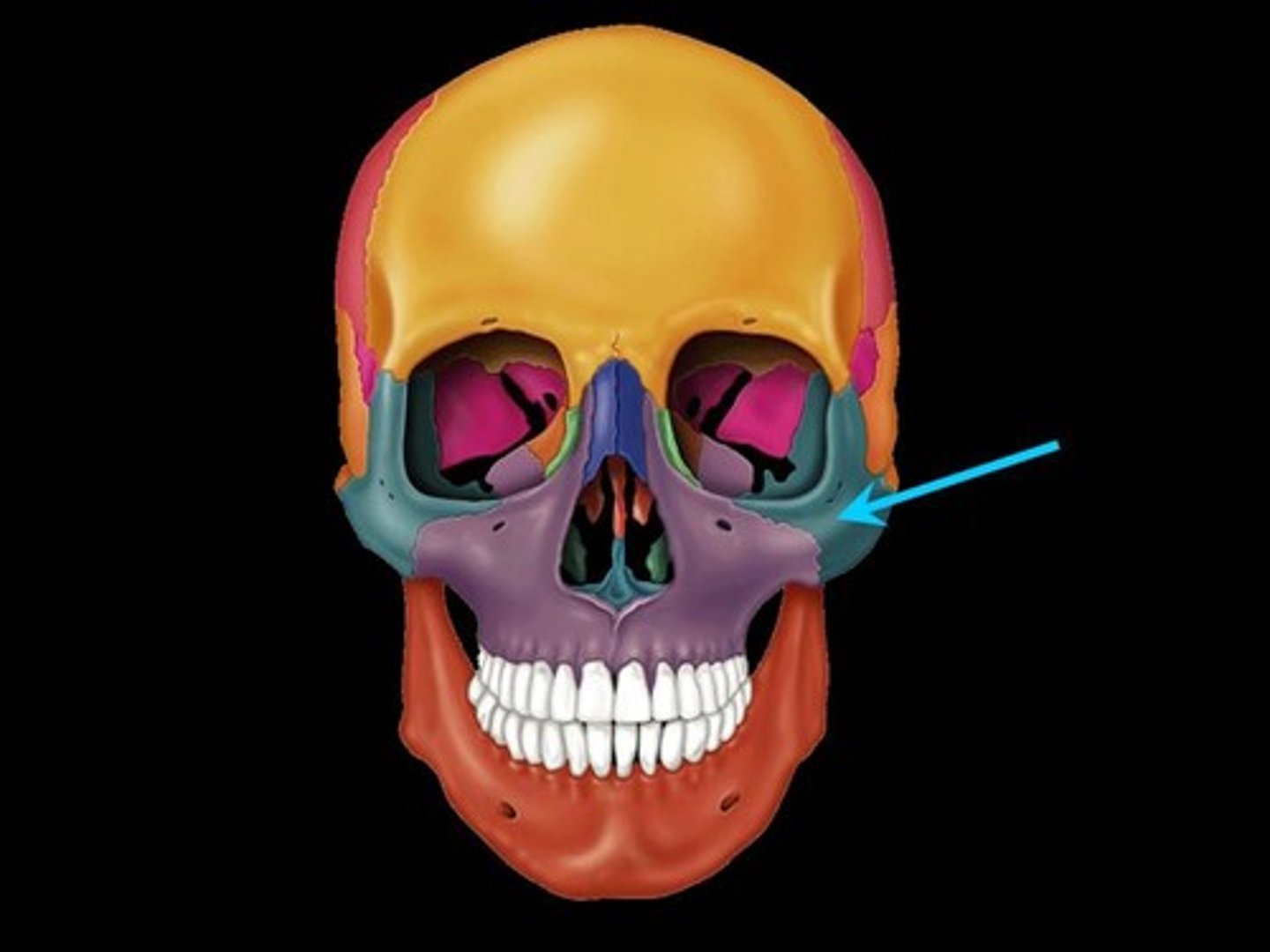
Lacrimal bones
Hyoid
one occipital bone
two parietal bones
one frontal bone
two temporal bones
one sphenoid
one ethmoid
Name the 6 types of cranial bones and whether they are unpaired (one) or paired (two).
Occipital bone
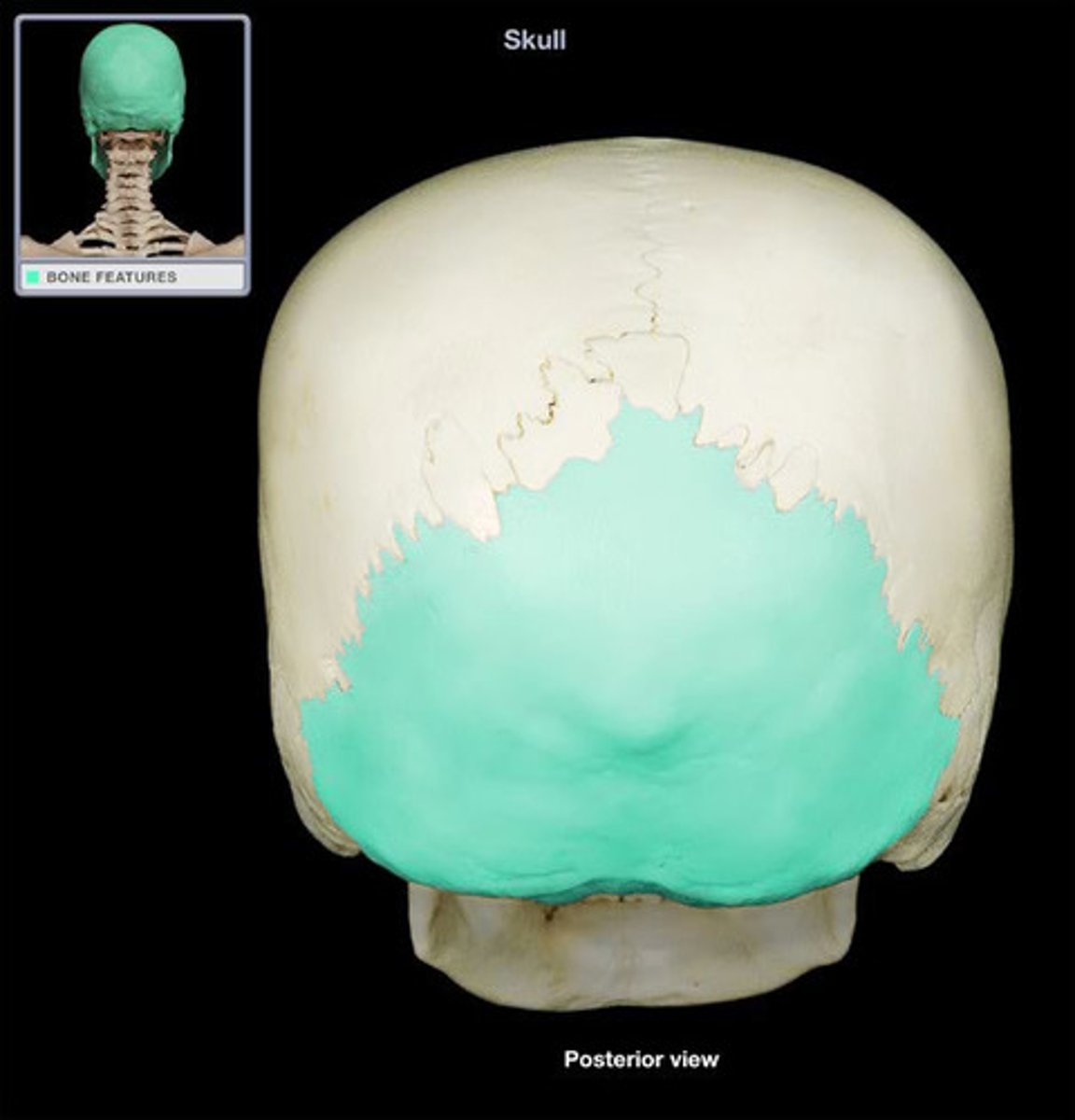
Parietal bones
