Chapter 8 - Brain Development (copy)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is Phylogenetic development?
Evolutionary development of a species from lower to higher species.
What is Ontogenetic development?
Development of an individual from the time of fertilization to the organism’s mature form.
In this course, we focus on this type of development.
What are Vertebrates?
Animals characterized by brain and spinal cord.
What is remarkable regarding embryos and evolution?
Embryos of different species more closely resemble one another than their respective parents.
Embryos are not simply miniature versions of adults.
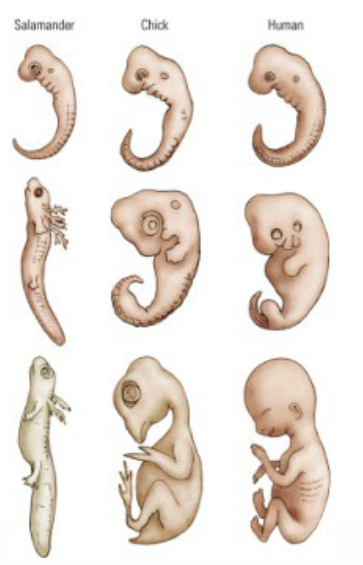
What are the distinctions of the gross development of a baby?
Zygote → Conception to 2 weeks.
Embryo → 2-8 weeks.
Fetus → 9 weeks to birth.
Baby → Birth.
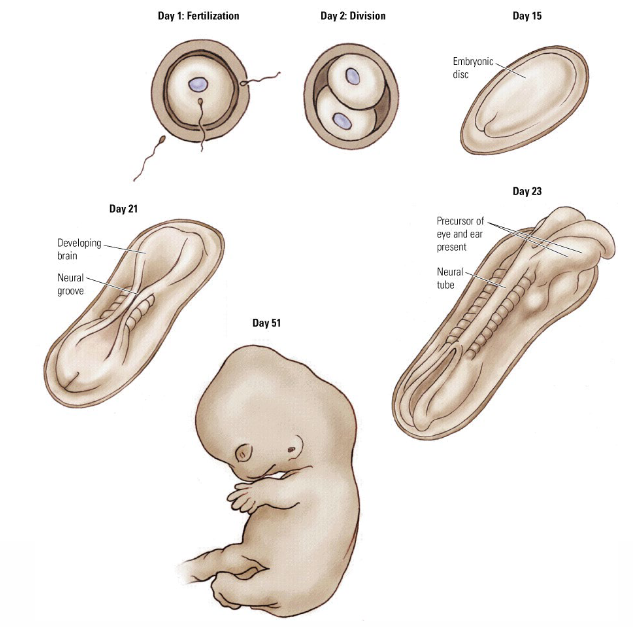
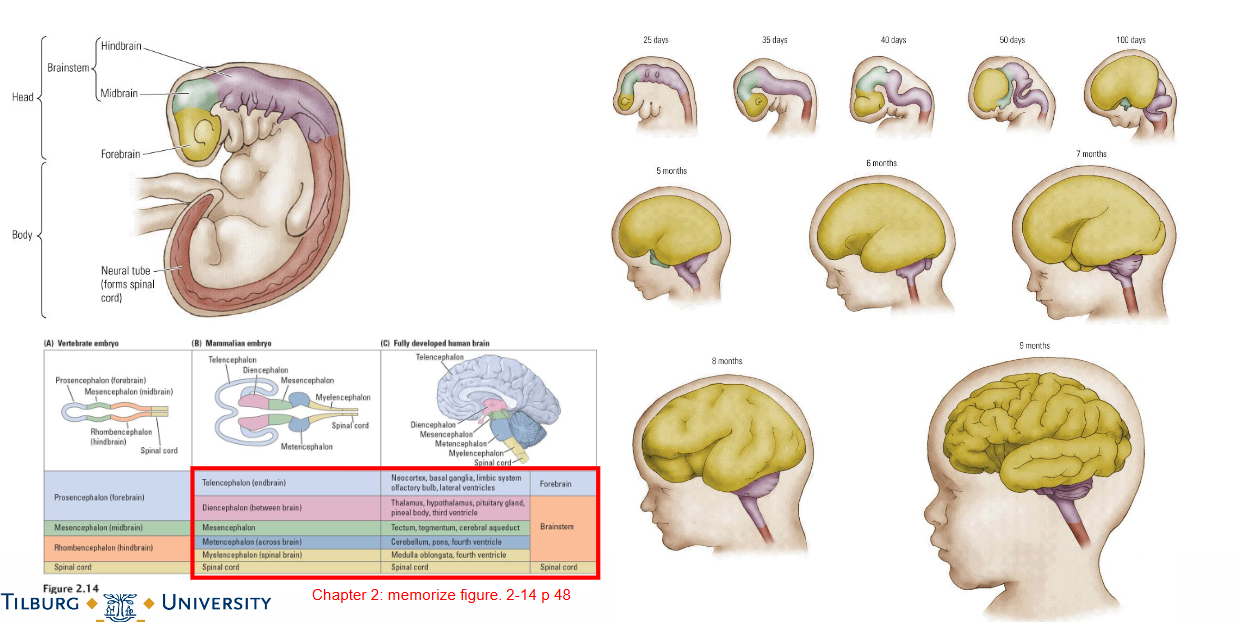
How does formation of the neural tube happen?
