Intro to cardiovascular Physiology and Pathology; CAD and MI
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
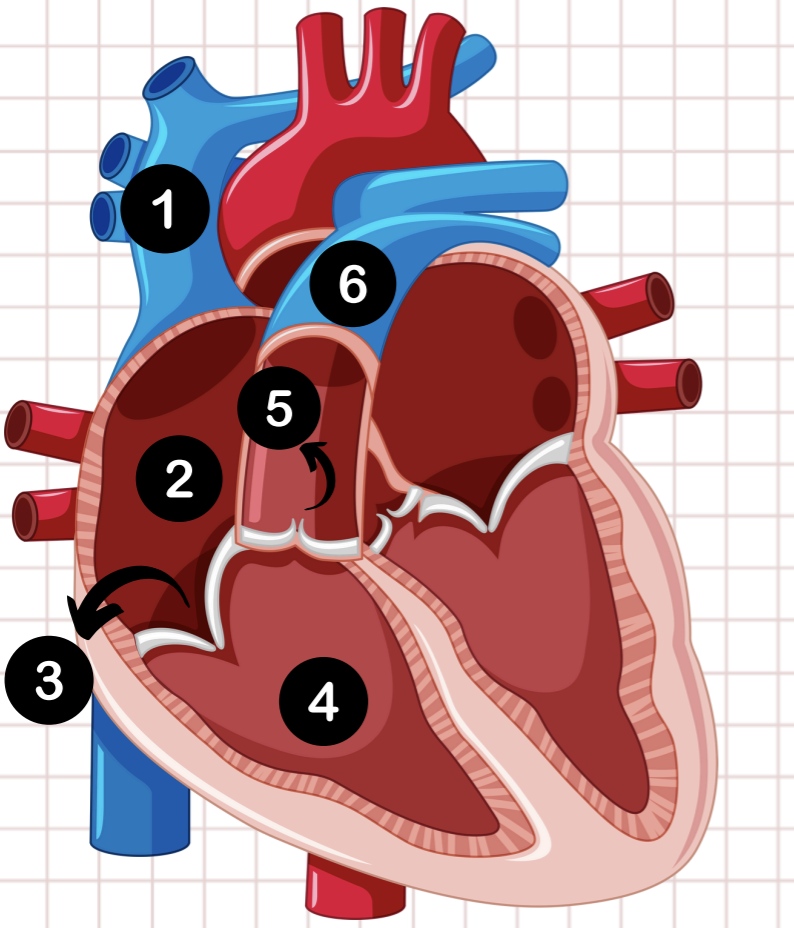
1
vena cava
2
right atrium
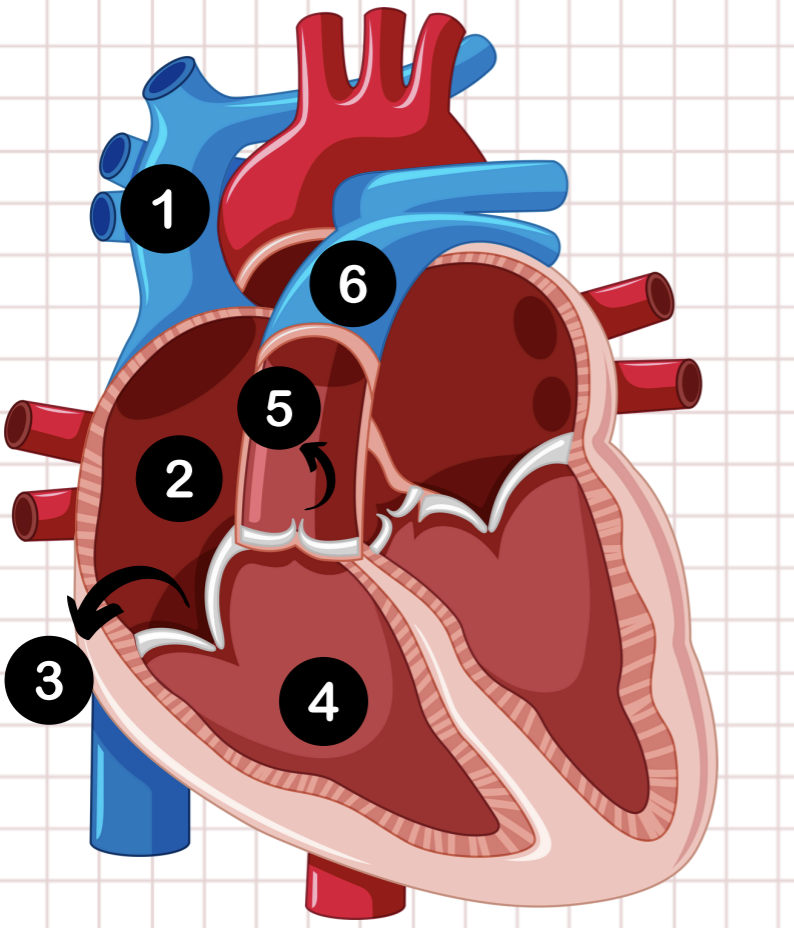
3
tricuspid valve
4
right ventricle
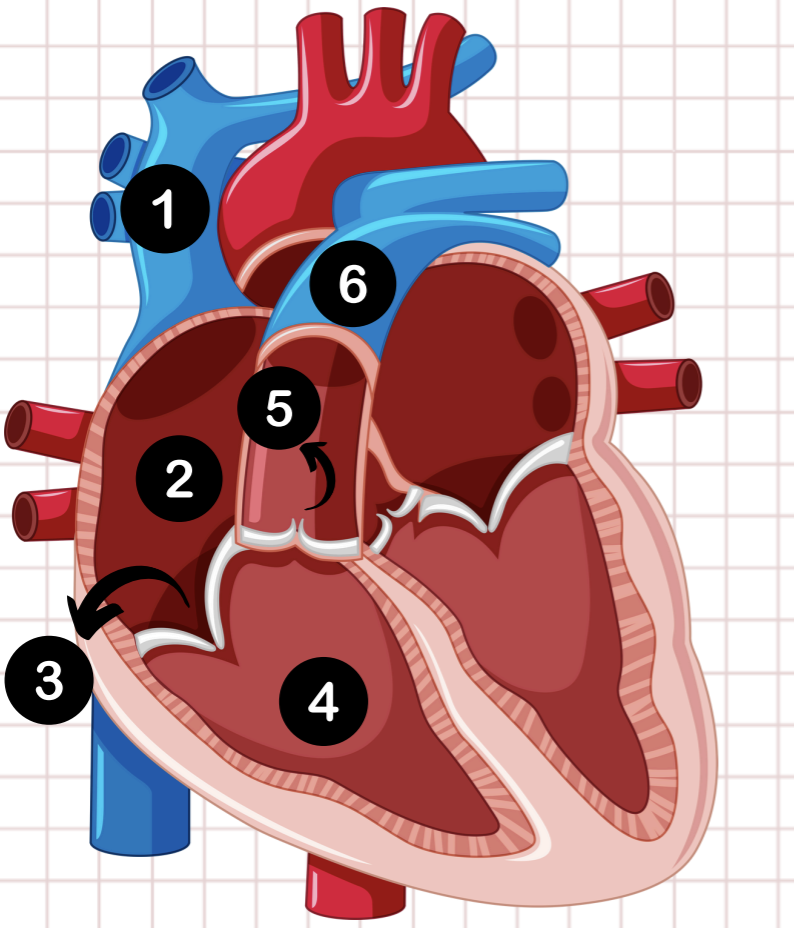
5
pulmonary semilunar valve
6
pulmonary artery
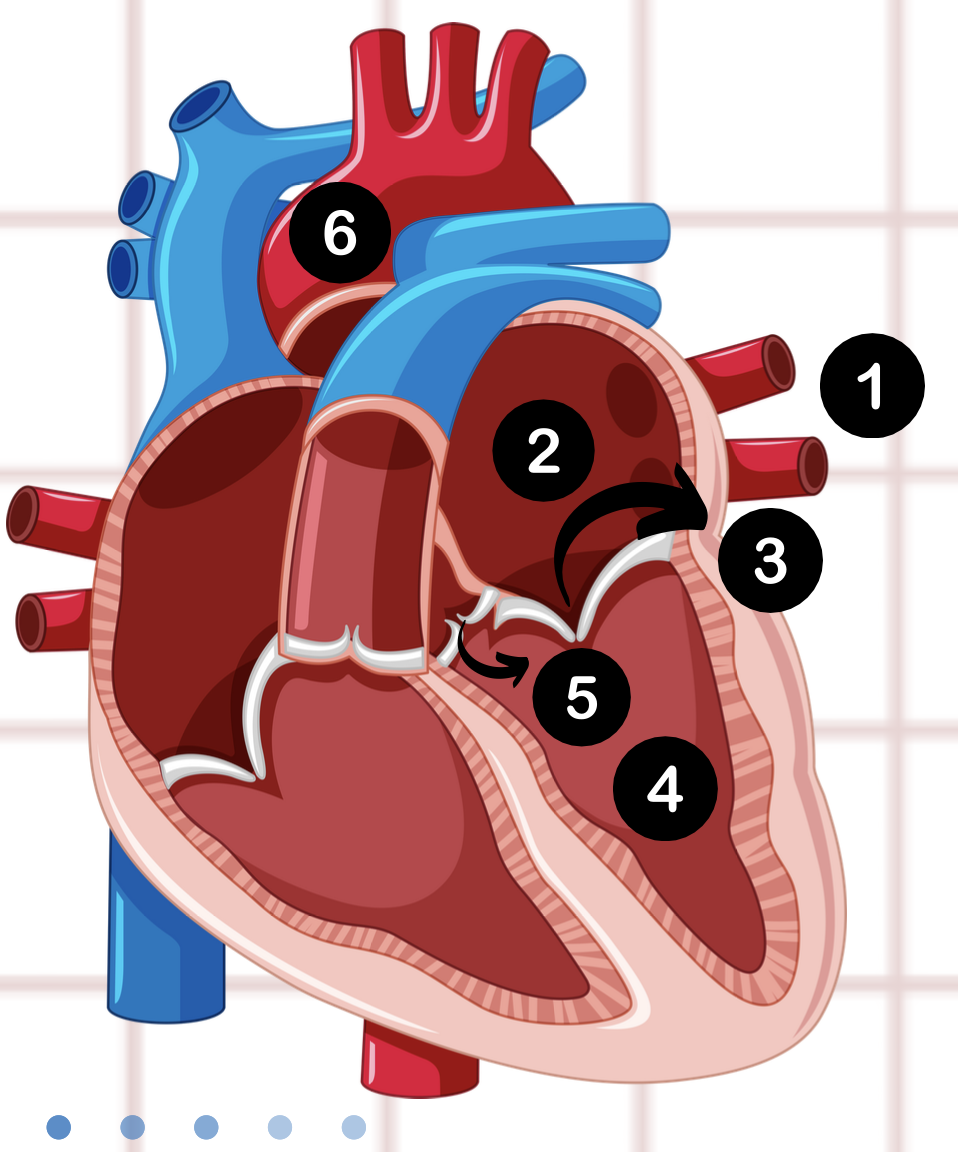
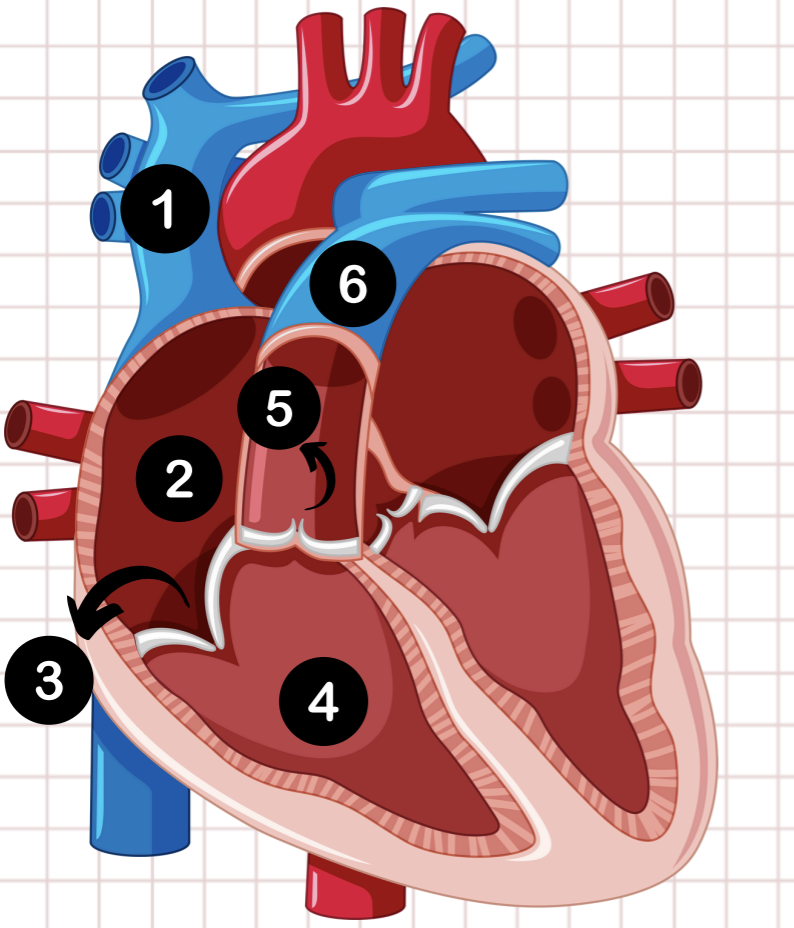
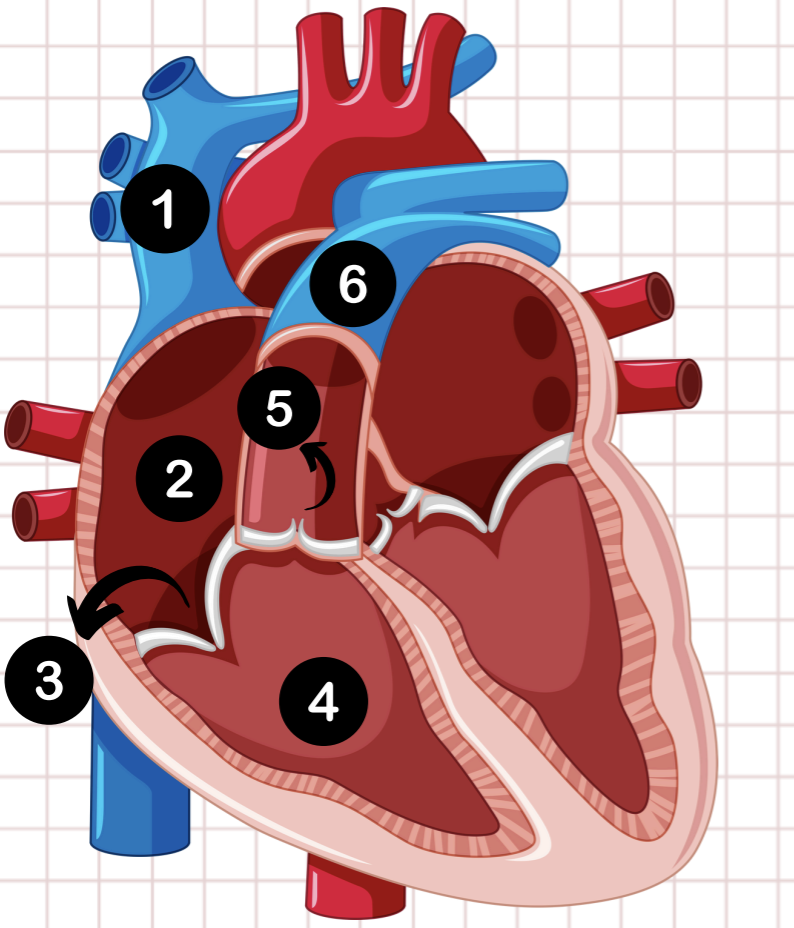
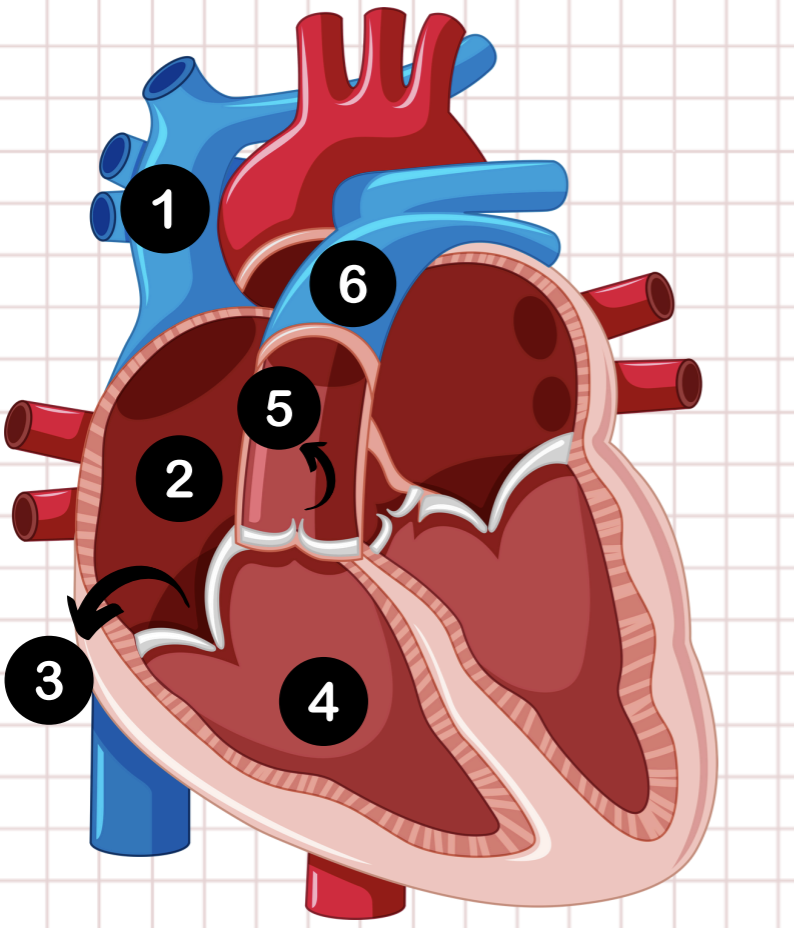
1
pulmonary vein
