Unit Two Exam
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
Why is the first law of thermodynamics not enough to predict if a process will occur?
Due to the presence of the system to achieve low energy and increased entropy, additional factors such as temperature and pressure must be considered.
When talking about thermodynamics, Kelvin stated that a specific conversion can not occur. Think about a heat pump?
This principle, known as Kelvin's statement of the second law of thermodynamics, asserts that it is impossible to convert all absorbed heat from a heat source into work without any waste energy.
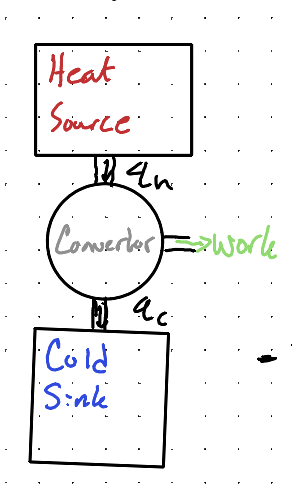
What is Kelvin’s ideal heat engine?
A theoretical engine that operates in a reversible cycle between two heat reservoirs, converting heat absorbed from the hot reservoir into work and releasing waste heat to the cold reservoir, achieving maximum efficiency.
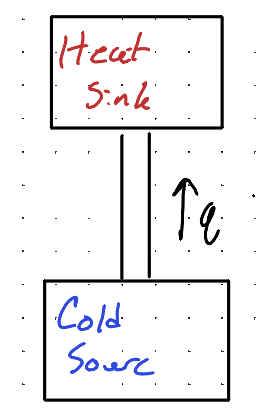
What did Clausius state about the cold engine in relation to the second law of thermodynamics.
The movement of heat from cold sink to heat source cannot occur because heat does not spontaneously flow from a colder body to a hotter body without external work being done.
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
The entropy(s) of an isolated system increases for a spontaneous change (∆totalS > 0)
Equation of Second Law of Thermodynamics?
Stotal = S +Ssurr
What is the idea when viewing Entropy from a Classical View?
Heat stimulates random motion & increase disorder.
What is the differential equation for disorder?
dS = dqrev/T
When talking about entropy, if the temperature is high then, …
heat causes a small increase in disorder.
When talking about entropy, if the temperature is low then, …
adding heat causes a large increase in disorder.
What is the integrated form of entropy?
∆S = ∫dqrev/T; Note: this is an extensive property and has the units of J/K
What is the equation for isothermal reversible expansion of a perfect gas when talking about entropy?
∆S = nR ln(Vf/Vi) or ∆Sm = R ln(Vf/Vi)
When looking at the entropy of surroundings, assuming the surround is a large heat reservoir (Volume adn Temperature of Surrounding don’t change), what is the equation?
dSsurr = dqsurr/Tsurr
If the system is an adiatic change q = 0, then…
qsurr = 0 and dSsurr = 0.
What is a microstate?
A microstate is a specific configuration of a system's particles at a given energy level, representing one possible arrangement within a macrostate. The total number of microstates contributes to the entropy of the system, indicating its level of disorder.
As the temperature increases, then what happens to microstates?
The number of accessible microstates increases, leading to higher entropy and greater disorder in the system.
A larger 𝒲 means
larger S
If all molecules are in 1 energy state, then…
the number of microstates is minimized, resulting in the lowest possible entropy for the system. 𝒲 = 1 and S = 0
At higher temperatures, molecules do what?
Spread over more available energy states and increase the number of accessible microstates.