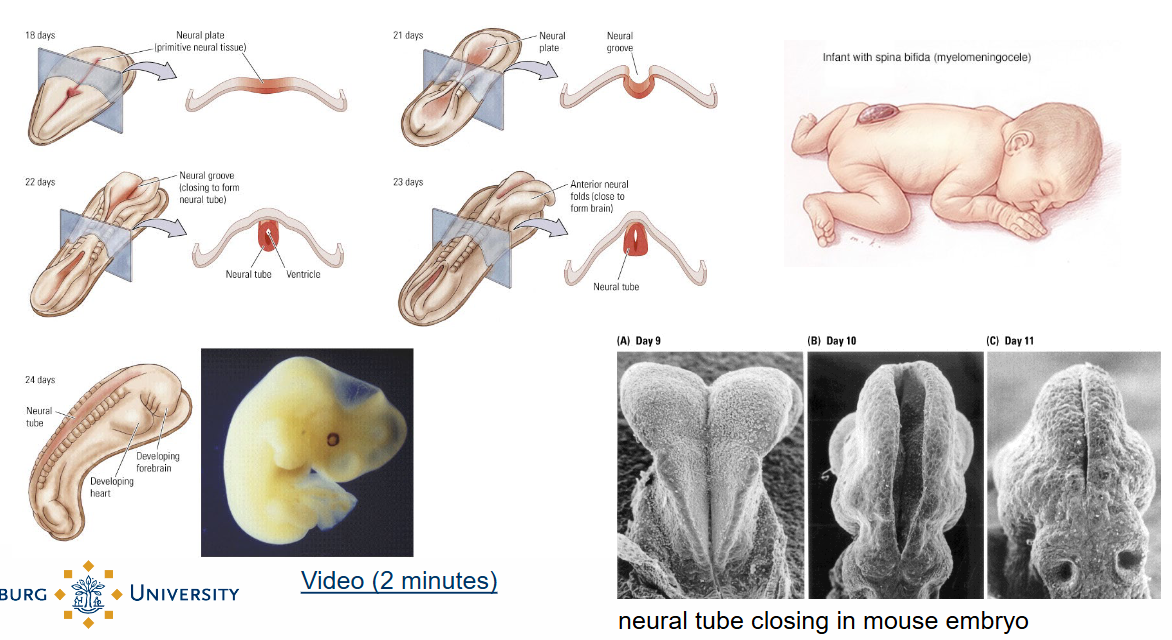
What does Prenatal brain development look like?
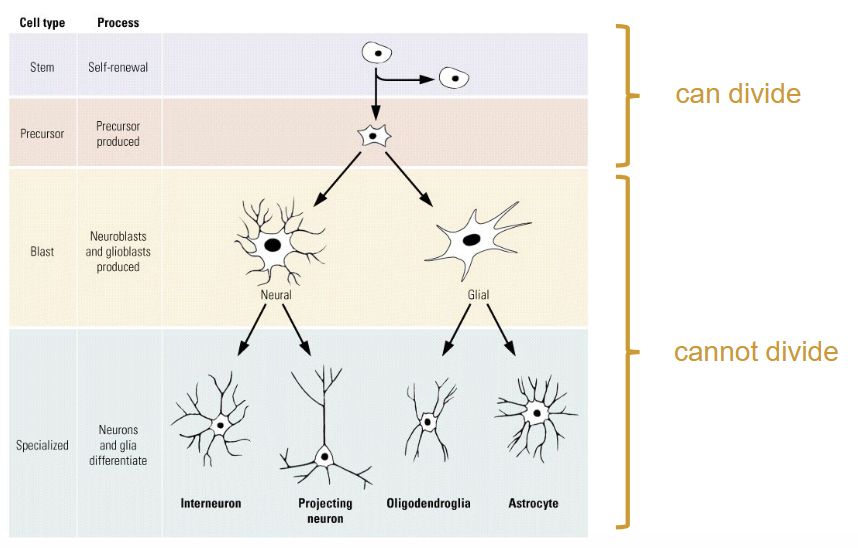
What are the 4 different types of Brain Cells?
