Path: Tumors of the Kidney and Urinary Tract
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
uriniferous tubule
functional unit of the kidney
papillary adenoma
small, discrete adenomas arising from the renal tubular epithelium
found commonly at autopsy
<1.5 cm in diameter
well demarcated and low-grade nuclei
appear grossly as pale yellow-gray discrete, well-circumscribed nodules
papillary adenoma
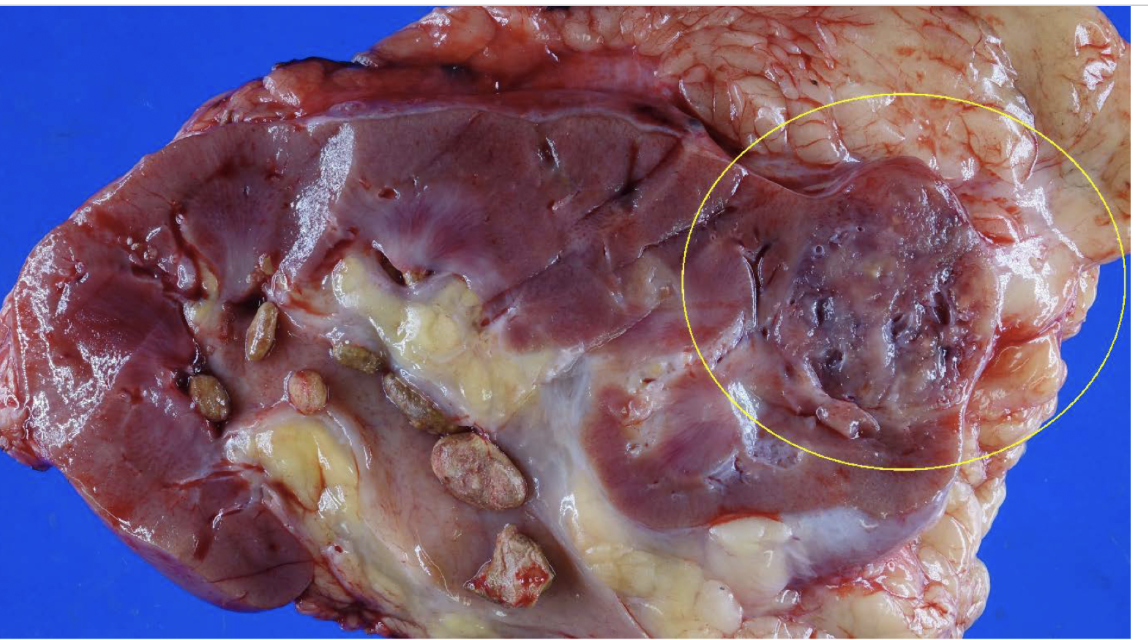
angiomyolipoma
benign vessels + smooth muscle + fat tumor
angiomyolipoma
originate from perivascular epithelioid cells
