INTRO TO CLOUD COMPUTING - First Half
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What is multitenancy?
One or more instances run as guests of a physical host system, these guests are called tenants
For multitenancy that defines many tenants running on the same host
Performance issues might happen (noisy neighbors)
How does hardware virtualization work
Uses a hypervisor to create and manage VM instances to act as dedicated computers
What is a cloud API
Provided by cloud providers to provision resources automatically
What is an m5?
General purpose instance type (the m is general purpose and the 5 is the generation)
What is c5, [i3, d2], [r4, x1], [p1, g3, f1]
Compute optimized
Storage optimized
Memory optimized
Accelerated computing (GPUs)
Difference between vertical and horizontal scalability
Horizontal: adds more machines to run a server faster
Vertical: Increasing the size of an instance
Describe instance storage and persistent storage
AKA ephemeral drives
Volatile and is destroyed with the instance
For persistent you have three types:
File store - files over NFS (AWS = EFS)
Block store - such as blocks over iSCSI (AWS = EBS)
Object store - over an API - HTTP based (AWS = S3)
What is EC2
Elastic compute cloud
Web service with a basic interface for launching app instances under several different OS
What is Kubernetes
It is kinda like Docker containers, but it automates those containers’ deployment, scaling, and general management
Reduces operational complexity
What are the 5 essential characteristics of cloud computing?
1) On demand self service
2) Broad network access
3) Resource pooling
4) Rapid Elasticity
5) Measured service
Describe the four cloud deployment models
Private Cloud: Provisioned for exclusive use of a single org and can have multiple consumers that represent the business units
Community cloud: Specific community of consumers that have shared concerns (i.e. compliance stuff). Could be owned by someone in there or a third party.
Public cloud: For use by the general public - exists on premises of the cloud provider
Hybrid cloud: Two or more cloud infrastructures that remain unique entities
Define the following:
Cloud Consumer
Cloud Provider
Cloud Auditor
Cloud Broker
Cloud Carrier
Consumer - a person or org that maintains a business relationship with and uses services from a cloud provider
Provider - person or org responsible for making a service available to interested parties
Auditor - Third party to conduct independent assessments of cloud services
Broker - manages the use, performance, and delivery of cloud services
Carrier - Intermediary that provides connectivity and transport of services from cloud providers to cloud consumers
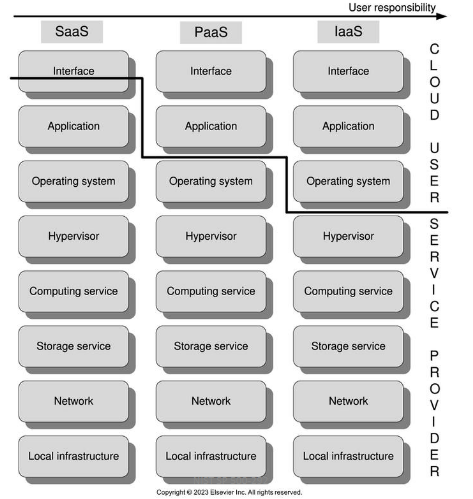
Describe the User Responsibility graph
What is the typical communication pattern for a WSC?
WSC is a Warehouse Scaled Computer
The typical pattern is to serialize the data to the protocol buffer, then execute an RPC (Remote Procedure Call) to pass the buffer to the callee, and then the caller de serializes the buffers received in response to the RPC
What is the difference between control flow and data flow
Control flow is sequential, has program counters, loads instructions into register
Data flow - operations are carried out at the time when their input becomes available, BUT they are inefficient with cache (used by network routers)
What is Mesos
Has master process that manages daemons running on all cluster nodes while other frameworks run the tasks on cluster nodes
master dishes out fair sharing of resources
Has a scheduler which receives resource offers from the master and an executor on each machine to launch the tasks
What is a node cluster in the cloud?
A node is a machine and a cluster is a group of machines. Since the cloud is distributed you want to share that job across a bunch of machines for speed, so you spin up a cluster to do this.
Your cluster will have a master node and n worker nodes
What are the two sides of cluster management
App developers - simple means to locate resources and then to control their use
Service providers - system availability, reliability, and the resource utilization
What are the four types of cluster schedulers?
