ANAT3001 - Cartilage and Bone & Skeleton
1/245
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
246 Terms
Cartilage
A connective tissue that is more flexible than bone and that protects the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together.
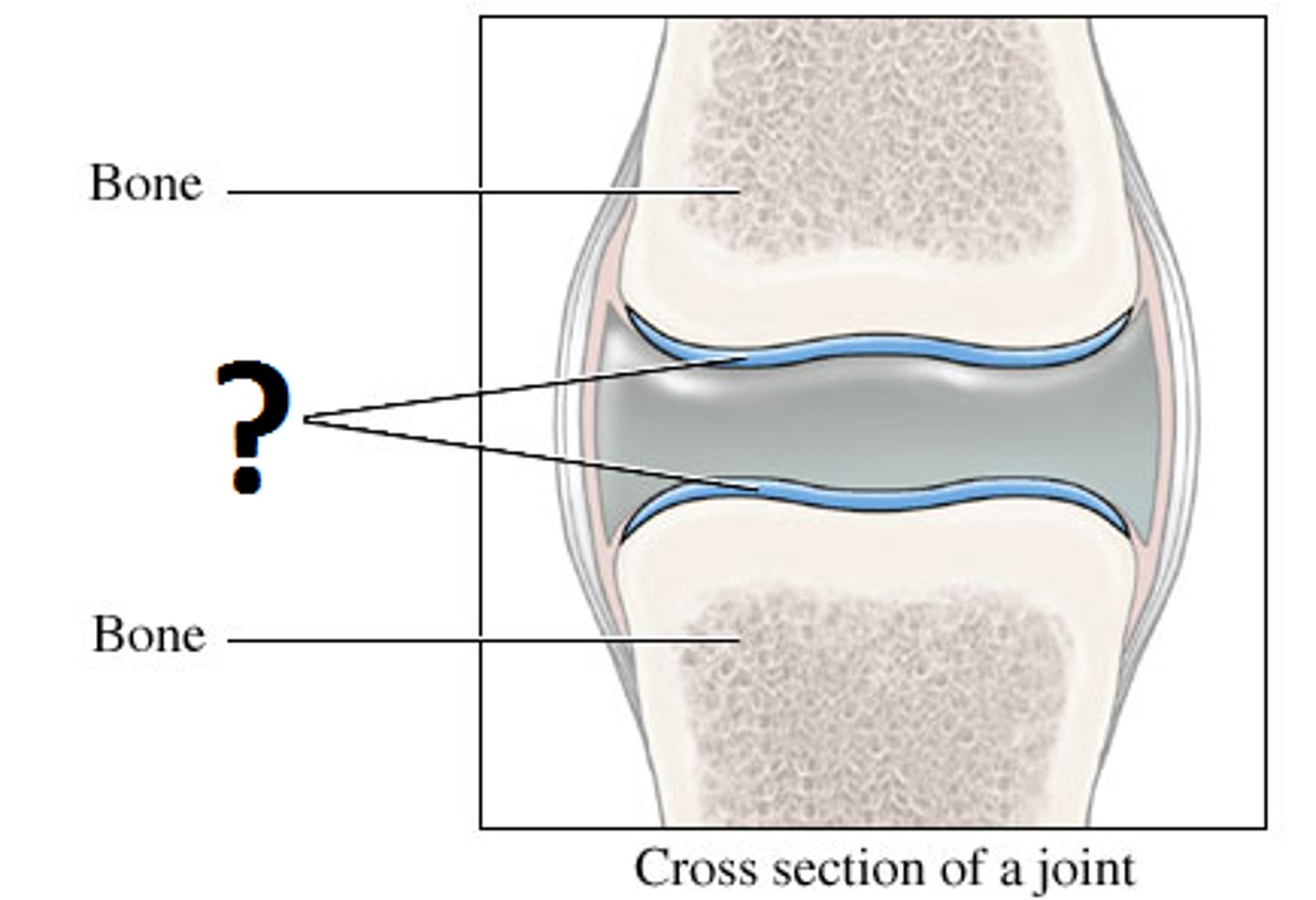
Functions oF Cartilage
1. Support and protect soft tissue.
2. Cover ends of bones at joints.
3. Provide a model for bone formation.
Characteristics of Cartilage
Perichondrium - connective tissues that surround cartilage, provides nutritional support, and protects and regenerates cartilage.
Primary cells are chondrocytes which are found in a space called a lacunae.
Has an extracellular matrix. Collagen fibers resist tension. Has ground substance with watery-gel-like consistency which helps to resist compression.
It is avascular and lacks innervation. Receives nutrients via diffusion. Movement helps nutrients diffuse through the ground substance.
Hyaline (Type II Collagen)
Most abundant type of cartilage. Found in the trachea, nose, and ends of joints.
Contains few collagen fibers (these fibers are not present on micrographs).
Provides. model for the formation of the fetal skeleton.
Provides cushioning between joints.
Elastic (Type III Collagen)
Least common. Contains branched elastic fibers. Elastic fibers are highly flexible and provide elasticity. Found in ear and epiglottis.
Fibrocartilage (Type I Collagen)
Found between slightly mobile bones, such as the pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs.
Provides a cushion between the bones of the knee joint (menisci of the knee).
Resists stretching and compression.
Contain abundant collagen fibers with chondrocytes arranged in parallel.
Bone Functions
1. Support and protection of soft tissue (ex. skull and rib cage).
2. Movement - Muscles anchor onto bone and shorten to produce movement at joints.
3. Energy Metabolism - Some bone cells help regulate blood sugar and fat storage through hormone secretion.
4. Mineral Storage - Holds reserves of calcium and phosphate.
5. Blood Cell Formation (Hematopoiesis) and Energy Storage - Functions that occur in the different types of marrow within bones.
Characteristics of Bone
Made up of cells and extracellular matrix.
Extracellular matrix has both mineralized and organic components.
Hydroxyapatite provides hardness and rigidity to resist compression and organic component
Ground substance and collagen fibers provides flexibility to resist tension.
Cells include osteoblasts (bone forming cells), osteocytes (mature one maintaining cells), and osteoclasts (bone destroying cells).
Flexible and dynamic organics; vascular and innervated; have the capacity to grow, develop, heal and regenerate.
Long Bones
Longer than they are wide.
Humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, fibula, metacarpals, metatarsals & phalanges.
Short Bones
Approximately cube shaped.
Carpals (wrist bones) and tarsals (ankle bones).
Flat Bones
Generally flat and thin.
Neurocranial bones, scapula, and sternum.
Irregular Bones
Have unusual shapes that don't fit into other categories.
Vertebrae, os coxae (hip bones), and facial bones.
Sesamoid Bones
Found within muscle tendons (e.g., patella).
Diaphysis
Shaft of the long bone.
Epiphysis
Ends of the long bones, form joints with other bones. Contains spongy bone.
Medullary Cavity
Space within the shaft of only long bones that contains bone marrow.
Epiphyseal Line
Internal line separating the diaphysis and epiphyses, remnant of the growth plate.
Periosteum
Connective tissue that lines the outside of bone (does not cover epiphyses which are lined by articular cartilage).
Endosteum
Connective tissue that lines the inside of bone including the medullary cavity and central canals.
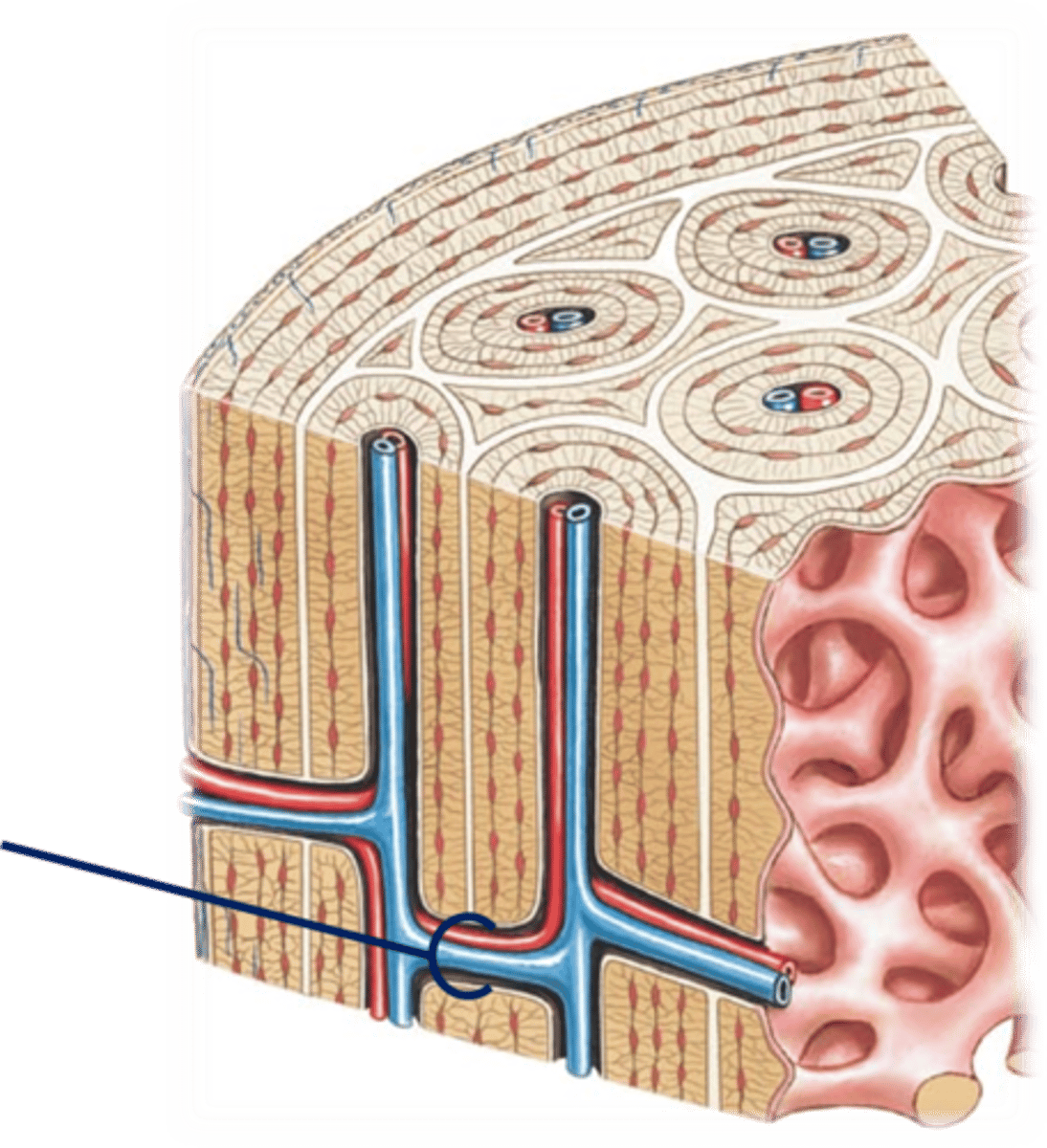
Compact Bone
Also known as dense or cortical bone, forms the outer surface of bones and is composed of rings of bone surrounding a central Haversian canal.
The canal allows for the passage of nerves and blood vessels through the bone.
Each canal and surrounding ring is called a Haversian system or osteon. These run parallel to and along the entire length of the bone.
Haversian (Central) Canal
Opening through the core of the osteon.
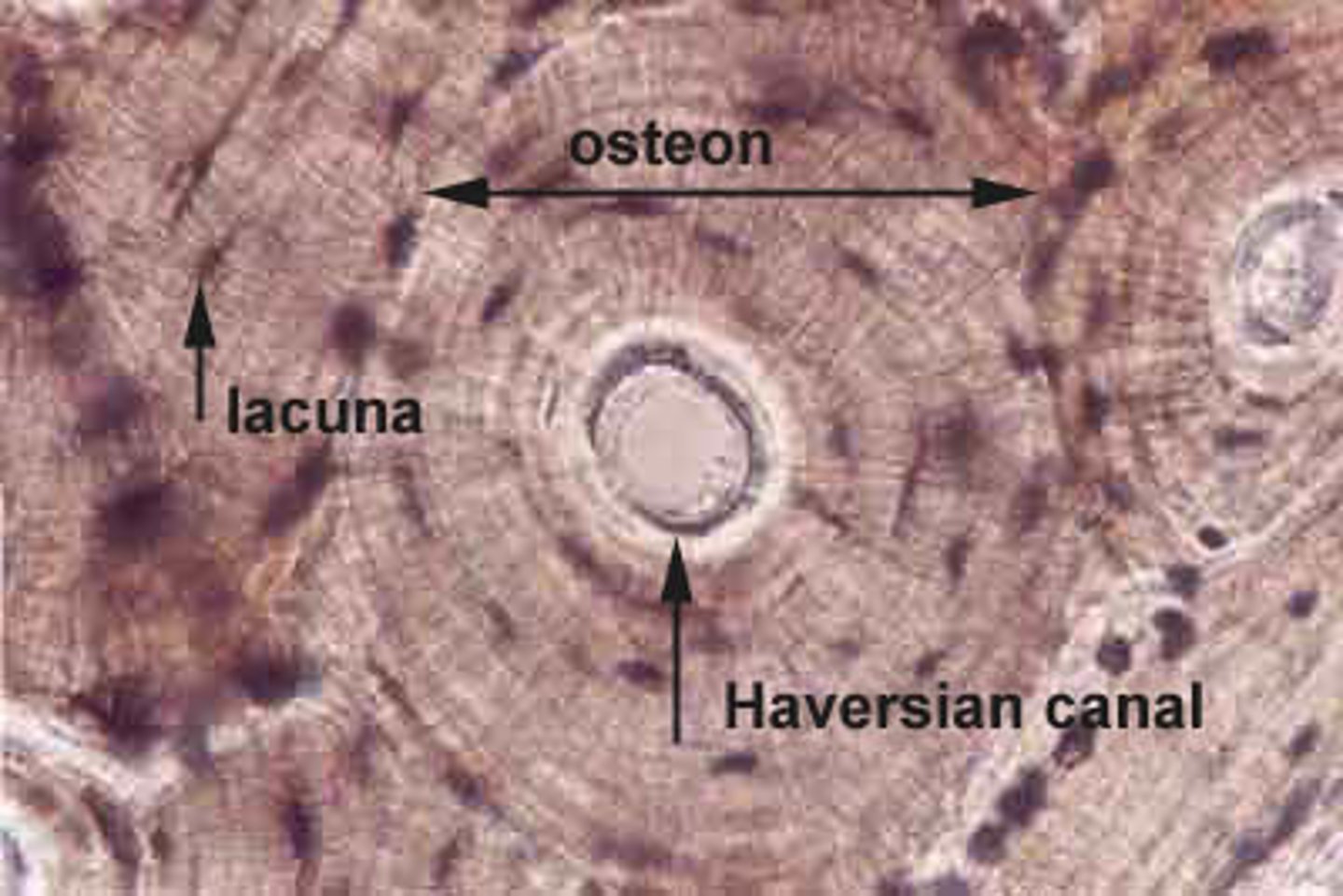
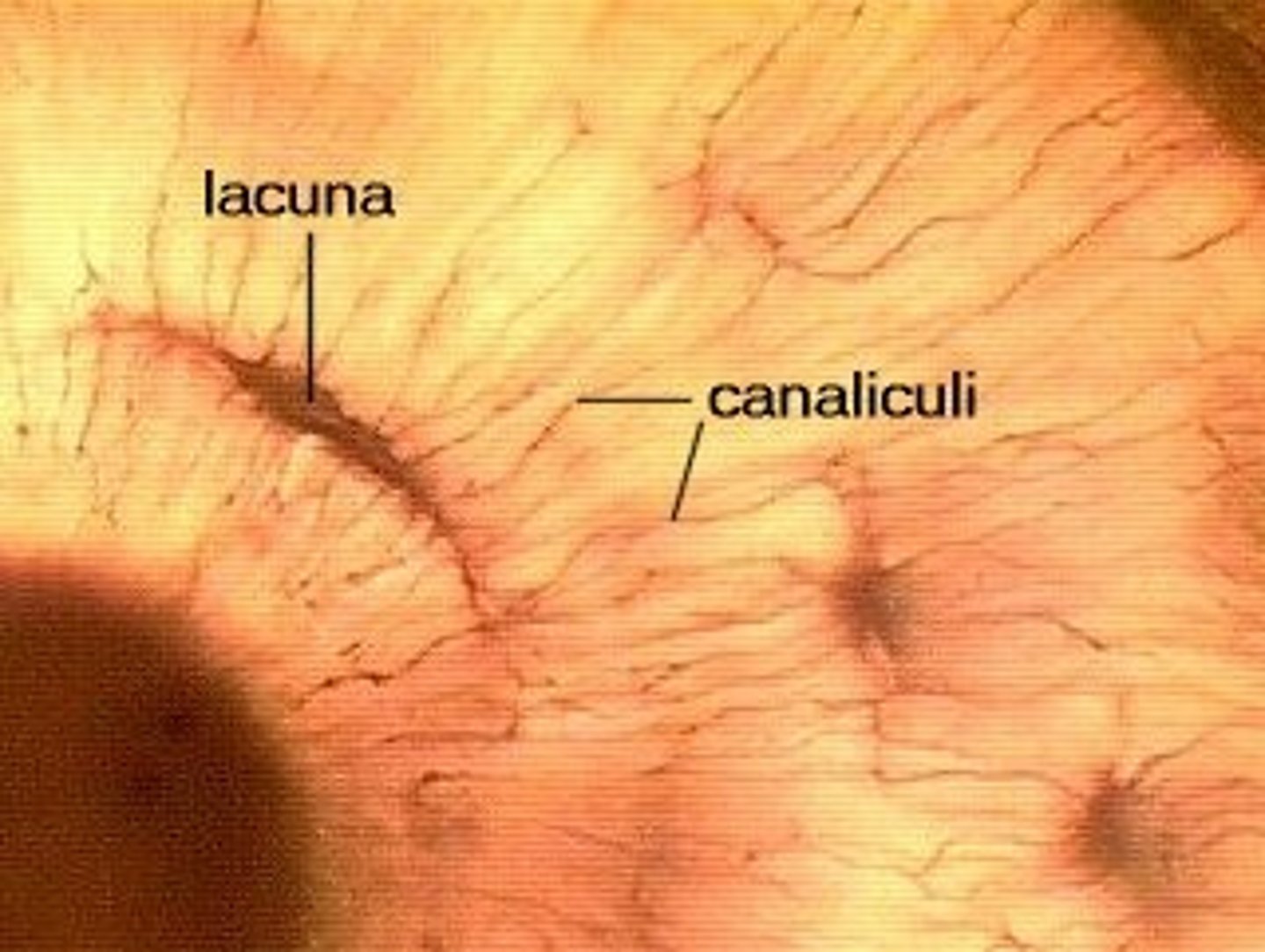
Lacunae
Small spaces in the bone matrix where osteocytes live.
