Biology: Unit 2 (Cell Chemistry, Structure, and Transport)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
Atom
The smallest part of a substance that cannot be broken down chemically
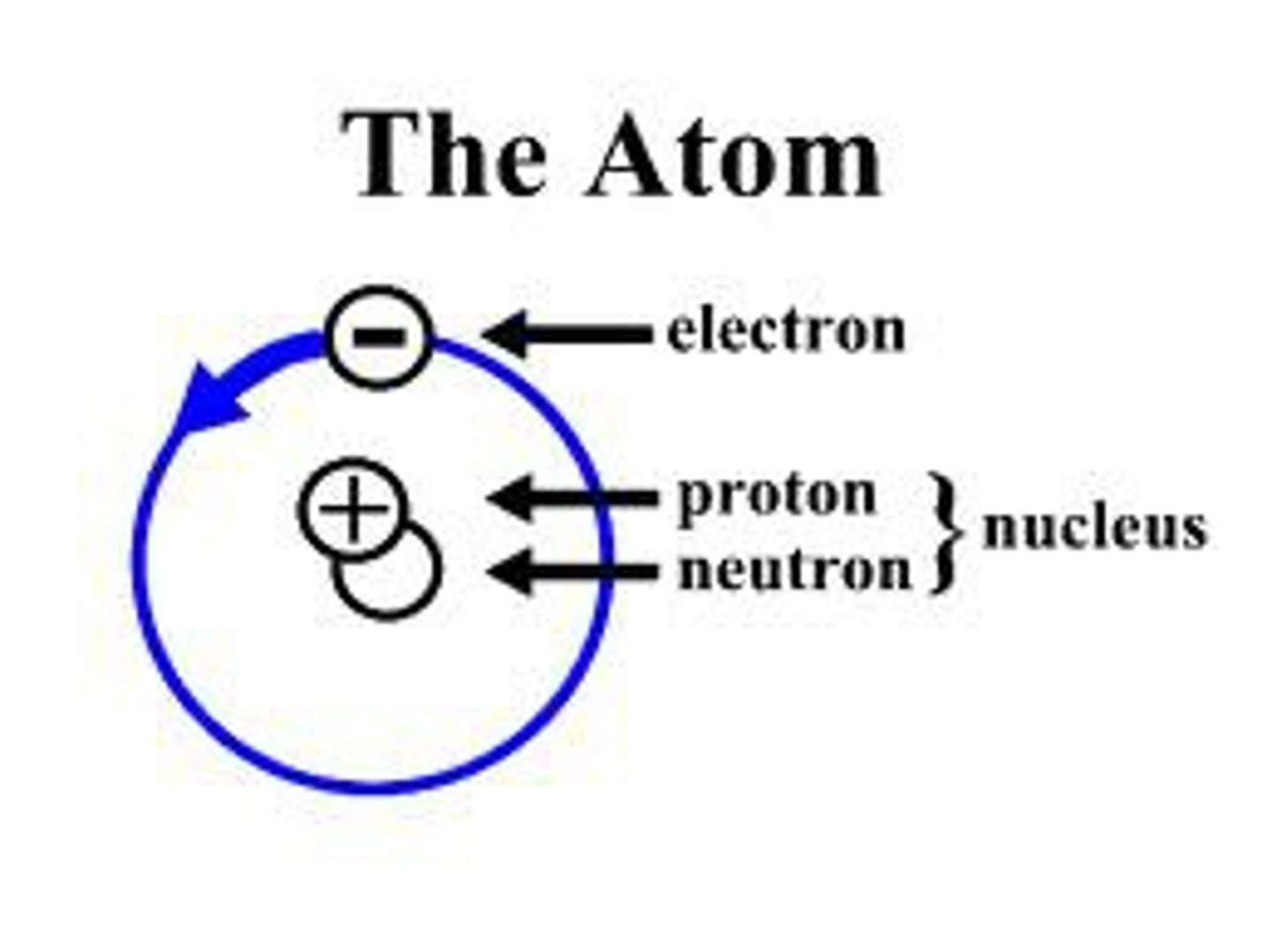
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