Neural stem cells
Progenitor/precursor cells
Neuroblasts or glioblasts
Specialized cells
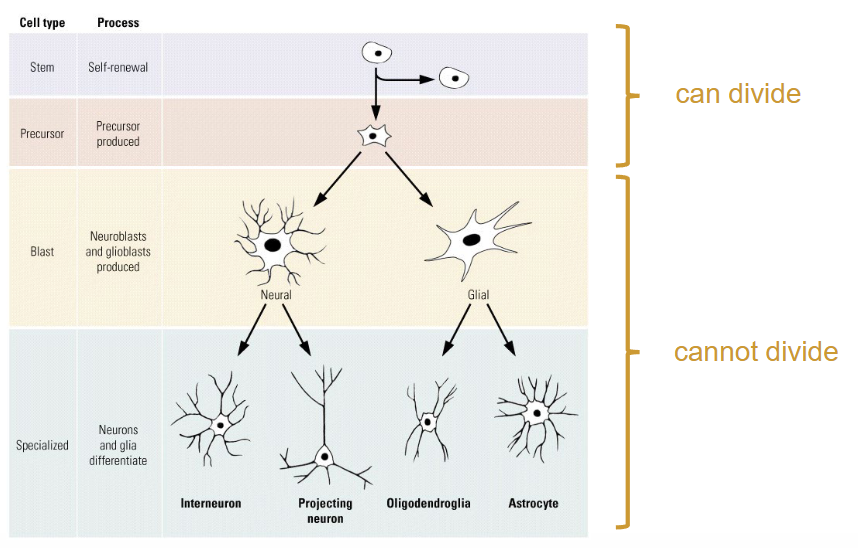
Which brain cells can divide and which brain cells cannot divide?
Can divide:
Neural stem cells
Progenitor / precursor cells
Cannot divide:
Neuroblasts or glioblasts
Specialized cells
Neural stem cells are Multipotent; what does this mean?
They give rise to all the many specialized cell types in CNS.
What is the Development of brain cells influenced by?
Chemical signals.
Stem cell → Progenitor cell → Neuro- or glioblast → Specialized neuron or glial cell.
What is Gene expression influenced by?
Neurotropic factors (chemicals), which may express (turn on) specific genes and thus signal a cell to develop in a particular way.
Gene methylation, which may suppress (turn off) specific genes.
What are Neurotrophic factors?
Chemicals which may turn on specific genes and thus signal a cell to develop in a particular way.
Influences gene expression.
What does Gene methylation do?
It may turn off specific genes.
Influences gene expression.
What is Epigenetics?
Environmental influences may alter gene expression.
e.g. 10% more genes are expressed (turned on) in prenatally stressed infants.
What are the 7 stages of Brain development?
