108.2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Filtration
first step in urine formation; filters excess fluid and waste products out of blood
reabsorption
renal tubules return nutrients and water back into capillaries
secretion
waste ions and hydrogen ions pass from the capillaries into the renal tubules
25%
The kidneys receive approximately what percentage of the blood pumped through the heart at all times?
1200 mL/min
How much blood flows through the kidneys per minute?
600-700 mL/min
How much plasma flows through the kidneys per minute?
The afferent arteriole supplies blood to the kidneys; the efferent arteriole carries the blood leaving the kidneys
What is the difference between the efferent and afferent arterioles?
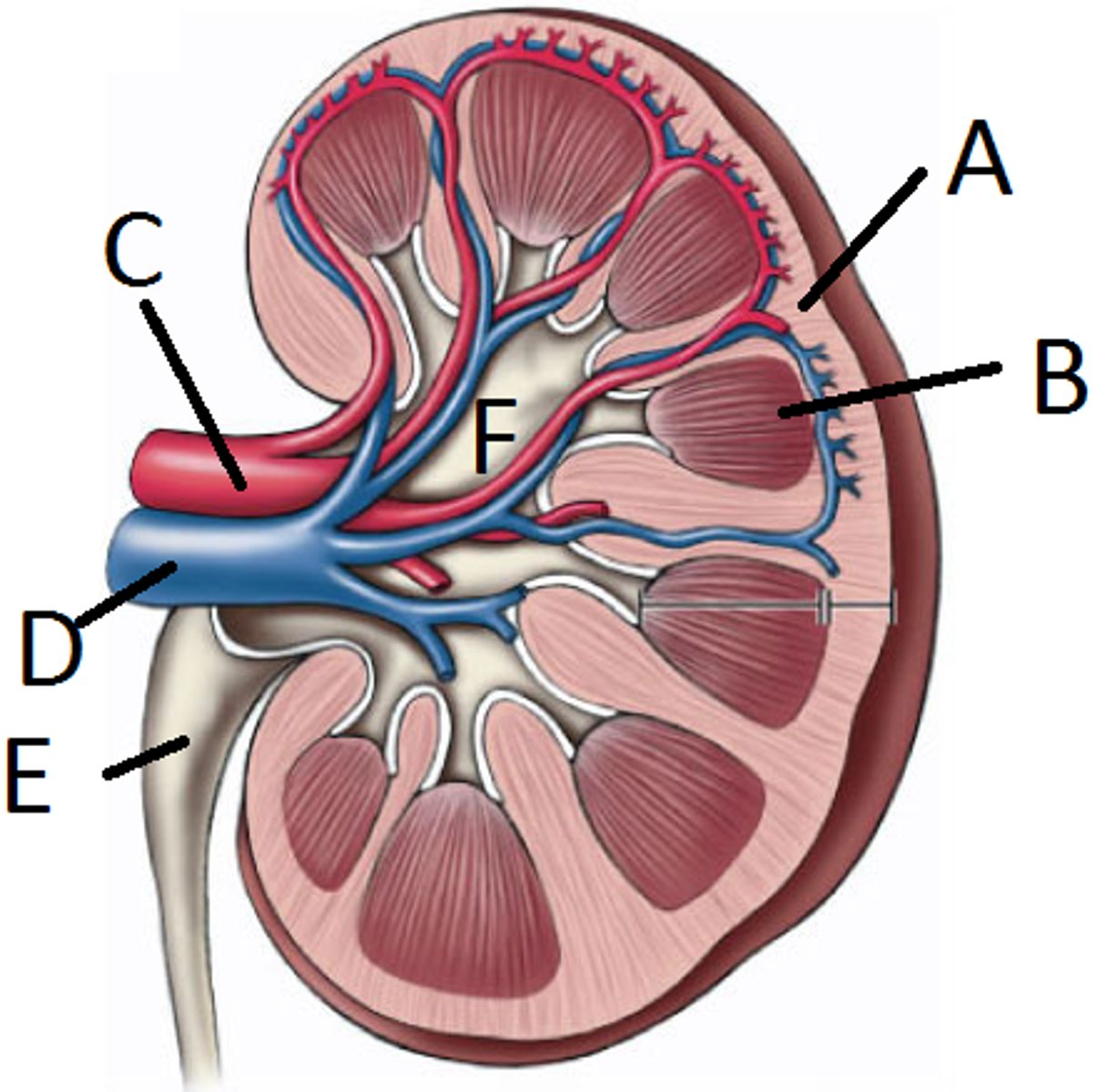
Enters through C (renal artery) leaves through D (renal vein)
Map the renal blood flow from the renal artery to the renal vein.
