Triglycerides and Lipids: Overview, Health Implications, and Management
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Triglycerides (TGs)
Esters of glycerol + 3 fatty acids; most common body fat.
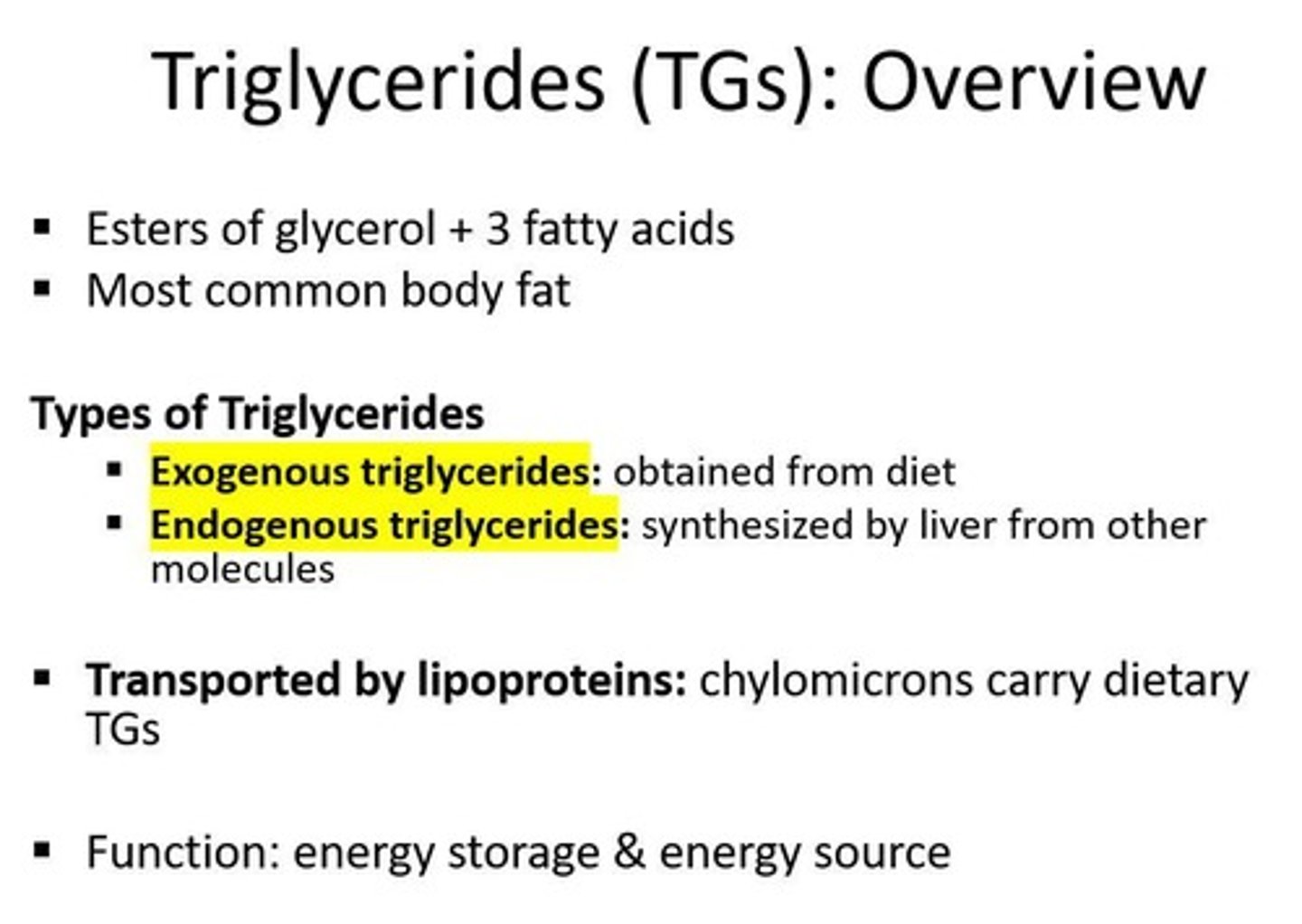
Exogenous triglycerides
Obtained from diet.
Endogenous triglycerides
Synthesized by liver from other molecules.
Chylomicrons
Lipoproteins that carry dietary triglycerides.
Normal fasting TG
<150 mg/dL.
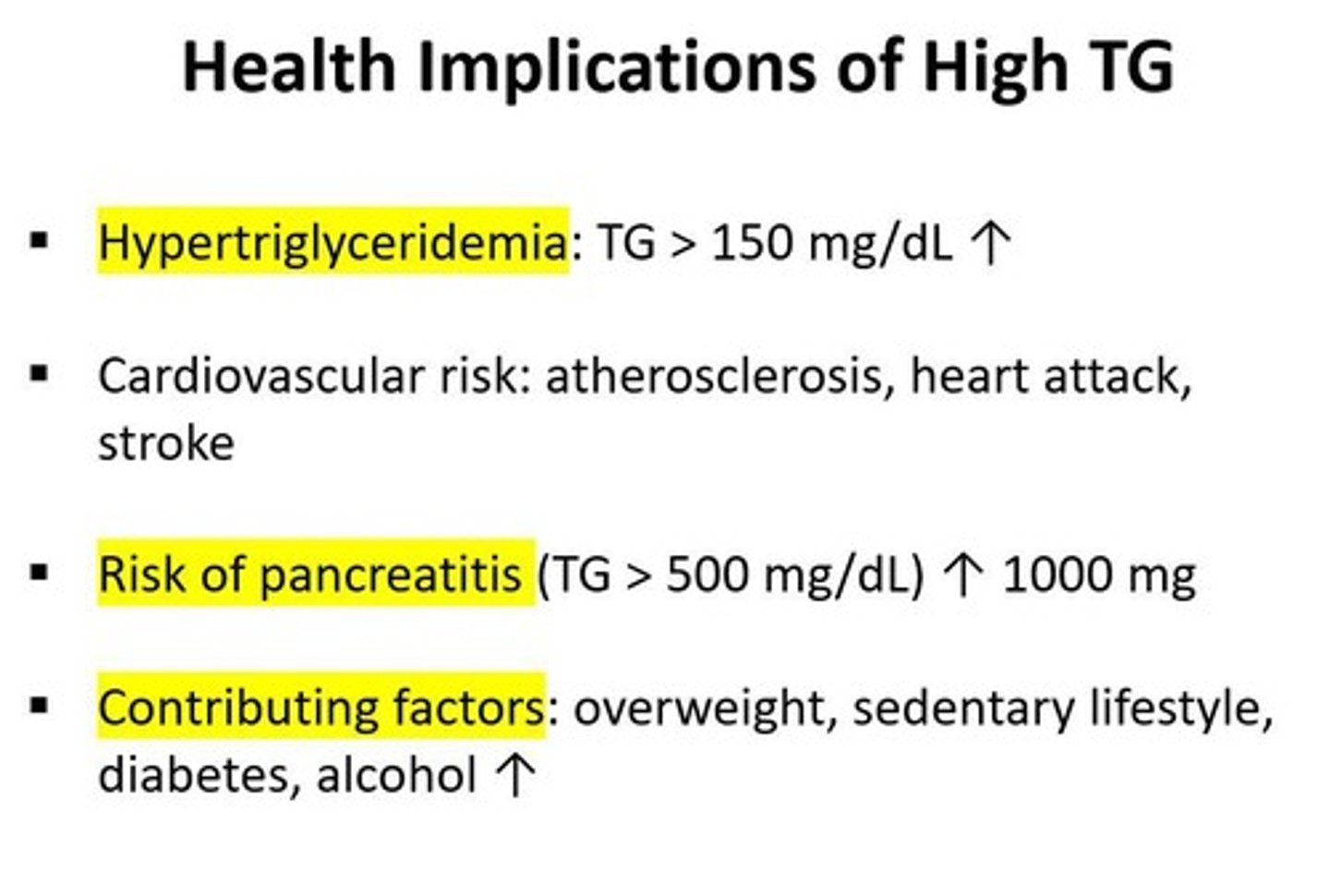
Hypertriglyceridemia
TG > 150 mg/dL.