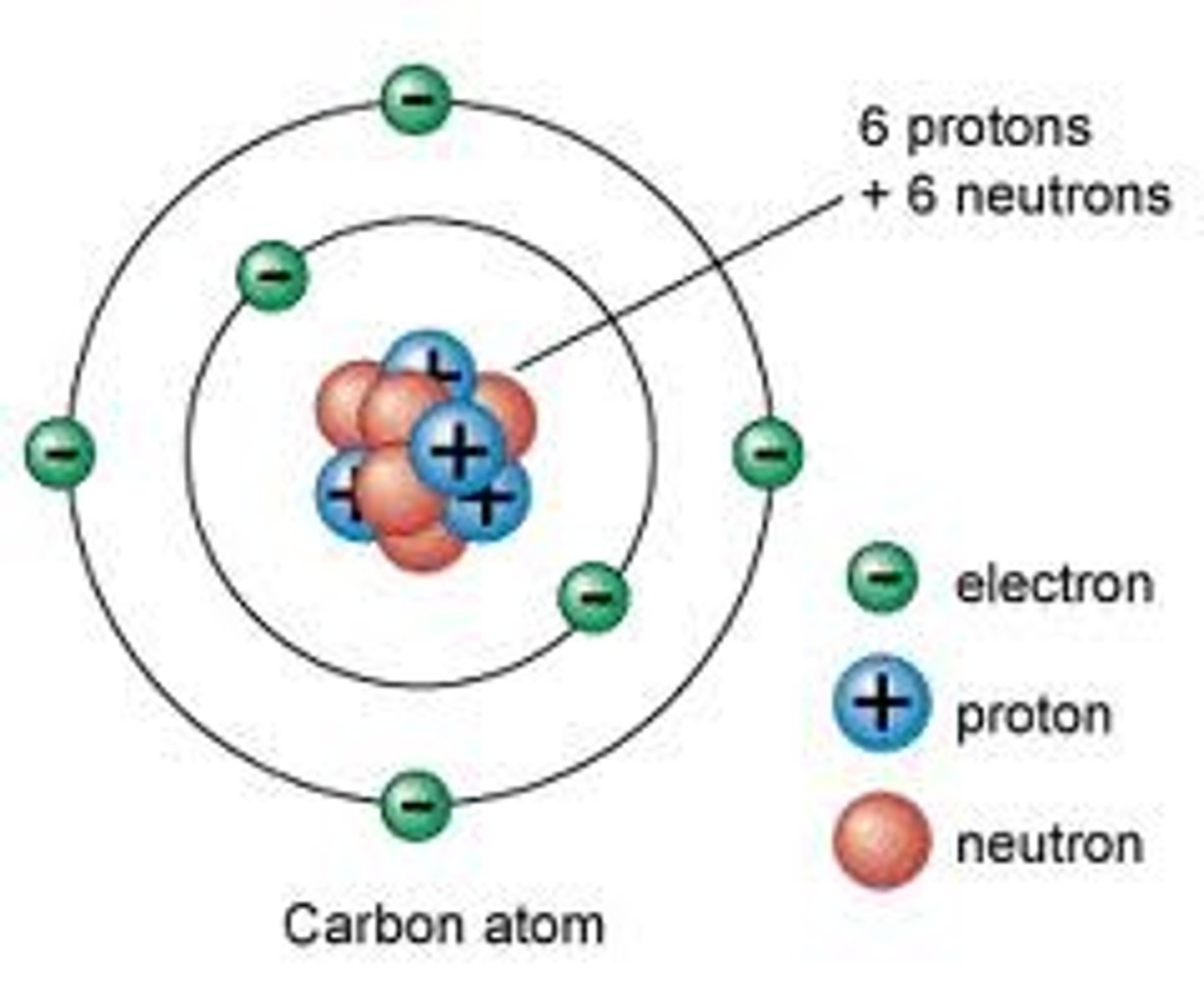
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
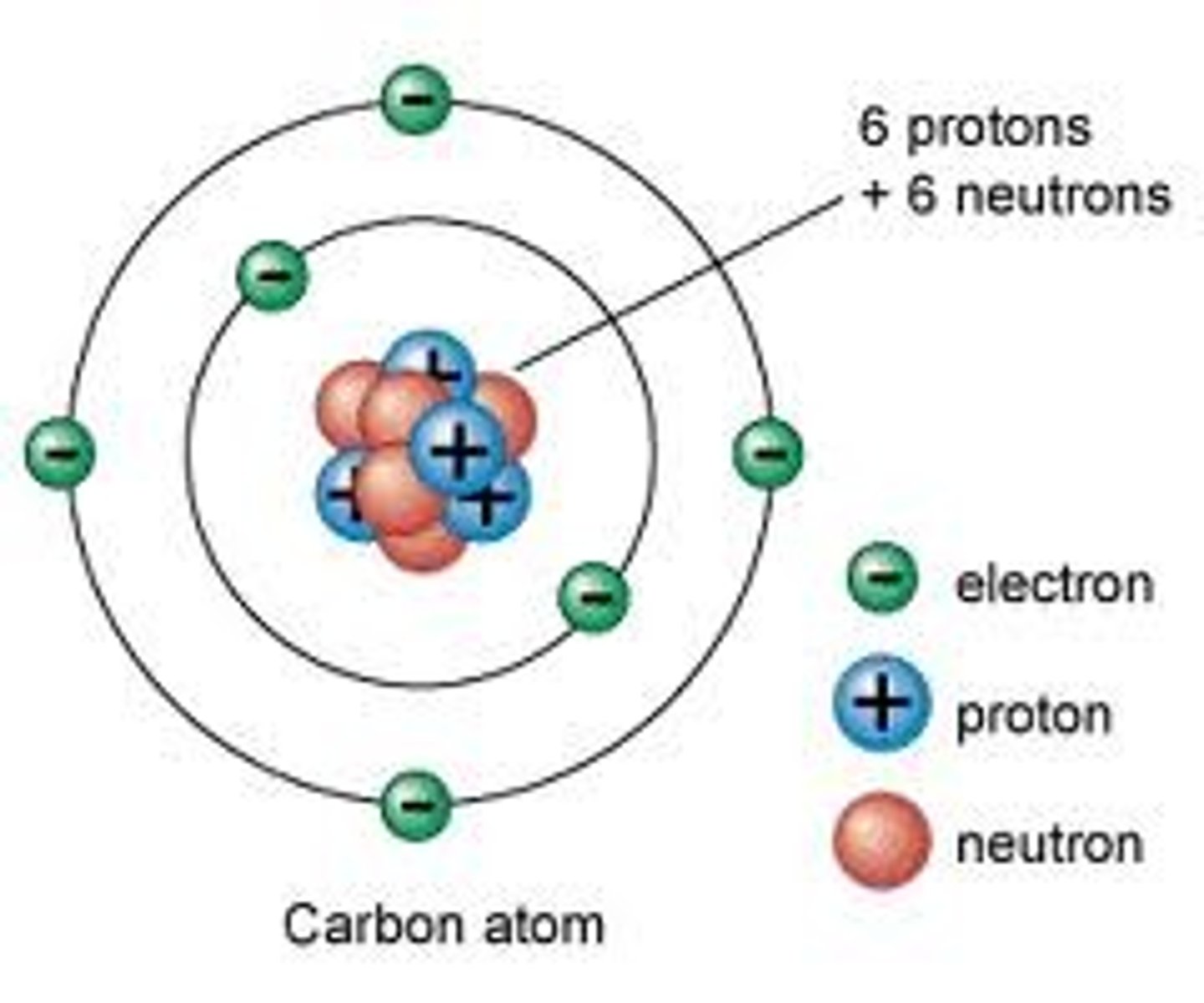
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
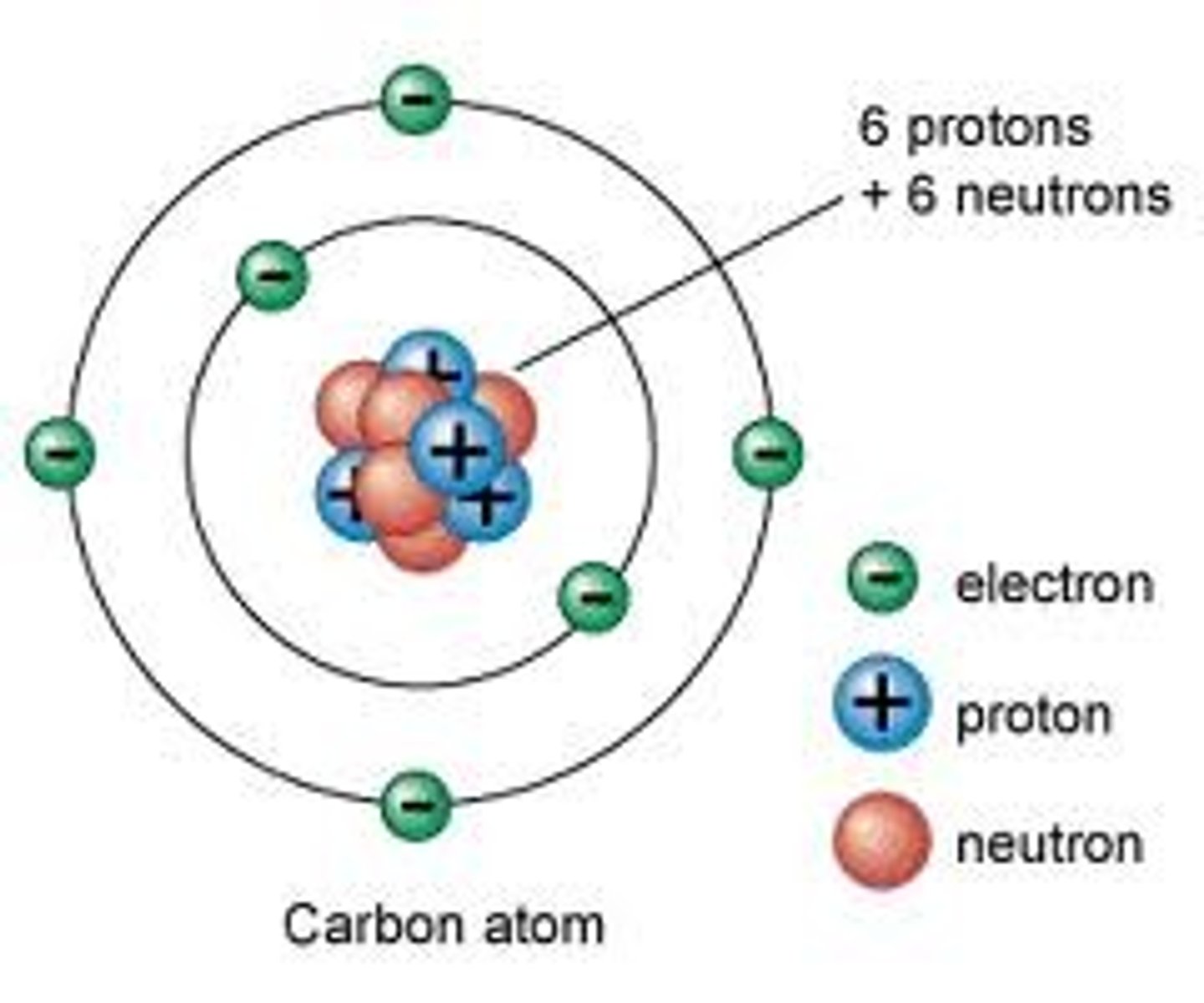
