Anatomy & Physiology: Body Structures, Systems, and Homeostasis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Anatomy
Describes the structures of the body.
Physiology
Is the study of functions of anatomical structures.
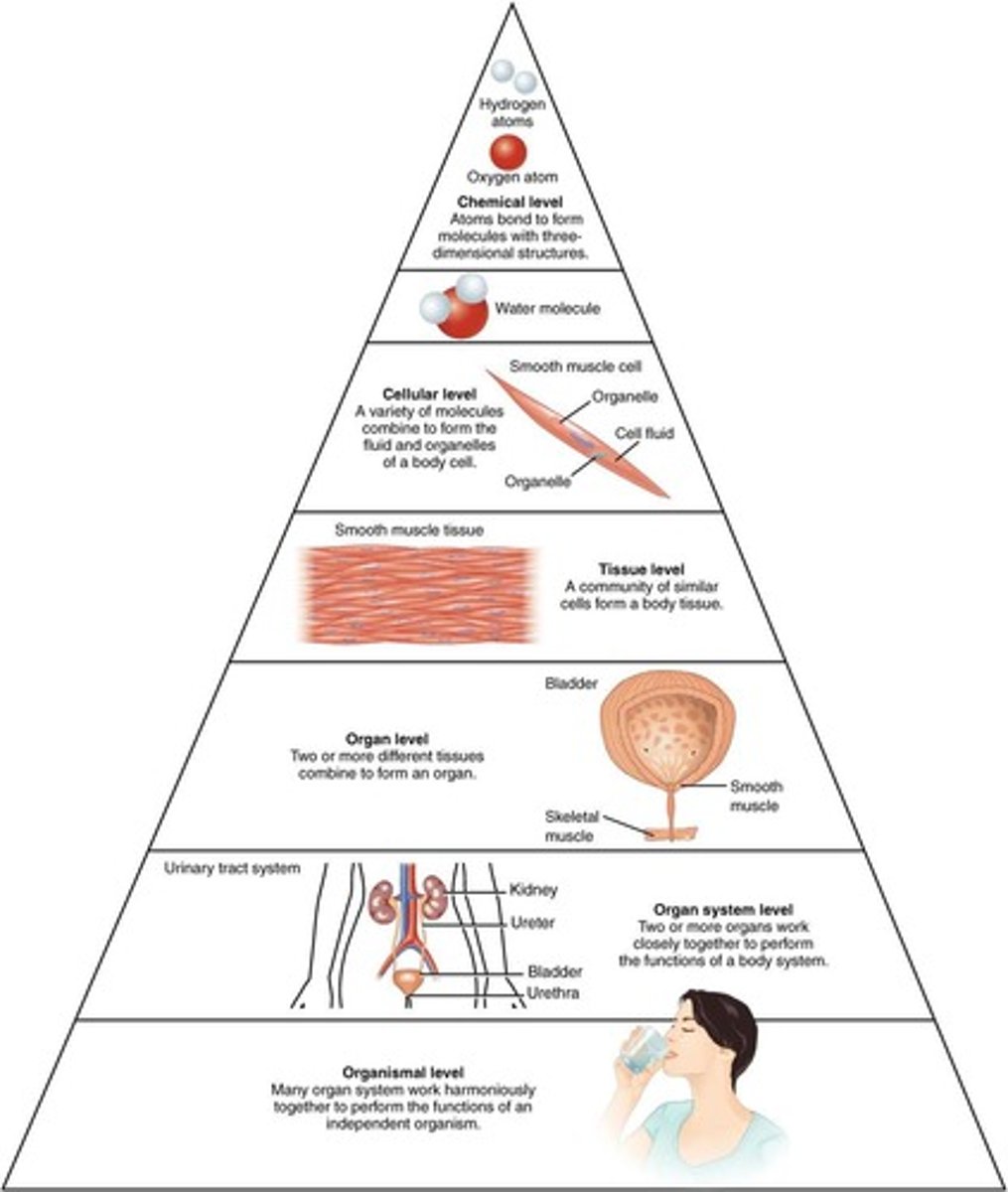
Levels of Organization
Hierarchy of biological structures from atom to system.
