NEUR305: Action (lower motor neurons)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is voluntary control of muscles?
Movements under control of the brain (cortex)
What is rhythmic control of muscles?
Timing and spatial organization; controlled autonomously by spinal or brain stem circuitry.
What are reflexes?
Response to specific stimuli that are generated by simple neural circuits in spinal cord or brain stem
What is the motor system hierarchy?
An internal representation is generation by the brain of the world. This representation is continuously updated by sensory information to maintain accuracy.
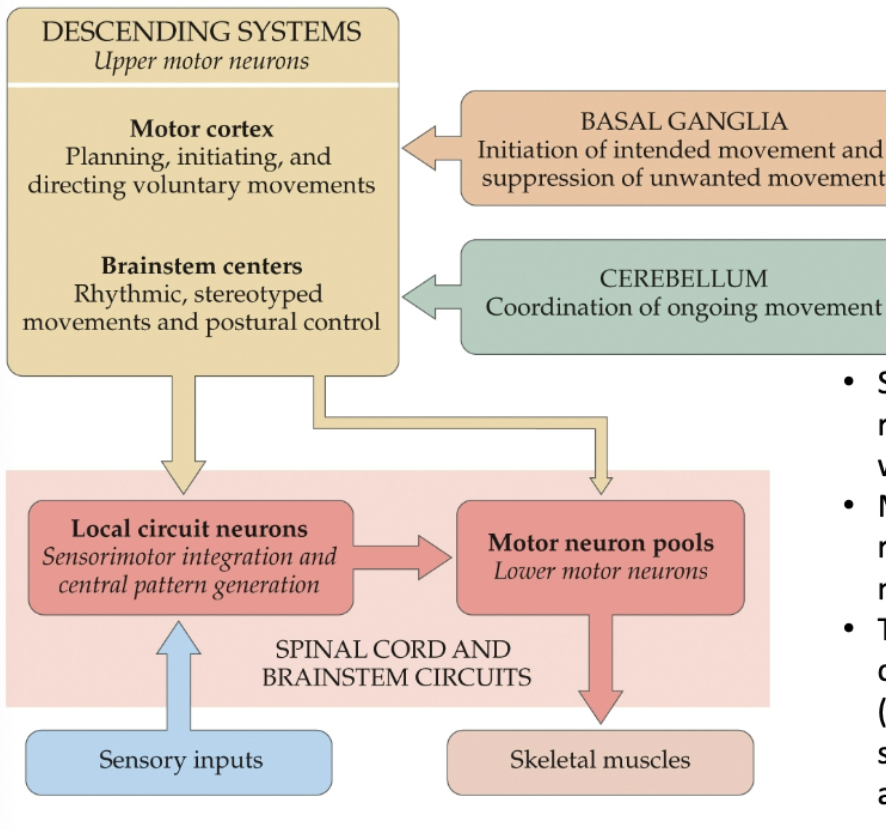
What is an efference copy?
Copy of movement signal generated by the motor system (compared to sensory re-afferance copy)
What neurons are in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord?
Sensory neurons
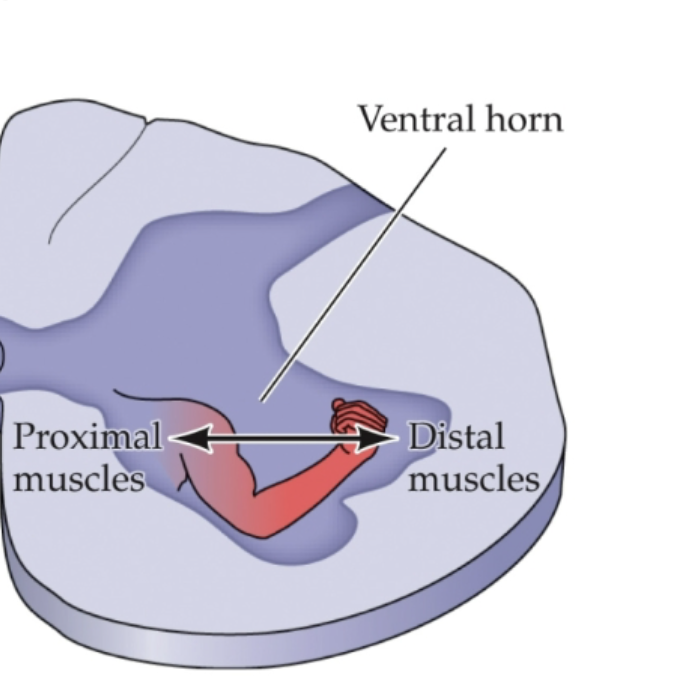
What neurons are in the ventral horn of the spinal horn?