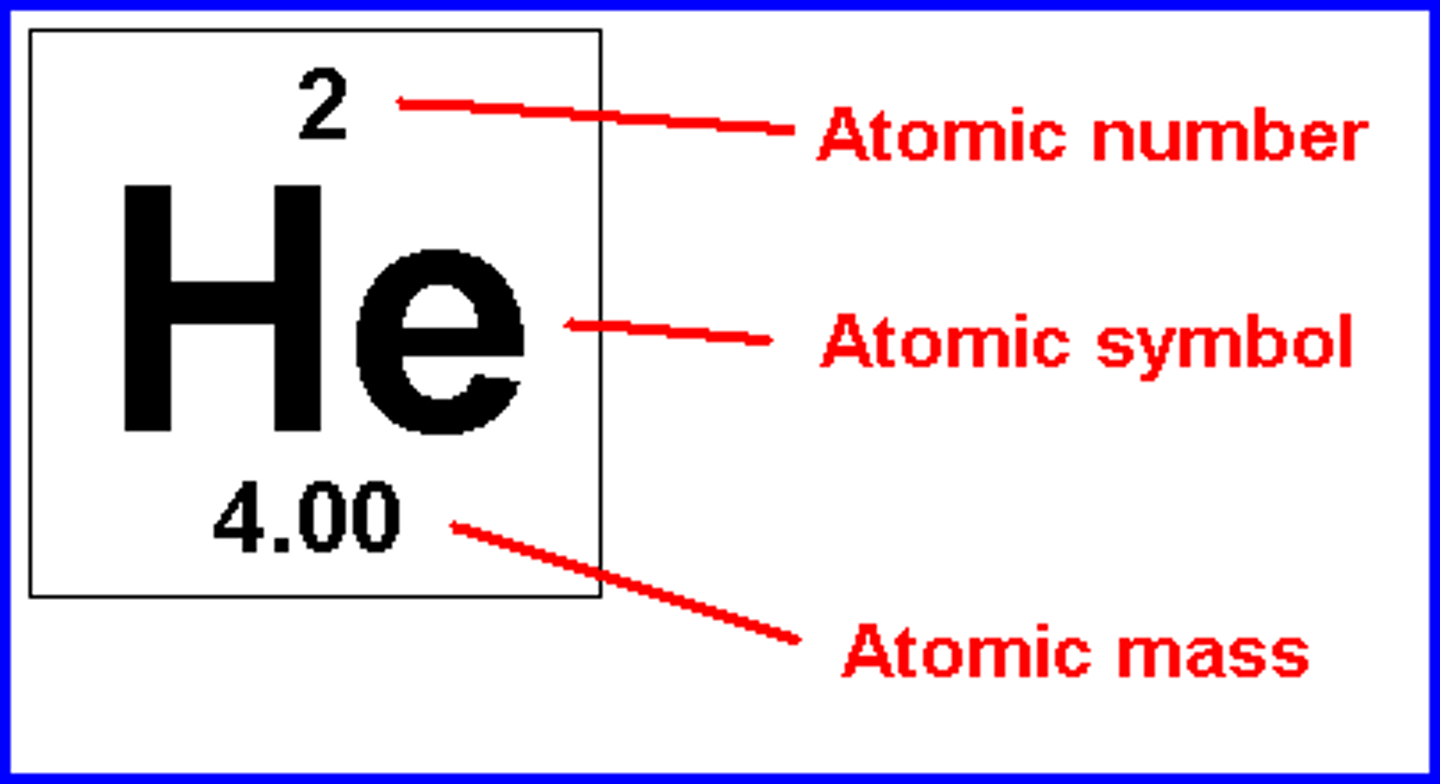
Atomic Number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
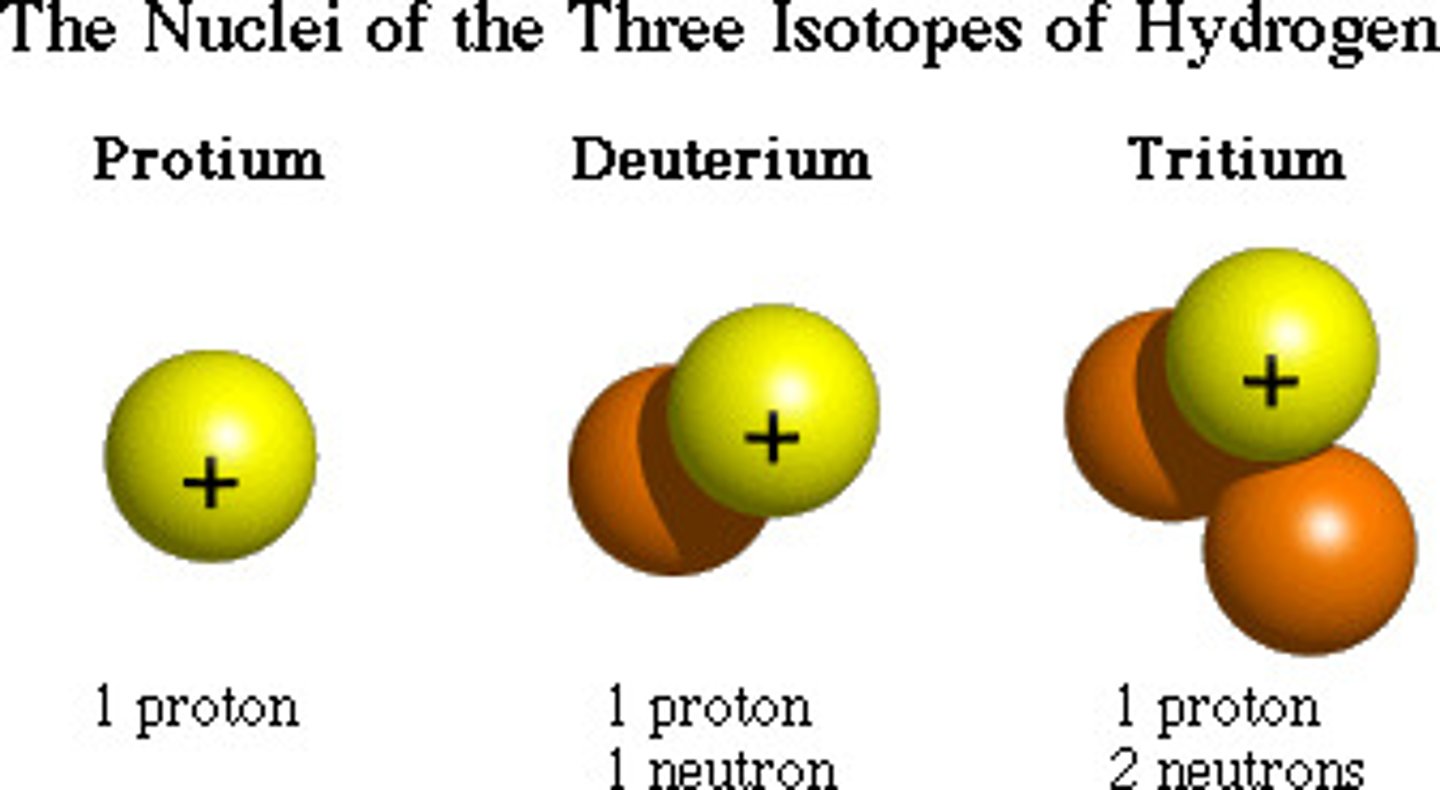
Isotope
An atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons from other atoms of the same element.
