Brain and Cranial Nerves
Secondary vesicles during embryonic development (superior to inferior)
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Mesencephalon
Metencephalon
Myelencephalon
Spinal cord
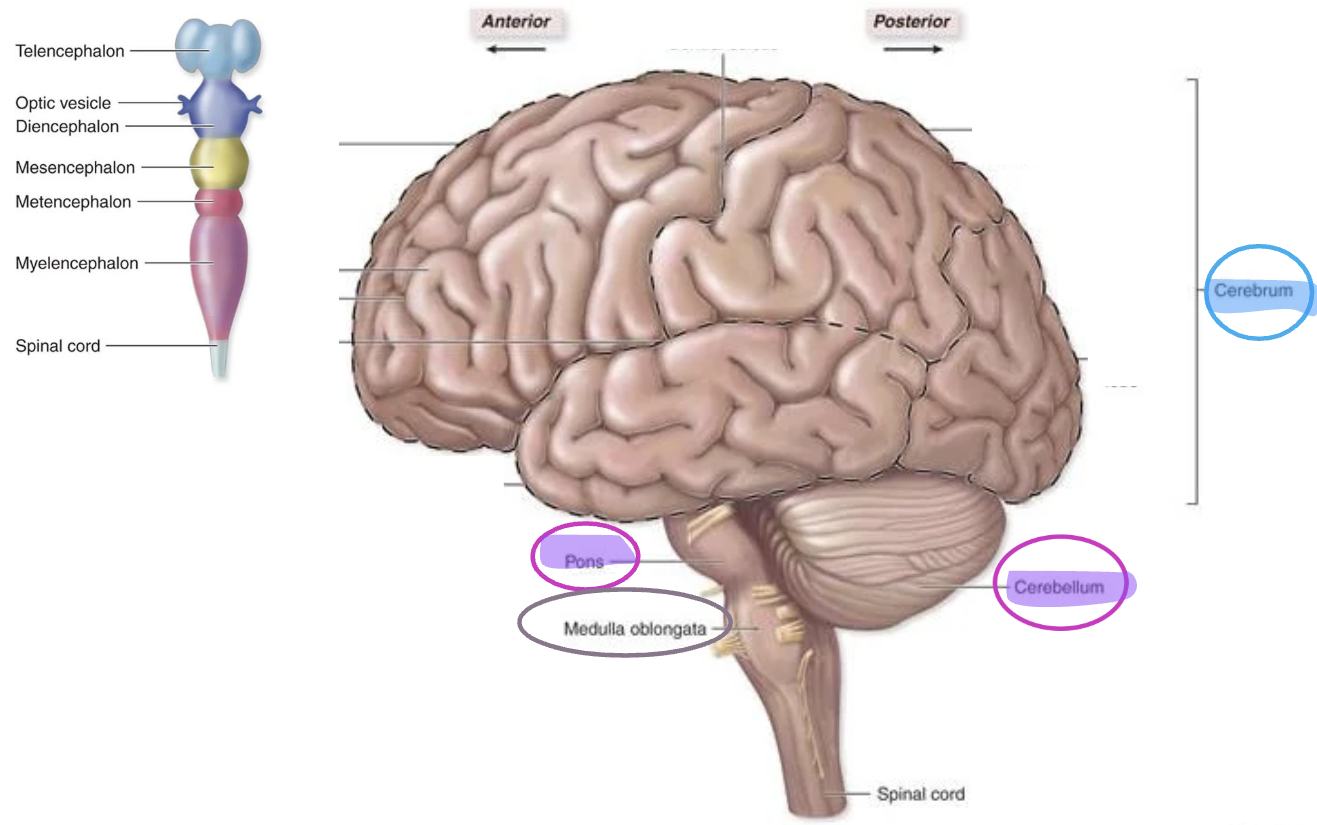
forms cerebrum
Telencephalon
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
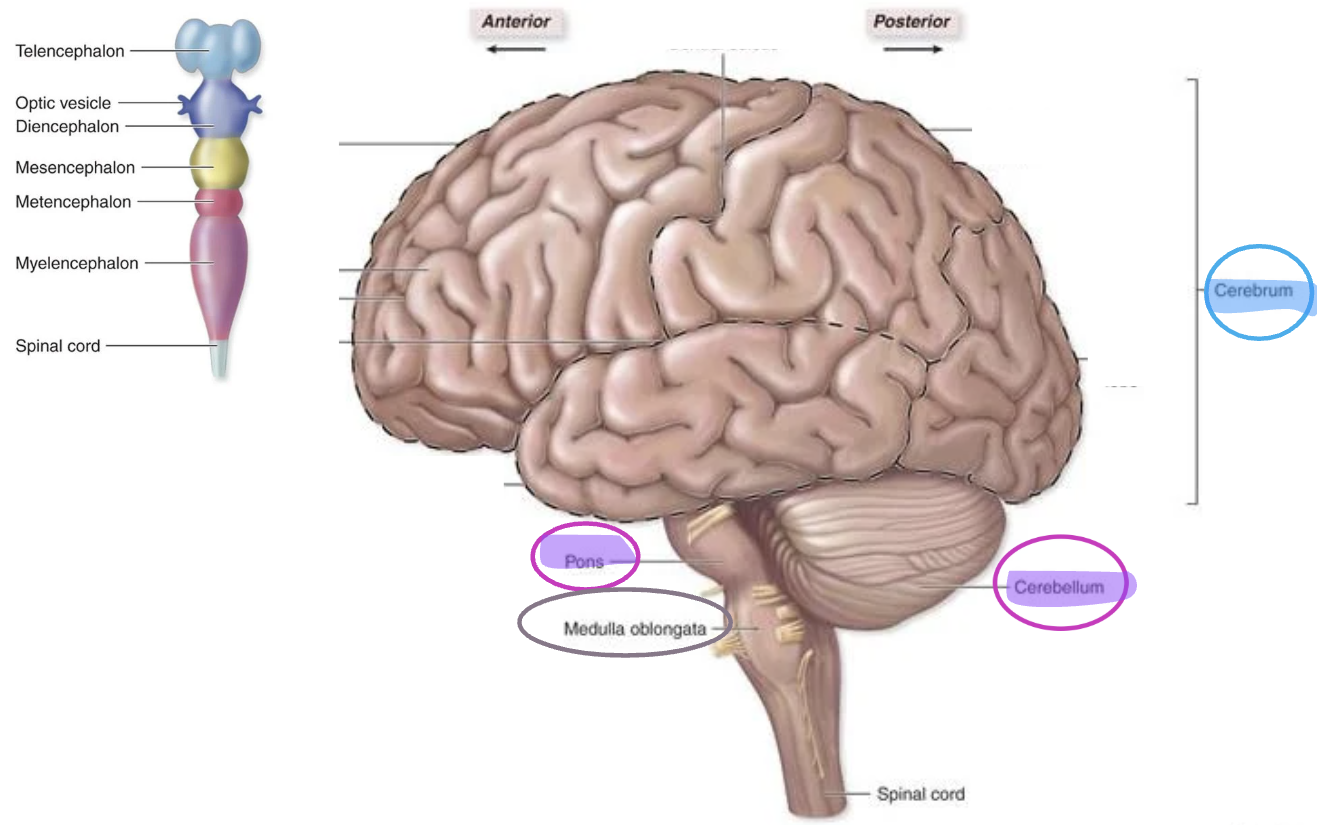
Secondary vesicles during embryonic development (superior to inferior)
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Mesencephalon
Metencephalon
Myelencephalon
Spinal cord

forms cerebrum
Telencephalon
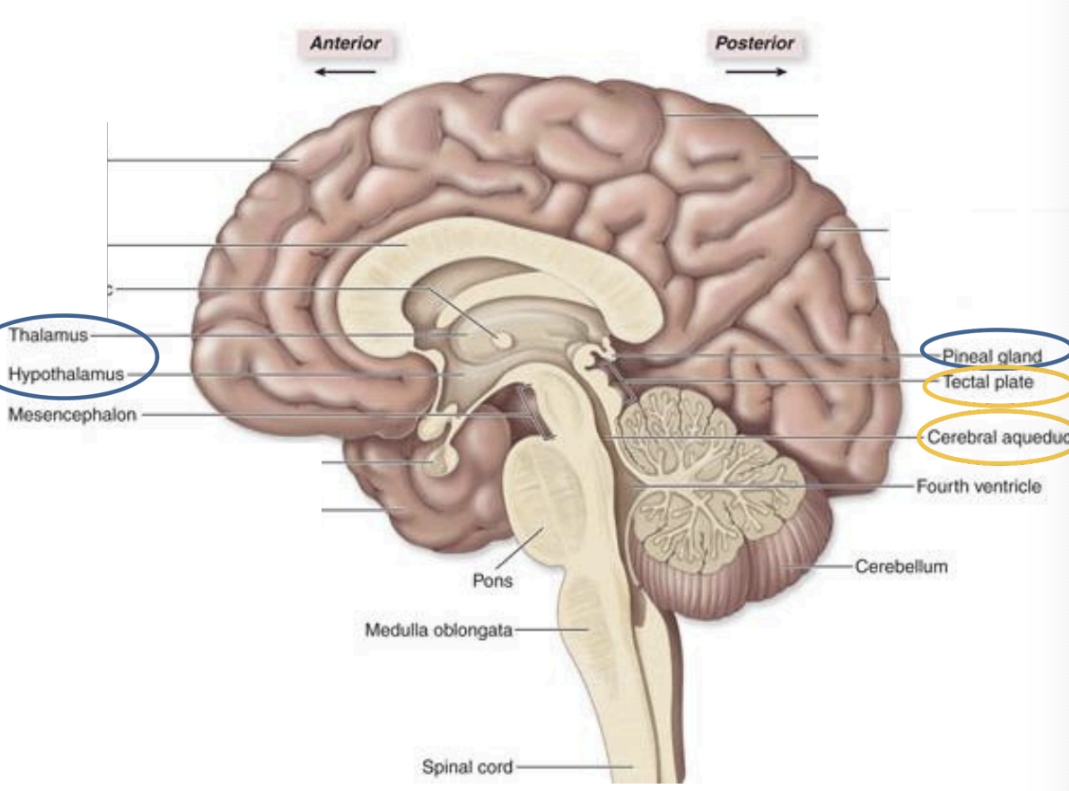
Epithalamus
Thalamus,
Hypothalamus,
pineal gland
Diencephalon
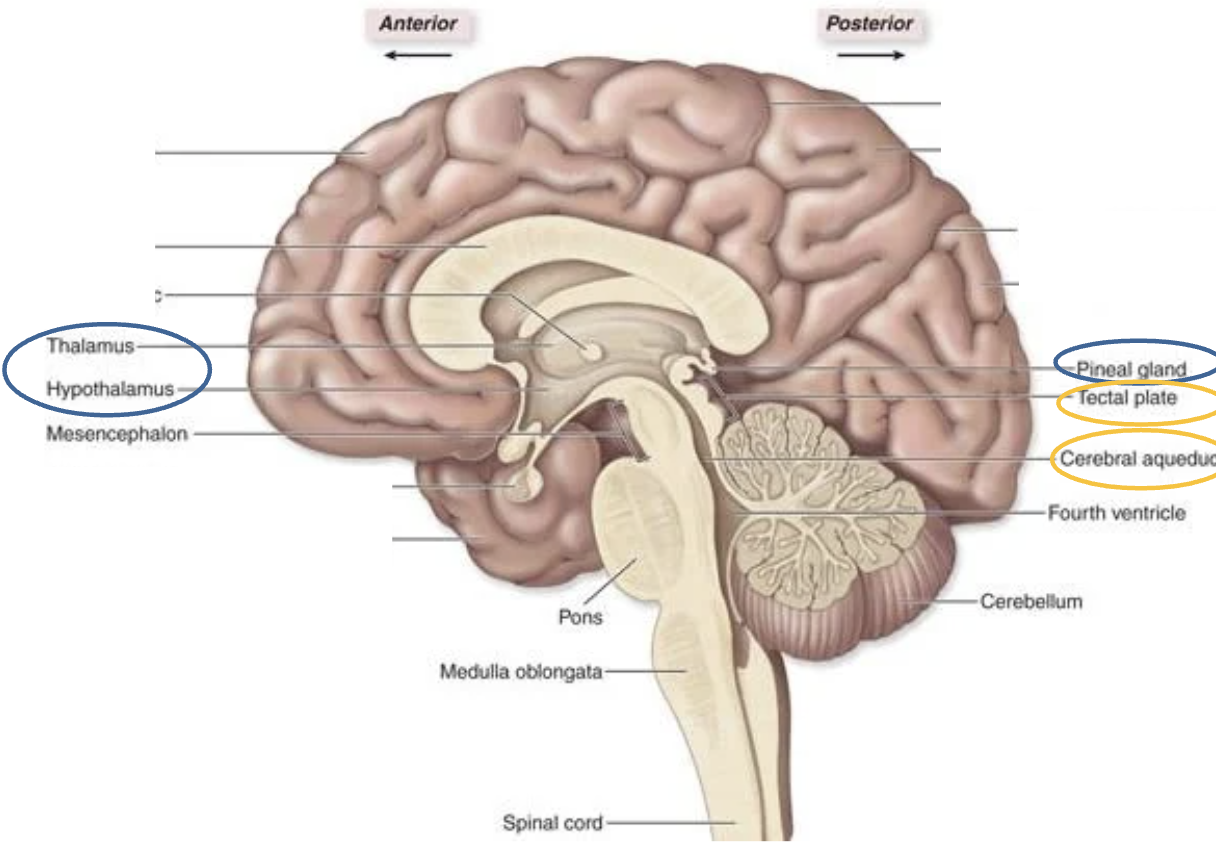
midbrain
mesencephalon
Pons
Cerebellum
Metencephalon
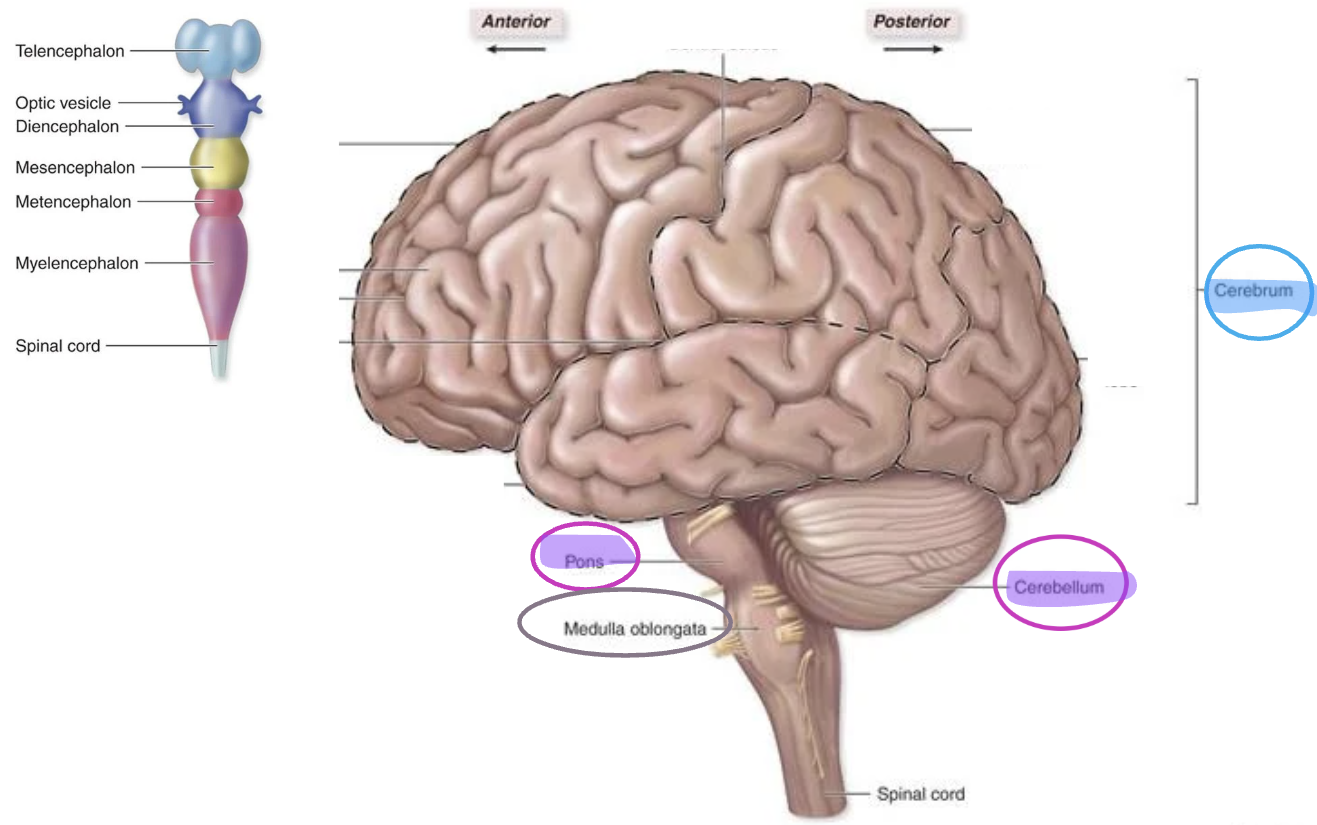
Medulla Oblongata
Myelencephalon
Neuron cell bodies
Dendrites
Unmyelinated axons
structures found in gray matter
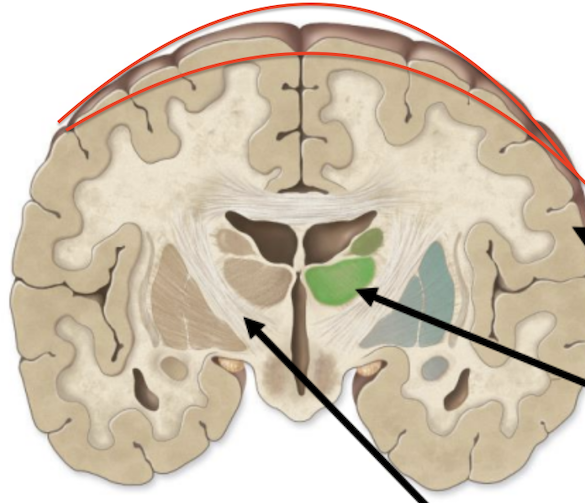
superficial layer of gray matter
cortex
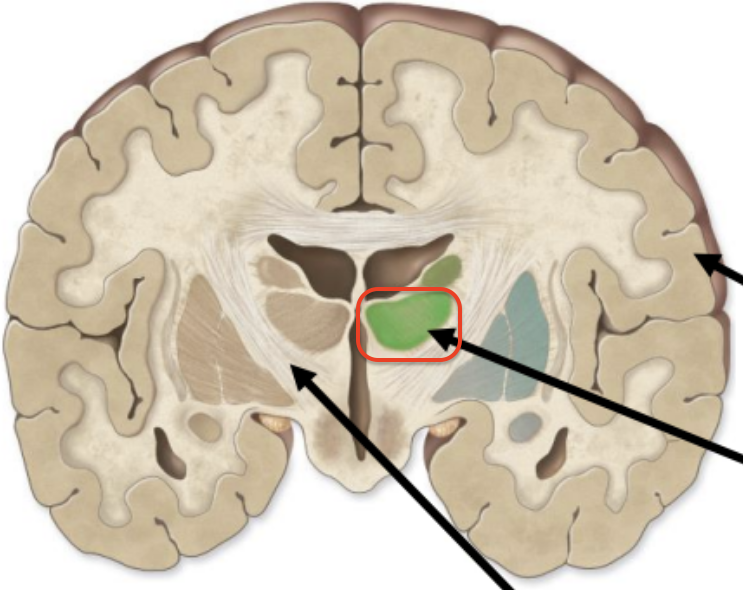
clusters of gray matter deep within the brain
Nuclei
three meninges from superficial to deep
Dura mater (Superficial)
Arachnoid mater (Middle)
Pia mater (Deep)