Lower motor neurons; clustering of neurons with similar function is seen here!
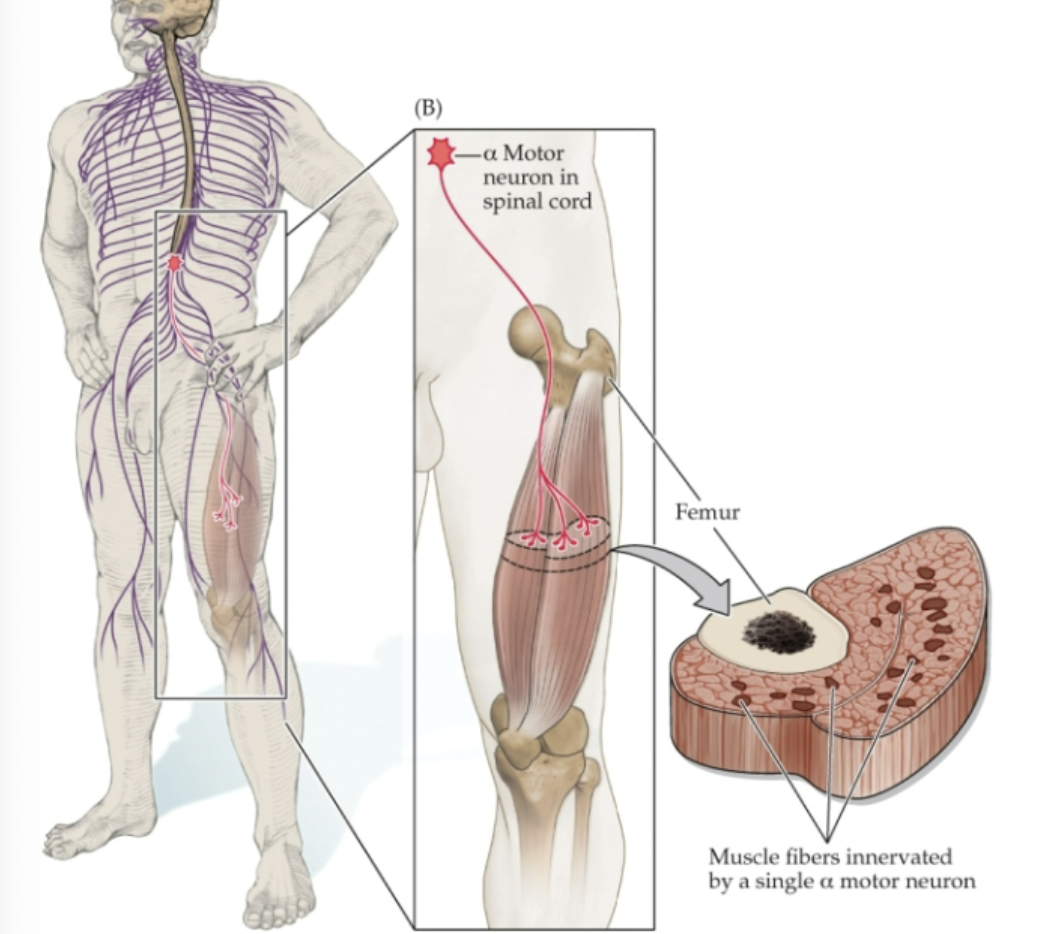
What is a motor unit made up of?