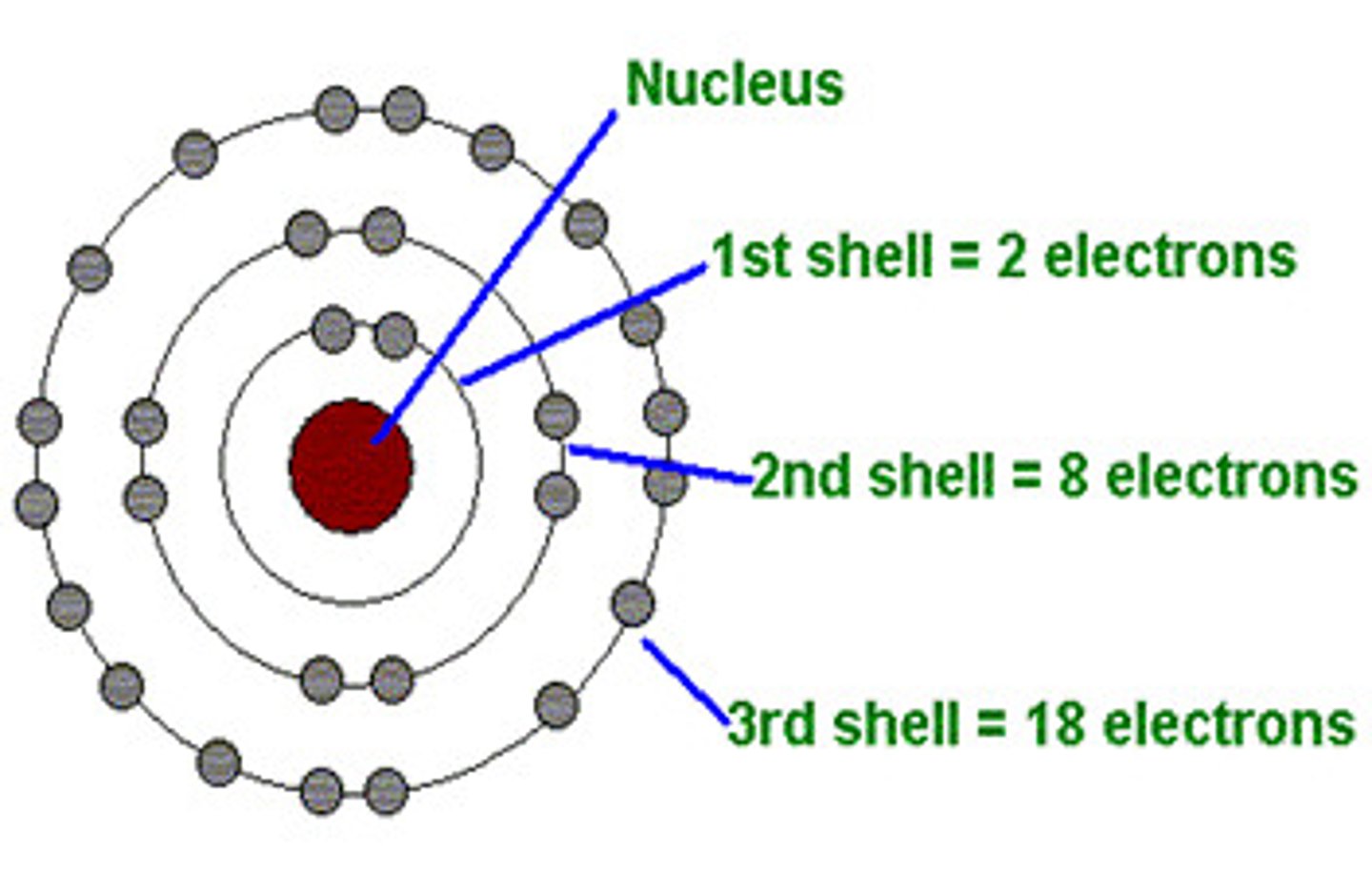
Electron Shells
Regions surrounding the atomic nucleus containing a specific number of electrons
Chemical bonds
The attractive force that holds atoms or ions together
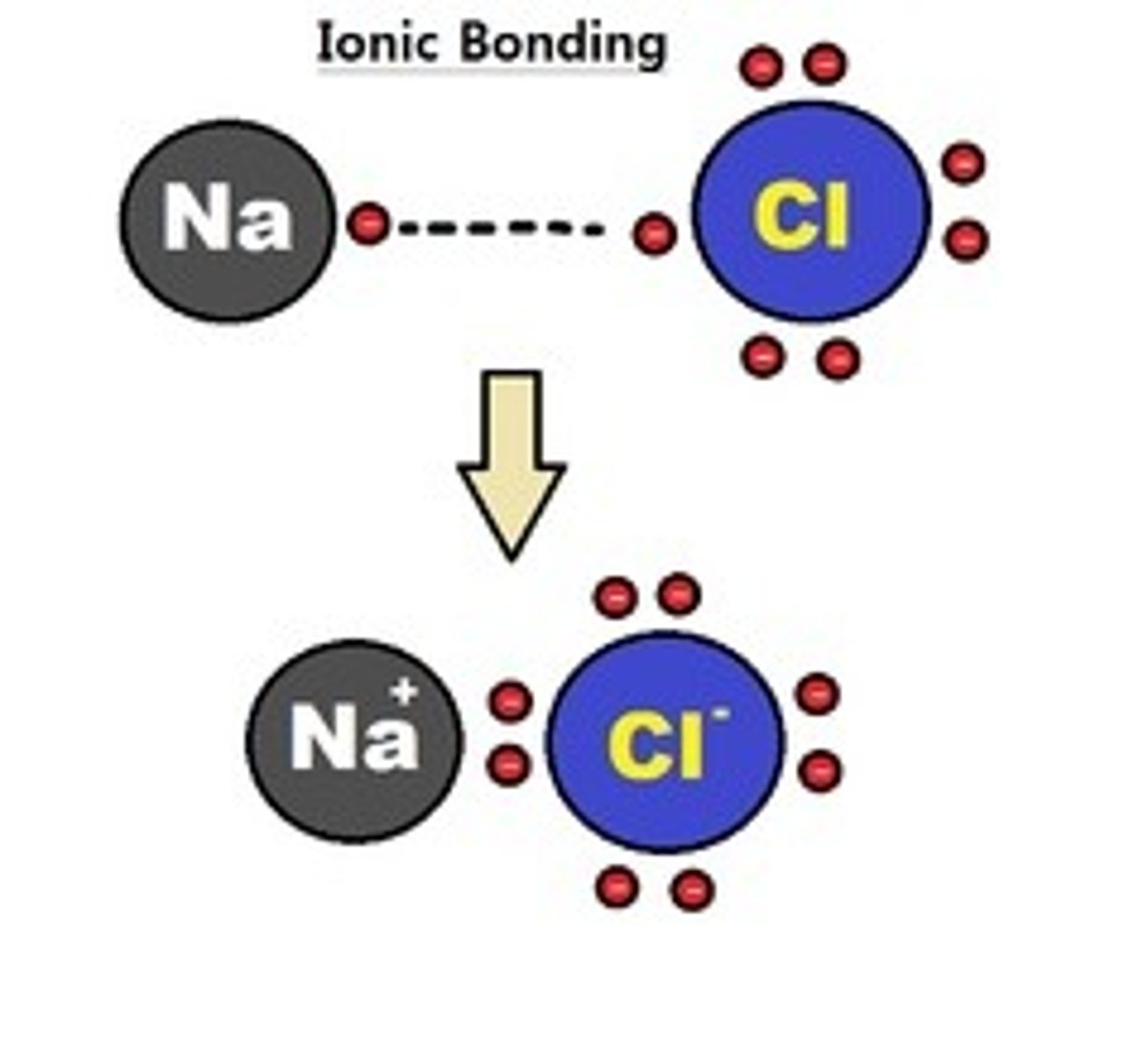
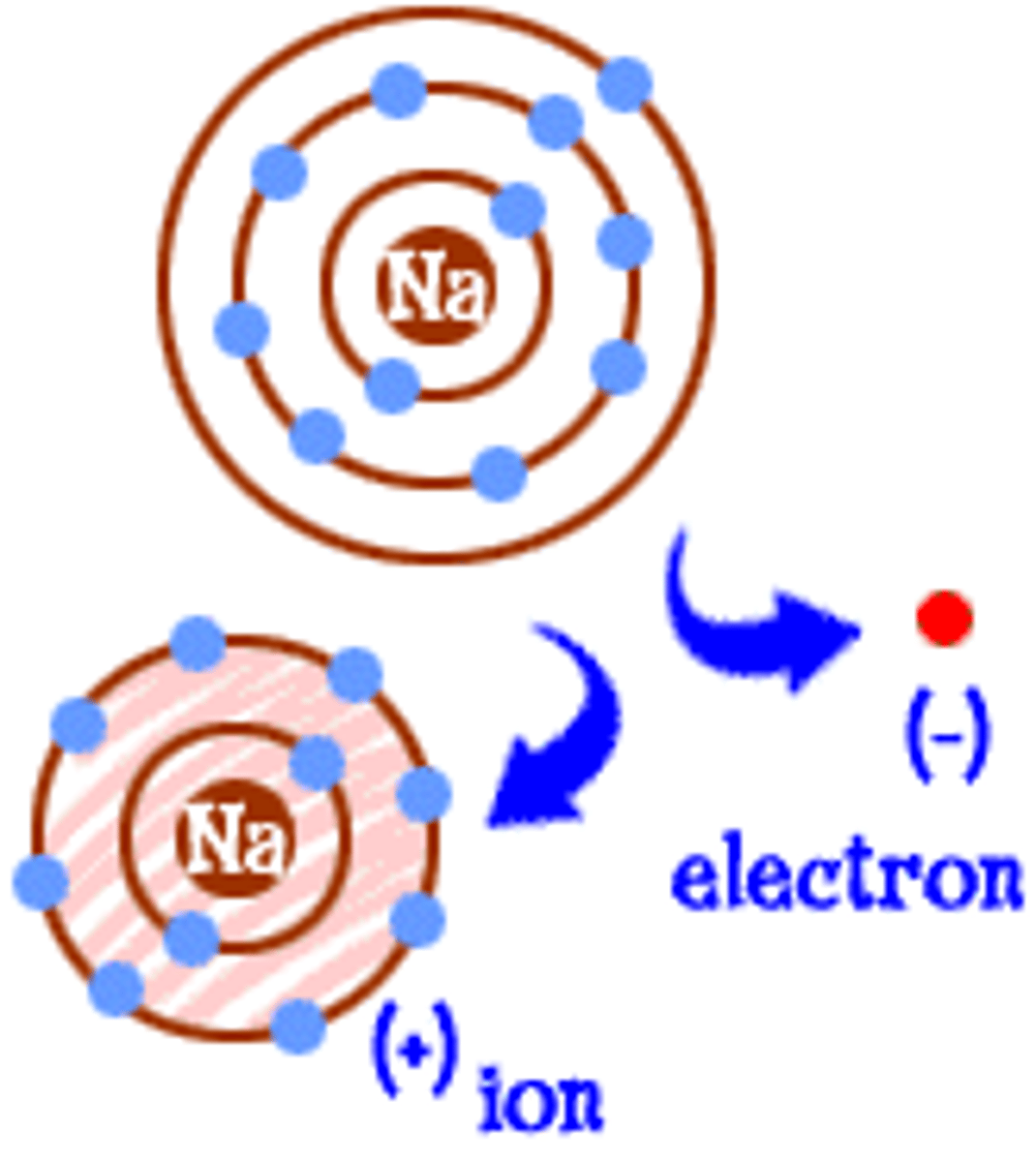
Ionic bonds
Attractions between oppositely charged atoms or groups of atoms where electrons are donated and accepted.
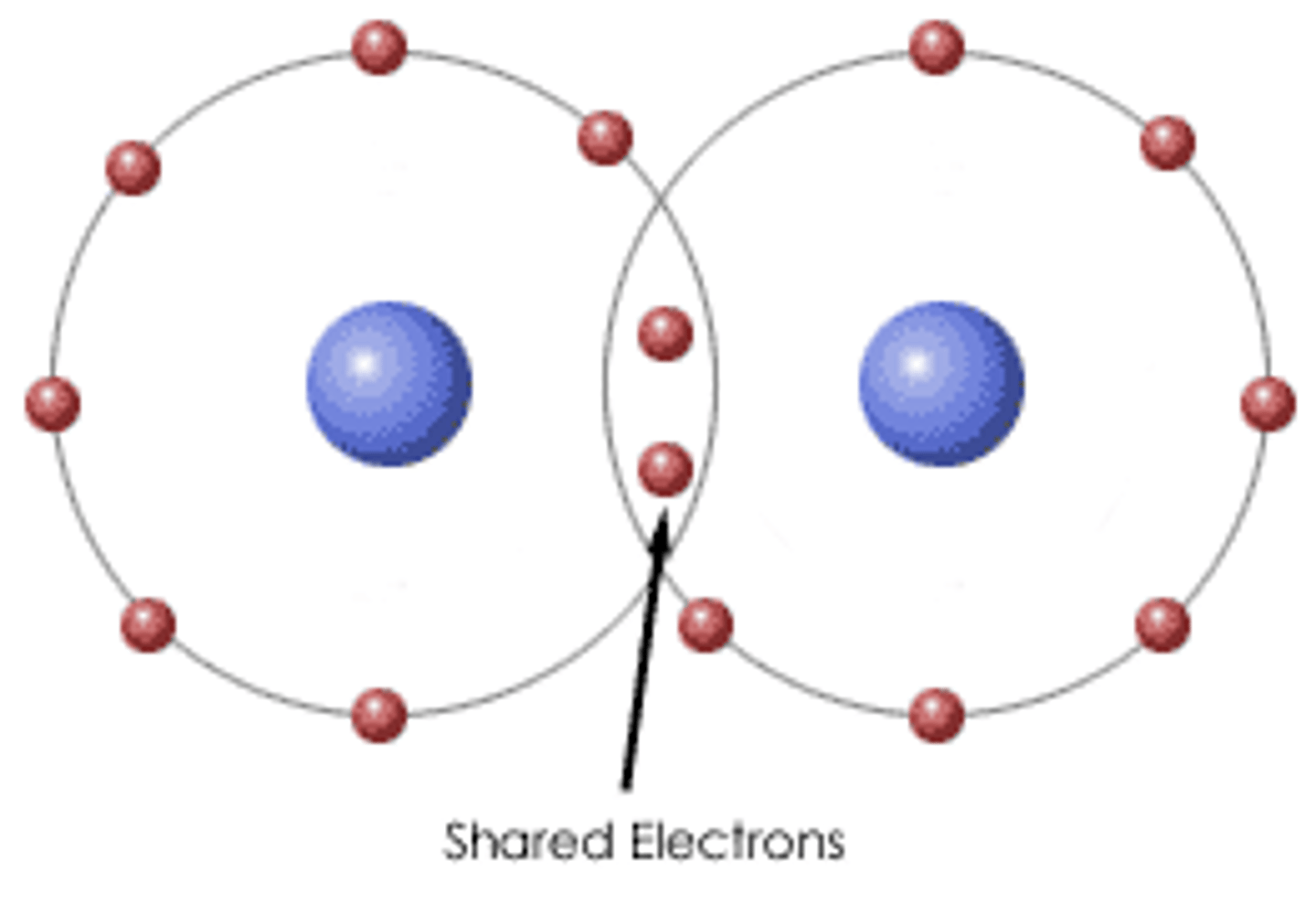
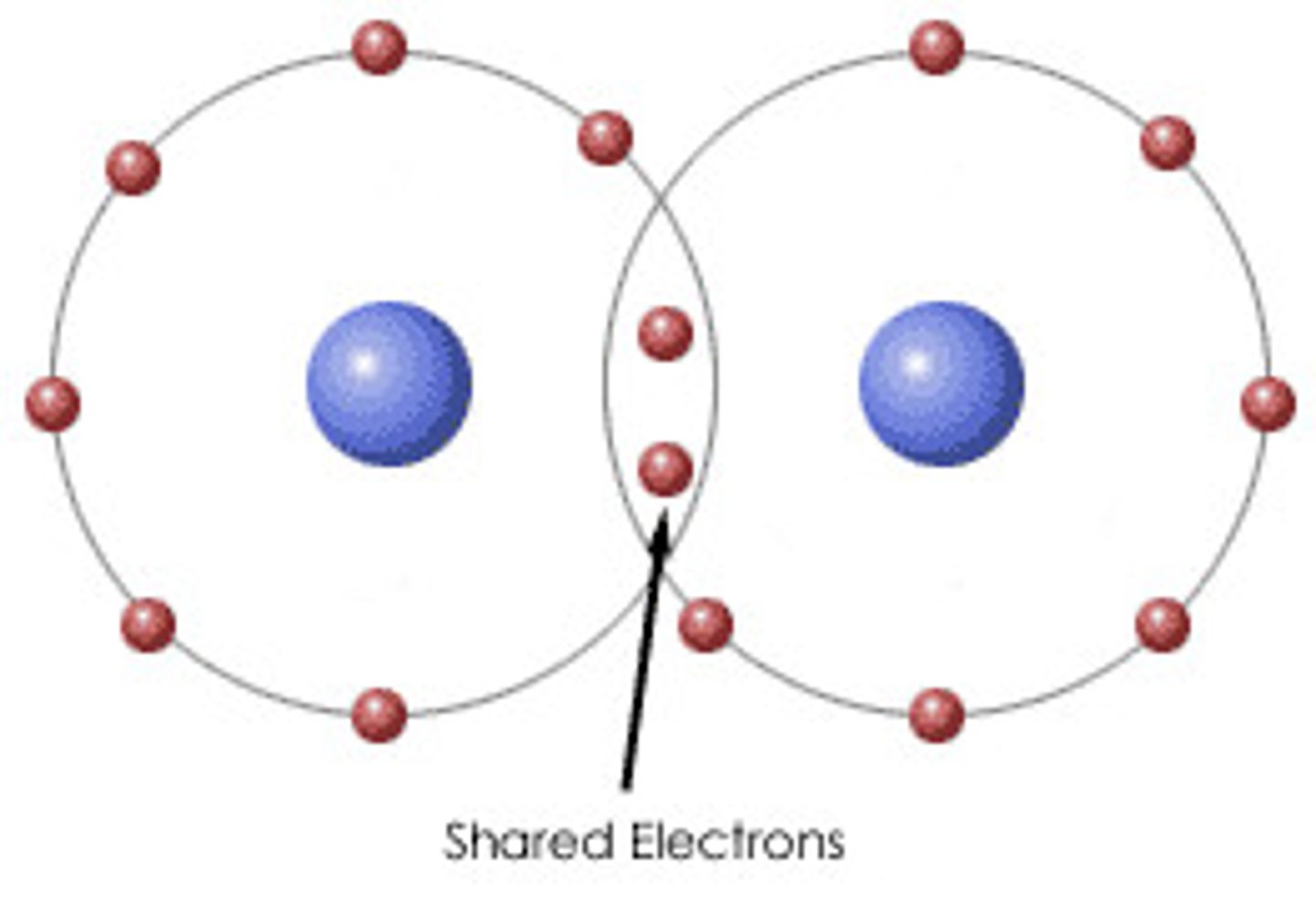
Covalent bonds
A chemical link between atoms where electron pairs are shared
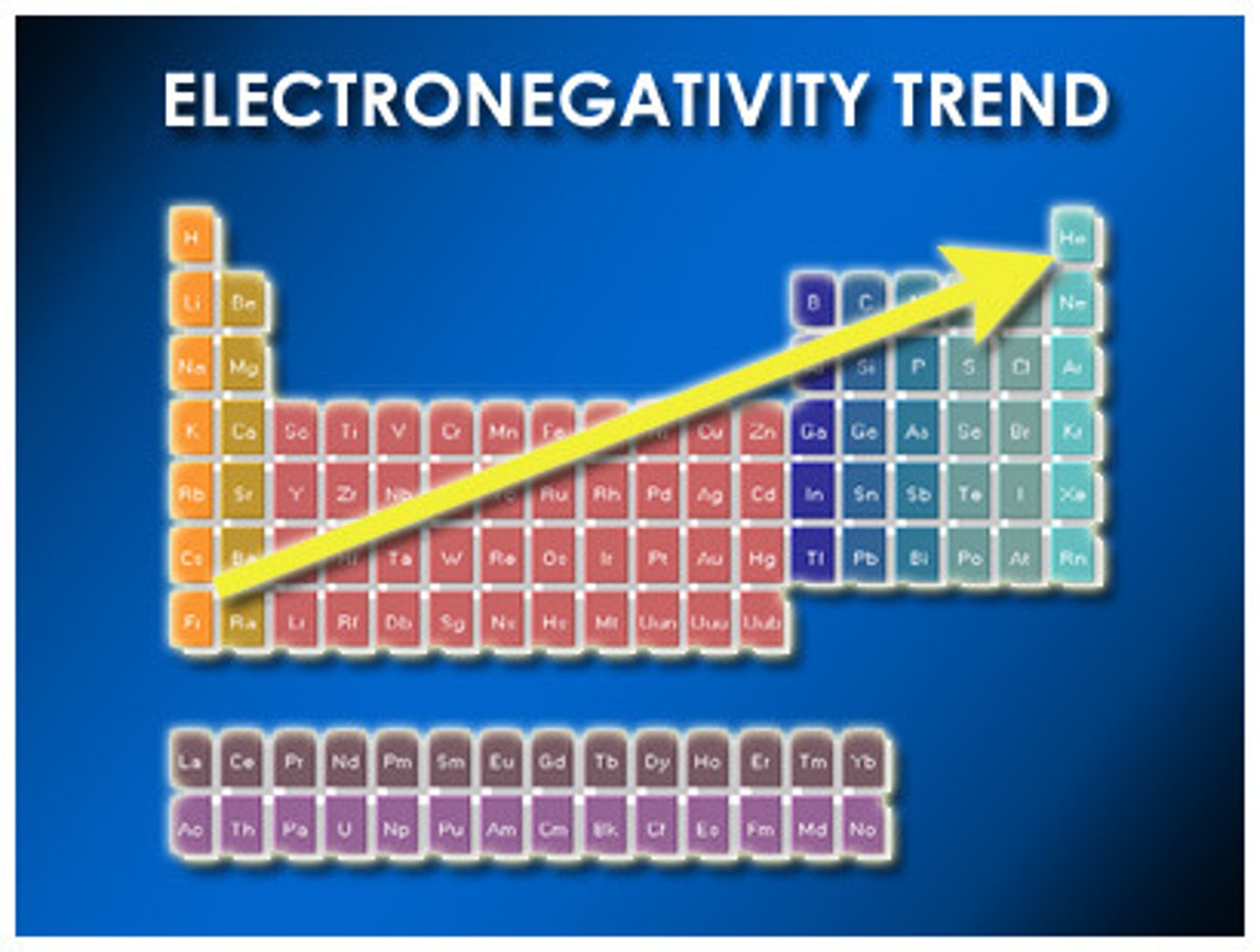
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a molecule
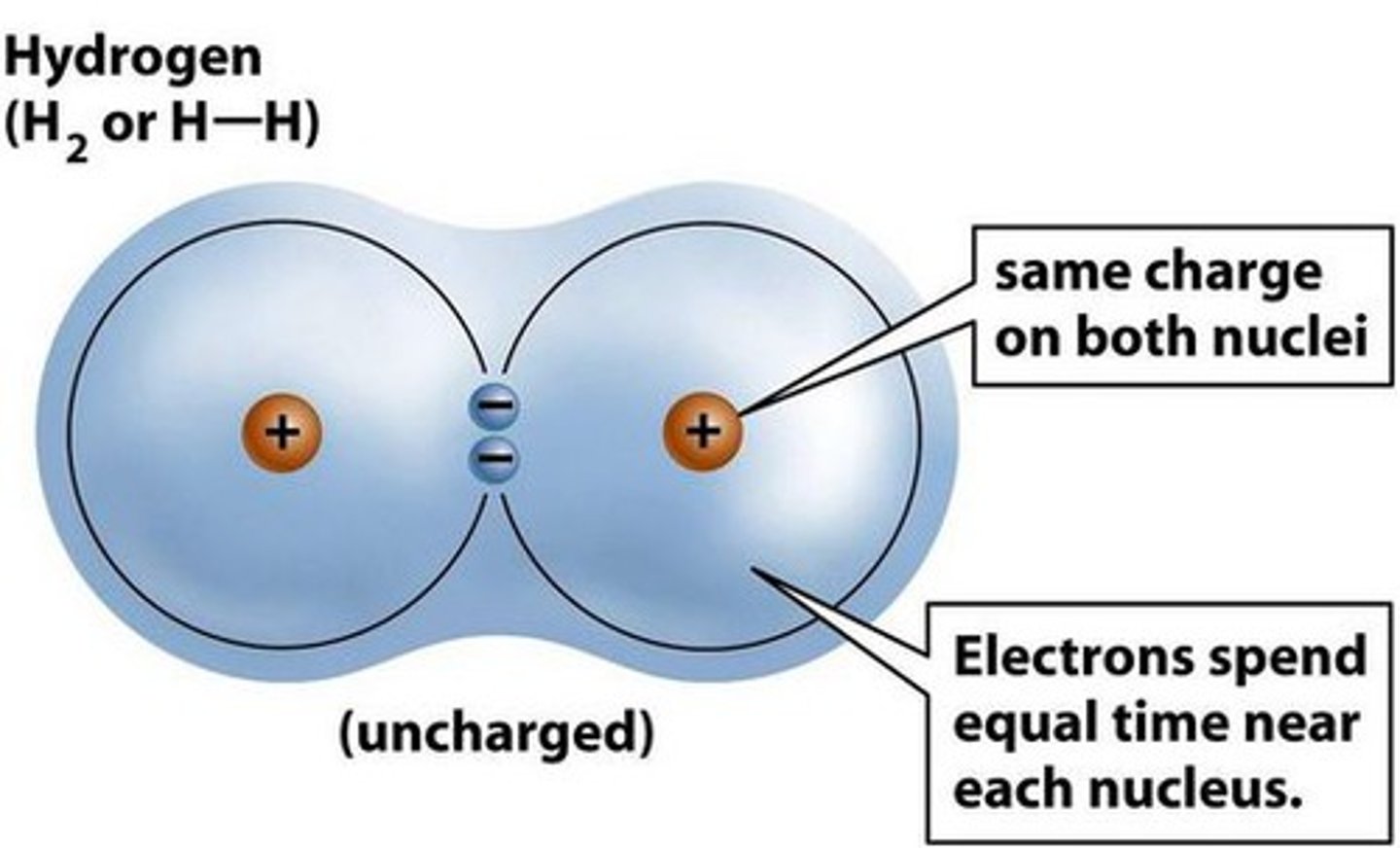
Nonpolar covalent bonds
A type of covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally between two atoms of similar electronegativity.
Polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
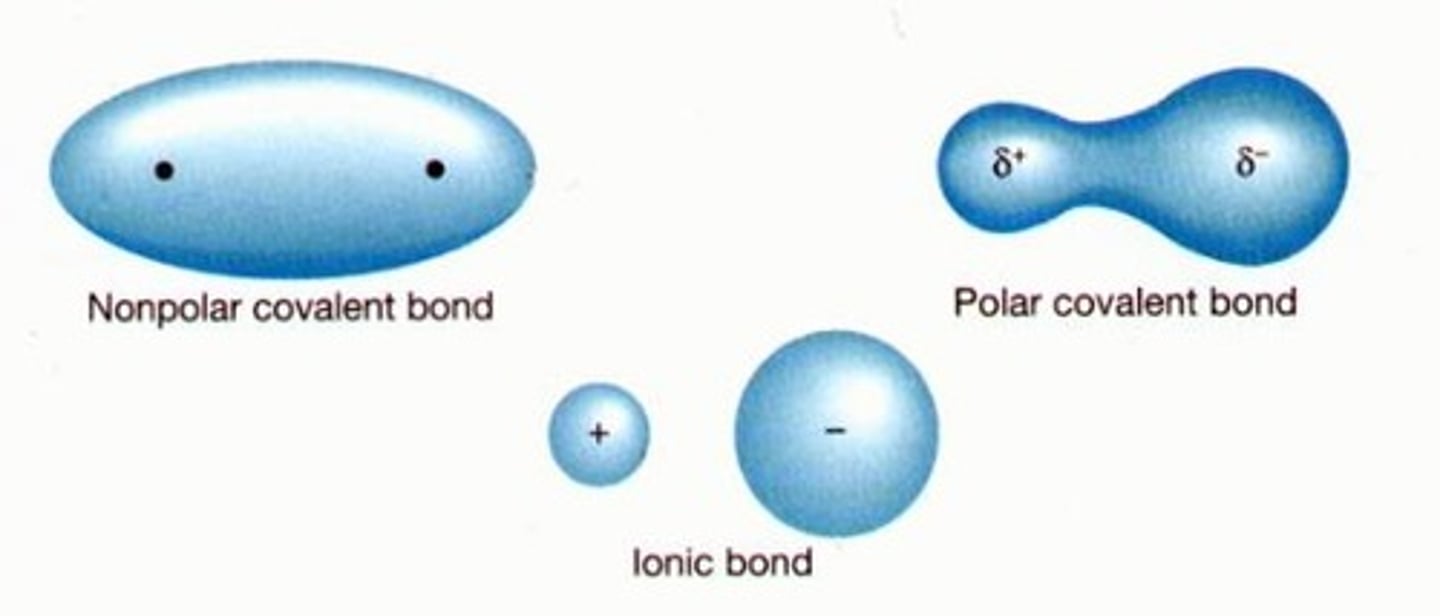
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has an electric charge
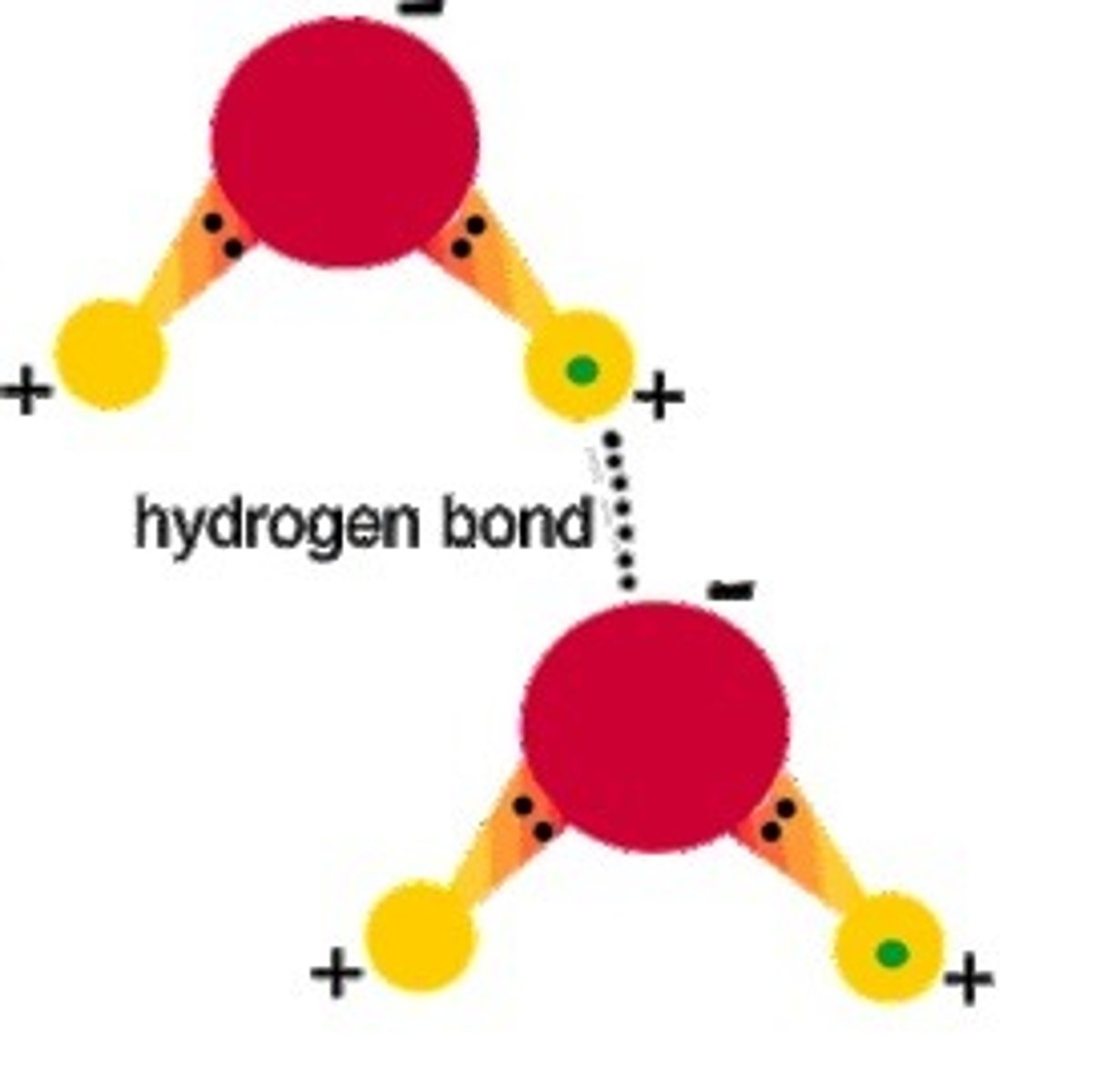
Hydrogen bond
Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
Surface tension
The property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force, due to the cohesive nature of its molecules
Solvent