Monolithic (Borg) - Big guy - uses priority and preemption, all resources
Static Partition (Dryad) - Fixed subset of resources and is scheduler dependent policy wise
Two Level (Mesos) - Dynamic resources, very strict fairness
Shared-state (Omega) - All resources, also uses priority and preemption
What is the difference between Containers and Hardware VMs
1) A Hardware VM has its own full guest OS and has higher overhead
2) A container is more lightweight BUT you share your infrastructure. You still retain your little space though
Talk about the relationship between kernel and containers/VMs
A full VM has its own kernel so you can run custom modules and all that
A container has a shared kernel so if you wanted to extend the functionality of the kernel (device drivers etc) without restarting then you cannot do that
It’s also hard since you cannot analyze the kernel for performance stuff since it is shared, and the shared makes it less secure
What is the relationship between docker and Kubernetes
Docker is easy to use - think developers
Kubernetes is by Google and is performance based
What is weird about linux and containers
Linux dgaf about what a container is, BUT you can use user-space software (i.e. Docker) to create containers.
Even if you have four containers and all of them have some process with ID of 1, then they are actually different.
Windows knows how to do this stuff, or at least has it more down
Why is Kubernetes good
Multiple containers can be created to share the same namespaces as part of a Pod
Those containers in a Pod can communicate quickly
Namespace filters that view down so that containers really only care about that smaller area
What is Amazon’s Container Service Called?
ECS (Hosts regular EC2 instances)
Describe the Kubernetes Architecture
Master - makes the global decisions about scaling and all that
API server - users and tools talk to this as like a front door
etcd - key value store that holds your cluster state
Scheduler - helps put a pod onto a certain node
Controller Manager - makes sure the desired state is actually the state (if a pod crashes then spin up a new one)
What is a Kubernetes Pod?
Groups of containers scheduled on the same host
Units for scheduling and deployment and share fate and resources such as storage volumes
This helps you avoid running multiple applications like you might in a single Docker container
Horizontal would be changing the number of nodes, and vertical would be resizing the nodes
A hardware instance is also called an ______
Infrastructure as a Service
In cloud computing, guest/tenant is another name to _________
Instance
What is a hybrid cloud?
A combo of public and private clouds
What is orchestration
Also Kubernetes. Software that manages application deployment using containers
Which lowest layer is considered user responsibility in the service model SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
S: User Specific Application Configuration
P: Application
IaaS: Operating System
What are the four deployment models in cloud and fog computing?
Private: A cloud or fog node used by a single organization
Community: Exclusive use for a specific community of consumers from organizations that have shared concerns
Public: For open use
Hybrid: Two or more of those
What is the difference between a cloud federation and a cloud provider?
Federation is essentially an environment where users in Org A can discover and invoke services in Org B
Service providers in Org B can validate credentials from Org A and make the proper access decisions
What are the two additional characteristics associated with fog computing but not with cloud computing
Predominance of wireless access
Support for mobility
List the three flavors of SIMD architectures discussed
Vector architectures
SIMD extensions for mobile and multimedia
GPUs
GPUs runs with CPUs. How are they treated? Does the OS run on a GPU?
CPU acts as a host connected with a GPU (device)
OS does not run on a GPU
What is a TPU?
Tensor Processing Unit
Not a multithreaded SIMD device and is specific for deep learning
What is SoC and what is the purpose?
System on a Chip and it is used for maximizing power efficiency
One of the desired properties of a distributed system is failure transparency. Give it a definition or description.
The concealment of faults
Software modularity may require information hiding. What is that?
The user of a module doesn’t need to know anything about the internal mechanism of the module to use it effectively
What is the difference between a client server system and a P2P system?
P2P is decentralized, dynamic, and unstructured
Supercomputers these days are more likely based on ____
A very large number of processors and cores
What is a computing grid and what is it to do with cloud computing?
A distributed system of a large number of geographically dispersed systems like an electric grid
What common procedures cause most of the WSC “tax”
RPC, serialization, deserialization, and compression
Give an example of an application that requires coarse grained parallelism
A passport application, since that unit of work is much large to process each form
Give an example of an application that requires fine grained parallelism
Matrix Multiplication since each computation is small
Dryad improves on MapReduce with ______ architecture
Data-Flow
Mesos handles fine grained parallelism with a Zookeeper that selects a ______
Master - that’s the Zookeeper’s job
In Borg, a task may be in one of three states: pending, running, and dead. What action transits the state from running to pending? What action turns dead to pending?