A alpha motor neuron and all the skeletal muscle fibers it acts upon!
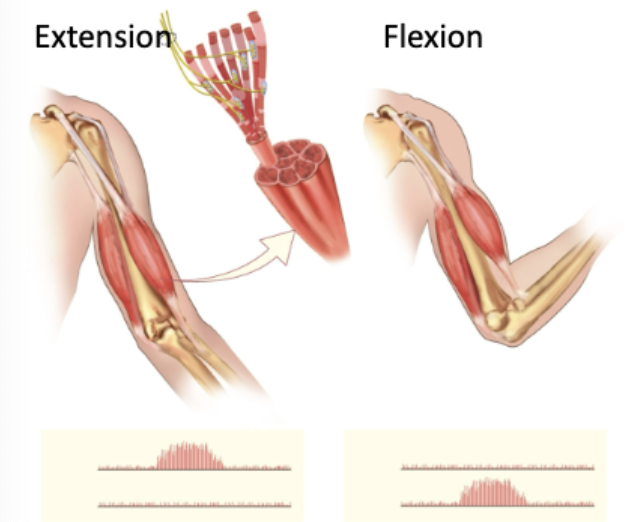
What’s important of extensors and flexors?
Extensors are NOT active when flexors are active! Can’t do both at the same time!
Forced exerted by a muscle depends on the # of motor units and 3 properties:
contraction speed
maximal force
fatiguability
How do we measure motor unit properties?
Measured by EKGs, force of individual motor units:
Twitch contraction - response to a single action potential
Contraction time - time until twitch reaches peak force
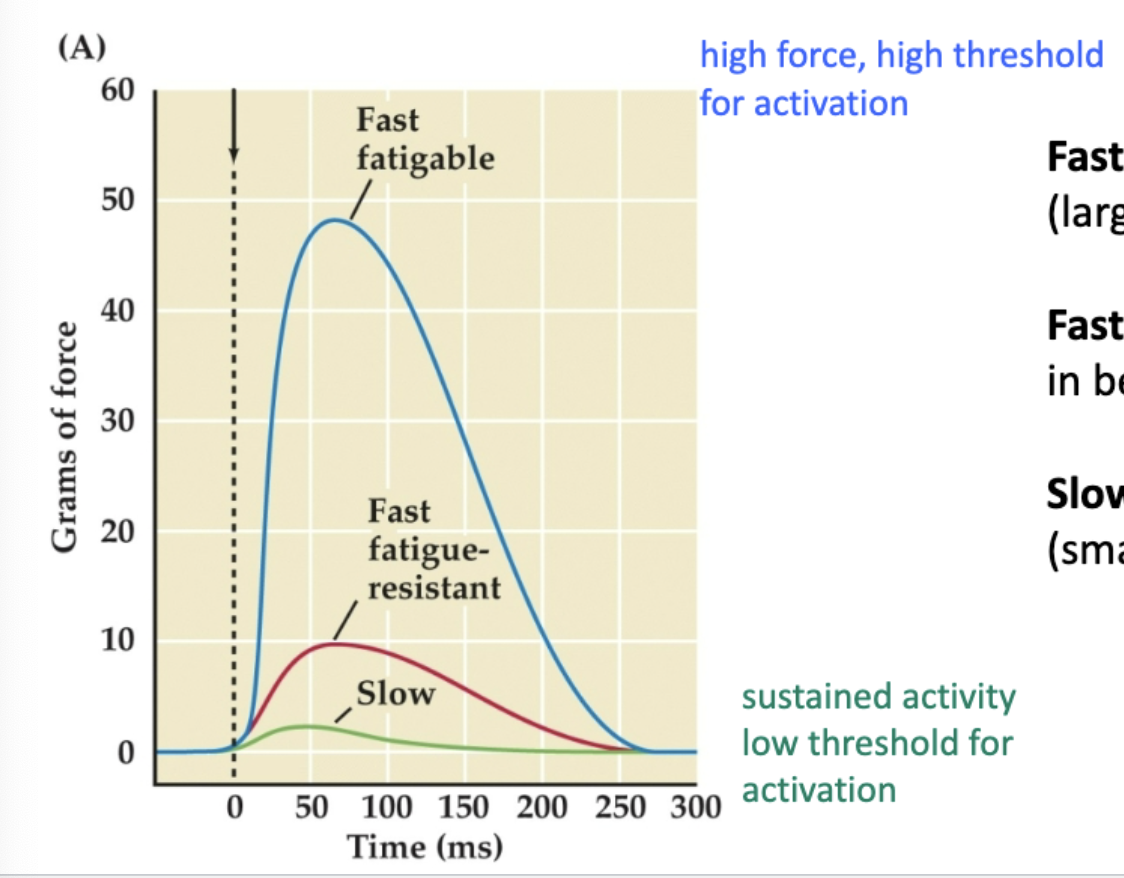
Types of motor neurons?