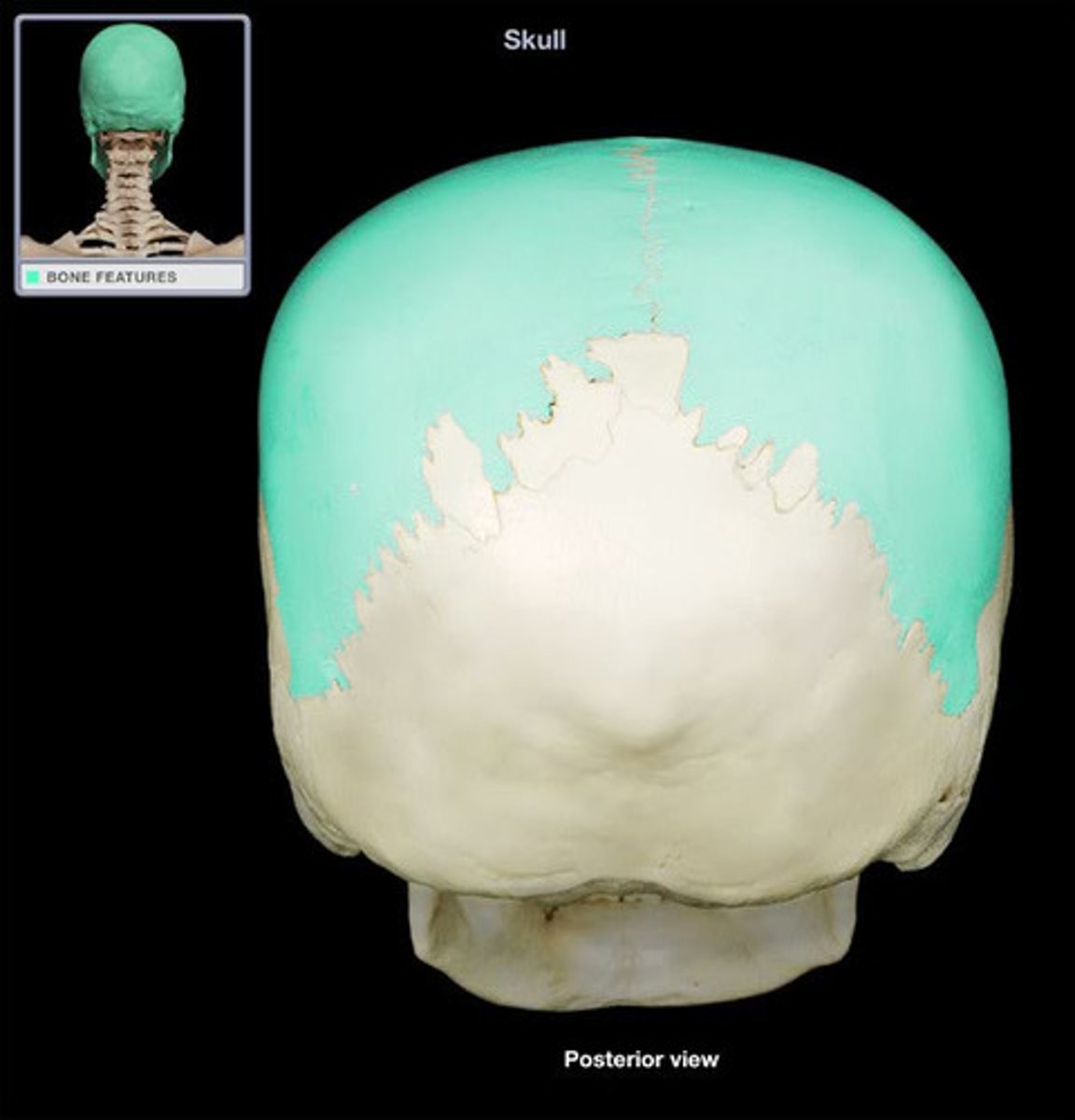
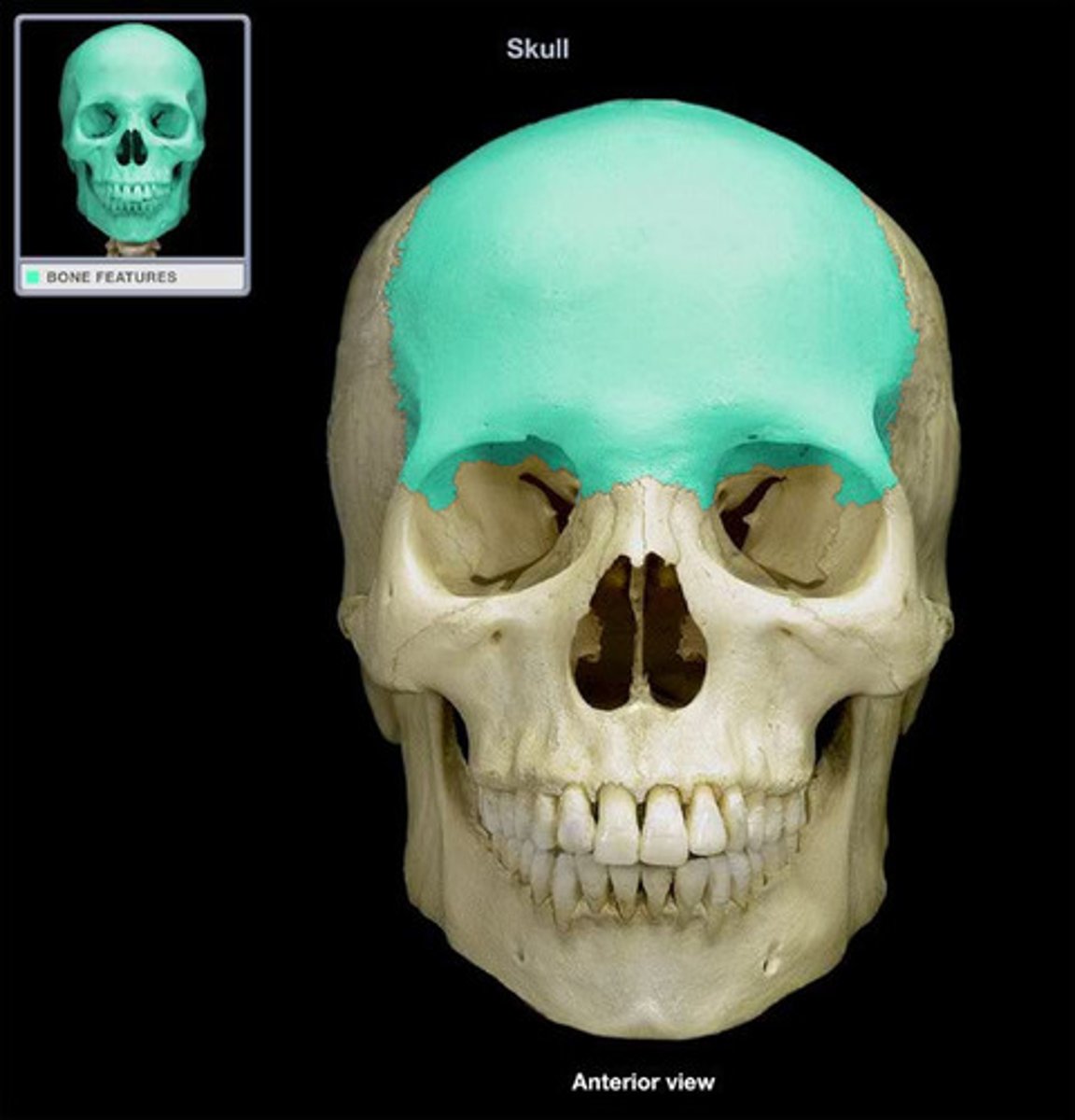
Frontal bone
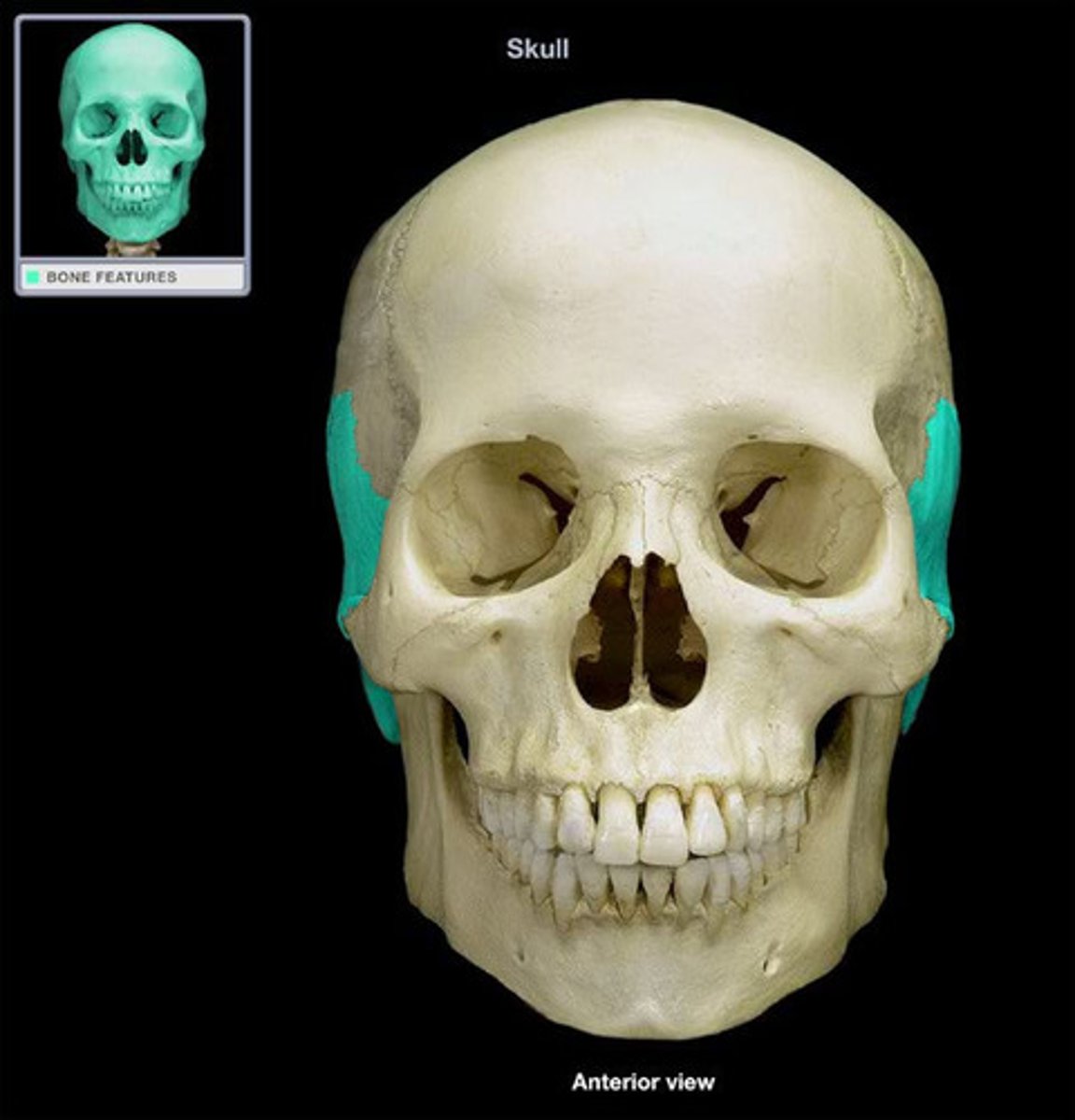
Temporal bones
Sphenoid bone
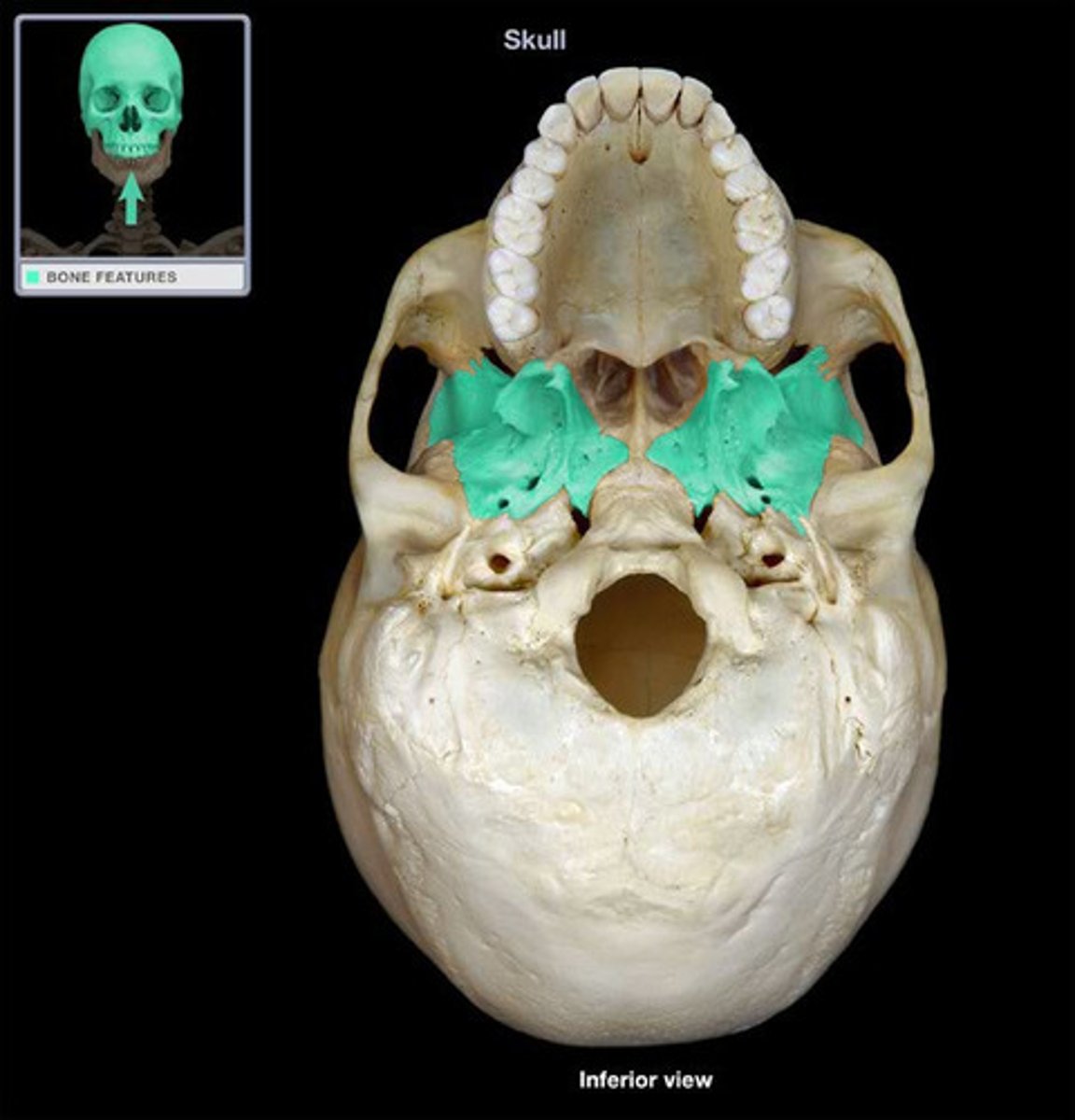
Ethmoid
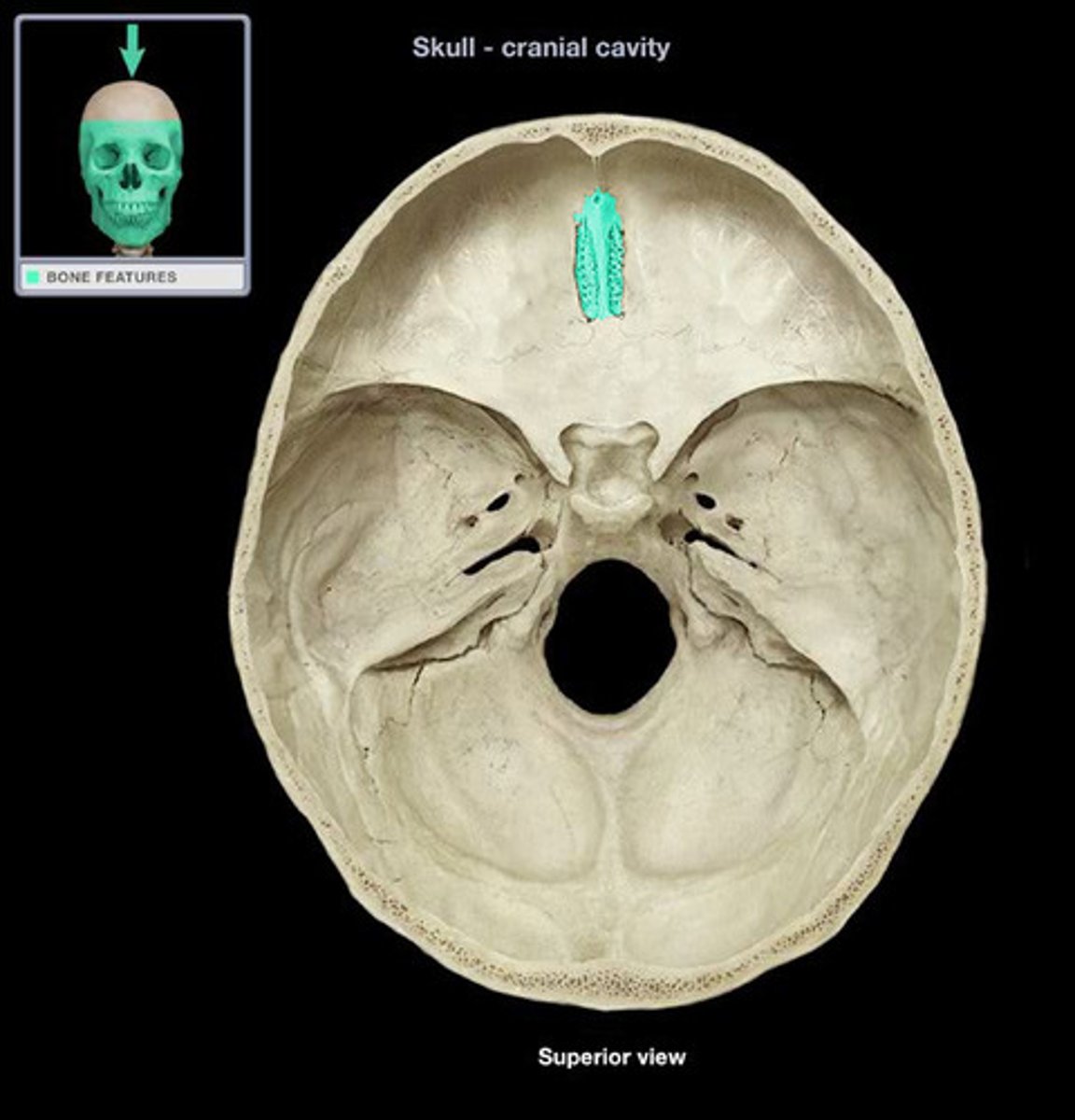
Lambdoid
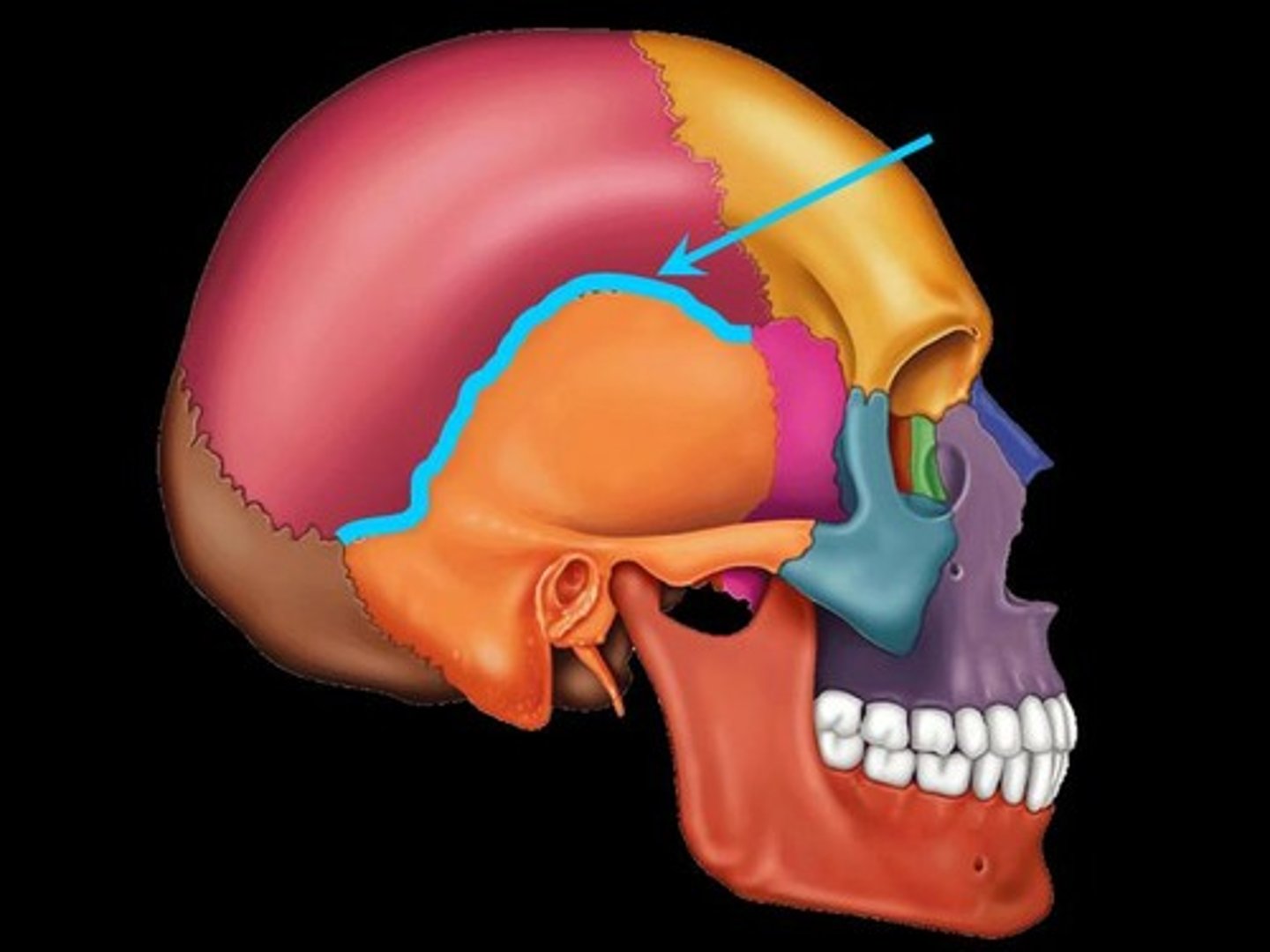
Coronal
Sagittal
Squamous
Name the 4 cranial sutures.