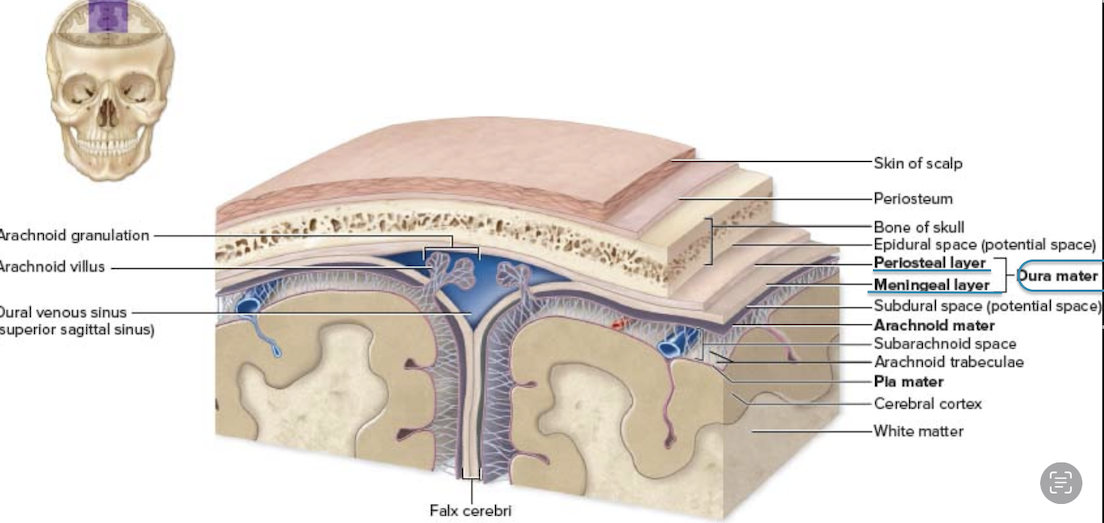
type of tissue dura mater is made of
Dense irregular connective tissue (CT)
two layers of the dura mater
Periosteal layer – Attached to the skull
Meningeal layer – Forms dural septa (folds that support the brain)
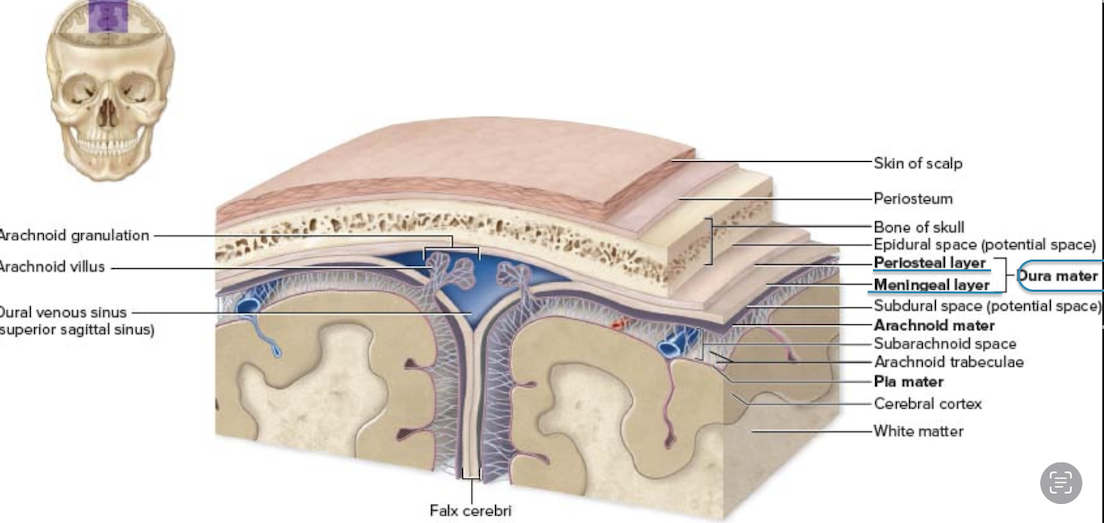
middle meninge layer between the dura matter and pia matter
Arachnoid matter (archne = spider )
“web” of collagen elastic fiber
Contains CFS in subarachnoid space
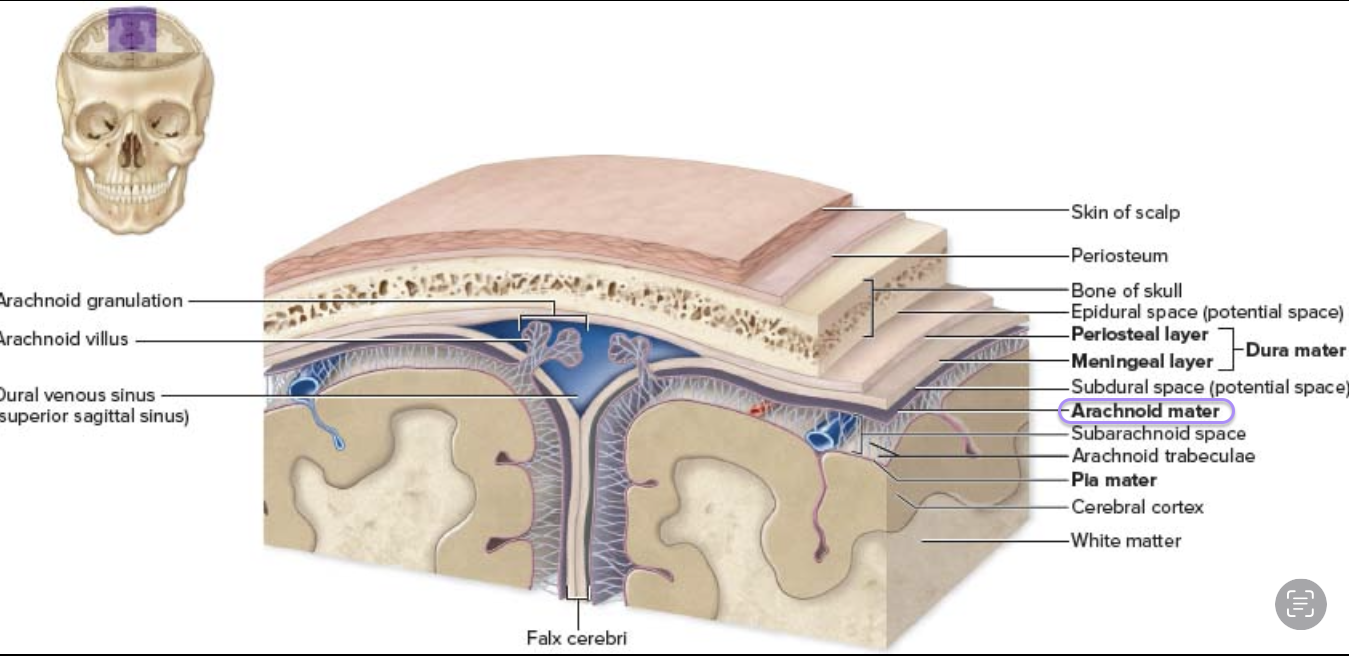
space is between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater
subdural space (contains csf)
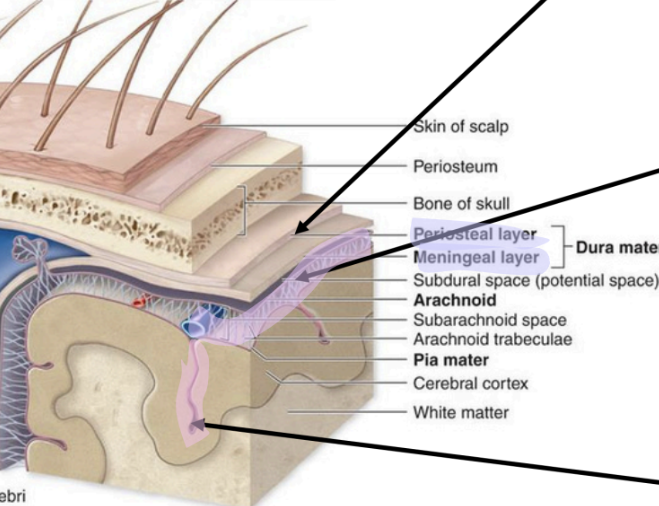
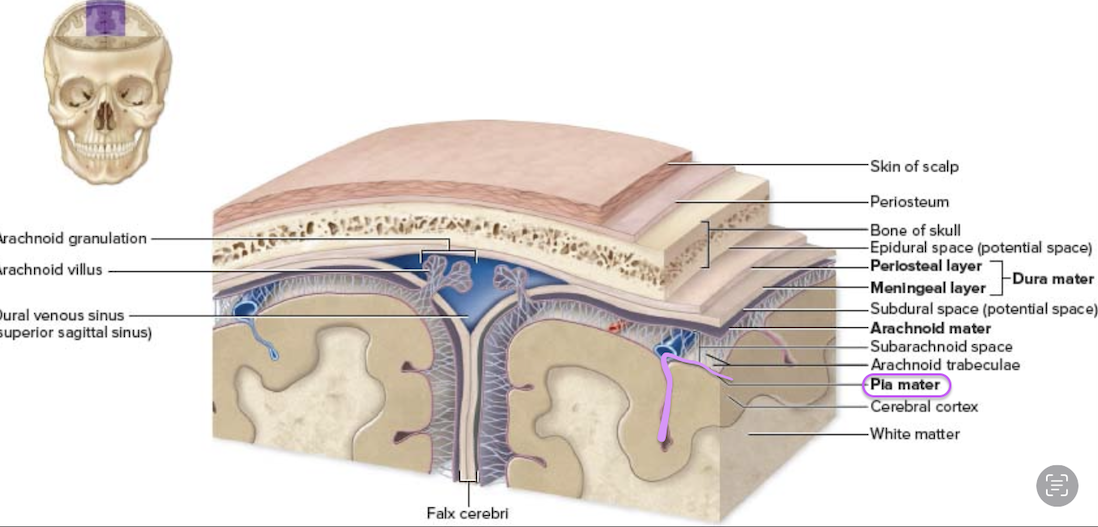
innermost meninge layer
Pia matter (tender mother)
areolar CT
“form-fitting”
Brain ventricles
Lateral ventricles (1st & 2nd) – in each hemisphere
Third ventricle – in the diencephalon
Fourth ventricle – between the brainstem & cerebellum
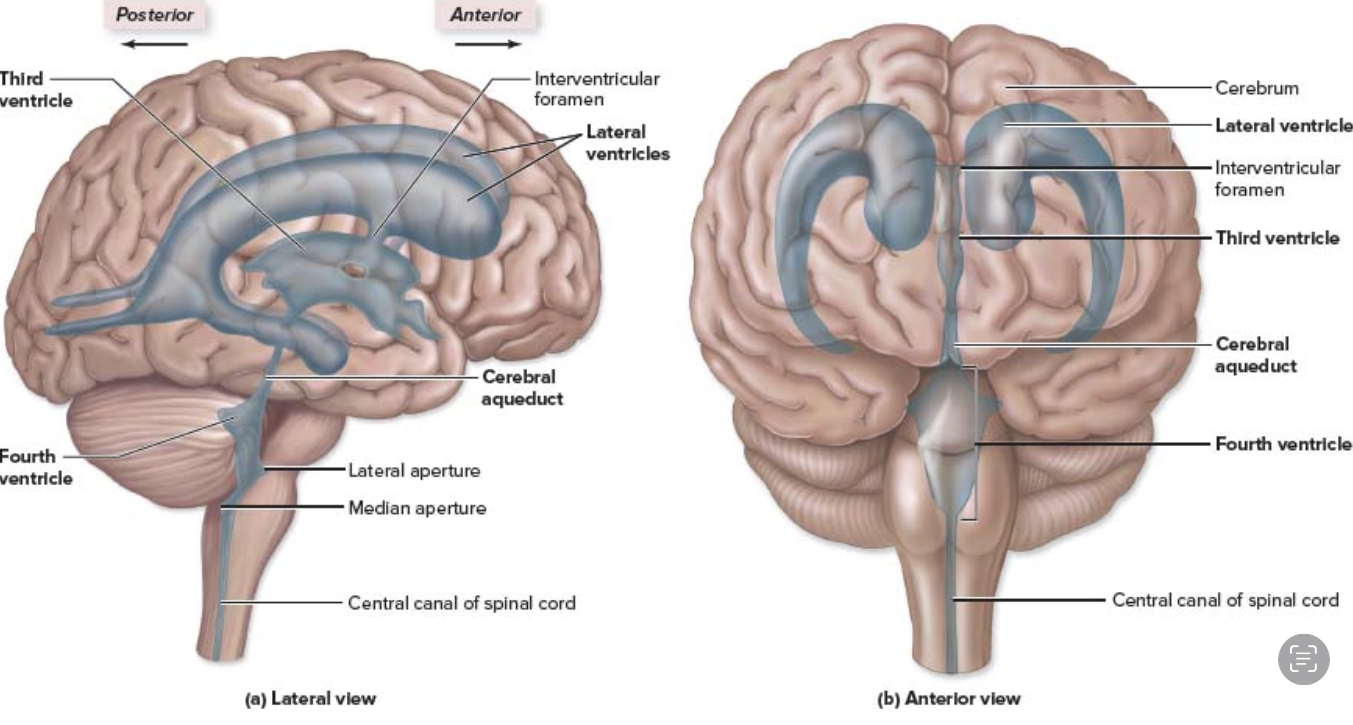
In the cerebrum, one in each hemisphere
lateral ventricles
In the diencephalon, between the left & right thalamus
third ventricle
Between the brainstem & cerebellum
fourth ventricle
What two structures form the BBB?
Astrocytes – Their end feet wrap around capillaries