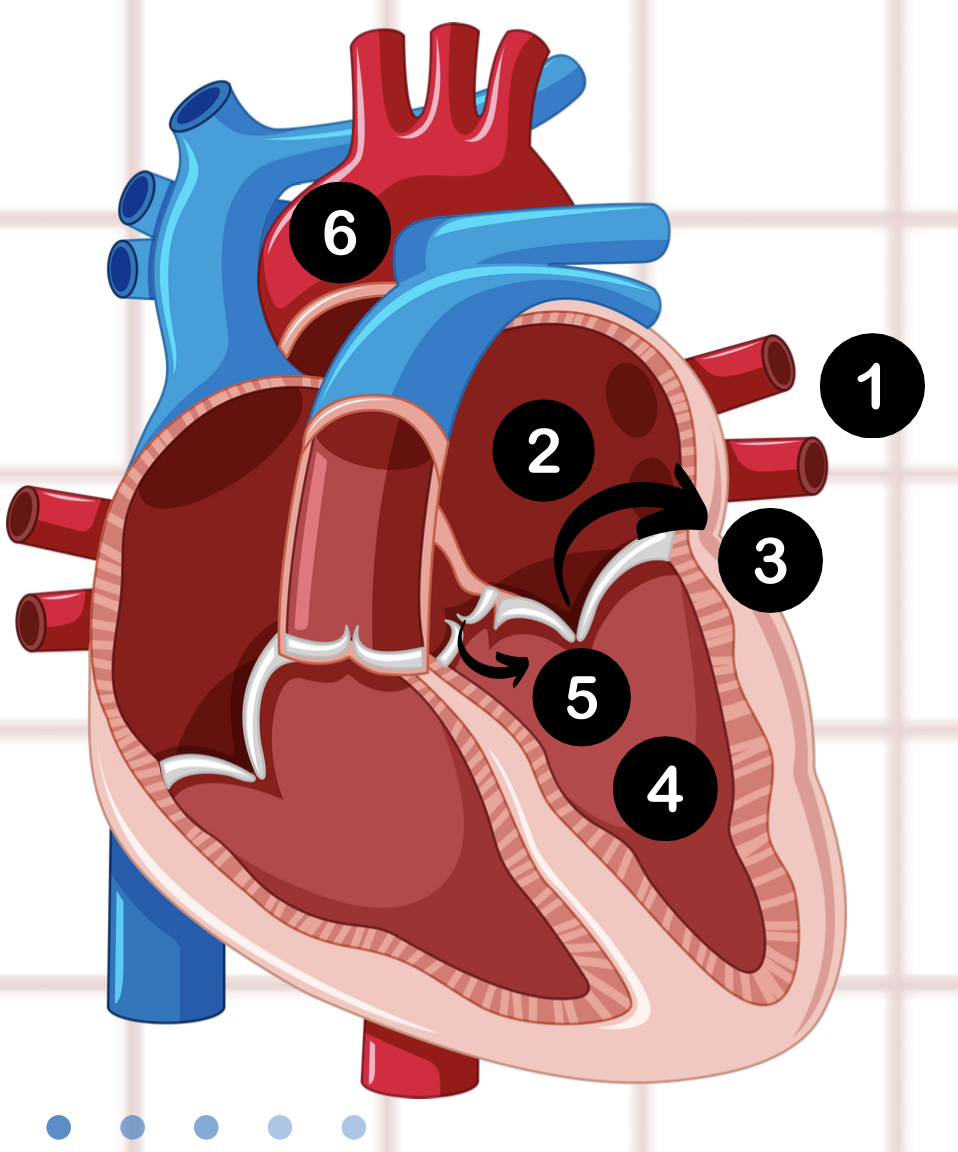
2
left atrium
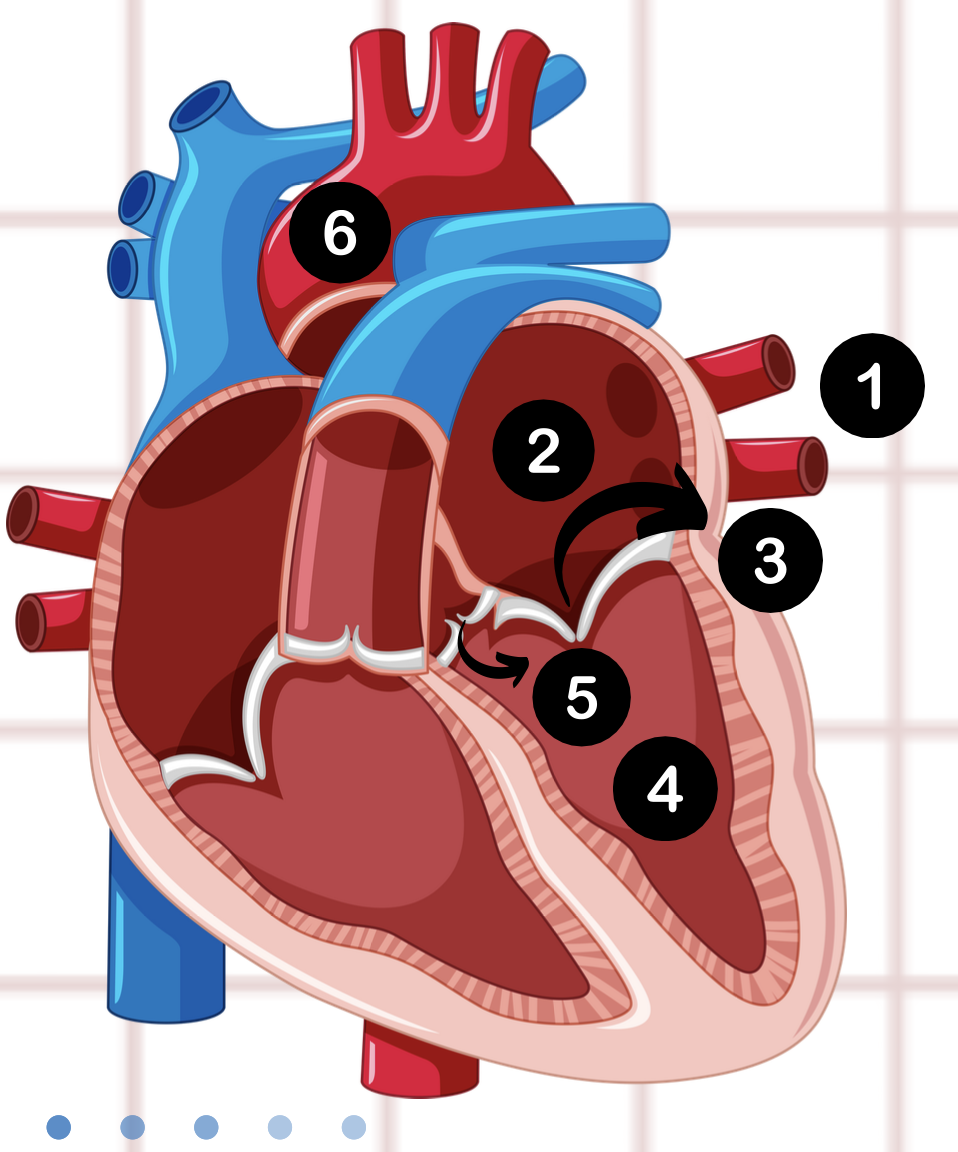
3
bicuspid valve
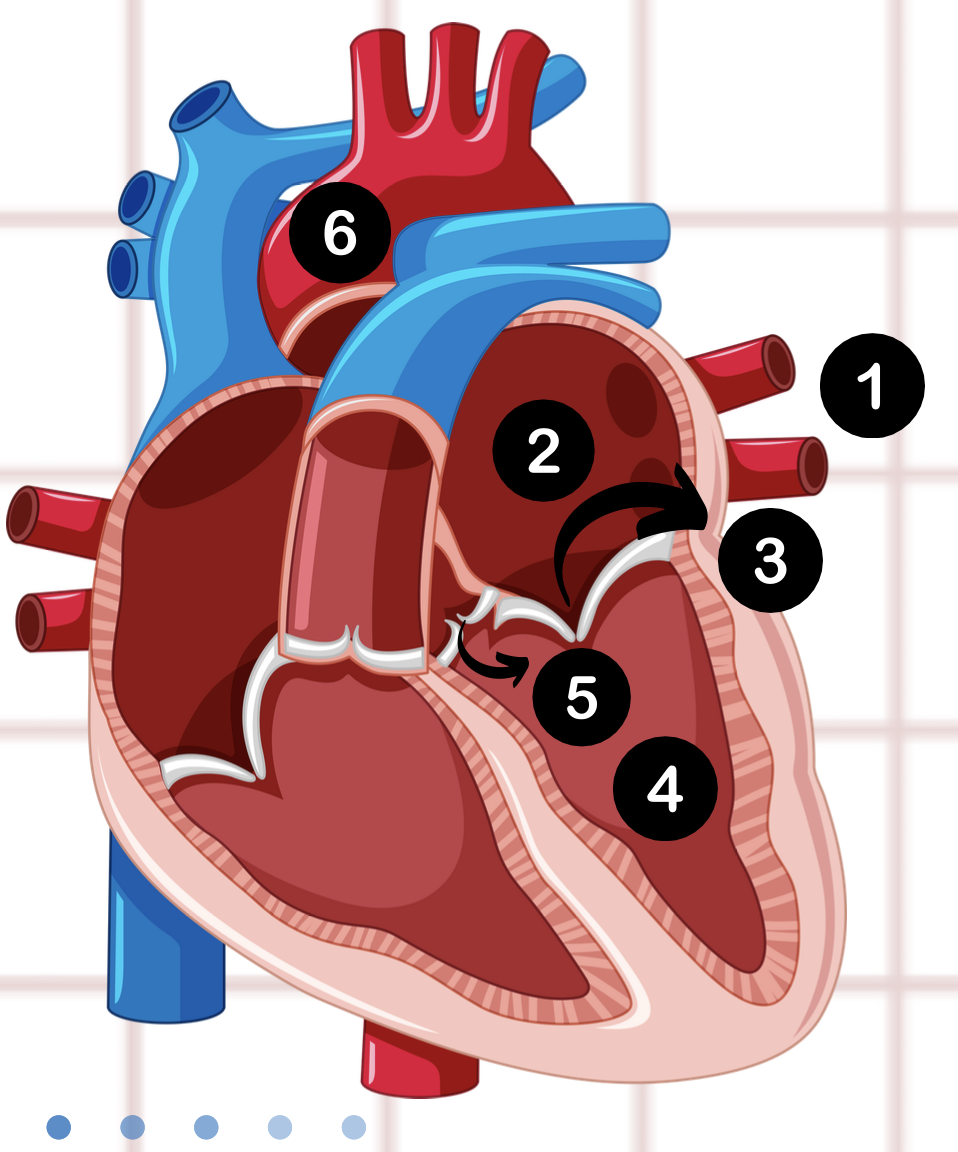
4
left ventricle
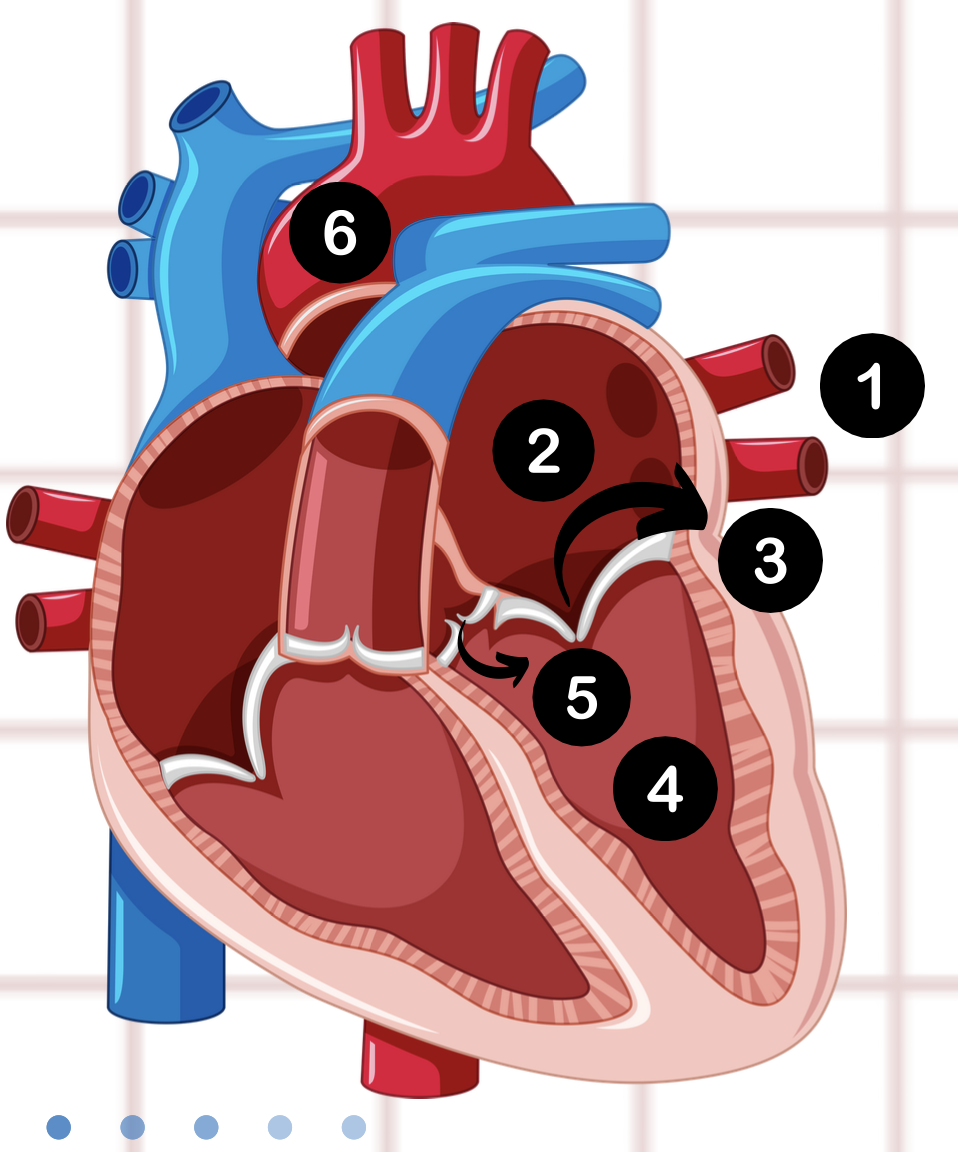
5
aortic valve
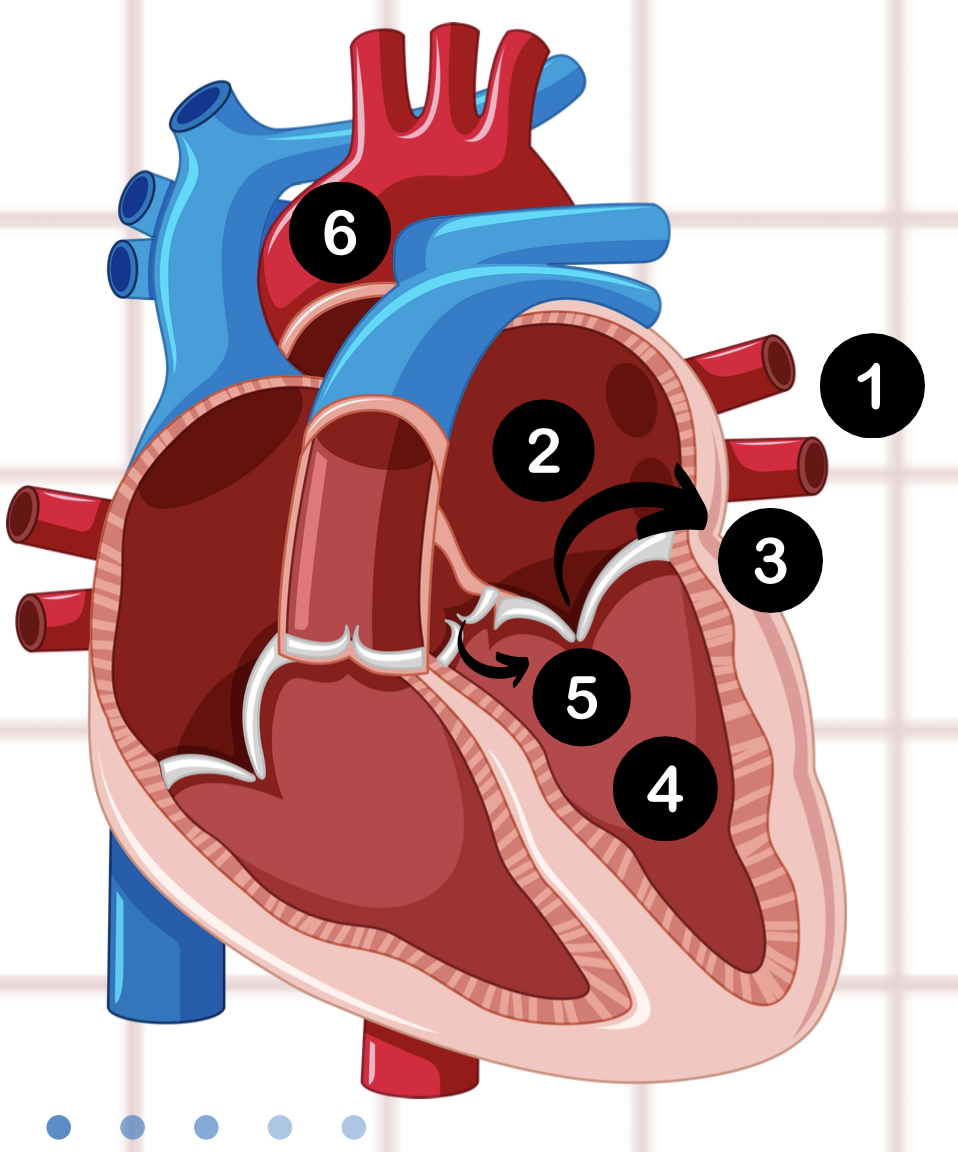
6
aorta
lungs
where does blood go after it leaves the pulmonary arteries?
the body
where does blood go after it leaves the aorta?
cardiac output
the amount of blood leaving the heart
HR and SV
cardiac output is determined by _____
stroke volume
volume of blood in the left ventricle being ejected by each heartbeat