Fast fatigable (Type II fibers) - largest fibers, most powerful (one and done)
Fast fatigable-resistant (Type IIa fibers) - in between (maintains peak for a LITTLE longer)
Slow (Type I fibers) - motor units, little fatigue (very small peak)
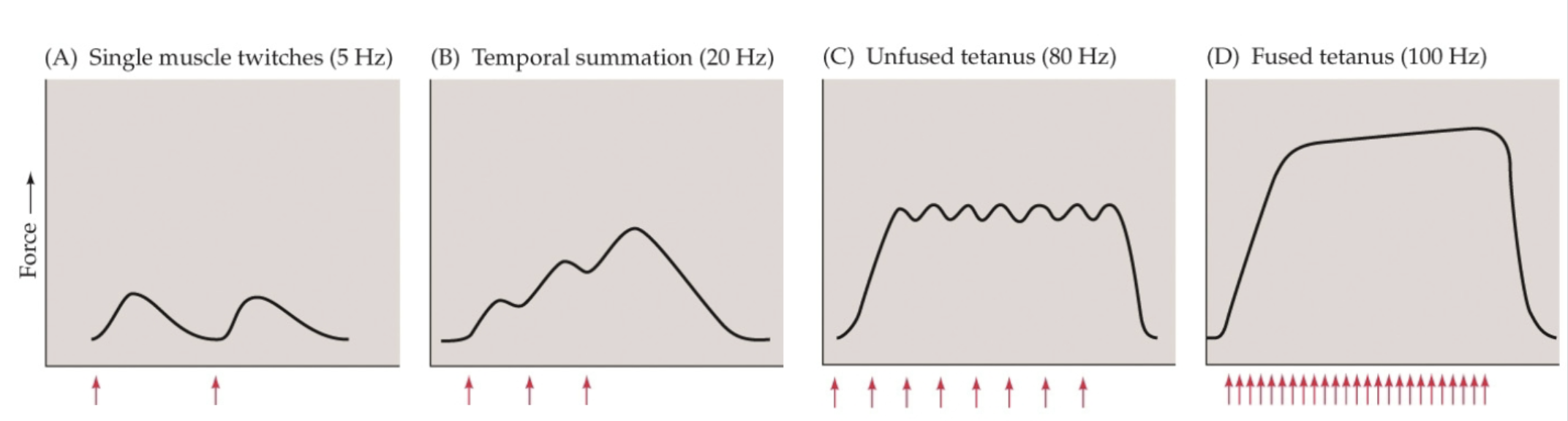
What does force depend on?
Rate of action potentials (rate coding)!
Single muscle twitches, temporal summation, unfused tetanus, fused tetanus
What does vigorous exercise for a short period of time do?
Increases maximal force of motor unit and contract speed! If you do it routinely you’re building strength, you want the muscle to respond quickly.
Rating coding changes!