Blood capillaries – Have tight junctions preventing leakage
function of the blood-brain barrier (BBB)
Prevents neuron exposure to harmful substances like toxins, drugs, and waste
Where is CSF produced?
Choroid plexus in the ventricles
Cells involved in producing CSF
Specialized ependymal cells in the choroid plexus
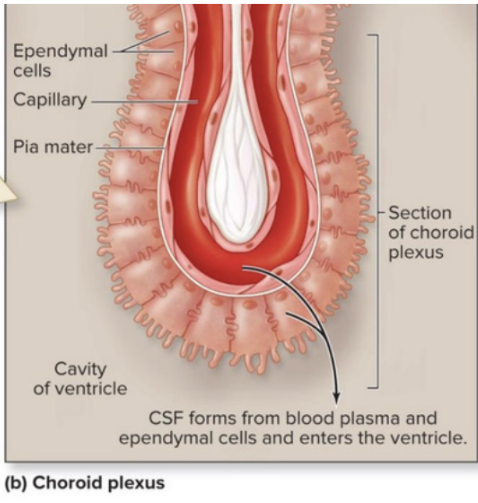
What are the three main functions of CSF?
Cushioning (protection)
Buoyancy
Transport – Delivers nutrients & removes waste
What are the main functions of the cerebrum?
conscious thought & complex intellectual functions
↳ Intelligence & reasoning
↳ Thought, memory, & judgment
↳ voluntary motor, visual auditory
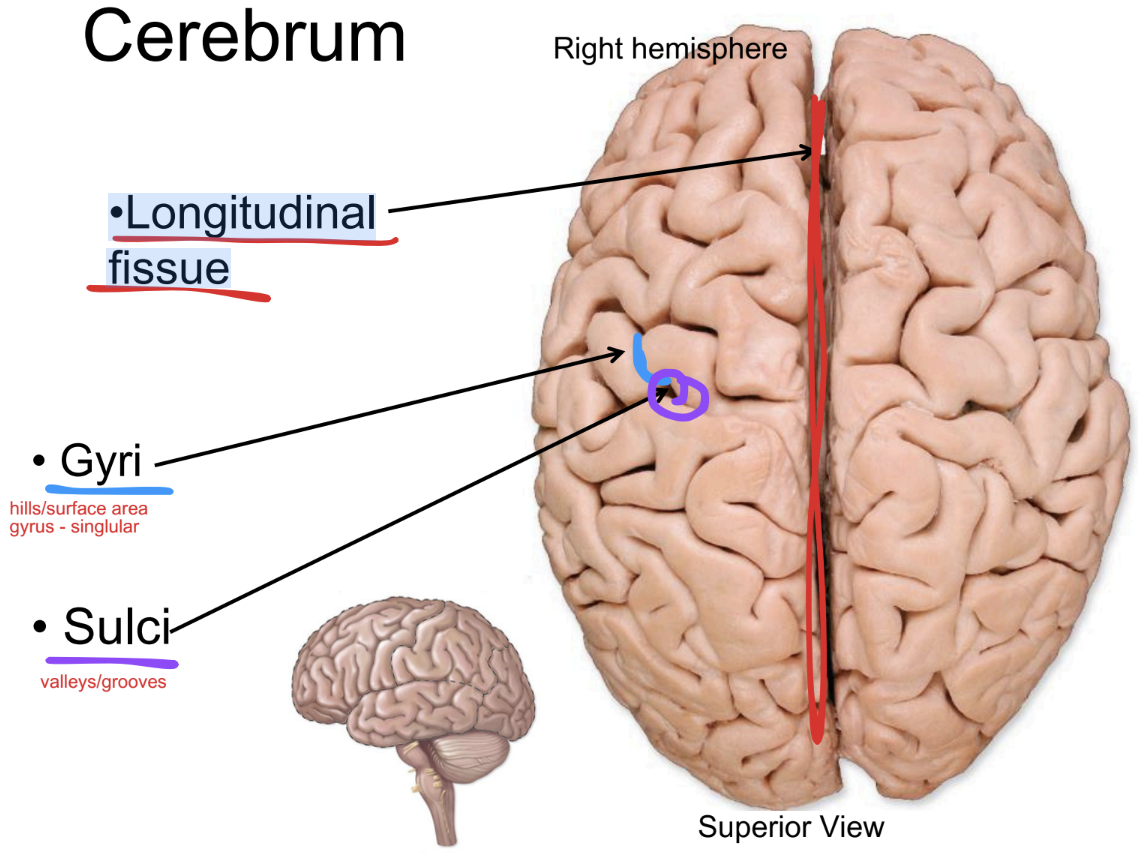
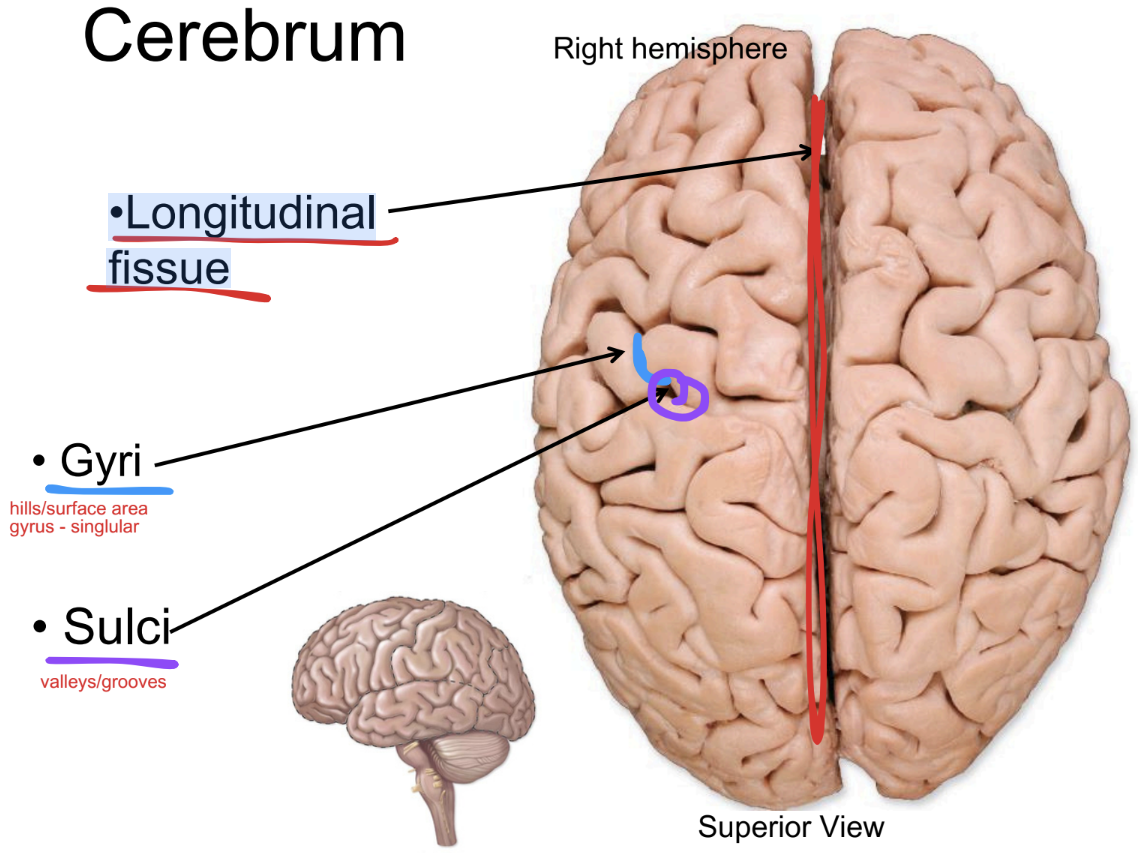
Longitudinal fissue
paired cerebral hemispheres are separated by a…
gyri (singular: gyrus)
Ridges or folds on the brain’s surface that increase surface area for neurons
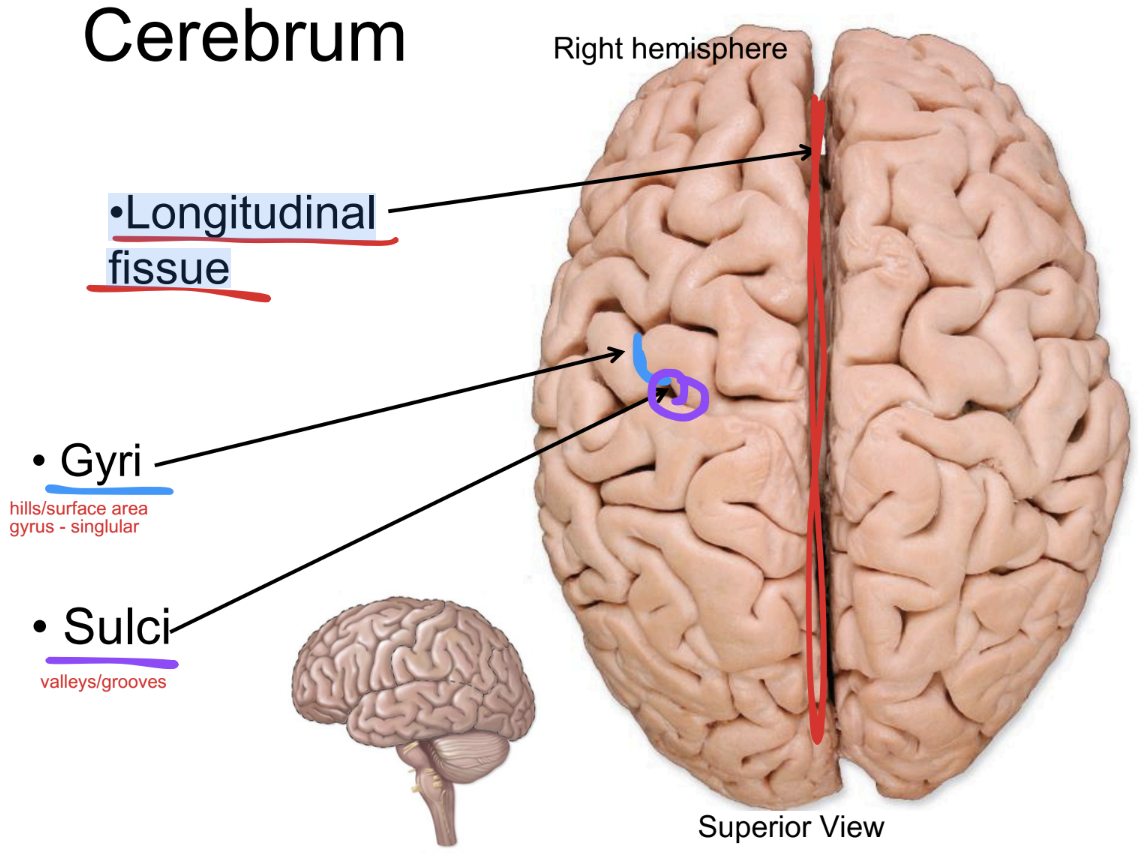
sulci (singular: sulcus)
hallow grooves between gyri that help separate brain regions
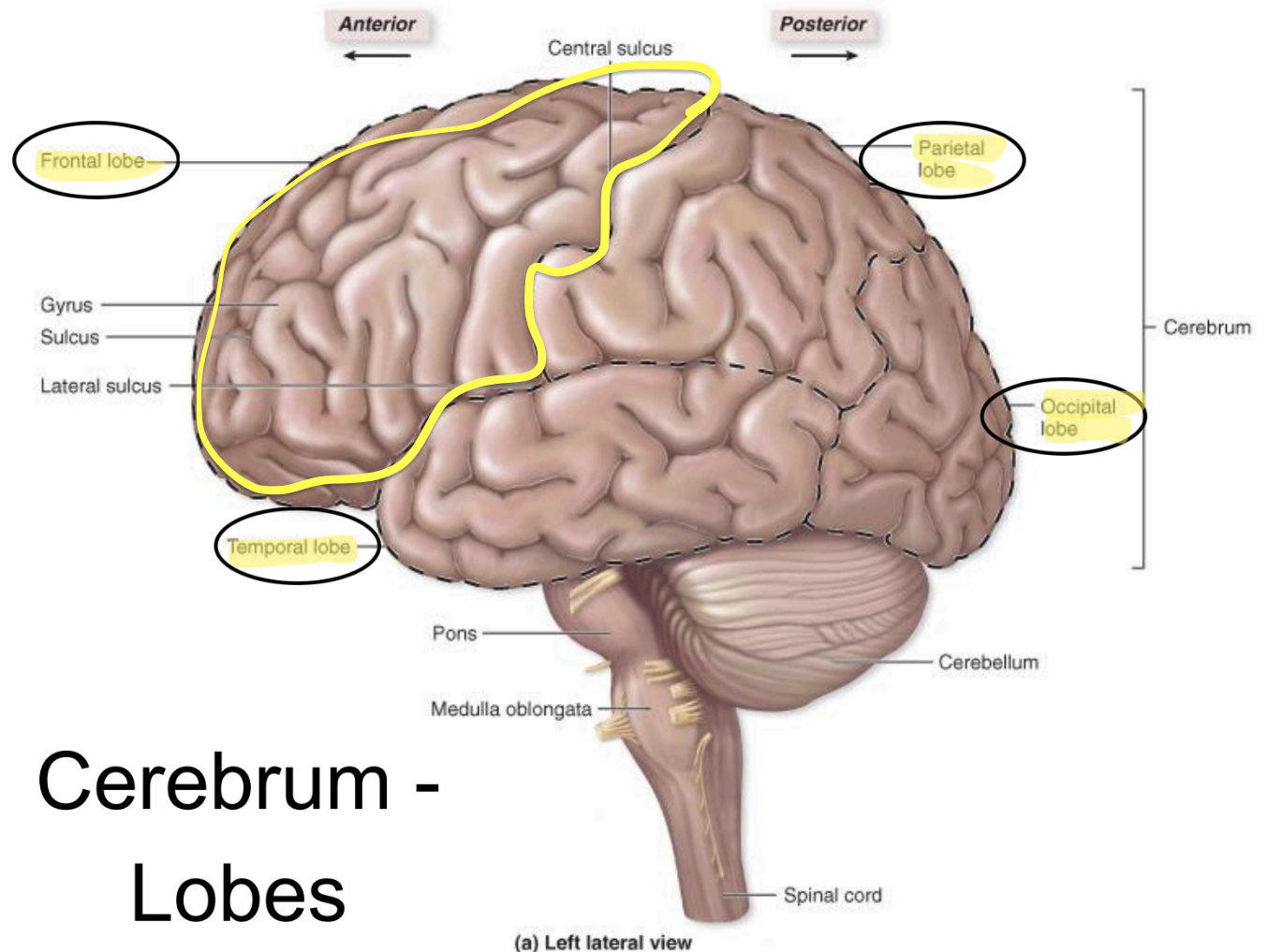
Frontal lobe - functions
who u are/motor
Higher intellectual functions
(concentration, decision-making, planning);