blood pressure
determined by the cardiac output and vascular resistance
vascular resistance
amount of resistance in the vascular walls
vascular resistance; blood flow
_____ must be overcome to push blood through the circulatory system and create _____
decrease
as we age there is a ____ in cardiovascular capacity
relationship between cardiovascular capacity and age
a loss of muscle mass, decreased elasticity of blood vessels, reduced lung function and accumulation of plaque
chronic pathology on cardiovascular capacity
Accumulation of risk factors, such as obesity, low physical activity, smoking, drug use, or alcohol
Lead to cellular adaptation (ex. ventricular hypertrophy)
acute pathology on cardiovascular capacity
Pathogens, trauma, and acute renal failure
leads to cellular necrosis
(example – ischemia (MI))
physical reserve
the distance between an individual’s capacity and metabolic cost of an activity
less reserve
the ____ the harder and more taxing a task will be for a person
signs and symptoms of cardiovascular pathology
•Pain
•Palpitations
•Fatigue
•Syncope – dizzy or lightheaded
•Cough – or shortness of breath
•Cyanosis
•Peripheral edema
•Claudication
angina
pain associated with cardiovascular pathology classified by pressure, tightness, squeezing, and heaviness in the chest, neck, jaw, shoulder, or arm
greater; below
Angina occurs when the demand for oxygen is ___ than the supply. it is commonly seen when a person’s capacity is at or ___ the tast cost
60-100
normal resting heart rate
bradycardia
slow heart rate
tachycardia
fast heart rate
relationship between angina and the supply and demand of oxygen to the heart (or skeletal muscle for claudication).
an imbalance between oxygen supply and demand in the heart muscle. Inadequate oxygen supply to the heart muscle during periods of increased demands leads to myocardial ischemia and chest pain.
pulmonary edema
occurs when there is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the lungs; occurs due to increased pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs or damage to the lung tissue. This can be caused by heart failure, MI, or hypertension.
peripheral edema
Accumulation of fluids in tissues, typically in lower extremities like the legs, ankles and feet;Occurs due to increased pressure within the veins and capillaries of the lower extremities. This increased pressure can be caused by heart failure, venous insufficiency, live/kidney disease
Hormone Replacement Therapy
_______has not been shown to provide “cardio-protective” benefits.
Oral contraceptives
_________ may increase the risk of blood clots and subsequent MI/stroke. This is especially true in women over 35 who are smokers.