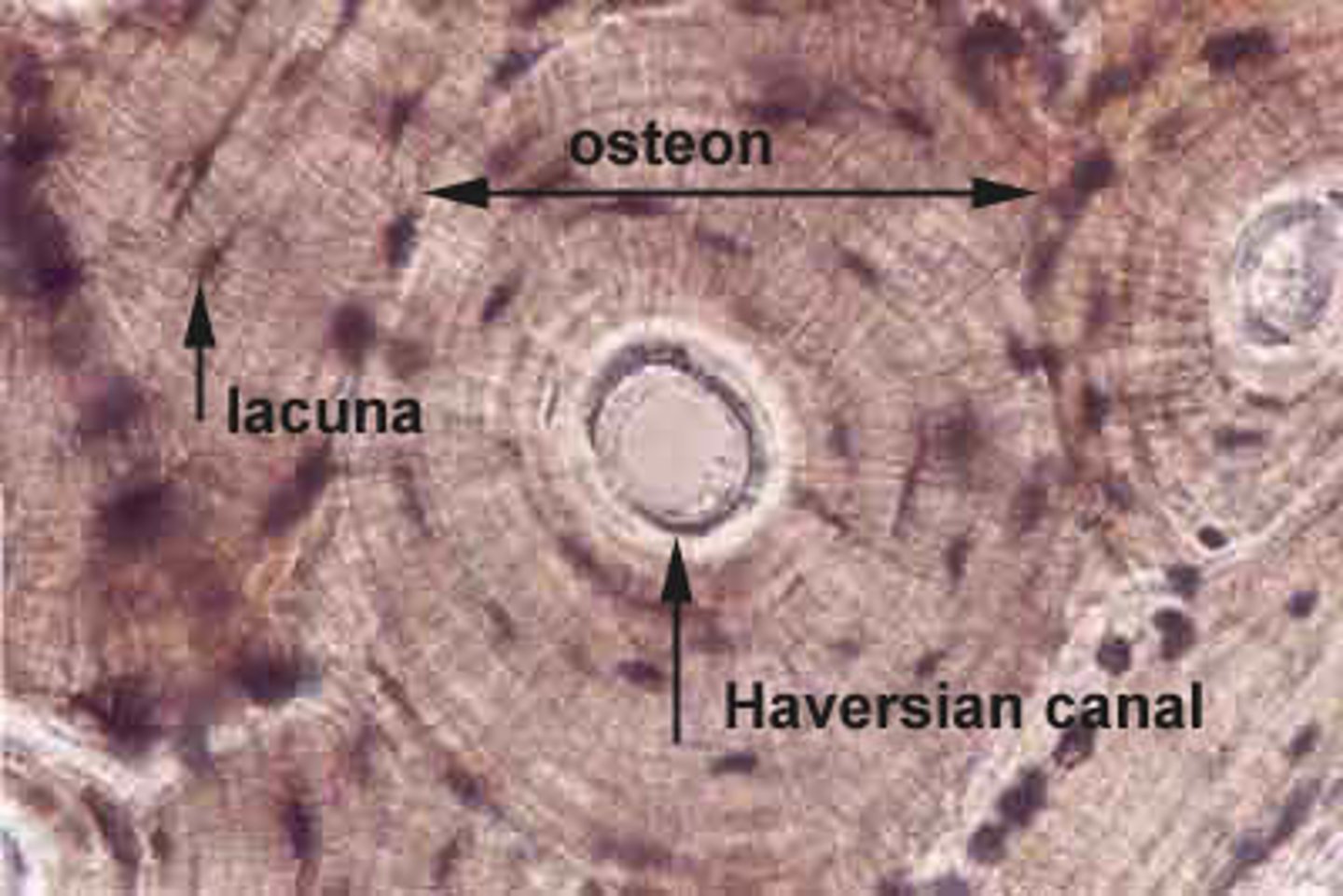
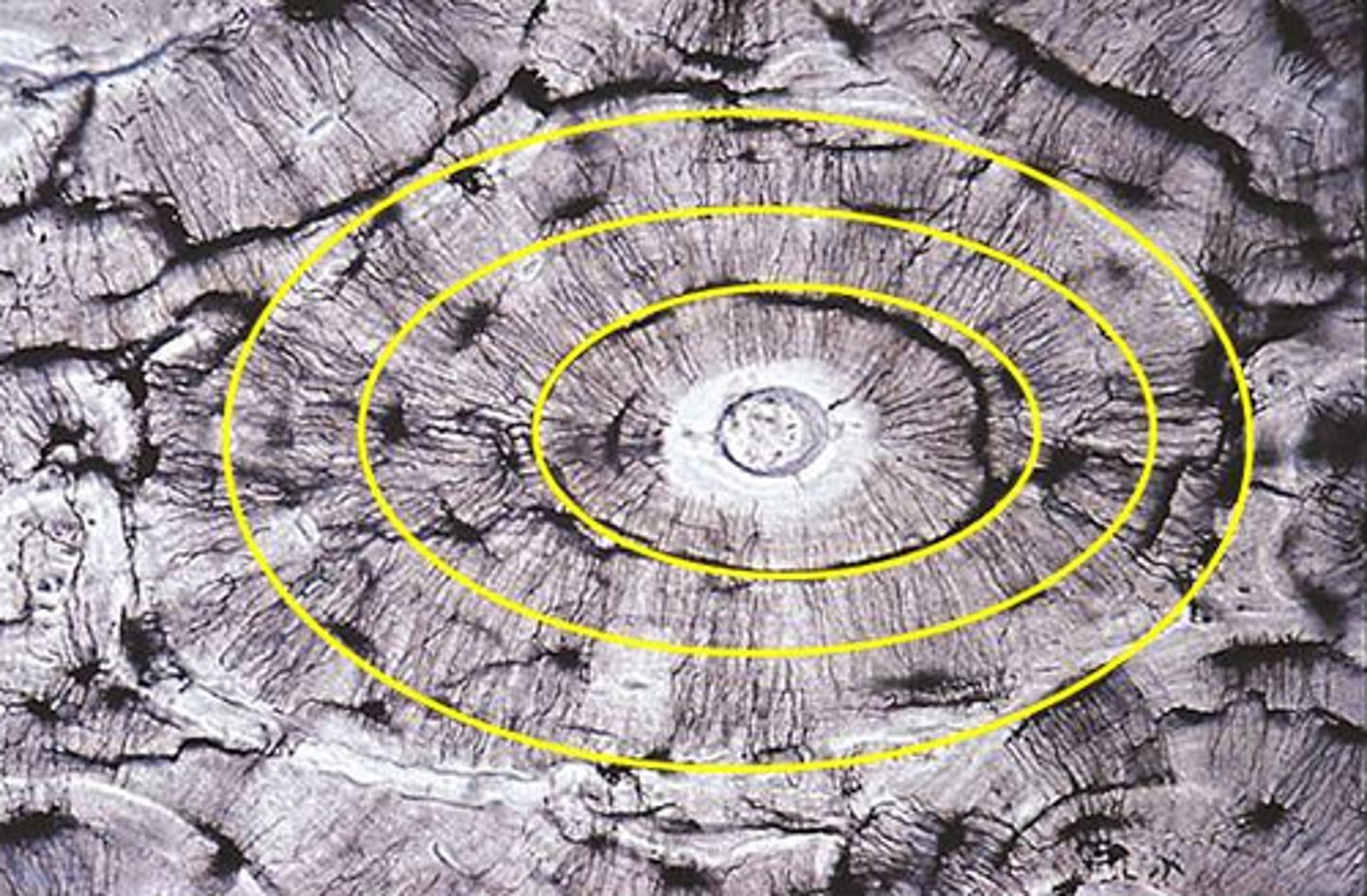
Lamellae
Rings of bone matrix surrounding the central canal (similar to rings of a tree).
Canaliculi
Small channels connecting lacunae to allow osteocytes to communicate.
Volkmann's (Perforating) Canals
Passageways connecting central canals.
Spongy Bone
Also called trabecular or cancellous bone, it is located inside bones and has a mesh or lattice-like appearance.
It is not soft.
Trabecular organize along lines of stress to strengthen bone.
Interstitial Growth
Growth in length; occurs during childhood and adolescence.
Growth in length occurs at a growth plate made of hyaline cartilage that sits between the diaphysis and epiphyses.
Results in increased stature or height through the end of adolescence.
Growth stops when growth plate ossifies and the diaphysis and epiphyses fuse together.
A remnant of the growth plate remains as the epiphyseal plate.
Appositional Growth
Growth in diameter of bone. Can continue to occur throughout life as remodeling occurs.
Osteoblasts secrete bone matrix underneath the periosteum to form new rings (lamellae) of matrix around the bone.
This new bone matrix is then broken down and replaced as cylindrical osteons.
Osteoclasts remove bone matrix inside the bone to increase the size of the medullary cavity.
Bone Remodeling
Ongoing replacement of old bone tissue by new bone tissue.
Occurs to maintain fluid concentrations of calcium and phosphate in the body.
Also occurs to respond and strengthen the bone to resist mechanical stress.
A coordinated process occurring between osteoclasts and osteoblasts, breaking down bone and depositing new bone matrix. Coordination is important to maintain a constant overall bone mass.
Osteoporosis
Low bone mass and a deterioration of the microscopic architecture of the bony skeleton.
Bone respiration outpaces bone deposition with an elevated number of osteoclasts.
Due to loss of bone mass, fractures are common in bones that support most of the body weight such as the neck of the femur and vertebrae.
Occurs most commonly in older females who have gone through menopause with estrogen deficiency as estrogen help maintain bone density.
If there is a hole or opening in a bone, if it is round:
It is a foramen.
If there is a hole or opening in a bone, if it is slit-like:
It is a fissure.
If there is a hole or opening in a bone, if tube-like:
It is a canal or meatus.
If there is a hole or opening in a bone, if a hollow space:
It is a cavity or sinus.
If there is a ridge on a bone, if extensive:
It is a crest.
If there is a ridge on a bone, if it is thin:
It is a line.
If there is a projection on a bone, if it is large:
It is a trochanter, tuberosity, or malleolus.
If there is a projection on a bone, if it is small:
It is a tubercle or process.
If there is a projection on a bone, if it is pointed or spear-like:
It is a spinous process or styloid process.
If there is a depression in a bone, if it is larger and deeper:
It is a fossa.
If there is a depression in a bone, if half-moon shaped:
It may be called a notch.
If there is a depression in a bone, if it is long:
It may be called a sulcus or groove.
When one bone articulates with another capped with hyaline cartilage, if rounded:
It is called a condyle or head.
Human Skeleton
Composed of 206 named bones that can be divided into axial and appendicular groups.
Axial Skeleton
Forms the central axis of the body.
Includes: skull bones, auditory ossicles, teeth, hyoid, vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, ribs, and sternum.
Skull Bones
29 bones.
Vertebral Column
26 bones.
Thoracic Cage
25 bones.
Upper Limbs
64 bones.
Lower Limbs
62 bones.
Neurocranial Bones
Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones.
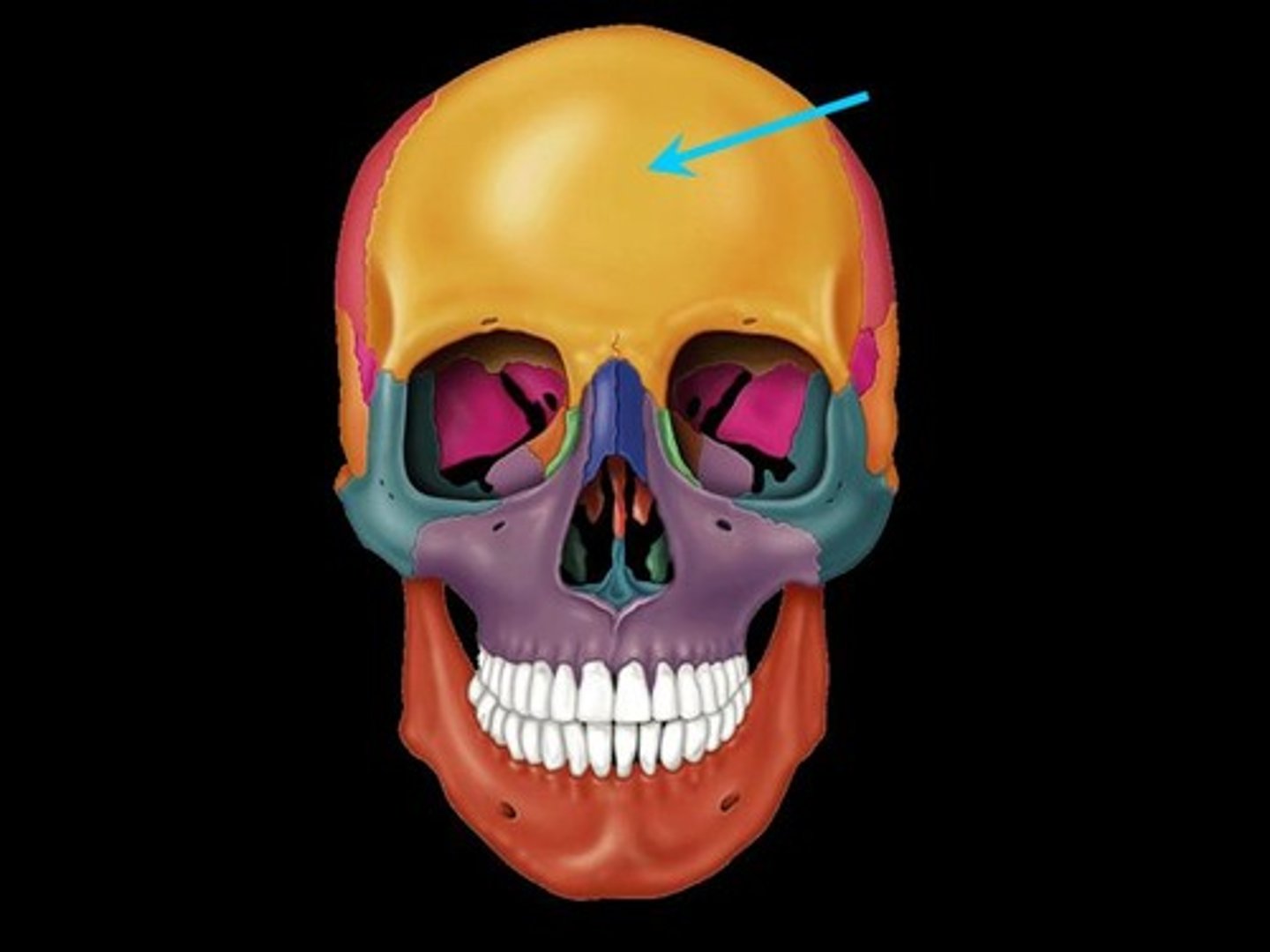
Frontal Bone
Bone of the forehead.
Unpaired.
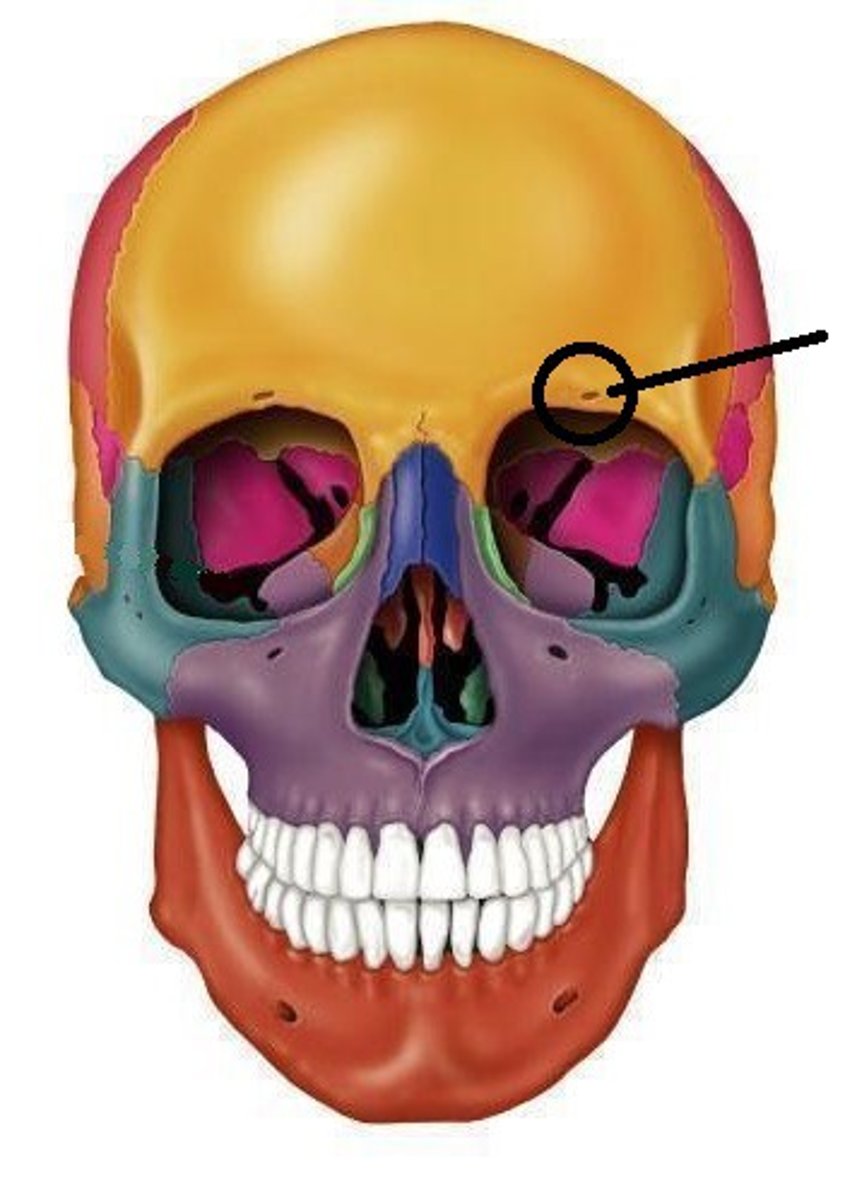
Supraorbital Foramen (or notch)
Frontal Bone.
Passageway for nerves and vessels above the orbit.
Sometimes it is a hole, sometimes it just looks like a notch.
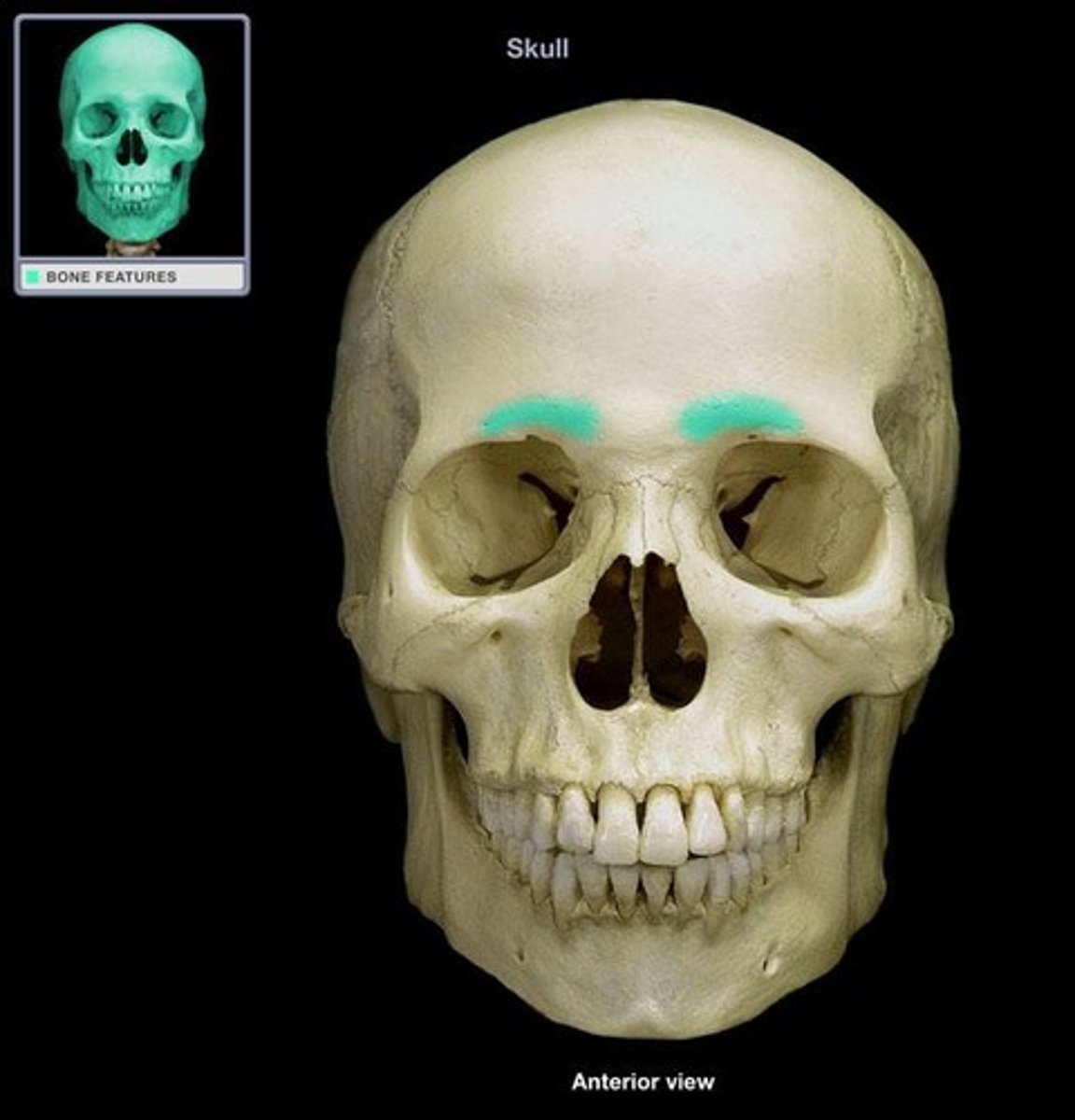
Superciliary Arch
Frontal Bone.