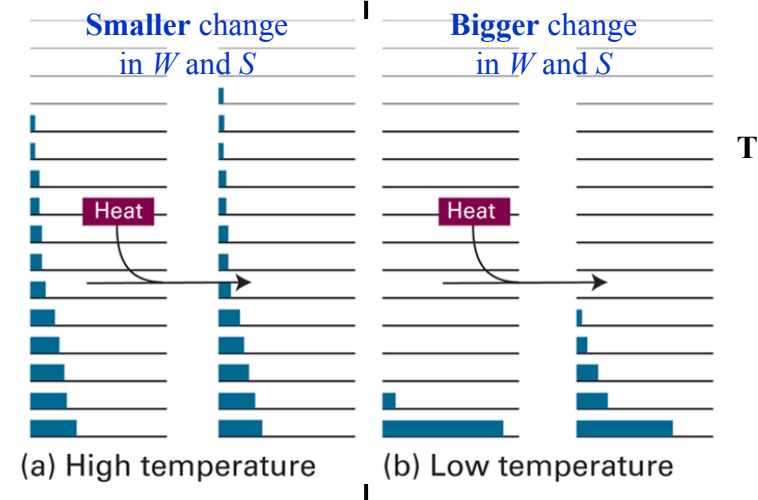
Why is ∆S proportional to 1/T?
At higher Temp, molecules spread over a large number of energy states, then for a given q there is a small increase in microstates and a small increase in entropy.
At smaller Temp, molecules spread over a large number of energy states, then for a given q there is a large increase in microstates and a large increase in entropy.
When using the statistical view of entropy, what is it possible to calculate?
The absolute entropy and cannot readily apply the Boltzmann formula to study the surroundings (too complex for microstates to be meaningful)
When using the thermodynamic view of entropy, what is the difficult to study?
The absolute entropy although ∆S can be found, and can be easily applied to study entropy of the surroundings.
If the goal is to prove that entropy is a state function, what should we do?
Use the Carnot cycle of a perfect gas as a working unit (the converter of heat to work) to show that ∆S is independent of the path taken between two states and only depends on the initial and final states.
What is the Carnot Cycle?
A special operation of a theoretical heat engiune in the most efficient way (converts heat into work)
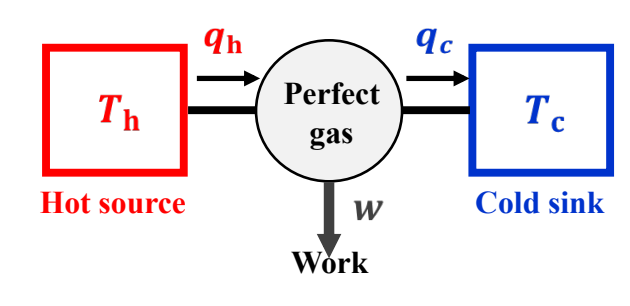
How do we break up a reaction to prove entropy as a state function?
To first perform reversible isothermic expansion (T = Th), followed by reversible adiabatic expansion (q=0, t decr). Third, perform isothermic compression (T=Tc), and finally Reversible adiabatic compression (q=0, T incr)
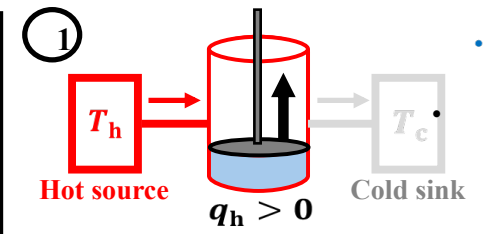
What is the entropy change during the first step of Carnot Cycle?
∆S = qh/Th
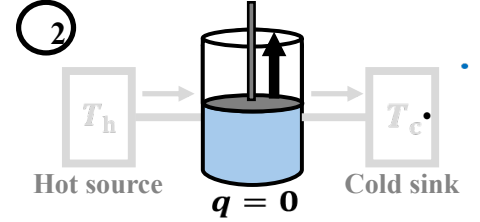
What is the entropy change during the second step of Carnot Cycle?
∆S = 0
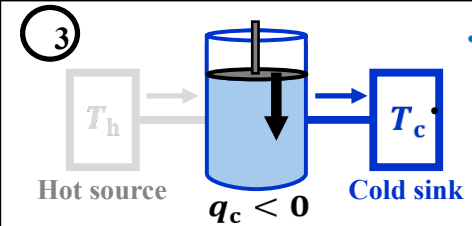
What is the entropy change during the third step of Carnot Cycle?