Anatomical Position
Hands at sides, palms forward, body erect, feet apart.
Anatomical Directions
Use to describe location of two structures on the body relative to each other.
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Divides the body into Anterior and Posterior.
Sagittal Plane
Divides the body into Right & Left.
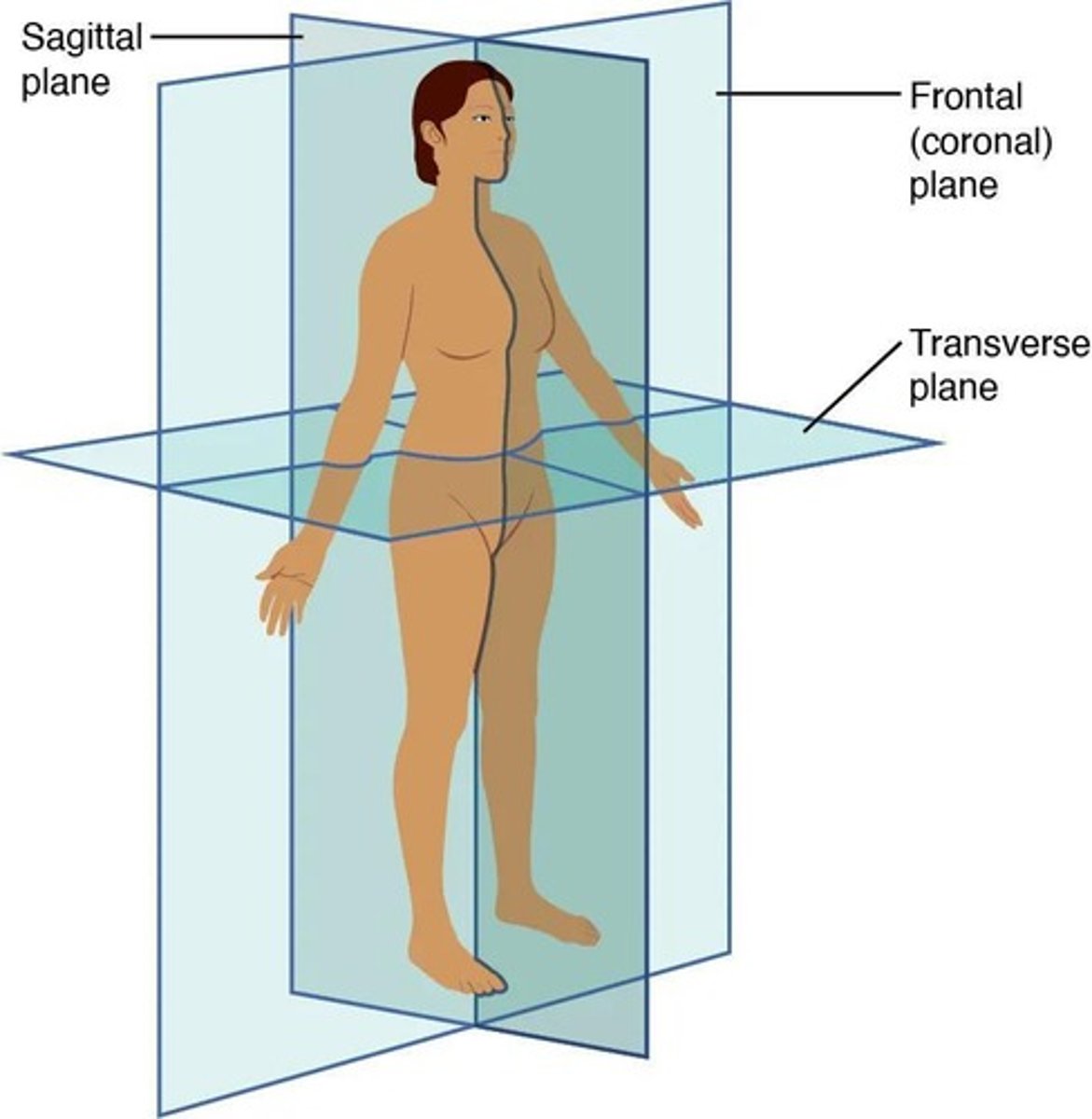
Transverse Plane
Divides the body into Superior and Inferior.