Cell birth (neurogenesis)
Cell migration
Cell differentiation
Cell maturation (dendrite and axon growth)
Synaptogenesis (formation of synapses)
Cell death and synaptic pruning
Myelogenesis (formation of myelin)
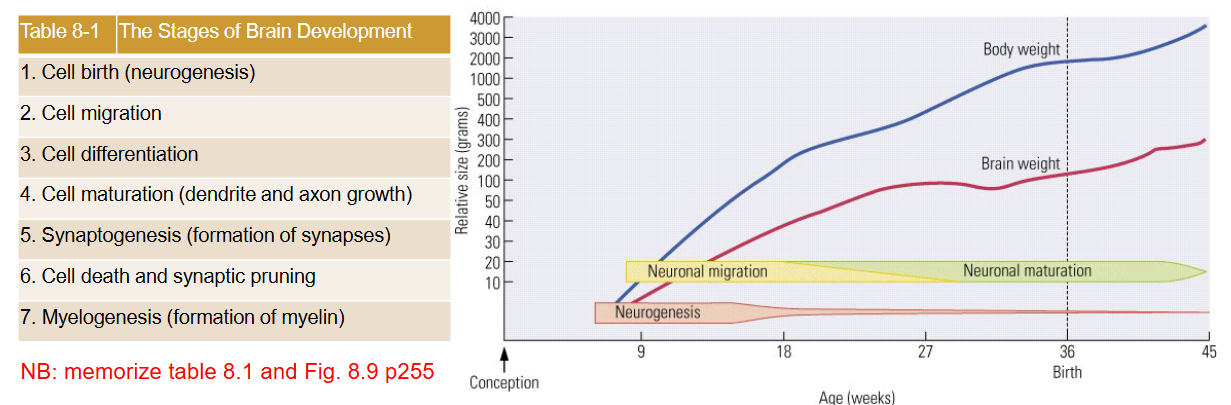
When is the formation of neurons from stem cells in the neural tube (neurogenesis) complete?
It is largely complete ~25 weeks after conception (some growth until ~5 years of age).
What part of the brain is an exception for neuron formation?
Hippocampus, new neurons continue to develop throughout life.
Choose the right answer: Coping with injury, neurotoxins and trauma is [easier / more difficult] during neurogenesis than during later stages of brain development.
Easier → it is difficult to start neurogenesis up again once it is slowed down.
What type of brain cells do brain tumors in adults arise from?
From glial cells (glioblastoma).
What type of brain cells to brain tumors in children arise from?
Brain tumors may be neuronal (neuroblastoma) → sign of lingering neurogenesis.
When does neural migration happen?
8-29 weeks (but throughout life in hippocampus).
How do the cells know where to go in Neural migration?
Radial glial cells pathways
Paths run from subventricular zone to cortical surface
Cortical layers develop from the inside out: first layer VI, then V, etc.
NB: some neurons go ‘off-road’ and follow chemical signals.
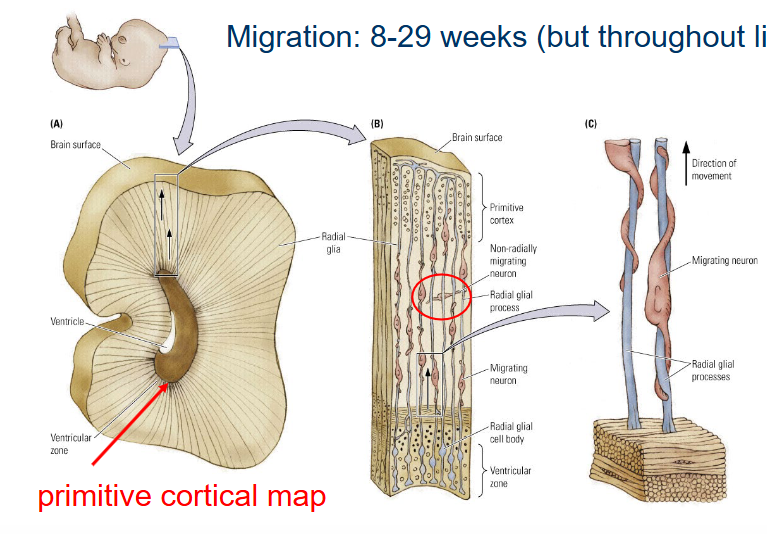
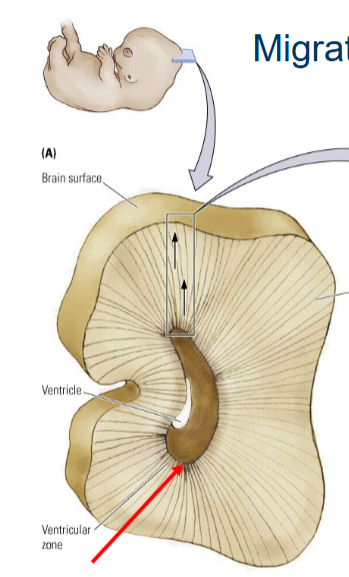
What is this part called?
Primitive cortical map.
How does the process of Cell differentiation occur?
The brain relies on a general-purpose neuron that matures into a specific cell type in a specific location when exposed to local environmental chemicals (e.g. neurotrophic factors produced by other cells).