25-50% of patients with tuberous sclerosis (TS) - TSC1 and TSC2
angiomyolipoma
buzzword: retinal hamartomas and cardiac rhabdomyomas
angiomyolipoma
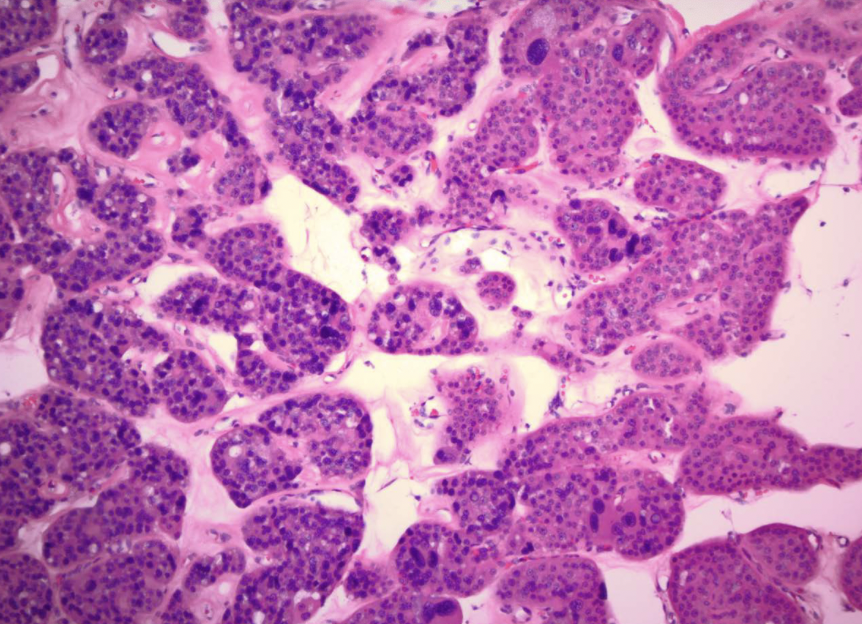
oncocytoma
arises from intercalated cells of CD
oncocytoma
numerous mitochondria = granular eosinophilic cytoplasm
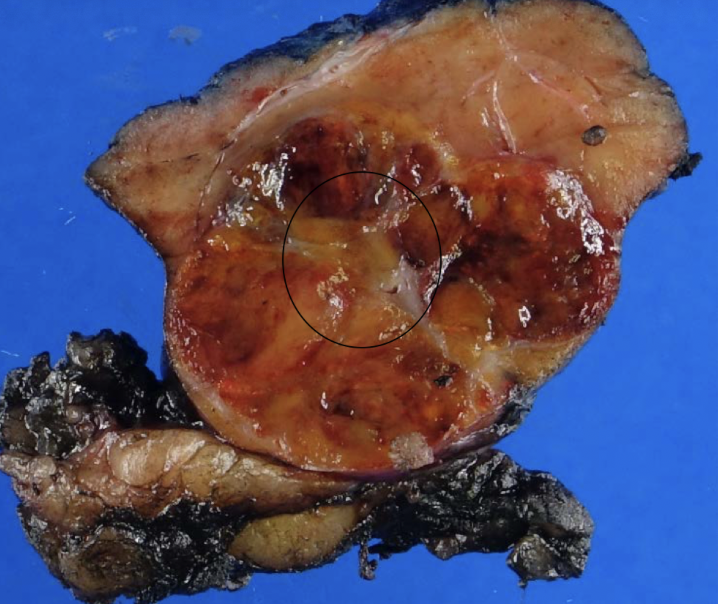
oncocytoma
mahogany brown with central scar
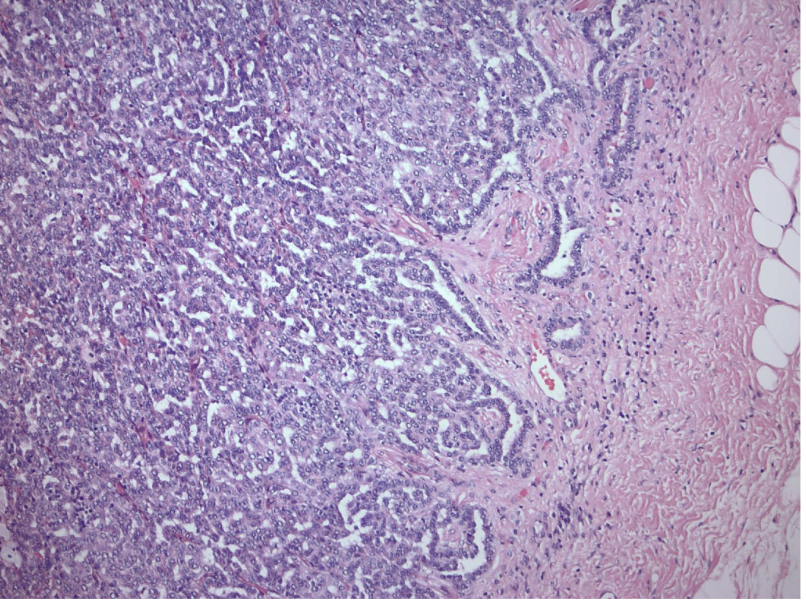
xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
proteus (>50%), E coli, pseudomonas, klebsiella
urine cultures negative!!