Dorsal Body Cavity
Includes Cranial and Spinal cavities, lined by meninges.
Ventral Body Cavity
Divided by the diaphragm into Thoracic and Abdominopelvic cavities.
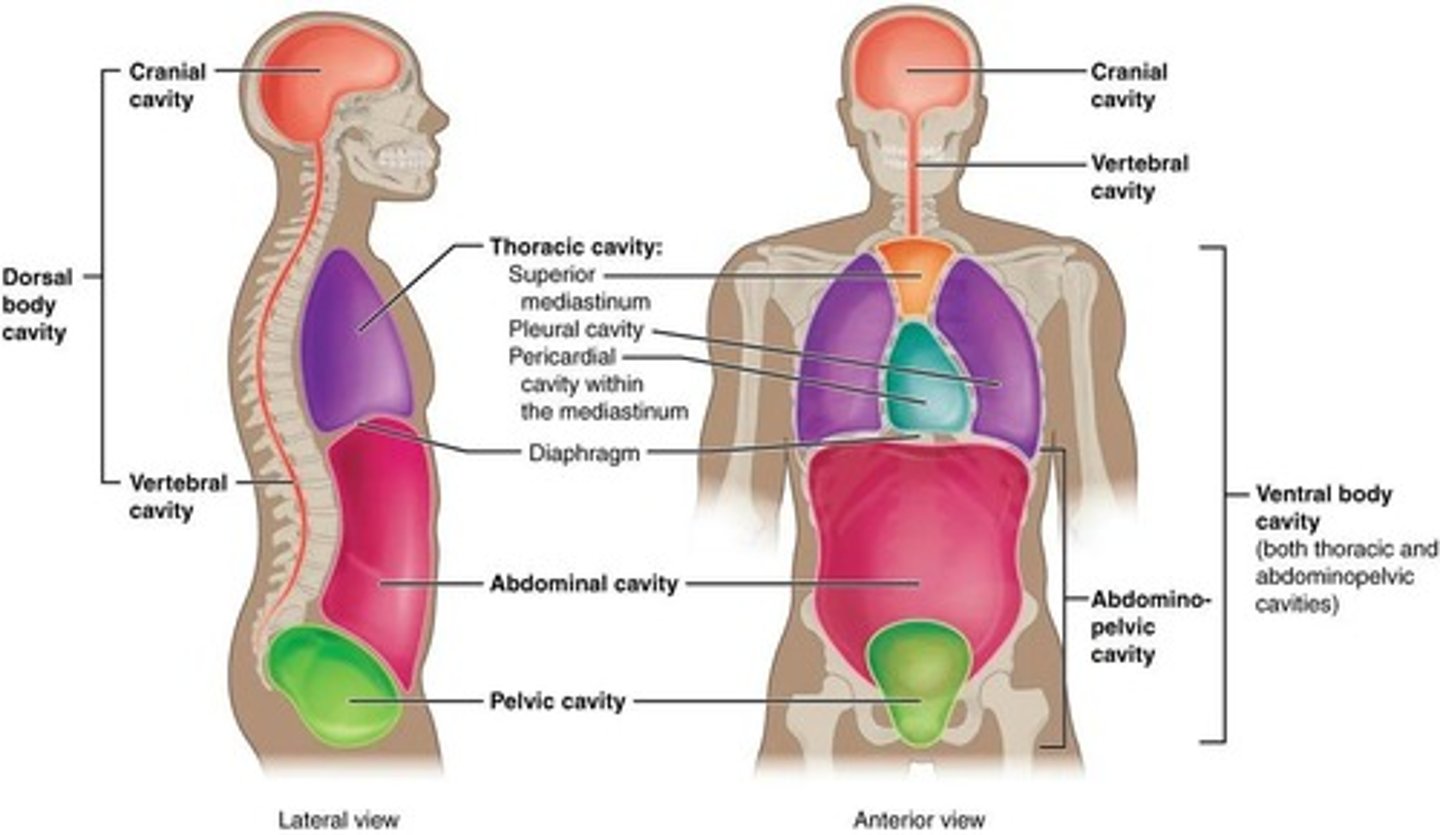
Thoracic Cavity
Contains right and left pleural cavities.