Lambdoid Suture
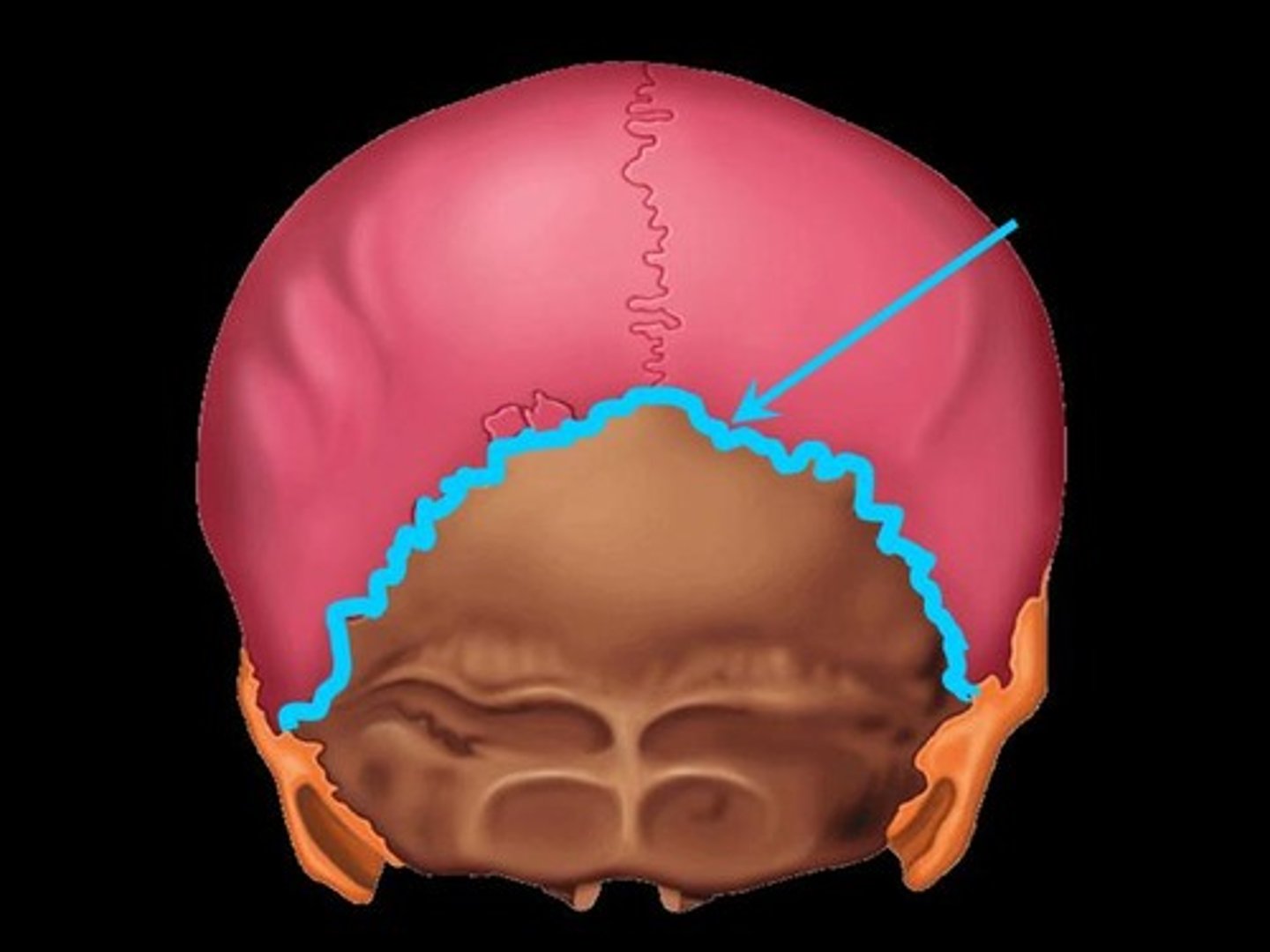
Coronal Suture
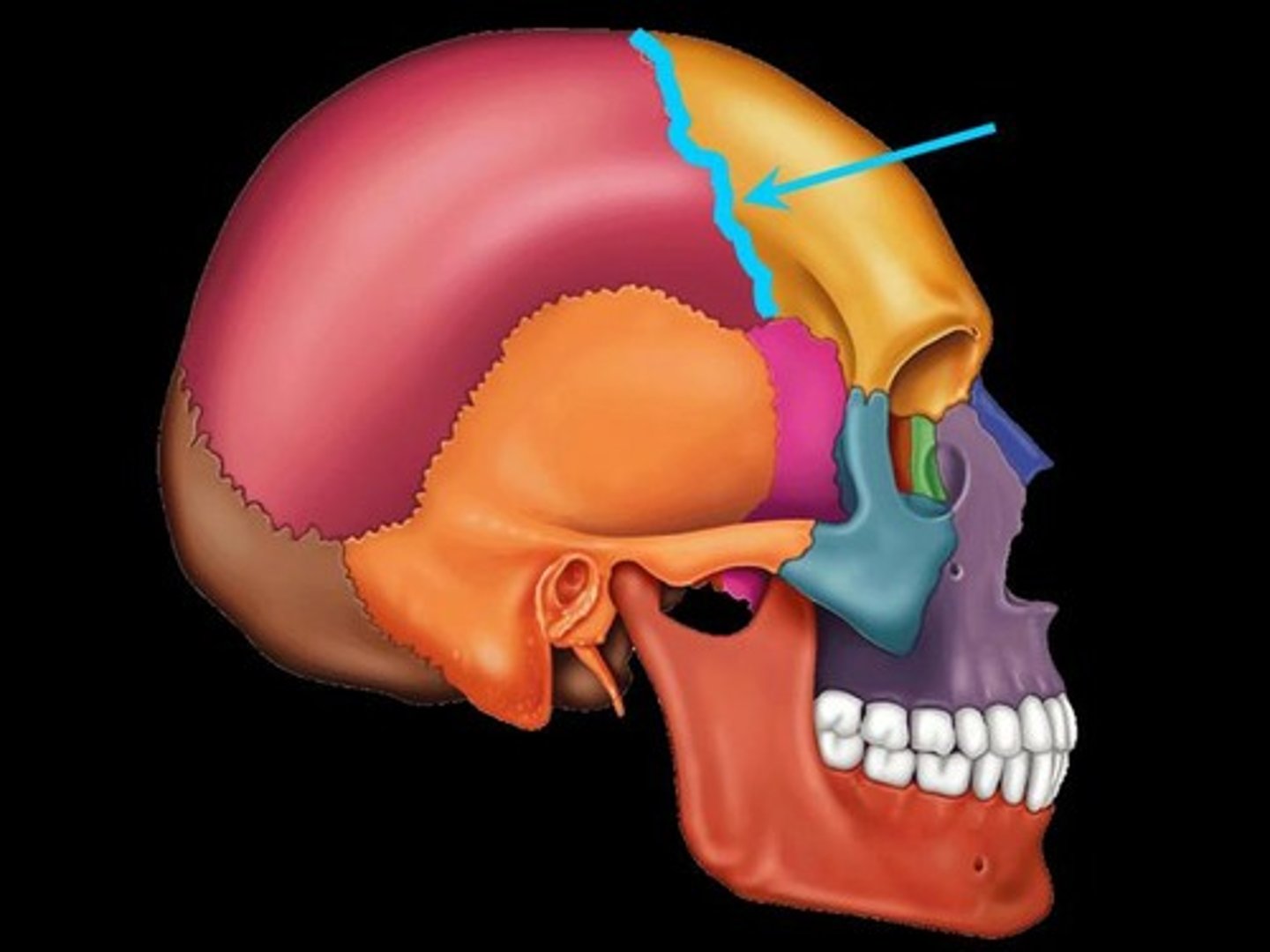
Sagittal Suture
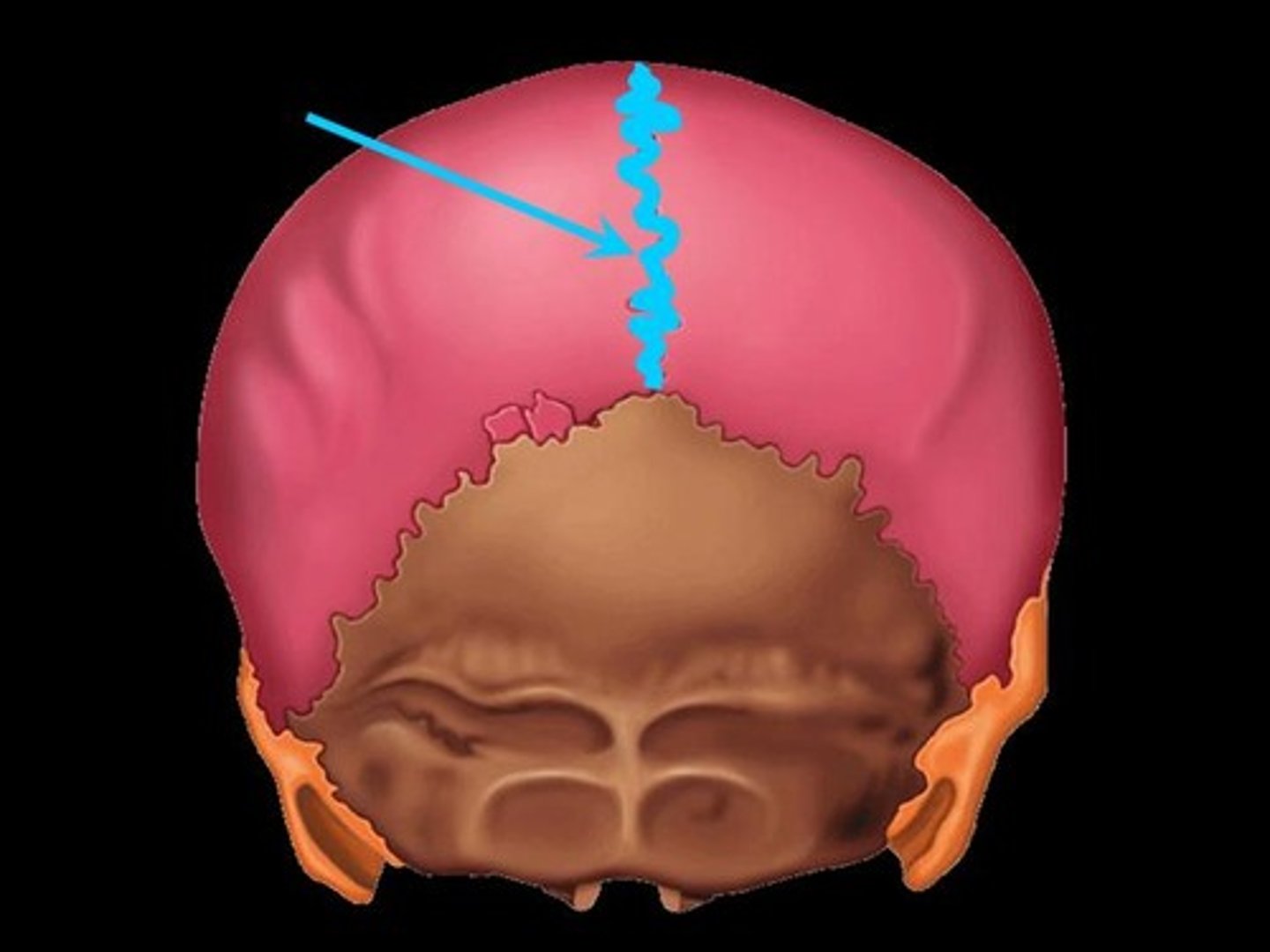
Squamous Suture
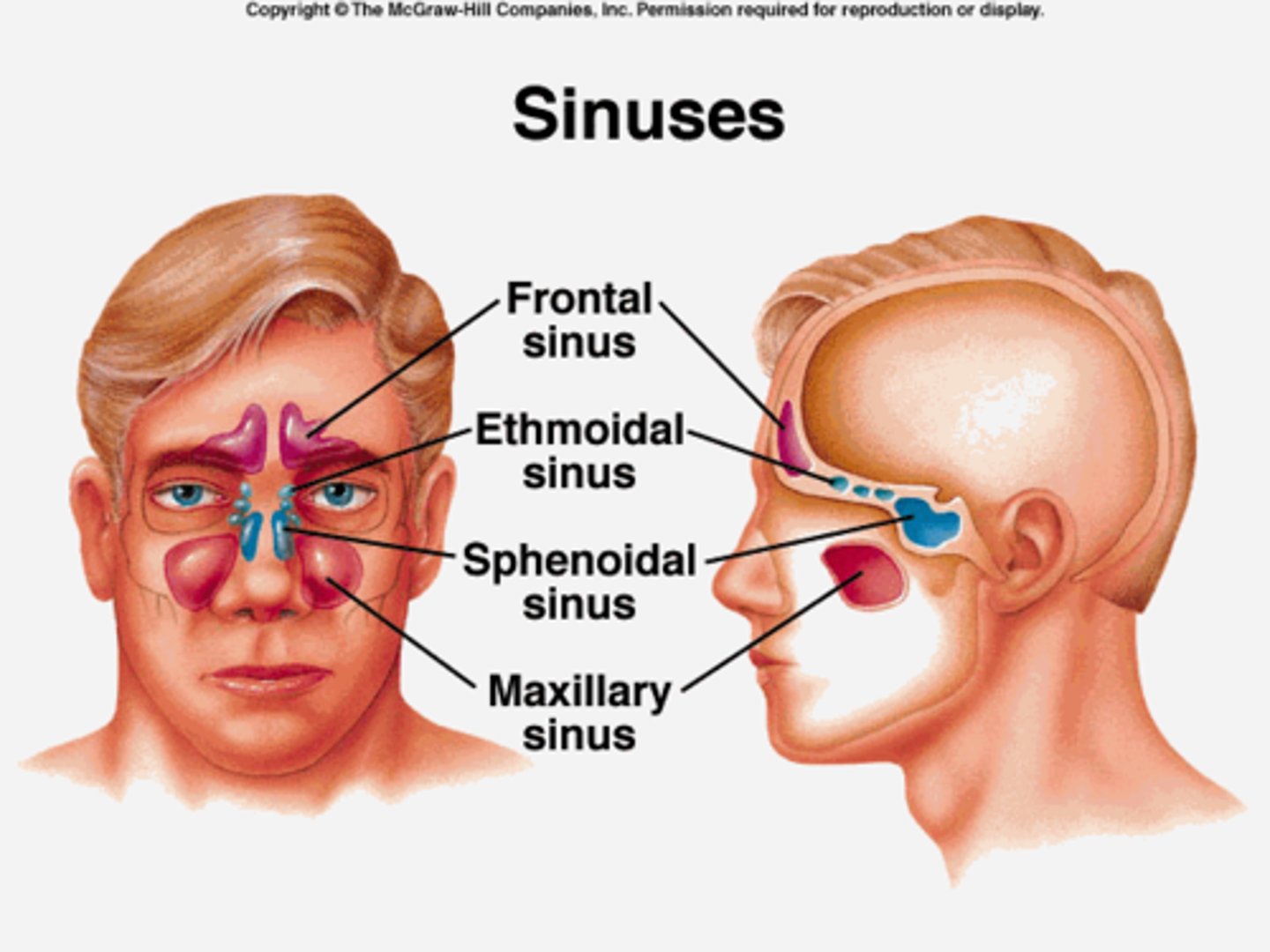
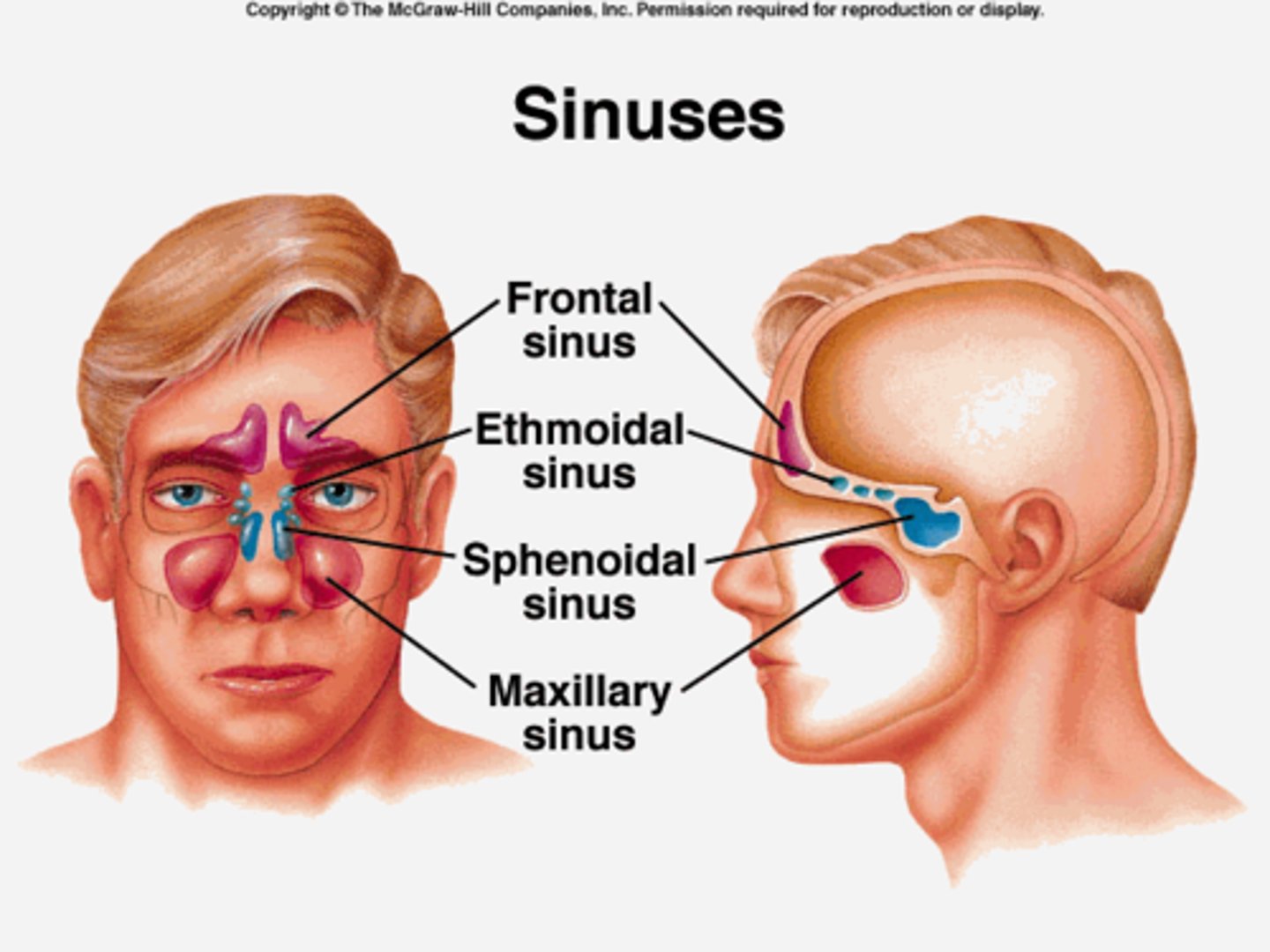
Paranasal sinuses
-Hollow portions of bones surrounding the nasal cavity
- Functions of paranasal sinuses:
> Lighten the skull
> Give resonance and amplification to voice
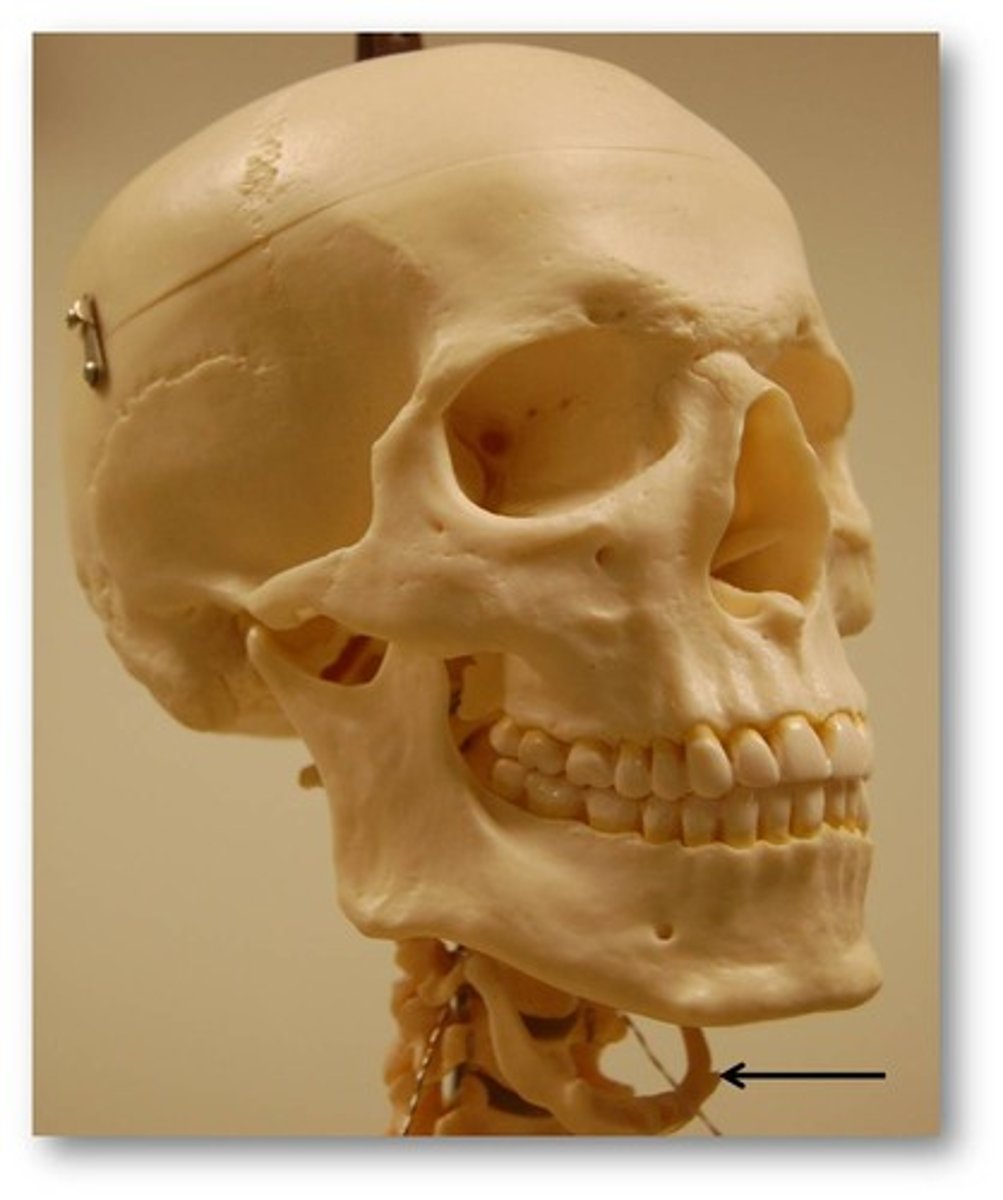
Hyoid bone
*The only bone that does not articulate with another bone
-Serves as a moveable base for the tongue
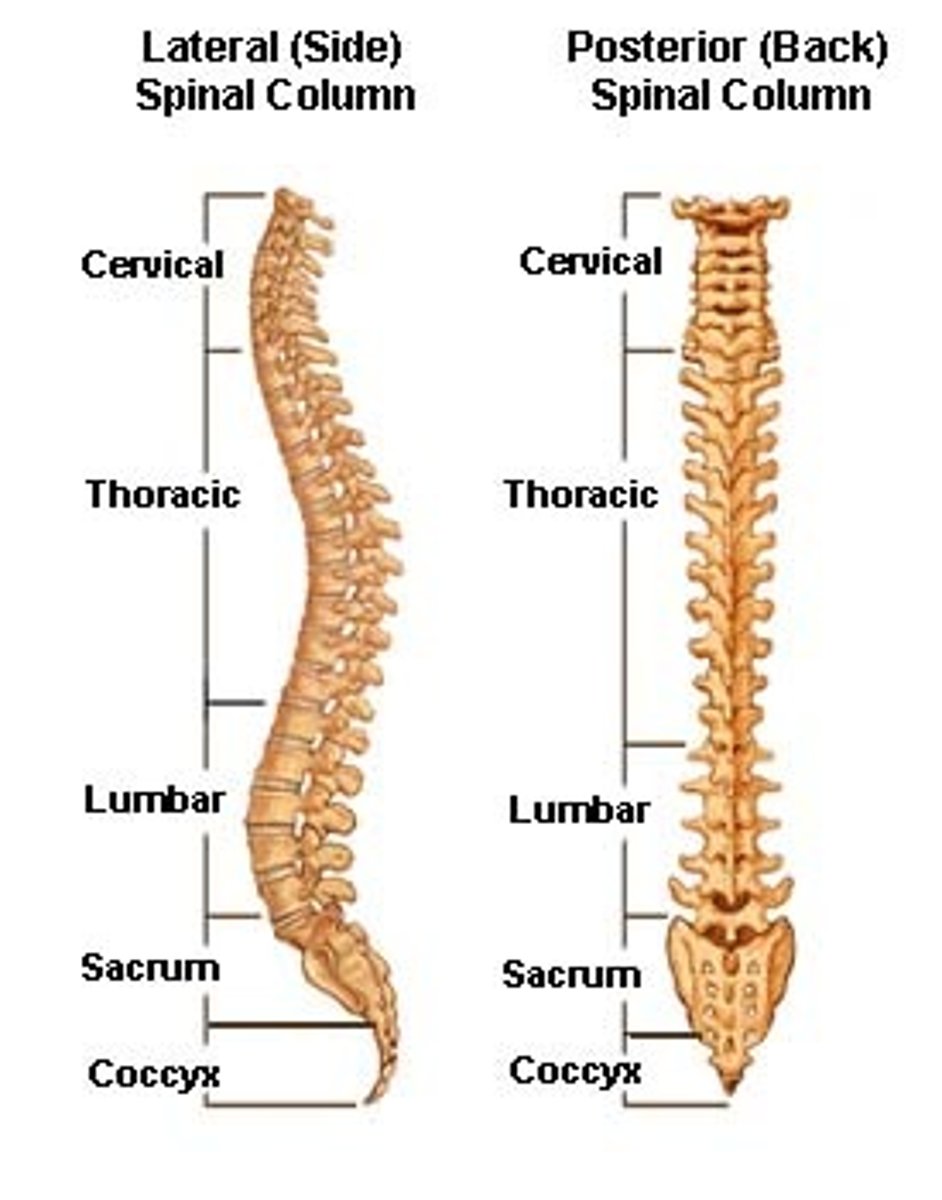
Vertebral column
Vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
>7 cervical vertebrae
>12 thoracic vertebrae
>5 lumbar vertebrae
BREAKFAST, LUNCH, DINNER
>Sacrum and coccyx are fused vertebrae
Vertebral anatomy
-Typically has a body and vertebral arch
-Superior and inferior articular processes
-Separated by intervertebral discs
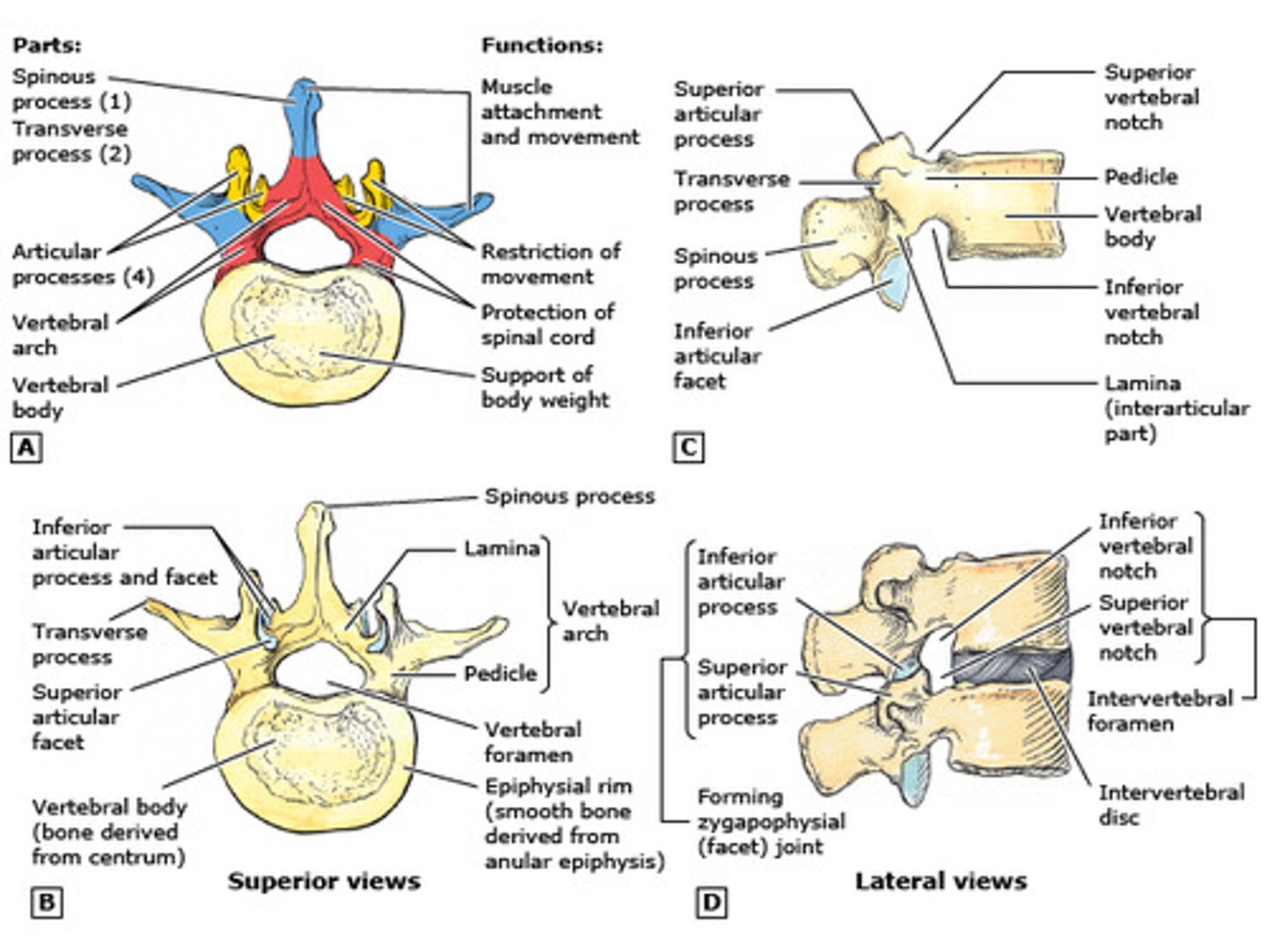
Structure of vertebrae
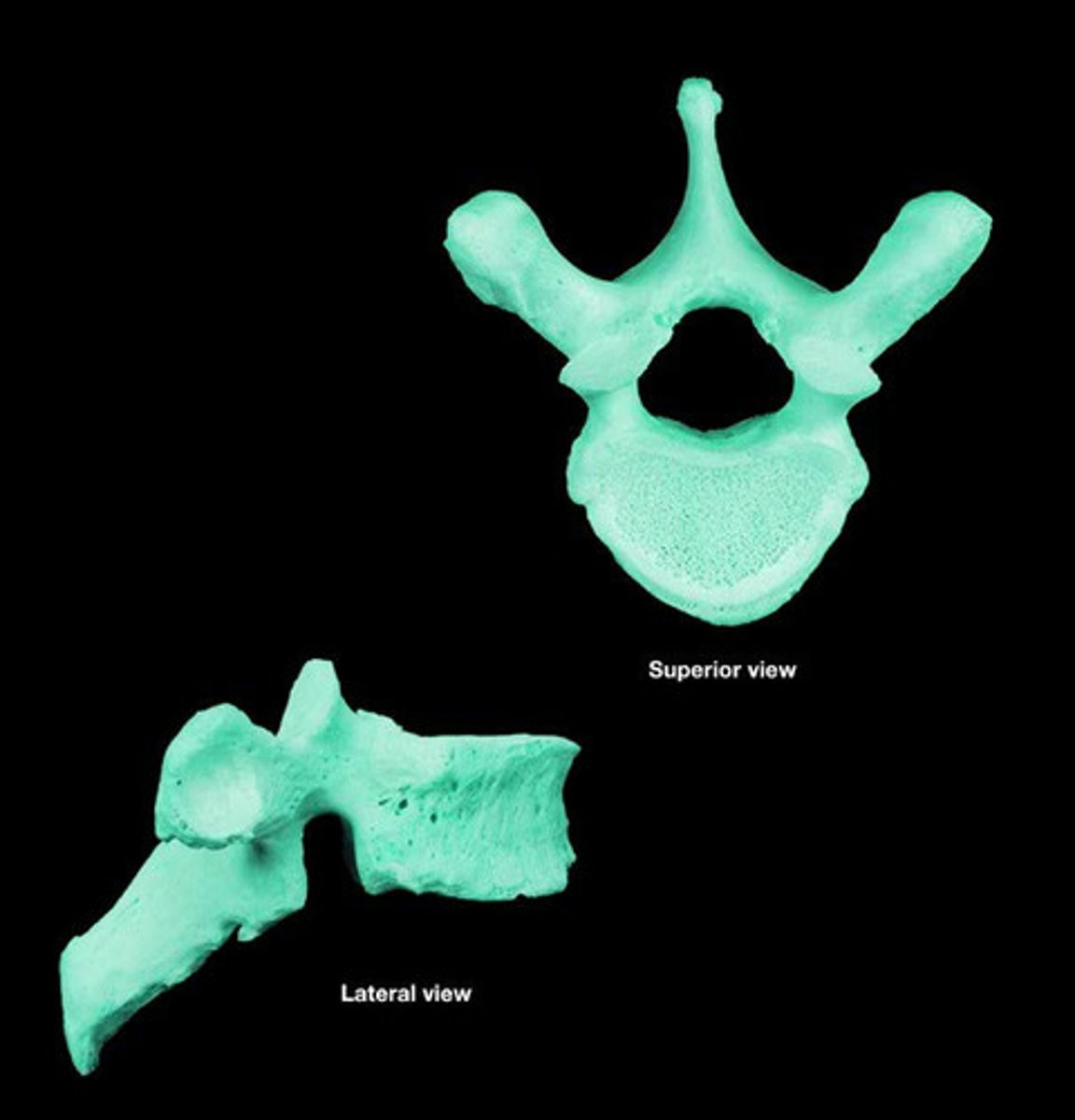
Sacrum
-Protects reproductive, digestive and urinary organs
-Articulates with pelvic girdle and fused elements of coccyx
Coccyx
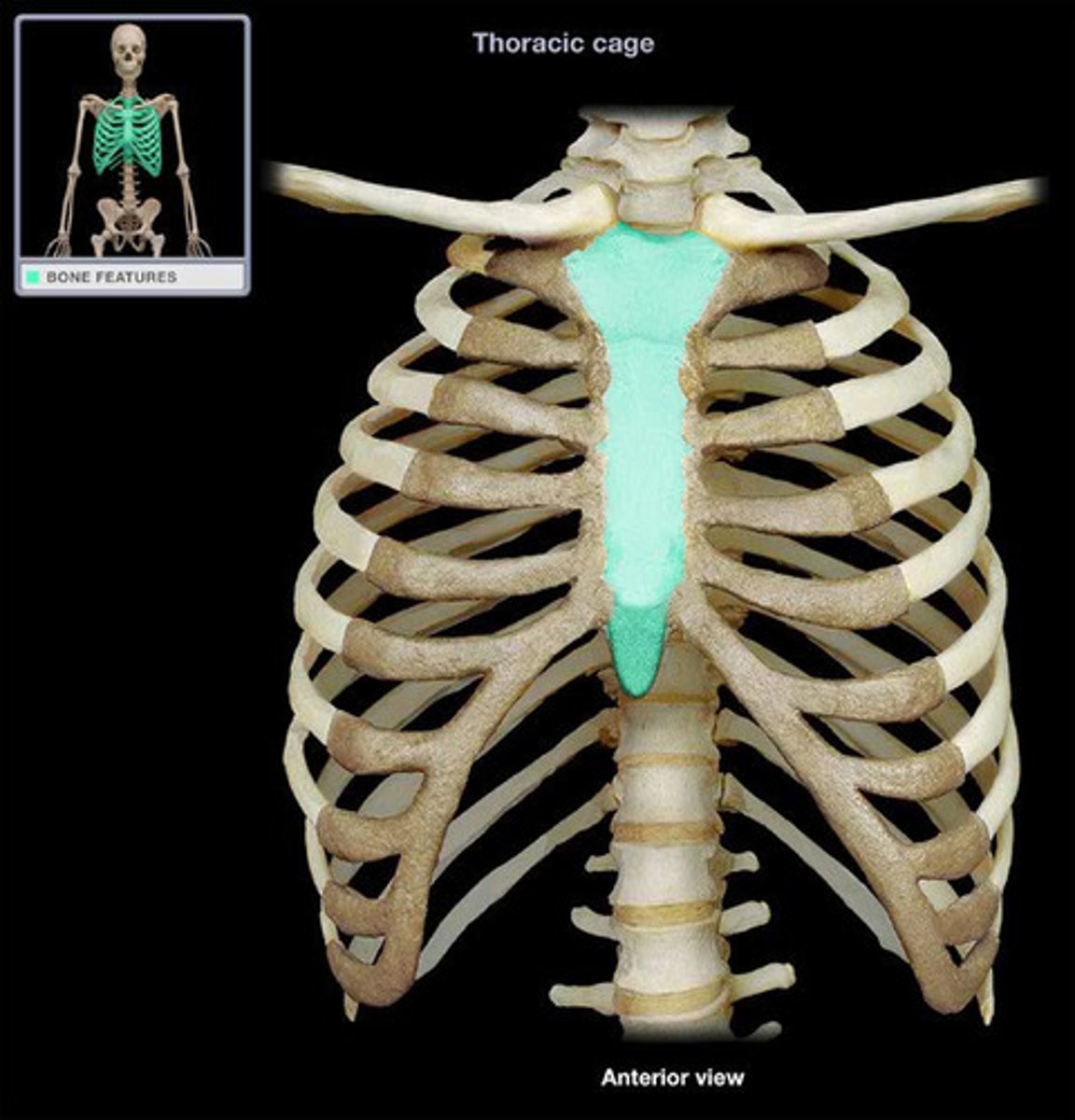
Thoracic Cage
-Thoracic vertebrae
-Ribs
