2 - Macrotaxonomy: The tree of life - looking at the patterns
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Tree of Life
Foundational concept in evolutionary biology, symbolizing the interconnectedness and shared ancestry of all living organisms.
Tree of Life
It serves as a metaphor and conceptual model to explore the evolution of life and describe the relationships between organisms, both living and extinct
Divergent Evolution
A group splits into new species over time, becoming increasingly dissimilar
Convergent Evolution
occurs when unrelated species evolve similar characteristics or adaptations because they occupy similar ecological niches or face similar environmental challenges
Homologous traits
arise through divergent evolution, where a common ancestral trait evolves differently in descendant lineages, often leading to new functions
Analogous characteristics
have developed independently in different species to perform similar functions, despite not sharing a common evolutionary origin
Cladogram
a tree structure that represents the (evolutionary) relationships within a group of organisms.
hypothesis
dendrogram
Cladogram emphasizes that the diagram represents a ________ about the actual evolutionary history of a group, lengths: arbitrary. "_________"
clade
a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all of its descendants. It consists of a single common ancestor and all its offspring
Descendants
Ancestor
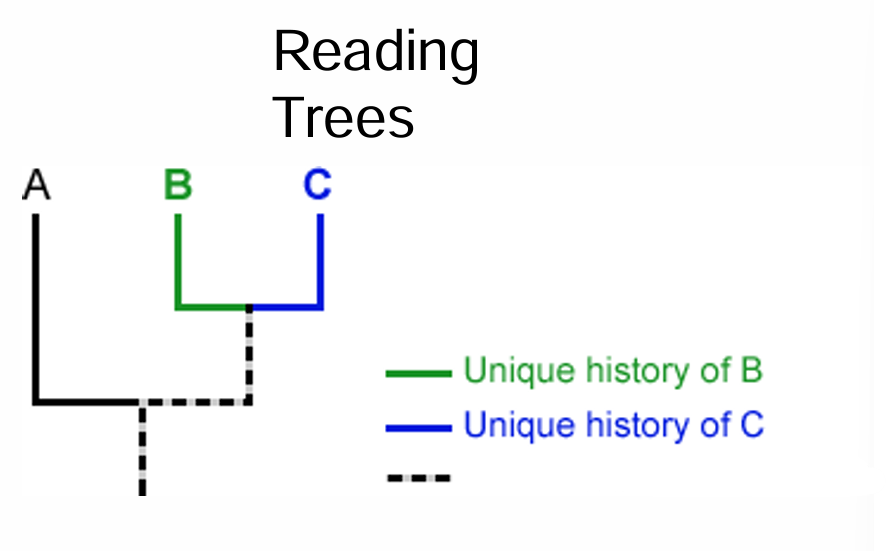
shared history of B and C
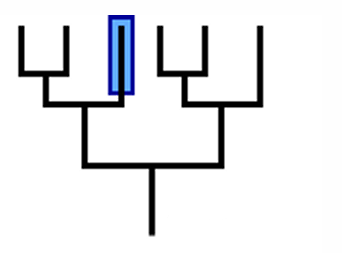
clade
determine whether a clade or not
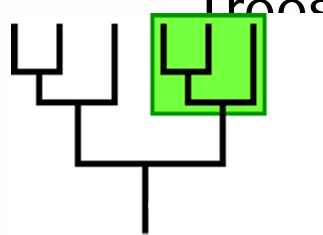
clade
determine whether a clade or not
not a clade
determine whether a clade or not