What does prolonged periods of low-intensity exercise do?
Reduces motor fatigability!
Rating coding changes!
Changes in ankle dorsiflexor muscle?
Fatigues much faster
Responses are sooner and more amplified before fading
More action potentials sooner!
Is there evidence for plasticity in motor neurons?
Yes!
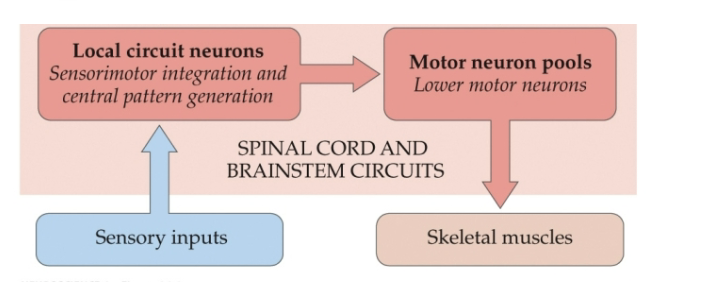
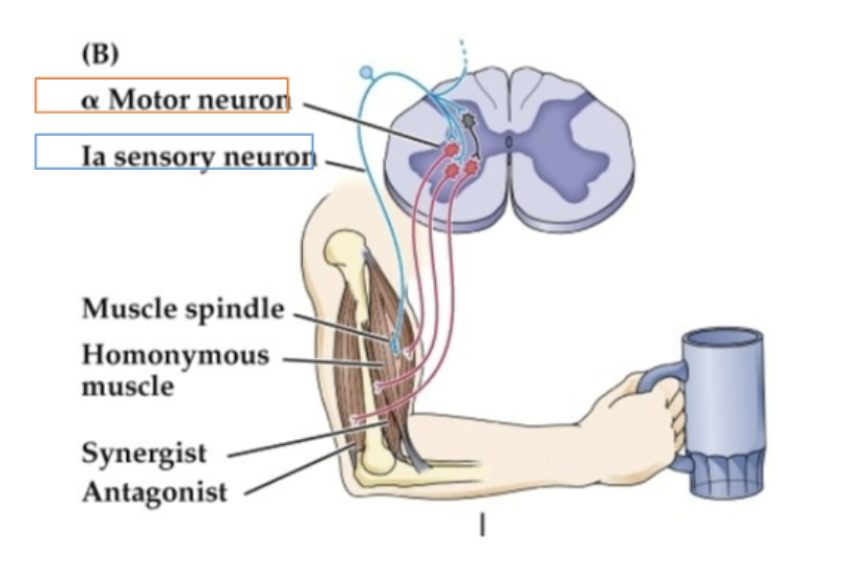
What is the stretch reflex
sensory input (afferent neuron) → local circuit neuron (cross section of spinal cord w/ interneuron)→ motor neuron pools (efferent neurons) → skeletal muscle
Difference between muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs?
Muscle spindles respond to STRETCH and golgi tendon organs respond to FORCE!
How do spindle sensory neurons work?
Stretch activations the spindle sensory neuron → spindle sensory activates the flexor muscle alpha motorneurons → inhibition of extensor motor neurons
What are positive feedback loops?
Change in given direction caused additional change in same direction.