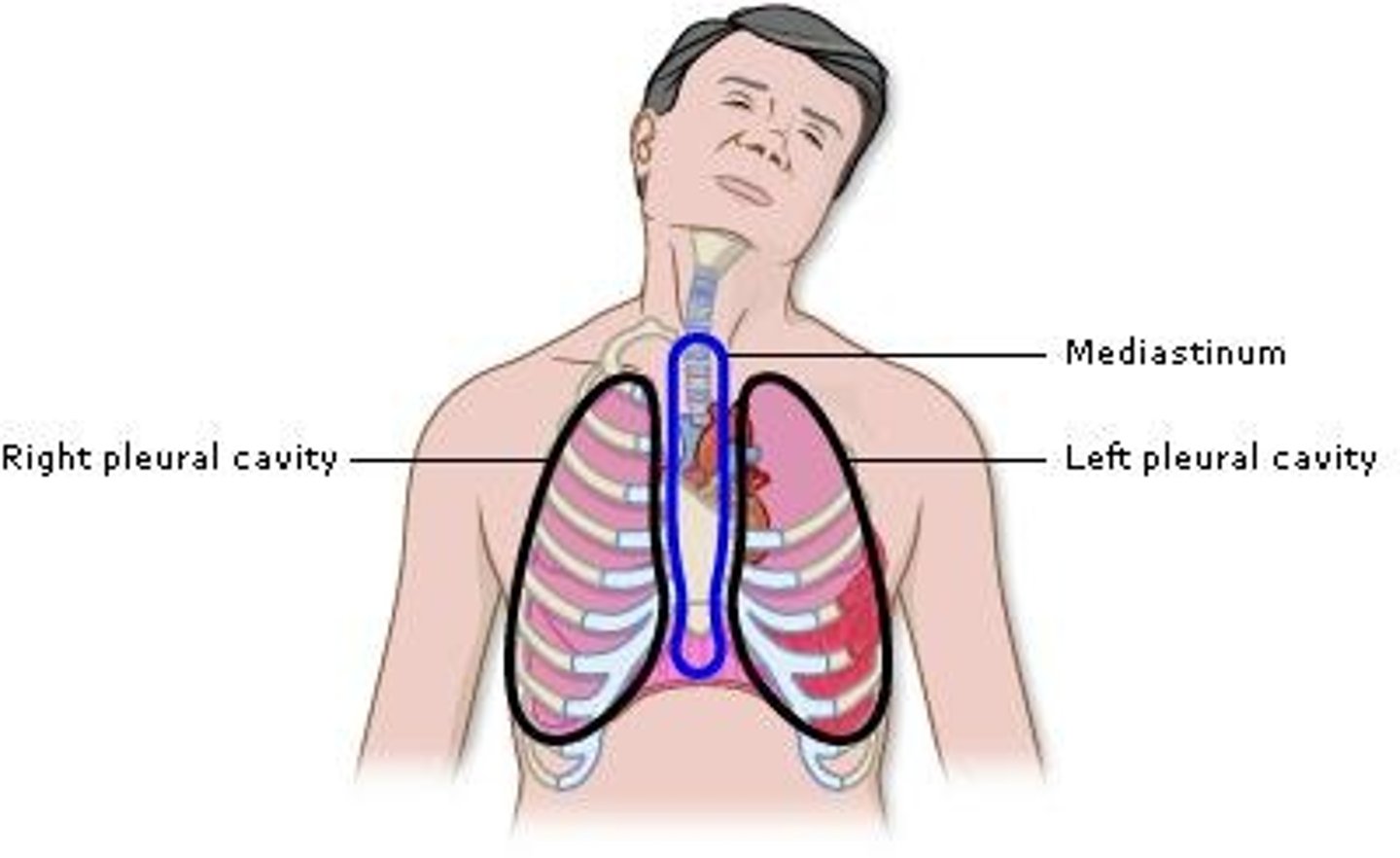
Visceral Pleura
Covers the lungs.