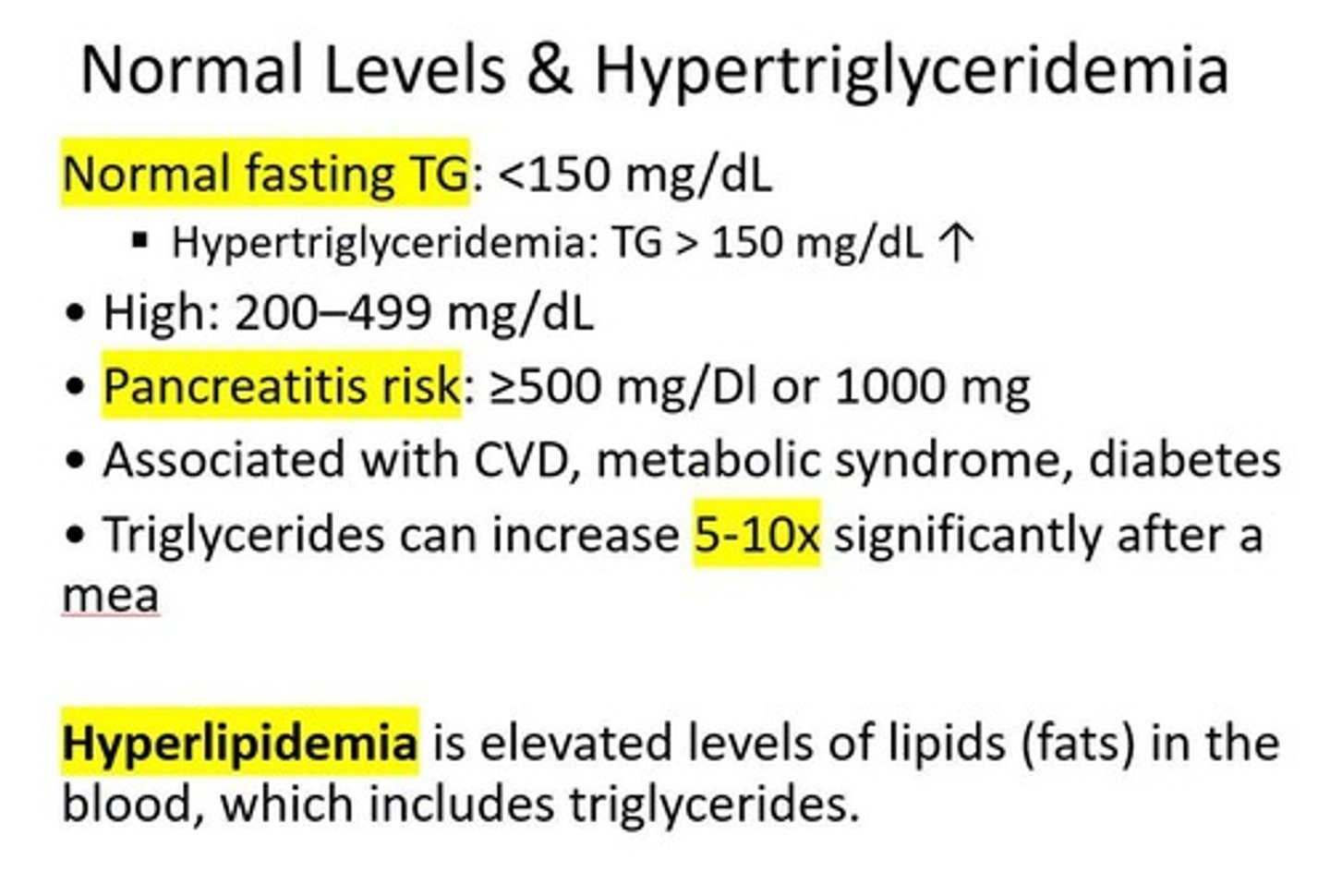
High triglycerides
200-499 mg/dL.
Pancreatitis risk
TG ≥500 mg/dL or 1000 mg.
Hyperlipidemia
Elevated levels of lipids (fats) in the blood, which includes triglycerides.
Health implications of high TG
Increased risk for cardiovascular diseases and pancreatitis.
Management - dietary interventions
Reduce alcohol consumption, achieve healthy weight, healthy diet (low sugar, high fiber), choose healthy fats (unsaturated fats), avoid trans fats and hydrogenated oils.