personality;
verbal communication;
voluntary motor
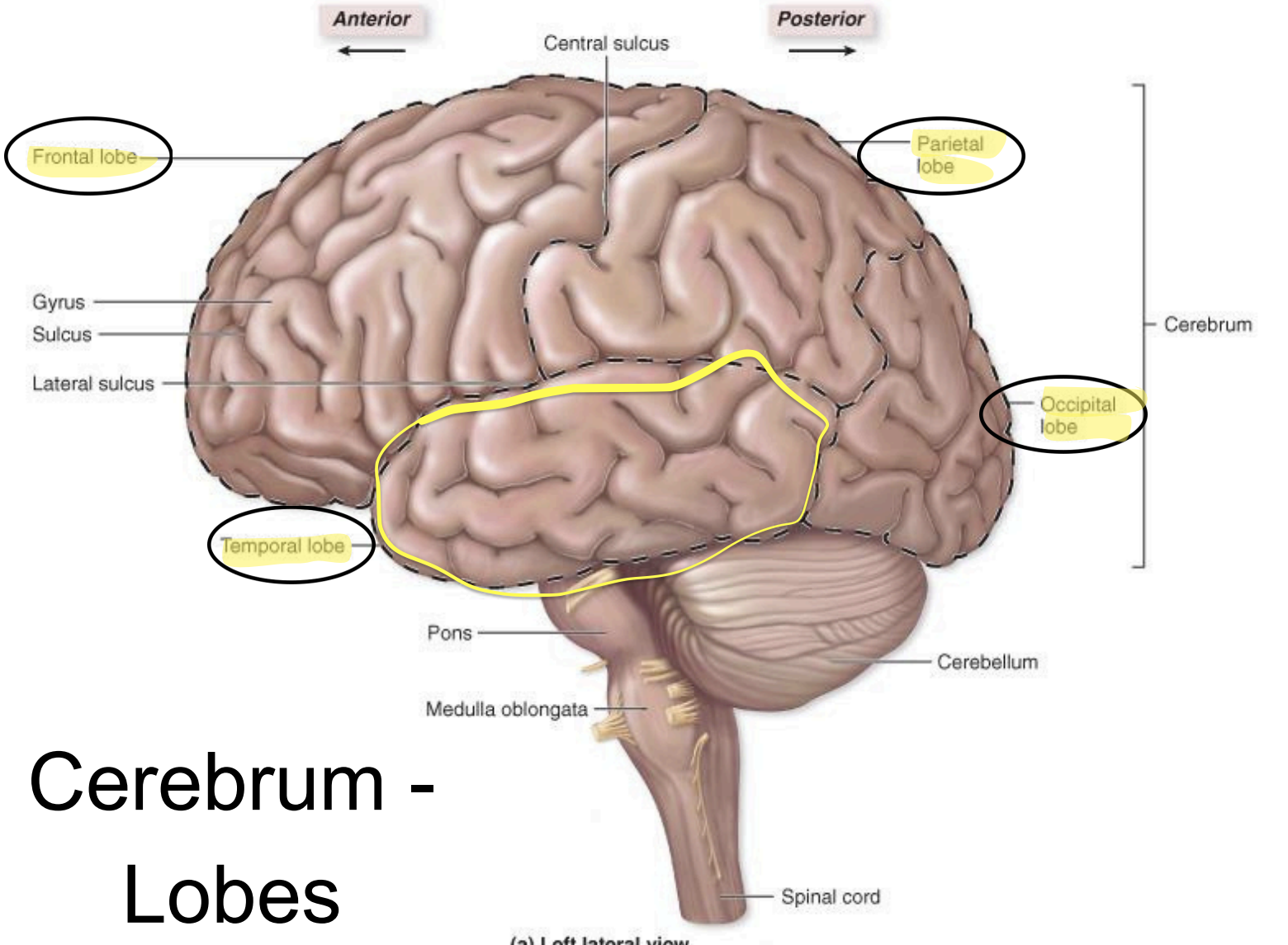
temporal lobe - functions
language
emotion
smell
auditory
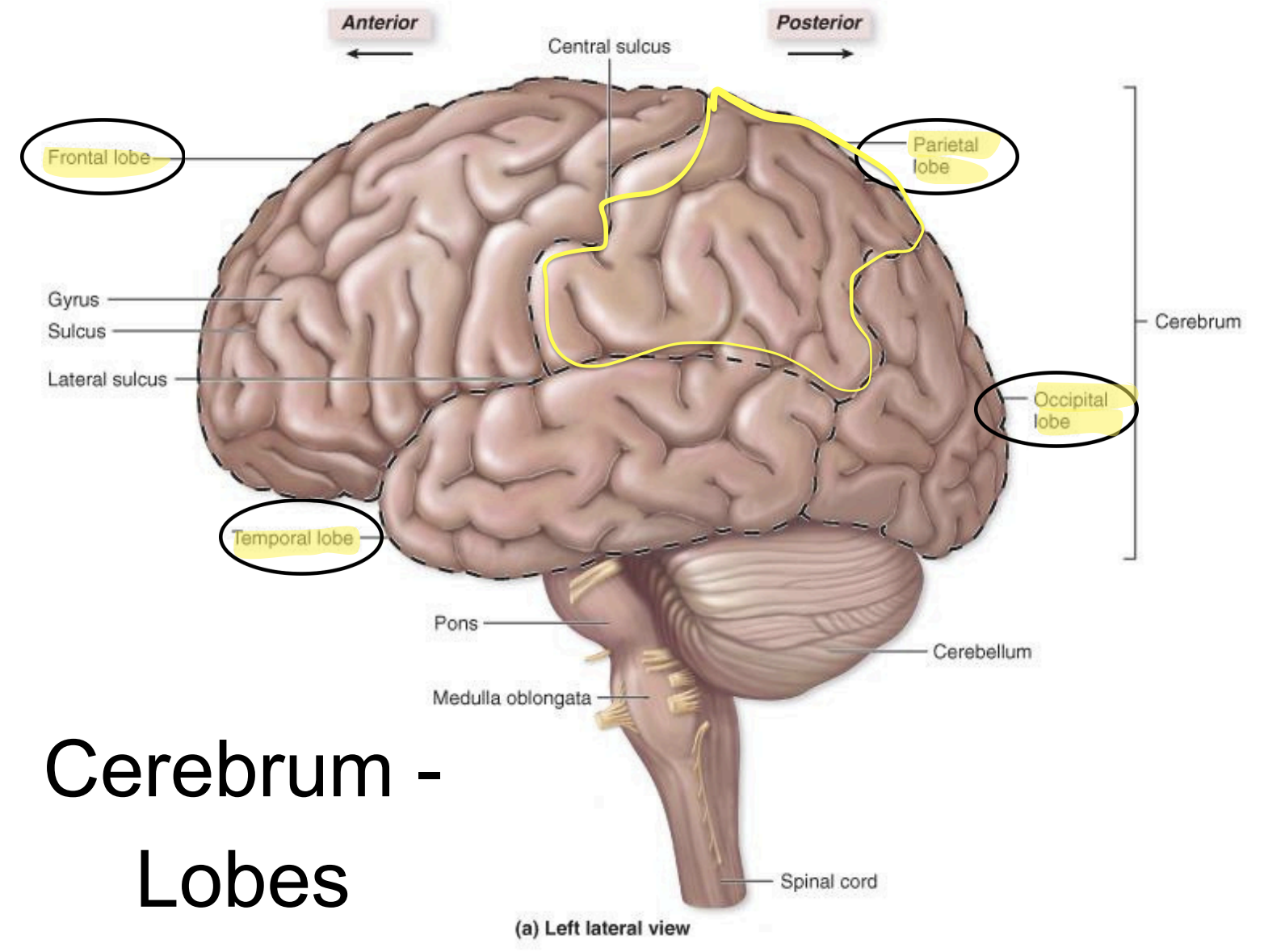
Parietal lobe - functions
general sensory
understand position in the environment
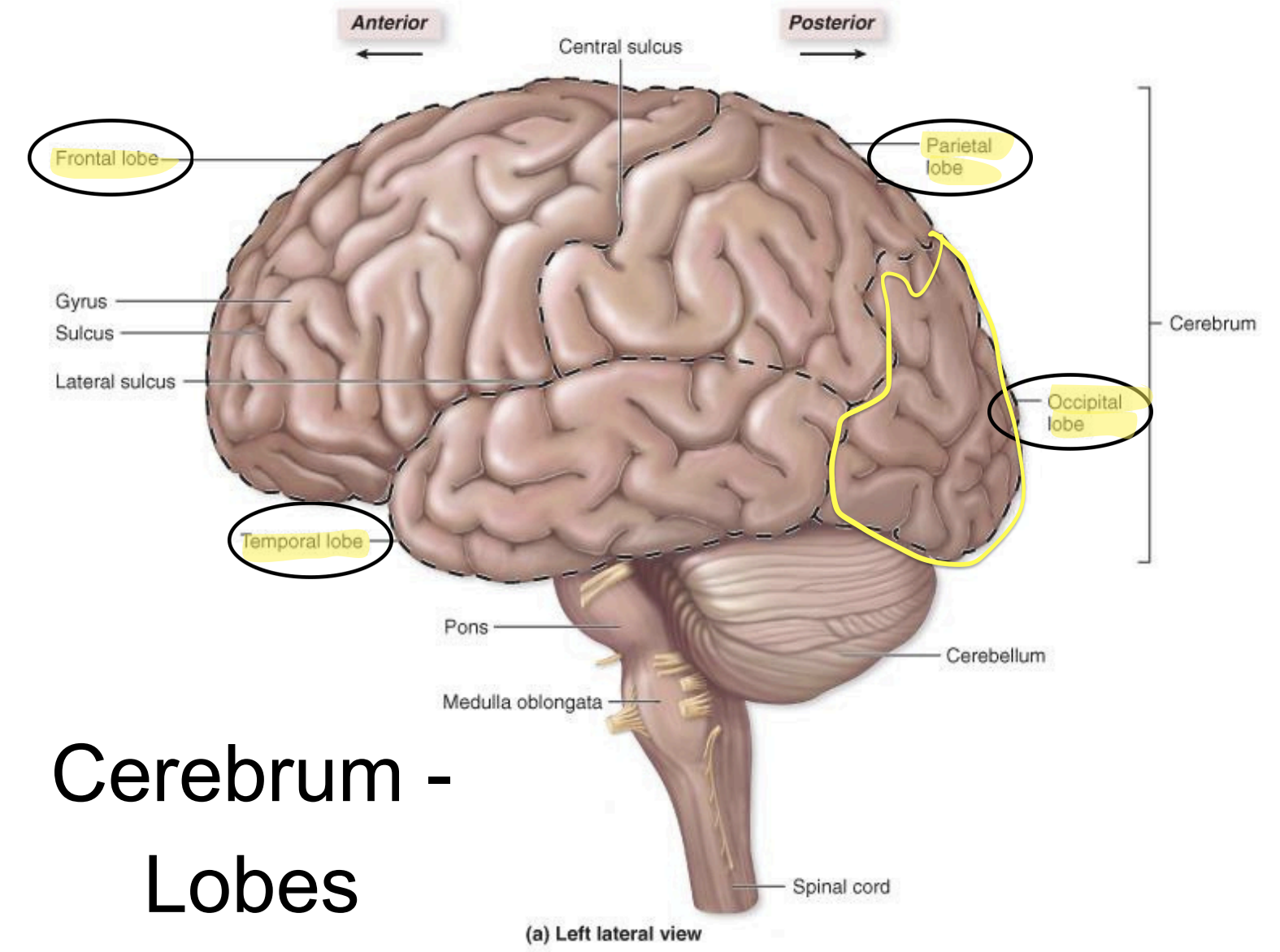
Occipital lobe - functions
visual input
visual memories
memory, sense of taste
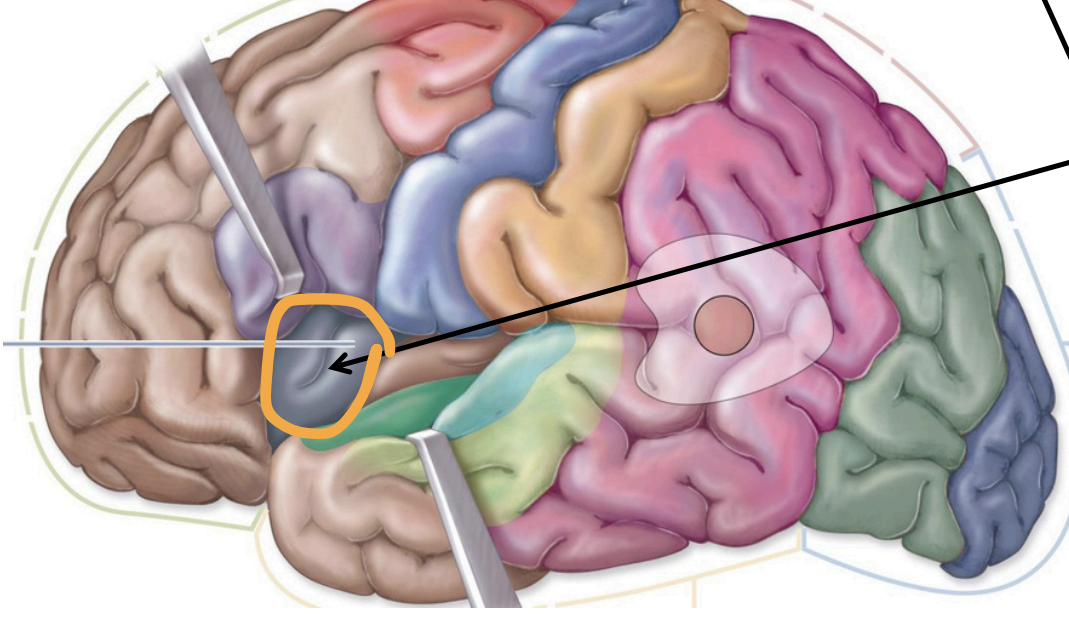
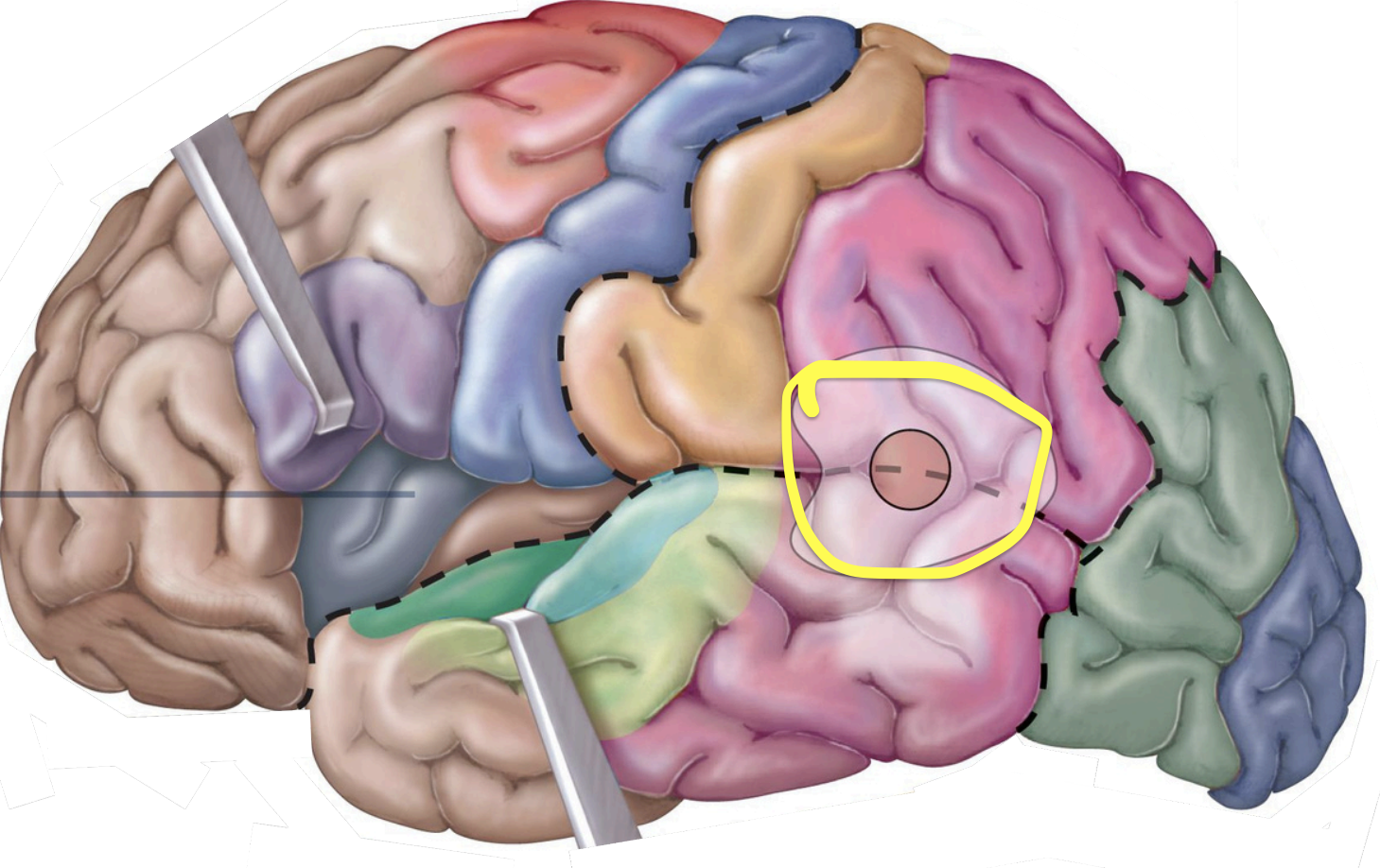
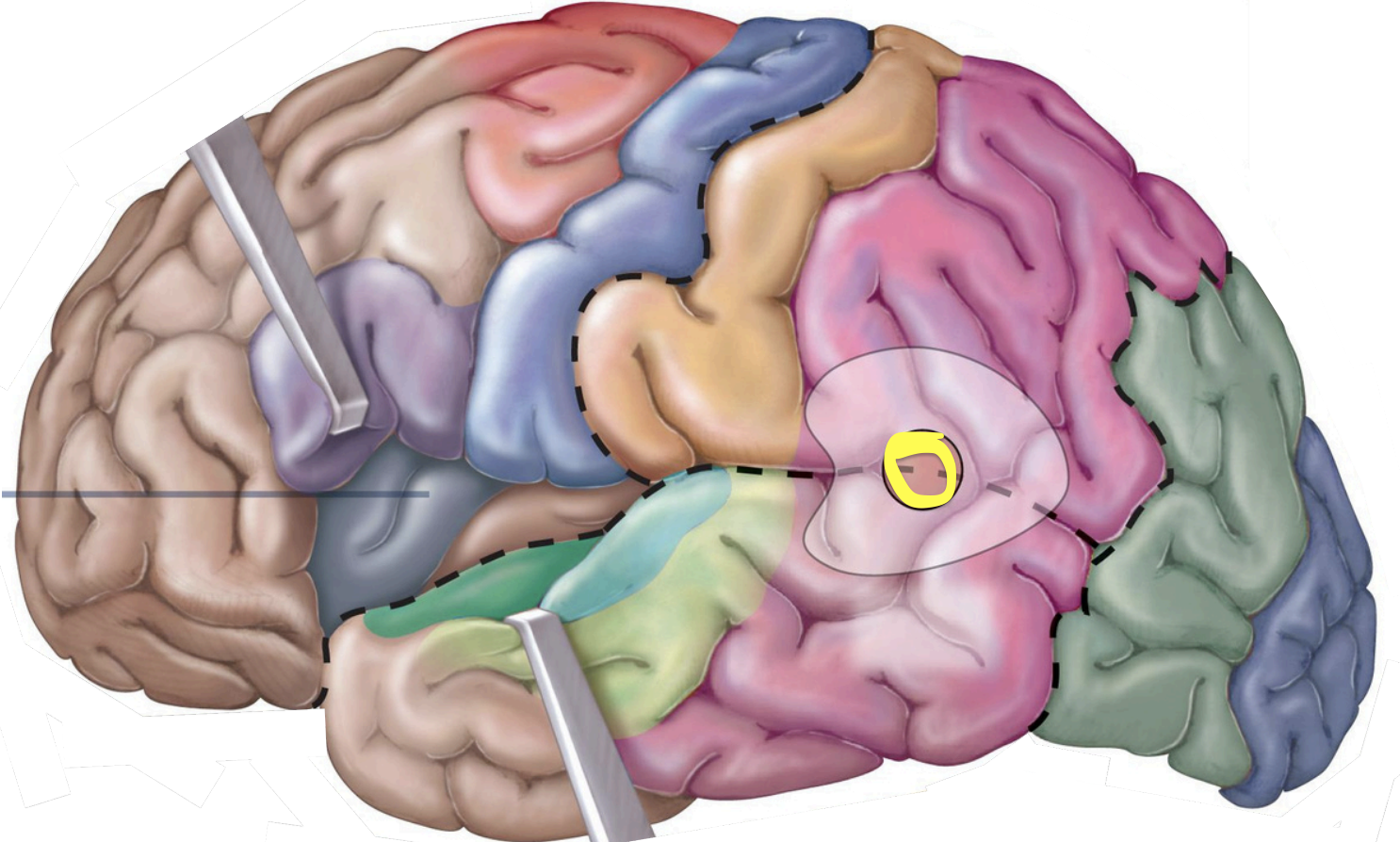
Insula
Motor areas
↳Control voluntary motor functions
↳ Info going out
↳ Frontal lobe
precentral gyrus;
voluntary contralateral skeletal
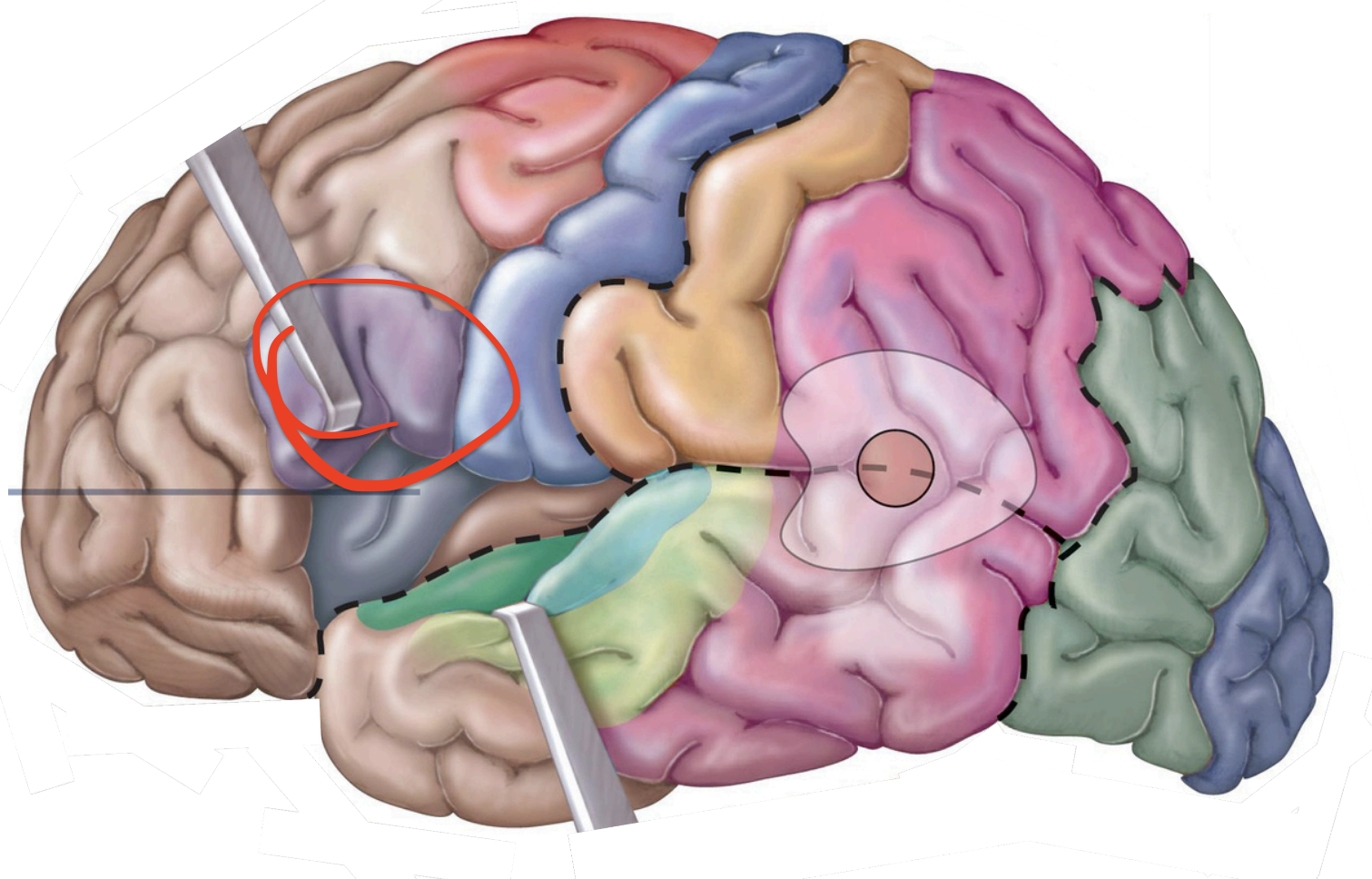
Motor Area - Primary (1°) motor cortex
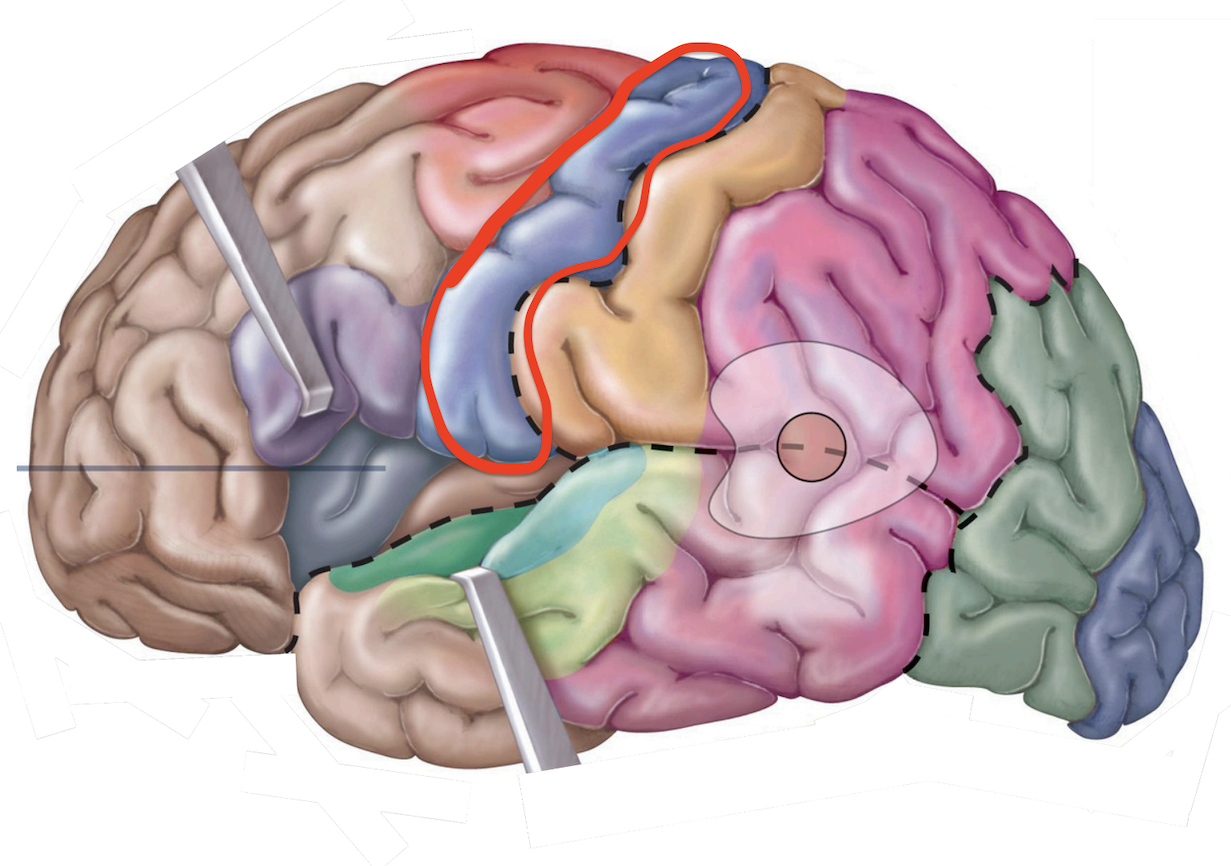
muscles for eye movement;
reading and coordinating
binocular vision
Motor Area - Frontal eye field
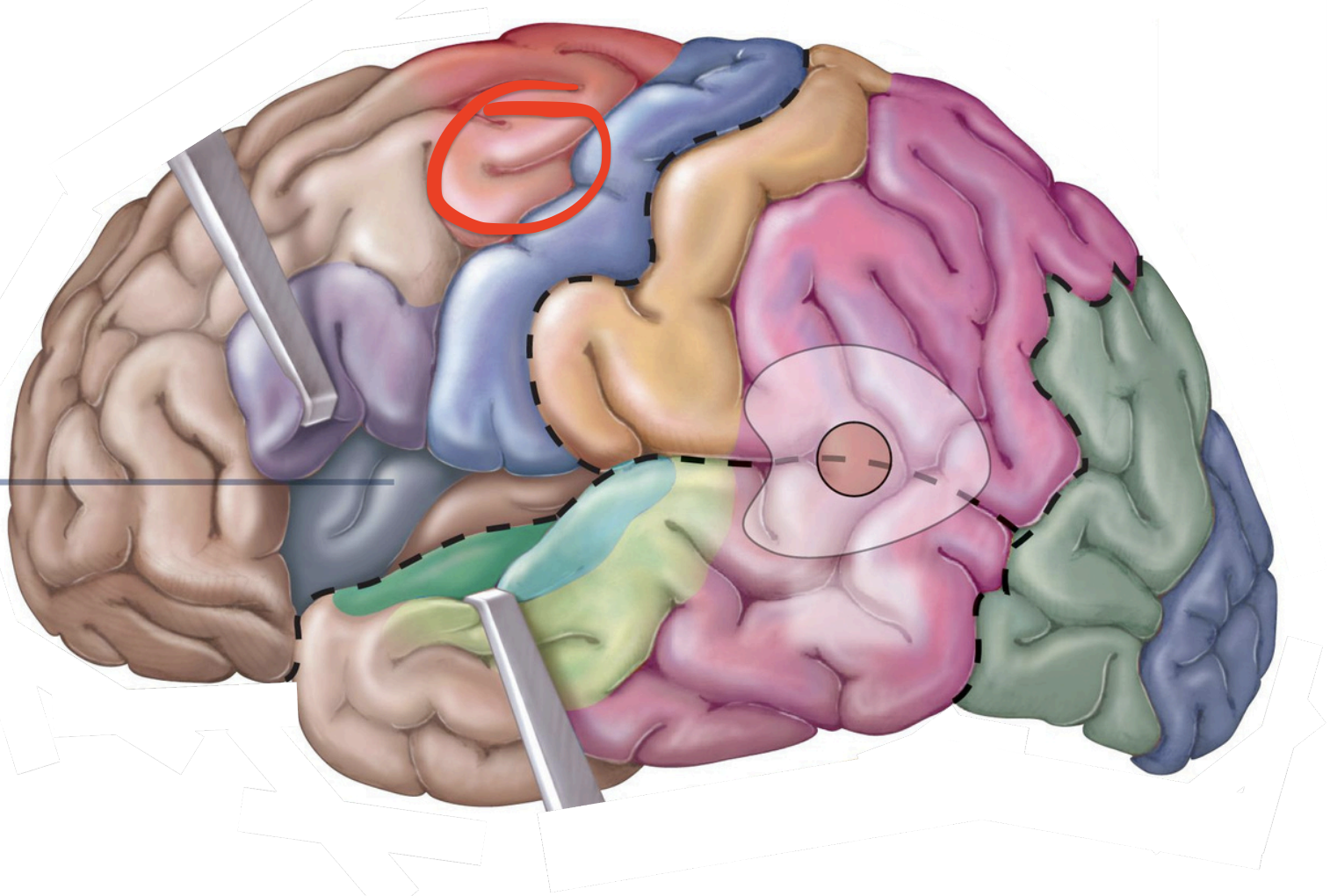
muscles used in speech;
usually left front lobe only
Motor Areas - Motor speech area (Broca area)
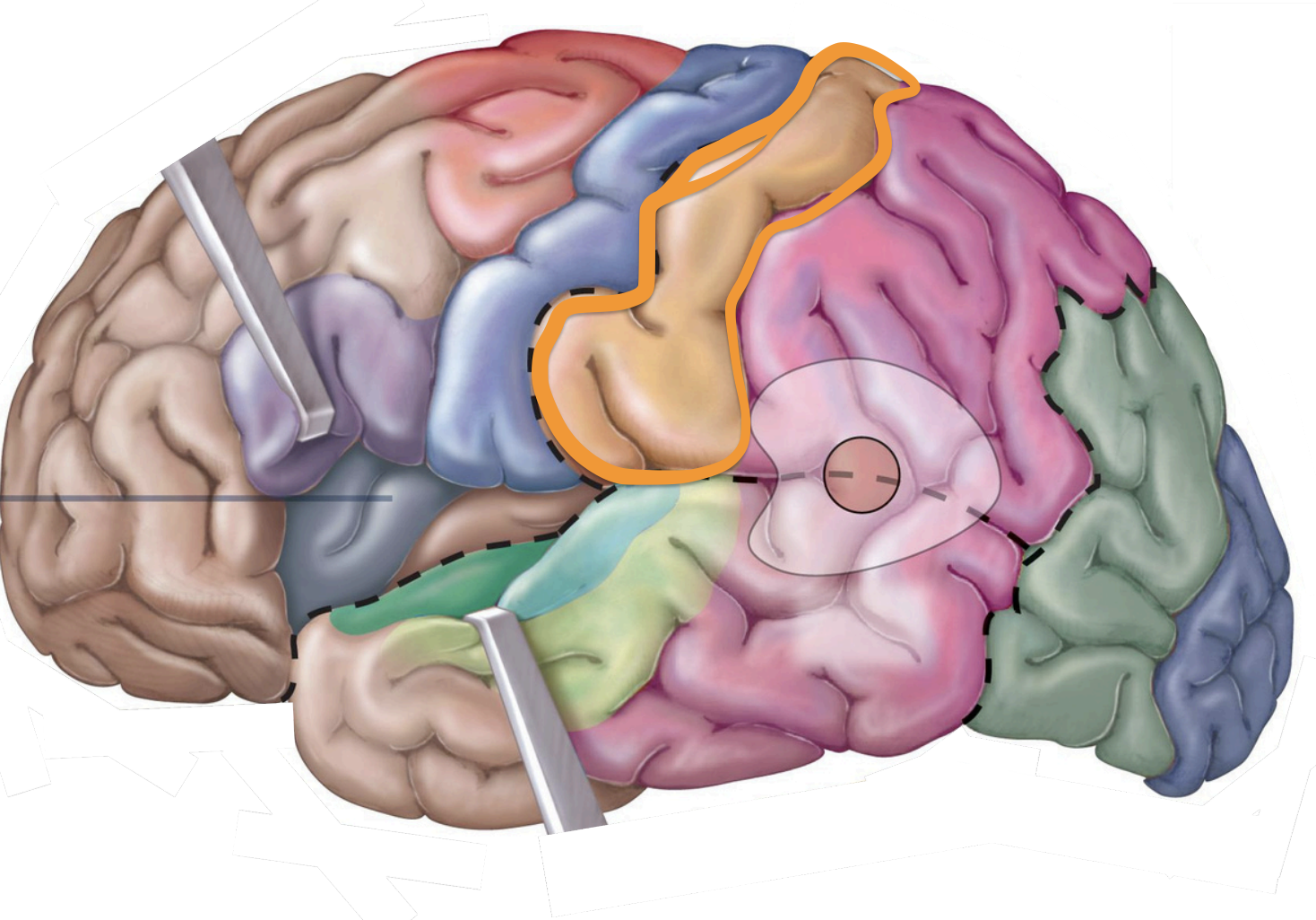
↳ Involved w/ the conscious awareness of sensation
↳ Info going in
↳ parietal lobe
Sensory areas
postcentral gyrus;
general sensory info.
