Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Anatomy and Physiology Definition
Study of the structure and function of the body
Cytology
Study of individual cells
Histology
Study of different types of tissue
Gross Anatomy
Study of structures by sight
Levels of Anatomy
Atoms→ moleculues→ cell→ tissue→ organ→ organ system→ organism
Homeostasis
Stable normal range of function compared to the set point
Homeostasis Components
Variable→ Receptor→ Control Center (Medula Omblongata that determines if its at set point or not)→ Effector (Causes the actual change)→ Effects the variable.
Negative Feedback
Getting back to the set point/homeostasis. most common and self terminating.
Positive Feed Back
Magnifies the original stimulus (Child birth and blood clot example)
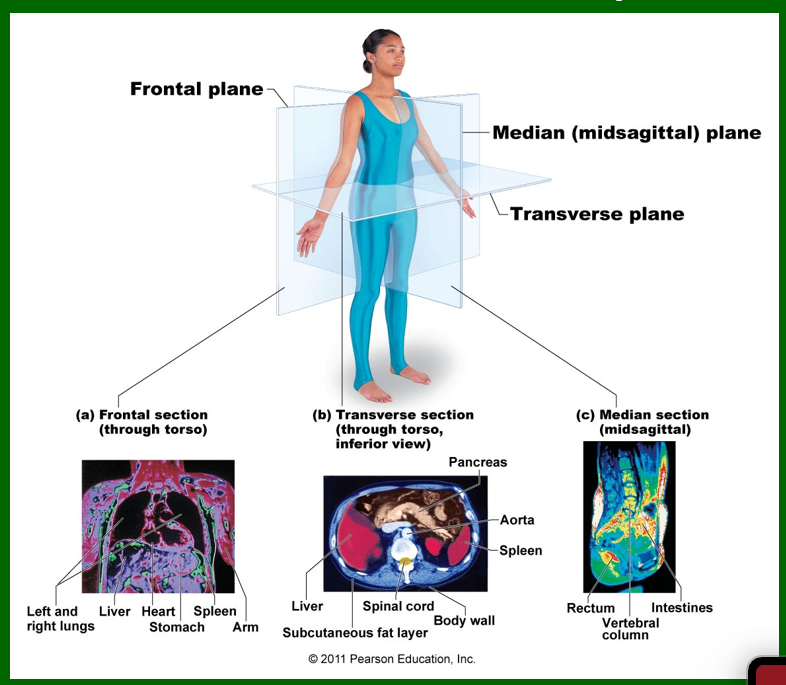
Planes of the Body
Frontal Plane: Front and Back
Transverse Plane: Top and Bottom
Midsaggital Plane: Right and Left
Body Cavities
Dorsal Cavities: Cranial Cavity- contains brain, Vertebral Cavity- contains spinal cord
Ventral Cavities: Thoracic Cavity- contains heart and lungs, Abdominal Cavity- contains digestive viscera, Pelvic Cavity- contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs and rectum
Thoracic Cavity- Superior mediastinum , Pleural Cavity, Pericardial Cavity
Directional Terms (13)
Superior: above
Inferior: Below
Superfacial: Close
Ventral: in front of
Dorsal: behind
Anterior: Towards Belly
Posterior: Towards Spine
Medial: Towards the center
Distal: LIMBS that are far
Proximal: LIMBS that are close
Deep: Deep
Lateral: Towards the outside of the body
Intermediate: BETWEEN two structures