When you evict from running and submit from the dead
Which scheduler is considered as pessimistic in conflict resolution?
Mesos
used for fine grained for the most part
Pessimistic means it assumes conflicts will occur if multiple things compete for the same resources so it waits for a decision before offering them elsewhere
What QoS’s does Quasar try to guarantee?
Response time and execution time
Quasar is like smarter mesos almost
Clock rates of processor cores can be changed with DVFS, which stands for _________
Dynamic voltage and frequency scaling
In Heracles, memory bandwidth saturation may result in cores being removed from ____ tasks
BE
BE are low priority tasks
What are three revolutions named in the book?
Cloud Computing, DevOps, and containers
What is the devops movement
Bring software dev skills to operations
What is the difference between OS Virtualization and Hardware Virtualization
OS partitions the OS into instances (containers)
It differs from hardware because only one kernel is running
What kind of virtualization does WSL embody
Hardware
What is a pod in kubernetes
Group of containers that share a network namespace
What is a container orchestrator
Software designed to join together many different machines into a cluster
What does a Dockerfile do for a container?
Specifies what needs to go into the container image
What does port forwarding do when a container is run?
Converts a container port to a host port
Why do we need to register a Docker container?
Make it globally available
What is a hypervisor
AKA VMM and runs on the physical hardware and exports hardware level abstractions to guest OS
What is a VM
Isolated environment with access to a subset of physical resources of a system
What is a process VM
Created for individual process and destroyed once that process terminates
What is a traditional VM
One supported by a bare metal hypervisor that runs directly on the hardware
What is a hosted VM
One that runs on top of an existing OS
Some machine instruction may be nonvirtualizable, what are the two methods that a guest OS can run applications with a hypervisor
Binary translation: Hypervisor monitors the execution of guest OS and replaces nonvirtualizable instructions executed by a guest OS with other instructions
Paravirtualization: The guest OS can only use instructions that can be virtualized
VT-x provides Virtual Machine Control Structure (VMCS). Explain what and from where will be loaded by VMEntry and VMExit?
Entry - loads VMX non root from guest state in VMCS
Exit - loads VMX root from host state in VMCS
What is KVM
Kernel based Virtual Machine, virtualization infrastructure of Linux
What is QEMU and what is it doing in KVM?
Virtualizer and machine emulator. Emulates devices in KVM using dynamic binary translation
What is AMI
Amazon Machine Image
Extra copy of the original image without config dependent info like the hostname
What is the main purpose of a hypervisor
Creating VMs
What is another (older) name for a hypervisor?
Virtual Machine Manager
Why are Type 1 hypervisors also called bare metal or native ones
Executing directly on the processor
Why is KVm a Type 2 hypervisor?
This hypervisor is scheduled by the host kernel CPU scheduler and guests appear as processes on the host
Which component of KVM is eliminated in Nitro?
I/O Proxy
What is a Xen domain
VM
What is the main function function of Xen’s Dom0?
Administration and launching of new VMs/domains
How does hypercall demonstrate the para virtualization of Xen
Apps make system calls using hypercalls processed by Xen
What network communication feature is degraded by Xen guests but greatly enhanced by Xen 2.0
Send data rate
In nested virtualization, how sensitive instructions by a guest hypervisor are handled depends on the hardware support. How differently these instructions are handled with single level vs multi level/nested hardware virtualization support
Single: All traps handled by the host/bottom hypervisor
Multi-level: Each Hypervisor handles all traps caused by sensitive instructions of guest hypervisors running directly above of it
What is a VMBR? What can it support a malicious OS to do?
VM Based rootkit. Observe the data, the events, or the state of the target system (and others)
Can a virtual CPU run on more than one physical CPU at the same time?