Disease independent age related changes to cardiovascular system
o Reduced # of cardiac myocytes, and cells within the conduction system
o Development of cardiac fibrosis
o Reduced calcium transport across the membrane
o Reduced capillary density
o Reduced responsiveness to beta-adrenergic stimulation
o Impaired autonomic reflex control of HR
o Thickening of the left ventricular wall (“especially in the face of underlying hypertension”)
o stiffening/calcification of the ventricles, valves, and arteries
o Increased likelihood of clinically significant atherosclerosis heart disease
Collectively age related changes to cardiovascular system
Decrease in maximal HR
Decrease in cardiac output
Decrease in VO2max
Increase in the incidence of arrhythmia's
cardiovascular changes and disease risk for men
o increased incidence of Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP);not getting good closure of the mitral valve
o Increase in left ventricular mass with aging
o Increased risk of dangerous arrhythmias
o Decreased responsiveness to anticoagulants and thrombolytics, but a higher incidence of bleeding
cardiovascular changes and disease risk for women
o Risk for cardiovascular disease (CAD specifically) increased sharply after menopause
o May experience angina in the mid-scapular region of the back
o Hormonal Influences
Hormonal influences for women with cardiovascular changes and disease risk
Estrogen appears to be “cardio-protective”
Increased HDL levels (“good cholesterol”)
Reduces clotting risks
Both estrogen and estradiol have a dilating effect on the blood vessels, helps maintain normal BP and blood flow
Oral contraceptives may increase the risk of blood clots and subsequent MI/stroke. Especially for women over 35 who are smokers
Response to injury theory
Explains the atherosclerotic disease, including coronary artery disease (CAD) and cerebrovascular disease (CVD)
proposes that atherosclerosis develops in response to endothelial injury, initiating a cascade of inflammatory and cellular processes that lead to the formation of plaque within the arterial walls
Non-modifiable risk factors for CAD
o Age (83% of deaths from CAD occur in individuals > 65 y/o)
o Gender (males are at a greater risk, especially when compared to pre-menopausal women)
o Genetics (a family history of premature heart disease is associated with elevated risk)
modifiable risk factors for CAD
o HTN- Hypertension (SBP > 130 or DBP > 80 mmHg)*
o Cholesterol ((Total chol. > 200 mg/dl)
o Smoking (there is no safe amount)
o Inactivity (increases risk for many chronic disease conditions including heart disease)
o Obesity (BMI > 30 kg/m2)
o Diabetes (fasting glucose level > 126 mg/dl)
o Stress
less than 120/80
What is normal blood pressure
greater than 140/90
what is considered high blood pressure
under 100
normal LDL value
60 and higher
normal HDL value
under 200
normal total cholesterol value
99 mg/dl or below
normal fasting glucose value
18.5-25
Normal BMI value
25-30
overweight BMI value
30-35
obese class 1 BMI value
Metabolic syndrome
Cluster of risk factors in a single individual
Three or more of the following:
o Waist > 35” in women, > 40” in men
o Triglyceride levels > 150 mg/dl
o HDL < 50 mg/dl in women,
< 40 mg/dl in men
o BP > 130/85 mmHg
o Blood sugar > 100 mg/dl
Stable Angina
o Predictably induced with a given level of exertion
o Treat with rest and/or medications
o Monitored exercise is safe
Unstable angina
may or may not be brought on by exertion.
Characterized by increasing frequency, duration, and intensity of ischemia, and/or a reduced “ischemic threshold”.
Physical activity
______ is contradicted with un stable angina
Common changes on an EKG with myocardial ischemia
presence of T wave or an ST segment depression
Cardiac angioplasty (coronary angiography)
Invasive procedure that allows visualization of the coronary arteries and identification of obstructive lesions
Catheter access may be from groin, arm, or neck. A dye is injected that allows for visualization of the coronary arteries using “fluoroscopy”
Stent can be placed to reopen arteries
Catheter; “fluoroscopy”
During Cardiac angioplasty (coronary angiography), ____ access may be from groin, arm, or neck. A dye is injected that allows for visualization of the coronary arteries using ______
Stent; reopen
A ____can be placed to ____ arteries in cardiac catheterization angioplasty procedures.
Most common coronal arteries for occulsion
Left anterior descending a. (most common)
Left circumflex a.
Right circumflex a.
“Open Heart Surgery”, in which vessels are harvested and used to bypass occlusion
what happens when a CABG procedure is done?
commonly used bypass vessels in open heart surgery
Internal Mammary (preferred for LAD occlusion)
Radial artery
Saphenous Vein (associated with chronic pain post-surgery and with physical activity)
Sternotomy
the sternum is separated to allow access to the heart, the sternum is wired closed post-opperatively
Sternal precautions
· No lifting, pulling, pushing (10 lb limit) for 6 weeks
· Log roll technique in/out bed
· No driving (4-8 weeks)
· ROM exercise - neck, shoulders, torso ("caution with sternectomy")
· Scar mobilization when incision is healed
· Be conservative if: osteoporosis, diabetes, advanced age
Acute myocardial infarction
Permanent damage (“necrosis”) to myocardial due to interrupted blood flow
Ischemia is often a precipitating factor. Typically, the result of significant CAD that culminates in a complete blockage
Often fatal, the mortality rate for AMI is approximately 30%
Types of acute myocardial infarction
transmural
subendocardial
Myocardial ischemia
when blood flow to the myocardium is obstructed by a partial/complete blockage of a coronary artery by a buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis). If the plaques occur, ___will occur
transmural
refers to full thickness
subendocardial
refers to partial thickness
ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
transmural- full thickness
account for 70% of AMI
Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NonSTEMI)
Subendocardial- partial thickness
MI that does not demonstrate ST segment elevation on the EKG
Common complications following myocardial infarction
Dysrhythmias (Commotio Cordis)
Heart Failure
Mural Thrombus
Ventricular Aneurysm
Ventricular rupture with tamponade
Commotio Cordis
Dysrhythmias
Blunt force trauma to the pre-cordial chest region occurring during the early ventricular repolarization period triggering an arrhythmia
Sudden Cardiac Death
Phase I of Cardiac Rehabiliation
Inpatient phase: (typically 3-7 days)
Review sternal precautions if post-CABG
Initiate physical activity and provide home exercise/activity guidelines.
Refer to comprehensive out-patient cardiac rehabilitation program
Phase II of Cardiac Rehabiliation
Acute outpatient: (may last up to 12 weeks)
Comprehensive program including individually prescribed and monitored exercise, and individual and group educational sessions aimed at reducing risk factors and secondary events.
Phase III of Cardiac Rehabiliation
may last 6 months or more
patients no longer receive continuous telemetry monitoring during exercise and are more independent.