Chap 9 Population Growth
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
population growth
describes how the number of individuals in a population changes over time
individuals are added to a population through
births and immigration
individuals leave the population through
deaths and emigration.
open population has
immigration and emigration
closed population
does not have (or has a very low level of) immigration and emigration that doesn't influence population growth
N
the number of individuals in a population
t
time
Nt
number of individuals in the population at a given time (t)
if the initial population size is 100 at time zero (day zero t= 0)
N0= 100
- If N
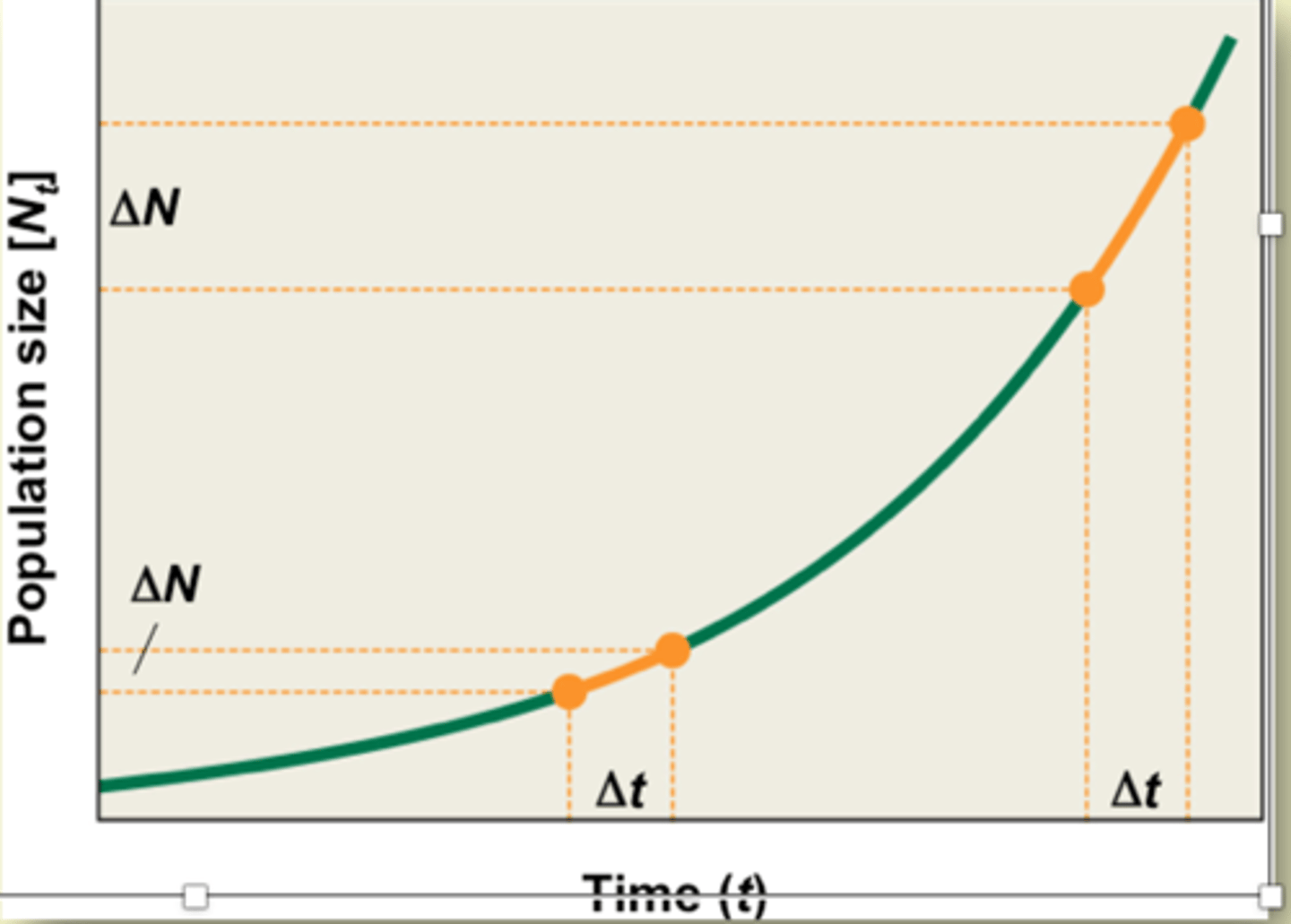
Exponential population growth model
dN/dt = rN
----------------
- r = instantaneous per capita rate growth (intrinsic to population)
- differential equation can integrated and the resulting equation can be used to predict population size under conditions of exponential growth at any value of t
- can insert value t = 1 day, 1 year, or 1 sec
Nt = N0ert
N0 = initial population size at t = 0
e = base of the natural logarithm, approximately 2.72
- r = intrinsic rate of
growth of the
population
when r= 0 aht is the relationship between b and d? what happens to the size of the population?
ert =e0 =1
- so Nt= no... b=d
population growth is zero
exponential growth results in
in a continuously accelerating or decelerating rate of population growth as a function of population size.