∆S = qc/Tc
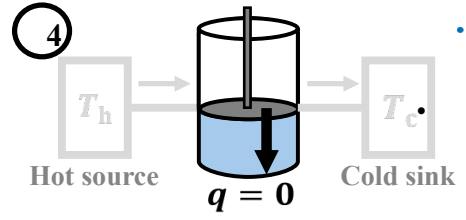
What is the entropy change during the fourth step of Carnot Cycle?
∆S = 0
What equation is shown from the Carnot Cycle for a heat engine?
qh/qc = - Th/Tc
Using the carnot cycle we can define efficiency in an engine which is the rate of using work provided compared to heat supplied. What is the equation?
𝓃 = lwl / lqhl
What is the Carnot efficiency in terms of temperature which shows the highest efficiency theoretically possible for a heat engine.
𝓃 = 1 - Tc/Th
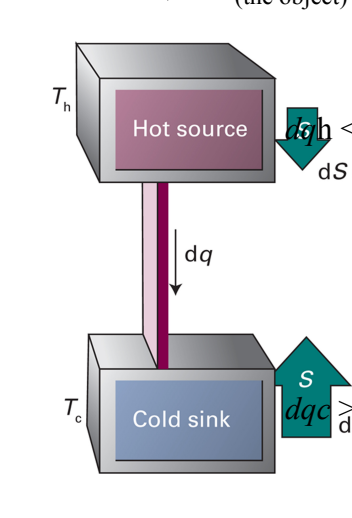
What is the Clausius Inequality and what does it show use?
ds ≥ dq/T; The Clausius Inequality states that the change in entropy (ds) of a system is greater than or equal to the heat transfer (dq) divided by the temperature (T) at which the transfer occurs. It highlights the second law of thermodynamics, indicating that entropy in an isolated system can only increase.
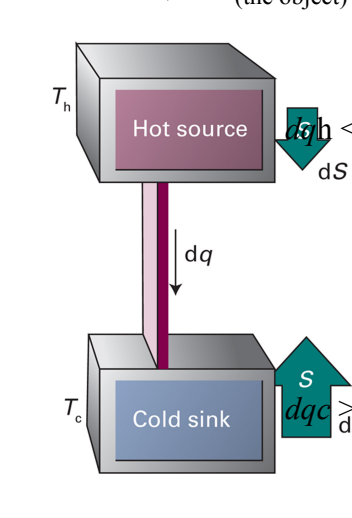
What are the implications of a Clausius Inequality?
In an isolated system, S cannot decrease for a spontaneous change. (dq = 0 and thus dS ≥ 0).
Spontaneous processes are necessarily irreversible (dStot ≥ 0 where dStot≥0 is irreversible and dStot = 0 is reversible)
A process is at equilibrium if it is reversible and if dStot=0
The cooling of an object to the temperature of the surroundings is spontaneous and so the cooling process of the object is spontaneous.

What is the ∆Stot for a reversible isothermal expansion of a perfect gas?
∆Stot = 0, which makes sense because the system is at equilibrium with the surrounding.

In a reversible isothermal expansion of a perfect gas, as gas expands (Vf>Vi) then
S increases and Ssurr decreases

In a reversible isothermal compression of a perfect gas, as gas compresses (Vi>Vf) then
S decreases and Ssurr increases.
At equilibrium what happens with entropy?