-Sternum
>Ribs and sternum forms the rib cage
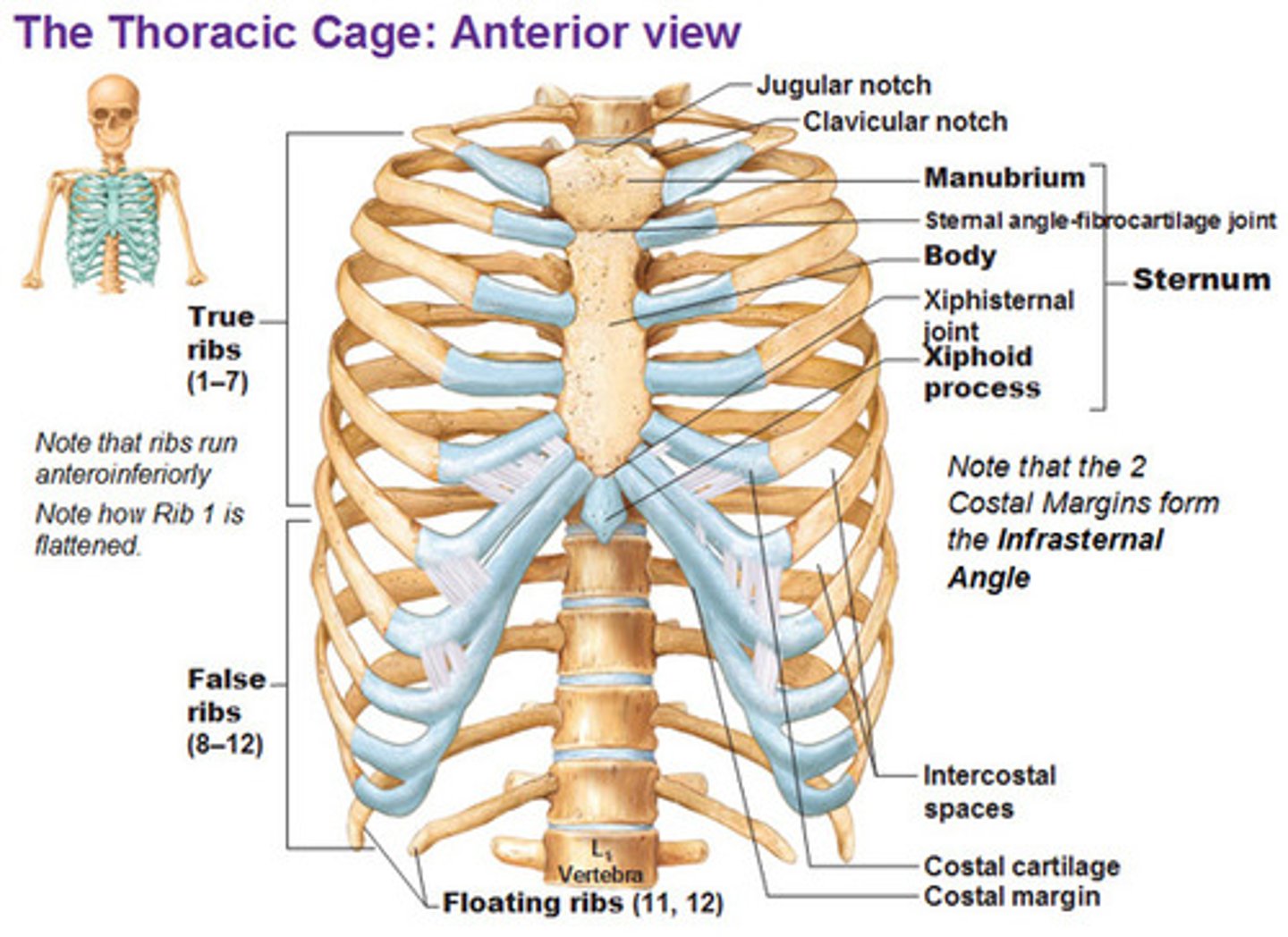
The ribs
-Ribs 1-7 are attached to vertebrae ("true ribs")
-8-12 are attached to the cartilage of the 7th rib ("false ribs")
-11-12 are floating ribs
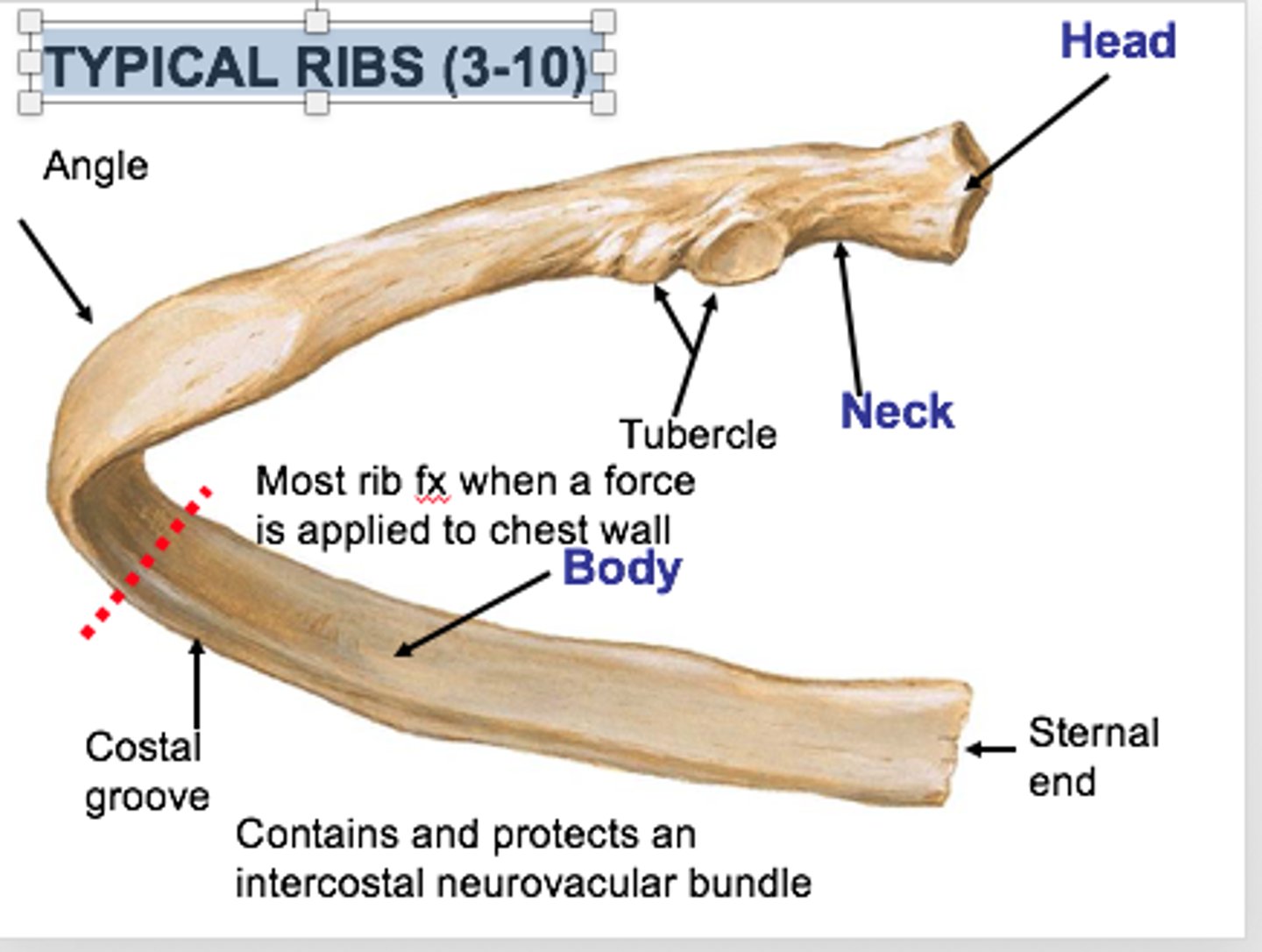
The typical rib anatomy
-Has a head, neck, tubercle and a body
-Costal groove marks pathway of blood returning to the heart
The sternum consists of
-Manubrium
-Body
-Xiphoid process
2 types of bone markings
-Projections (aka processes) that grow out from the bone
-Depressions (cavities) that indent the bone
Function: Allow blood vessels or nerves to pass through.