1.73 m^2
What is the average BSA?
size; filters out molecular weights smaller than 70,000
What is non-selective filtration in Bowman's capsule based on?
cellular structure of capillary walls and Bowman's capsule; hydrostatic and oncotic pressure; RAAS
What other factors influence filtration in Bowman's capsule?
capillary wall - endothelial cells have pores (fenestrated) that block large molecules and cells
basement membrane- further restricts large molecules
Bowman's capsule inner layer - intertwining podocytes and membrance covered filtration slits
What are the three cellular layers of the Glomerulus?
shield of negativity
repels molecules with a negative charge; filters molecules that would otherwise pass through barrier
renin starts RAAS which helps maintain a consistent glomerular blood pressure; if systemic blood pressure is low, it dilates the afferent arteriole and constricts the efferent arteriole; if system BP is high, afferent arteriole constricts and efferent arteriole dilates
How does renin affect renal blood flow?
ultrafiltrate has proteins filtered out
How does ultrafiltrate differ from plasma?
proximal convoluted tubule
When does reabsorption of ultrafiltrate begin?
active transport
transport in tubular reabsorption in which substance must combine with a carrier protein
passive transport
transport in tubular reabsorption that takes place due to concentration or electrical potential differences
renal threshold
The concentration at which a substance in the blood that is not normally excreted by the kidneys begins to appear in the urine
tubules
where concentration of plasma ultrafiltrate mainly takes place in the nephron
descending loop of henle
part of loop of henle in which water reabsorbs due to osmotic pressure
ascending loop of henle
part of loop of henle in which chloride and sodium are actively reabsorbed; water impermeable
aldosterone
hormone that controls sodium reabsorption
collecting duct
where final concentration of filtrate takes place
anti-diuretic hormone
hormone that regulates reabsorption of water in collecting ducts; prevents dehydration
decreased ADH levels, increased urine output
How is ADH levels and urine output affected when the body is well hydrated?
increased ADH levels, decreased urine output
How is ADH levels and urine output affected when the body is dehydrated?
secretion
from blood to tubule
reabsorption
from tubules to blood
tubular secretion
eliminates waste products; regulates acid-base balance in body
phosphate and ammonia
two compounds that H+ ions combine with in urine elimination
glomerular, tubular, intersitial
three categories of renal disease
immunologic disorders, nephrotic syndrome, chemical exposure
examples of glomerular renal disease
damaged tubules, acute tubular necrosis, metabolic and hereditary disorders
examples of tubular renal disease
infections, UTI, inflammatory conditions, Pyelonephritis
examples of interstitial renal disease
Renal Lithiasis
kidney stones
urinary stasis, chemical concentration, pH
causes of renal lithiasis
filtering capacity of glomeruli
what glomerular filtration tests measure
it cannot be reabsorbed or secreted by tubules
what is an important criteria for substances used in filtration tests
endogenous
substance that is already present in body
exogenous
substance that must be added to body
urea
substance that is present in all urine specimens
40% of urea is reabsorbed
Why is Urea Clearance test not considered the best to measure filtration?
creatinine clearance test
most common laboratory test used for measuring renal filtration
must be a 24 hour urine specimen; urine must be refrigerated to prevent bacterial breakdown; tubular secretion increases with high blood creatinine levels; highly pigmented urine affects results
disadvantaged of creatinine clearance test
serum creatinine, cystatin C, Beta2microglobulin
What are some newer tests being used for filtration rate?
mL/min
unit of measure for creatinine clearance
to determine the amount of creatinine completely cleared from the plasma in one minute
principle of creatinine clearance test
C = UV/P x 1.73/BSA
formula for creatinine clearance test
can be used for routinely screening patients as part of a metabolic profile, to monitor patients already diagnosed with renal disease, and when prescribing medicine that require adequate renal clearance
clinical significance of glomerular filtration rate tests
1: GFR greater than or equal to 90 ml/min/1.73 m
2: GFR 60-89
3: GFR 30-59
4: GFR 15-29
5: GFR less than or equal to 15
stages of chronic kidney disease
Renal concentrating ability
what does renal reabsorption tests measure?