There is a “trade of disorder”
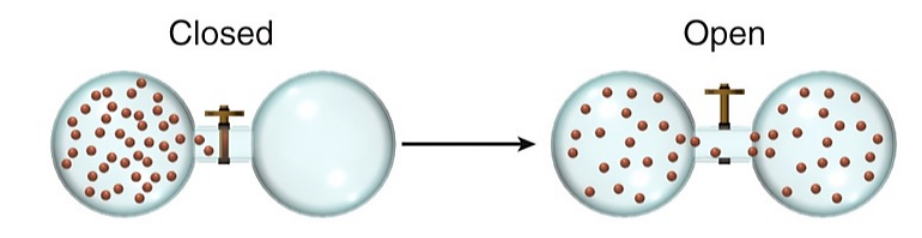
What is the ∆Ssurr of a irreversible free isothermal expansion (pex = 0)
is equal to zero, as no external work is done and the surroundings do not experience a temperature change.
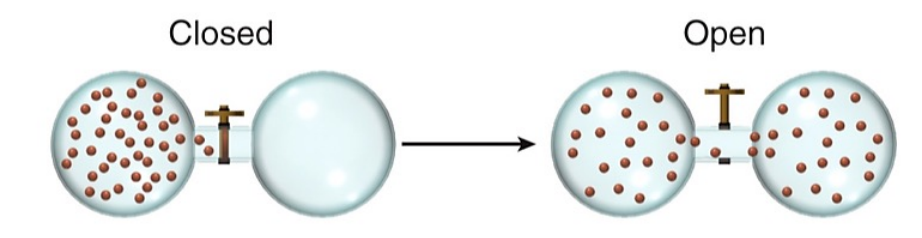
What is the ∆Stotal equal to in an irreversible free isothermal expansion?
Since nRln(Vf/Vi) > 0; ∆Stotal > 0, which makes sense because this is an irreversible, spontaneous change because the system entropy goes up but the entropy of the surroundings is not affected in this case
What do we anticipate during a phase transition?
A change in entropy, because of a change in the ordering of molecules
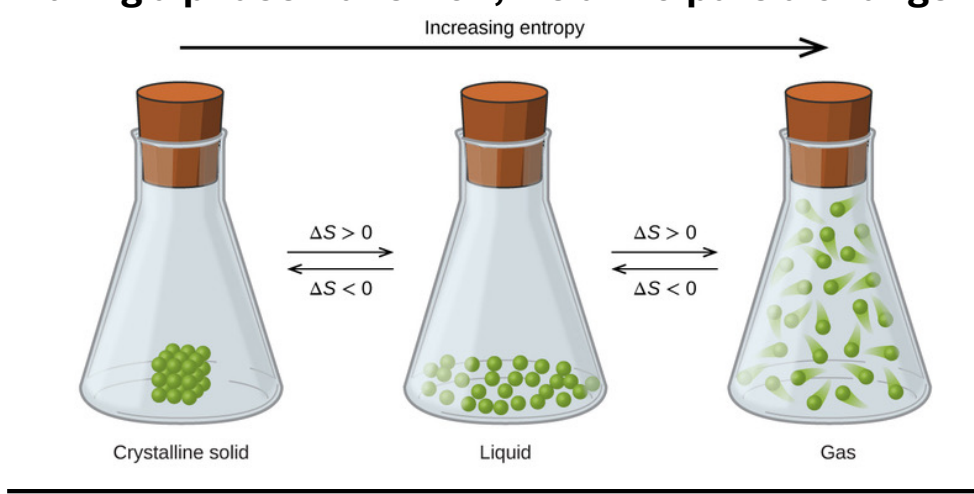
What is normal transition temperature?
The temperature at which a substance changes its phase, such as solid to liquid or liquid to gas. This transition occurs at a specific temperature unique to each substance under given pressure conditions.
What is the entropy of a phase transion?