Bony arch above the orbit.
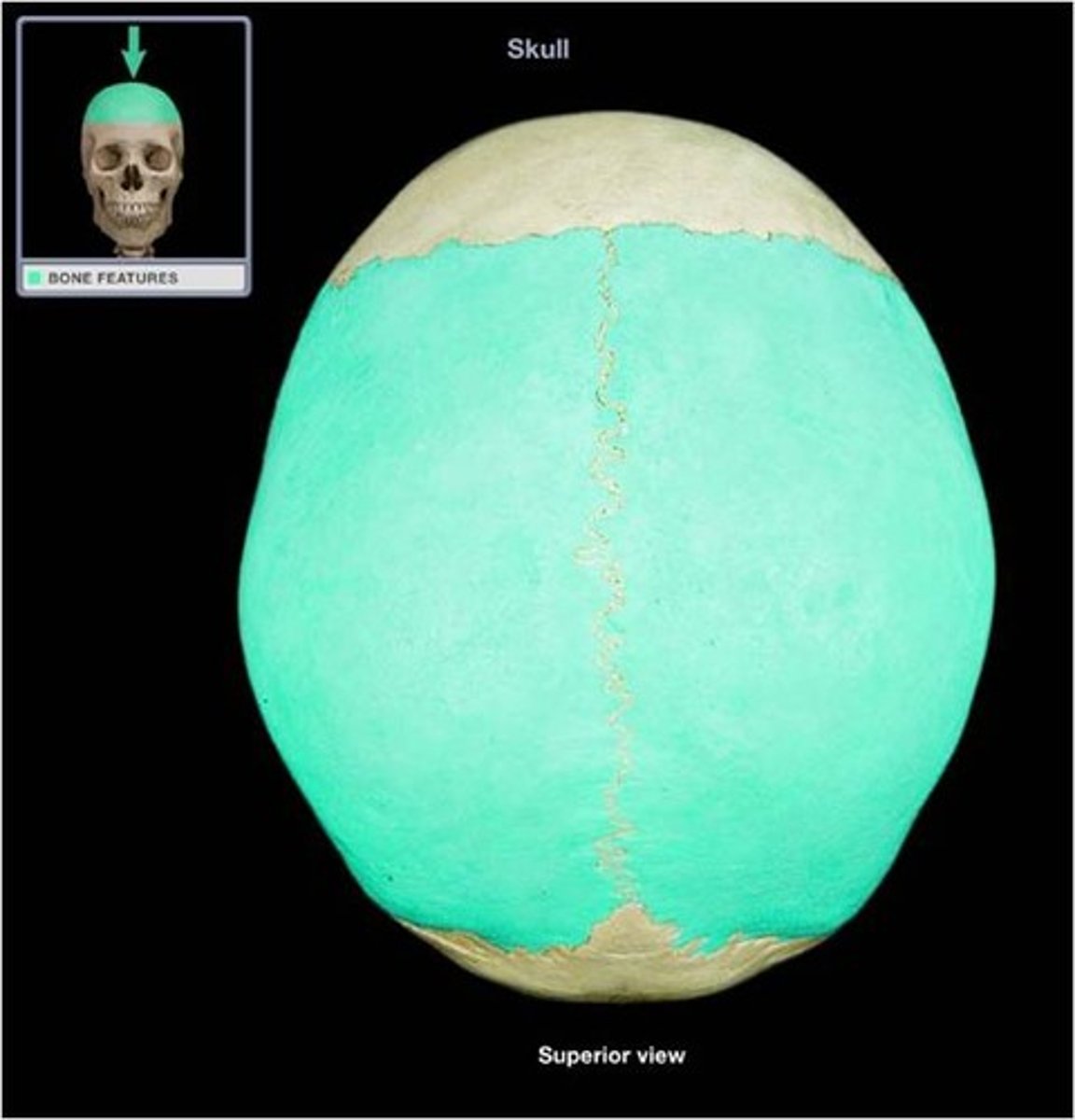
Parietal Bone
The paired bones form the superior and lateral portions of the neurocranium.
Paired.
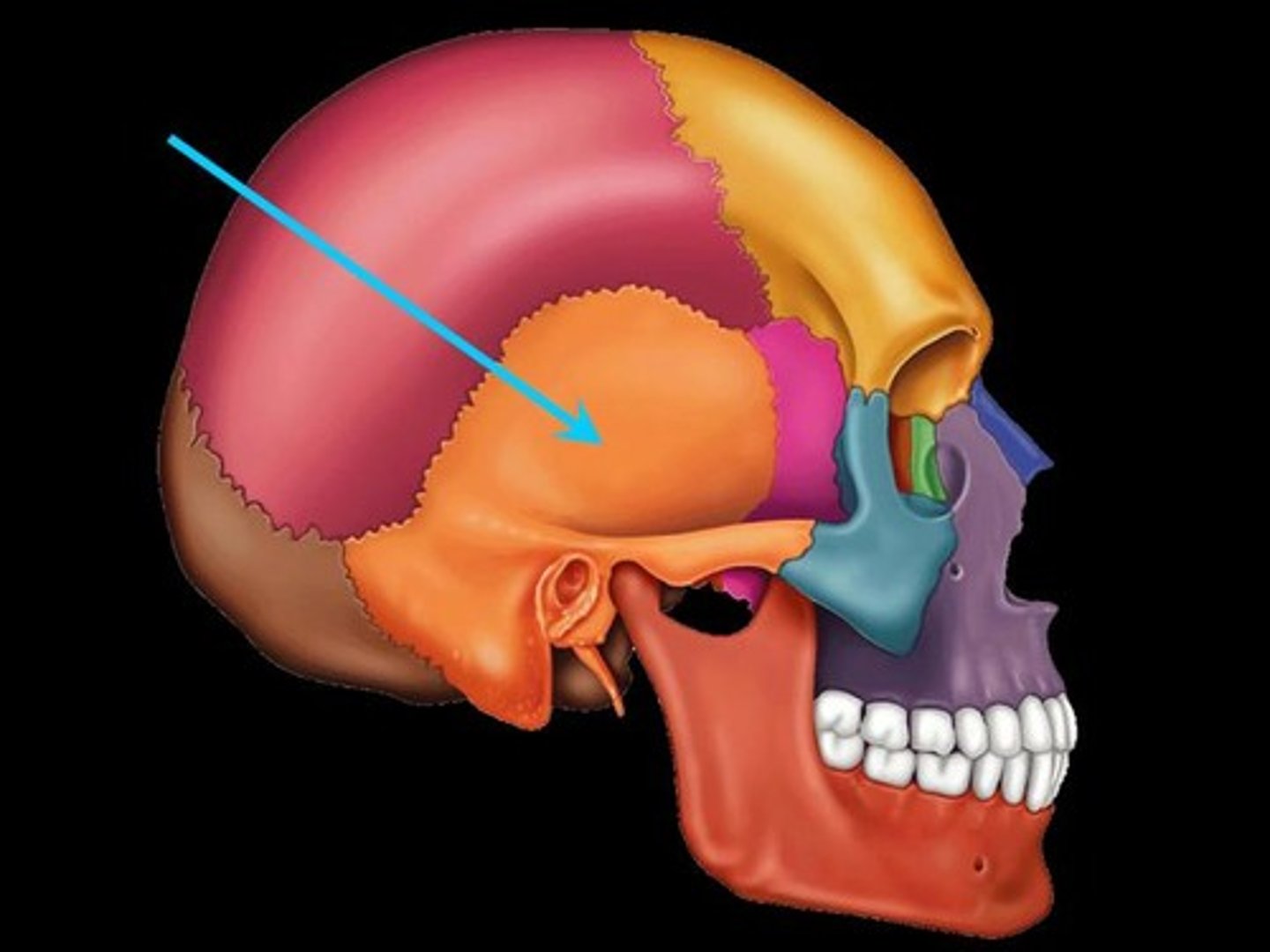
Temporal Bone
Has a flat part along the lateral side of the cranium (near the external ear) and another part that forms a section of the cranial base which holds the inner and middle ear structures.
Paired.
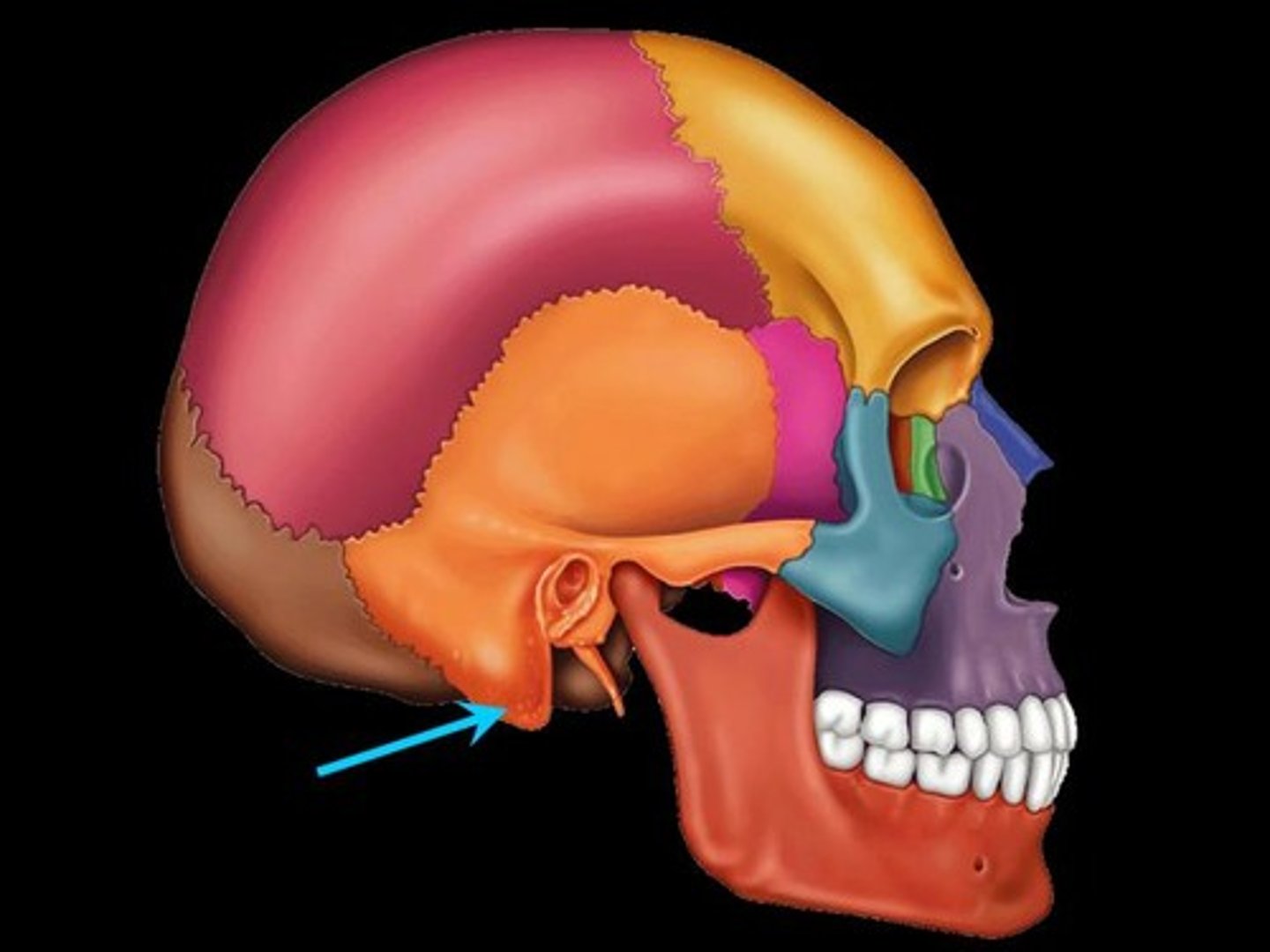
Mastoid Process
Bony projection for attachment of muscles.
Styloid Process
Thin bony projection for attachment of muscles.
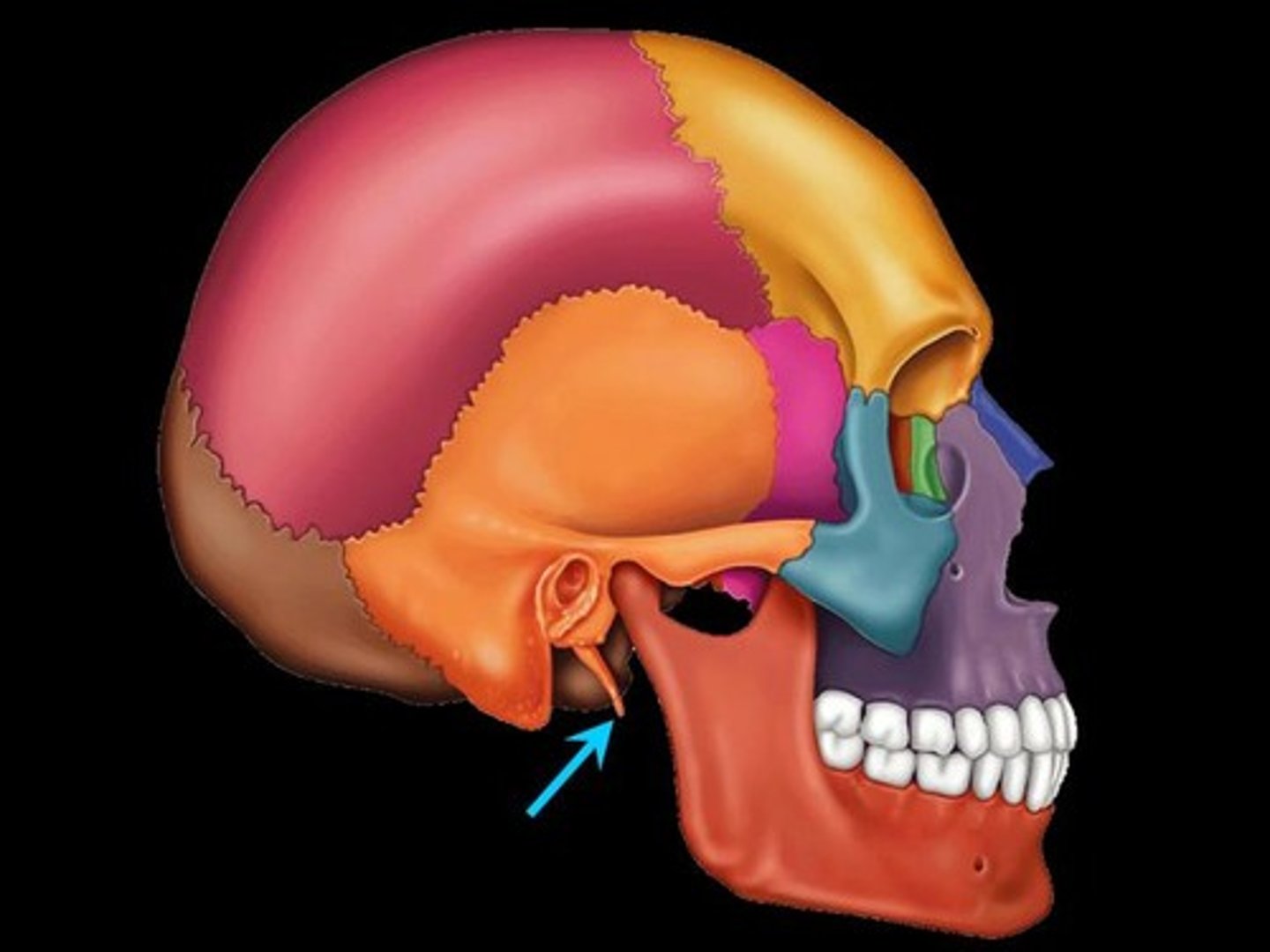
External Acoustic (Auditory) Meatus
Canal through temporal bone for vibrations in air to travel to contact tympanic membrane (ear drum).
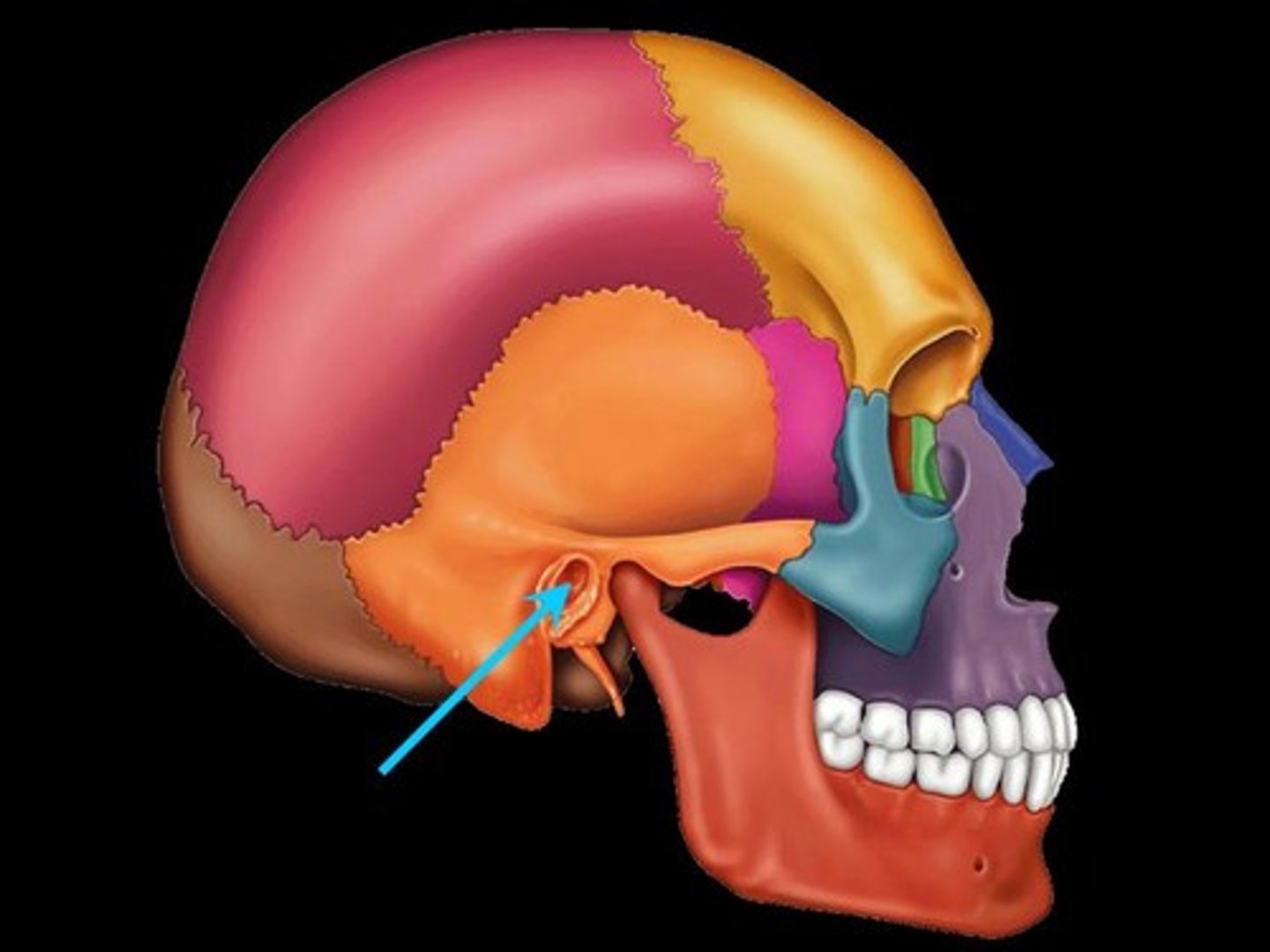
Mandibular Fossa
Depression in bone, articulation site for mandibular condyle (of the mandible) to form the temporomandibular joint (TMJ or jaw joint)
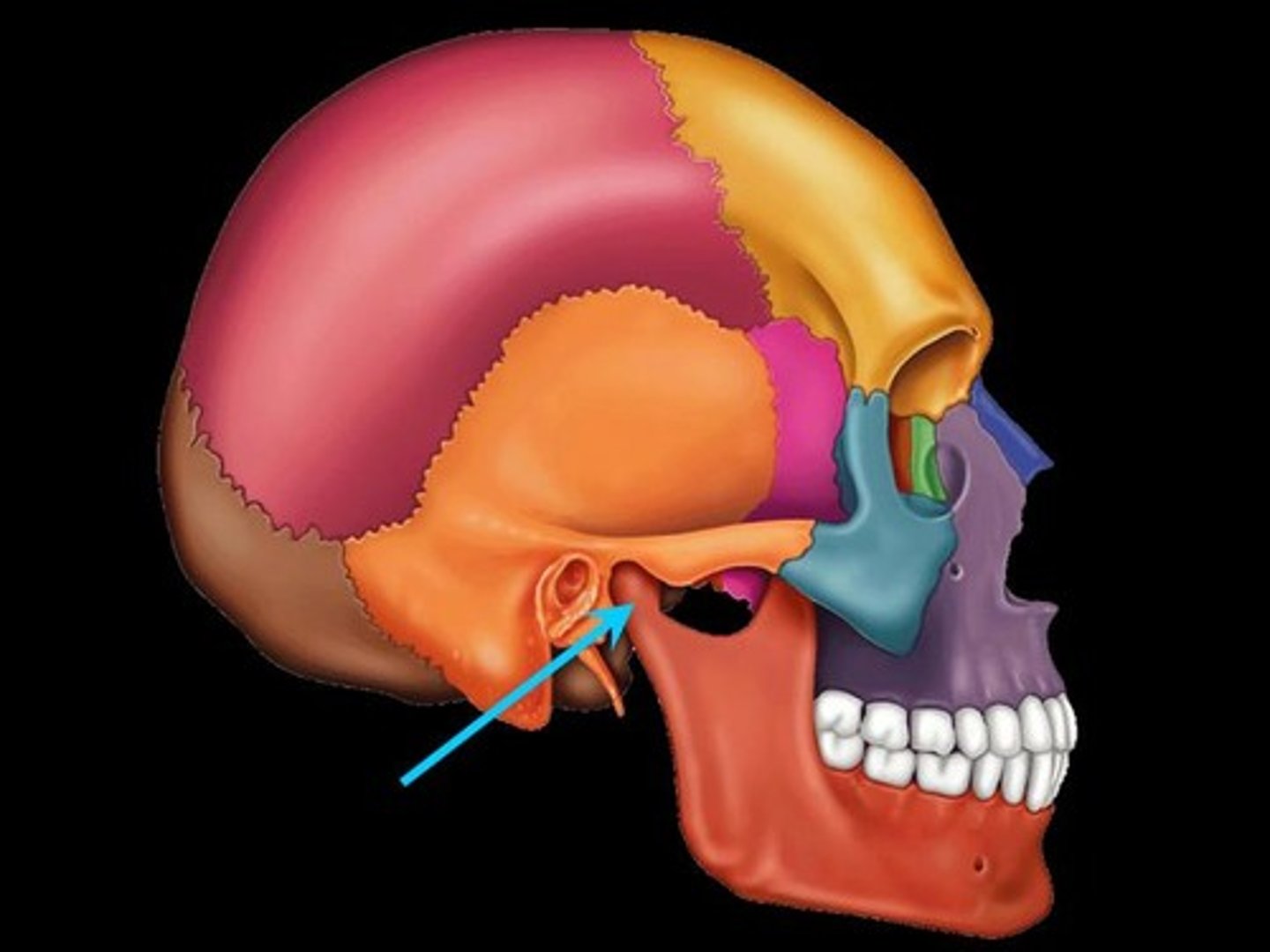
Petrous Portion
The internal part of the temporal bone which contains the middle and inner ear structures (best viewed within the cranial cavity).