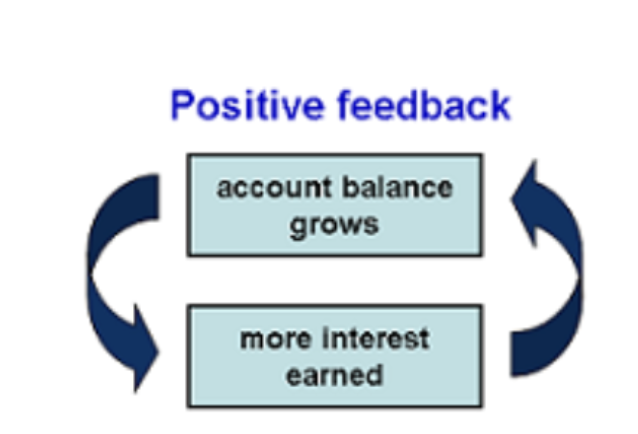
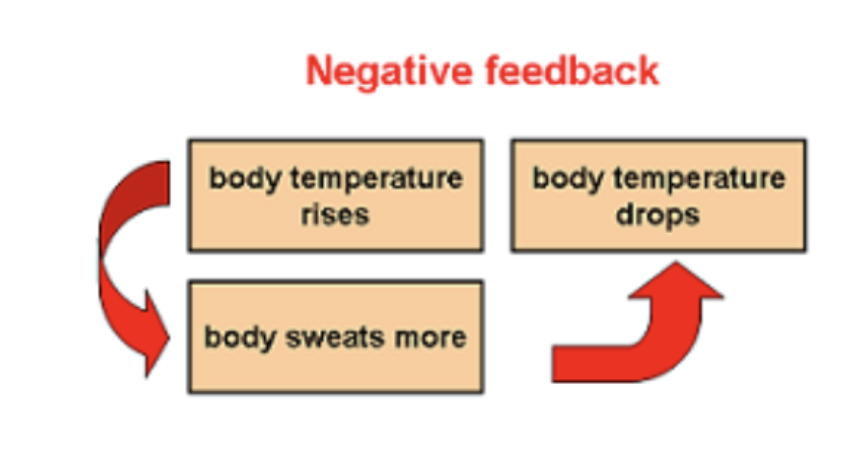
What are negative feedback loops?
Change in a given direction causes change in OPPOSITE direction.
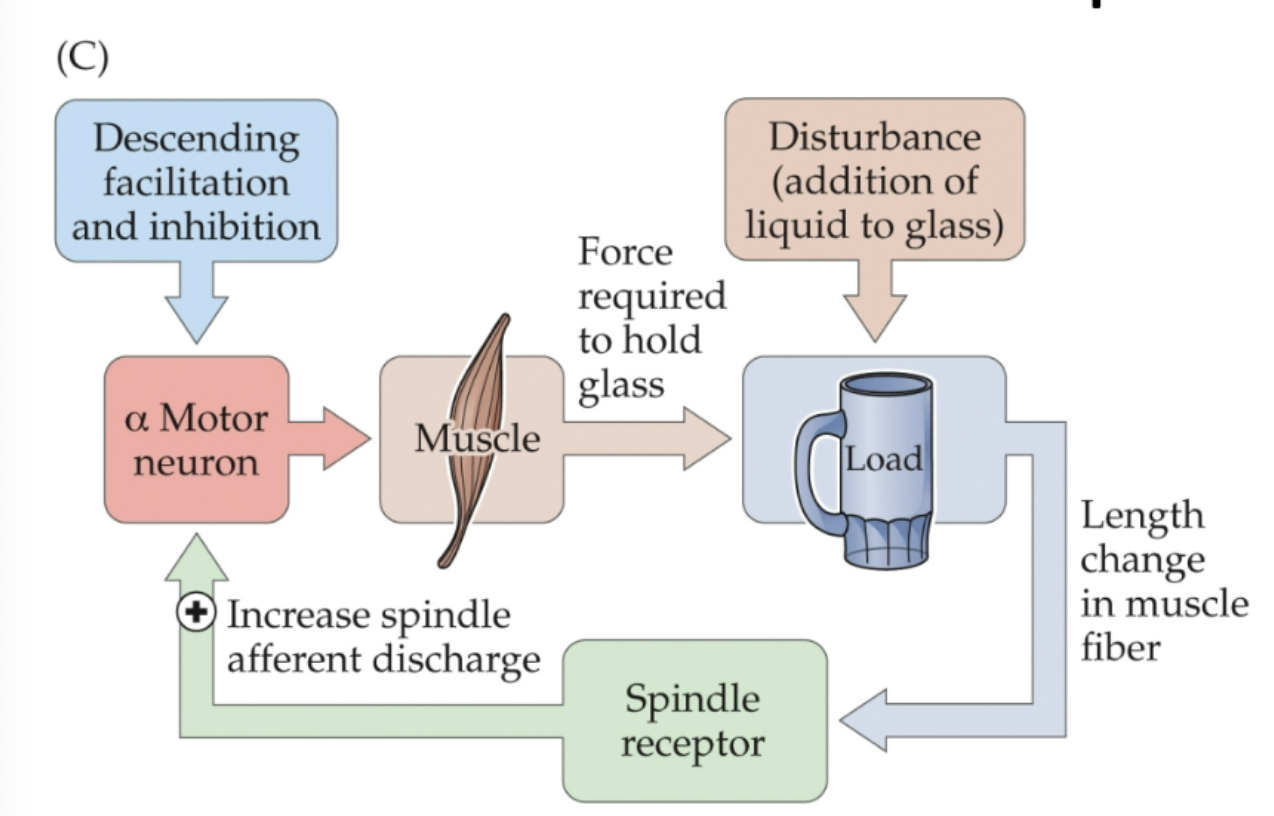
How is the stretch reflex a feedback loop?