4 joint projections
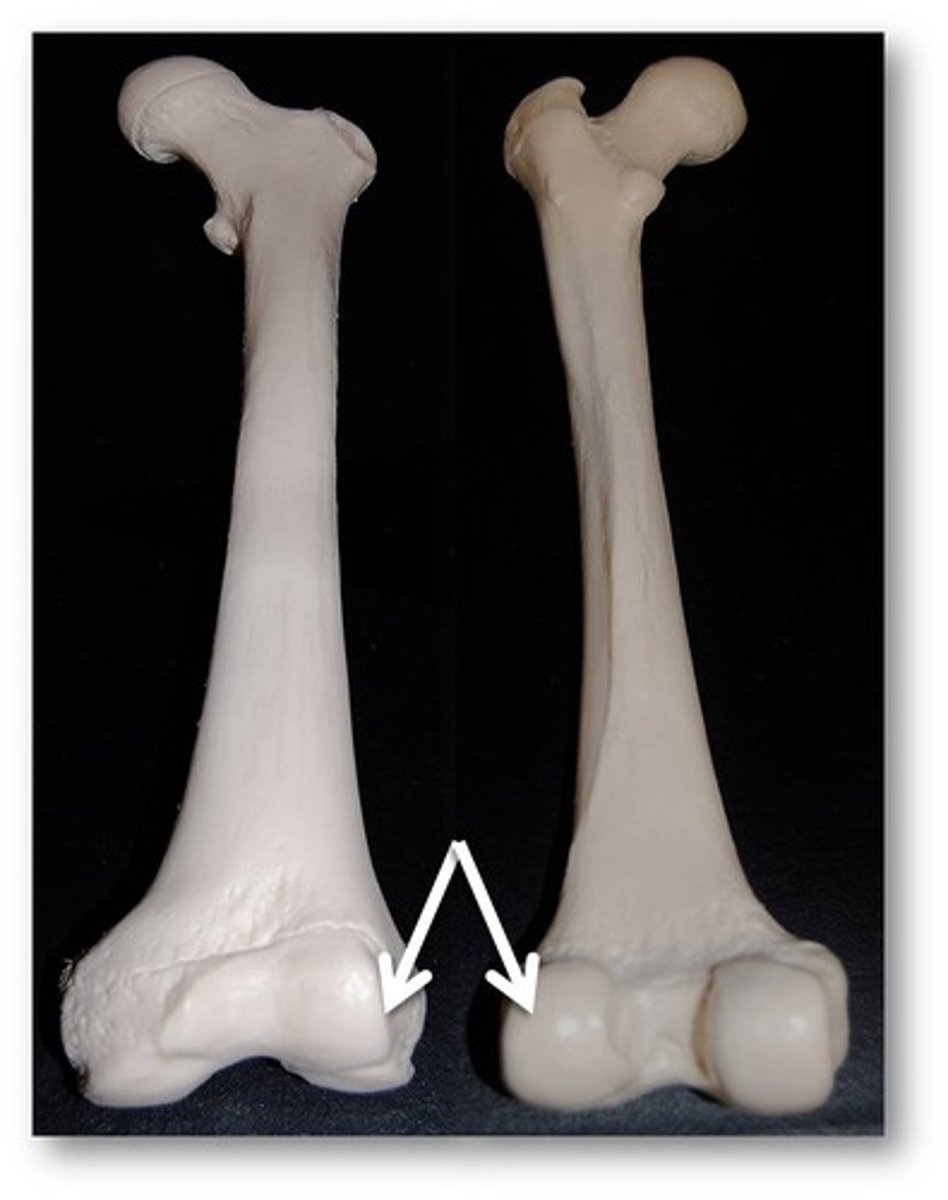
1) Condyle: Rounded articular projection
2) Head: bony expansion on a narrow neck
3) Facet: smooth, nearly flat articular surface
4) Ramus: Armlike bar of bone
Condyle
Name the joint projection:
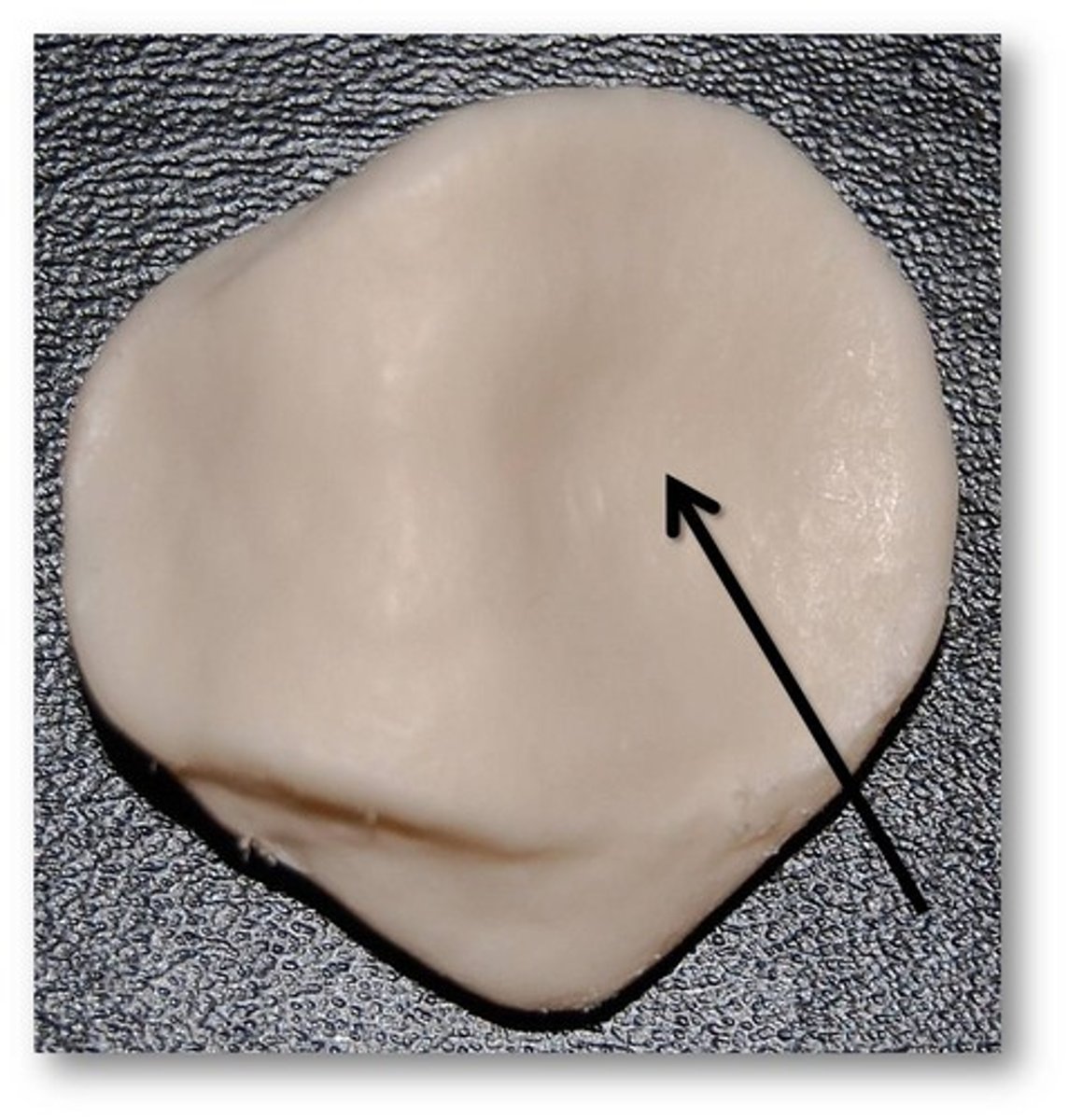
Head
Name the joint projection:
Facet
Name the joint projection:
Ramus
Name the joint projection:
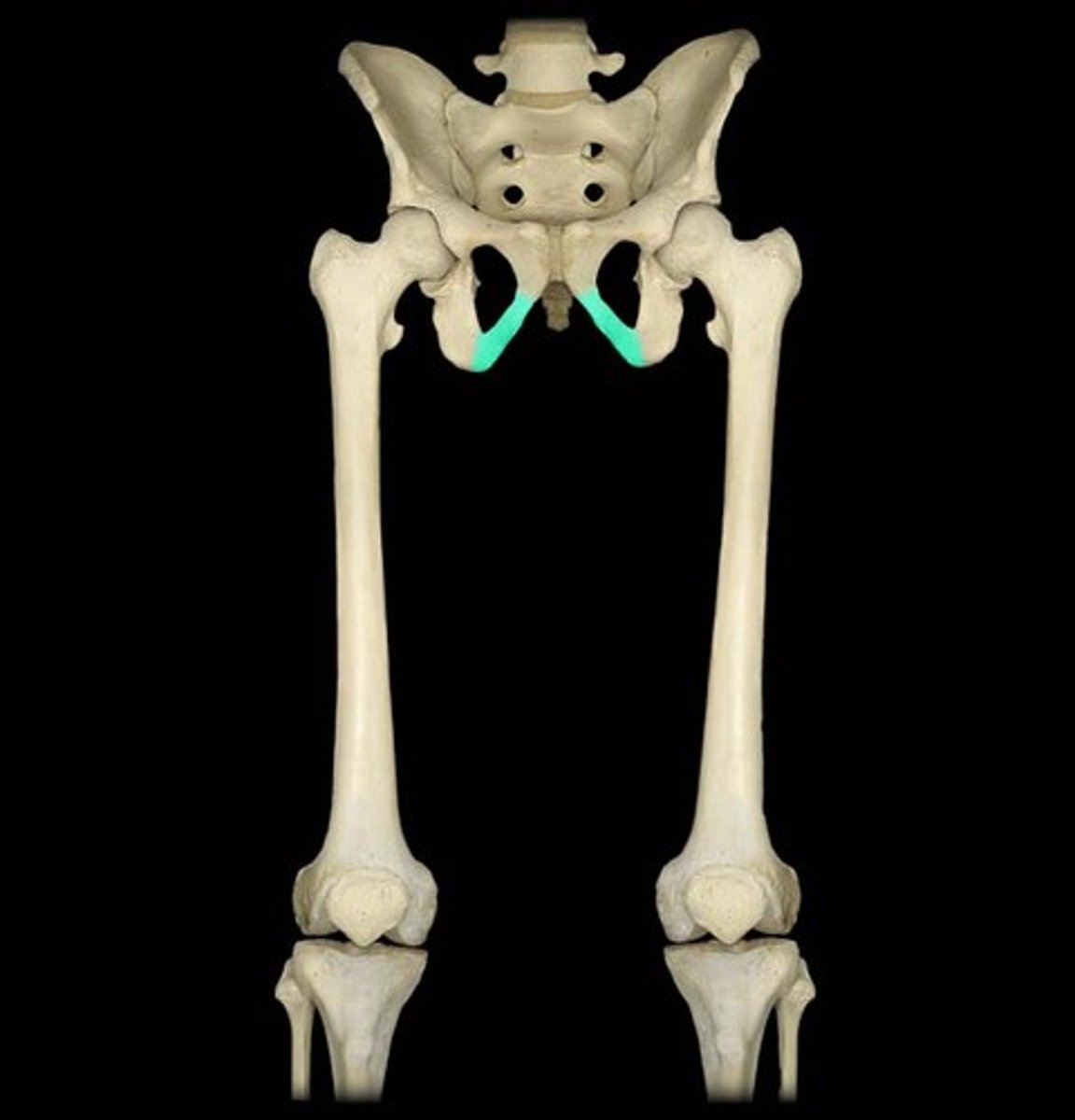
6 Ligament/Tendon projections
1) Crest: Narrow ridge of bone (Line: smaller than a crest)
2) Epicondyle: Raised area on or above a condyle
3) Tubercle: Small rounded projection
