2.3.4 National income + Injections and withdrawals
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Ways to measure national income
National output
National expenditure
National income
National output (O)
Total value of goods and services produced by firms in an economy (most commonly measured using GDP
National expenditure (E)
Total value of spending by all economic actors (consumers, firms, governments, net exports)
National income (Y)
Total value of income of all producers (wages, owner income, corporate profits)
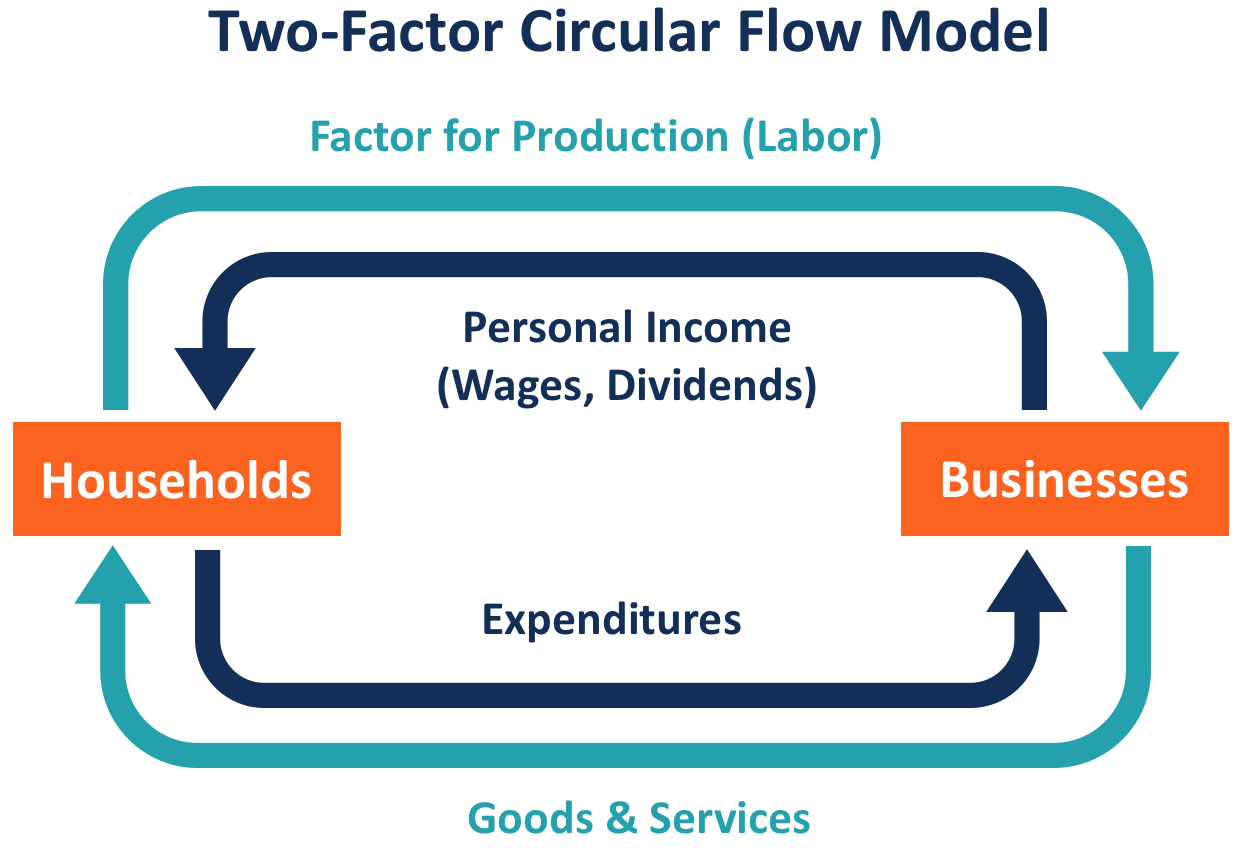
Circular flow of income
Ways of thinking about money flowing around an economy
No foreign trades, closed economy - O = E= Y, no taxation
Households supply firms with factors of production in exchange for rent, wages
Firms supply households with goods and services
Income vs wealth
Income: flow of money received after a period
Wealth: stocks of asset accumulated over time
Injections
Spending not generated by households
Investments by firms (factors/machinery, spending on goods and services used in production)
Government spending (Subsidies, benefits)
Exports - spending by foreigners on goods and services
Withdrawals
Spending that does not flow back to households and firms
Saving by households and firms
Taxes paid to the government by households and firms
Imports - goods and services purchased from abroad by households and firms
Equilibrium
injections = withdrawals
outputs, expenditure and income remain the same
National income rises
Injections > withdrawals
(spending increases)
National income falls
Injections < withdrawals
(spending decreases)
How do classical economists believe RNO is increased
Supply-side policies (shift supply)
Shifts in AD only lead to inflation
How do keynesian economists believe RNO is increased
Demand-side policies (if in recession), followed by shifts in supply
The multiplier effect
Increase in components of AD will lead to greater increase in GDP
Autonomous spending results in induced spending
MPW + Components
Marginal propensity to withdraw:
Change in income that is withdrawn from the circular flow of income
MPS (save)
MPT (tax)
MPM (import)
MPW = MPS + MPT + MPM
Formulas for the multiplier
1 / 1 - MPC
1 / MPW
Formula with MPC and MPW
MPC + MPW = 1
Example evaluations for multiplier effect
Also leads to larger fall in GDP
Time lag
Difficult to measure (size and complexity of economy)
Factors that affect multiplier
Spare capacity
MPM
MPT
MPC