The material that is able to dissolve the solute to make a solution
Acid
Any hydrogen-containing substance that is capable of donating a proton (hydrogen ion) to another substance
Base
A substance that can accept protons or donate a pair of valence electrons
Buffer
Organic substances that maintain a constant pH over a given range by neutralizing the effects of hydrogen ions
Hydrophilic
Water loving, molecules that can interact with water
Hydrophobic
Water fearing, a property of molecules that do not mix with water
Macromolecules
A very large molecule important to biological processes, ex. protein
Carbohydrates
Broken down to glucose to provide energy.
Monosaccharide
The simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built
Glucose
The main type of sugar in the blood and is the major source of energy for the body's cells
Disaccharide
A double sugar molecule made of two monosaccharides bonded together through dehydration synthesis
Polysaccharide
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
Starch
A polysaccharide or complex carbohydrate that is made up of a chain of glucose molecules joined together in covalent bonds
Glycogen
A polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in fungi and animals
Cellulose
A molecule, consisting of hundreds - and sometimes even thousands - of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, main substance in walls of plants
Lipids
Fatty, waxy, or oily compounds that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in polar solvents such as water
Fat
A large lipid molecule made from an alcohol called glycerol and three fatty acids; a triglyceride. Most fats function as energy-storage molecules.
Phospholipids
Compound lipids, consisting of phosphoric acids, nitrogen base, alcohol and fatty acids
Steroid
Any of a group of lipids (fats) that have a certain chemical structure
Saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids without double bonds in their hydrocarbon chain
Unsaturated fatty acids
A fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain
Trans fatty acid
unsaturated fats with trans double bonds instead of cis bonds
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
Amino acid
Building blocks of protein
Polypeptide
A continuous, unbranched chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
DNA
The molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages
Nucleotide
A molecule that is the basic building block of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA
Prokaryotic
An organism whose cells do not have an enclosed nucleus, such as bacteria.
Eukaryotic
Cell with a nucleus (surrounded by its own membrane) and other internal organelles.