palpable mass that can mimic tumor
UT obstruction, staghorn, DM
xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
pus, scarring, stones
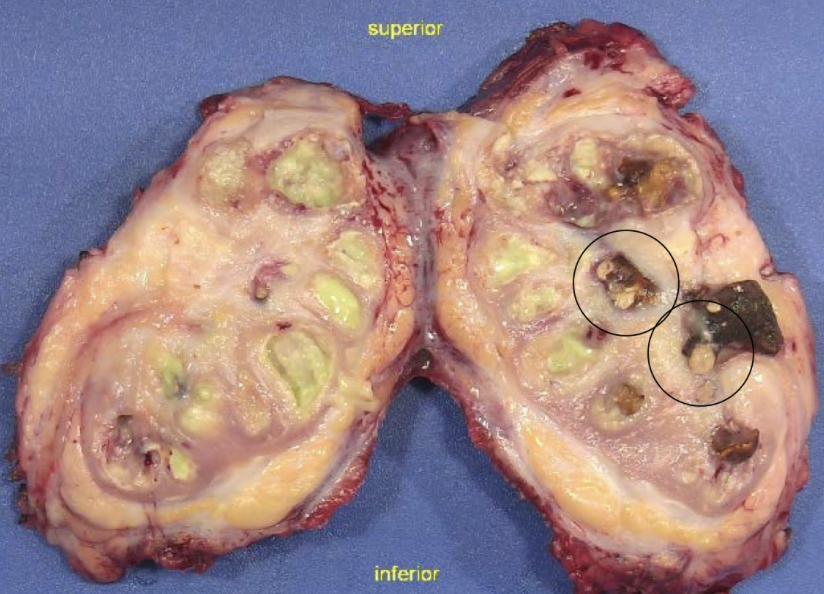
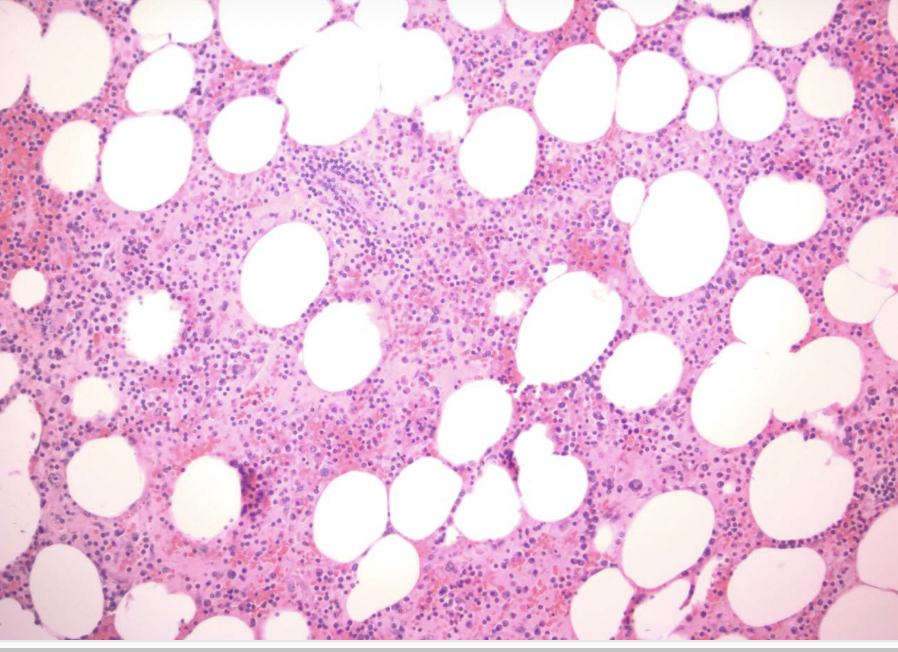
xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
sheets of foamy, lipid-laden macrophages
cigs
long term dialysis or hypertension
ESRD, chronic kidney disease
trichloroethylene (metal degreaser and chemical additive)
RF for renal cancer
RCC
von hippel-lindau syndrome (VHL)
AD
chromosome 3p mutation
renal cysts and bilateral, multiple
von hippel-lindau syndrome (VHL)
retinal and CNS hemangioblastomas
pheos
pancreatic serous cystadenoma
cafe au lait
hereditary papillary carcinoma