4) Tuberosity: large rounded or roughened projection
5) Trochanter: very large, blunt projection
(only on femur)
6) Spine: Sharp, pointed projection
Crest
Name the Ligament/tendon projection:
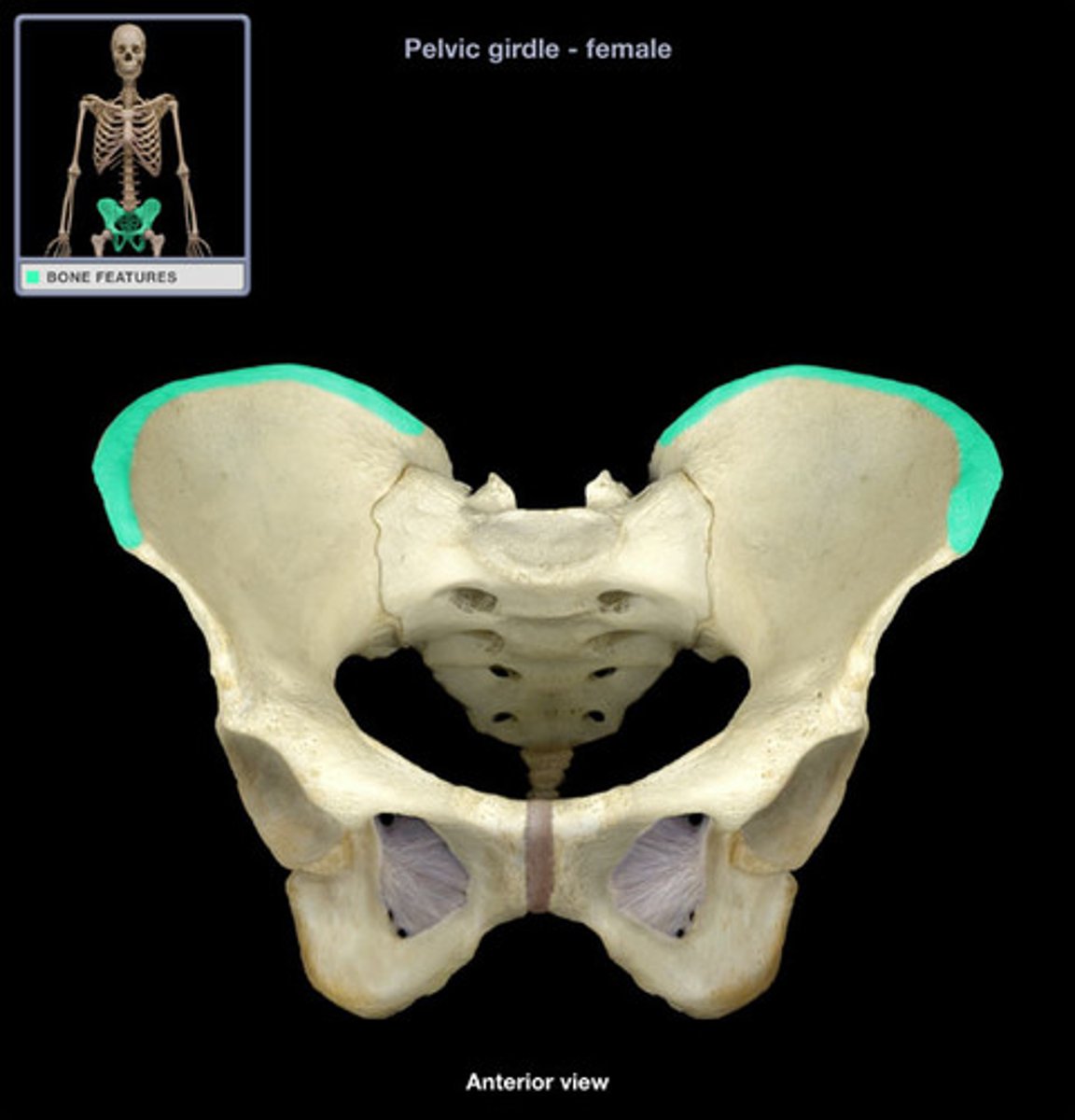
Epicondyle
Name the Ligament/tendon projection:
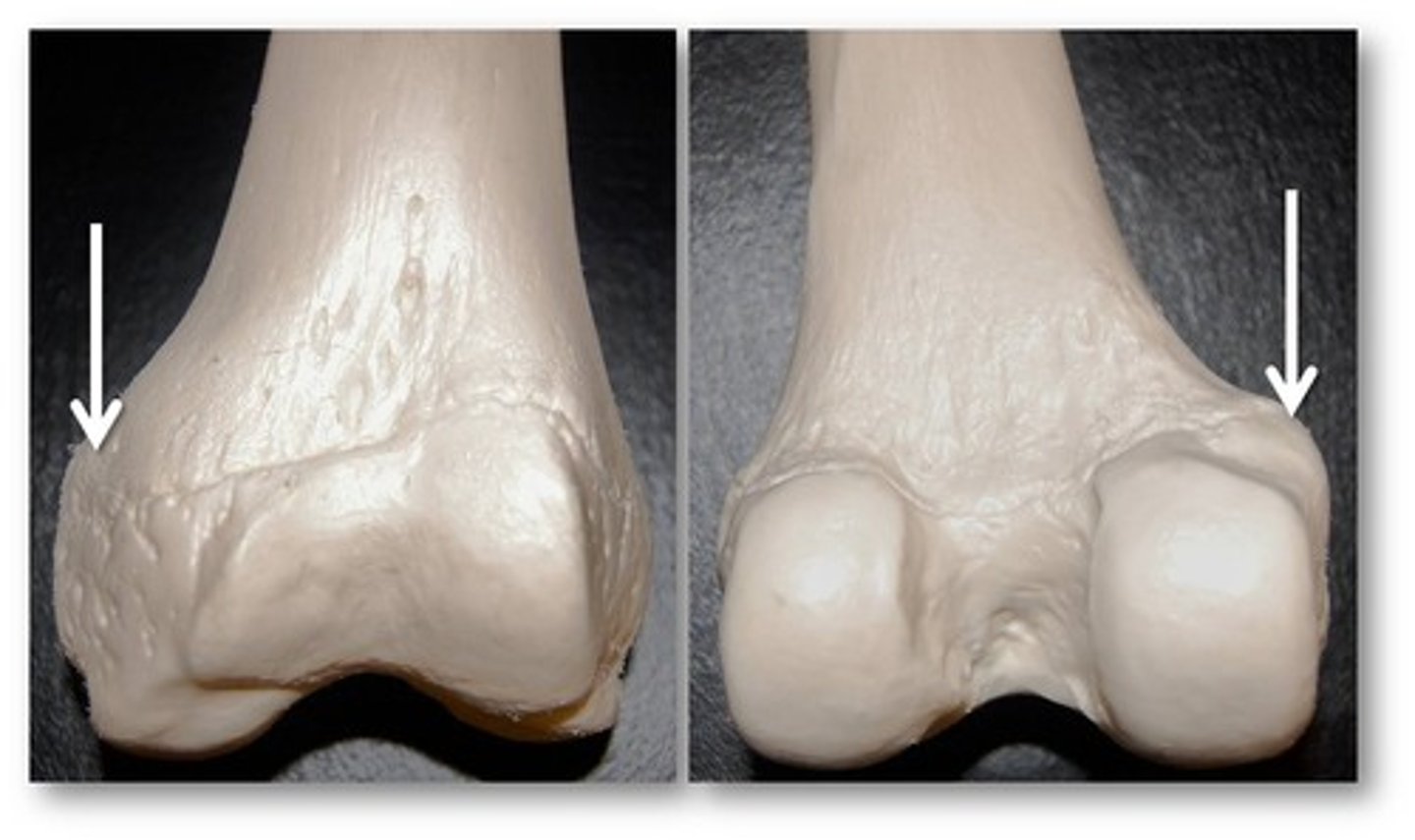
Tubercle
Name the Ligament/tendon projection:
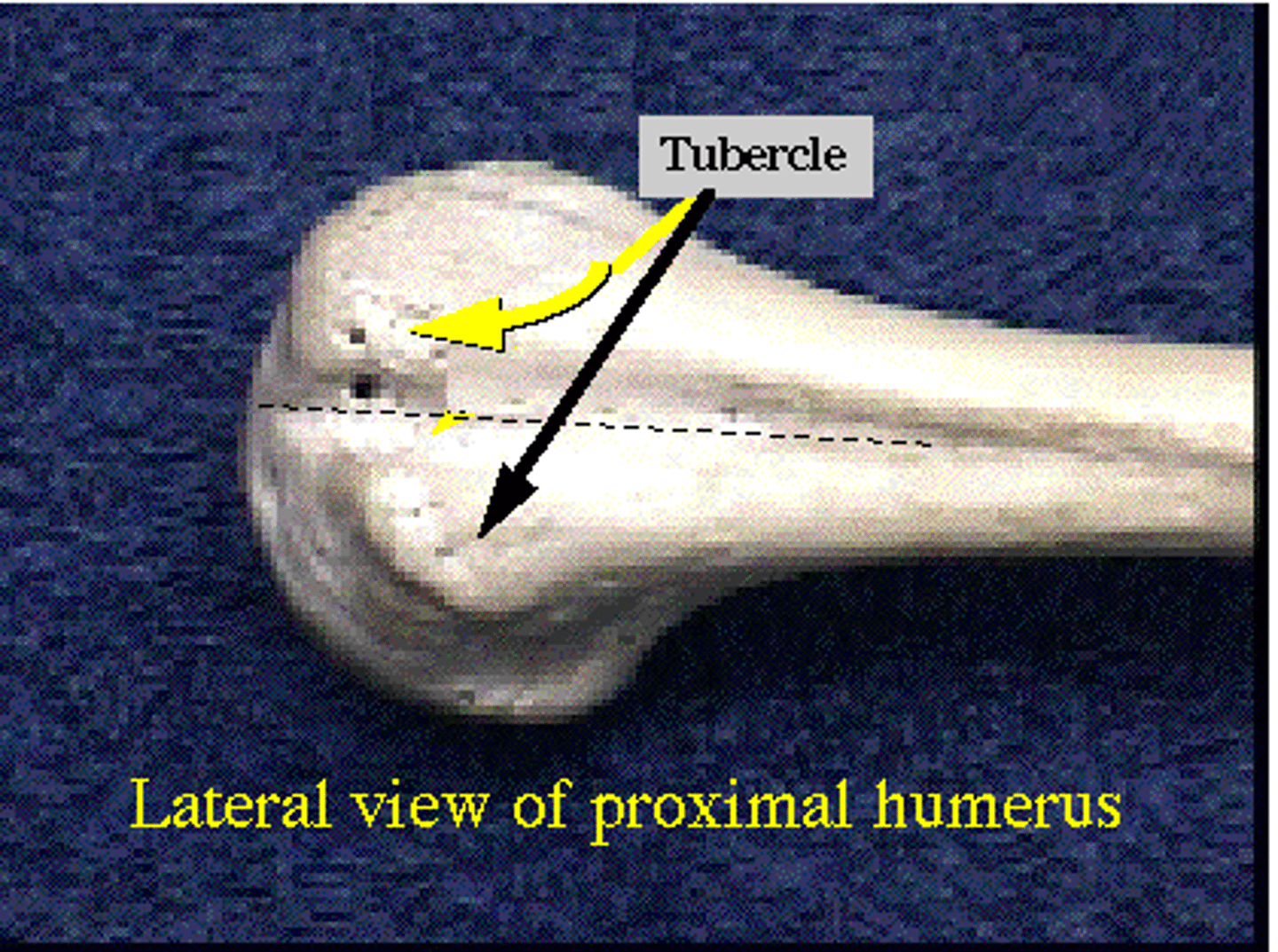
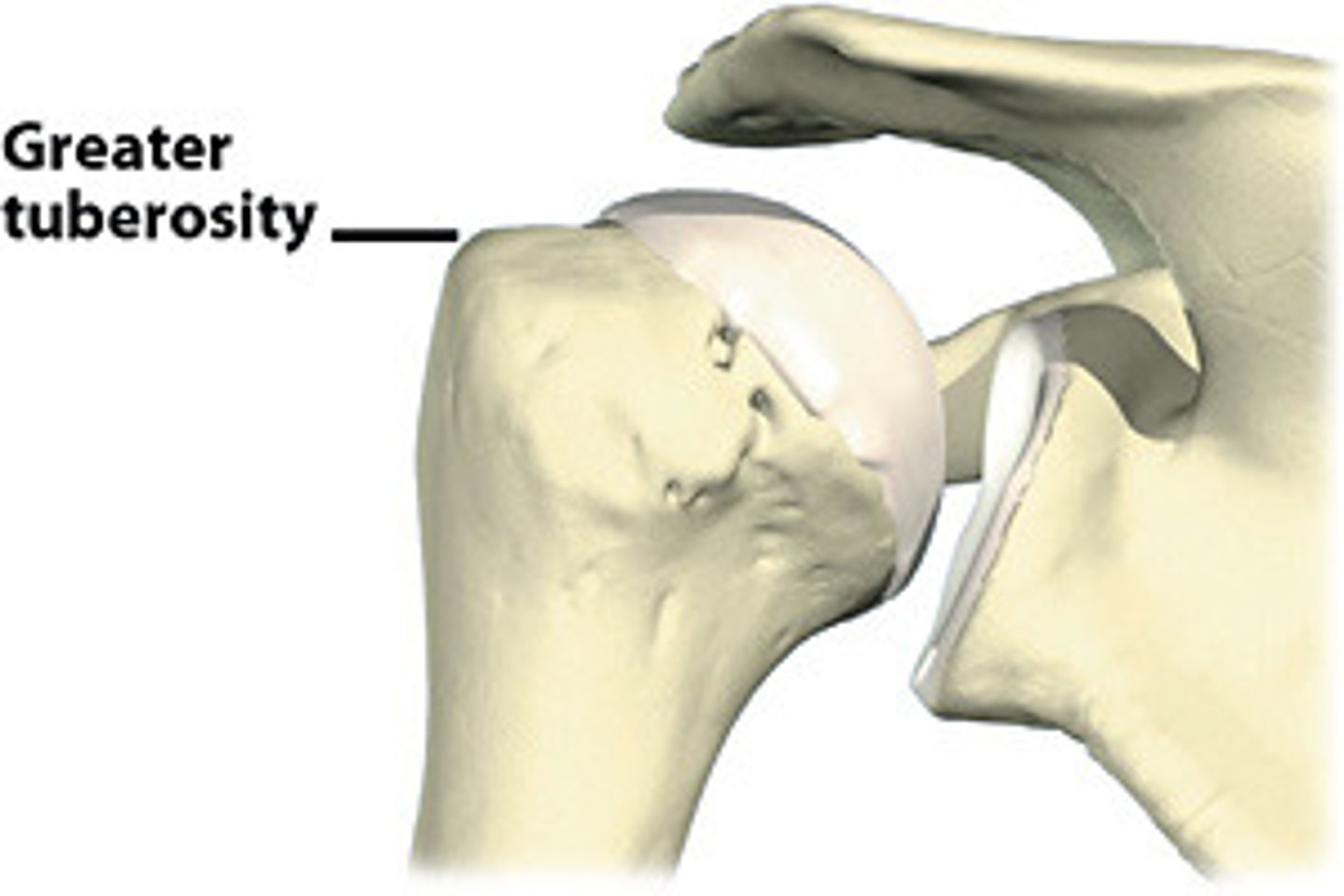
Tuberosity
Name the Ligament/tendon projection:
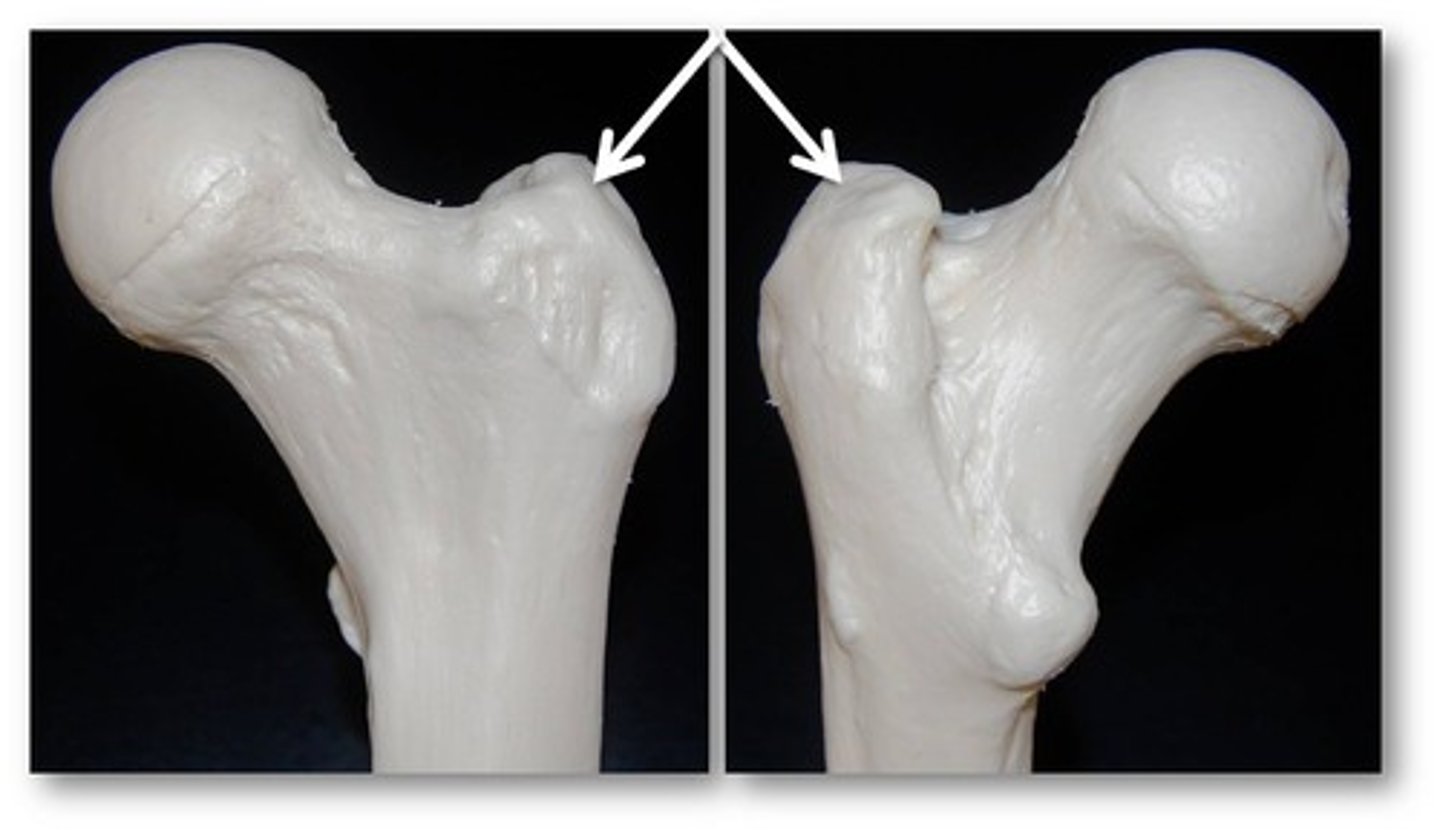
Trochanter
Name the Ligament/tendon projection:
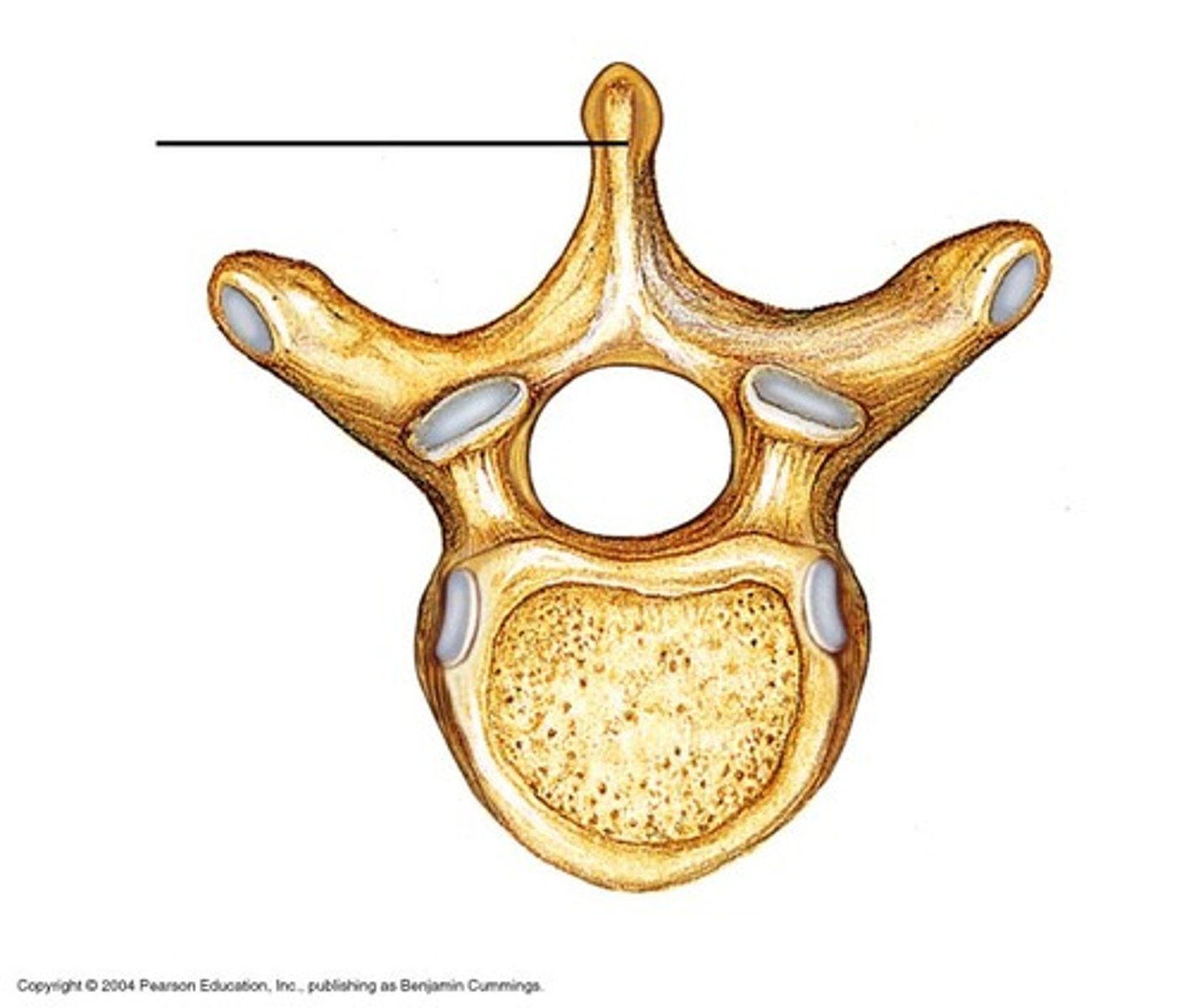
Lumbar vertebrae