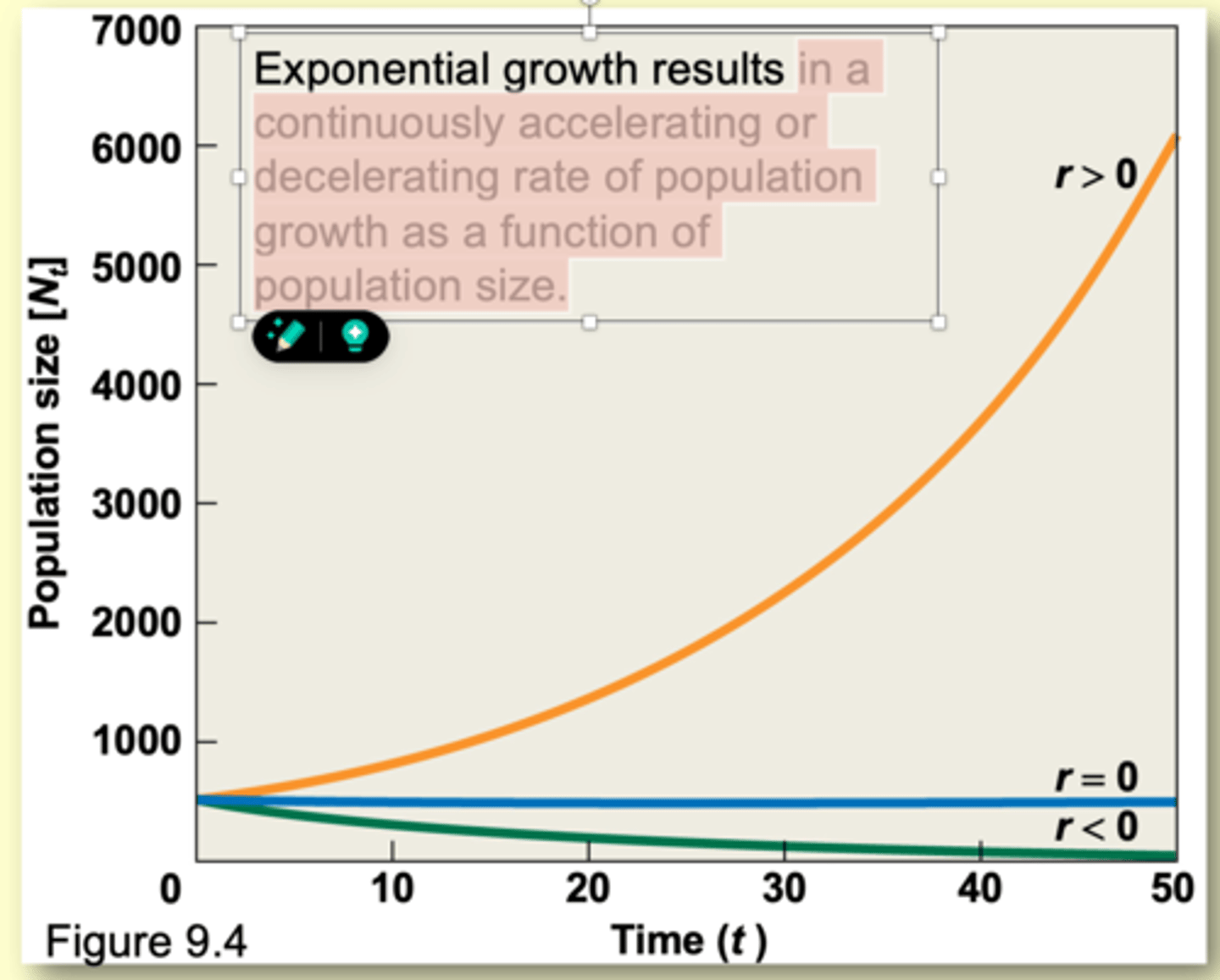
populations that show positive exponential growth generally
- live in favorable environments
- are at low population densities
--------------
these conditions are present during the process of colonization and establishment in new environments
a population is declinging when deaths exceed births
r<0
why are small populations more vulnerable to extinction
- loss of genetic variability
- deaths of small # of reproductive individuals can have large (negative) consequences
extreme environmental events can increase mortality rates and reproduce population size
- drought
- flood
- heat waves
- cold snaps
if environmental conditions exceed the bounds of tolerance for the species, an extreme event could lead to extinction.
