Chapter 8: Joints
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Synarthroses
Immovable joints; largly restricted to the axial skeleton
What are examples of some synarthrosis joints?
Sutures of the skull and the articulations between the teeth
Amphiarthroses
Slightly movable joints; largely restricted to the axial skeleton
What are examples of some amphiarthrosis joints?
The pubic symphysis and the intervertebral discs
Diarthroses
Freely movable joints; predominates in the appendicular skeleton
What are example(s) of some diarthroses joints?
The finger joints
Joint capsule
The two layered capsule that encloses the joint cavity; consists of fibrous layer and the synovial membrane
Synovial membrane
The inner layer of the joint capsule that is composed of loose connective tissue
What is the function of the synovial membrane?
To cover all internal joint surfaces that are not hyaline cartilage and to make/secrete synovial fluid
Synovial fluid
Slippery fluid that occupies all the free spaces within the joint capsule
What is the function of the synovial fluid?
To reduce friction between the cartilages
Articular cartilage
The glassy-smooth hyaline cartilage that covers the joints surfaces
What is the function of the articular cartilage?
To absorb compression placed on the joints
Meniscus
The C-shaped fibrocartilage that separates the articular surfaces
What is the function of the meniscus?
To modify the shape of bone ends to stabilize the joint and minimize wear and tear on the joints surfaces
Ligament
Bands made of flexible fibrous connective tissue; connecs bone to bone
What is the function of the ligaments?
To reinforce and strengthen the synovial joints & connect the bones
Tendon
Cord(s) made of dense regular connective tissue; connects muscle to bone
What is the function of the tendons?
To connect muscle to bone
Bursae
Flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane
What is the function of the bursae?
To act as “ball bearings” and reduce friction between adjascent structures during joint activity by taking pressure off the actual synovial membrane
Joint structure determines..
Direction and distance of movement (range of motion)
How are joints classified?
Based on their structure or degree of movement
What are the 3 different kinds of joint structures?
Fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial
What are the 3 different types of joint degrees of movement?
synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis, and dairthrosis
Fibrous joints
Joints that are jointed by collagen fibers; permits little or no movement
What are the 3 types of fibrous joints?
Suture, syndesmosis, and gomphosis
Suture
Joints held together with very short, interconnecting collagen fibers, and bone edges interlock; found only in the skull
Syndesmosis
Joints held together by a ligament; fibrous tissue can vary in length, but is longer than in sutures
Gomphosis
"Peg in socket' fibrous joint that binds the teeth to its bony sockets
Gliding
Flat bone surface glides or slips over another without appreciable angulation or rotation
Example(s) of a gliding joint
intercarpal/intertarsal joints and flat articular process of vertebrae