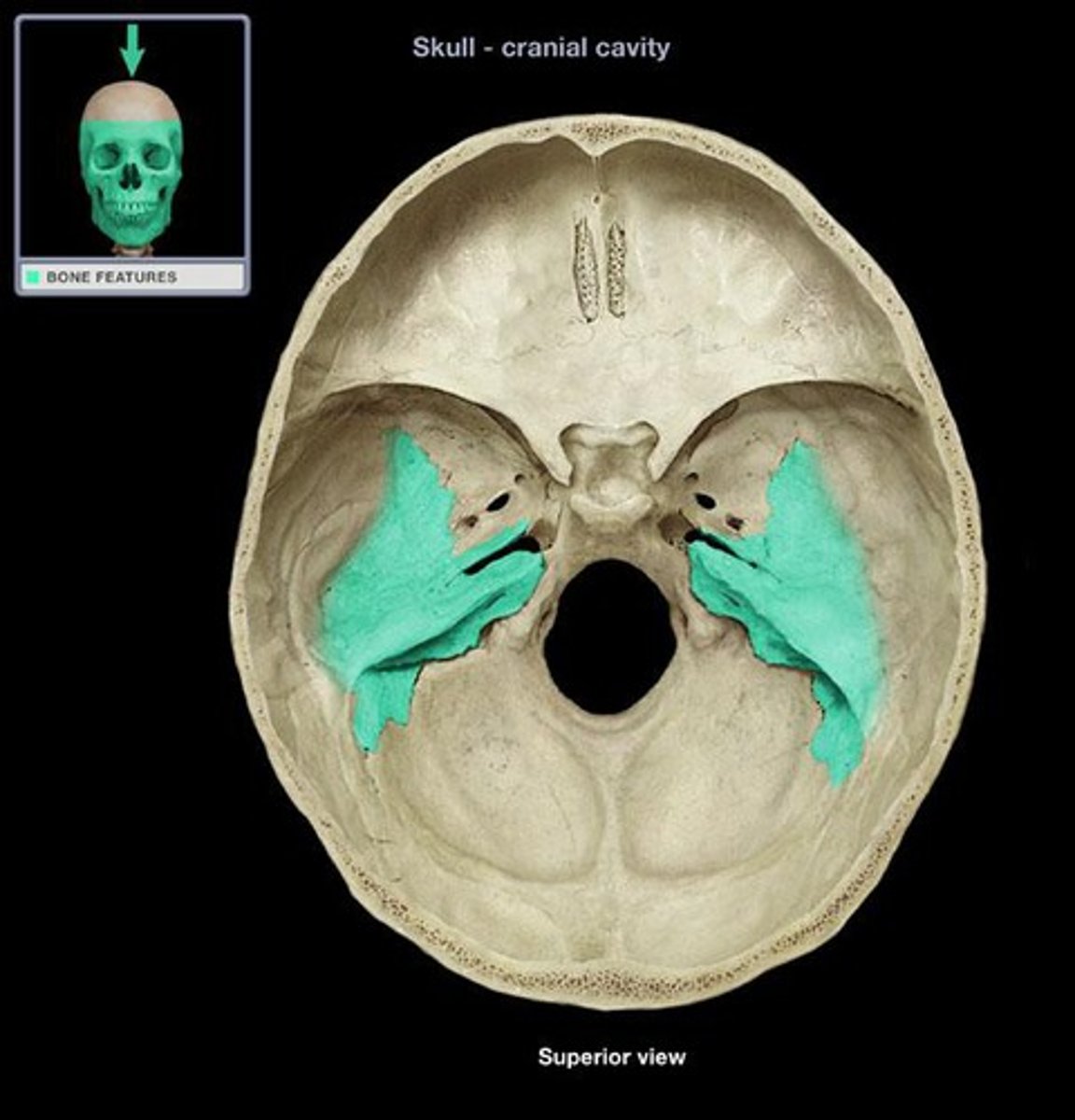
Internal Acoustic (Auditory) Meatus
Passageway through the petrous portion of the temporal bone. This is how nerves from the brain access hearing and balance related structures (viewed within cranial cavity).
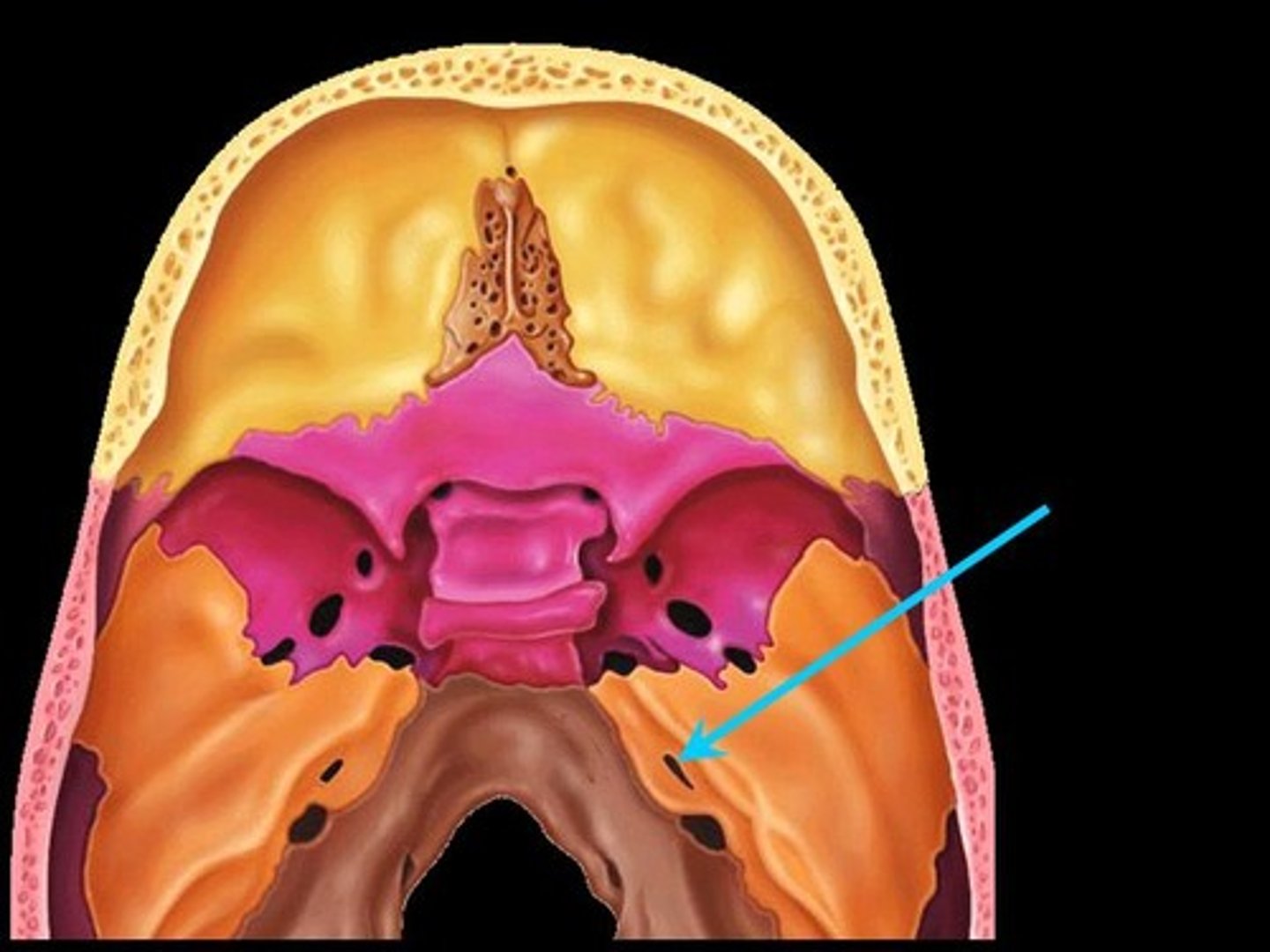
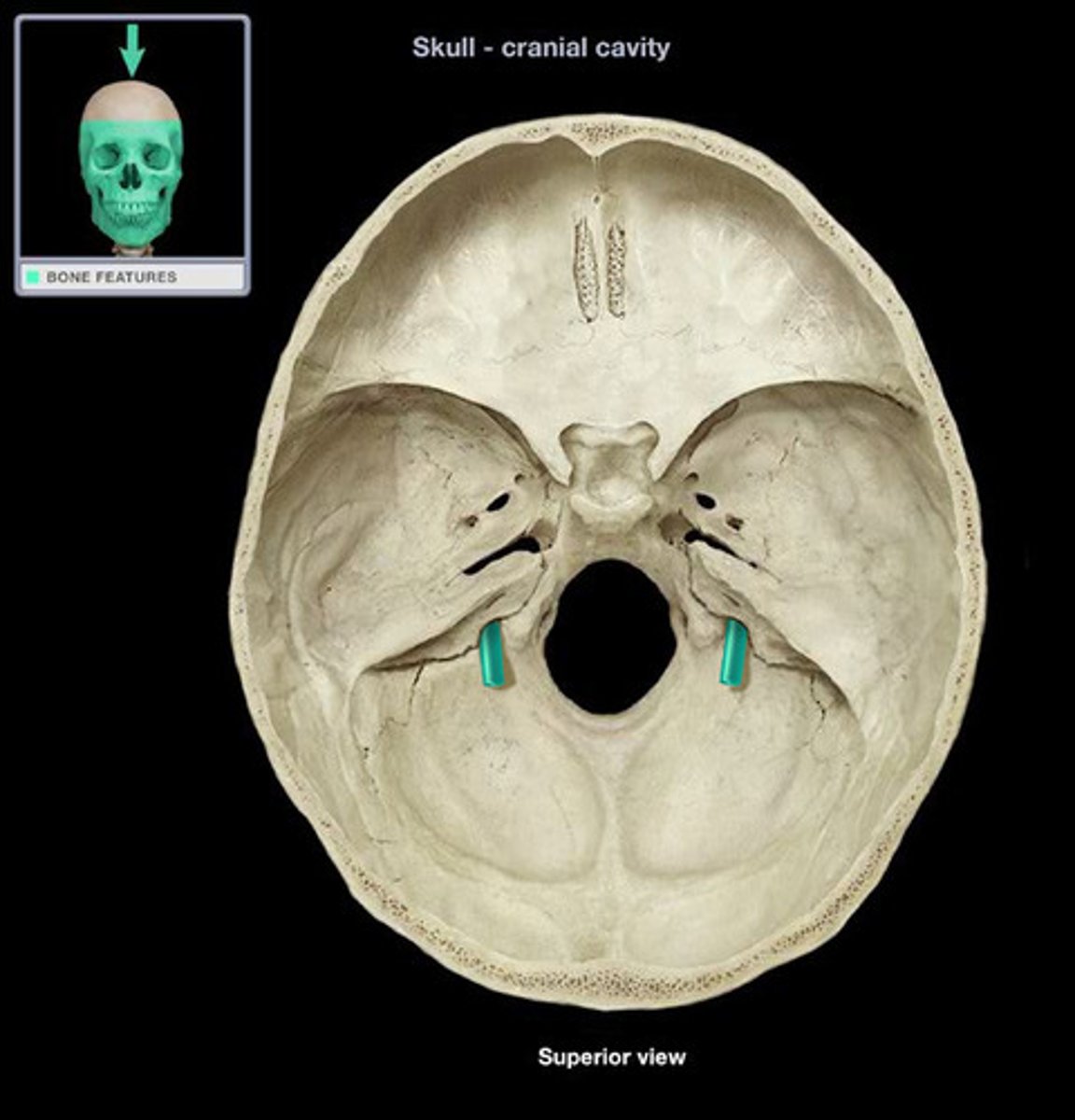
Jugular Foramen
Passageway formed at the junction of the temporal and occipital bones. Passageway for cranial nerves and blood leaving cranial cavity (viewed within cranial cavity or from cranial base).
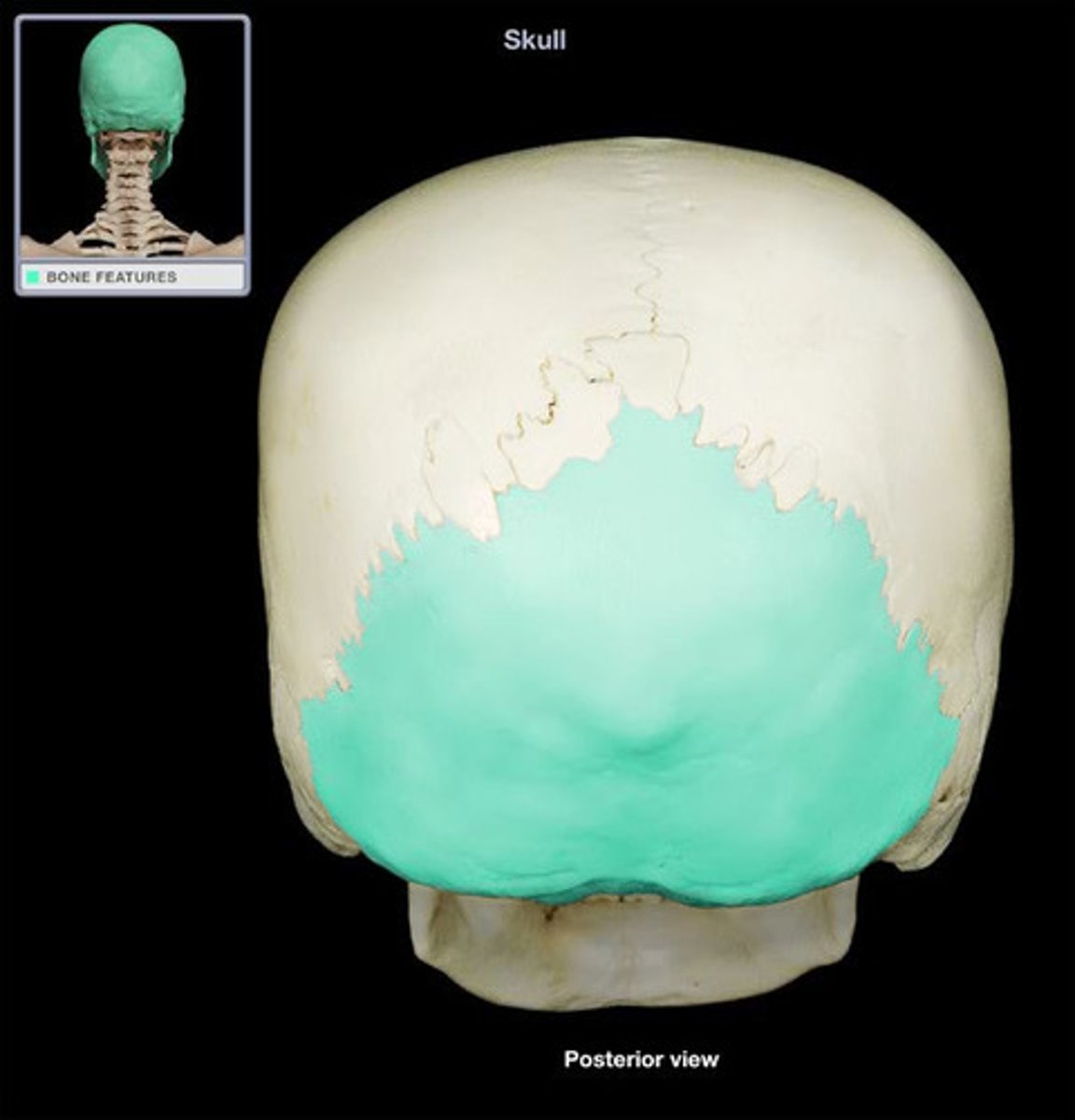
Occipital Bone
Forms the posterior and part of the inferior portions of the neurocranium.