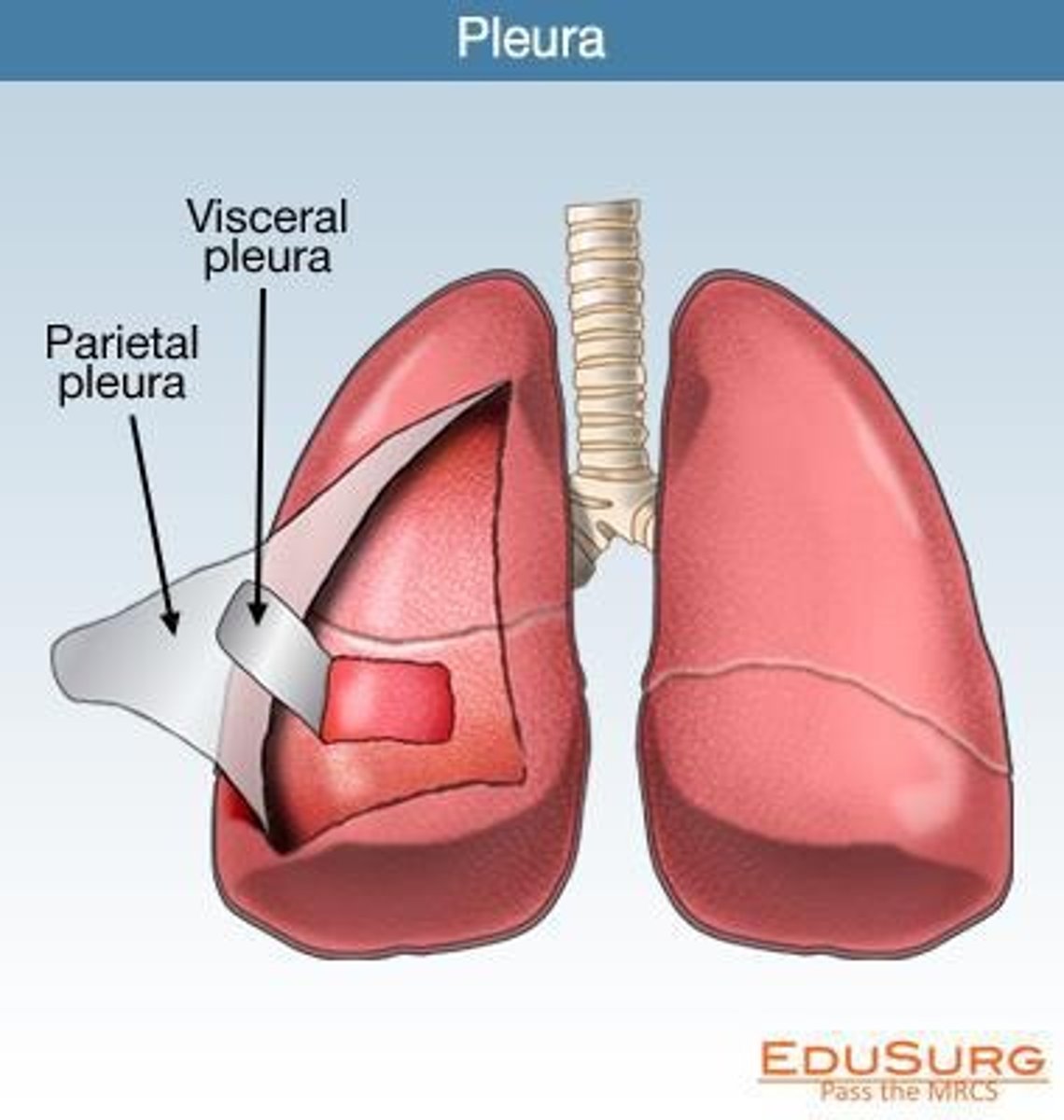
Parietal Pleura
Covers the inside of the thoracic cavity.
Parietal Peritoneum
Lines the internal body wall of the abdominopelvic cavity.