AD
MET proto-oncogene mutations
multiple bilateral
hereditary leiomyomatosis and RCC syndrome
AD
mutations of FH gene (fumarate hydratase)
cutaneous and uterine leiomyomas
aggressive with increased propensity for mets
birt-hogg-dube syndrome
AD
folliculin mutation
skin, pulmonary (cysts or blebs), renal tumors (oncocytic and chromophobe)
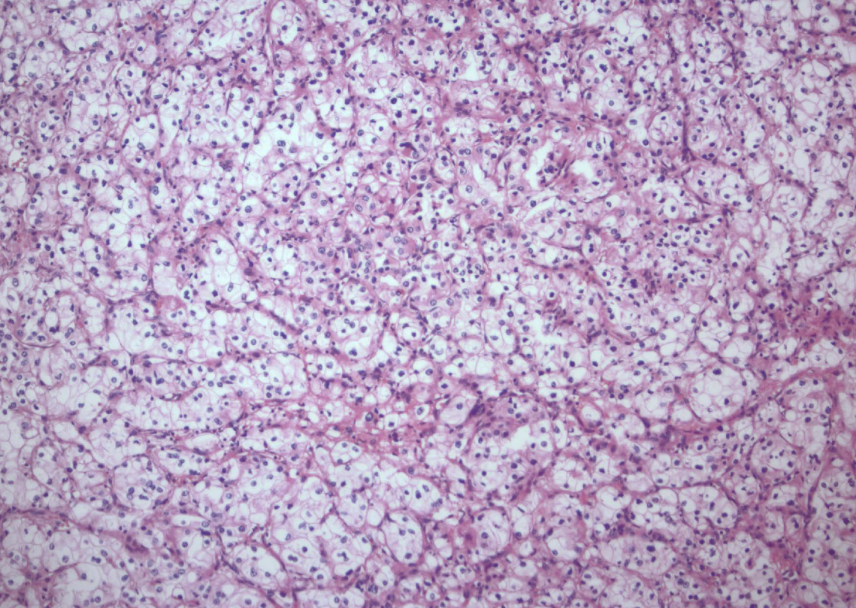
clear cell RCC
most common RCC
arise from proximal tubular epithelium
tendency to invade renal vein
von hippel-lindau syndrome (VHL)
buzzword: high HIF-1, increase VEGF and IGF-1
clear cell RCC
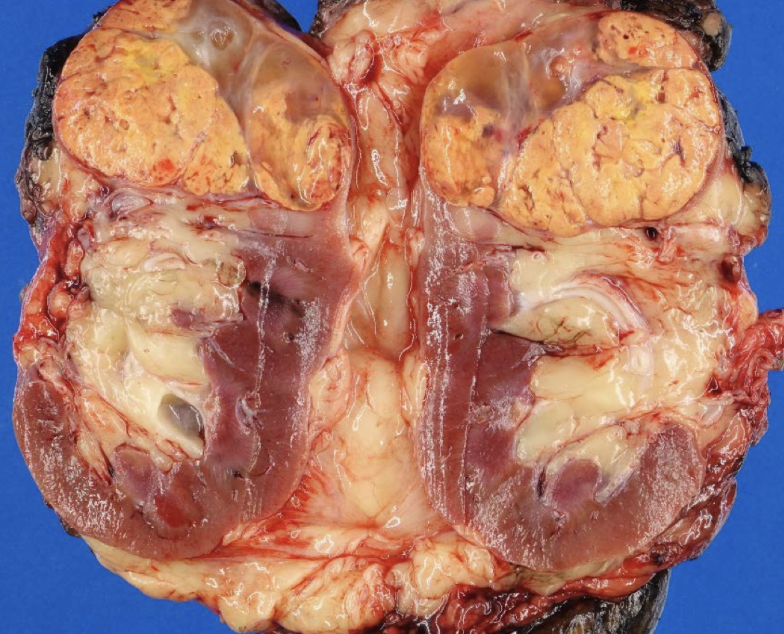
clear cell RCC
glycogen and lipid cytoplasm with rich vascular network