Probably not
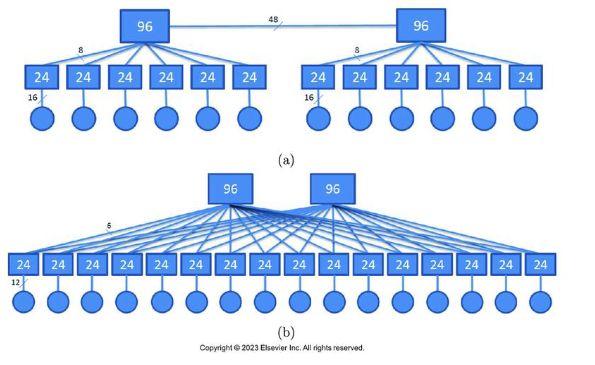
How do you find how many servers this connects for A and B
For a it is 16 × 12 because you count the servers which are the circles.
For B it is 12 × 16 for the same reasons
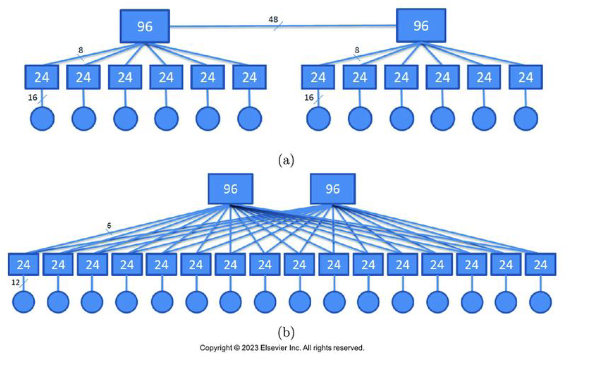
How many switches does each use?
For A it is 12 + 2 because that is the rectangles
For B it is 16 + 2 for the same reasons
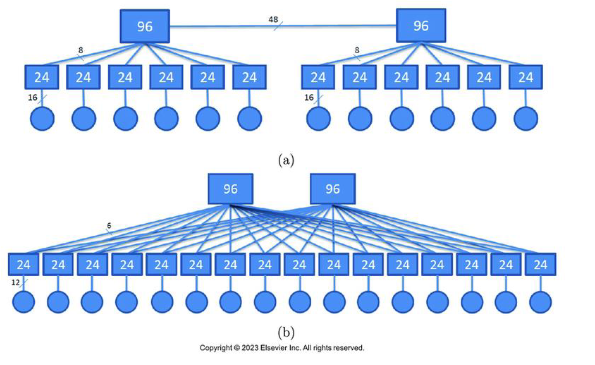
How many different path lengths a pair of servers need to go through to connect in each network
For A it is lengths (2, 4, 5), this is the circles to the big rectangles
For b it is lengths (2, 4) for the same reasons
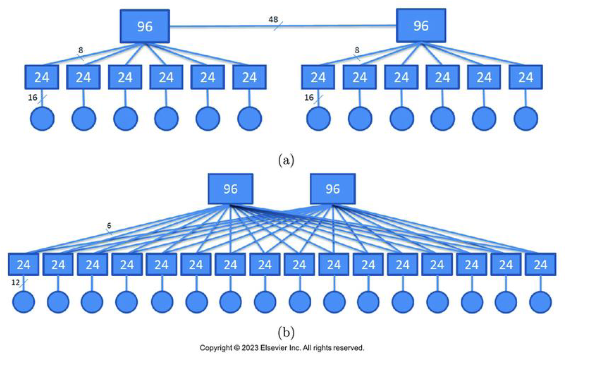
What is the total number of wires used in each network?
For A it is 24 * 12 + 48. We have 24 on the middle rectangles, 12 total servers, and you have to include the number between the two top ones
For B it is 24 * 16
NVMe may give one queue to each process or thread for read, write and other commands, thus provides high [blank] performance
I/O
GFS eliminates caching at the client site. Caching increases the overhead for maintaining what among cached copies
Consistency
The Chubby cell in GFS may consist of k replicas, one of which is elected as the master. When it receives a write request, the master propagates the request to all replicas and waits for a reply from [blank] replicas before responding
Majority
When it receives a read request does the master respond with or without consulting the replicas
WithoutG
GFS’s Chubby cell uses a version of the Paxos algorithm to elect a master among the surviving what after a loss of the current master
ReplicasT
The Paxos algorithm is a protocol for distributed what
Consensus