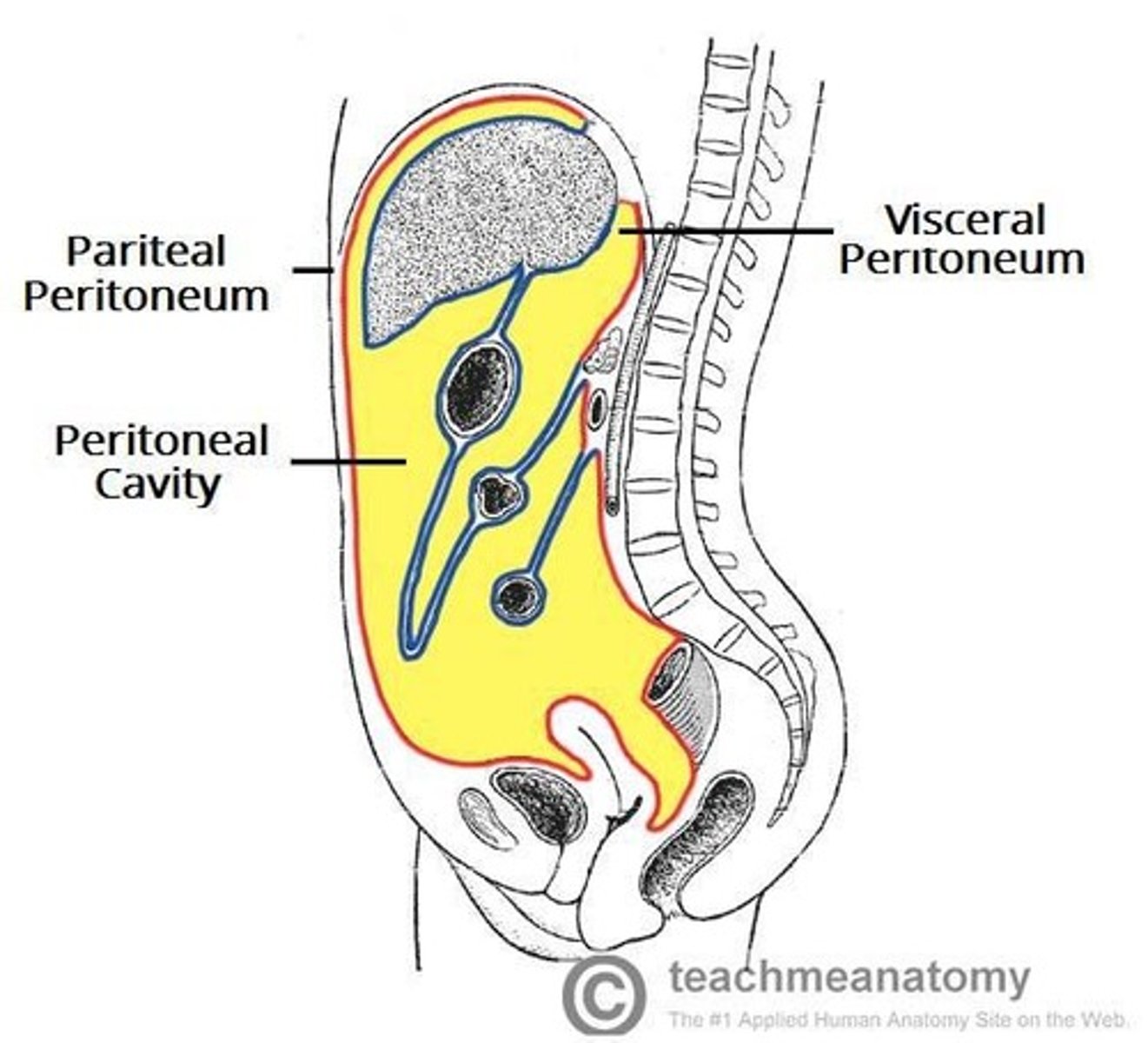
Visceral Peritoneum
Covers the organs in the abdominopelvic cavity.
Mediastinum
Contains the trachea, esophagus, thymus, and pericardial cavity.