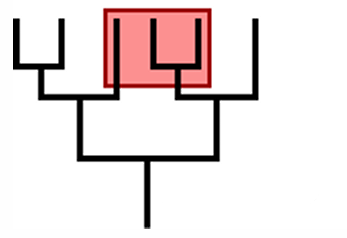
not a clade
determine whether a clade or not
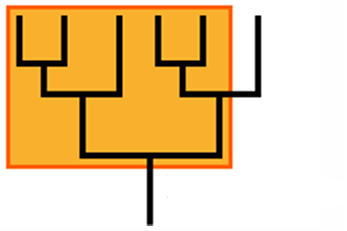
Phylogenetic pitchforks
depict historical moments when a gene pool was irrevocably split in two
lack of knowledge
Reading trees: Phylogenetic pitchforks
instances where single common ancestor would have several descendants (happens when lack of plannage)
Rapid
Reading trees: Phylogenetic pitchforks
-fast process of evolution (lack of knowledge, undocumented = pitchfork)
-cichlids fishes
evolution
-is not progressive
- doesn’t NOT ALWAYS CREATE “better traits”
-dependent on the selection of environmental pressures
ladder
reading trees, not ________
phylogenetic classification
using trees for classification example
Important Assumptions in Trees
Change in characteristics occurs in lineages over time
There is a bifurcating, or branching, pattern of lineage-splitting
Any group of organisms is related by descent from a common ancestor
Change in characteristics occurs in lineages over time
Important Assumptions in Trees
There is a bifurcating, or branching, pattern of lineage-splitting
Important Assumptions in Trees
Any group of organisms is related by descent from a common ancestor
Important Assumptions in Trees
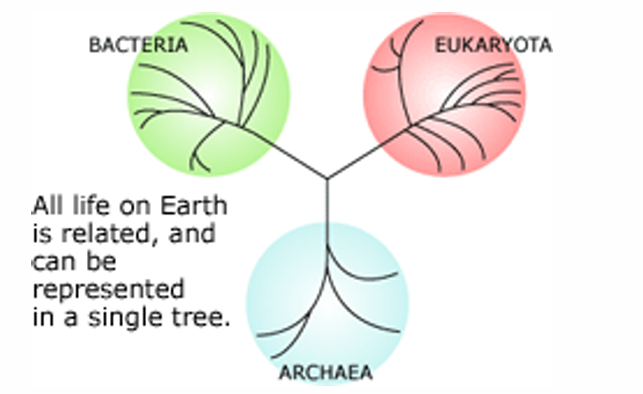
Monophyletic clades
complete sub-trees
Monophyletic clades
• Contains all descendants of a common ancestor
• Recognized through synapomorphies
• Synapomorphies are homologous traits that are present in two or more taxa (groups of organisms) but not in their common ancestor's closest relatives
synapomorphies
Monophyletic clades are recognized through _________
Synapomorphies
are homologous traits that are present in two or more taxa (groups of organisms) but not in their common ancestor's closest relatives