Management - lifestyle modifications
Quit smoking, increase physical activity, achieve healthy weight, reduce alcohol consumption.

Fibrates
Medications such as Fenofibrate and Gemfibrozil.

Statins
Medications such as Atorvastatin.
Fish oil/Lovaza
A supplement used for managing triglyceride levels.
Niacin
A supplement that affects blood clotting; use with caution.
Cholesterol
Fat-like substance that supports cell membranes.
Fatty acids
Building blocks of fat that give energy, build cells, create hormones, and support brain and nerve health.
Saponification
Turning fat into soap using a strong base (commonly NaOH).

Role of lipids in the brain
Build and maintain cell membranes, form myelin sheaths, support brain signaling, store energy for brain cells, protect and repair neurons.

Brain lipids
Structure + insulation + signaling + energy + protection.
LDL ('Bad') cholesterol
Contributes to plaque; normal LDL: <100 mg/dL.
HDL ('Good') cholesterol
Anti-atherogenic; 40-60 mg/dL males, 40-65 mg/dL females.
Thyroid hormones
Regulate LDL clearance.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids (Omega-3)
Beneficial for heart and brain, reduces inflammation.
Saturated Fatty Acids
Linked to heart disease.
Lipids
Insoluble in water.
Triglycerides
React with a strong base (like NaOH) to produce soap (fatty acid salts) and glycerol.
Glycerin
Special name of the glycerol produced during soap-making.
Cholesterol in the Brain
Major lipid in brain, concentrated in white matter.
Sphingolipids & Phospholipids
Maintain myelin.
Omega-3 fatty acids (DHA)
Essential for brain function.
ApoE
Related to cholesterol metabolism; ApoE4 increases Alzheimer's disease risk.
Neurofibrillary tangles
Twisted fibers of protein inside neurons.
Amyloid plaques
Extracellular deposits of beta-amyloid protein that interfere with neuron communication.
Neuronal loss
Death of neurons in key brain areas leading to memory loss.
Age as a risk factor for Alzheimer's
Higher risk of Alzheimer's because the brain becomes more vulnerable to damage over time.

Patient safety interventions
Soft foods, remove confusing decorations, support daily activities to prevent accidents.
Lovaza (Omega-3)
Lowers very high triglycerides.
Fish oil
Natural source of DHA; helps reduce triglycerides and supports heart and brain health.
Niacin (vitamin B3)
Lowers LDL ('bad') cholesterol and raises HDL ('good') cholesterol.
Liquid Oils
Unsaturated; vegetable oils; liquid at room temperature.
Solid Fats
Saturated; animal fats like butter/lard.