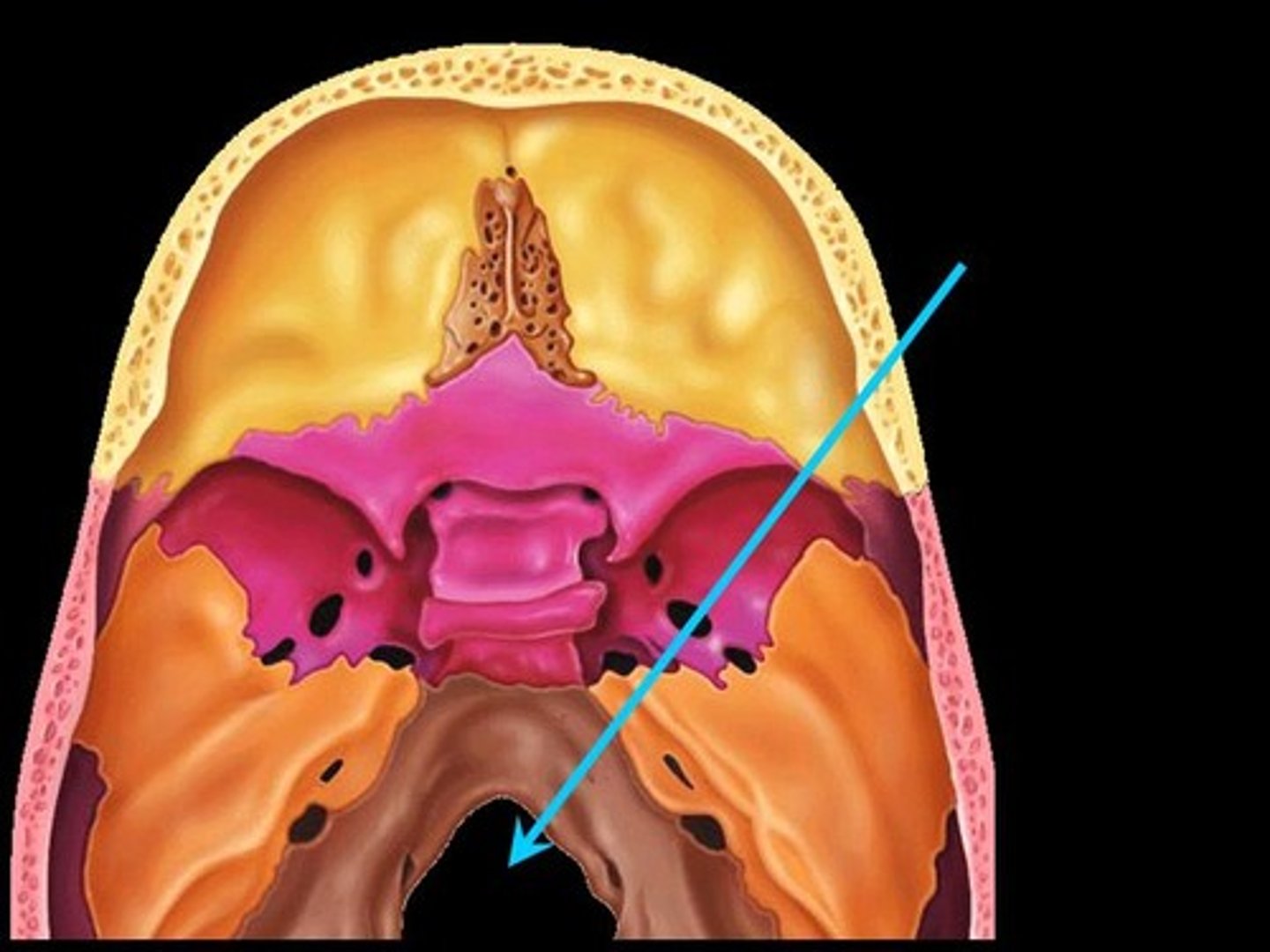
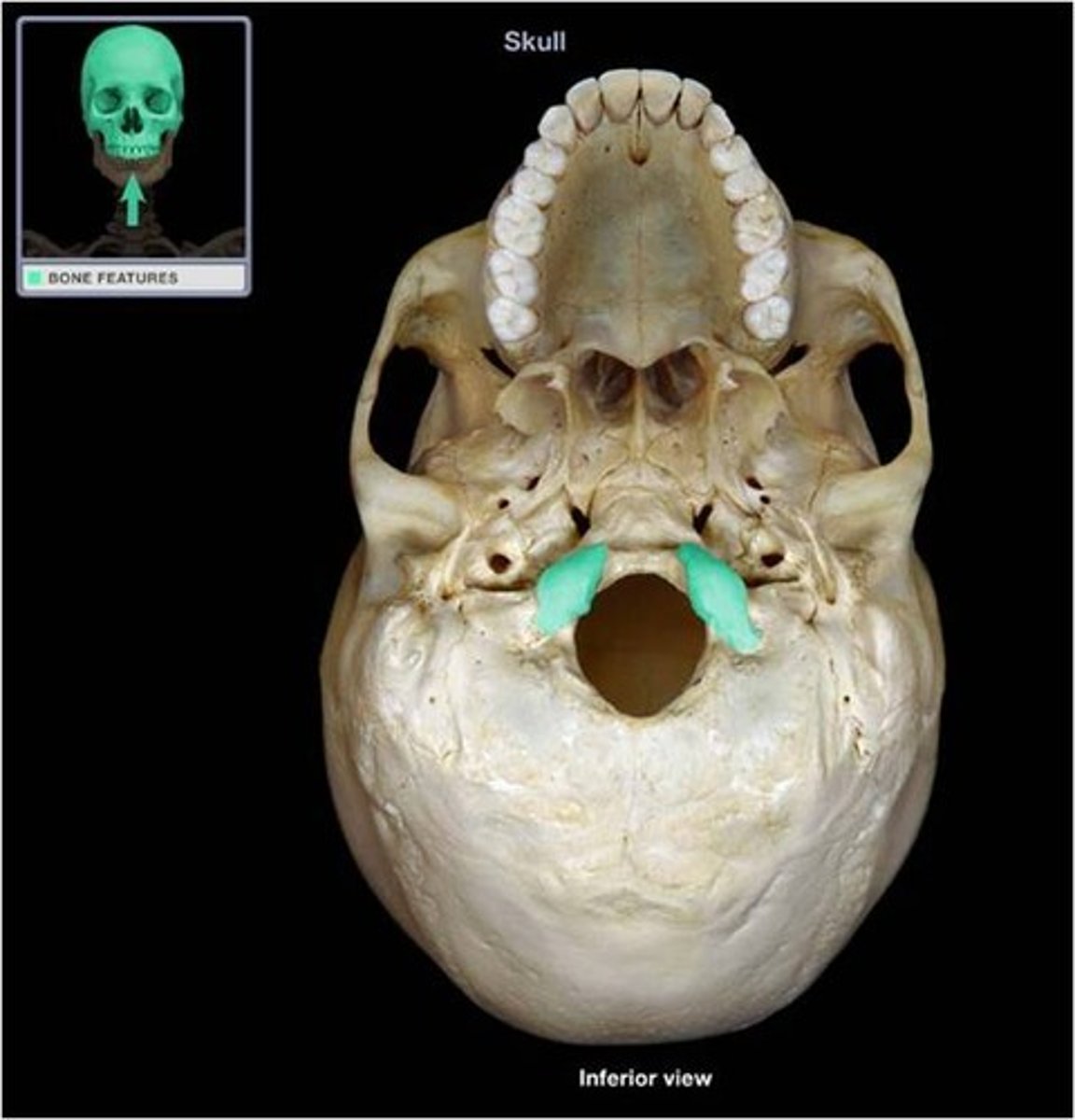
Foramen Magnum
Large opening in the base of the skull for the passage of the spinal cord.
Occipital Condyles
Smooth surfaces for articulation with first cervical vertebrae (atlas).
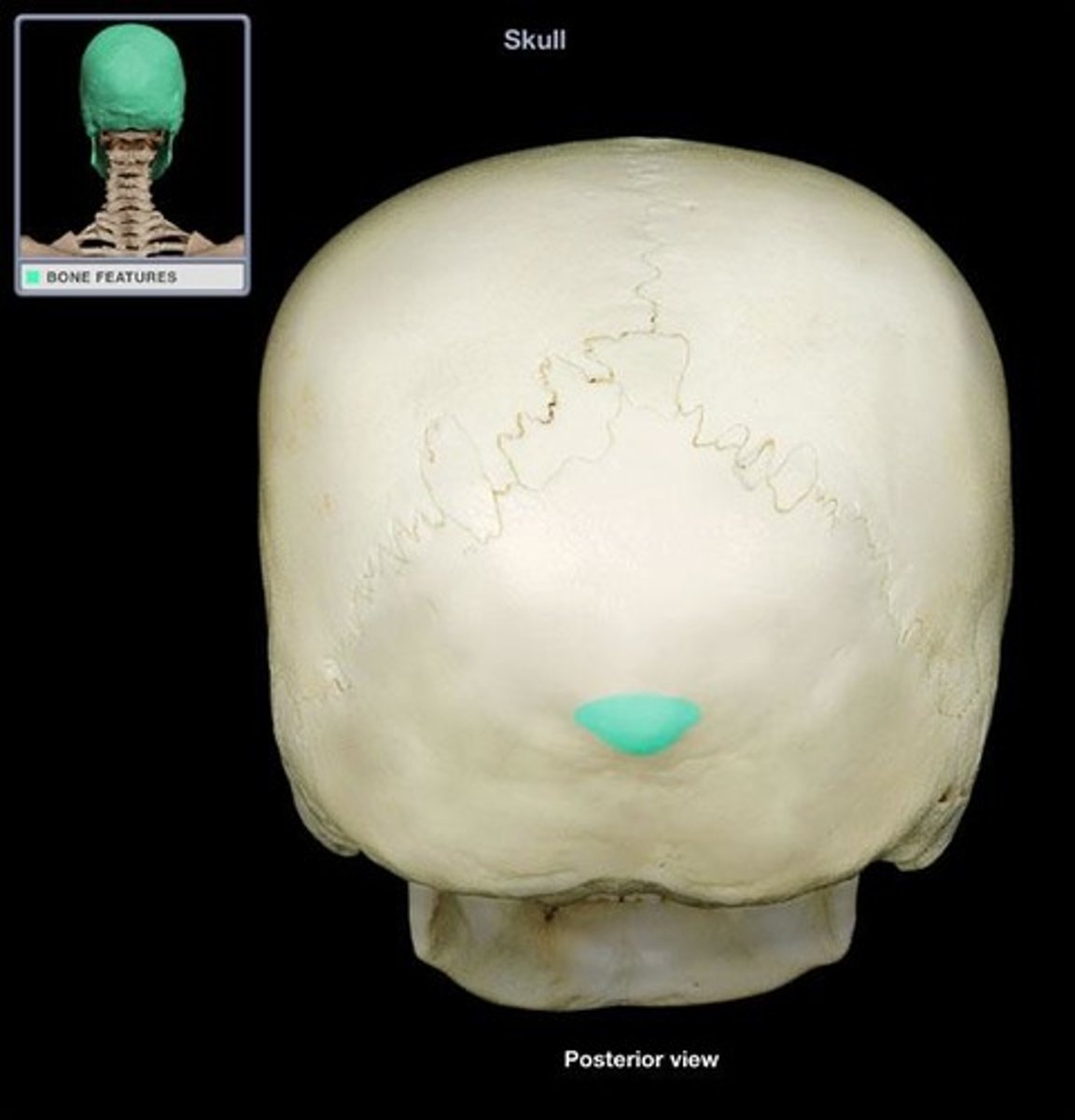
External Occipital Protuberance
Bump of bone along the posterior, midline of the occipital bone. A site for muscle attachment.
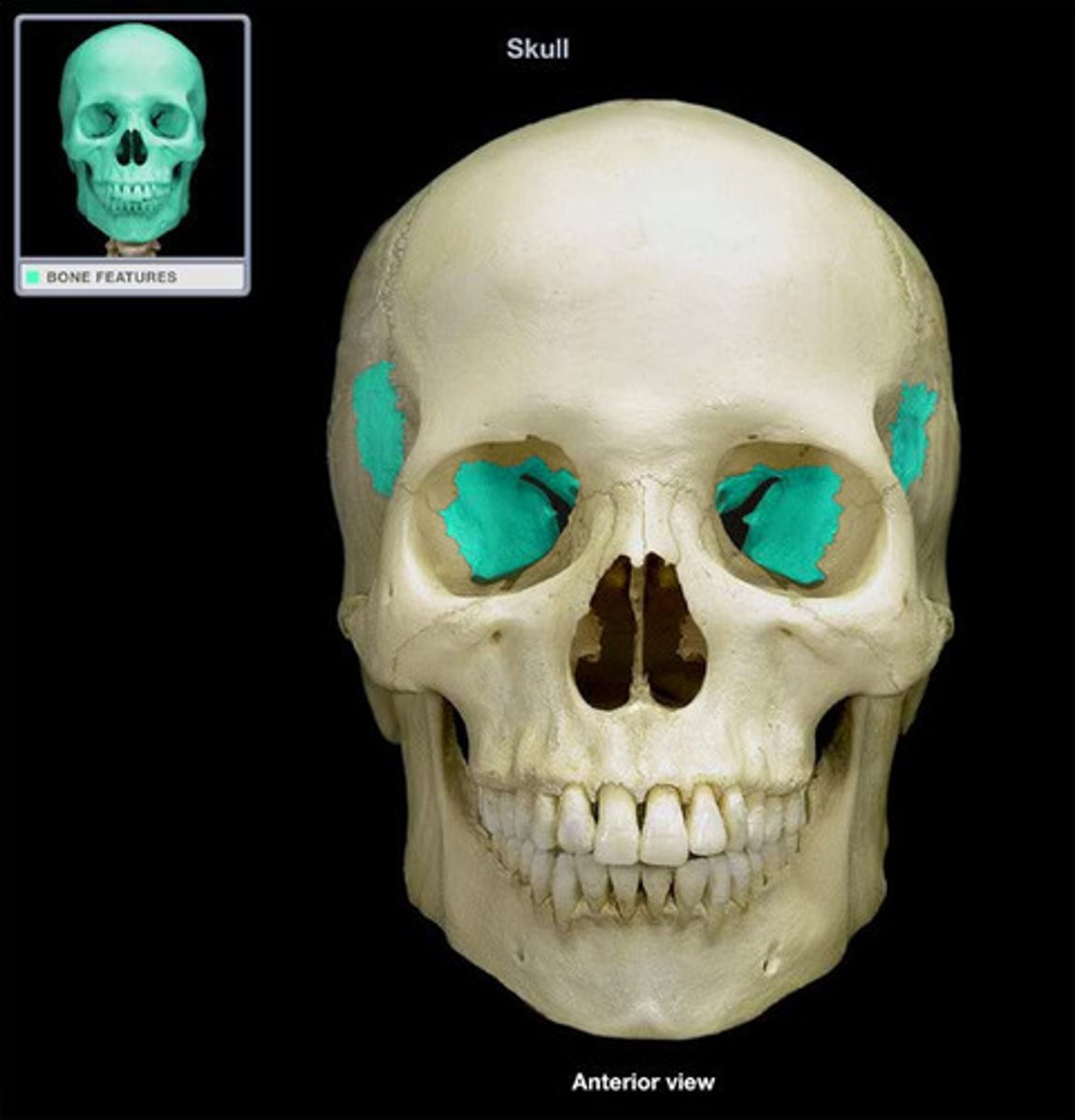
Sphenoid Bone
Sits between the face and neurocranium.
Unpaired.
Greater Wing
Larger lateral projections of the sphenoid bone.
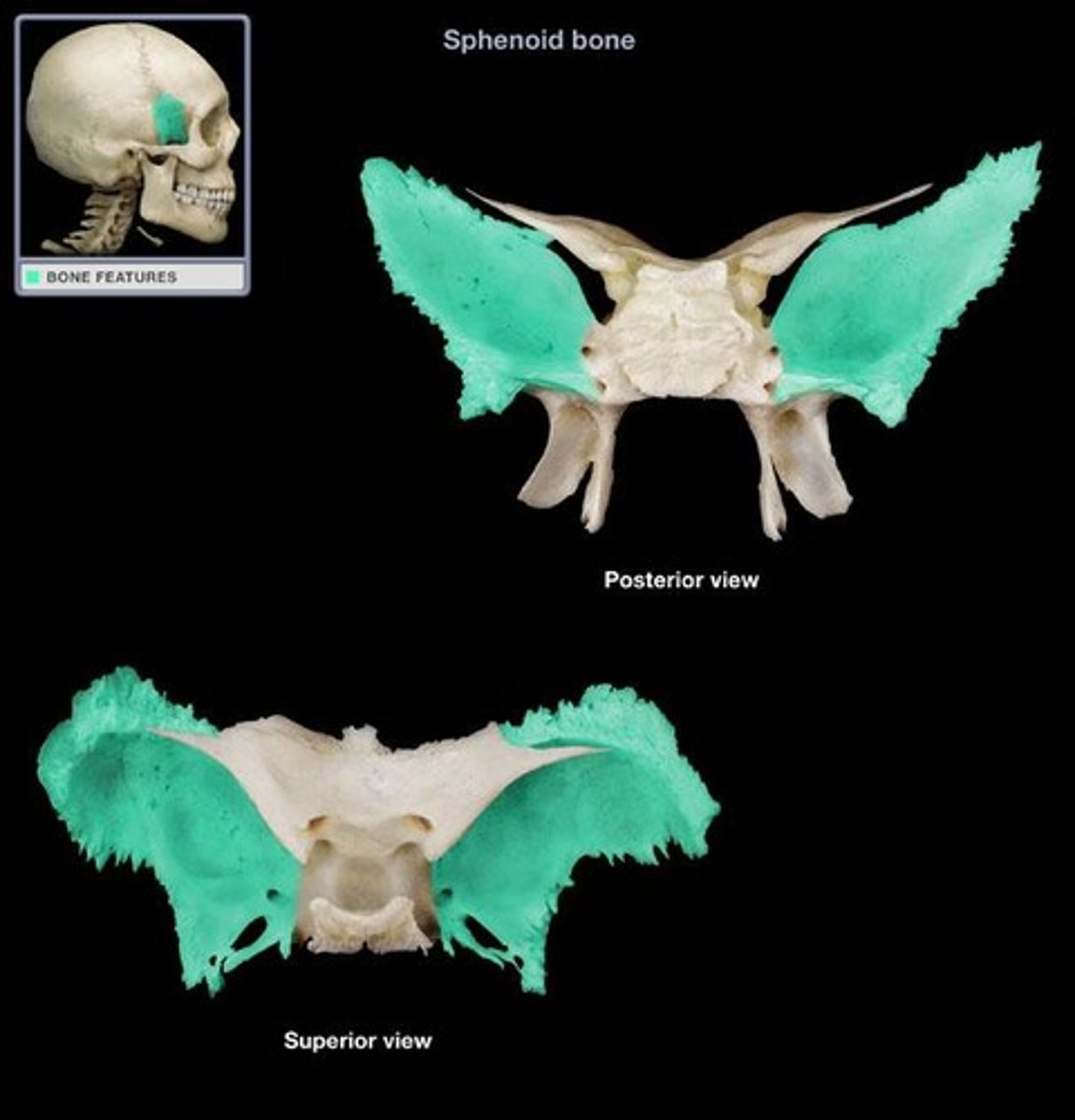
Lesser Wing
Flat, superior portions of the sphenoid bone.
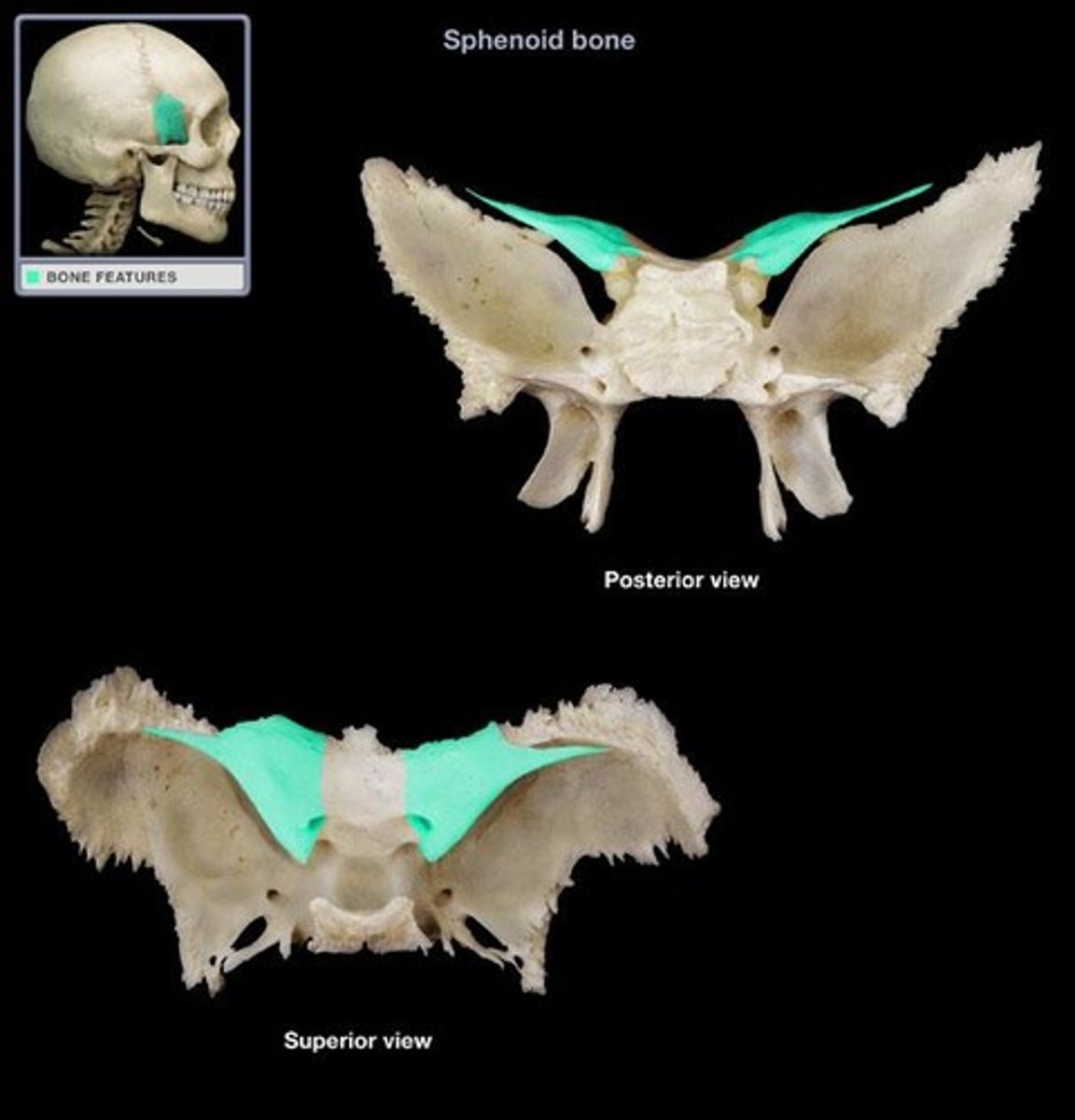
Sella turcica
Means "Turkish saddle." Saddle-shaped depression where the pituitary gland sits.