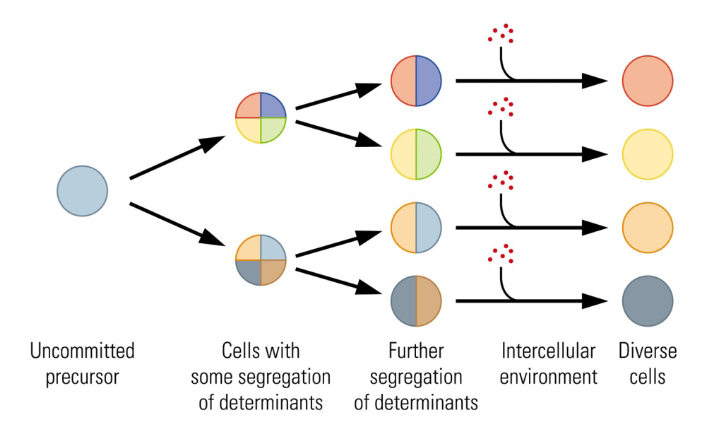
When is Cell differentiation complete? And Maturation?
It is complete at birth, but maturation goes on for years and in some parts of the brain may continue throughout life.
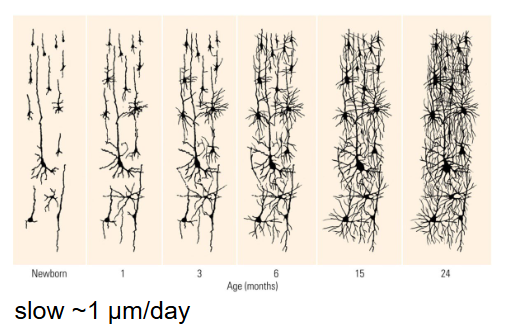
What is the difference between Dendrite and Axon growth?
Dendrite development is slow ~1 μm/day.
Axon development is fast ~1 mm/day.
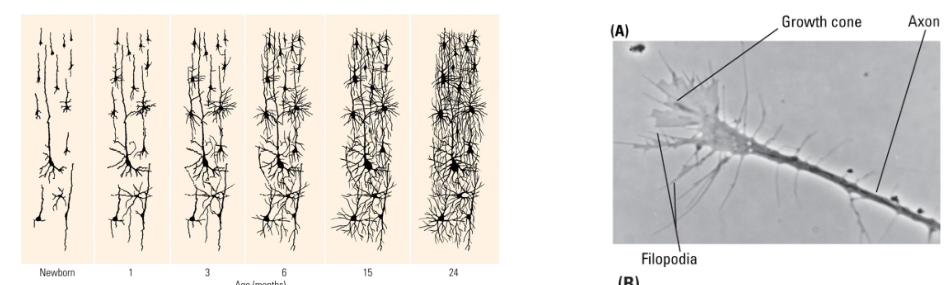
How long does Dendritic arborization (branching) take?
It begins prenatally and continues up to 2 years after birth.
Followed by the growth of dendritic spines.
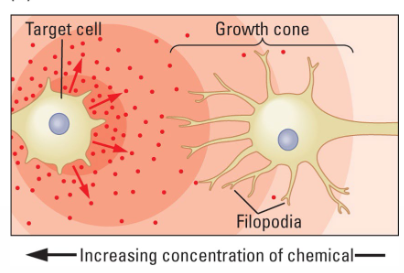
What influence do Neurotropic chemicals have on growth cones?
They attract or repel approaching growth cones.
How many synapses does the human brain have?
~100 trillion synapses (10^14 )
When do simple synaptic contacts happen for the first time?
5 months after conception.
When does Extensive synaptic development happen and where?
7 months after conception in the deepest cortical layers.
What happens to synapse numbers after birth?
The synapse numbers increase rapidly after birth.
e.g. in visual cortex synaptic density doubles between 2-4 months after birth.
Are all synapses in e.g. virtual cortex visually related?
No, there’s Synesthesia.
What is Synesthesia?
The ability to perceive a sensation of one sense as a sensation of another sense.

When does cell death happen?
When there is overproduction, then superfluous neurons die.
How do Superfluous neurons die?
They die through apoptosis because they depend on neurotrophic (nourishing) factors produced by target cells.
What is Apoptosis?
Programmed cell death.
When do Synapses on remaining neurons persist until adulthood and when are they eliminated?
Synapses on remaining neurons persist into adulthood only when they are incorporated into a specific functional network.