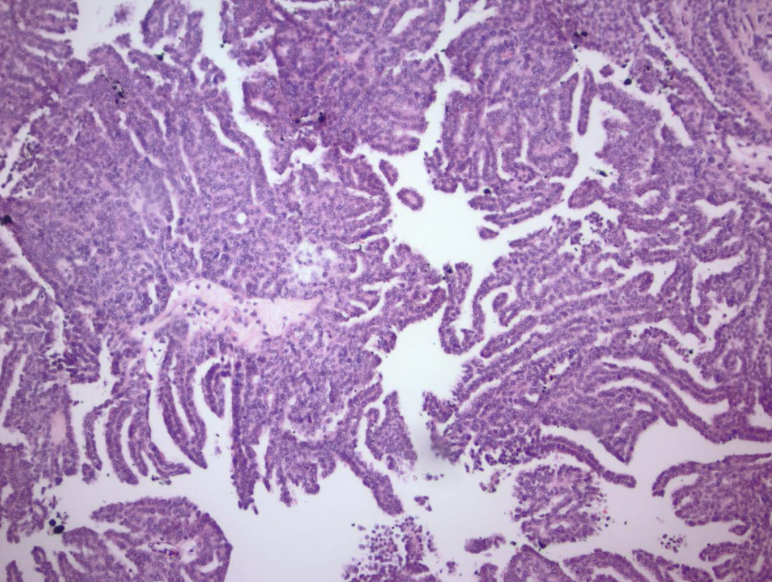
papillary RCC
arise from distal convoluted tubules
multifocal and bilateral
MET
proto-oncogene that encodes the tyrosine kinase receptor for hepatocyte growth factor
papillary RCC
papillary vs. clear cell: multifocal
clear cell RCC
papillary vs. clear cell: arise in proximal tubular epithelium
papillary RCC
papillary vs. clear cell: arise in distal tubular epithelium
papillary RCC
papillary RCC
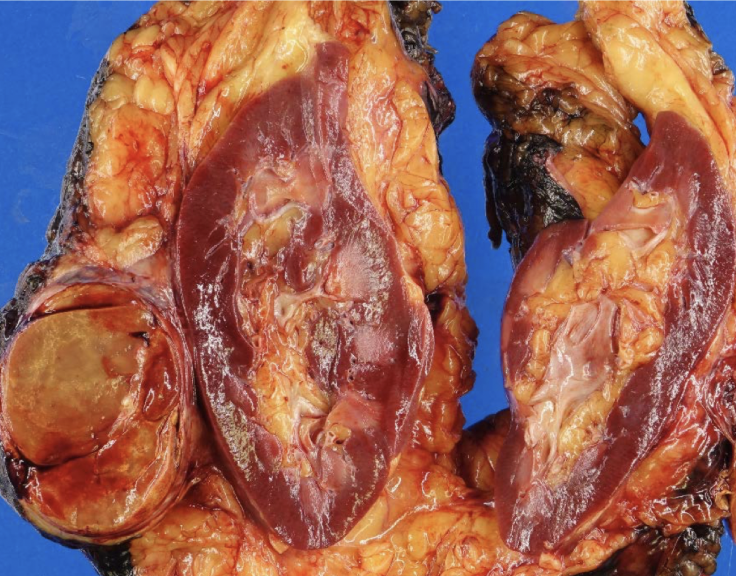
chromophobe RCC
arise from intercalated disc of collecting ducts; multiple chromosome loss and extreme hypodiploidy
chromophobe RCC
RCC with best prognosis
intercalated cells
chromophobe RCC and oncocytomas both arise from?