Hinge
Movement that allows movement in only one plane/direction
Example(s) of a hinge joint
elbow joints and interphalangeal joints
Ball and socket
Allows joints to move in many directions
Saddle
Two concave, straddle joints that allows for medial/lateral and anterior/posterior movement
Example(s) of saddle joints
Carpometacarpal joints of the thumbs
Ellipsoid
Ovoid joint that allows joint to move medial/lateral and anterior/posterior
Example(s) of ellipsoid joints
Knuckle and wrist joints
Pivot
Uniaxial movement; allows rotary movement around a single axis
Example(s) of a pivot joint
Proximal radioulnar joints
What are the articulating bones of the skull?
Cranial and facial bones
What are the articulating bones of the elbow?
Ulna, radius, & the humerus
What are the articulating bones of the coxal?
Hip bone and femur
What are the articulating bones of the knee?
Femur and tibia
The _____ ____ is the only bone that does not articulate with any other bones.
Hyoid bone
Flexion
The bending movement along the sagittal plane that decreases the angle of the joint andd brings the articulating bones closer together
Extension
Opposite of flexion — movement along the sagittal plane increases the angle between the articulating bones and typically straightens a flexed limb or body part
Hyperextension
The movement of a joint beyond its normal range of motion
Dorsiflexion
Lifting the foot so its superior surface approaches the shin
Plantar flexion
depressing the foot (pointing the toes)
Abduction
moving a limb away from the body midline in the frontal plane
Opposition
Movement used to touch your thumb to the tips of the other fingers on the same hand
Adduction
Moving a limb towards the body midline in the frontal plane
Rotation
Turning a bone around its longitudinal axis
Circumduction
Moving a limb or finger so that it describes a cone in space
Supination
Rotating the forearm laterally so that the palm faces anteriorly or superiorly
Pronation
Forearm rotates medially and the palm faces posteriorly or inferiorly (Radius crosses over)
Inversion
The soles of the foot turn medially
Eversion
The sole of the foot faces laterally
Describe the structure of cartilaginous joints
Joined together via cartilage, no joint cavity present, and not very movable (ex: epiphyseal plate, pubic symphysis, intervertebral joint)
What are the two kinds of cartilaginous joints?
Synchondrosis and symphyses
Synchondrosis
A bar/plate of hyaline cartilage unites the bones — virtually all of these are synarthrotic (no movement)
What is an example of a synchondrosis cartilaginous joint?
Epiphyseal plate
Symphyses
A type of cartilagineous joint in which the bones are united via fibrocartilage
What is an example of symphysis cartilaginous joints?
Intervertebral joints and the pubic symphysis
Describe the synovial joint structure
Bones are covered with articular cartilage, separated by a joint cavity and enclosed in articular capsule lined with the synovial membrane
Name the 6 kinds of diarthrotic joints
Gliding, hinge, ball and socket, saddle, ellipsoid, and pivot
What is labeled “A”?
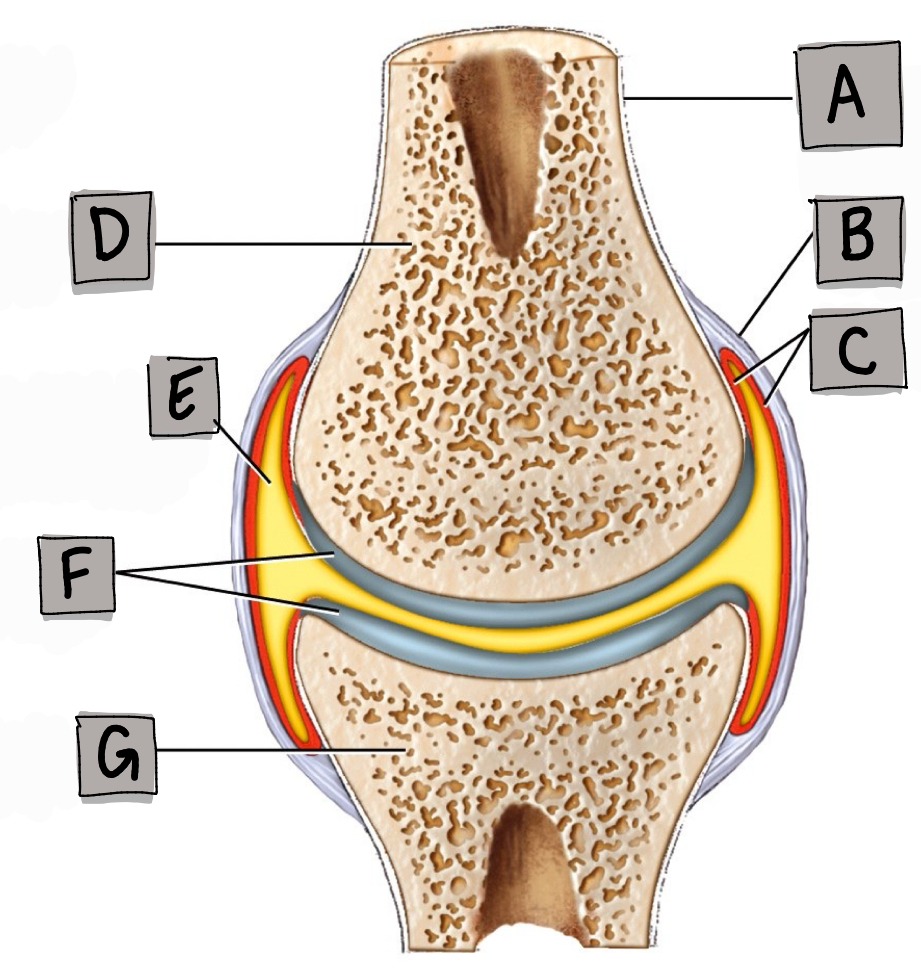
Periosteum
What is labeled “B”?