∆S = ∆trsH/Ttrs
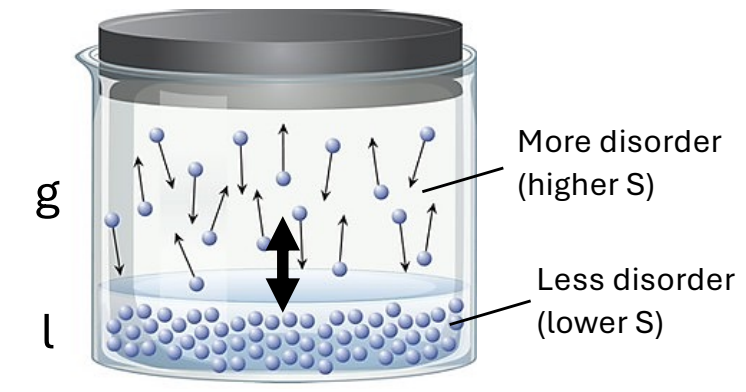
When going from a liquid to a gas what is the sign of ∆trsH?
positive, indicating that heat is absorbed during the phase transition.
When going from a gas to a liquid what is the sign of ∆trsH?
negative, indicating that heat is released during the phase transition.
When going from a liquid to a gas what is the sign of ∆trsS?
positive, indicating that disorder increases during the phase transition.
When going from a gas to a liquid what is the sign of ∆trsS?
negative, indicating that disorder decreases during the phase transition.
During a phase transition from liquid to gas, what happens to system?
Disorder increases
During a phase transition from gas to liquid, what happens to system?
Disorder decreases (more ordered)
What is Trouton’s Rule?
Liquidi Vaportization give approximately constant value for the entropy of vaporization for many liquids, because the change in volume that occurs is similar for most liquids. (Around 85-88 J/mol·K)
What is the exception to Trouton’s Rule?
When strong molecular interactions cause partial ordering in the liquid. (S increases more than expected compared to a fully disordered liquid.)
What is the increase in entropy during heating (at constant pressure)
S(Tf) = S (Ti) + ∫Cp/T dT
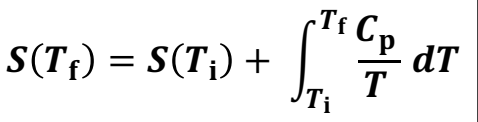
What is the increase in entropy during heating (with both constant pressure and heat capacity)
S(Tf) = S(Ti) + Cp ln(Tf/Ti)
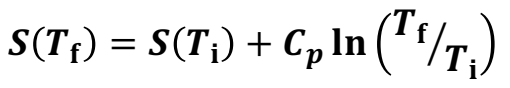
If both V and T change at the same time how do you find entropy?
By simplifying the problem to hypothetical paths with iso-properties.
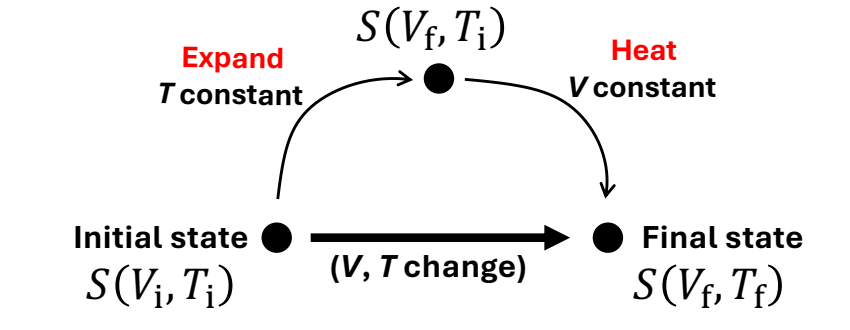
What are the two ways to determine the entropy of a system?
Using the Boltzmann equation or by using calorimetric data.
What is the entropy equation for a gas using calorimetric techniques?