chromophobe RCC
raisinoid nuclei
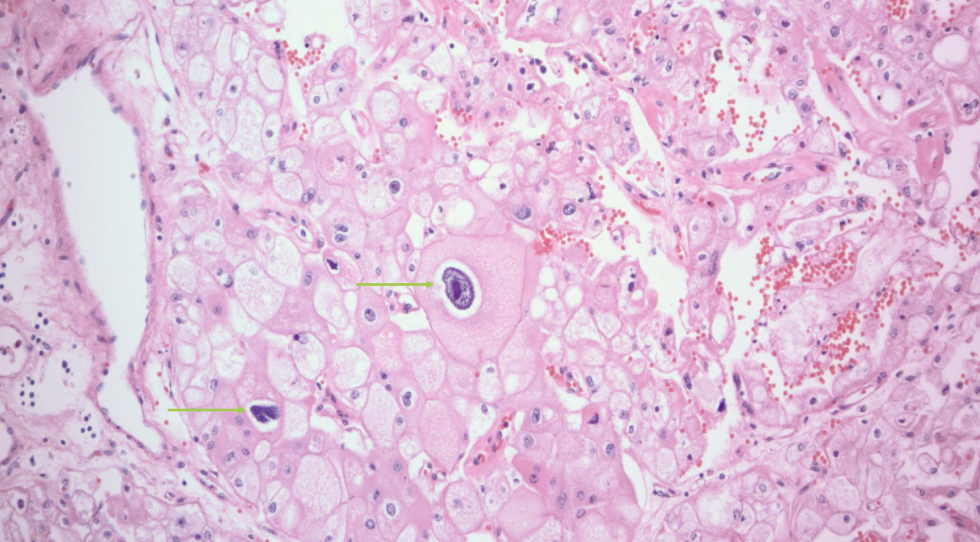
CD (bellini duct) RCC
very rare
several chromosomal losses and deletions
arise in collecting duct cells in medulla
CD (bellini duct) RCC
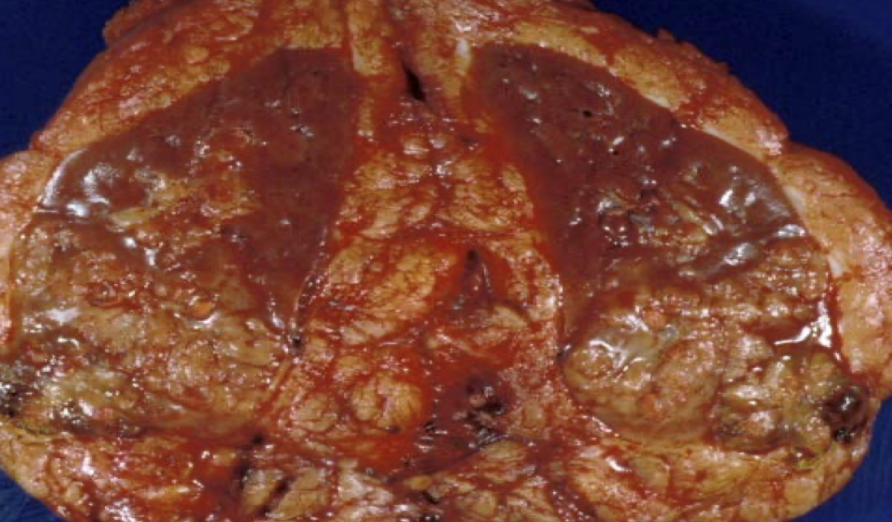
medullary carcinoma
buzzword: younger patients with sickle cell trait
Xp11 translocation carcinoma
genetically distinct subtype of RCC
young patients
TFE3 translocation
clear cytoplasm with papillary architecture
clear cell RCC
RCC type: -3p VHL
papillary RCC
RCC type: +7 (met), +17, -Y
hematuria
most reliable cue for RCC
costovertebral
palpable mass
hematuria
clinical triad for RCC
lung, bone (LN, liver, adrenal glands, brain)
most common RCC mets to?
UCC of renal pelvis
patients with Lynch syndrome have significantly increased incidence of
UCC
which usually diagnosed earlier, UCC or RCC?
UCC of renal pelvis
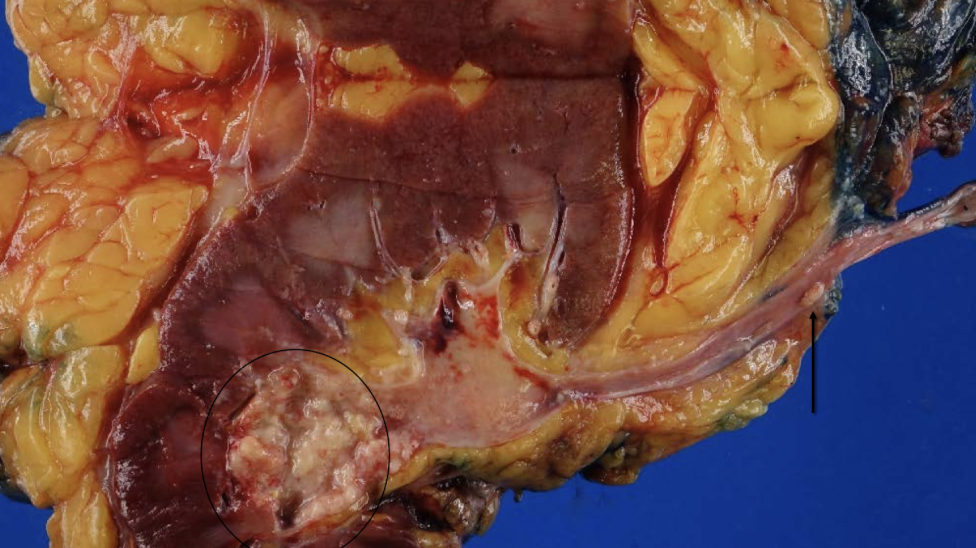
ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJ) of infants and children
most common cause of hydronephrosis
present early
males
bilateral
ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJ) of adults
women
unilateral
abnormal organization of smooth muscle bundles or excess stromal deposition of collagen between smooth muscle bundles
fibroepithelial polyp
tumor-like lesion of the ureter in children
loose, vascularized CT overlaid by urothelium
proximal
unilateral obstructive lesions of the ureter due to stones or neoplasms are usually proximal or distal?