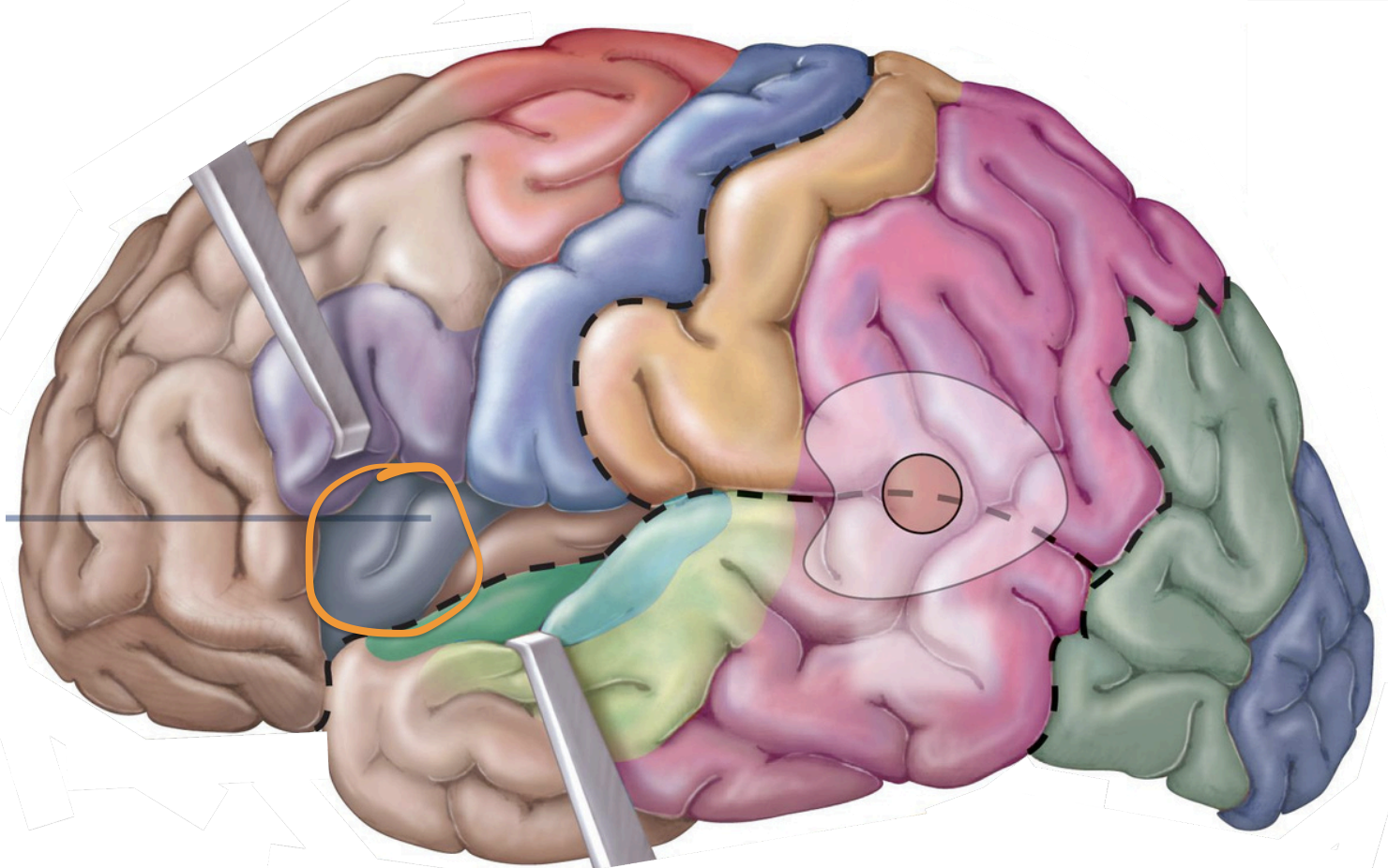
Sensory Areas - 1°somatosensory cortex
occipital lobe;
visual information from eye
Sensory Areas - 1°visual cortex
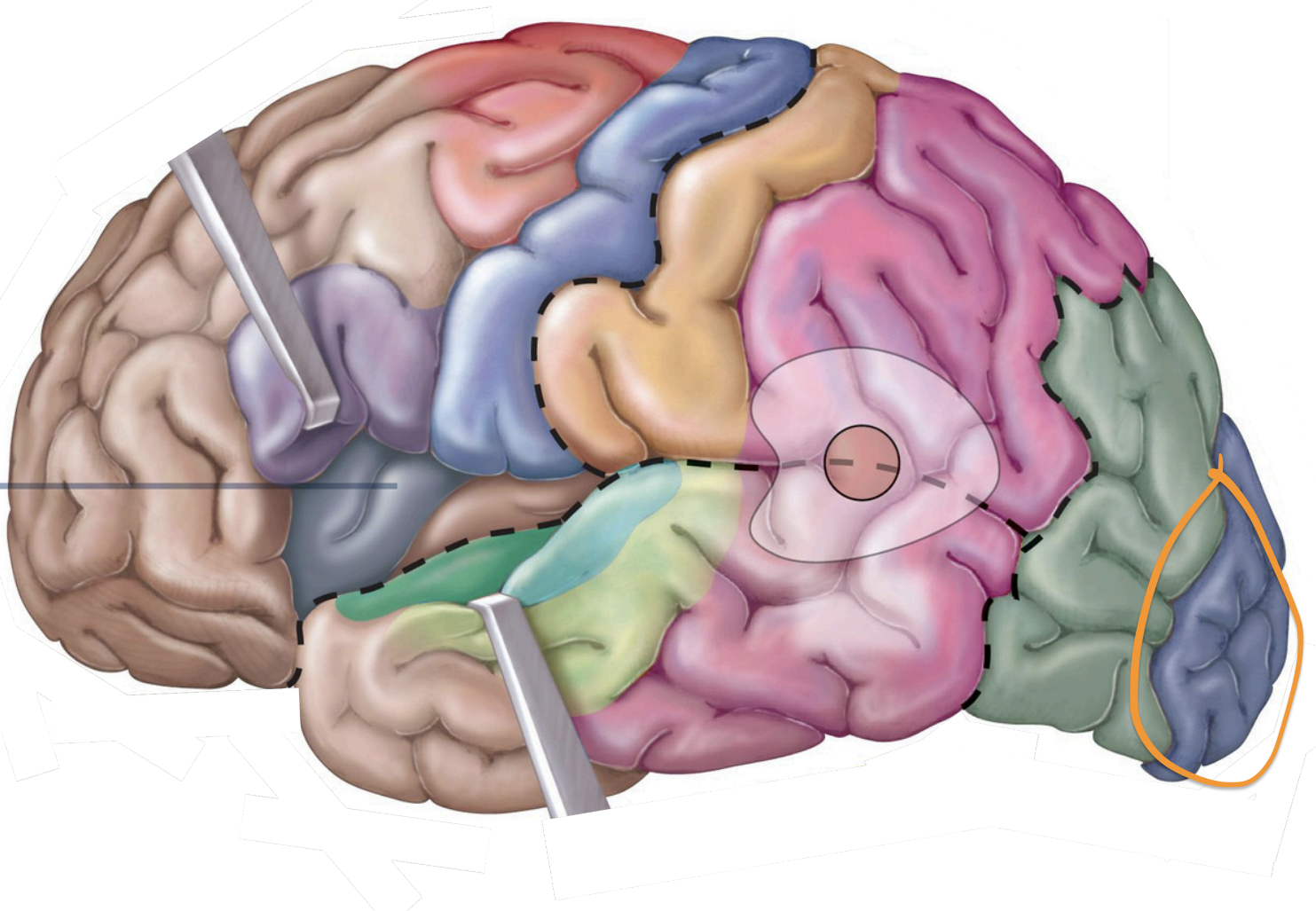
temporal lobe;
auditory info. from inner ear
Sensory Areas - 1°auditory cortex
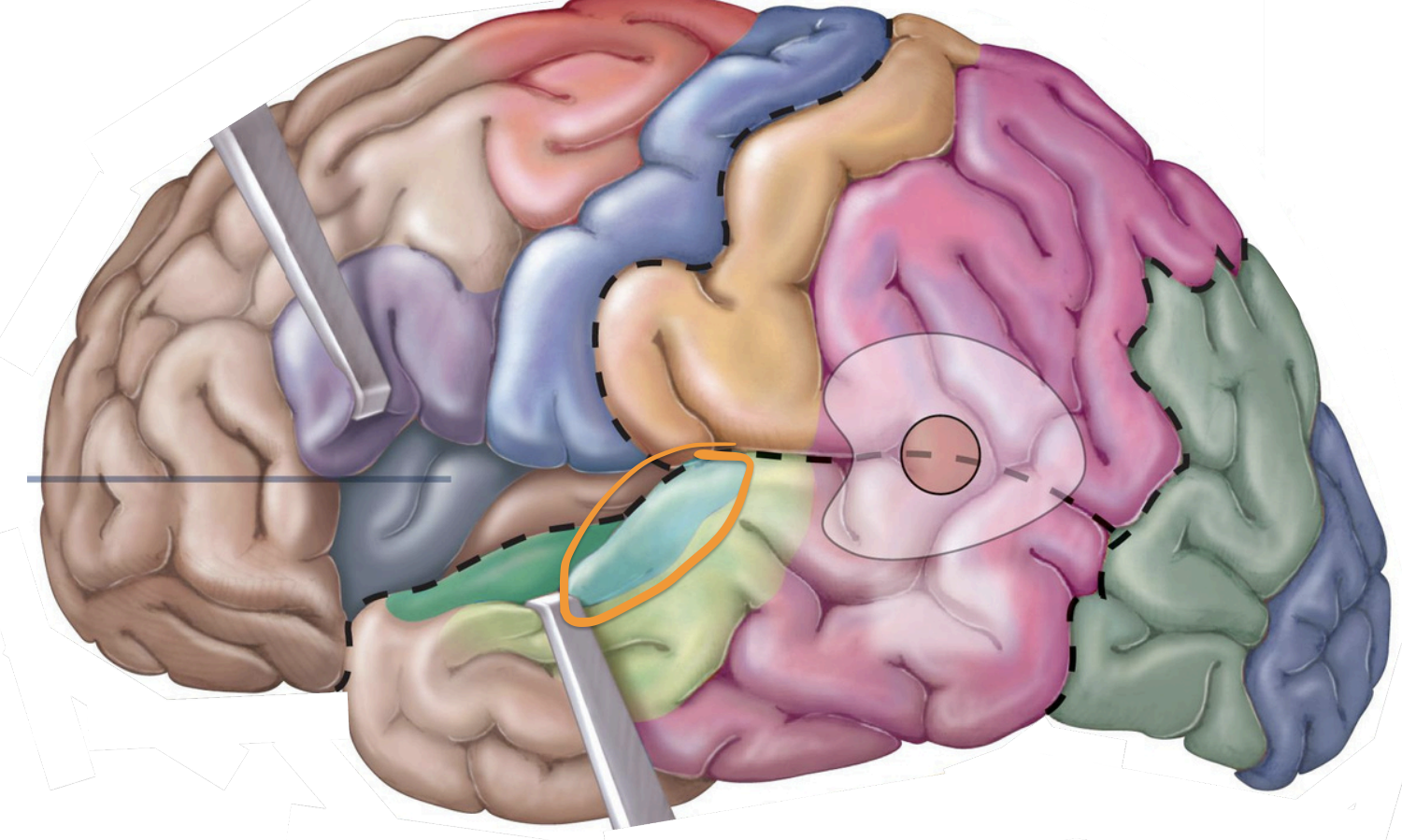
temporal lobe;
olfactory info. from nasal cavities
Sensory Areas - 1°olfactory cortex
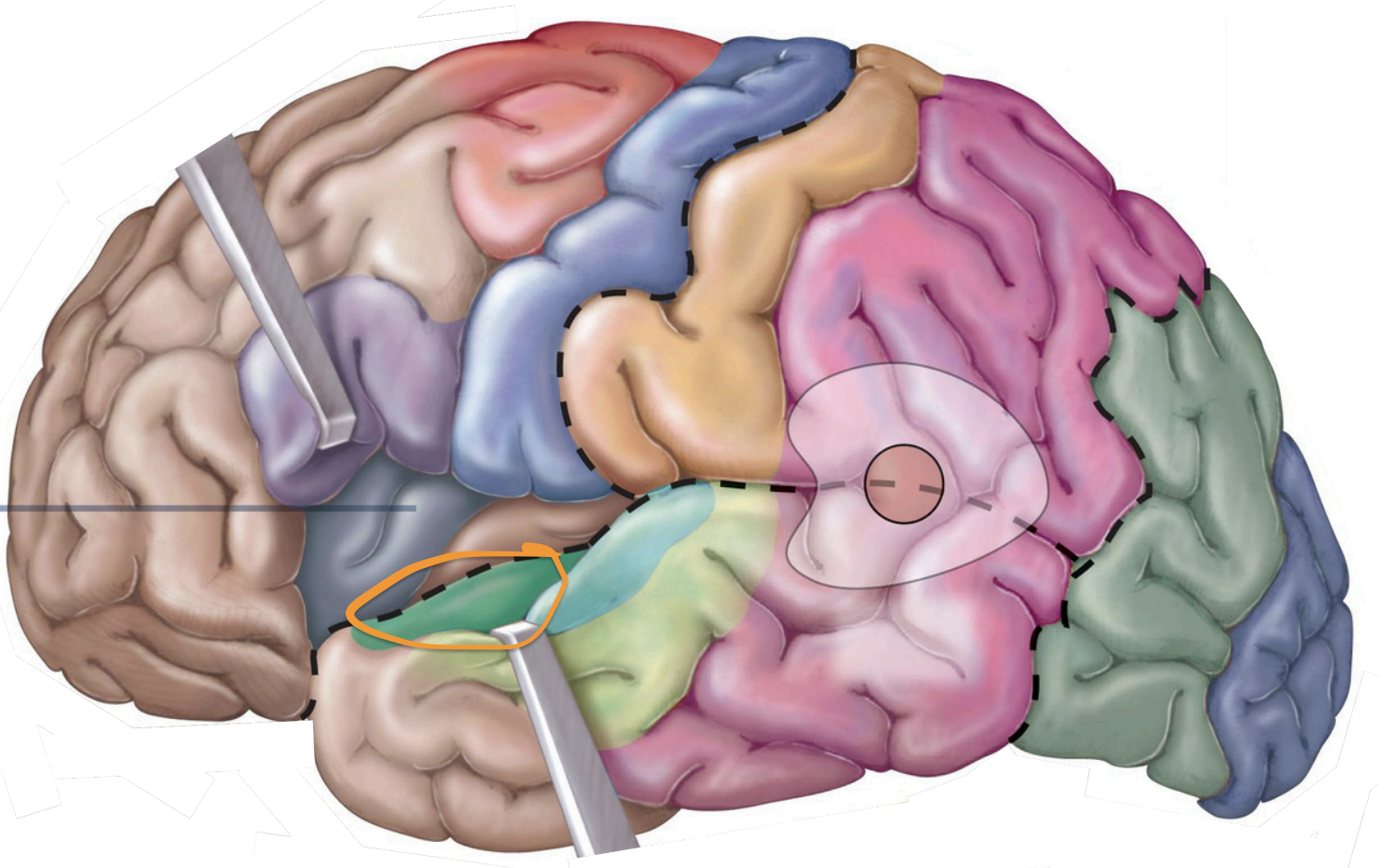
insula;
taste info. from taste buds
Sensory Areas - 1°gustatory cortex
↳ Process & interpret sensory input and /or coordinate motor output
↳ puts info together
all over
Association areas
coordinating learned,
skilled motor activities (e.g. reading, grasping)
Association areas - Premotor cortex (somatomotorassociation area)
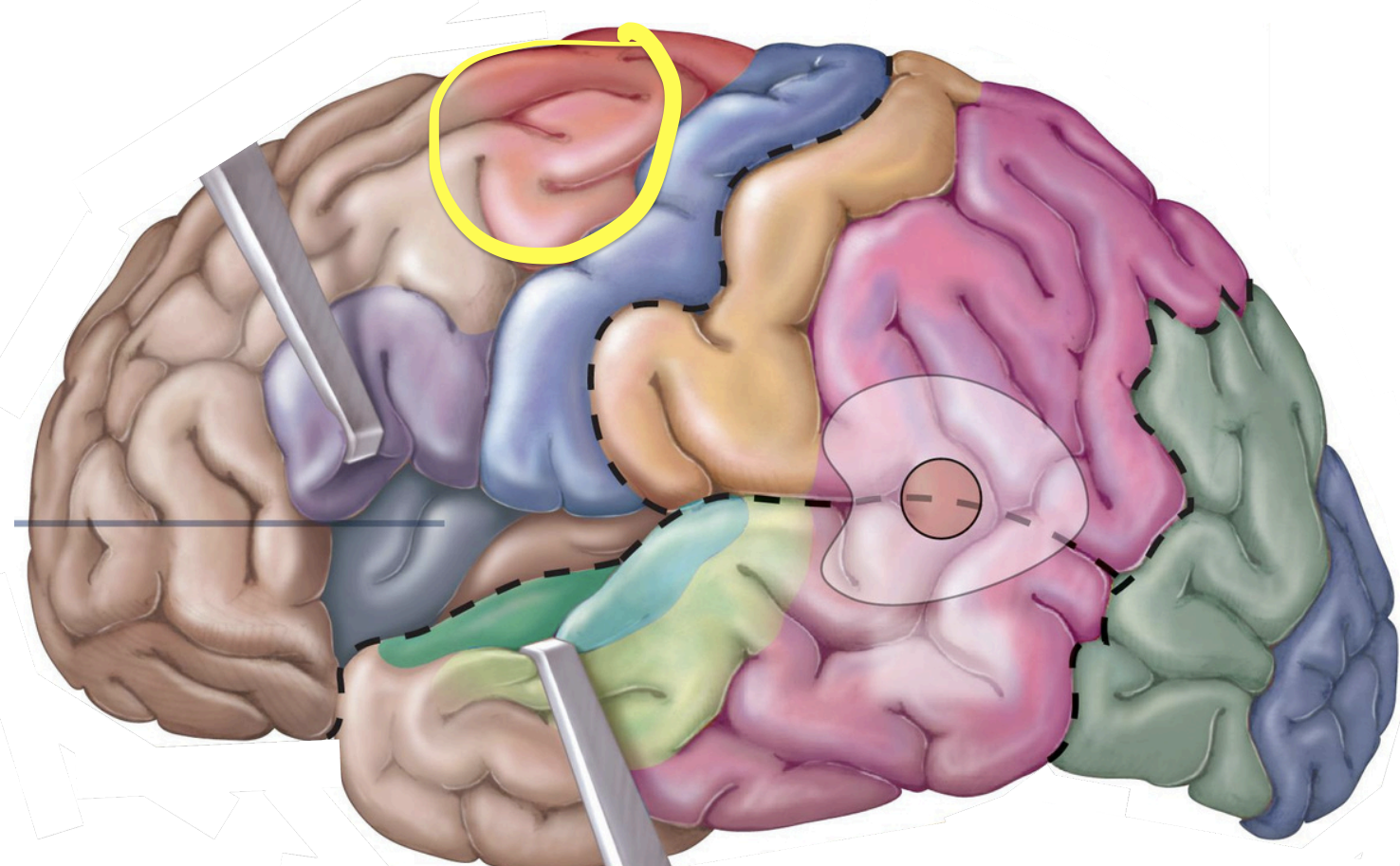
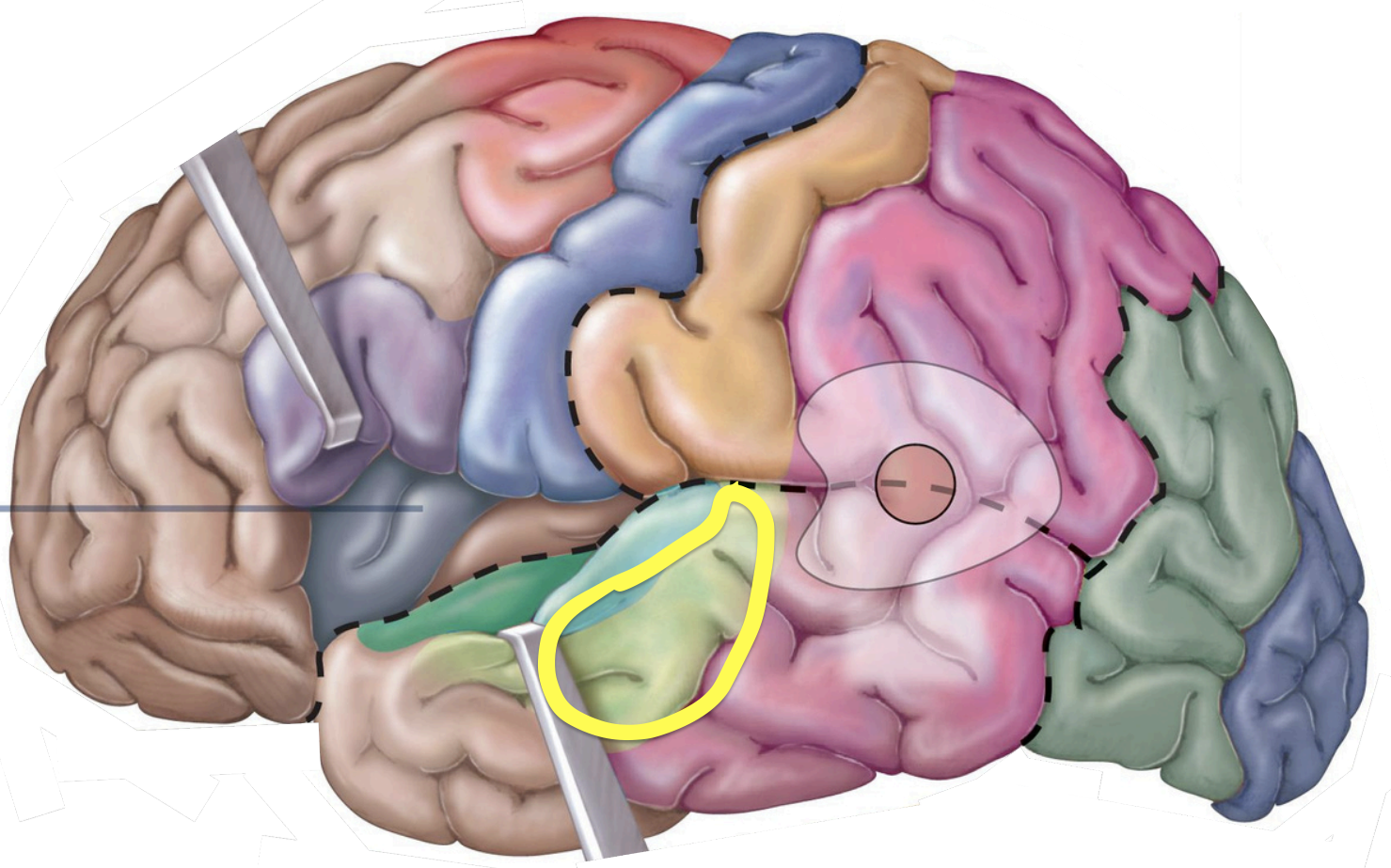
understanding of the object producing the stimulus
e.g. texture, temperature, pressure, shape
Association areas - Somatosensory association area
color, movement, form, facial recognition
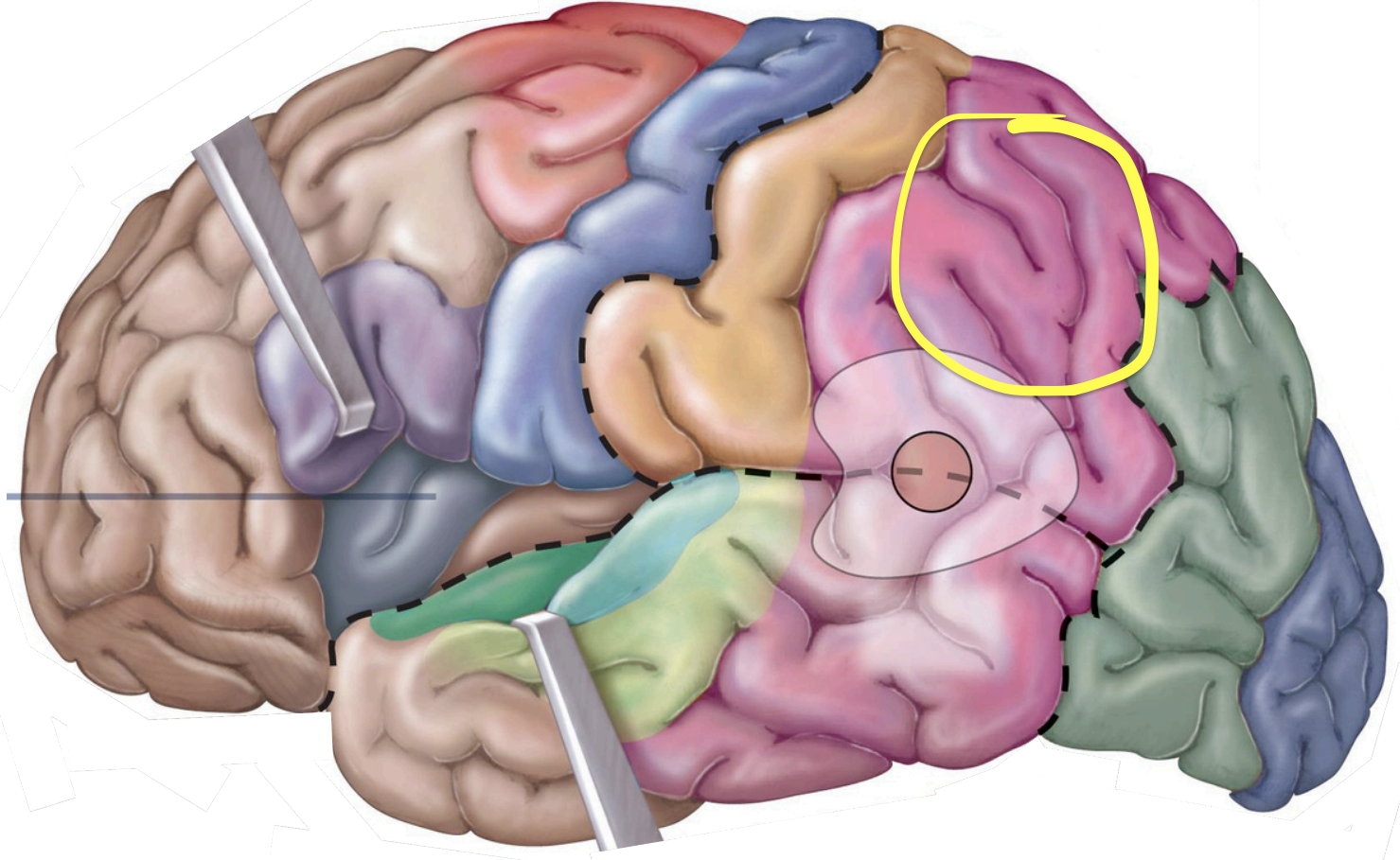
Association areas -Visual association area
correlates with memories of sound
music
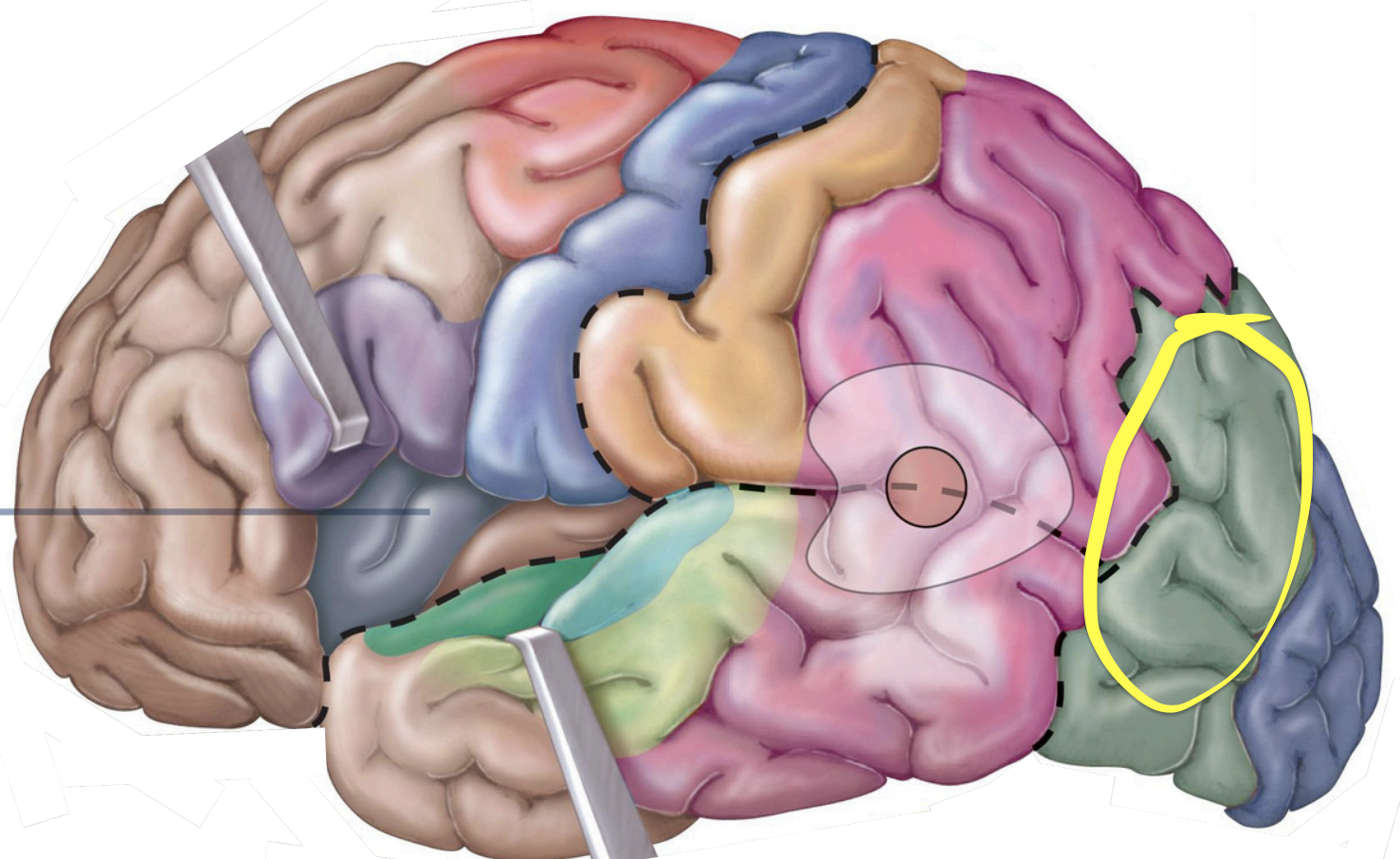