osmolality
most common renal concentration ordered in lab?
osmometer
what measures osmolality
freezing point/vapor pressure
two types of osmometers
evaluates renal concentration ability, monitors course of renal disease, monitors fluid or electrolyte therapy, differentiates between hyponatremia (not enough Na+2) and hypernatremia (too much Na2+), evaluates secretion and response to ADH
clinical significance of monitoring osmolality
3:1
normal urine to blood ration when monitoring hydration controlled osmolality
tubular secretion test
test used to measure complete blood flow through nephrons
p-aminohippuric acid (PAH)
example of tubular secretion test
Osmolarity
total concentration of all solute particles in a solution
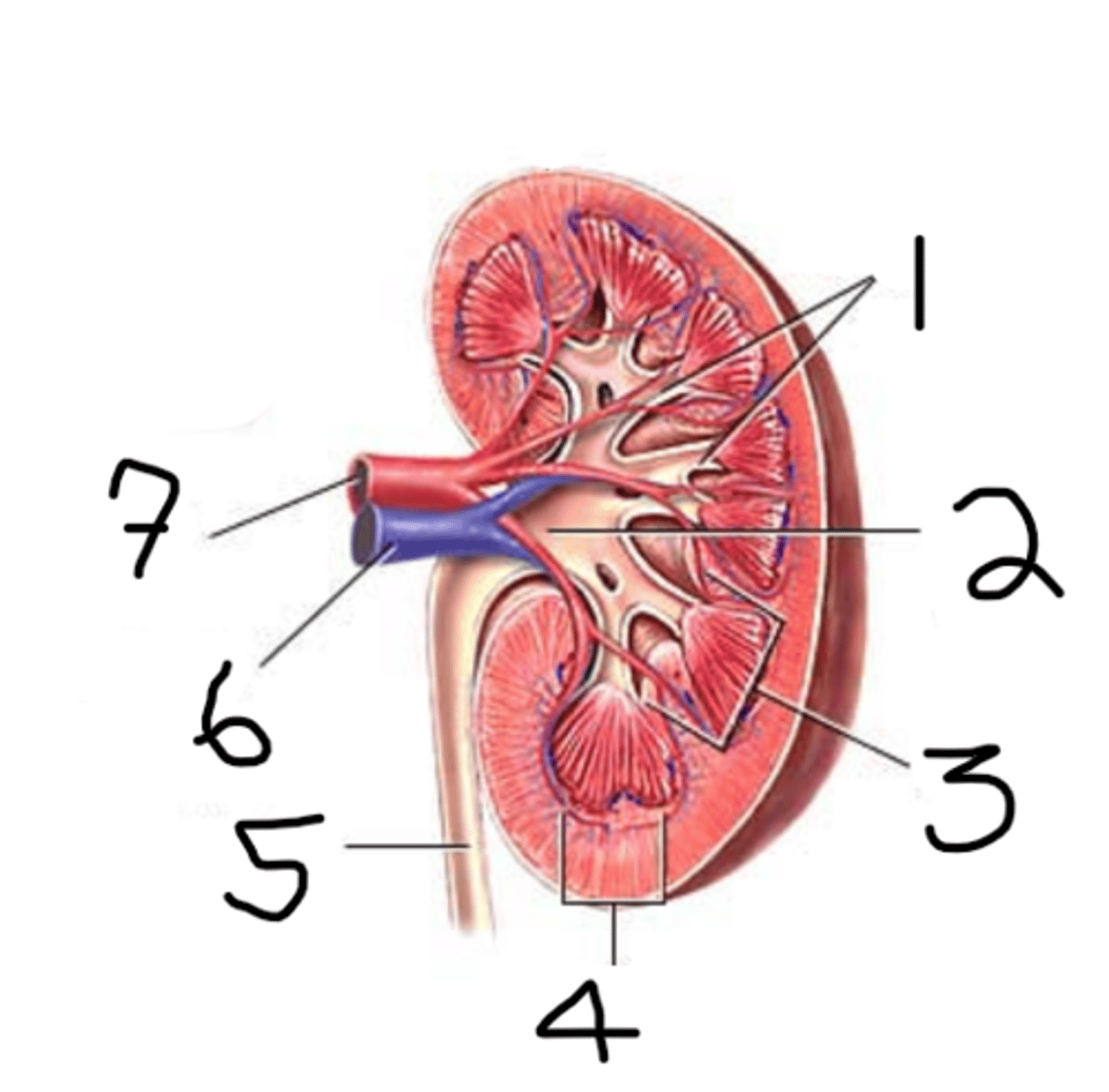
1. calyx
2. renal pelvis
3. medulla
4. cortex
5. ureter
6. renal vein
7. renal artery
label
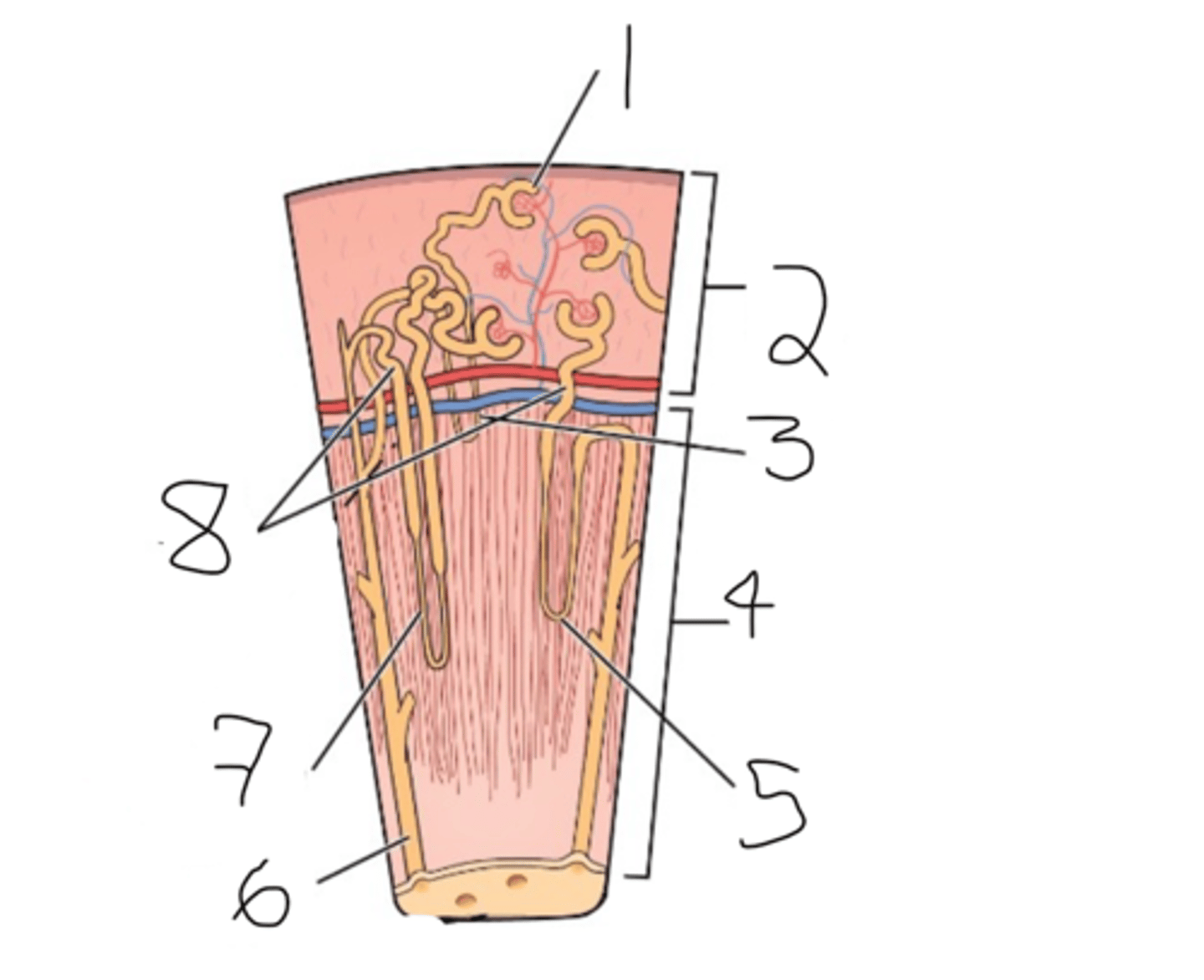
1. glomerulus
2. renal cortex
3. cortical nephron
4. renal medulla
5. juxtamedullary nephron
6. collecting duct
7. loop of henle
8. renal tubule
label