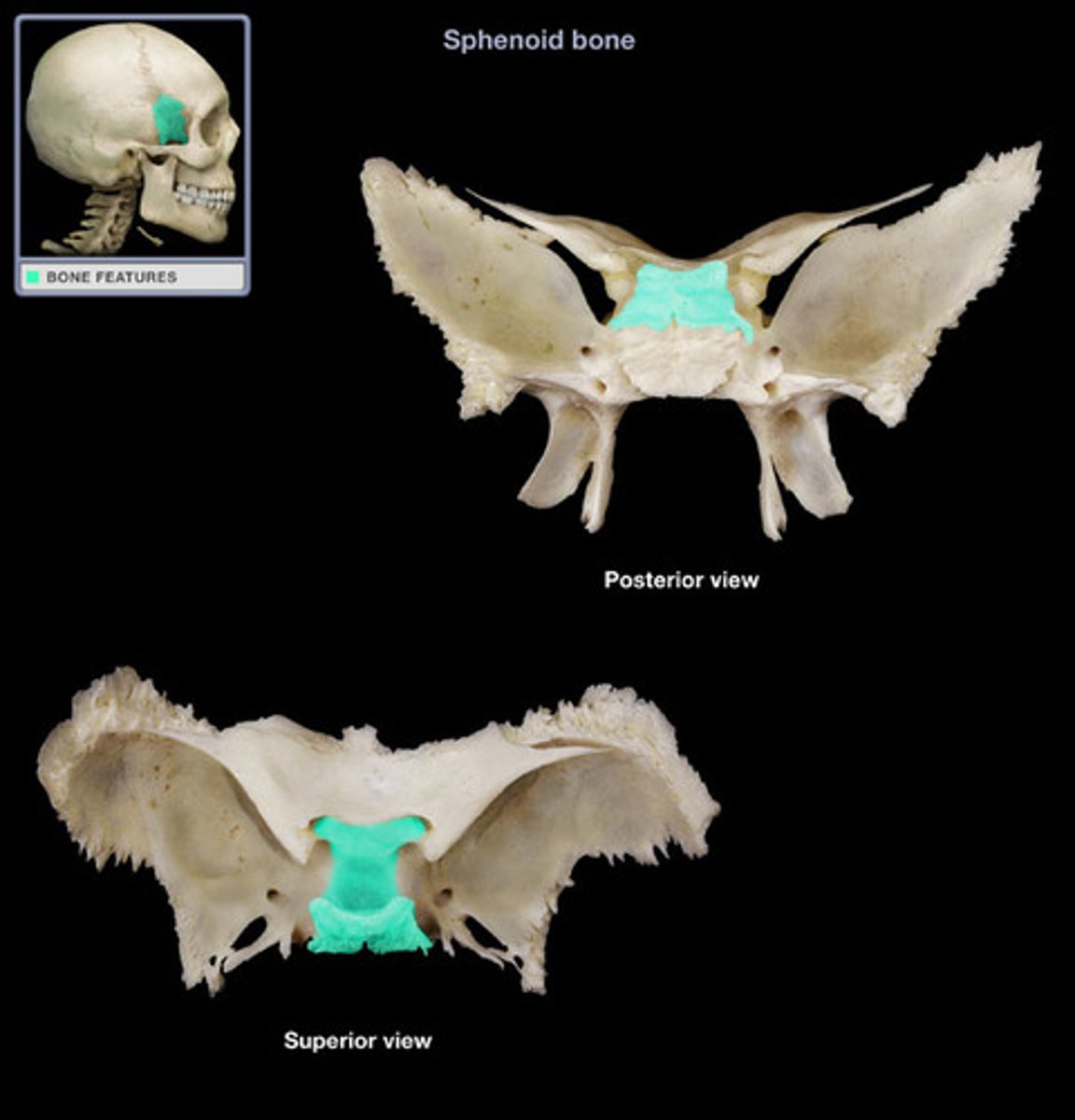
Pterygoid Process
Inferior projection consisting of 2 plates from the bottom of the sphenoid bone.
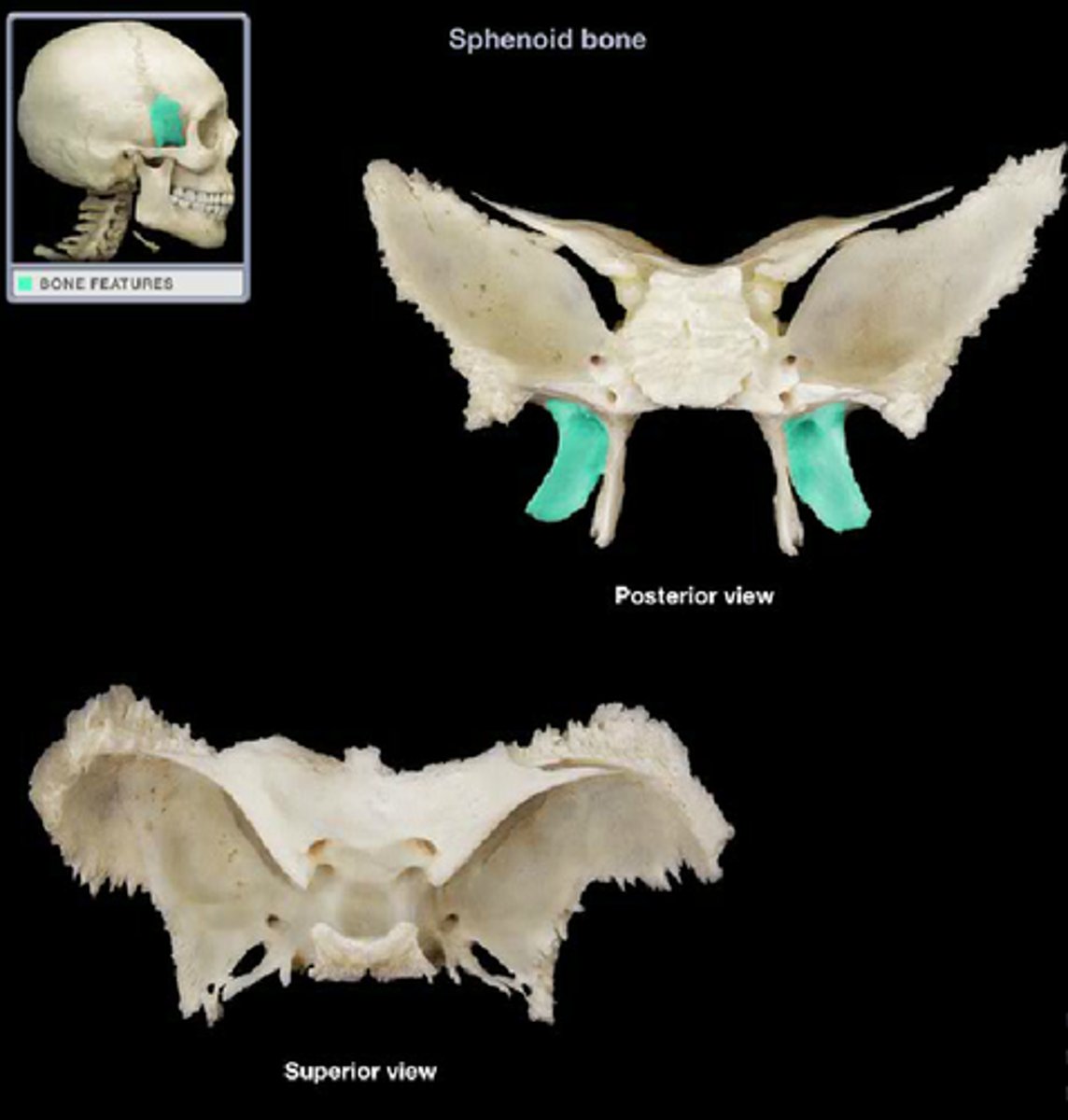
Optic Canal
Passageway located where the lesser wing meets the body of the sphenoid bone, allows passage of the optic nerve to the eye (viewed within cranial cavity or within orbit).
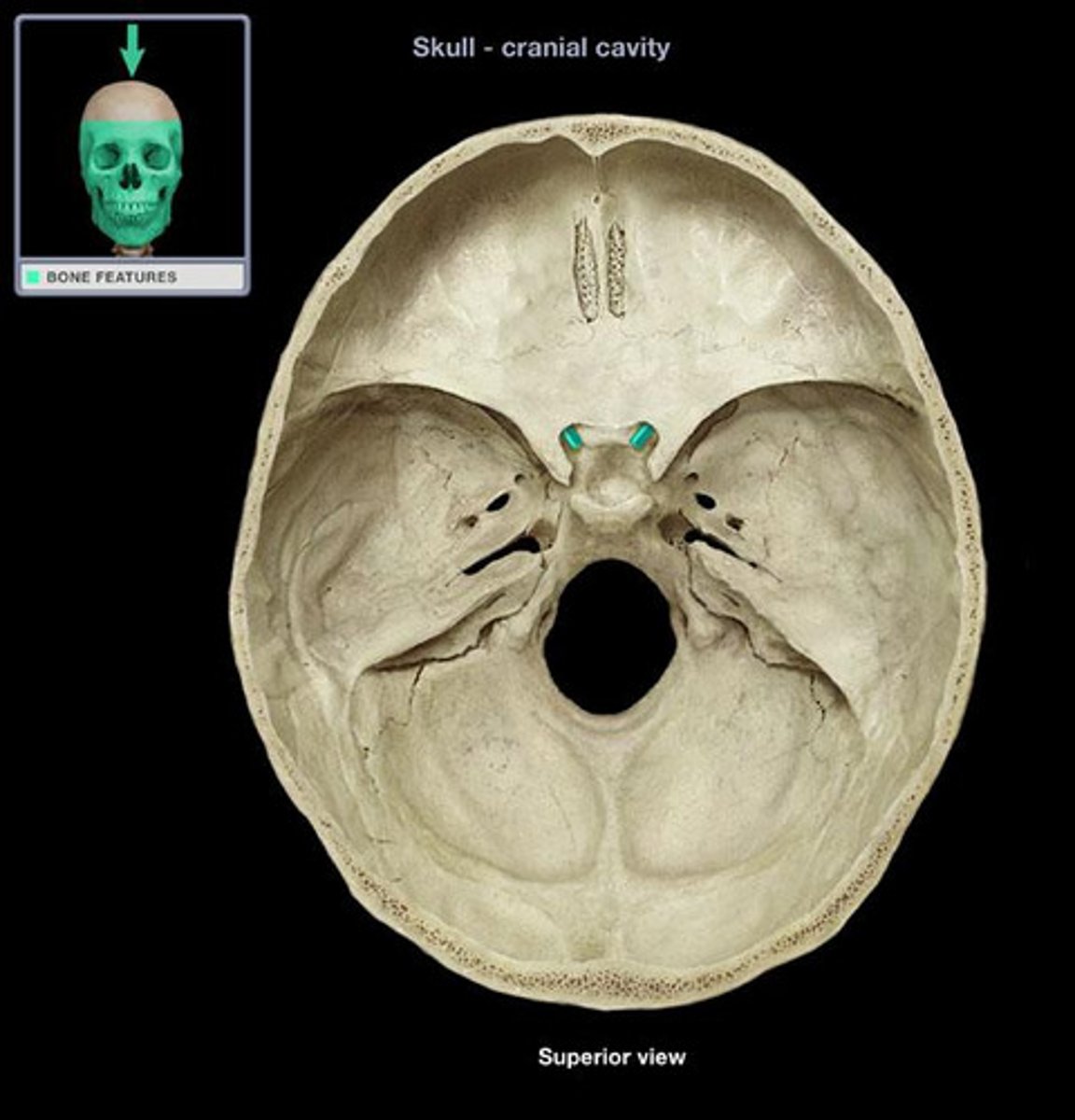
Foramen Ovale
Opening lateral to sella turcica for the passage of mandibular nerve (viewed within cranial cavity or from cranial base).
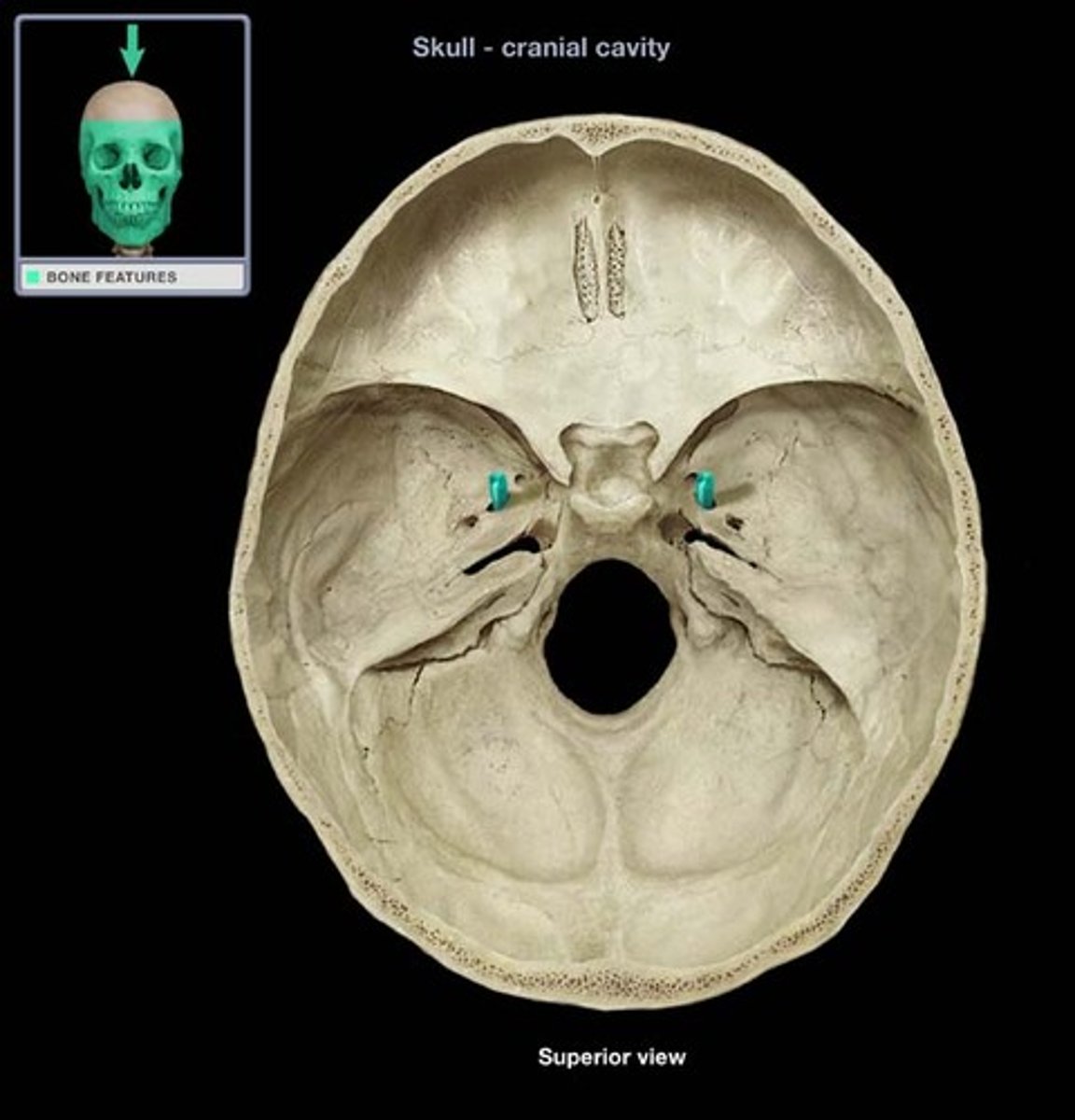
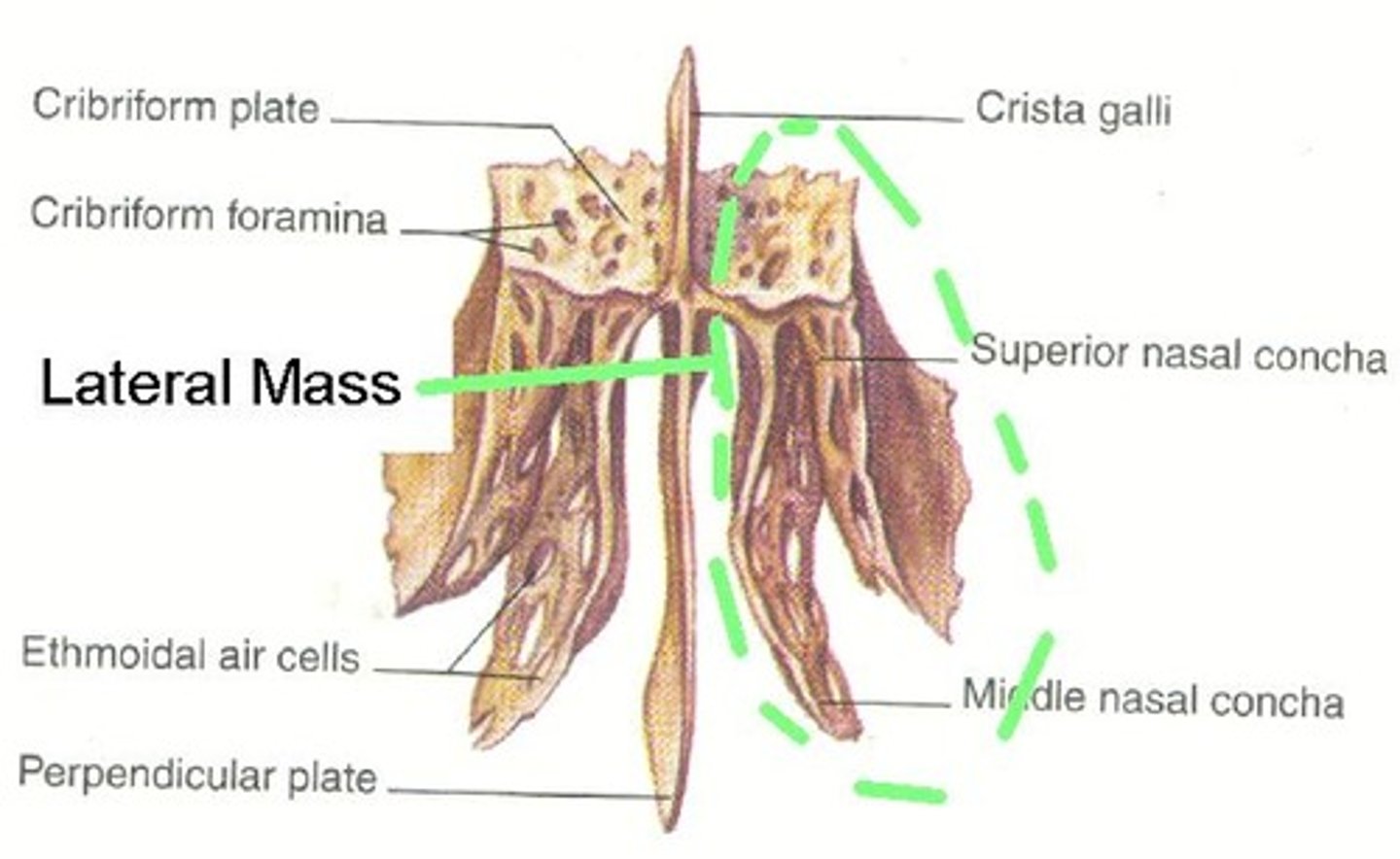
Ethmoid Bone
Located anterior to the sphenoid bone and between the orbits.