Association areas - Auditory association area
recognizing/understanding spoken & written language;
parietal and temporal lobes;
works w/ other areas to speak, type, & write
Association Areas - Wernickearea (hearing)
integrates all sensory input into a coherent whole
produce a comprehensive understanding of current activity;
Speaking
nostic=knowledge
Association Areas - Gnostic area
Axons that connect regions within the same hemisphere of the brain
arcuate - Connect adjacent gyri (precentral & postcentral gyrus)
longitudinal - Connect lobes of the same hemisphere (long-range connections
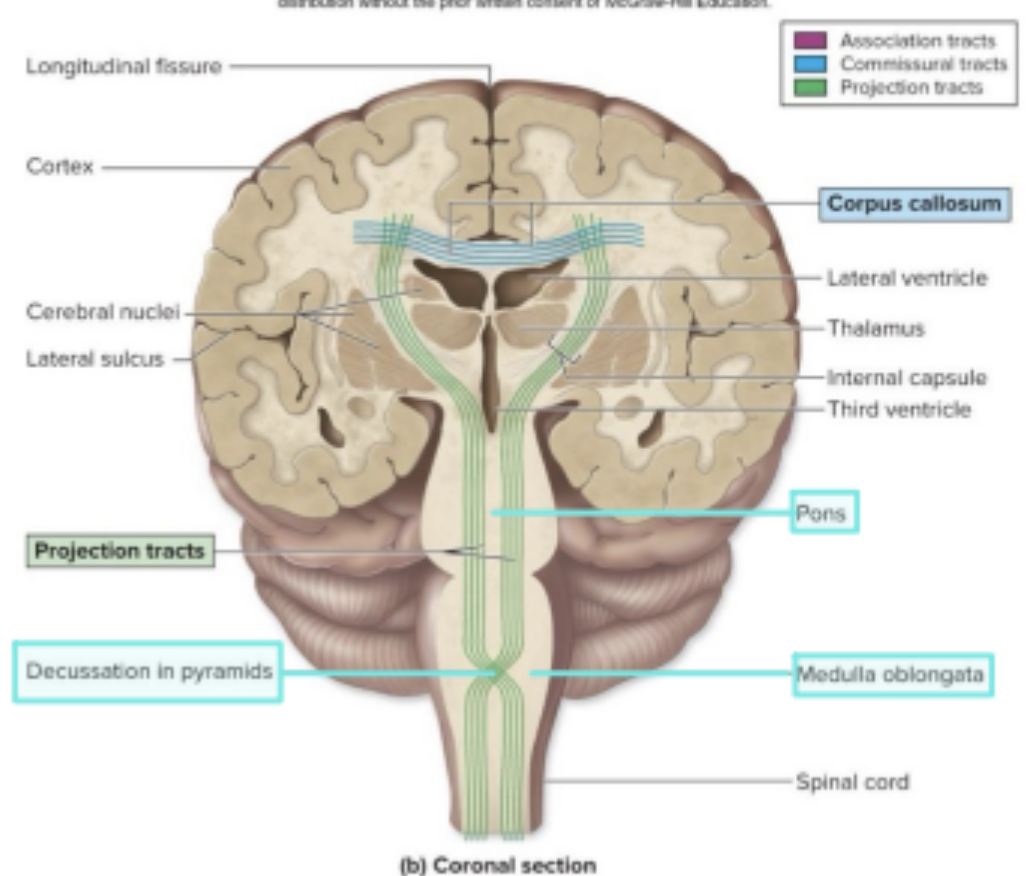
Cerebral White Matter - association tracts
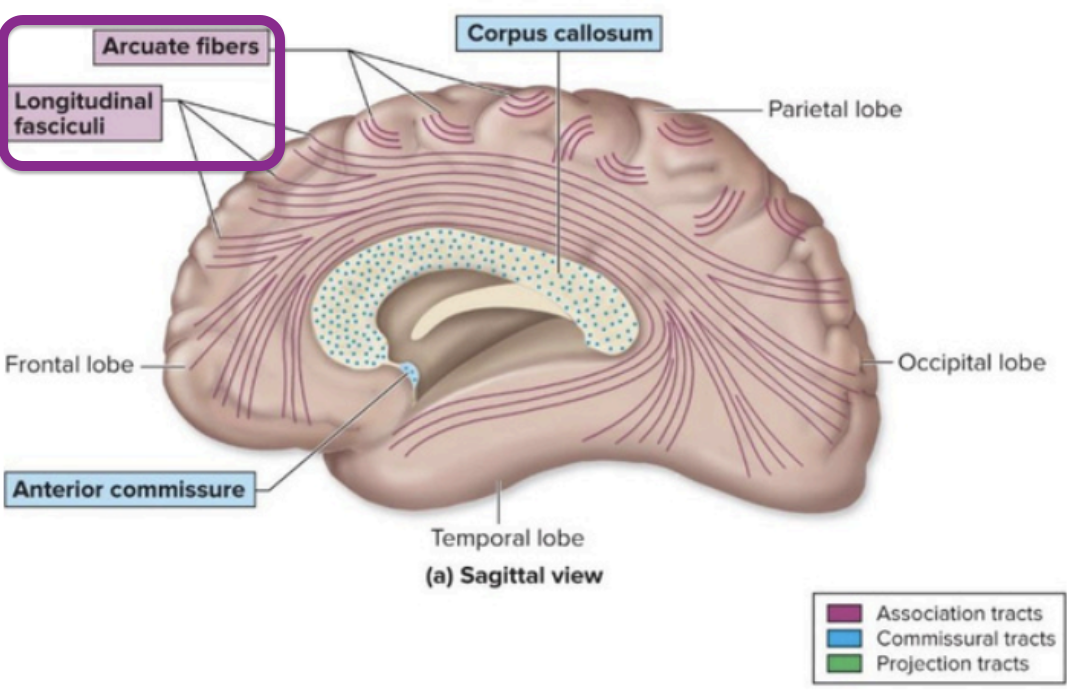
Curved fibers connecting areas within the same lobe of the brain.
Cerebral White Matter - accurate fibers
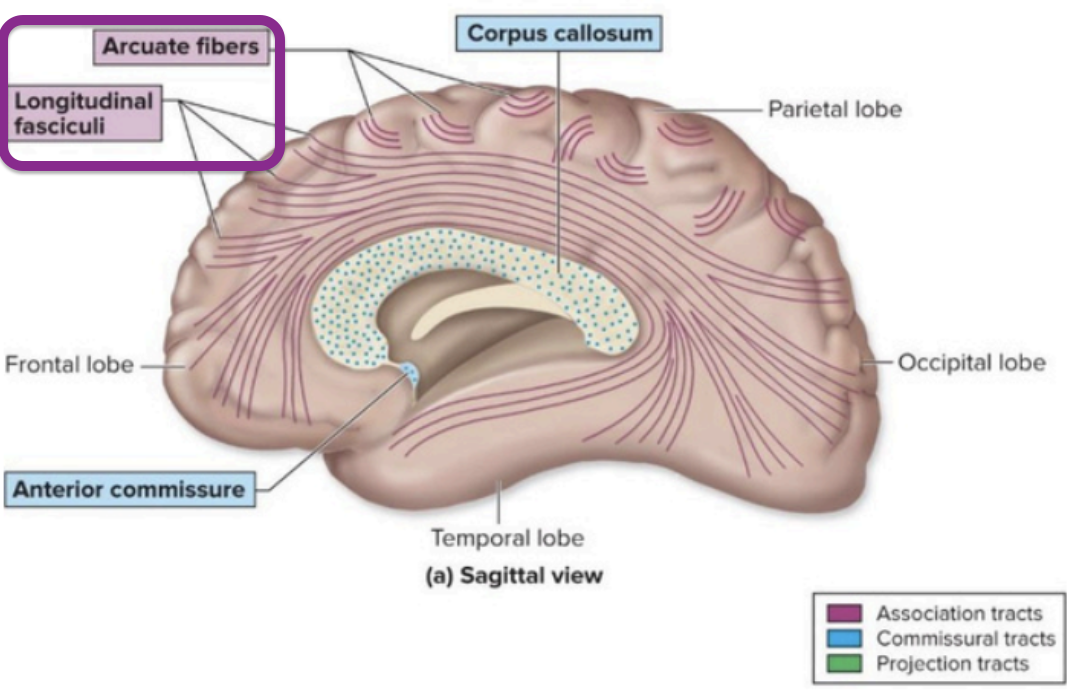
Association tracts that connect different lobes within the same hemisphere.
Cerebral White Matter - longitudinal fasciculi
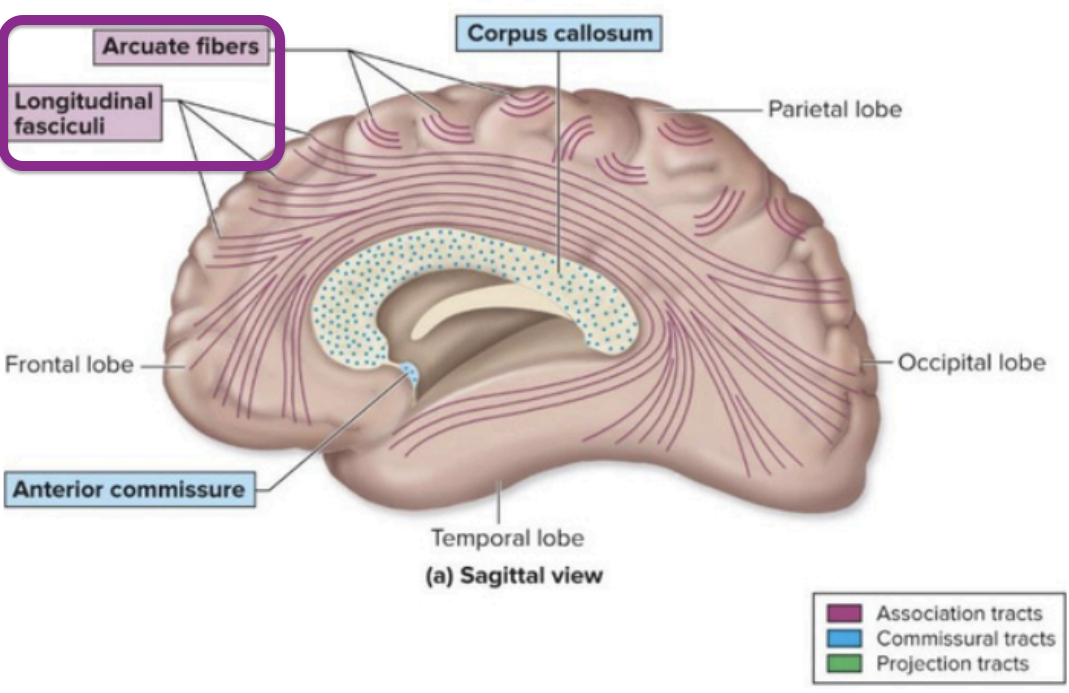
Fibers that connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
Cerebral White Matter - commissural tracts
The largest commissural tract connecting the two hemispheres of the brain.