Other synapses are eliminated (synaptic pruning).
What is Synaptic pruning?
The elimination of synapses.
Up to 42% of human cortex synapses are eliminated through pruning → mood and behavior changes in puberty.
NB: Synaptic pruning induced by environmental cues (e.g. culture, life events), may lead to variation in neural connectivity and perception. Alterations in pruning may be related to neurodevelopmental disorders (e.g. ASD).
What is Myelogenesis?
The formation of myelin, glial development.
What is Cerebral myelination (by oligodendrocytes)?
A rough index of cerebral maturation.
Increased connectivity in the default network is related to higher intelligence.
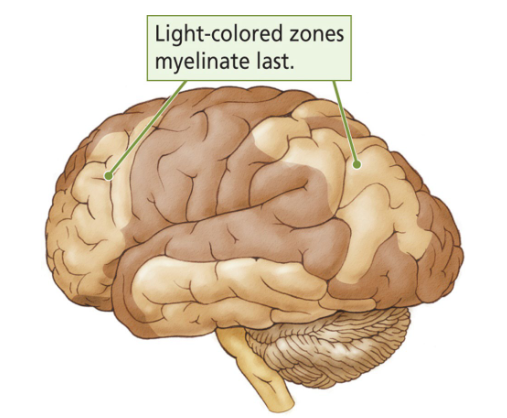
Until when does Myelination of the cerebral cortex continue?
Until adulthood.
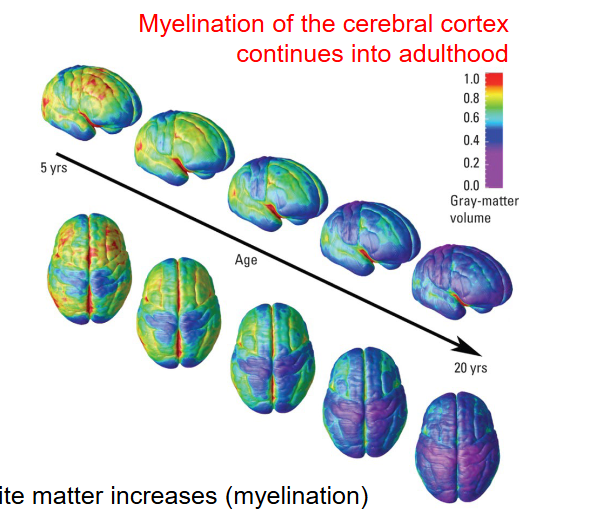
What happens to White and Grey matter during the process of Myelination over the years?
White matter increases (myelination).
Grey matter decreases (apoptosis and synaptic pruning).
In which region does Grey matter increase during the process of Myelogenesis over the years?
Gray matter in language regions increases (addition of synapses, astrocytes, and blood vessels).
Why do we use emerging behaviors to infer neural maturation?
Behavior cannot emerge until the required neural ‘hardware’ has developed.
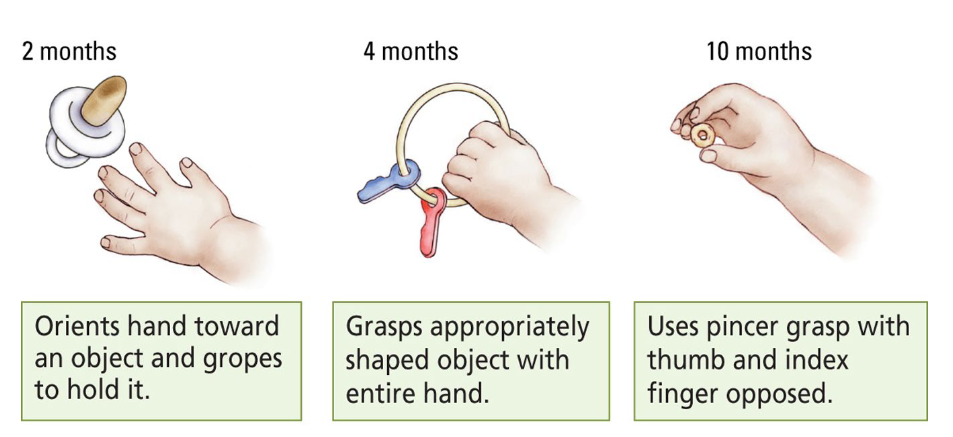
What are Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development?