distal
bilateral obstructive lesions of the ureter such as BPH are usually proximal or distal?
vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
most common and serious congenital anomaly of the bladder
abnormal movement of urine from the bladder into ureters and kidneys
predisposes to ascending pyelonephritis and loss of renal function
abnormal connections between the bladder and vagina, rectum, or uterus may create fistulae
primary
vesicoureteral reflux due to incomplete closure of the UVJ or failure of anti-reflux mechanism is due to shortening of the intravesical ureter
secondary
VUR due to abnormally high pressure in the bladder causing failure of the closure of the UVJ during bladder contraction
obstruction → hydroureter → hydronephrosis → pyelonephritis
effect of intrinsic or extrinsic ureteral obstruction?
renal stones
most common cause of intrinsic urinary tract obstruction
BPH
most common cause of acquired bladder diverticulum
focal failure of development of detrusor muscle or urinary tract obstruction during fetal development
most common cause of congenital bladder diverticulum
exstrophy of the bladder
developmental failure in the anterior wall of the abdomen and the bladder
communicates directly with the abdominal surface
chronic infection
increased risk of adenocarcinoma
urachal canal
connects the fetal bladder with the allantois and is normally obliterated at birth
failure to close can result in a fistulous urinary tract connection between the bladder and umbilicus
increased risk for adenocarcinoma
urachal cyst
central region of patent urachus persists
cystitis
inflammation of the bladder, more common in women
e coli (proteus, klebsiella, enterobacter)
most common cause of infectious cystitis
iatrogenic
non-infectious cystitis in patients receiving systemic chemotherapy or pelvic irradiation
hemorrhagic
non-infectious cystitis due to cytotoxic agents such as cyclophosphamide
interstitial (chronic pelvic pain syndrome)
cystitis with unknown etiology
mucosal fissures and punctate hemorrhages (glomerulations)
rule out CIS
symptoms > 6 weeks
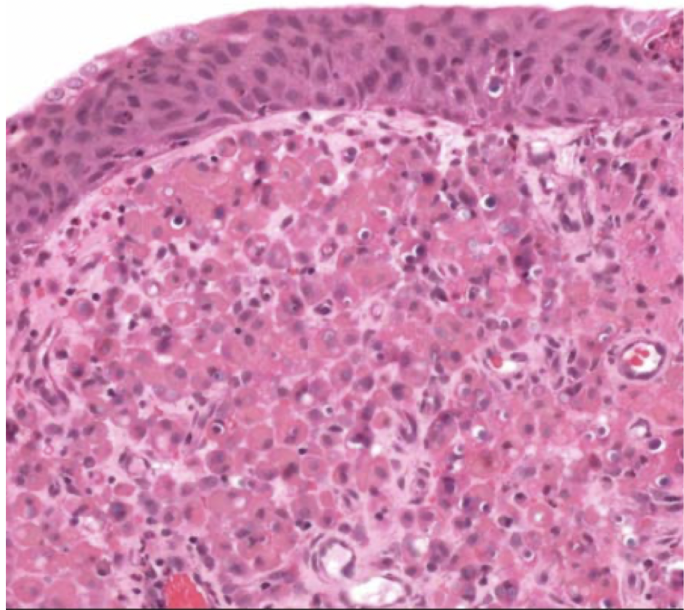
malakoplakia
distinctive chronic inflammatory reaction that appears to stem from acquired defects in phagocyte function
chronic E coli or proteus infection
renal transplant recipients! (immuno comp)