Homeostasis
All body systems working together to maintain a stable internal environment.
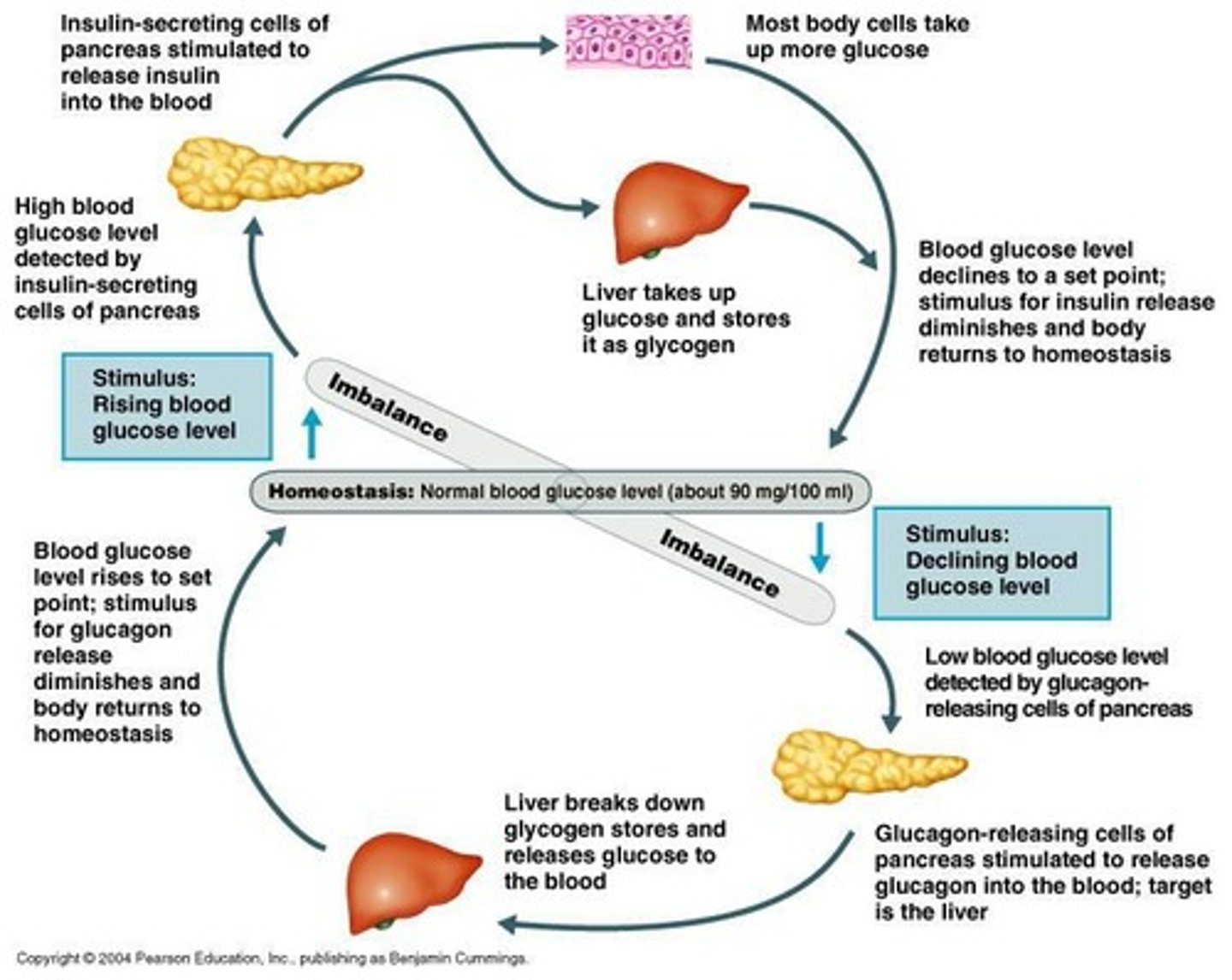
Negative Feedback
Body is brought back into homeostasis; if one thing goes up, response is to bring it down.