Ribosomes
Tiny spherical organelles that make proteins by joining amino acids together
Cytoplasm
The gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell
Organelles
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
Nucleus
The structure in a cell that contains the chromosomes
Nuclear envelope
A double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
Lysosome
An organelle containing digestive enzymes
Vacuole
Storage areas for cells and important cell parts
Peroxisomes
Small, membrane-enclosed organelles that contain enzymes involved in a variety of metabolic reactions, including several aspects of energy metabolism
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
Chloroplast
Organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Centrosomes
An organelle near the nucleus of a cell that contains the centrioles (in animal cells) and from which the spindle fibers develop in cell division.
Cilia
Small, slender, hair-like structures present on the surface of all mammalian cells
Flagella
Whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
Cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
Selective permeability
Condition or quality of allowing some, but not all, materials to cross a barrier or membrane
Concentration gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance.
Passive transport
The process of transporting molecules from one side of the membrane to the other without any energy requirements
Diffusion
The net movement of molecules from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration
Osmosis
Movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules
Isotonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell
Hypertonic
Any external solution that has a high solute concentration and low water concentration compared to body fluids
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration of solute compared to the cell
Facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
Active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
Endocytosis
The process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle
Pinocytosis
A process by which the cell takes in the fluids along with dissolved small molecules
Phagcytosis
Process by which certain living cells called phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
A form of endocytosis in which receptor proteins on the cell surface are used to capture a specific target molecule
Exocytosis
A process that occurs when a cell moves large materials from inside the cell to the outside of the cell using small spheres of membrane called vesicles