Unpaired.
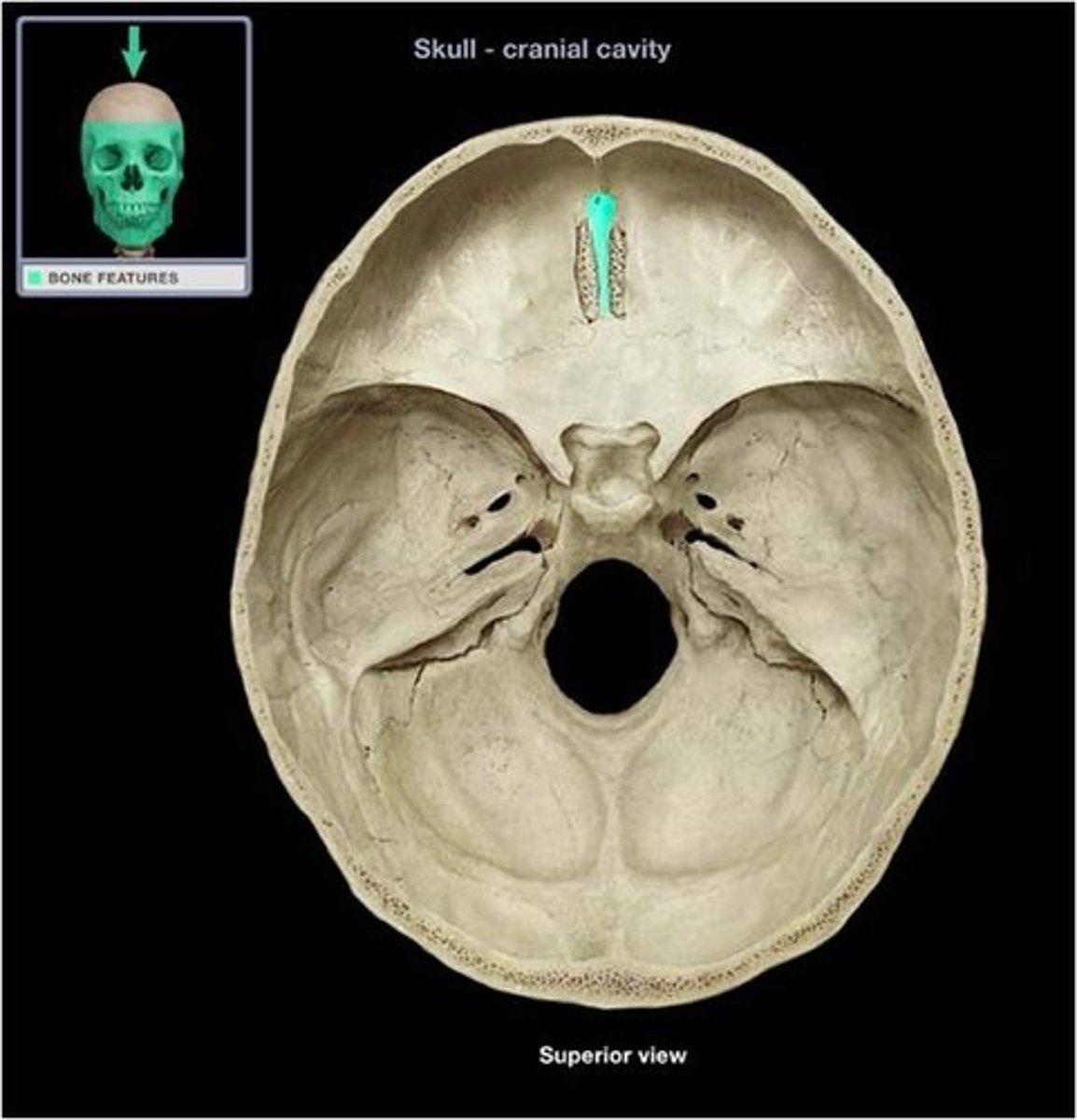
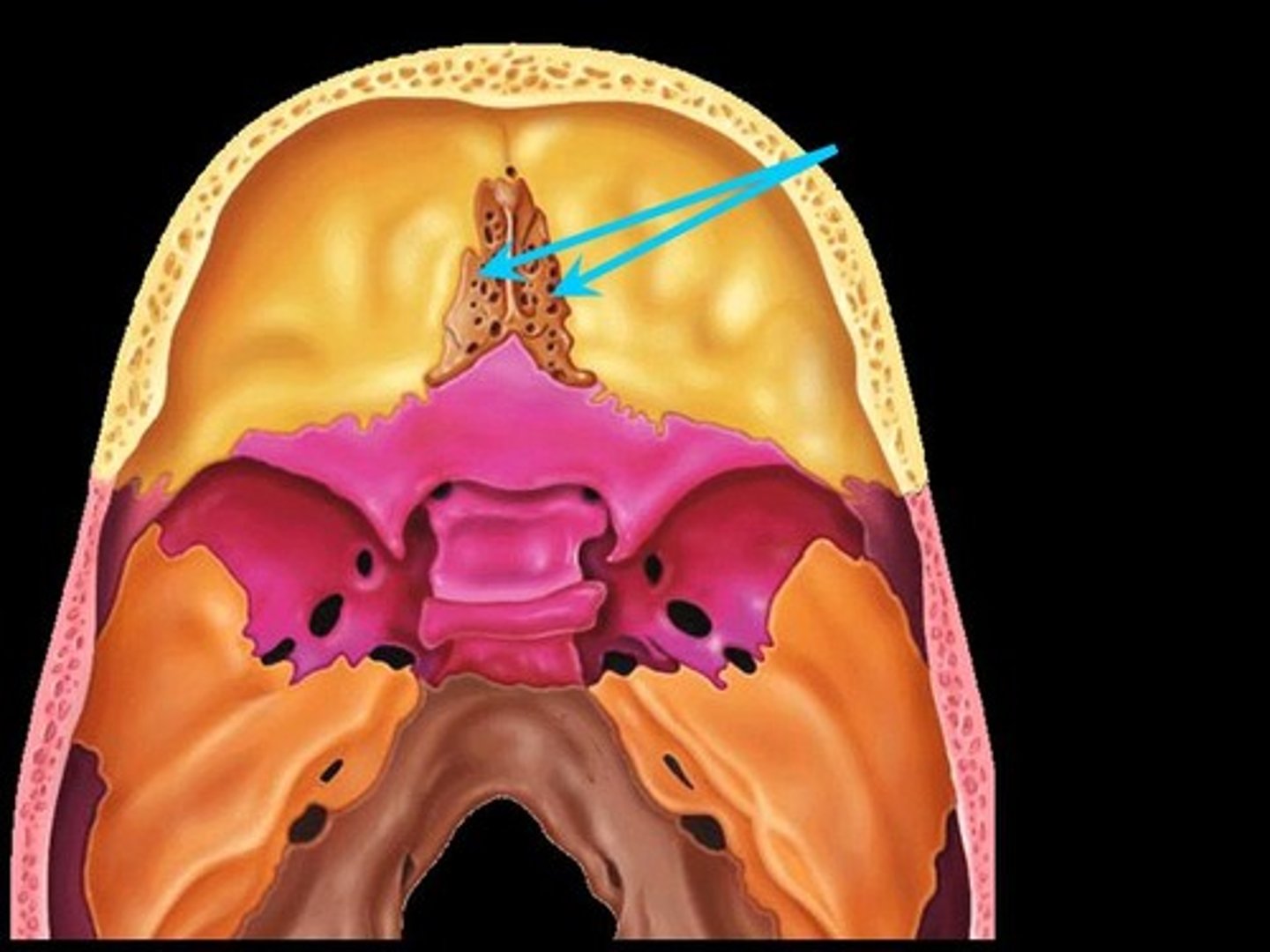
Crista Galli
Means "rooster's crest or comb". Superior projection into cranial cavity.
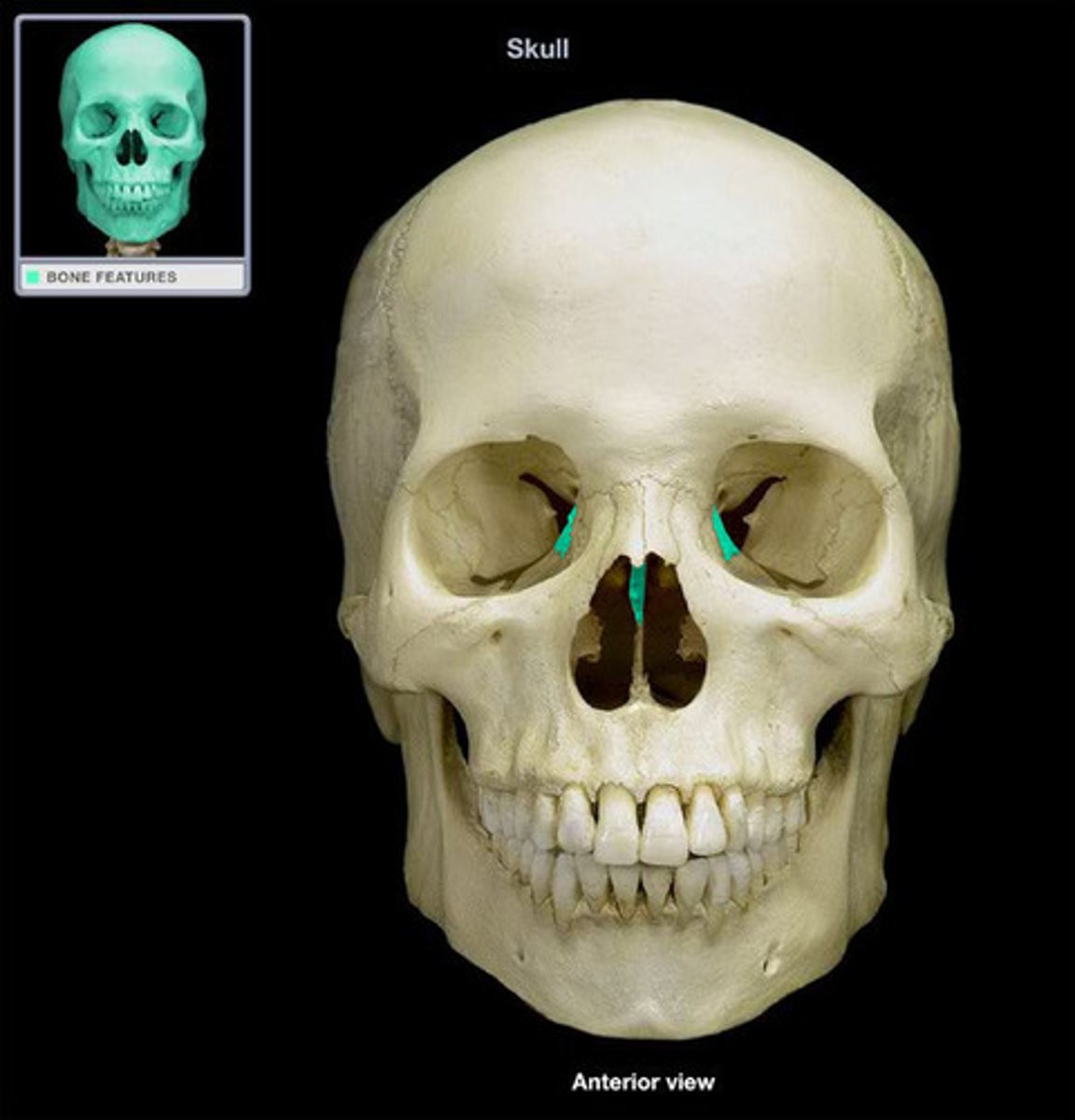
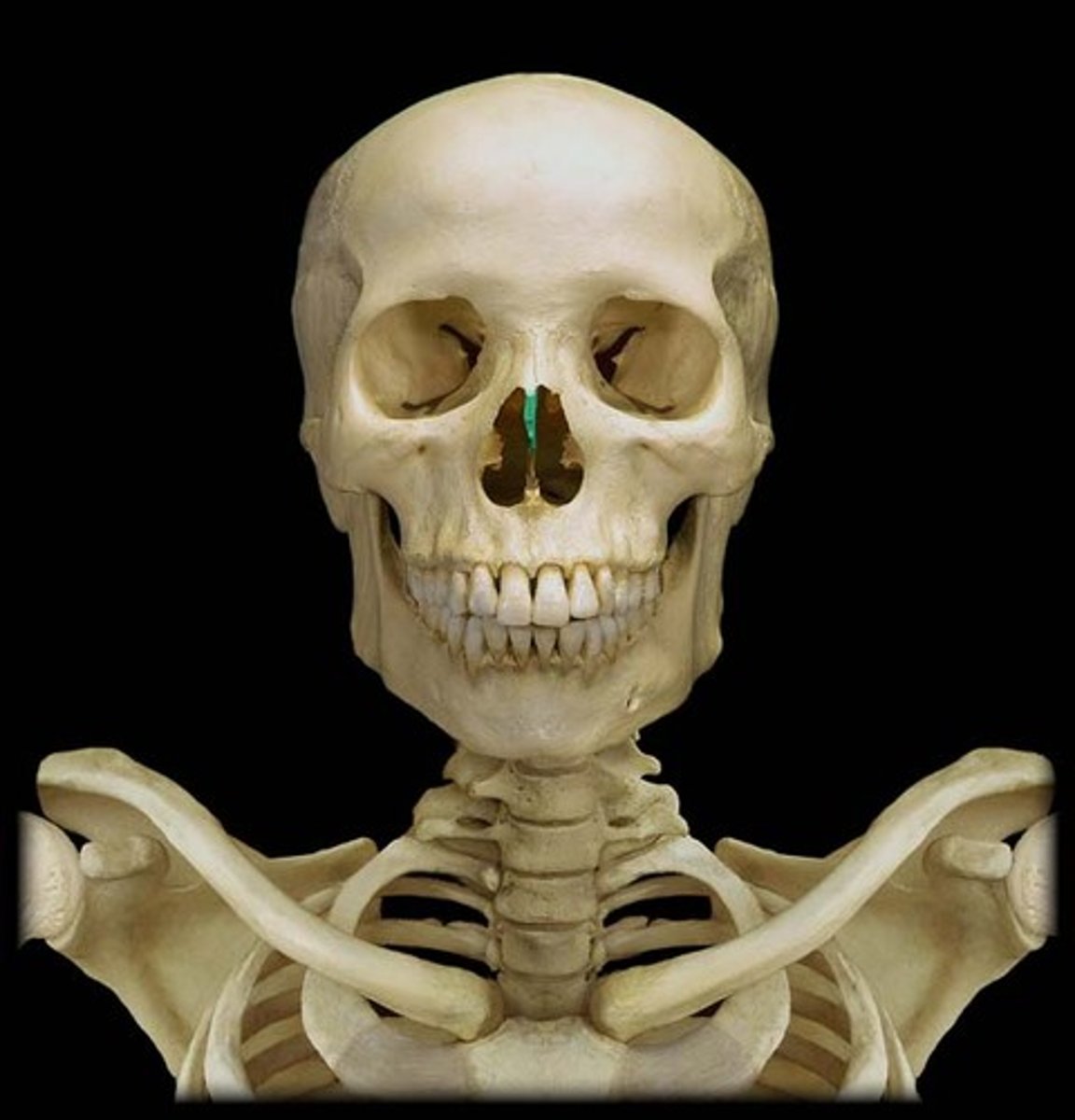
Perpendicular Plate
Inferior projection that forms the superior part of the nasal septum.
Lateral Masses
Lateral projections of the ethmoid bone, contain hollow spaces that are the ethmoid sinuses (or air cells).
Olfactory Foramina
Many small openings around Crista Galli. Passageway for olfactory nerves to enter the nasal cavity (viewed within cranial cavity).
Suture
Fibrous joints between neurocranial bones that allow for virtually no movement between bones.
Coronal Suture
Between parietal and frontal bones.
Sagittal Suture
Between left and right parietal bones.
Lambdoid Suture
Between parietal and occipital bones.
Squamosal Suture
Between parietal and temporal bones.
Fontanelles
Soft spots between neurocranial bones of an infant's skull where they have not yet fused together.
Bones are connected by membranes which are soft and later replaced by bone tissue.
They allow for more skull growth during infancy and flexibility during birth.
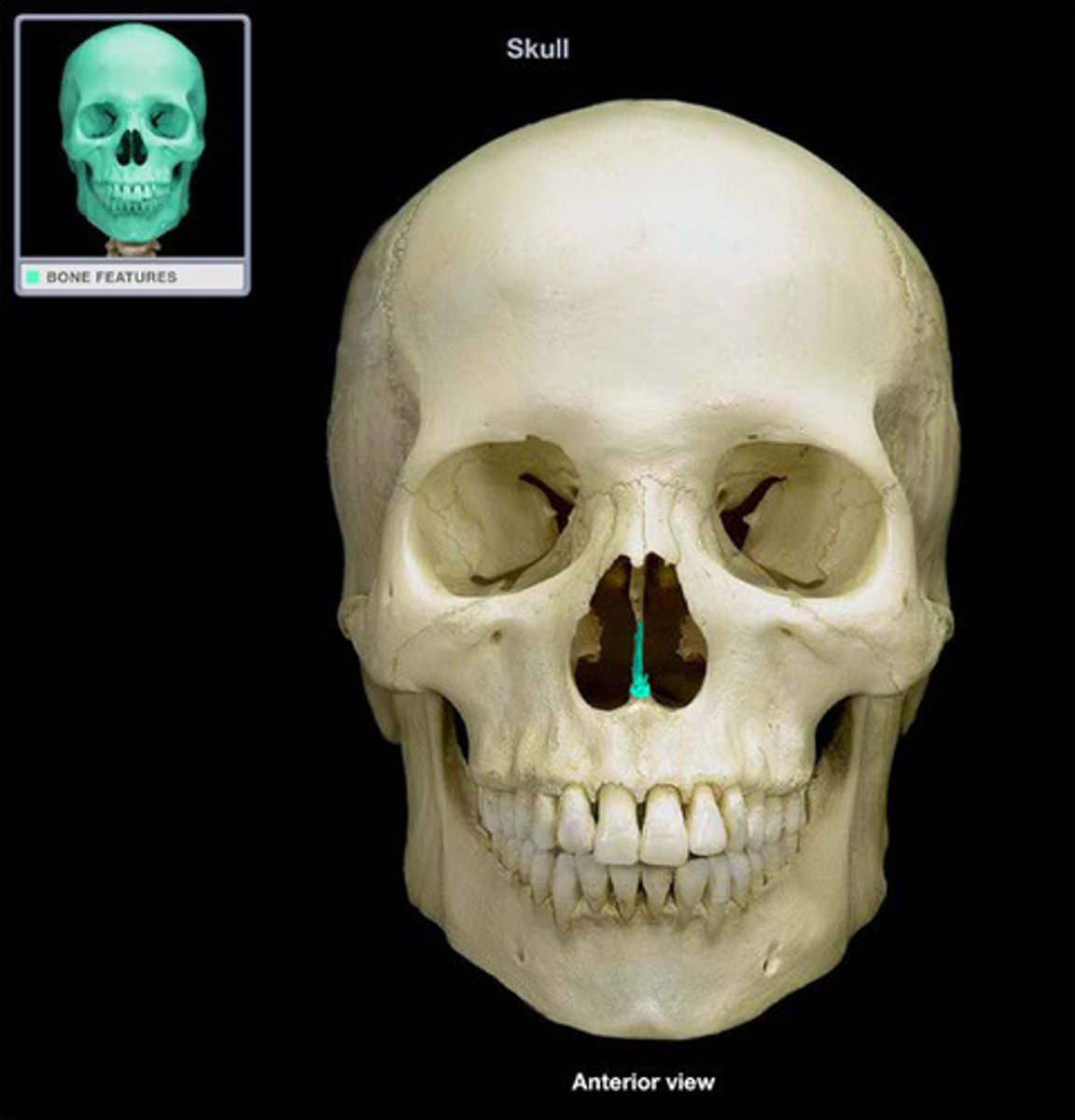
Vomer
Vertical plate that forms the inferior part of the nasal septum.