Sm(T2) = Sm(0) + ∫0Tf Cp,m(S,T)/T dT + ∆fusH(Tf)/Tf ∫TfTb Cp,m(S,T)/T dT + ∆vapH(Tb)/Tb + ∫TfT2 Cp,m(S,T)/T dT
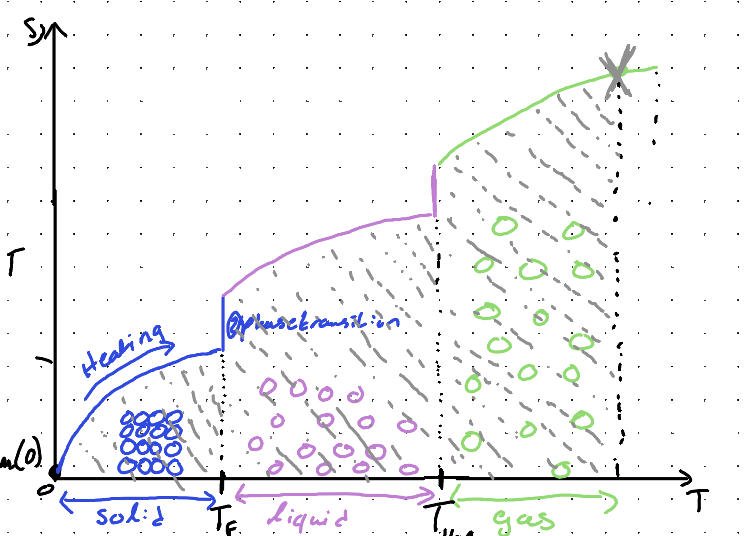
Why does the following graph jump at specific points?
This occurs due to phase transitions, where entropy changes rapidly as the system undergoes a change in state, such as melting or boiling.
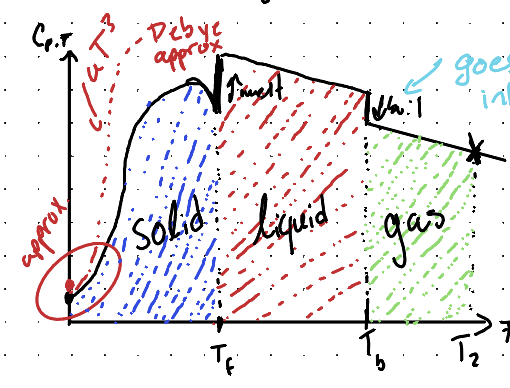
Why does the graph of heat capacity versus temperature go down after the transition from liquid to gas?
Due to the decrease in intermolecular interactions between molecules that results in an easier expansion of the compound.
What is the Debye Approximation?
A method used to model the specific heat of solids at low temperatures, which accounts for the contribution of phonons to the heat capacity.
What is the equation of Debye Equation for non metallic solids?
Cp,m = aT3
What is the equation of Debye Equation for metallic solids?
Cp,m = bT
Using the Debye Approximation for non-metallic solids, what is the equation of entropy?
Sm(T) = Sm(0) + 1/3 Cp,m (T)
Using the Debye Approximation for metallic solids, what is the equation of entropy?
Sm(T) = Sm(0) + Cp,m (T)
What is the Nernst Heat Theorem?
For any chemical or physical change the limT→0 ∆S = 0
What is an orthorhomic sulfur?
Orthorhombic sulfur is a crystalline form of sulfur that has a distinct symmetry characterized by three unequal axes at right angles to each other. It is one of the allotropes of sulfur and is stable at room temperature.
What is monoclinic sulfur?
Monoclinic sulfur is a crystalline allotrope of sulfur characterized by a unique symmetry with two equal axes and one unequal axis, typically forming needle-like crystals. It is stable at higher temperatures compared to orthorhombic sulfur. This form is stable at temperatures above 96 °C and can transform to orthorhombic sulfur upon cooling.
What does the third law of thermodynamics say?
The entropy(s) of every perfect crystalline substance is zero at T=0.
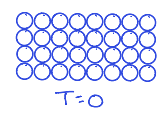
What is residual entropy?
refers to the entropy that remains in a system at absolute zero temperature due to incomplete order or randomness in the molecular arrangement. It indicates that some configurations are still accessible even when thermal motion ceases.