malakoplakia
sheets of large foamy macrophages with granular cytoplasm = von hansemann cells
malakoplakia
michaelis-gutmann bodies = laminated mineralized concretions resulting from deposition of calcium in enlarged lysosomes
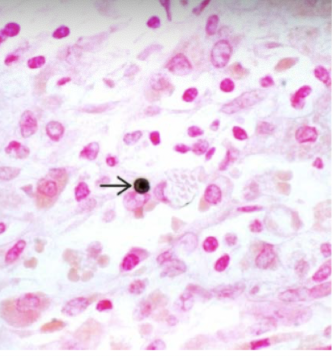
polypoid cystitis
inflammatory lesion resulting from irritation of the bladder mucosa
result of instrumentation (catheters)
mistaken for papillary UCC (clinically and histologically)
cystitis glandularis
metaplasia of von Brunn nests and take on a cuboidal or columnar appearance
cystitis cystica
metaplasia of von Brunn nests and take on a cuboidal or columnar appearance that being very dilated spaces
keratinizing
which type of squamous metaplasia of the bladder can be a precursor lesion to dysplastic lesions and often seen with schistosomiasis
nephrogenic adenoma
unusual lesion of the bladder that may not be a form of true metaplasia
same sex chromosome status with allograft kidneys in transplanted patients
overlying urothelium is focally replaced by cuboidal
urothelial (transitional)
most common neoplasm of the bladder
papillary
flat (CIS)
two types of noninvasive urothelial cell lesions that can become invasive
false (noninvasive papillary can be low or high grade, but flat are ALWAYS high grade)
T/F: noninvasive flat urothelial carcinoma (CIS) can be low or high grade
cigarette smoking
most important risk factor for UCC of the bladder
polypoid urothelial carcinoma of the bladder
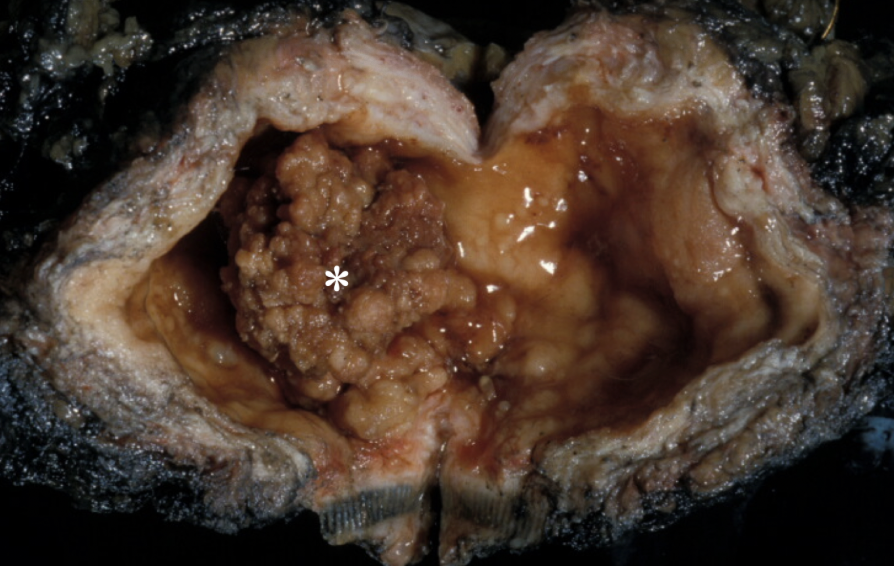
papillary urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential (PUNLMP)
thicker urothelium with greater density of cells
larger than papillomas
indistinguishable from cancers
can recur but progression rare
invasive UCC
painless hematuria, frequency, urgency, dysuria
occasional ureteral orifice obstruction may lead to pyelonephritis or hydronephrosis
depth of invasion into bladder wall
most important prognostic factor for invasive UCC and determine treatment modality
painless hematuria
most common symptom of bladder cancer
BCG (bacillus calmette-guerin)
intravesical instillation of an attenuated strain of mycobacterium to treat bladder cancer
schistosomiasis
most common risk factor for SCC of the bladder
false (rare)
T/F: metastatic spread of the bladder is very common