Unpaired.
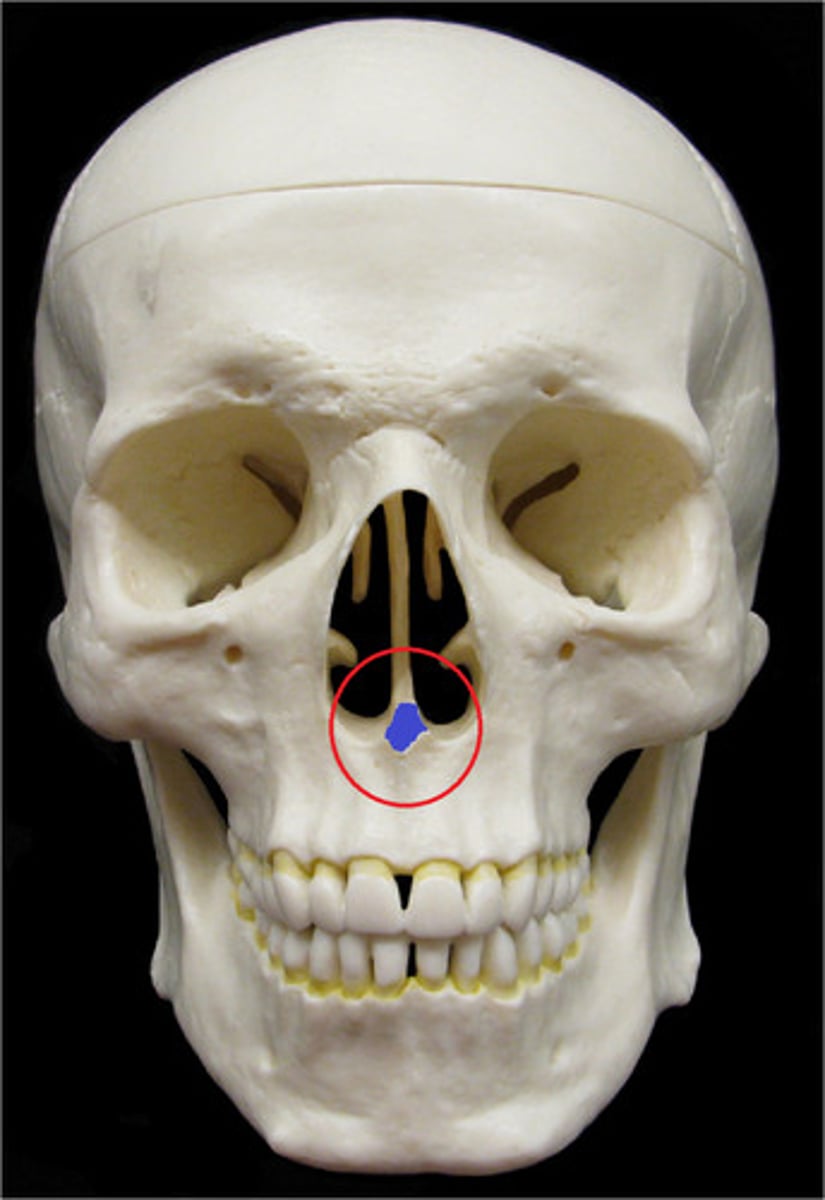
Nasal Septum
Divides the left and right spaces of the nasal cavity. It is made of cartilage anteriorly (septal cartilage) and bone posteriorly. The bony part of the septum is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and vomer.
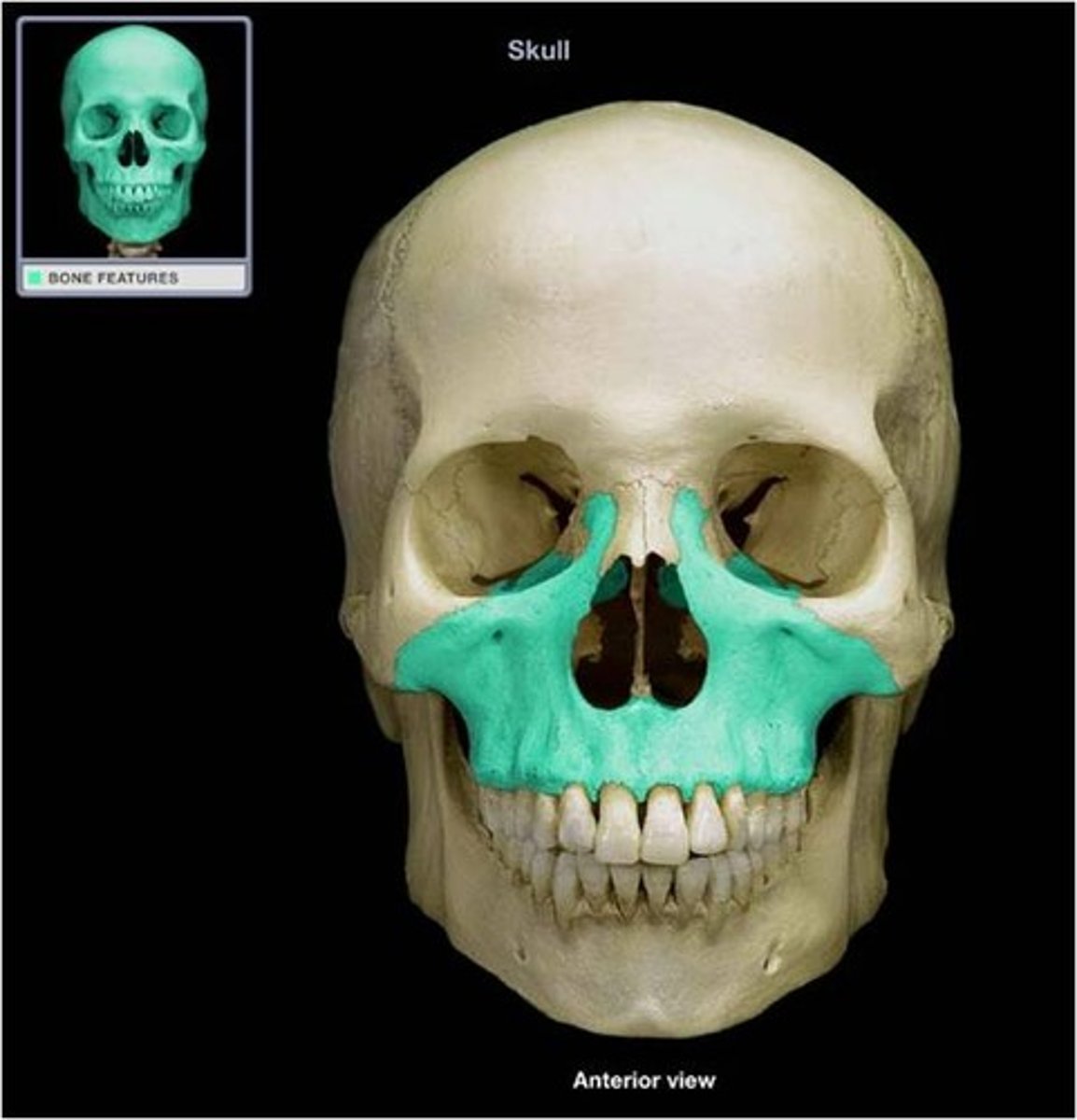
Maxilla
Upper jaw bone.
Paired.
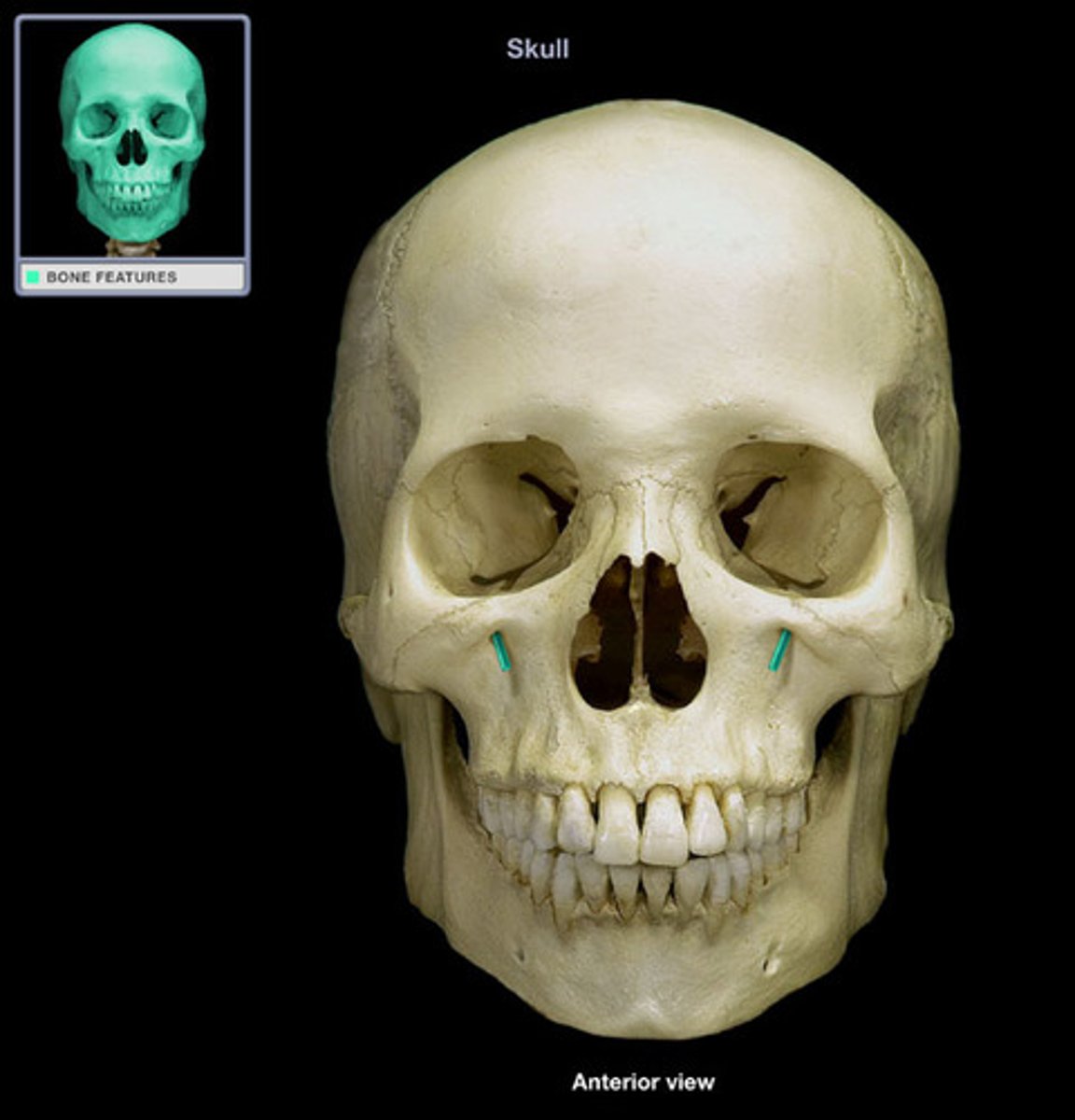
Infraorbital foramen
Opening below the orbit for nerves and blood vessels to pass onto the face.
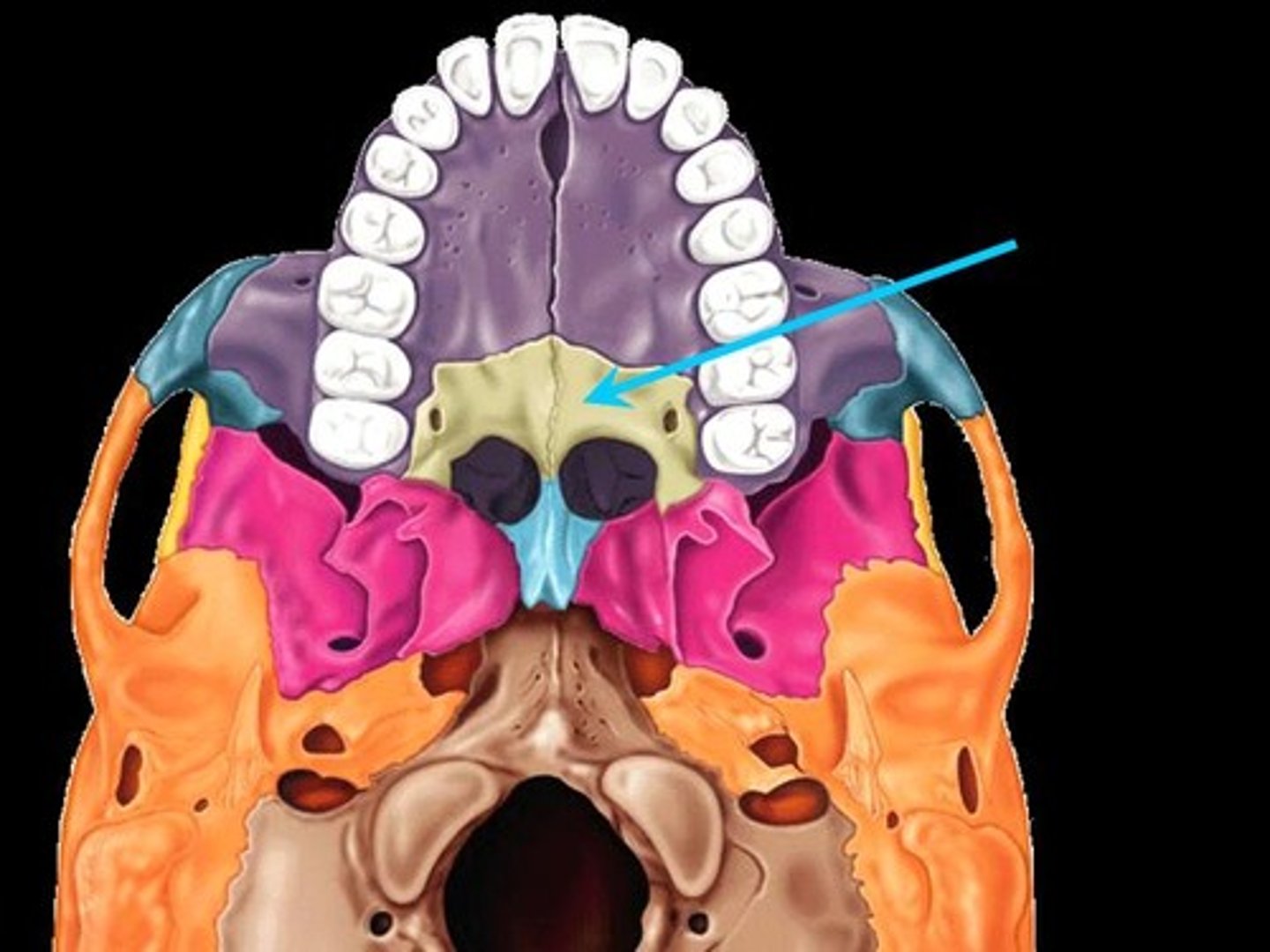
Palatine Bones
Located posterior to the maxillary bones (or maxillae). These bones articulate with the maxillae to form the hard palate.
Cleft Lip and/or Palate
Failure of the left and right palatine or maxillae to fuse together.
Zygomatic Bone
Cheek bone.
Paired.
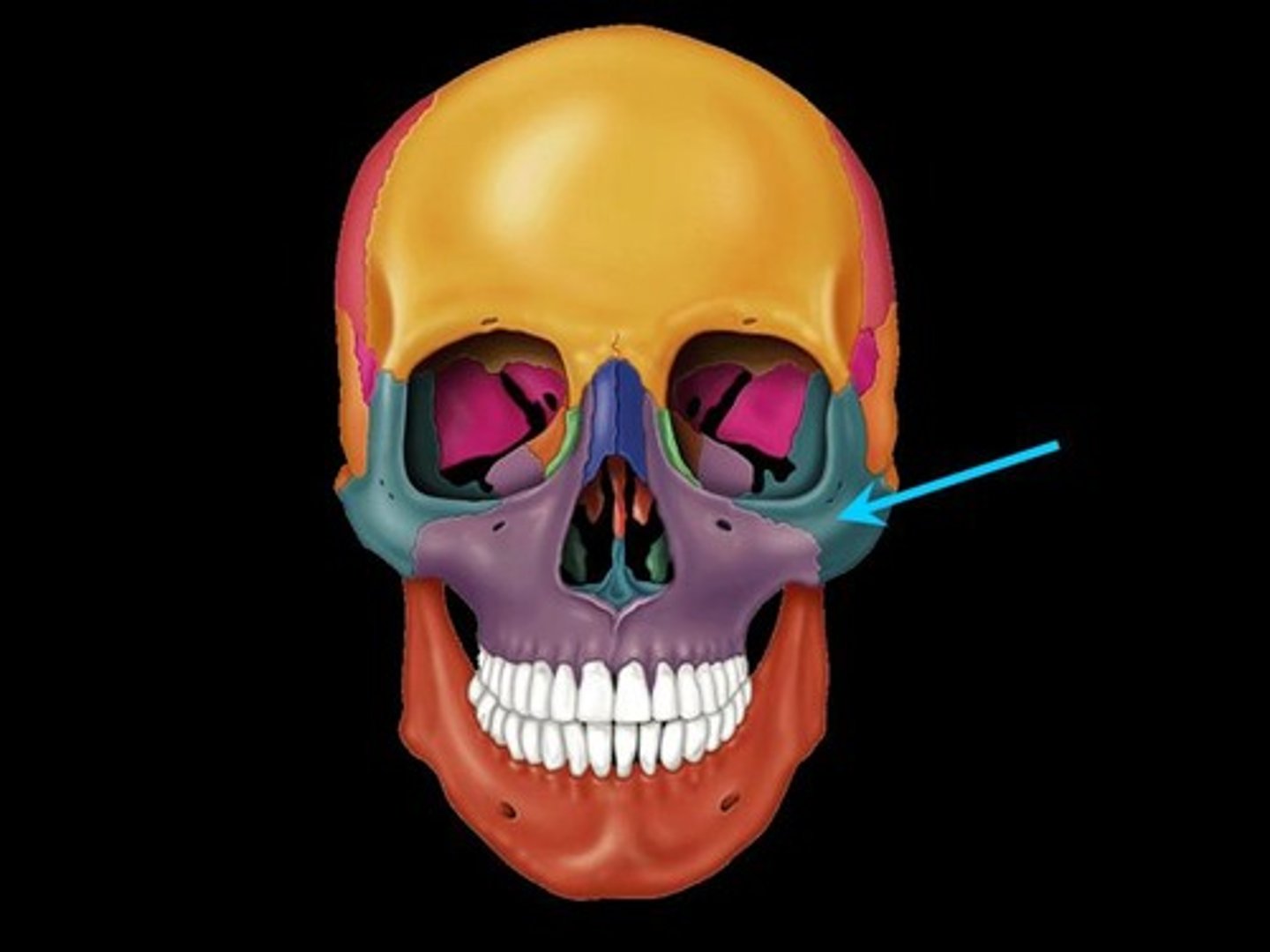
Zygomatic Arch
Projections from the zygomatic and temporal bones articulate to form the zygomatic arch.
Nasal Bones
Form the bridge of the nose.
Paired.
Lacrimal Bones
Bones at the corner of each eye that cradle the tear ducts.
Paired.
Nasolacrimal Duct
Passageway from the lacrimal bone (orbit) to the nasal cavity for the drainage of tears.
Mandible
Lower jaw bone.
Unpaired.
Ramus
Vertical portion of the mandible.
Corpus (Body)
Horizontal part of the mandible that holds the teeth.
Mandibular Condyle
Posterior projection from the ramus that articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone to form the temporomandibular joint.