Fibrous membrane
What is labeled “C”?

Synovial membrane
What is labeled “E”?

Synovial joint cavity
What is labeled “F”?

Articular cartilage
What is labeled “A”?
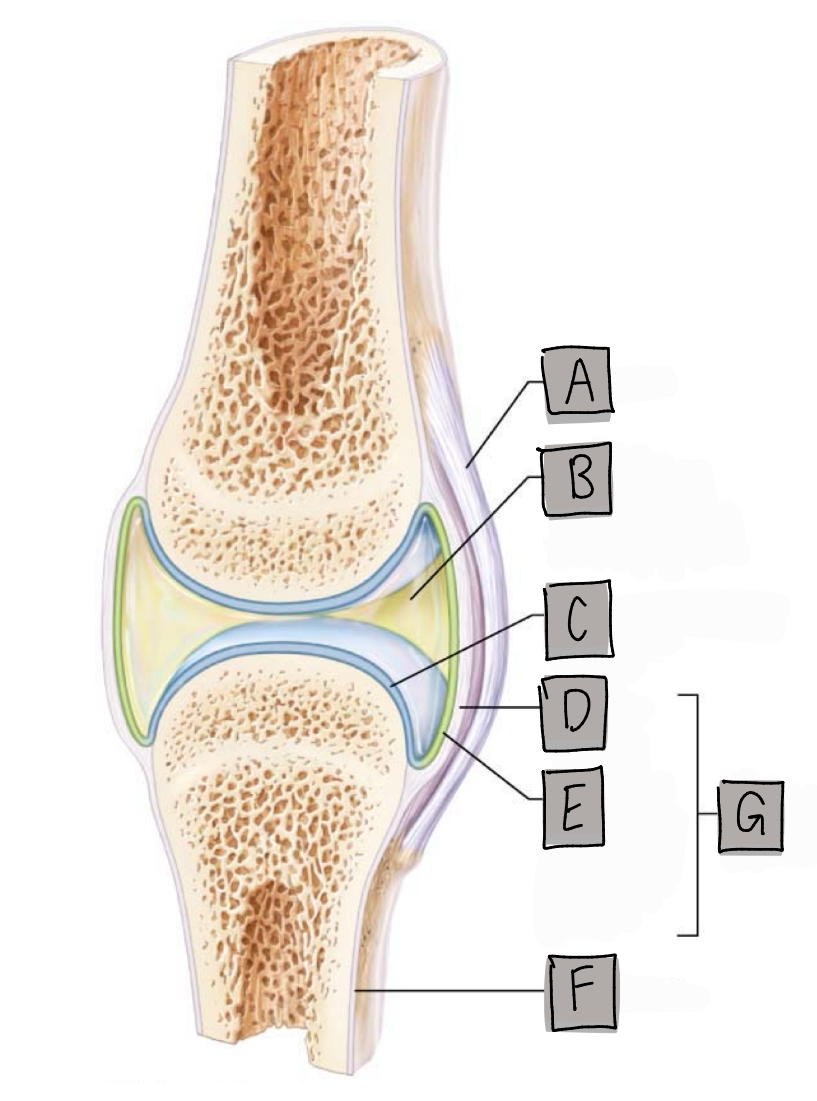
Ligament
What is labeled “B”?

Joint cavity
What is labeled “C”?

Articular cartilage
What is labeled “D”?

Fibrous layer
What is labeled “E”?

Synovial membrane
What is labeled “G”?