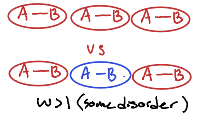
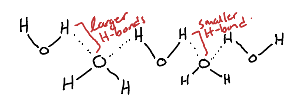
How does Ice not have zero entropy at absolute temperature, instead having 3.4 J/Kmol
Due to the difference in H-bond lengths between molecules of water.
When talking about the balance of the Helmoltz equation, dA = dU - TdS does what?
Moving to a lower energy state does not imply a spontaneous process, meaning that entropy also plays a role.
What is the equation of Helmholtz Energy?
A = U - TS
If the Helmholtz Energy is held to constant T, what is the equation?
dA = dU - T • dS
If V is constant T•dS ≥ dU, which means what?
dAt,V ≤ 0
What is the equation of Gibbs Energy?
G = H - T•S
If temperature is held constant then what is the Gibbs Energy equation?
dG = dH - T • dS
If pressure is held constatn then T•dS ≥ dH, then
dGp,T ≤ 0
If T•dS ≥ dU at a constant U then
dSU,V ≥ 0
If T•dS ≥ dH at a constant H then
dSH,p ≥ 0
What is the challenge of using entropy to predict spontaneity?
We have to also look at the entropy of the surroundings not just the system
If ∆rCpº is independent of temperature, then
∆rSº(T2) = ∆rSº(T1) + ∆rCp ln (T2/T1)
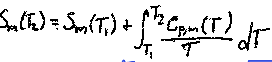
We say that
therefore
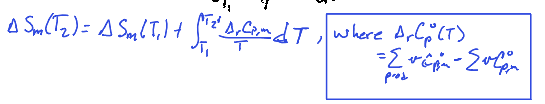
What are the notes of standard reaction entropy?
Generally ∆rSº > 0 if there is a net formation of gases in the reaction
Smº of elements in reference state is not zero (assuming T > 0)
What is the equation of Standard Reaction Entropy, ∆rSº
∆rSº = ∑prodSmº - ∑reacSmº
What is standard entropy?
The entropy of a substance in its standard state at temperatures
What is the 3rd Law of Entropies?
Entropiesa arte based on an absolute scale where S(0) = 0
When talking about dG, when is dG driven by an increase in entropy?
When it is an endothermic process where dG < 0 when TdS > dH
If entropy decreases (dS < 0), are only spontaneous when…
the enthalpy change is negative (dH < 0) and the temperature is low enough.
Why is Gibbs energy more common in chemistry than Helmholtz energy?
Gibbs energy is more common because it considers both enthalpy and entropy at constant temperature and pressure, which are typical conditions in chemical reactions.
what is dG equal to?
The change in reversible non-expansion wortk and is calculated as dG = dH - TdS. (dwadd,rev)
Since G is a state function hwo can standard reaction Gibbs energy be calculated?
∆rGº = ∆rHº - T ∆rSº when temperature is constant or ∆rG = ∑prodv∆fGº - ∑reacv∆rGº
What is the ∆rGº of an element in its reference state?
It is defined as zero, as elements in their reference state are considered stable and constitute the baseline for measuring Gibbs energy changes.
The sum of Gibbs Energy in a cycle is what?
It is equal to zero, as per the principle of conservation of energy in thermodynamic cycles.
What is the change in Helmholtz energy equal to?`
The maximum work possible in a system with constant volume.
What is dwmax equal to?
dU - TdS because you want wmax as negative as possible.
In the case of ∆S decreasing what does entropy act as?
An energetic tax for the max work in a system at constant volume, meaning that ∆A is the part of ∆U that is free to do work.
In the Case of ∆S increasing what does entropy act as?
As a tax refund given by nature meaning that ∆A is more negative than ∆U.
What is the fundamental equation?
dU = Tds - pdV
What assumptions are made for the fundamental equation?>
Constant Composition
Closed system
Only expansion work is done
equation applies to reversible or irreversible changes
What is the change in Potential Energy (U) over the change in entropy under constant volume equal to?
Temperature
What is the change in Potential Energy (U) over the change in volume under constant entropy equal to?
Pressure