Cerebral White Matter - corpus callosum
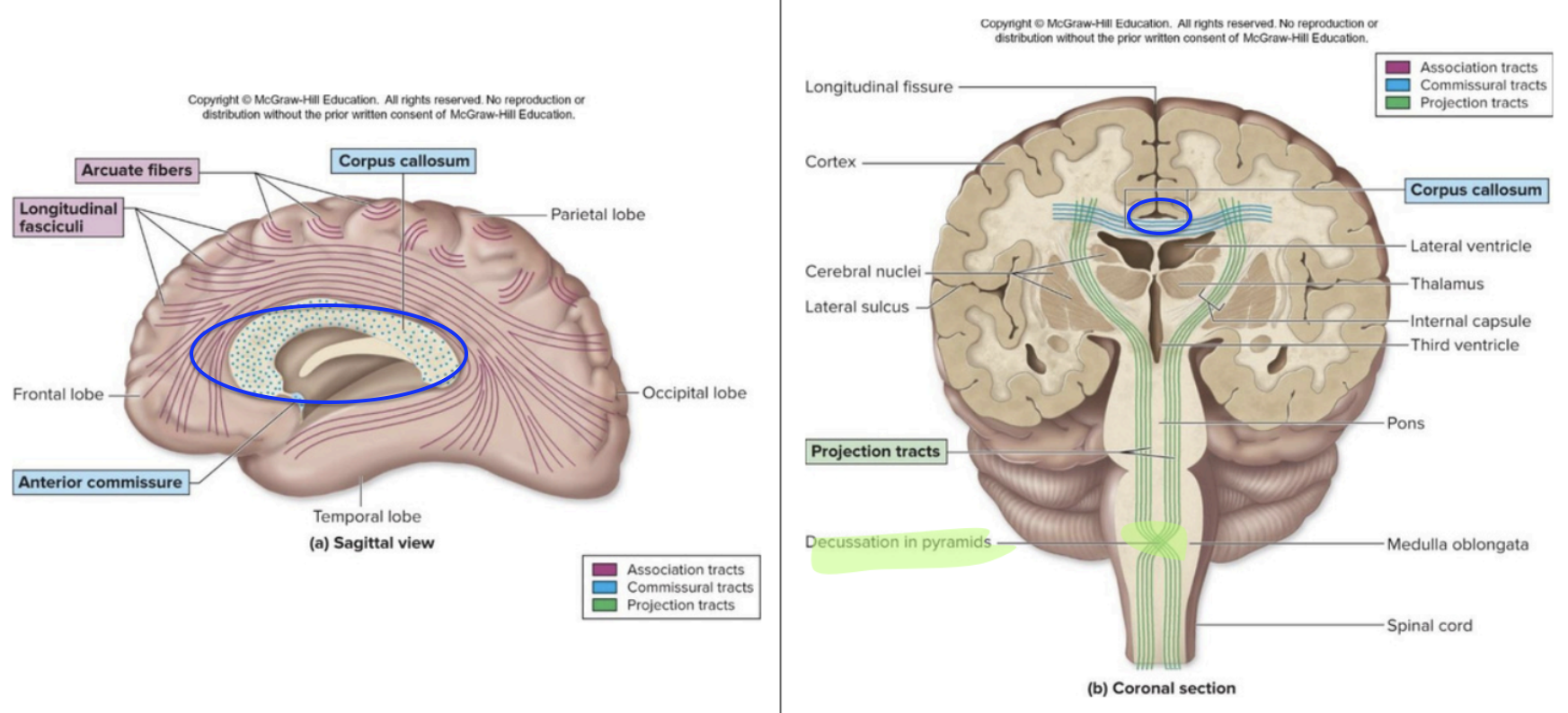
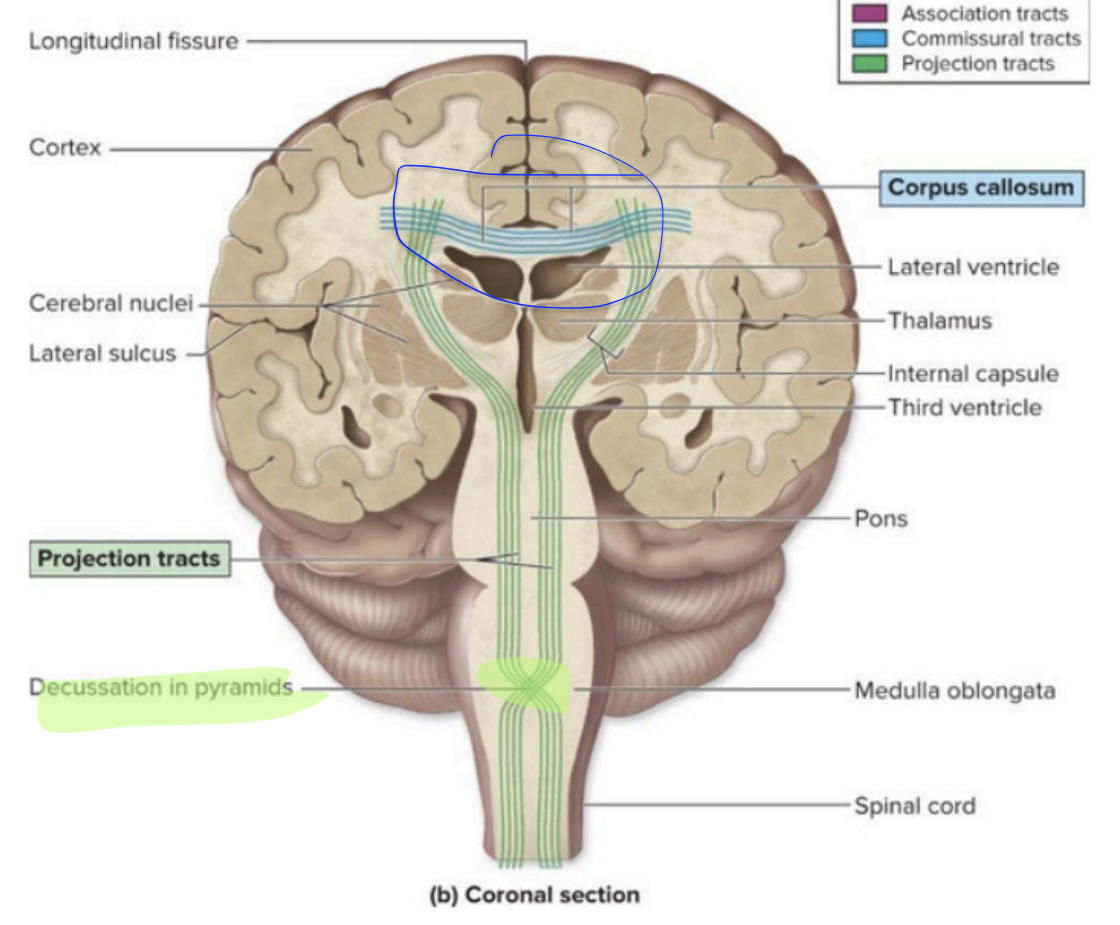
Fibers that connect the cerebrum to the lower brain
brainstem and spinal cord
Decussate = contralateralization
Cerebral White Matter - Projection tracts
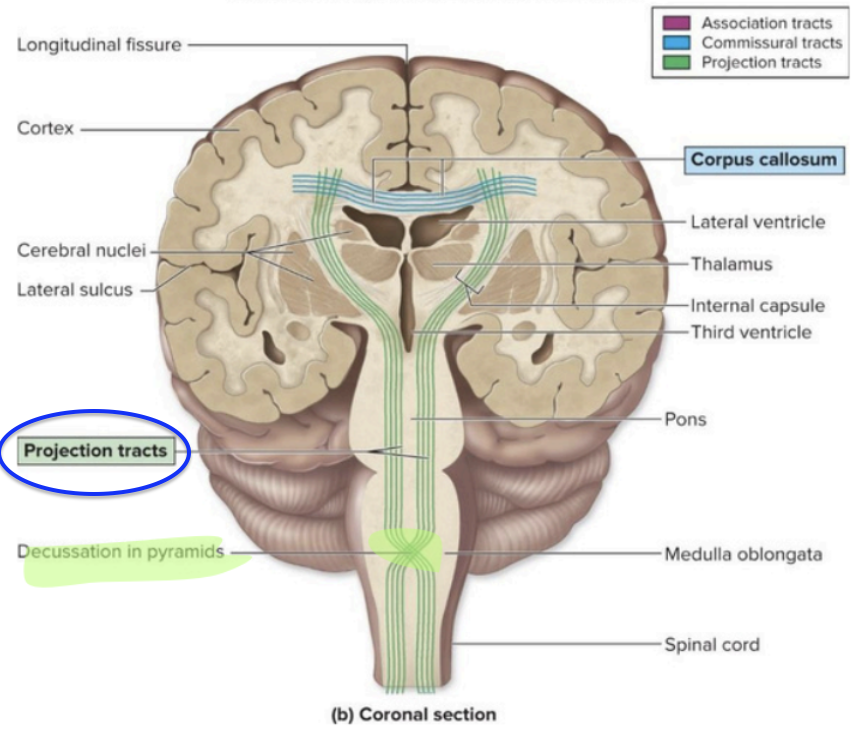
crossing over of nerve fibers
Cerebral White Matter - Projection tracts (Decussate = contralateralization)
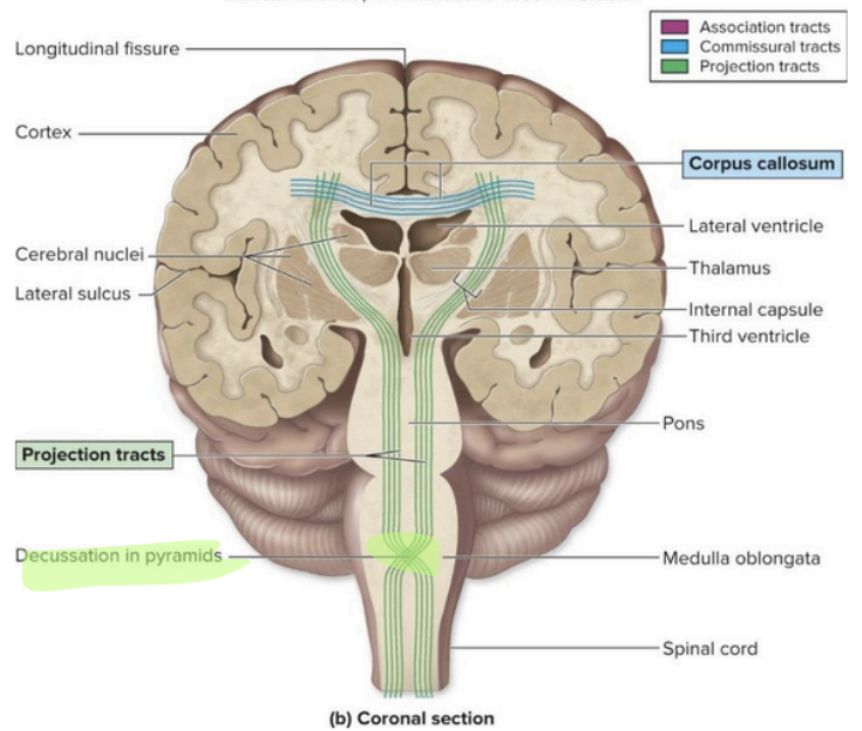
control autonomic NS
fight/flight/rest/digest
regulate
body temp
hunger
sleep/wake cycle
emotional behavior
Diencephalon – hypothalamus
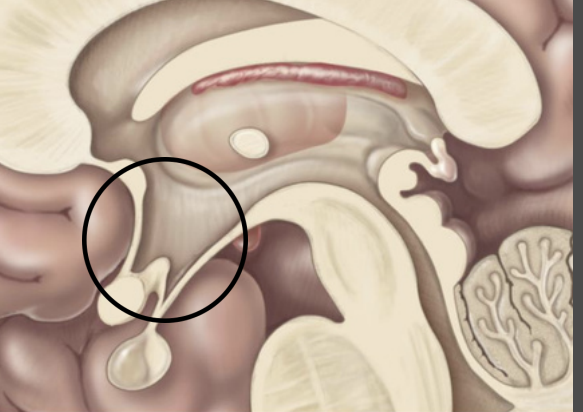
Receives conscious Senses
↳ Except olfaction - smell
Filters & relays to primary Cortices & association areas
Diencephalon – Thalamus
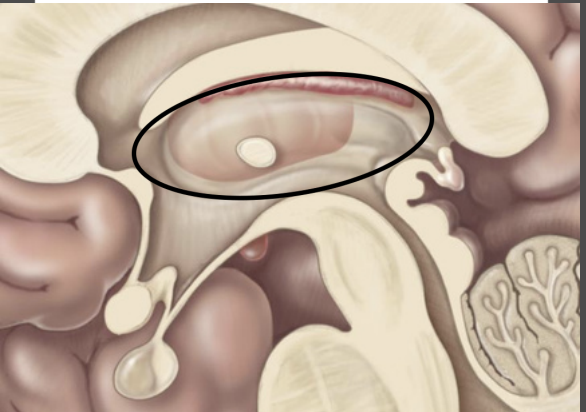
pineal gland
↳Endocrine gland Secretes melatonin
↳ Regulates Circadian rhythm
Diencephalon – Epithalamus
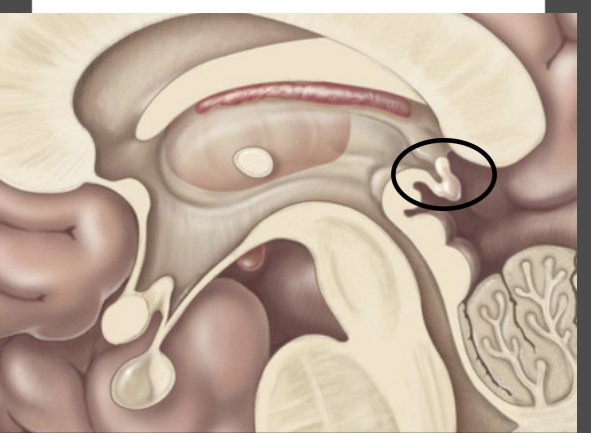
Brainstem – autonomic functions
Connects cerebrum, diencephalon, and cerebellum to spinal cord
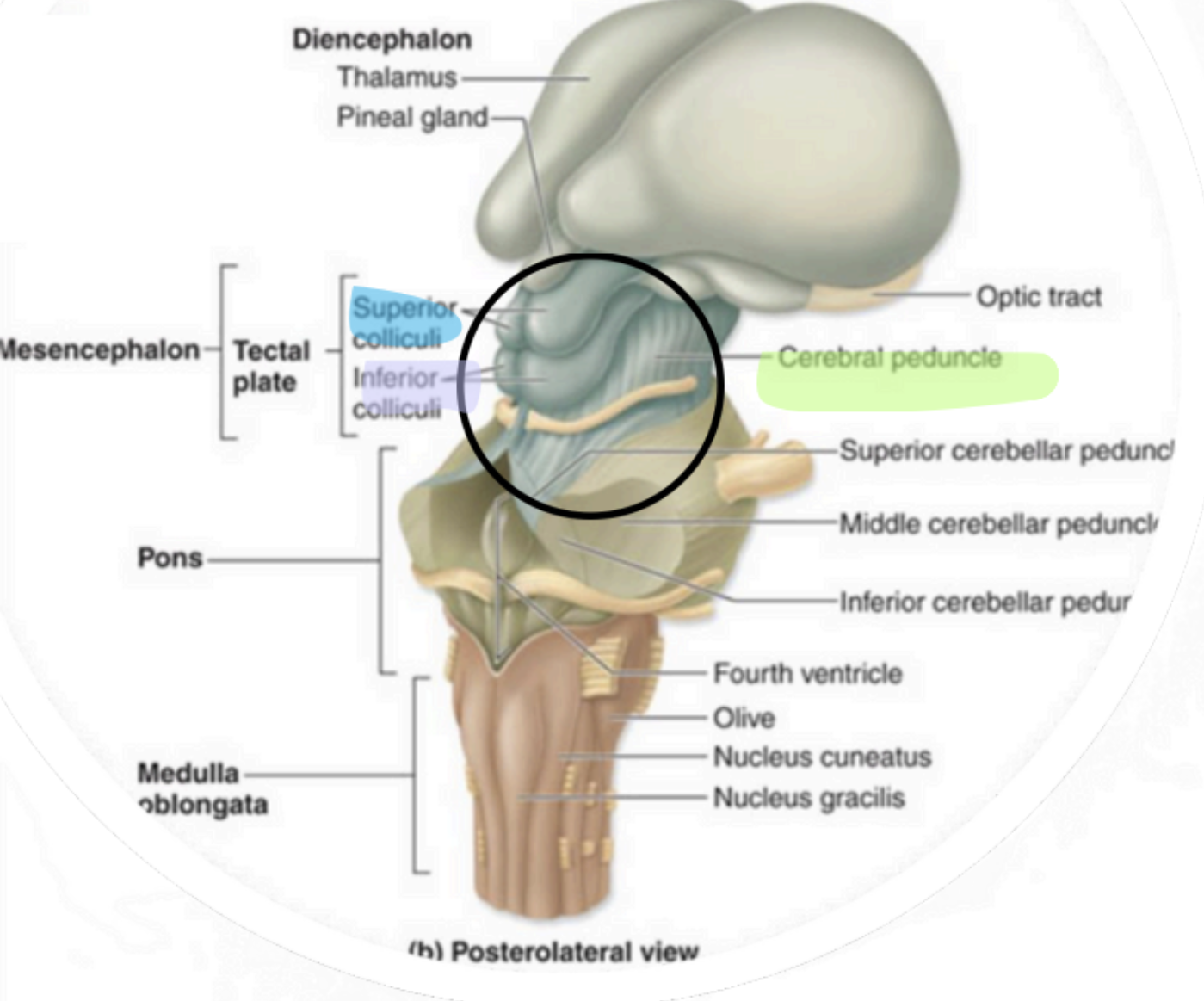
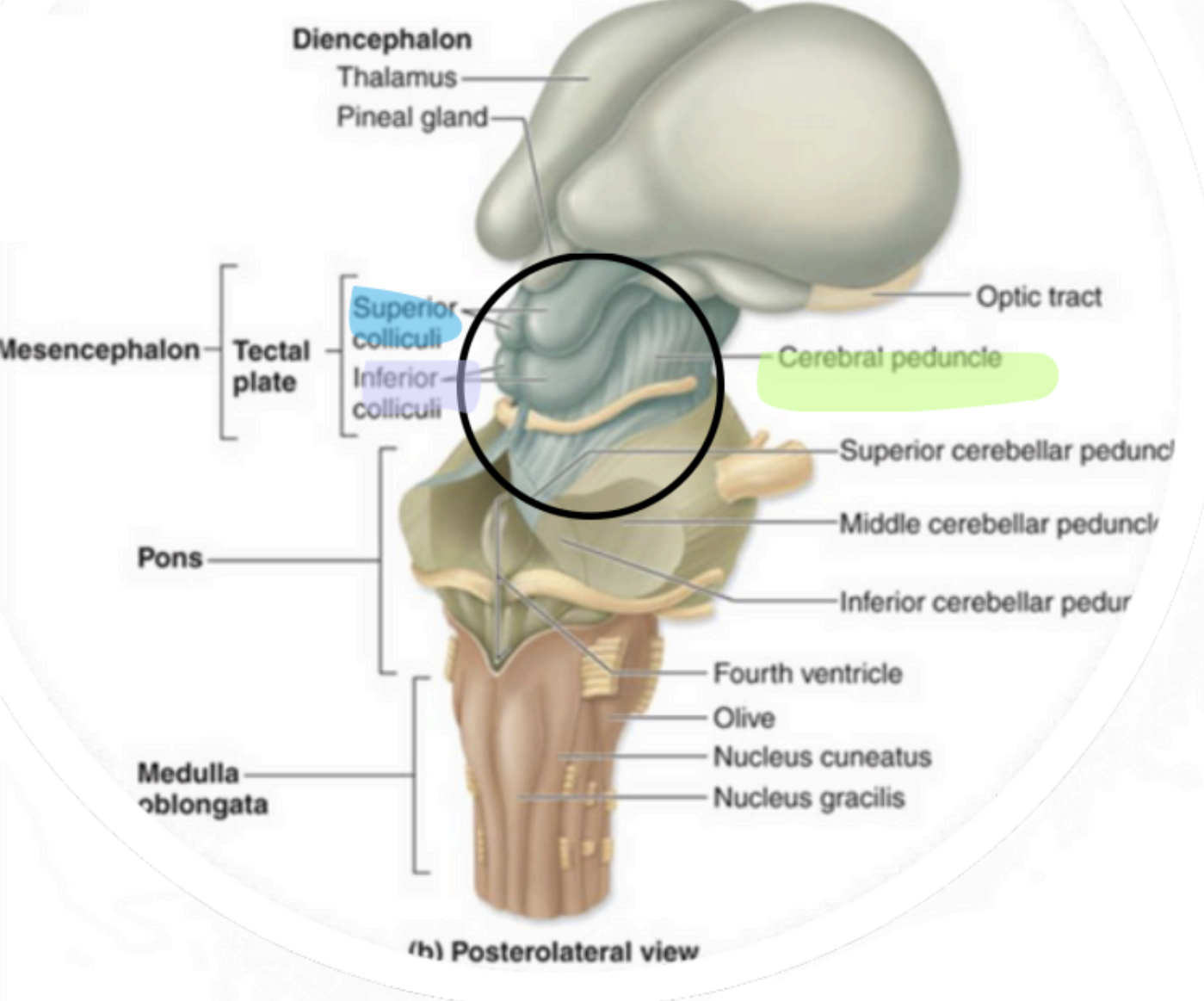
Mesencephalon -Midbrain
Superior portion of brainstem
Sensory & motor tracts connecting
brain to spinal cord
autonomic functions
descending motor axons
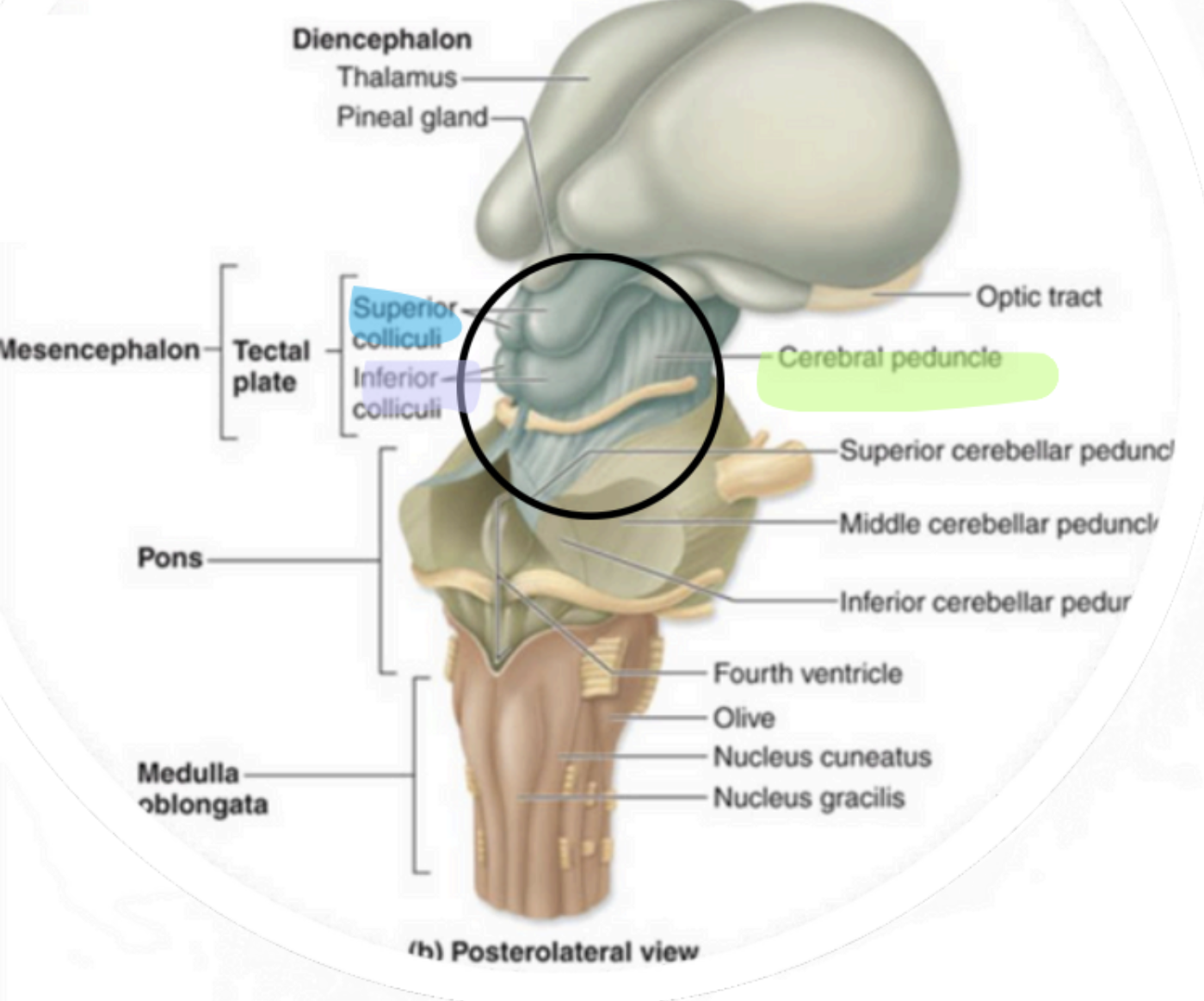
Mesencephalon - Cerebral Peduncles
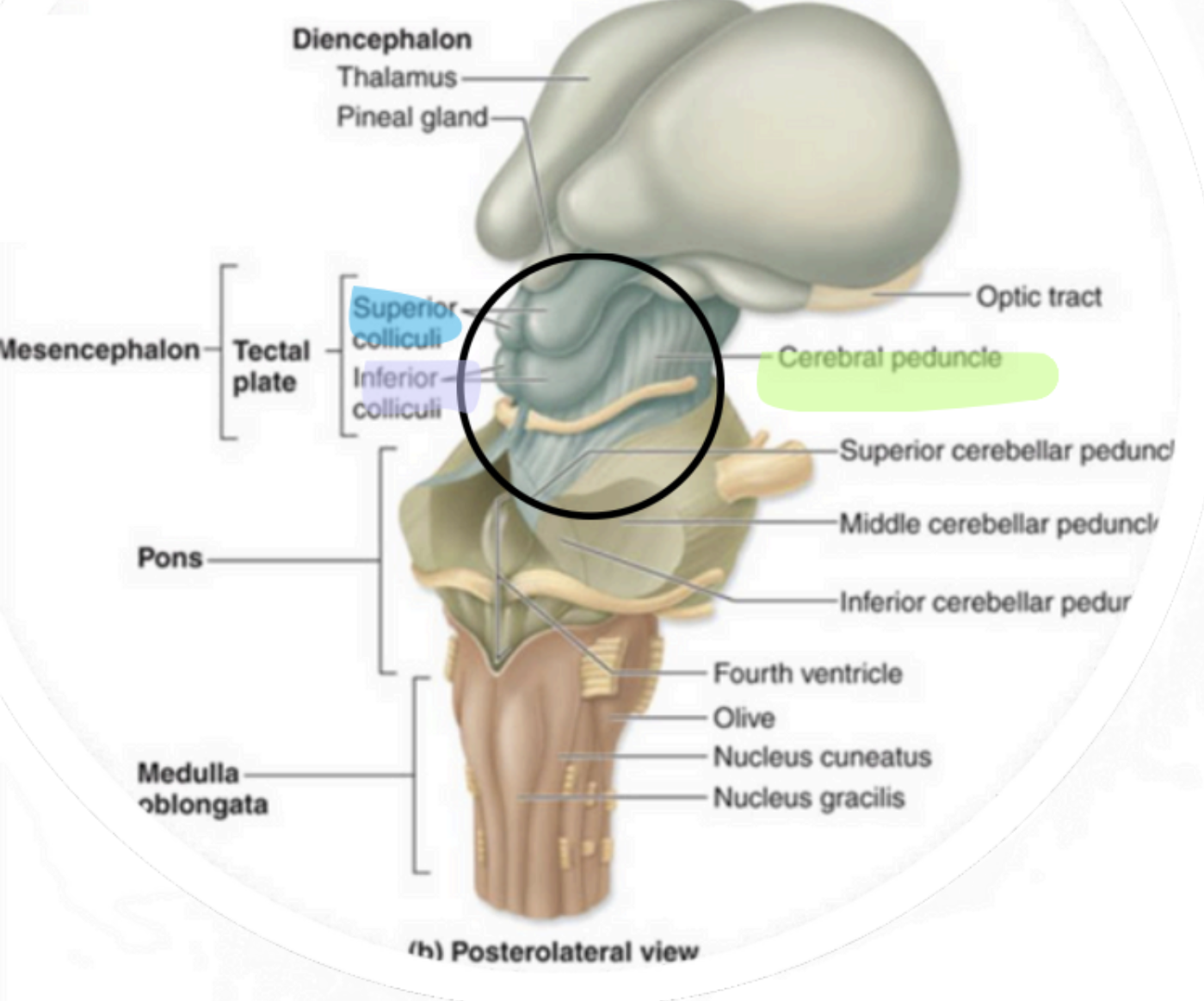
“visual reflex centers”
Mesencephalon - Superior Colliculi
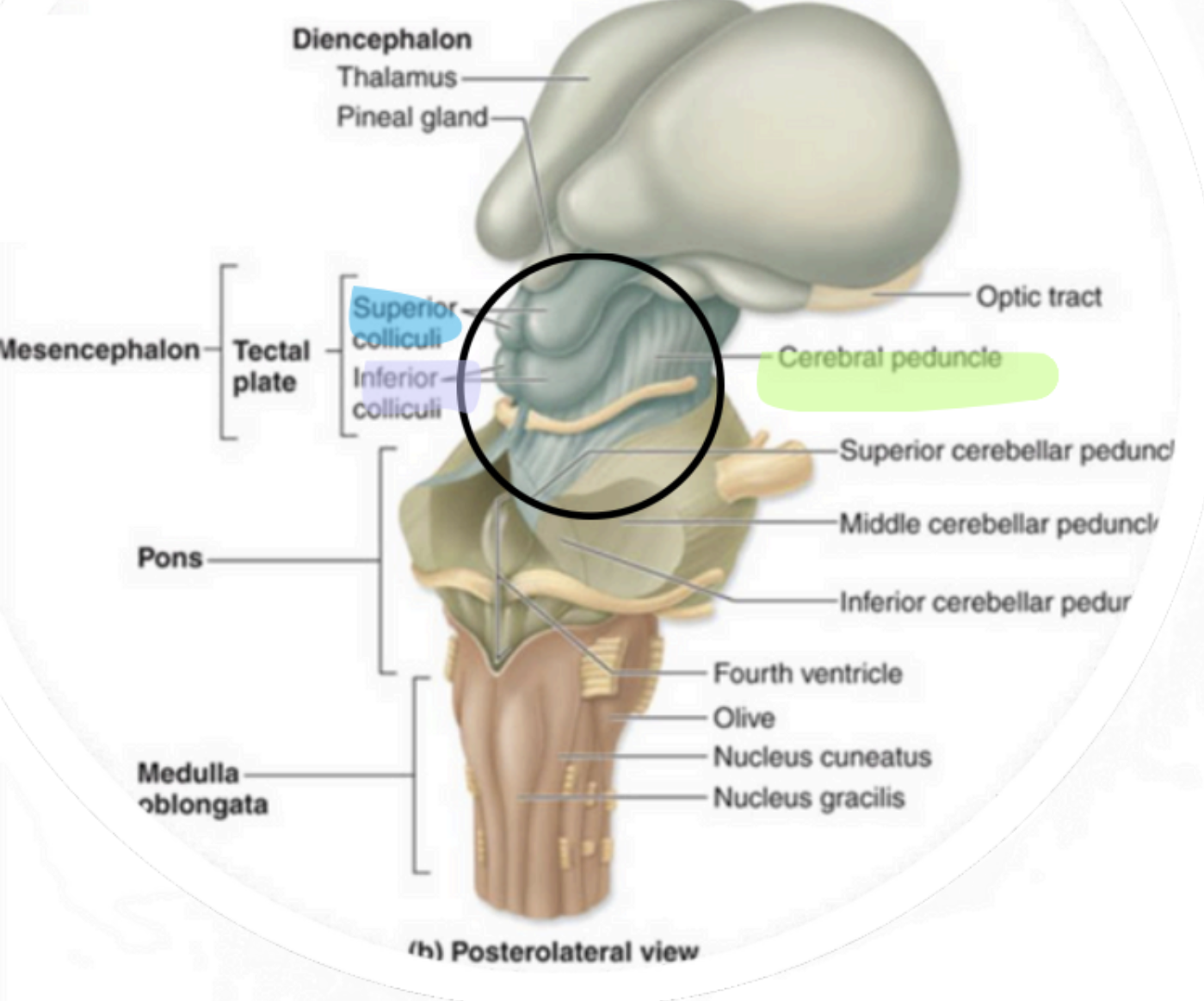
“auditory reflex centers”
↳ Only seen in cross section
Mesencephalon - Inferior Colliculi
Anterior, middle portion of brainstem
Sensory & motor tracts connecting brain to spinal cord
Autonomic functions
Metencephalon - Pons
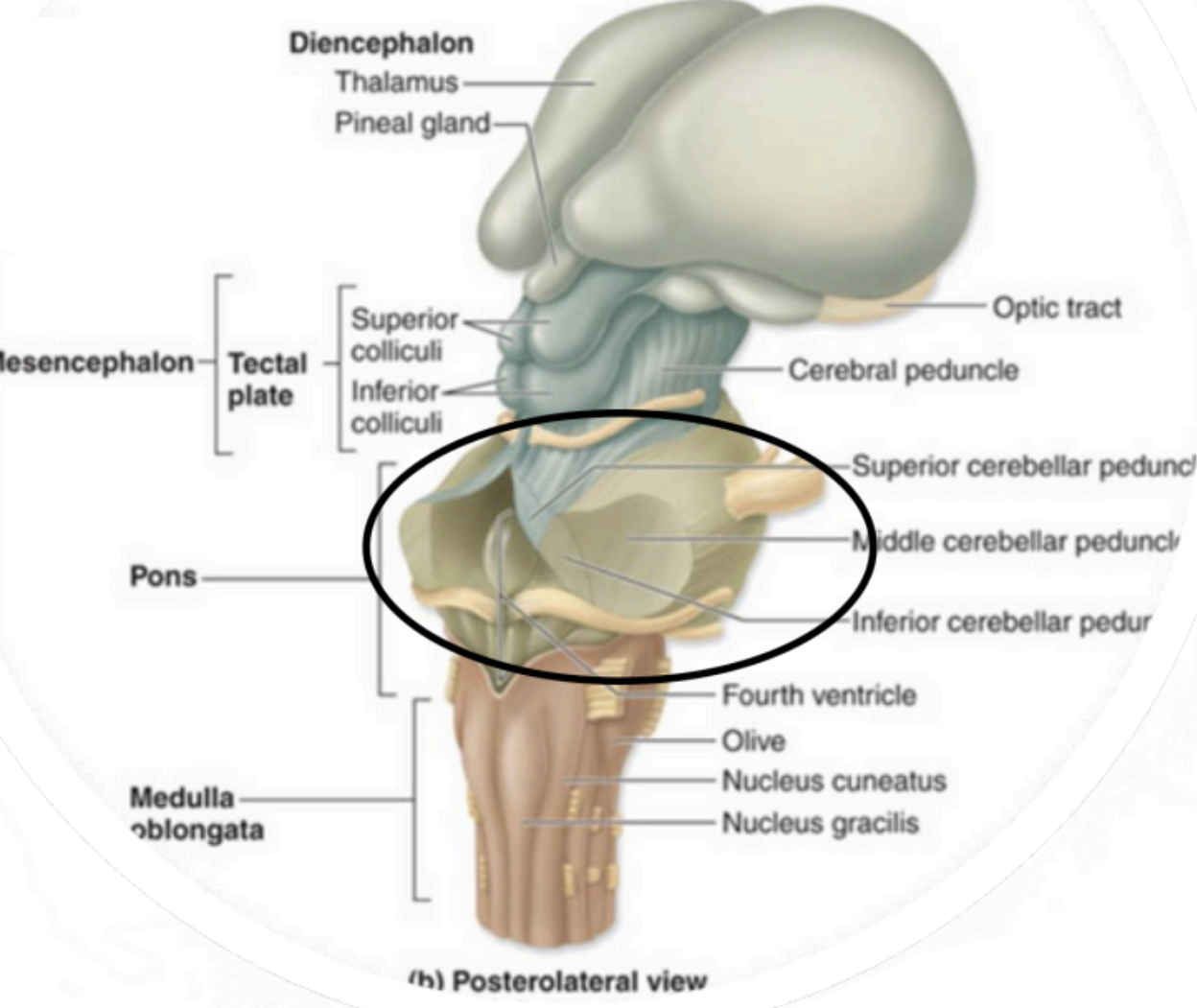
connects pons to cerebellum
Metencephalon - Middle Cerebellar Peduncles
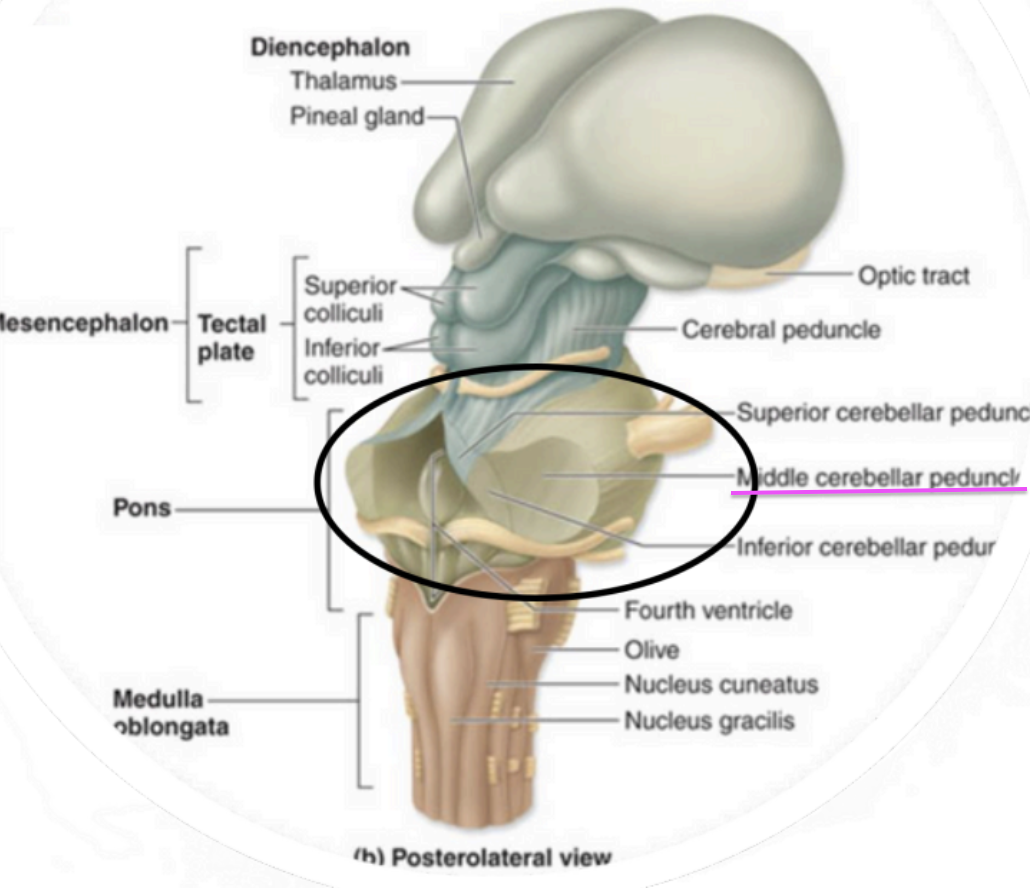
regulate rate and depth of breathing
Metencephalon - Autonomic
Respiratory Centers
↳ Involved in sound localization
Metencephalon - Superior Olivary complex
Inferior portion of brainstem