6 types of depressions
1) Meatus: Canal or tube
2) Fossa: shallow basin
3) Fissure: narrow, slit-like opening
4) Sinus: Cavity within a bone; filled with air and lined with mucous membranes
5) Foramen: Round or oval opening
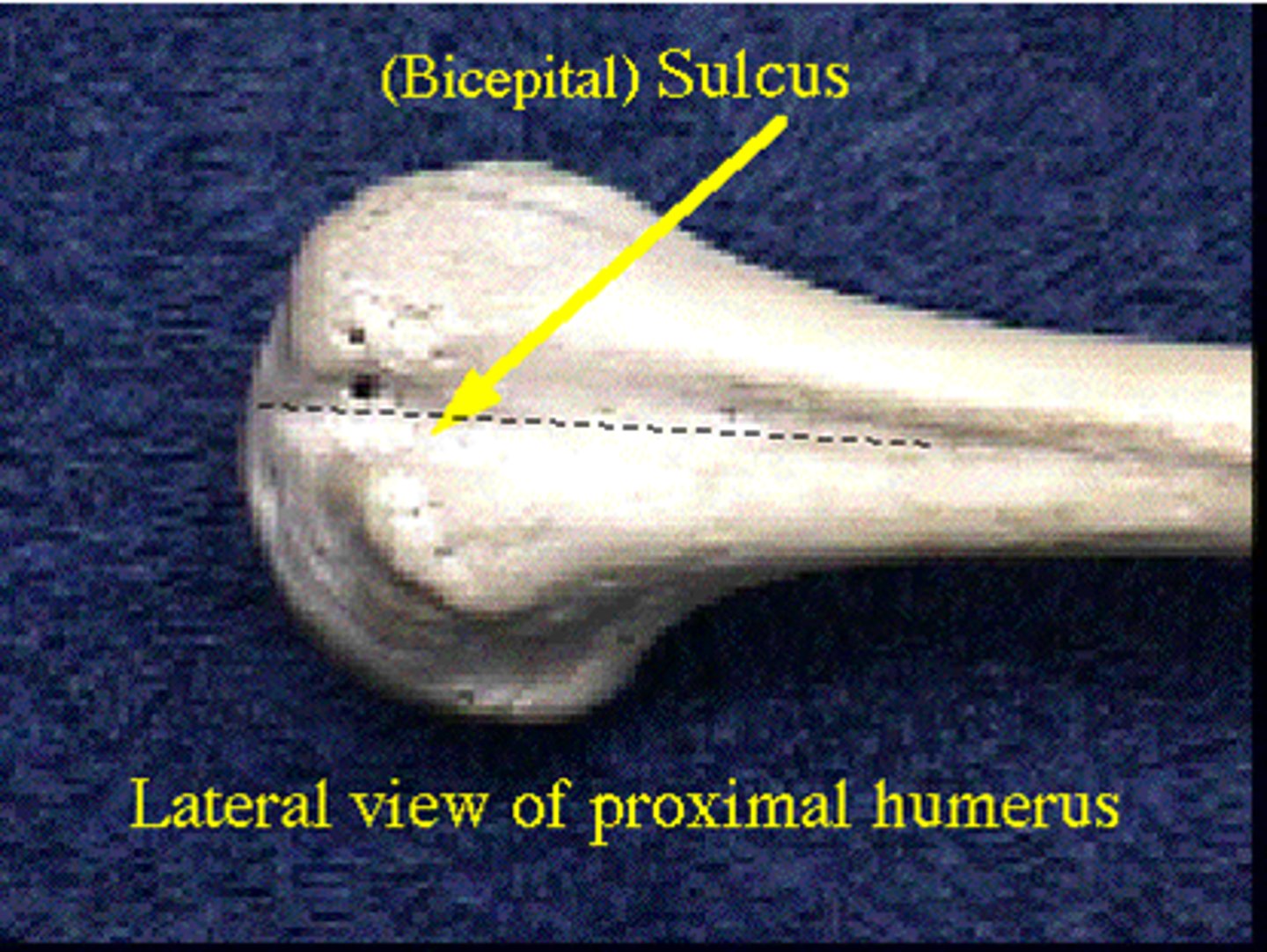
6) Sulcus, Groove or Furrow: a shallow depression
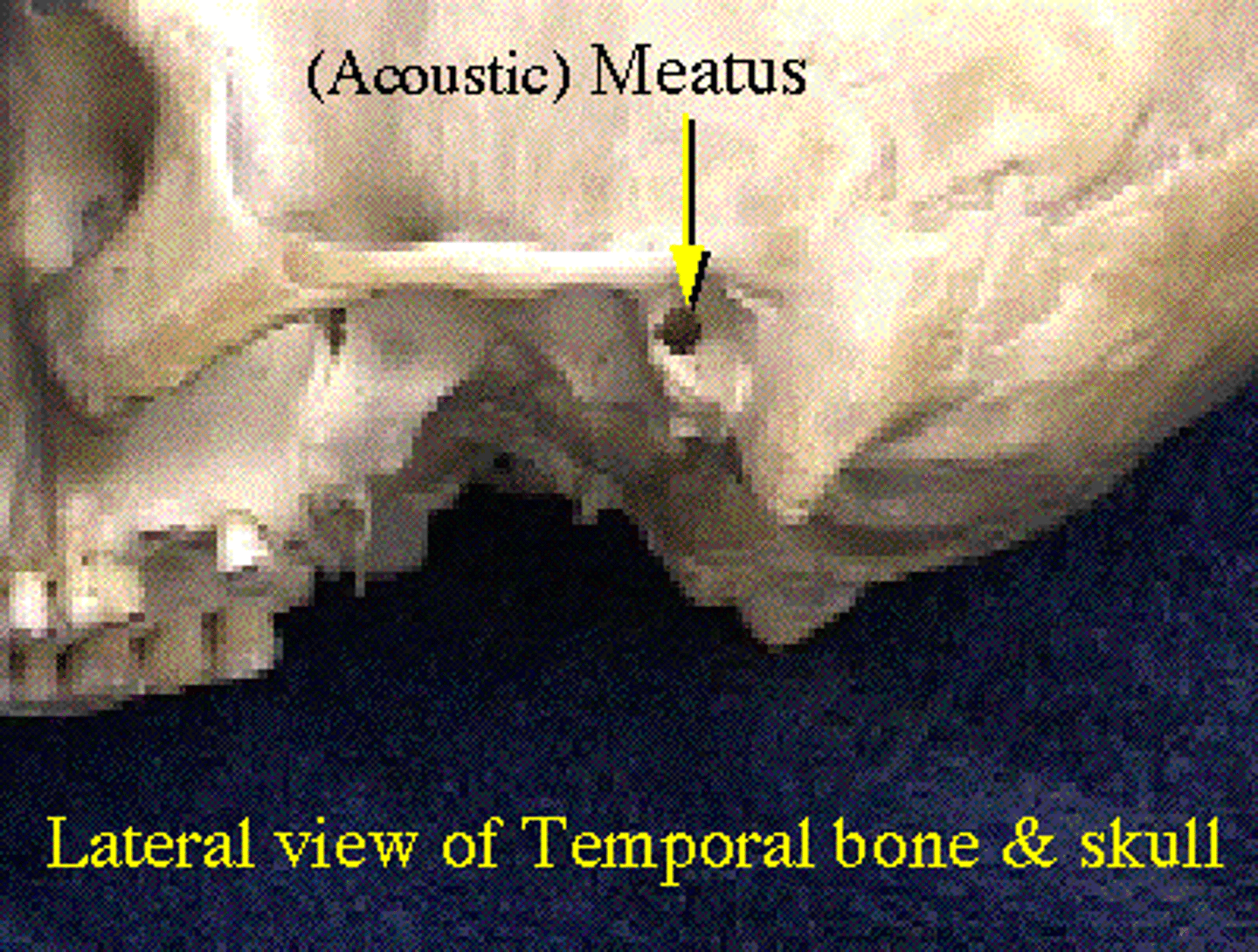
Meatus
Bone Depressions:
Fossa
Bone Depressions:
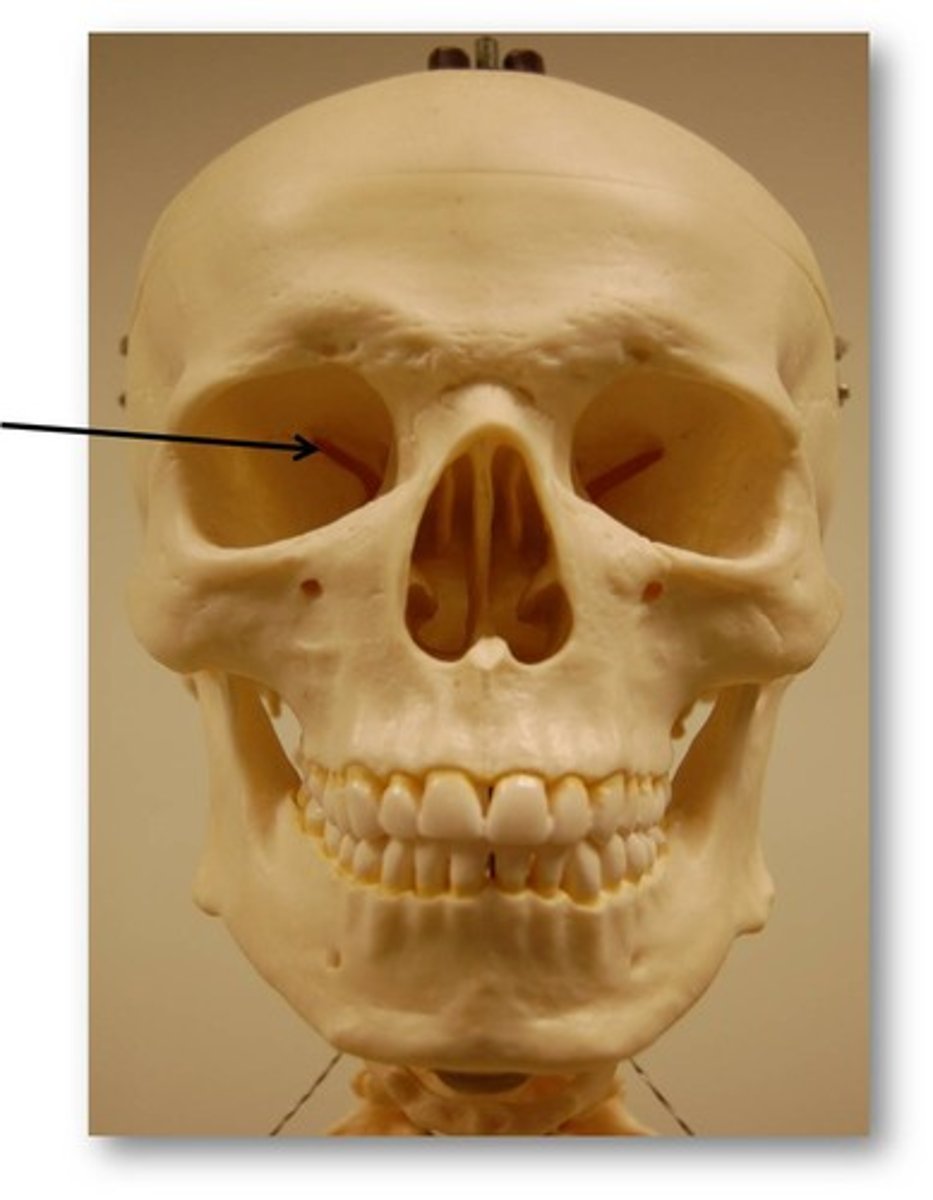
Fissure
Bone Depressions:
Sinus
Name the bone depression:
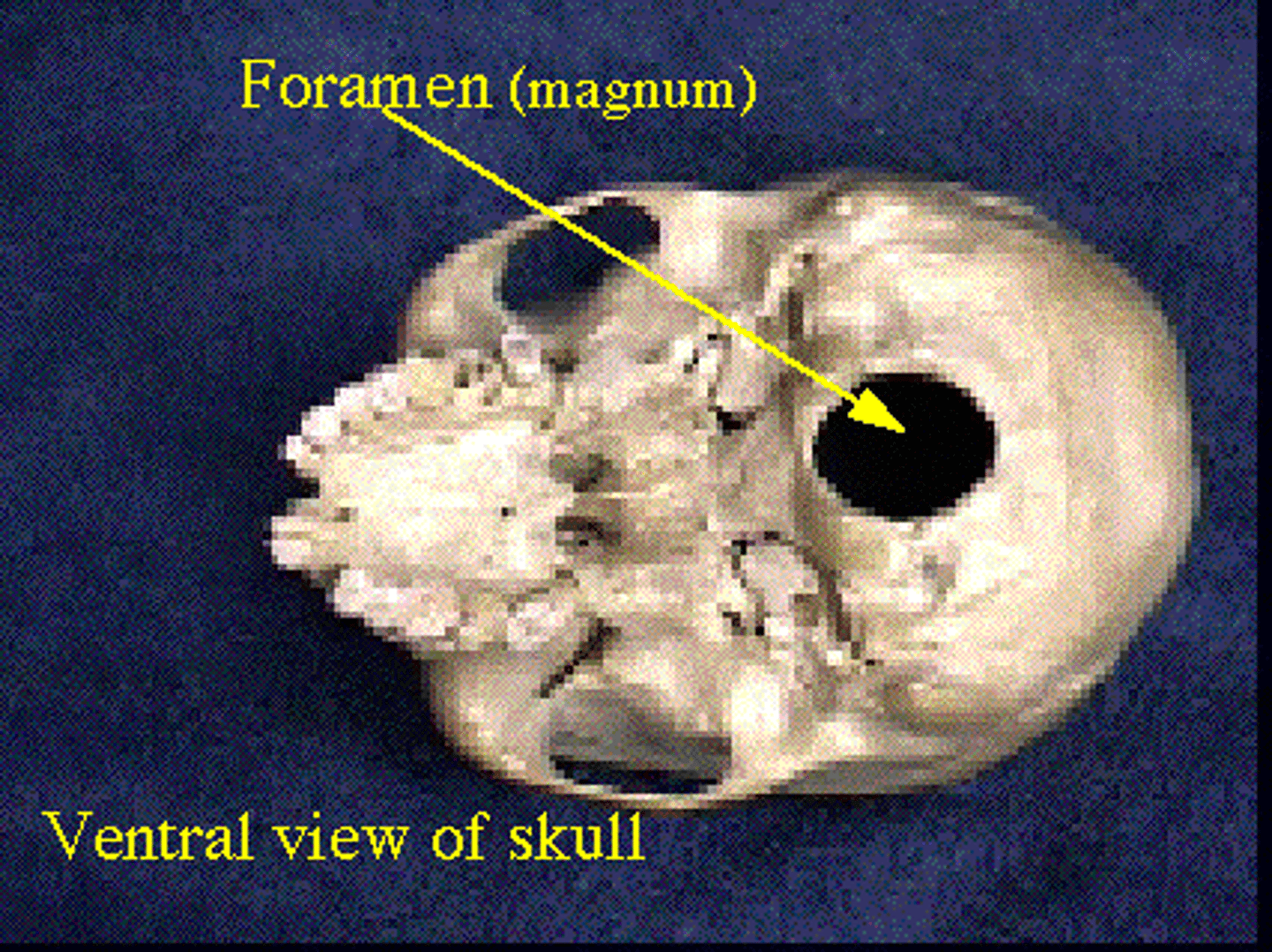
Foramen
Name the bone depression:
Sulcus, groove or furrow
Name the bone depression: