BY 124- Gibbons Ch 29- Plant Diversity I - How Plants Colonized Land
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Plants evolved from Green Algae and gained adaptations to move onto land like ______________.
Sporopollenin
A complex and highly resistant biopolymer found in the walls of spores and pollen grains of plants, algae, and some fungi. It is one of the most chemically inert organic substances known in nature. Here are its key characteristics and roles:
Chemical Composition: Sporopollenin is primarily composed of long-chain fatty acids and phenolic compounds. The exact composition can vary slightly depending on the species producing it.
Physical Properties: Sporopollenin is extremely resistant to chemical and biological degradation. It is insoluble in common organic solvents and acids, making it highly durable.
Function: Sporopollenin serves several important functions:
Protection: It provides a tough and resilient outer layer (exine) for spores and pollen grains, protecting them from environmental stresses such as desiccation, UV radiation, and microbial attack.
Pollen Dispersal: In plants, sporopollenin helps facilitate the dispersal of pollen grains by wind, water, or animals. Its tough outer layer ensures that pollen grains can withstand the rigors of transport to reach female reproductive structures for fertilization.
Survival: Sporopollenin also plays a role in the preservation of pollen and spores over geological timescales, contributing to their fossilization and aiding in the study of ancient plant species and environmental conditions.
Sporopollenin- deep dive
Five key derived traits appear in nearly all plants but are absent in the charophytes:
Alternation of generations.
Multicellular, dependent embryos
Walled spores produced in sporangia
Multicellular gametangia
Apical meristems
Phyla/Classifications of Extant Plants include
Nonvascular Plants (Bryophytes)
Vascular Plants; seedless (spore-bearing)
Vascular Plants; seed-producing (Chapter 30)
Plant and algae evolutionary tree
All developed from ancestral alga
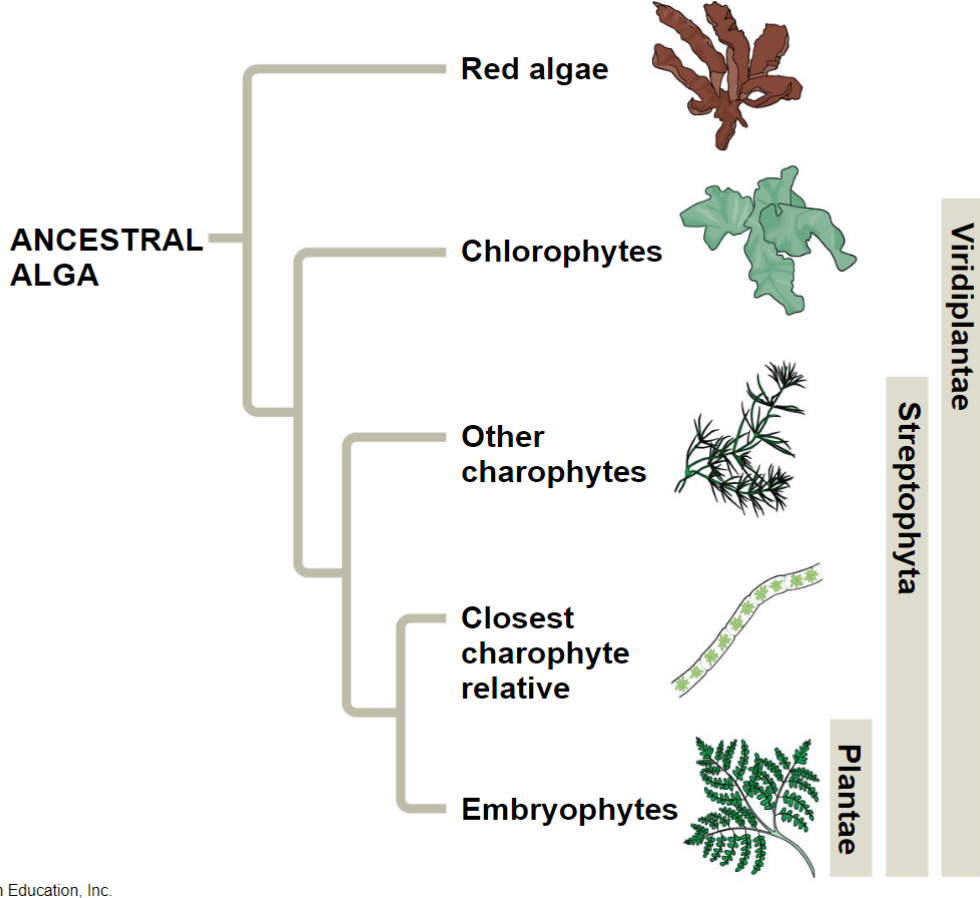
Green algae; closest relative to plants
Charophytes
Plants share ancestral characteristics like:
Chloroplasts with chlorophyll a and b
Rings of cellulose-synthesizing proteins
Structure of flagellated sperm
Charophytes are plants
A. True
B. False
B. False
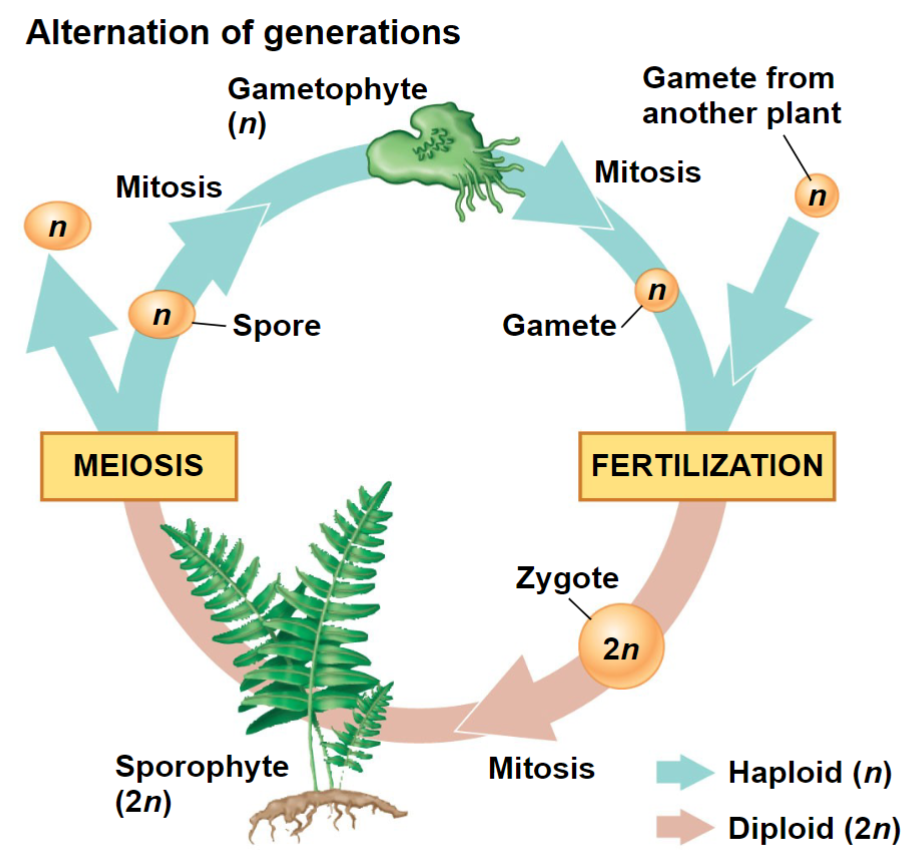
Alternation of generations
Plants alternate between two multicellular
generations, a reproductive cycle called alternation
of generationsThe gametophyte generation is haploid and
produces haploid gametes by mitosisFusion of a sperm and egg gives rise to the diploid sporophyte, which produces haploid spores by
meiosisSpores develop into gametophytes
Which of the following is NOT true of meiosis in plants?
A. Meiosis is the process of a diploid cell dividing into haploid cells.
B. Meiosis results in the production of spores.
C. Meiosis results in the production of gametes.
D. The direct result of meiosis develops into a gametophyte.
C. Meiosis results in the production of gametes.
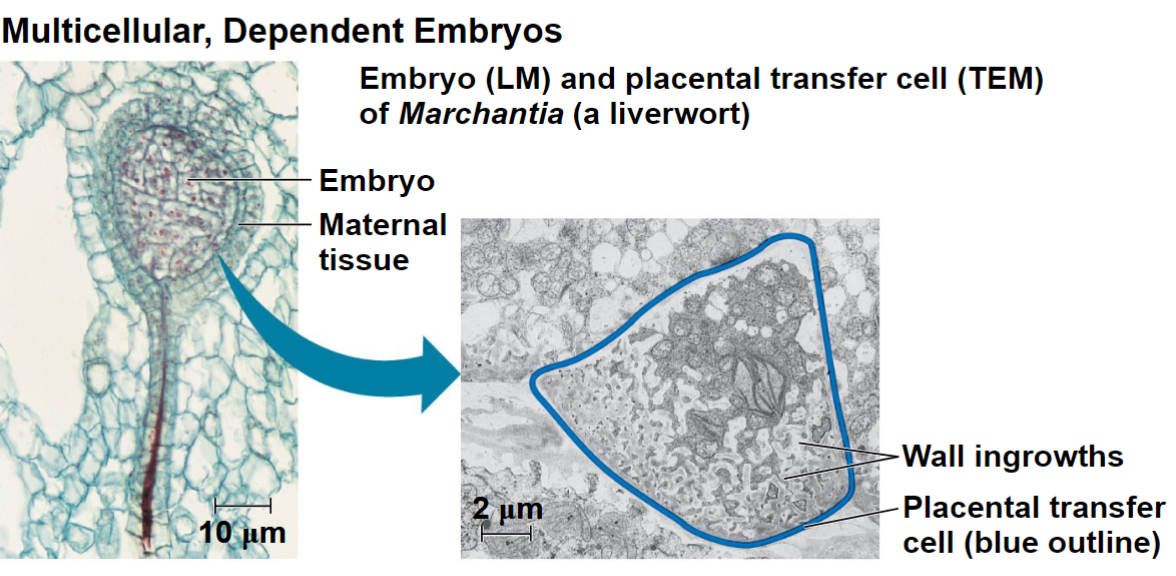
Multicellular, dependant embryos
The diploid embryo is retained within the tissue of the female gametophyte.
Plants are called embryophytes
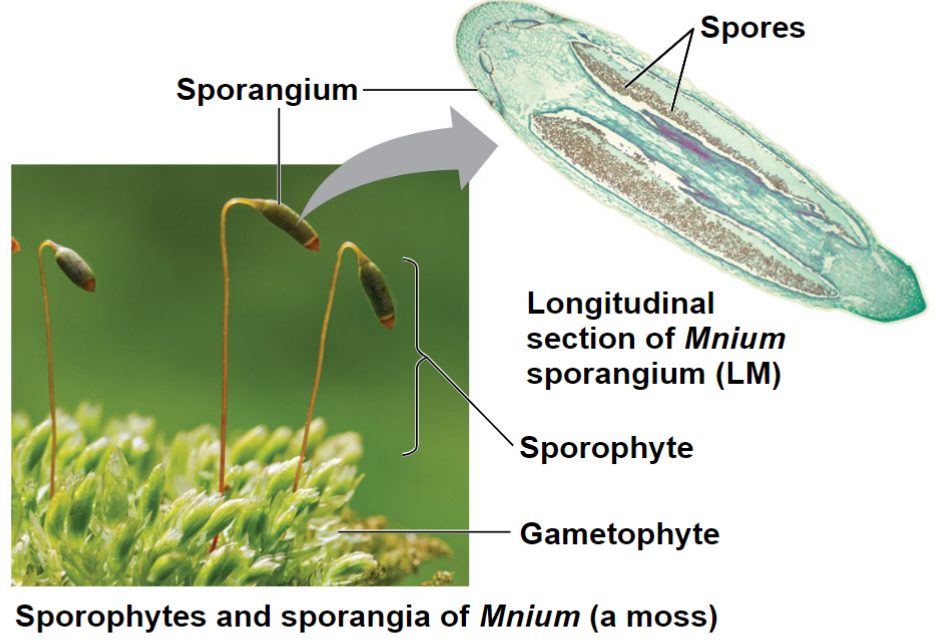
Walled Spores Produced in Sporangia
Sporangia- stage of the plant life cycle with multicellular organs
Spores- Produced by sporangia
Multicellular gametangia
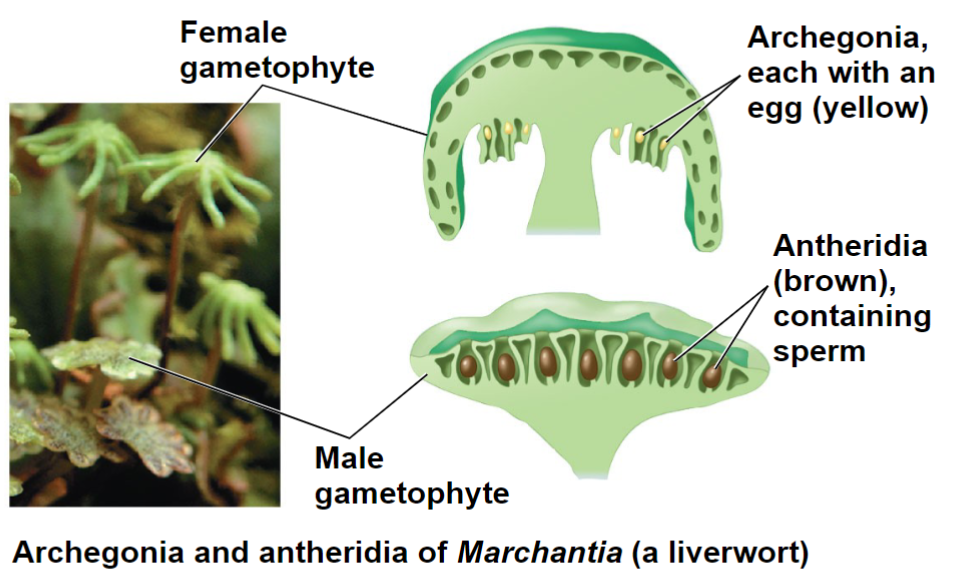
Which of the following groups is correctly ranked, from largest to
smallest structure within a plant?
A. Female gametophyte, archegonia, egg
B. Male gametophyte, archegonia, sperm
C. Female gametophyte, antheridia, egg
D. Male gametophyte, antheridia, egg
A. Female gametophyte, archegonia, egg
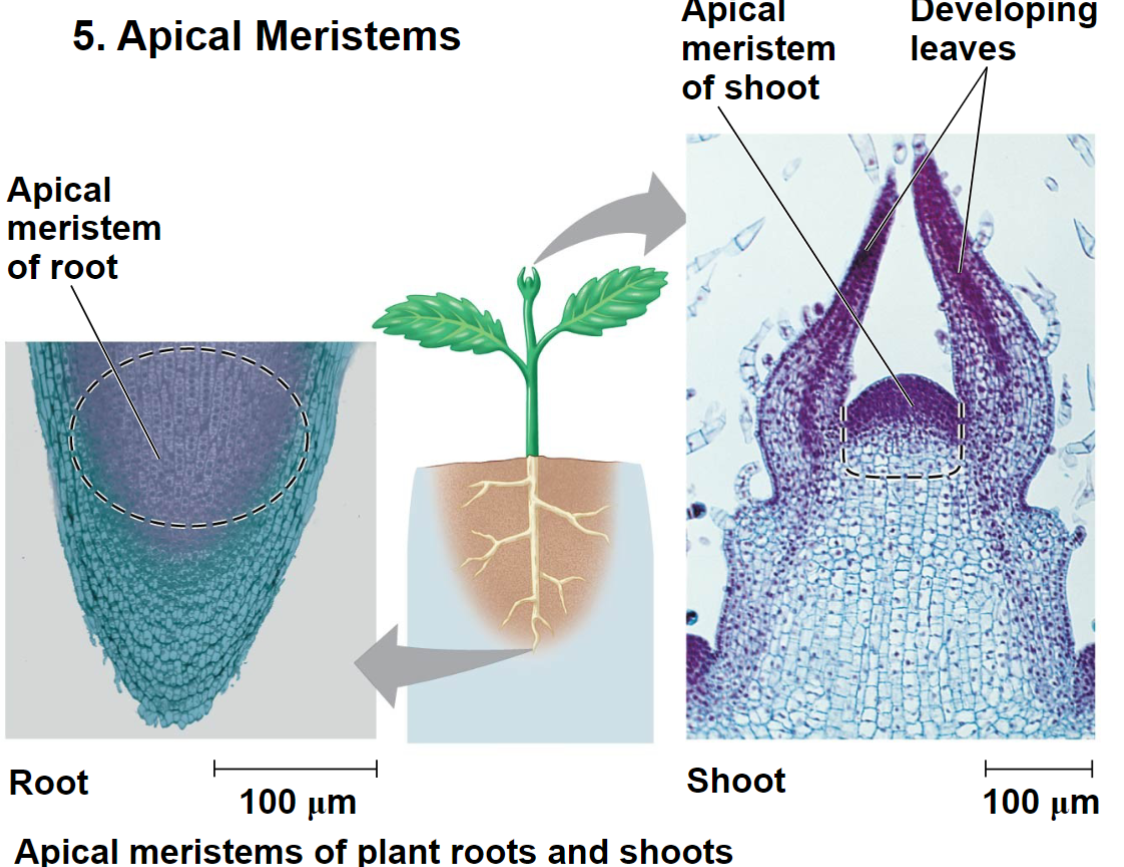
Apical meristem
Localized region of the cell at the tips of the roots. They enable roots and shoots to elongate, increasing the plants exposure to environmental resources
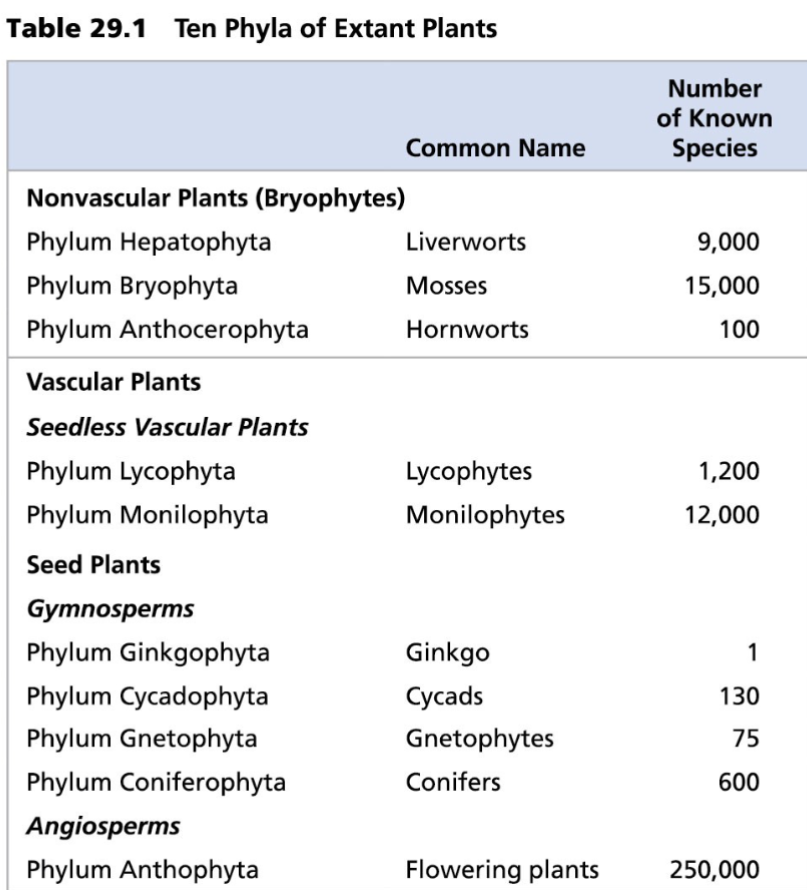
10 Phyla of Extant Plants
Non-vascular, spore-bearing plants (Bryophytes)
Hepatophyta
Bryophyta
Anthocerophyta
Vascular, seedless plants
Lycophyta
Monilophyta
Vascular, seed-bearing gymnosperms
Ginkgophyta
Cycadophyta
Gnetophyta
Coniferophyta
Vascular, seed-bearing angiosperms
Anthophyta
Evolutionary tree of plants
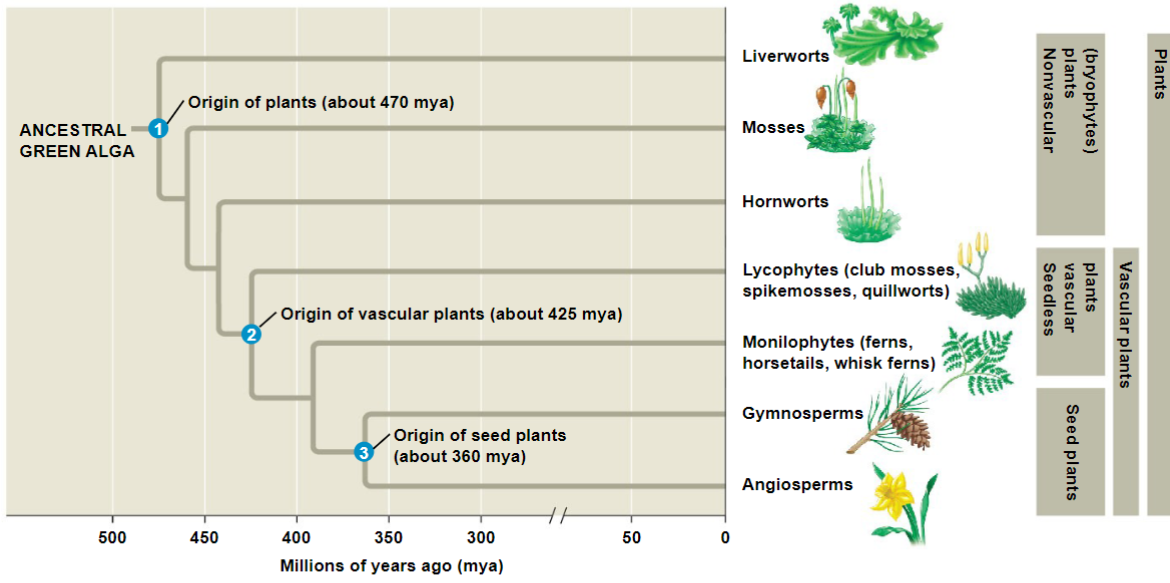
Non-vascular, spore-bearing plants are also called/belong to
Bryophyta

According to this phylogeny, are nonvascular plants a clade/monophyletic group?
A. Yes
B. No
B. No
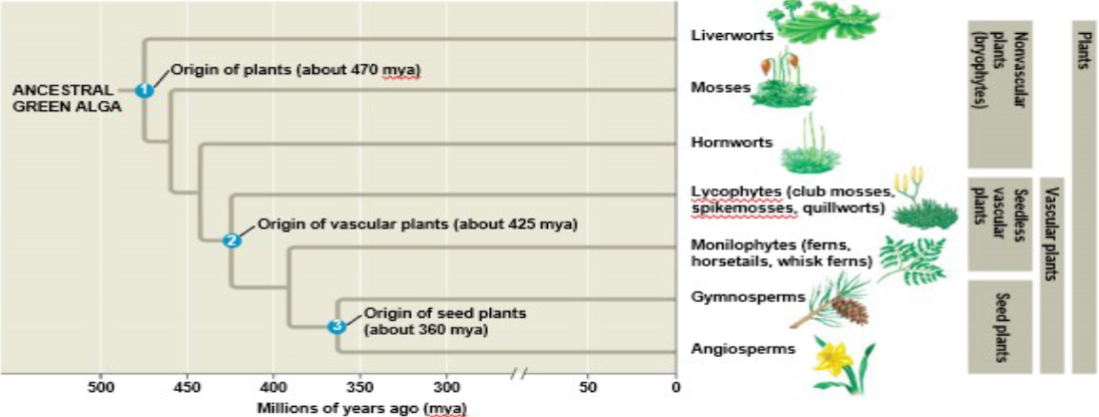
Bryophytes are the common name for three phyla. Give 3 characteristics of bryophytes.
Not a monophyletic group
Small, herbaceous (nonwoody) plants
Gametophyte-dominant
Bryophytes are the common name for three phyla. Name them.
Phylum Hepatophyta – liverworts
Phylum Bryophyta – mosses
Phylum Anthocerophyta – hornworts
Bryophytes Life Cycle
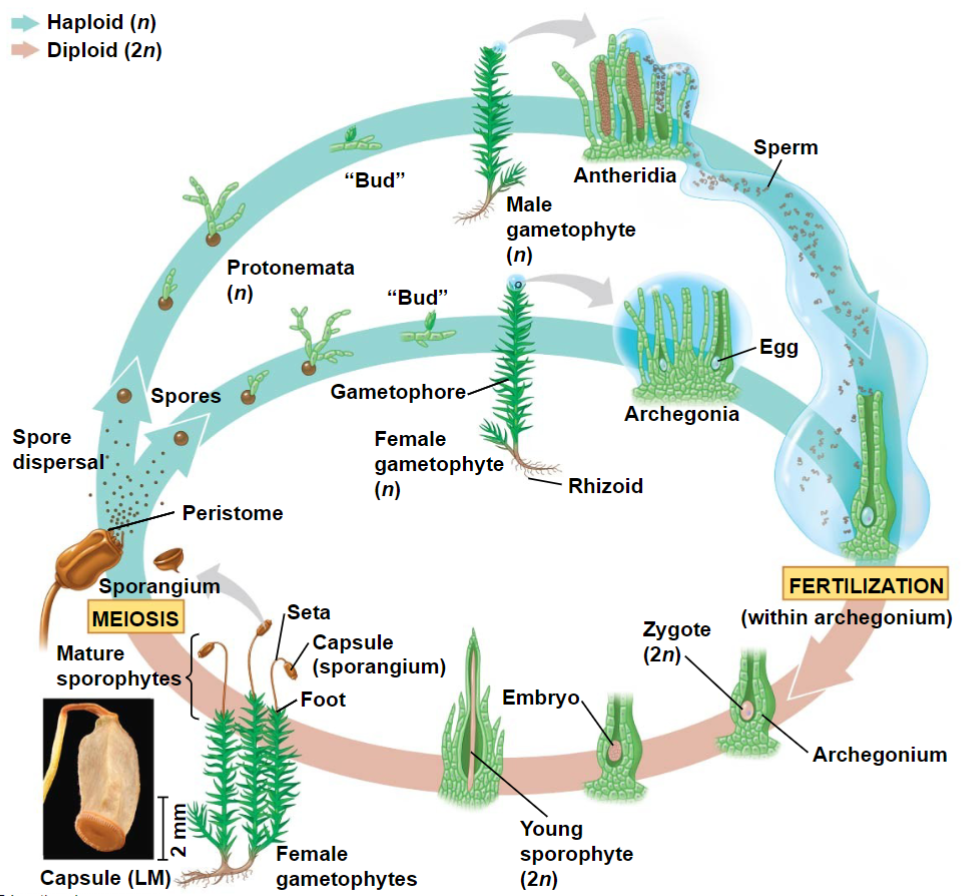
Why are bryophytes so short?
They lack lignin, a complex organic polymer that helps in structure, as well as vascular tissue, which usually has the presence of lignin.
Do bryophytes have true roots?
No, bryophytes (mosses, liverworts, and hornworts) do not have true roots. Instead, they have specialized structures called rhizoids. Rhizoids are filamentous structures that anchor the plant to the substrate and absorb water and minerals from the environment. They are not true roots because:
Structure: Rhizoids are single-celled or multicellular structures that lack vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) found in true roots. They do not have specialized tissues for transporting water and nutrients.
Function: While rhizoids anchor the bryophyte to the substrate and aid in water absorption, they do not perform the extensive functions of true roots, such as anchorage, nutrient uptake, and long-distance transport of water and nutrients.
Development: Rhizoids develop from the base of the gametophyte (the main body of the bryophyte) and are structurally different from the roots of vascular plants, which develop from the radicle of the embryo.
Despite not having true roots, bryophytes are successful in their habitats due to adaptations such as rhizoids and other strategies that allow them to absorb water and nutrients effectively from their environment.
Why is water important for reproduction in bryophytes?
Water is critically important for reproduction in bryophytes due to their reliance on external water for several key reproductive processes:
Sperm Dispersal: In bryophytes, the male gametophyte (antheridium) produces sperm cells (spermatozoids). These sperm cells are flagellated and require a film of water to swim through to reach the female gametophyte (archegonium) where the egg cell (ovum) is located. Water is necessary to provide a medium through which the sperm can move towards the egg for fertilization.
Fertilization: Bryophytes exhibit a water-dependent fertilization process known as external fertilization. After the spermatozoids swim to the archegonium, fertilization occurs within the protected environment of the archegonium. The presence of water is crucial during this stage because it facilitates the movement of sperm towards the egg and enhances the likelihood of successful fertilization.
Spore Dispersal: After fertilization, bryophytes develop sporophytes (the diploid stage) that produce spores. These spores are dispersed into the environment and require moisture to germinate and develop into new gametophyte plants. Without adequate water, spores may not germinate or establish new plants successfully.
Gametophyte Growth and Survival: Bryophyte gametophytes (the dominant haploid stage) rely on water for nutrient uptake, photosynthesis, and overall metabolic functions. Water helps maintain turgor pressure within cells, ensuring structural support and physiological processes necessary for growth and survival.
In summary, water is essential for reproduction in bryophytes because it facilitates sperm dispersal, external fertilization, spore dispersal, and supports the growth and survival of the gametophyte stage. The dependence on water highlights the adaptation of bryophytes to moist environments where these critical reproductive processes can occur efficiently.
Liverworts (Phylum Hepatophyta)

Hornworts (Phylum Anthocerophyta)
Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta)
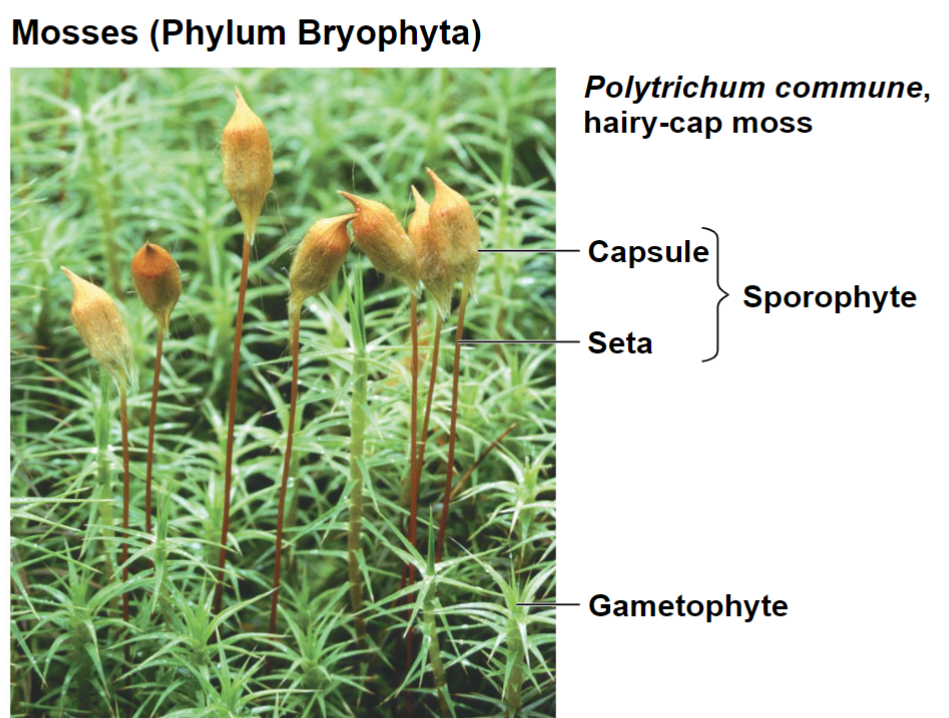
In this slide, which life form (generation) of the plant are you seeing?
A. Gametophyte
B. Sporophyte
A. Gametophyte

Vascular Seedless Plants- Derived characteristics
Sporophyte dominant life-cycles
Vascular tissue (xylem and phloem)
Well-developed roots and leaves
Spore-bearing leaves called sporophylls
Sporophyte-dominant Life Cycle
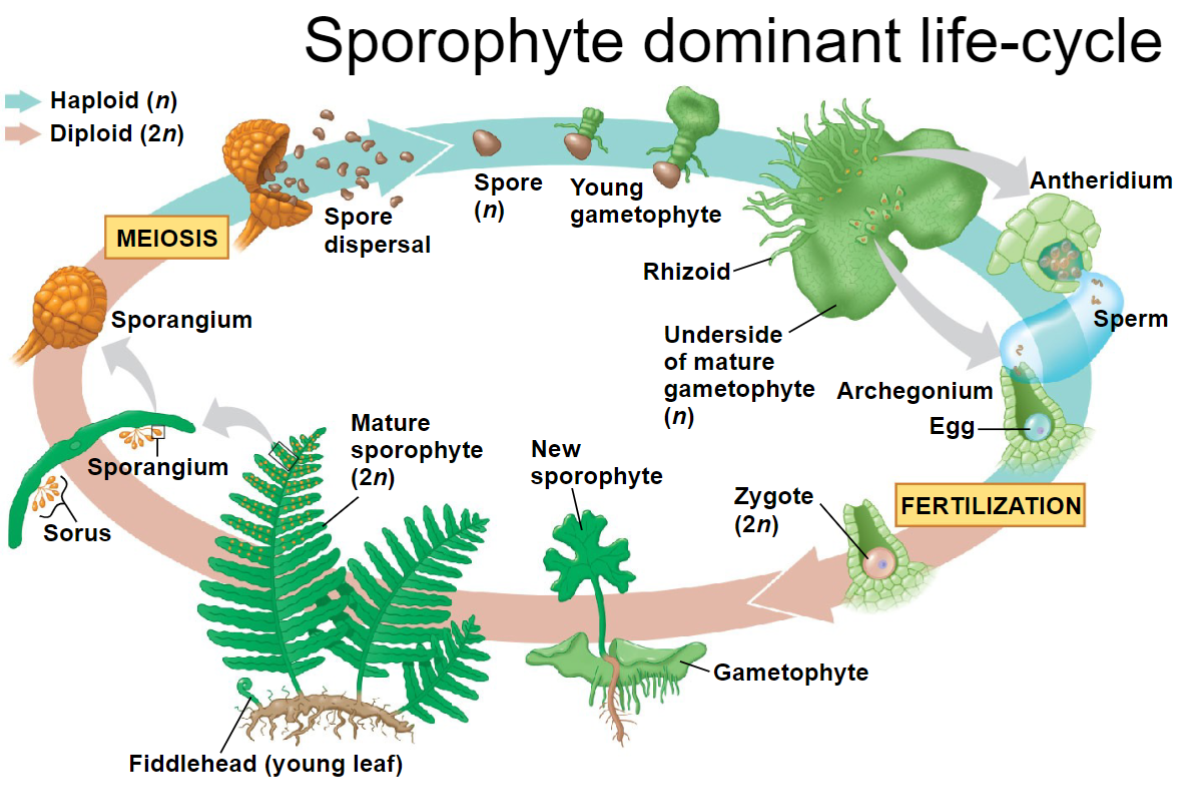
Vascular Tissue includes…
Xylem
Conducts water and minerals
Phloem
Distributes sugar, amino acids, and other organic products
Other characteristics common in vascular plants
Roots
Anchor the plant, enable water and nutrient uptake from soil
Leaves (megaphylls)
Increase surface area for photosynthesis
Vascular, spore-bearing leaves are called ____________.
sporophylls

What are the derived characteristics of vascular, seedless plants?
Sporophyte dominant life-cycles
Vascular tissue (xylem and phloem)
Well-developed roots and leaves
Spore-bearing leaves called sporophylls
What are the two clades of vascular, seedless plants?
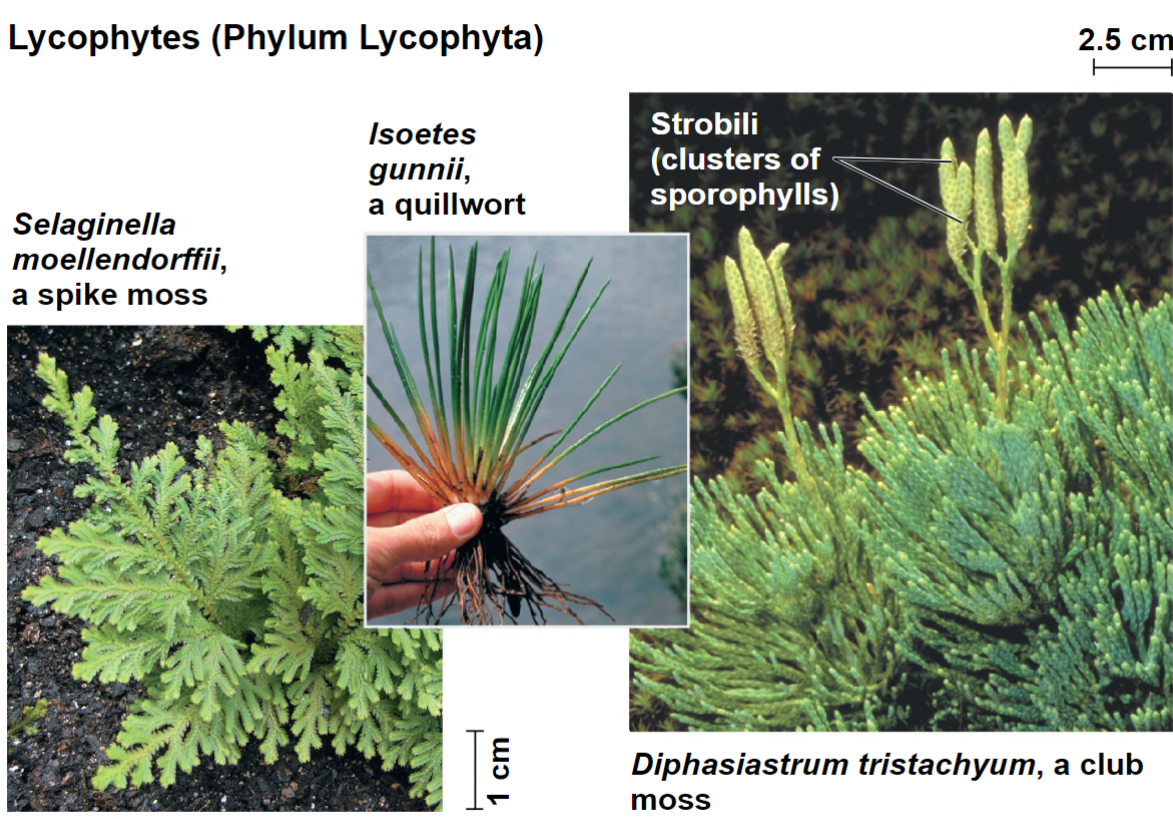
Phylum Lycophyta – club mosses
Phylum Monilophyta – ferns, horsetail
Vascular, seedless plants evolutionary tree
Lycophytes (phylum Lycophyta)
Monilophytes (Phylum Monilophyta)

Where would you find a fern gametophyte?
On moist soil
On the underside of the leaf (frond)
Attached to the underground stem (rhizoids)
In a freshwater stream
Inside a dissected seed
On moist soil
Water is brought into mosses primarily by __________.
diffusion through all cells
leaves
roots
rhizoids
xylem
Diffusion through all cells
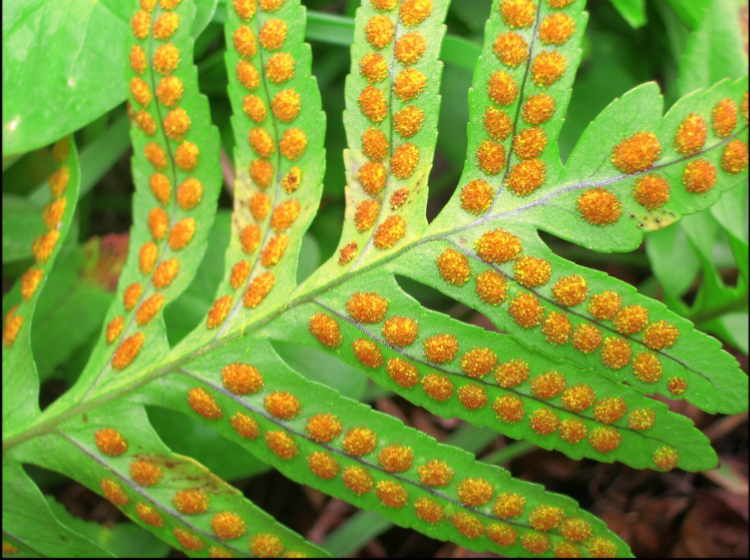
The "dots" on the underside of a fern frond are spore cases; therefore, what is true of the plant to which the frond belongs?
It is a sporophyte.
It is a spore.
It is a gamete.
It is a gametophyte.
It is a spermatophyte.
It is a sporophyte
A major division in plant systematics is based on whether a particular species has __________.
vascular tissue
sporophytes
apical meristems
gametophytes
alternation of generations
Vascular tissue
Sori can be found in which of the following?
Pterophytes
Mosses
Liverworts
Hornworts
Charophyceans
Pterophytes
Which of the following are traits shared by land plants and their closest relatives among the algae?
All of the listed traits of land plants are present in their closest relatives among the algae.
Rings of cellulose-synthesizing proteins in the plasma membrane
Structure of flagellated sperm
Formation of a phragmoplast
All the listed traits evolved exclusively in land plants.
All of the listed traits of land plants are present in their closest relatives among the algae.
Which is a key difference between alternation of generations in plants and sexual reproduction in nonplant organisms?
In plants, the haploid and diploid stages are both multicellular.
In plants, only the haploid stage is multicellular.
In plants, the haploid generation is always dependent on the diploid generation.
In other sexually reproducing organisms, the haploid and diploid generations are both multicellular.
In other sexually reproducing organisms, the fusion of gametes forms a zygote before an embryo.
In plants, the haploid and diploid stages are both multicellular.
What is the evolutionary significance of megaphylls?
They increase the surface area for photosynthesis.
They are modified leaves that have sporangia.
They allow plants to grow taller.
They provide a way to transport water and nutrients throughout the plant's body.
They increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients.
They increase the surface area for photosynthesis.
The development of the __________ prevents plants from drying out and protects them from microbes.
cuticle
apical meristem
gametangia
stomata
flavonoid
cuticle
In what way do megasporangia differ from microsporangia?
Megasporangia produce spores that develop into female gametophytes, whereas microsporangia produce spores that develop into male gametophytes.
Megasporangia produce many times the number of spores produced by microsporangia.
Megasporangia are possessed only by vascular plants, whereas microsporangia are present on all land plants.
Microsporangia are the early developmental stages of megasporangia.
Megasporagia produce spores that are protected by sporopollenin, whereas microsporangia produce naked spores.
Megasporangia produce spores that develop into female gametophytes, whereas microsporangia produce spores that develop into male gametophytes.
Evidence suggests that land plants arose from within which protist lineage?
Charophytes
Chlorophytes
Choanoflagellates
Ciliates
Cercozoans
Charophytes
To examine meiosis in ferns, you would study __________.
the sporangia
the antheridia
the archegonia
both the antheridia and the archegonia
both the archegonia and the sporangia
the sporangia
Typically, the upper part of a bryophyte capsule that contains the spores features a ring of interlocking, tooth-like structures known as the __________.
peristome
seta
strobili
protonema
microphyll
peristome
The embryophytes are __________.
the land plants
the haploid stage in plant alternation of generations
a protist group that possesses some of the reproductive traits of plants
the structures of a moss that produce and house eggs
the masses of one-cell-thick filaments through which moss spores absorb water and minerals
the land plants
What structures allow plants to readily take up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
Stomata
Cuticles
Gametangia
Mitochondria
Capsules
Stomata
Which of the following is a genus in the phylum Monilophyta?
Equisetum
Sphagnum
Isoetes
Selaginella
Marchantia
Equisetum
Alternation of generations in all land plants is between __________.
a multicellular haploid organism and a multicellular diploid organism
a single-celled haploid organism and a multicellular diploid organism
a multicellular haploid organism and a single-celled diploid organism
two anatomically distinct multicellular diploid organisms
two anatomically distinct unicellular diploid organisms
a multicellular haploid organism and a multicellular diploid organism
In moving to land, plants had to overcome which of the following challenges?
Desiccation
Less available CO2 in the atmosphere than in the oceans
Competition from other photosynthetic organisms such as cyanobacteria
Many herbivores on land
All of the listed responses are correct.
Desiccation
Which of the following is true of the life cycle of bryophytes?
A moist environment is required for sexual reproduction.
The gametophyte remains attached to and dependent on the sporophyte.
Reproduction is only asexual.
Gametes are transported through mutualisms with animals.
None of the listed statements is true of the life cycle of mosses.
A moist environment is required for sexual reproduction.
In sporophyte ferns, the leaves are __________.
megaphylls
microphylls
thalli
sporangia
blades
megaphylls
The tissue called phloem has what function in vascular plants?
Distribution of sugars, amino acids, and other organic products
Conduction of water and minerals
Absorption of water and minerals from the soil
Dispersal of spores
Bearing of sporangia
Distribution of sugars, amino acids, and other organic products
What characteristic of Sphagnum peatlands is responsible for their ability to inhibit decomposition?
All of the listed characteristics inhibit decomposition.
Phenolic compounds produced by Sphagnum
Low temperature
Low pH
Low oxygen
All of the listed characteristics inhibit decomposition.
Which of the following is a trait unique to land plants?
Walled spores produced in sporangia
Multicellular structures for carrying out photosynthesis
Cellulose
Chloroplasts
All the listed traits are unique to land plants.
Walled spores produced in sporangia
Fern gametophytes are __________.
free-living, multicellular organisms
photosynthetic diploid organisms
produced from haploid gametes
part of the asexual life cycle
found on the underside of fern leaves (fronds)
free-living, multicellular organisms
Which of the following statements about algae and plants is true?
Plants have a waxy, waterproof cuticle, and algae do not.
Plant cells have rigid cellulose walls, and algal cells do not.
Both plant and algal zygotes develop into embryos.
Algae have different types of chlorophyll molecules from plants.
Plants are multicellular, whereas algae are unicellular.
Plants have a waxy, waterproof cuticle, and algae do not.
The antheridia of mosses produce __________.
sperm
spores
buds
eggs
leaves
sperm
How are gametes produced by bryophytes?
By mitosis of gametophyte cells
By meiosis of gametophyte cells
By meiosis of sporophyte cells
By mitosis of spores
By meiosis of spores
By mitosis of gametophyte cells
During what period did seedless vascular plants form extensive forests of tall trees?
Carboniferous
Permian
Ordovician
Silurian
Triassic
Carboniferous
The gametophyte stage of the plant life cycle is most conspicuous in __________.
mosses
ferns
horsetails
club mosses
seed plants
mosses
What is advantage is conferred to algae and plants that possess sporopollenin?
Reproductive cells are more resistant to desiccation.
Asexual reproduction is possible.
Sexual reproduction can occur through the transfer of pollen.
Spores are protected by toxins that deter consumption.
The haploid stage of the life cycle can be eliminated.
Reproductive cells are more resistant to desiccation.