continuous w/ spinal cord inferiorly
sensory & motor tract connecting brain to Spinal cord
Autonomic function
Myelencephalon –Medulla Oblongata
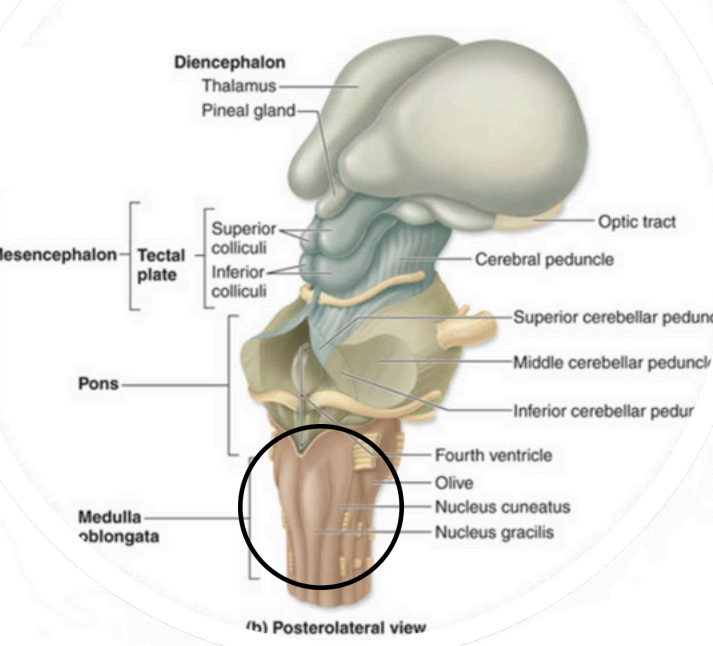
motor fibers crossover = contralateralization
Myelencephalon – medulla oblongata (Decussation of the Pyramids)
Regulate heart rate and strength
Controls blood pressure (arteriole control)
Respiratory rate (along with
pons)
Myelencephalon – medulla oblongata Important Autonomic Centers:
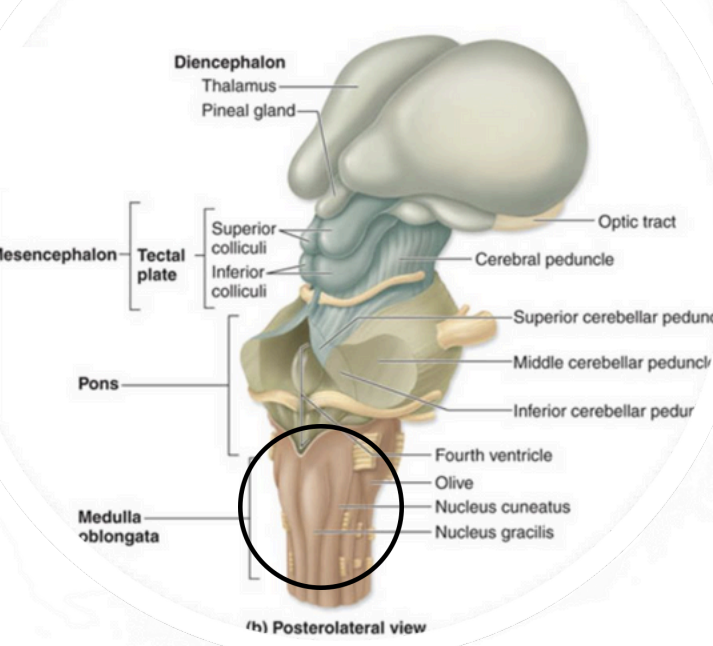
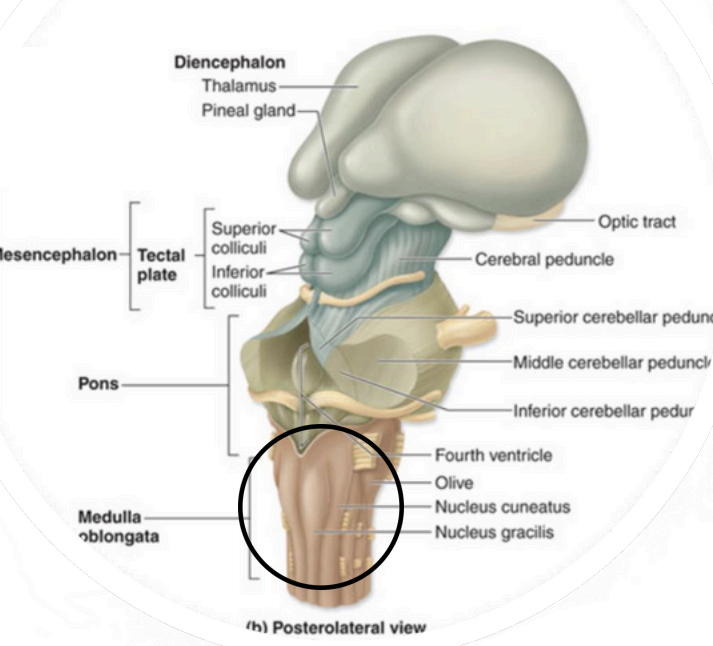
Meyelencephalon–Medulla Oblongata (centers controlling)
coughing
sneezing
salivating
swallowing
gagging
vomiting
hicupping
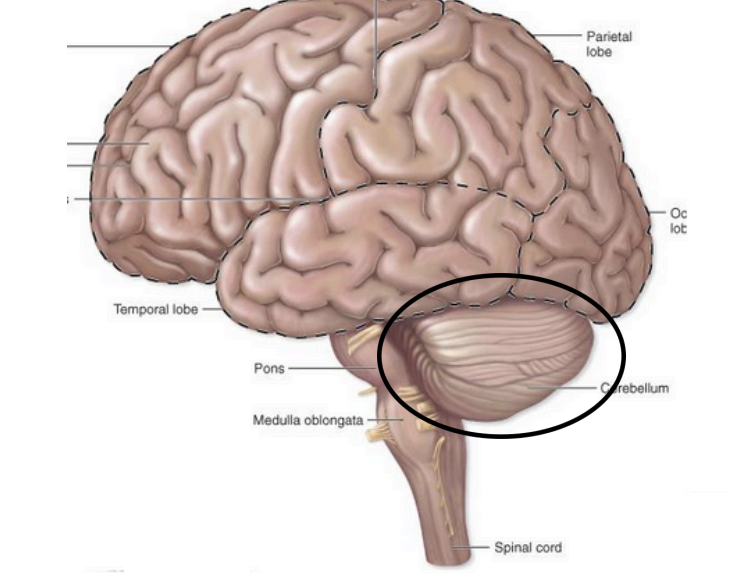
Responsible for:
coordinating & fine-tuning movements
↳ Planning & executing movements
agility (skill)
↳ Balance & Posture
↳ Adjusts & regulates movements (smoothness)
Metencephalon – cerebellum functions
How many cranial nerve pairs are there?
12 pairs
Where do cranial nerves originate and what regions do they serve?
Mostly the head and neck,
except Vagus (CN X)
extends to the thoracic and abdominal organs.
sensory - olfaction (smell)
Cranial Nerve I (olfactory)
sensory - vision
Cranial Nerve II (optic)
somatic motor - four extrinsic eye muscle
Cranial Nerve III (oculomotor)
somatic motor - One extrinsic eye movement
Cranial Nerve IV (trochlear)
sensory - general sensory from surface of head & mouth, including from anterior 2/3 mouth
motor - muscle of mastication
Cranial Nerve V (trigeminal)
motor - 1 extrinsic eye muscle
Cranial Nerve VI (abducens)
sensory - taste from anteiror 2/3 tounge
motor - muscle of facial expression
Cranial Nerve VII (facial)
sensory - hearing & equilibrium
Cranial Nerve VIII (vestibulococclear)
sensory - touch & taste 1/3 tongue
motor - one pharyngeal muscle
Cranial Nerve IX (glossopharyngeal)
sensory - visceral sensory most organs
motor - most pharyngeal & laryngeal muscle
Cranial Nerve X (vagus)
motor - two body muscle
Cranial nerve XI (accessory)
motor - muscle of tounge
Cranial Nerve XII (hypoglossal)