changes in regional and global climate
A severe resource shortage
caused by either extreme environmental conditions or overpopulation, can lead to a population decline
- extinction is possible if the resource base does not recover in time for survivors to reproduce
invasive species can cause
population declines
-----------
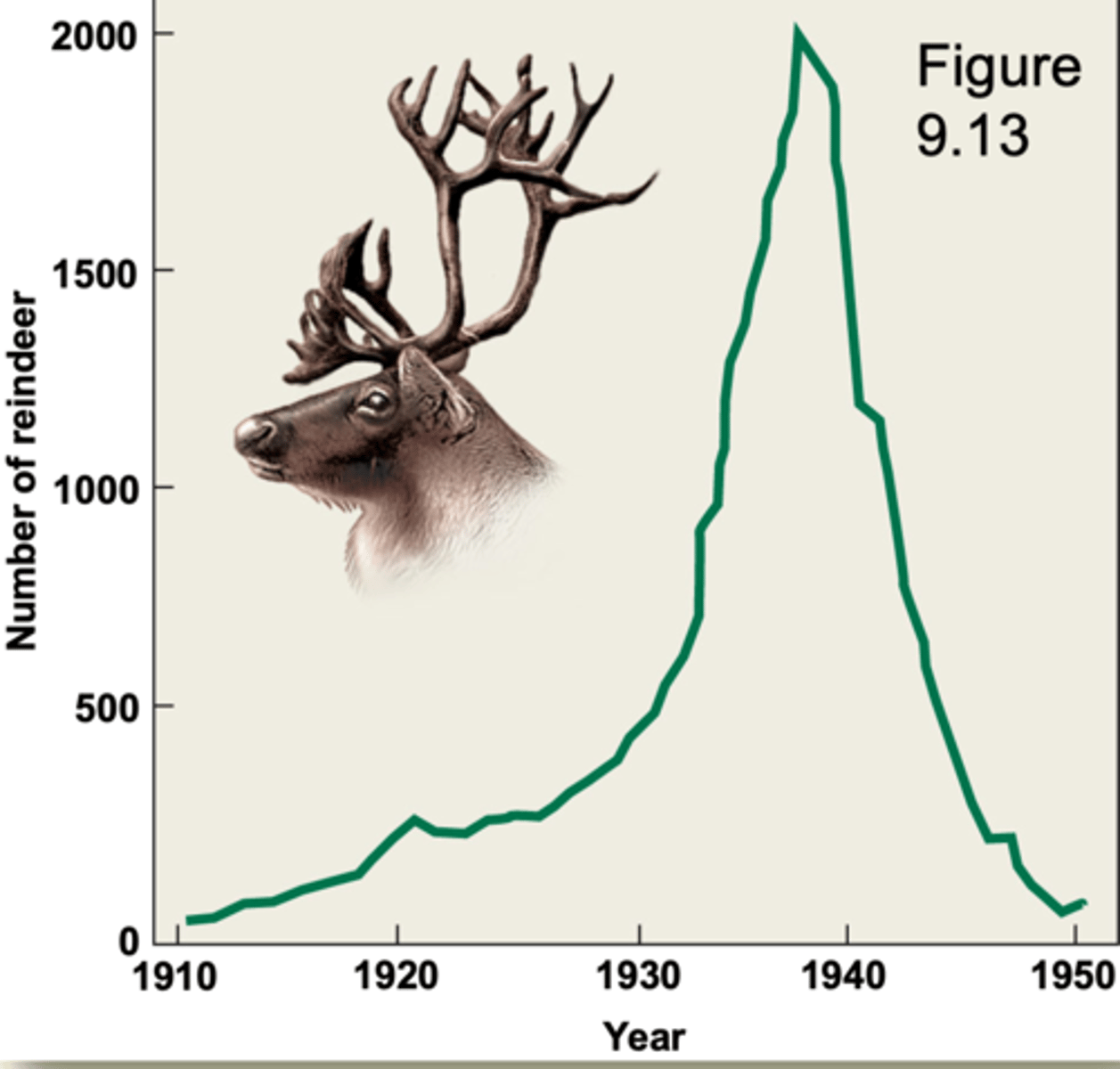
EX:
- reindeer on St. Paul island
- overgrazed the island severely
- herd size dropped from 2000 in 1938 to 8 in 1950
- such a population may recover or it may go extinct
what is the major way that humans impact population or species level extinctions
- habitat destruction
- pollution
- hunting
- invasive species
- climate change
human lands use changes the environment
leads to decliine in available habitat for many species
----------
types of land use include:
- habitat destruction
- pollution
- hunting
- invasive species
- climate change
Dams affect the characteristics of the water
- flow rate
- temperature
- oxygen levels
- sediment transport
-------------
have a negative impact on species that migrate, reducing their ability to move upstream