Articular/joint capsule
What component of the synovial joint is tagged with blue tape?
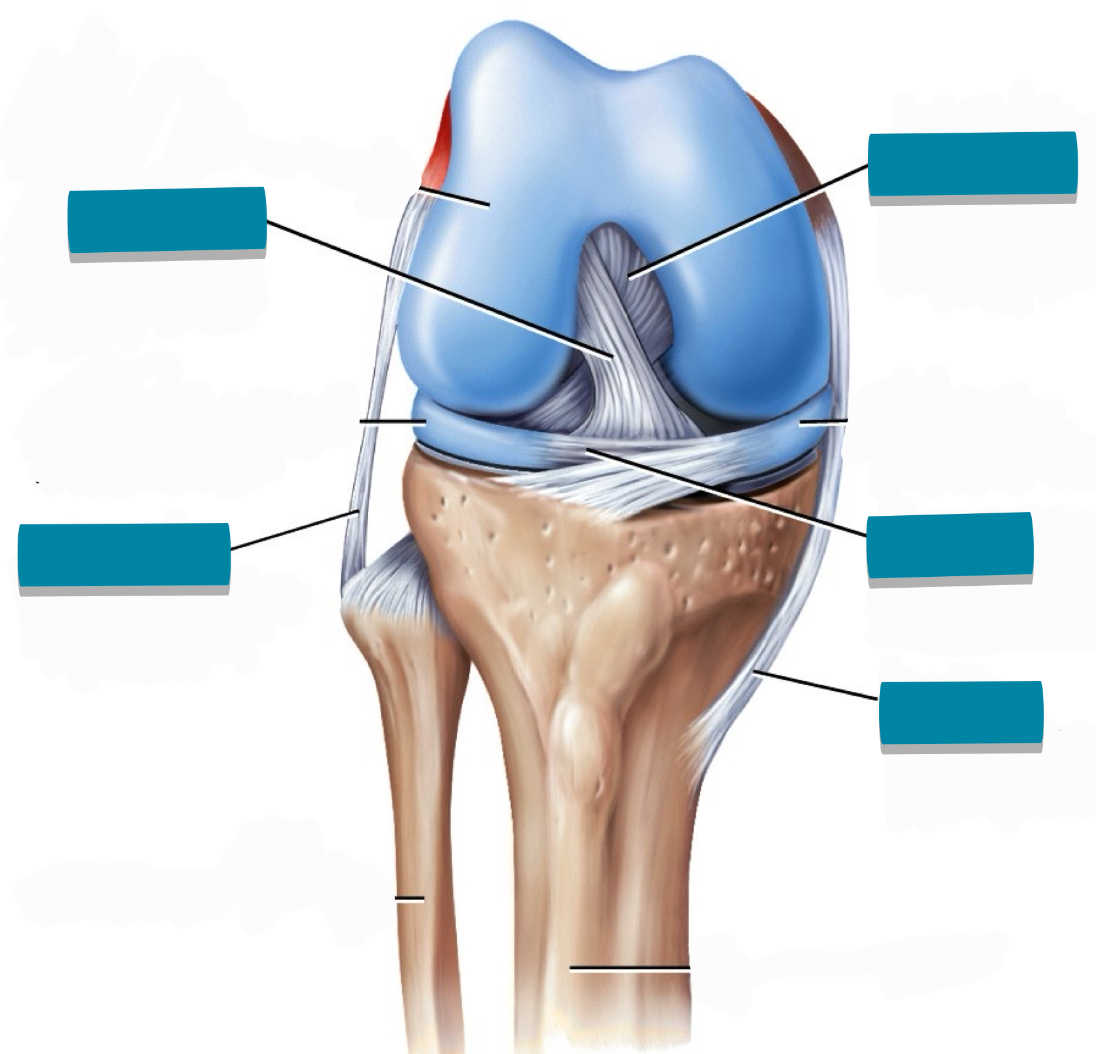
Ligament
What component of the synovial joint is tagged with blue tape?
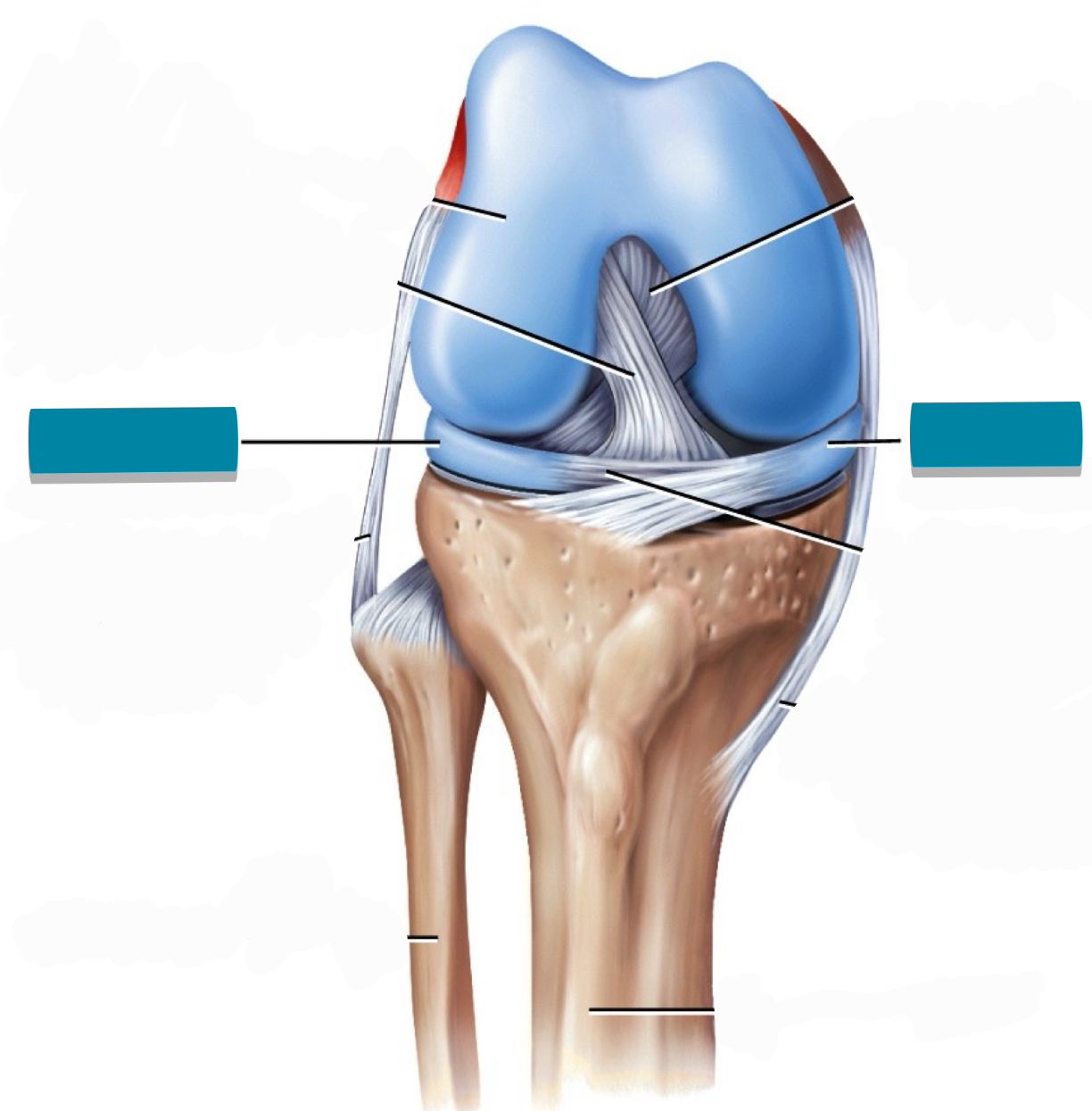
Meniscus
What is labeled “A”?
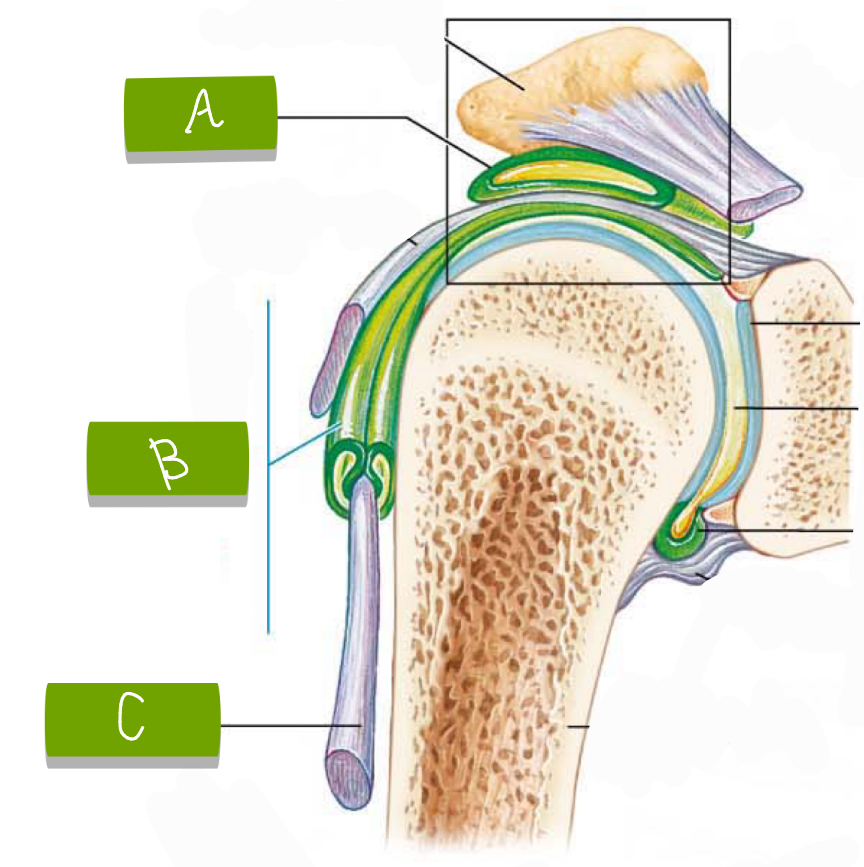
Bursa
What is labeled “B”?

Tendon sheath
What is labeled “C”?

Tendon
Synchondrosis
A type of cartilaginous joint where hyaline cartilage unites two bones
Cartilaginous joints
Joints that are joined via cartilage, contain no joint cavity, and are not very movable; two types
Cartilage discs
Modifies the shape of the joint to allow two bones of different shapes to fit together