It’s a negative feedback loop that prevents overextending!
What is a central pattern generator?
A neuronal network that generates rhythmic patterns of motor activity.
Can occur with or without sensory input (CLEAR DISTINCTION FROM REFLEXES)
ex. walking, running, flying, swimming, breathing
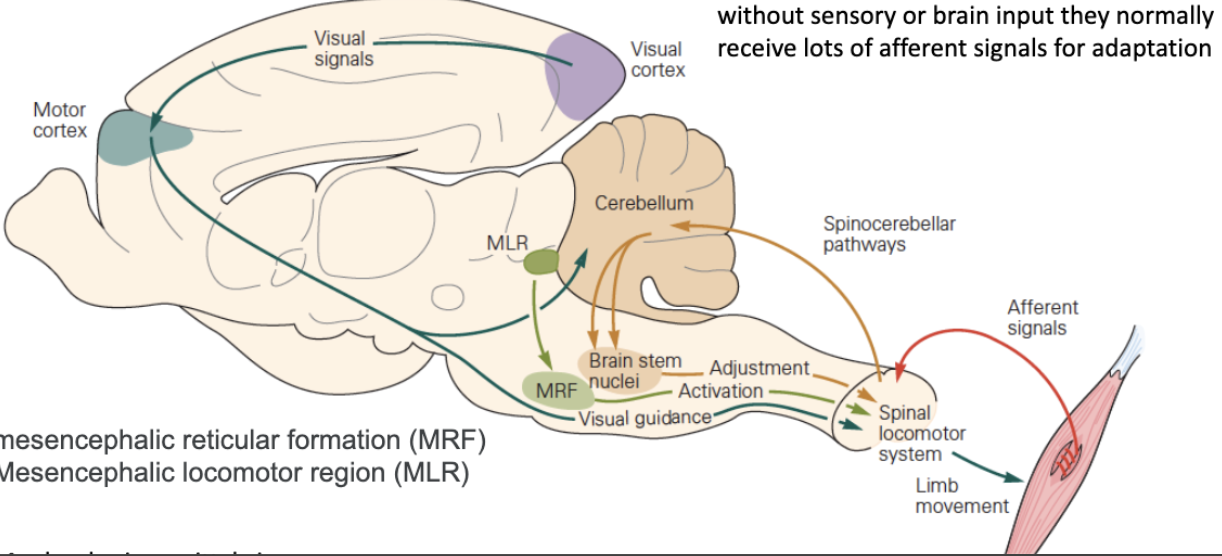
Can sensory input alter the properties of centrally generated motor patterns?
Yes!
They receive lots of afferent signals for adaptation.
What is neuromodulation?
Alternation of nerve activity through targeted delivery of a stimulus can reconfigure circuits so that neurons can provide a variety of behaviorally relevant outputs