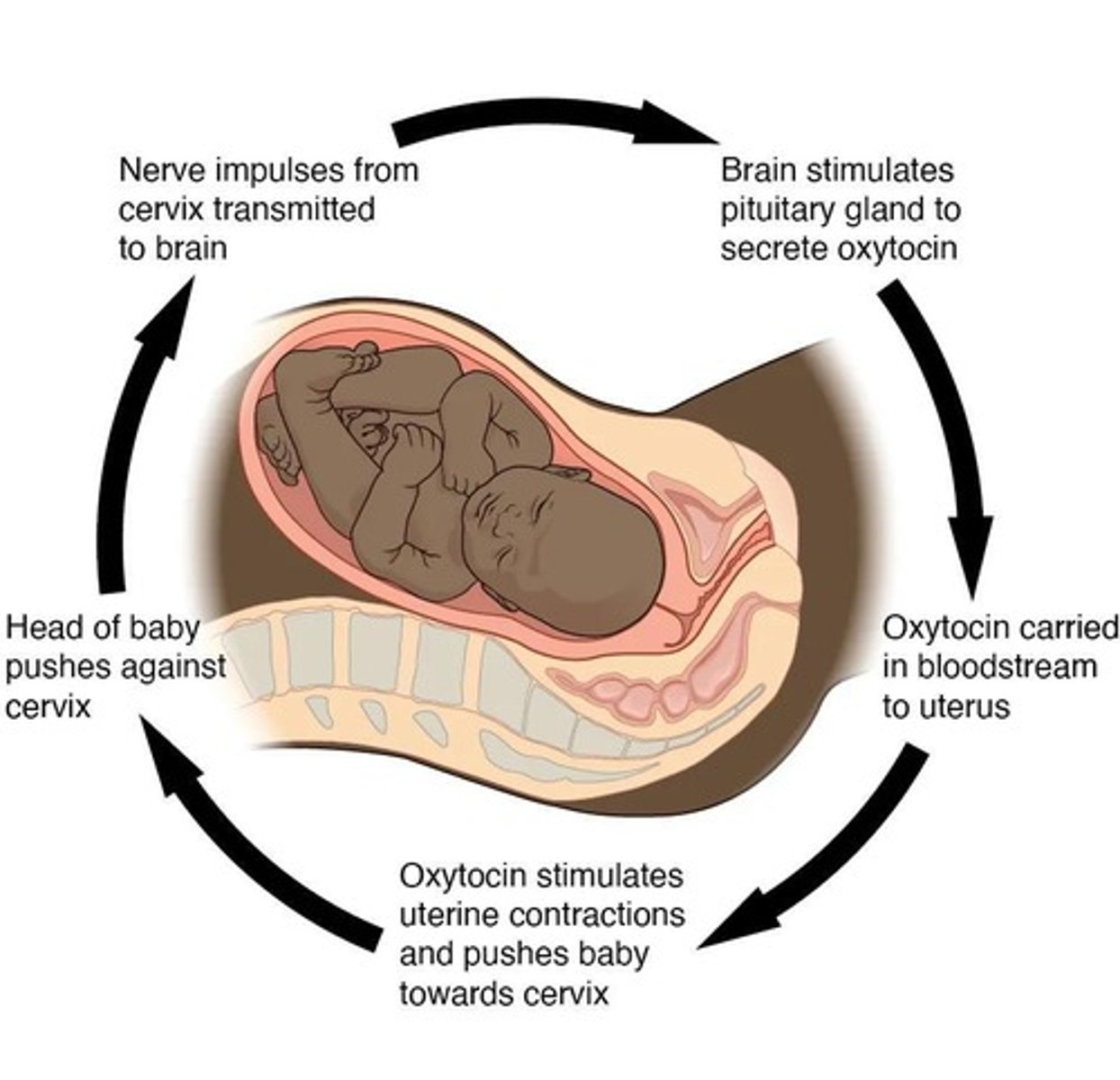
Positive Feedback
Body is moved away from homeostasis; used to speed up processes.
Insulin
Hormone that pushes blood sugar down when it gets too high.
Glucagon
Hormone that pushes blood sugar up when it gets too low.