Sensorimotor
Preoperational
Concrete operational
Formal operational
What does Neural plasticity mean?
The brain is a flexible organ, connections are not static.
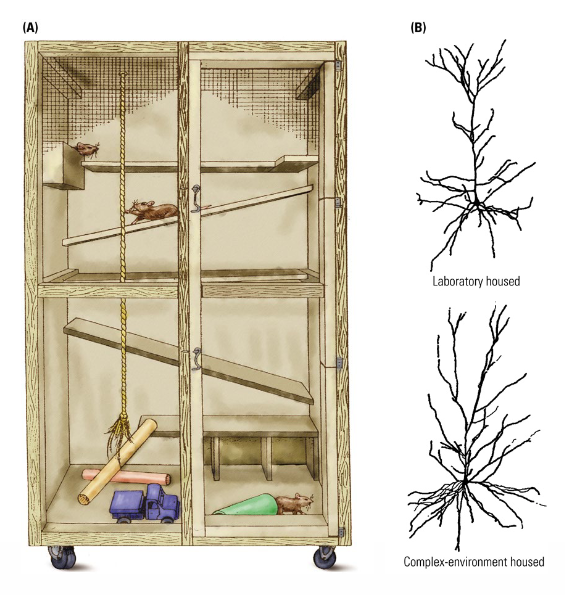
How does Growing up in an enriched environment lead to enhanched neural development?
Increase in synapses result from increased sensory processing in a complex environment.
What are Androgens?
Male sex hormone; mainly testosterone.
male sex characteristics
secondary sex characteristics
changes in the brain
What are Estrogens?
Female sex hormone; estrone, estradiol, estriol.
menstruation cycle, pregnancy
What induces changes in the brain?
Number of neurons
Branching of dendrites
Growth of synapses
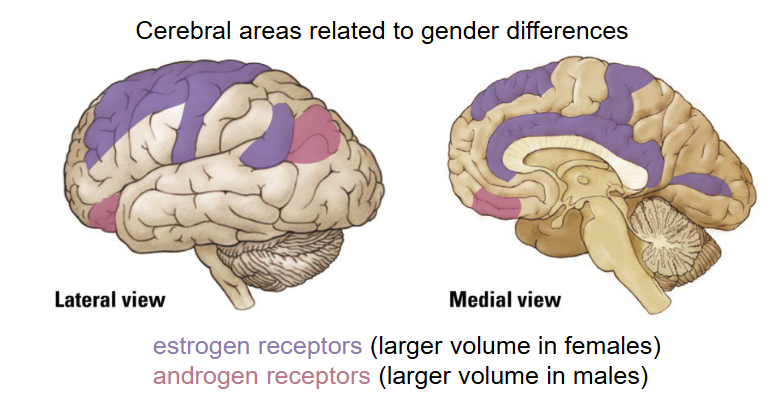
What are the cerebral areas related to gender differences?
NB: behavioral differences between males and females are not solely the result of environmental experiences.
What does the Chemoaffinity hypothesis entail?
Specific molecules in different cells in various midbrain regions give each cell a distinctive chemical identity.
Incoming axons seek out a specific chemical, and land in a general midbrain region.
e.g. axons from retinal neurons grow towards optic tectum.
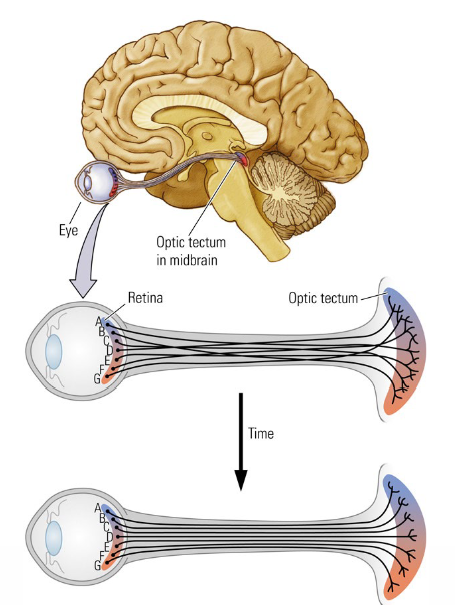
What is precise positioning (fine-tuning) of neural placement caused by?
By postnatal experience.
Adjacent receptors are typically activated at the same time, thus forms connections to the same neurons.
“Cells that fire together, wire together”.
What are Critical periods for Experience and Brain development?