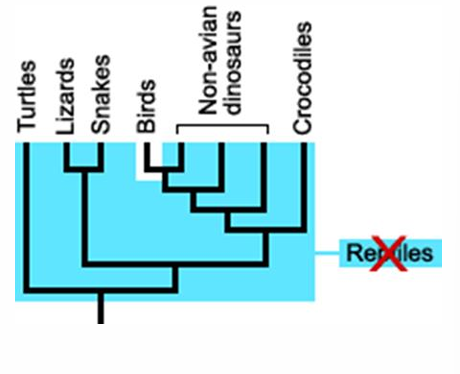
Paraphyletic clades
Pruned branches
paraphyletic group
contains a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants
shared ancestral character state
a trait that evolved in a common ancestor and is shared by multiple descendants, but not unique to a specific group
Paraphyletic clade
type of clade
Polyphyletic group
collection of organisms that are grouped together based on shared characteristics, but these characteristics are not inherited from a common ancestor
Similarities in polyphyletic groups arise through _____________, , where organisms adapt to similar environments or lifestyles independently
Parsimony principle
tells us to choose the simplest scientific explanation that fits the evidence. In terms of tree building, the best hypothesis is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary changes
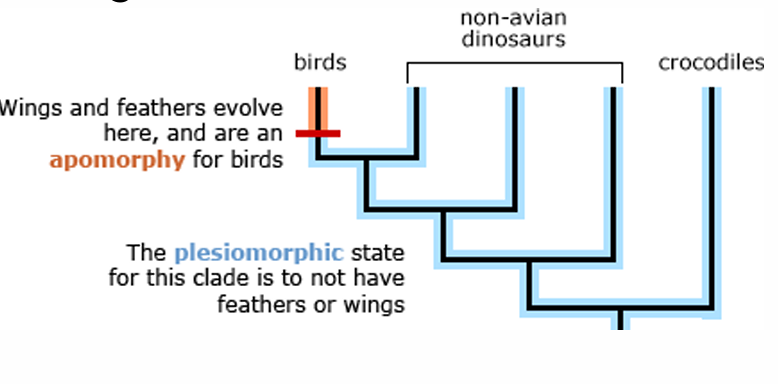
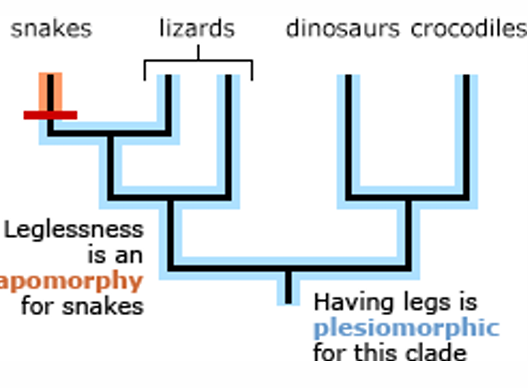
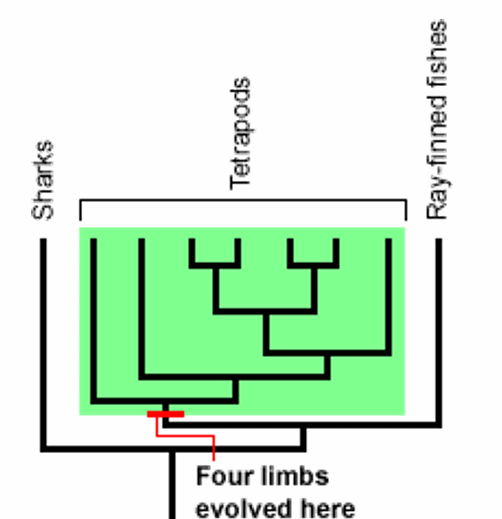
Homologous characters
Since a phylogenetic tree is a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships, we want to use characters that are reliable indicators of common ancestry to build that tree
Homologous characters
what trait is the red labeled
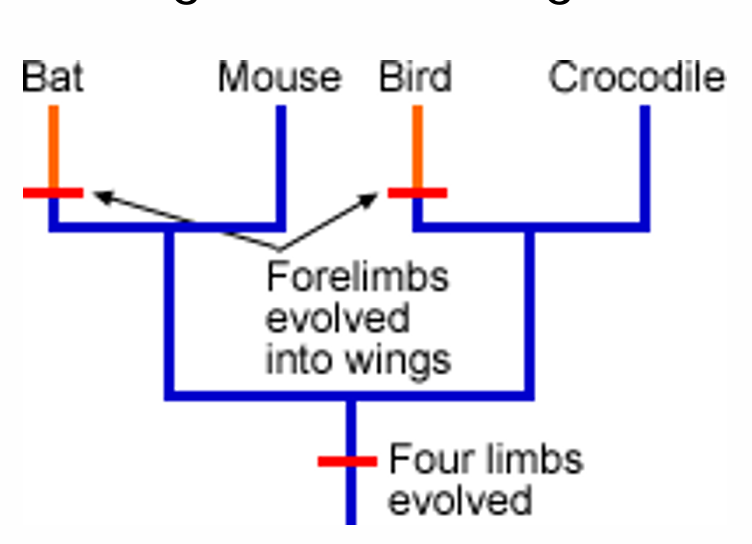
Analogies
Homologies
forelimbs evolved into wings are what trait?
How about four limbs evolved only?
using trees
to make predictions about fossils
fossils
poorly- studied
evolution
diversity
Using trees (importance):
- to make predictions about ______
- to make predictions about ____________ species: A new drug
- to learn about order of ______
- to learn about the evolution of _______: The beetles' diet